Investigation of the Relationship between Body Parameters and mAs Using Non-Contact Two-Dimensional Thickness Measurement in Chest Digital Radiography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Non-Contact Infrared Sensor
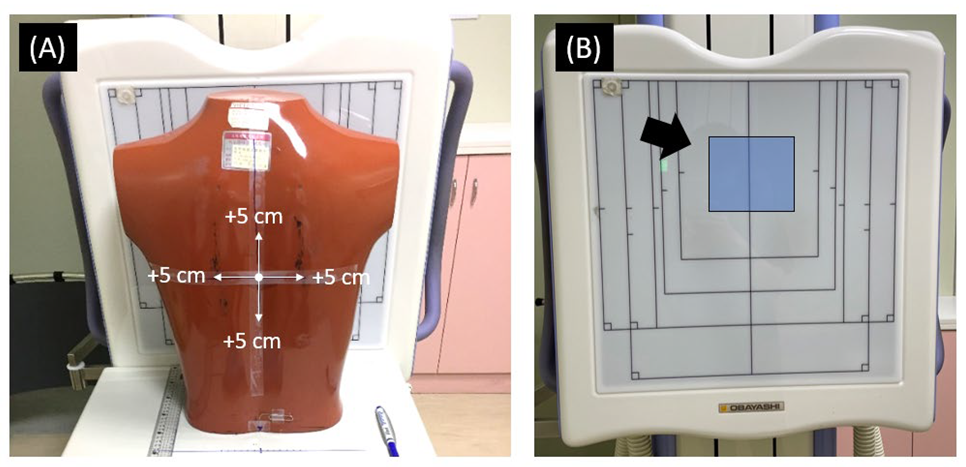
2.2. Phantom Study
2.3. Human Subjects
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, M.L.; Liu, K.; Niu, X.C.; Liu, X.L. A method to derive appropriate exposure parameters from target exposure index and patient thickness in pediatric digital radiography. Pediatr. Radiol. 2013, 43, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ofori, E.K.; Ofori-Manteaw, B.B.; Gawugah, J.N.K.; Nathan, J.A. Relationship between Patient Anatomical Thickness and Radiographic Exposure Factors for Selected Radiologic Examinations. J. Health Med. Nurs. 2016, 23, 150–162. [Google Scholar]
- Alzyoud, K.; Hogg, P.; Snaith, B.; Flintham, K.; England, A. Impact of body part thickness on AP pelvis radiographic image quality and effective dose. Radiography 2019, 25, e11–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, W.; Robinson, J.; McEntee, M. Patient-based radiographic exposure factor selection: A systematic review. J. Med. Radiat. Sci. 2014, 61, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatt, S.; Portelli, J.L.; Zarb, F. Optimisation of the AP abdomen projection for larger patient body thicknesses. Radiography 2022, 28, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.B.; Krupinski, E.A.; Strauss, K.J.; Breeden, W.K., 3rd; Rzeszotarski, M.S.; Applegate, K.; Wyatt, M.; Bjork, S.; Seibert, J.A. Digital radiography image quality: Image acquisition. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2007, 4, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMaio, D.N.; Herrmann, T.; Noble, L.B.; Orth, D.; Peterson, P.; Young, J.; Odle, T.G. Best Practices in Digital Radiography. Radiol. Technol. 2019, 91, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Assi, A.A.N. The rate of repeating X-rays in the medical centers of Jenin District/Palestine and how to reduce patient exposure to radiation. J. Med. Phys. Eng. 2018, 24, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaferro, R.J.; Balter, S.; Janower, M.L. The incidence and causes of repeated radiographic examinations in a community hospital. Radiology 1974, 112, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.-L.; Mak, A.S.-H.; Lam, W.-T.; Chau, C.-K.; Lau, K.-Y. Reject analysis: A comparison of conventional filme-screen radiography and computed radiography with PACS. Radiography 2004, 10, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, P.; Gentle, D.; Martin, C.J. Optimising automatic exposure control in computed radiography and the impact on patient dose. Radiat Prot. Dosim. 2005, 114, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Lee, H.K.; Lee, Y.S.; Cho, J.H. Evaluation of automatic exposure control system chamber for the dose optimization when examining pelvic in digital radiography. J. X-ray Sci. Technol. 2015, 23, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.S.; Wood, T.J.; Avery, G.; Balcam, S.; Needler, L.; Joshi, H.; Saunderson, J.R.; Beavis, A.W. Automatic exposure control calibration and optimisation for abdomen, pelvis and lumbar spine imaging with an Agfa computed radiography system. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, N551–N564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, N.W. An examination of automatic exposure control regimes for two digital radiography systems. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009, 54, 4645–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismailos, E.; Mastorakou, I.; Kelekis, N.L.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; Efstathopoulos, E.P.; Panayiotakis, G.; Kelekis, D.A. Clinical evaluation of manual and automatic exposure control techniques in film-based chest radiography. Br. J. Radiol. 1996, 69, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, C.; Larkin, A.; Dennan, S.; O’Reilly, G. Exposure variations under error conditions in automatic exposure controlled film-screen projection radiography. Brit. J. Radiol. 2004, 77, 931–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuillen-Martensen, K. Radiographic Image Analysis; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Uffmann, M.; Schaefer-Prokop, C. Digital radiography: The balance between image quality and required radiation dose. Eur. J. Radiol. 2009, 72, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibert, J.A. Digital Radiography: Image Quality and Radiation Dose. Health Phys. 2008, 95, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drost, W.T.; Reese, D.J.; Hornof, W.J. Digital radiography artifacts. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasoun. 2008, 49, S48–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-S.; Lim, C.-H.; Jeoung, S.-H. A study on the using of automatic exposure control in the chest radiography. J. Radiol. Sci. Technol. 2019, 42, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection. Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection; ICRP: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Alamer, A.; Alharbi, F.; Aldhilan, A.; Almushayti, Z.; Alghofaily, K.; Elbehiry, A.; Abalkhail, A. Healthcare-Associated Infections (HAIs): Challenges and Measures Taken by the Radiology Department to Control Infection Transmission. Vaccines 2022, 10, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyas, F.; Burbridge, B.; Babyn, P. Health Care-Associated Infections and the Radiology Department. J. Med. Imaging Radiat Sci. 2019, 50, 596–606.e591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.; Williams, C.; Taylor, A. COVID-19: Impact on radiology departments and implications for future service design, service delivery, and radiology education. Brit. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20210632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Y. Microsoft Kinect Sensor and Its Effect. IEEE Multimed. 2012, 19, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbolandi, H.; Lefloch, D.; Kolb, A. Kinect range sensing: Structured-light versus Time-of-Flight Kinect. Comput. Vis. Image Und. 2015, 139, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, A.; Giancola, S.; Mainetti, G.; Sala, R. A metrological characterization of the Kinect V2 time-of-flight camera. Robot Auton Syst. 2016, 75, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanhede, B.; Bath, M.; Kheddache, S.; Sund, P.; Bjorneld, L.; Widell, M.; Almen, A.; Besjakov, J.; Mattsson, S.; Tingberg, A.; et al. The influence of different technique factors on image quality of chest radiographs as evaluated by modified CEC image quality criteria. Brit. J. Radiol. 2002, 75, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamenhof, R.G.; Shahabi, S.; Morgan, H.T. An Improved Method for Estimating the Entrance Exposure in Diagnostic Radiographic Examinations. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1987, 149, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Board, N.R.P. Reference Doses and Patient Size in Pediatric Radiology; NRPB: Chilton, UK, 2000; Volume NRPB-R318.
- Seibert, J.A.; Morin, R.L. The standardized exposure index for digital radiography: An opportunity for optimization of radiation dose to the pediatric population. Pediatr. Radiol. 2011, 41, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mothiram, U.; Brennan, P.C.; Lewis, S.J.; Moran, B.; Robinson, J. Digital radiography exposure indices: A review. J. Med. Radiat. Sci. 2014, 61, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsalafoutas, I.A.; Blastaris, G.A.; Moutsatsos, A.S.; Chios, P.S.; Efstathopoulos, E.P. Correlation of image quality with exposure index and processing protocol in a computed radiography system. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2008, 130, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez Perez, S.; Marshall, N.W.; Binst, J.; Coolen, J.; Struelens, L.; Bosmans, H. Survey of chest radiography systems: Any link between contrast detail measurements and visual grading analysis? Phys. Med. 2020, 76, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sund, P.; Bath, M.; Kheddache, S.; Mansson, L.G. Comparison of visual grading analysis and determination of detective quantum efficiency for evaluating system performance in digital chest radiography. Eur. Radiol. 2004, 14, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcin, A.; Olgar, T.; Sancak, T.; Atac, G.K.; Akyar, S. Correlation between physical measurements and observer evaluations of image quality in digital chest radiography. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 3935–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Age (Years) | Height (cm) | Weight (kg) | BMI (kg/m2) | Thickness (cm) | Exposure Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25.3 ± 7.0 | 172.7 ± 5.9 | 72.2 ± 13.2 | 24.2 ± 4.1 | 19.1 ± 3.6 | 145.4 ± 18.1 |
| Model | Body Parameter | R-Square | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| First-order exponential | T | 0.9936 | 0.0949 |
| BMI | 0.9932 | 0.0979 | |
| T*BMI | 0.9520 | 0.2598 | |
| W/H | 0.9943 | 0.0897 | |
| Second-order polynomial | T | 0.9888 | 0.1258 |
| BMI | 0.9957 | 0.0778 | |
| T*BMI | 0.9942 | 0.0901 | |
| W/H | 0.9961 | 0.0736 | |
| First-order power | T | 0.9922 | 0.1049 |
| BMI | 0.9957 | 0.0777 | |
| T*BMI | 0.9921 | 0.1053 | |
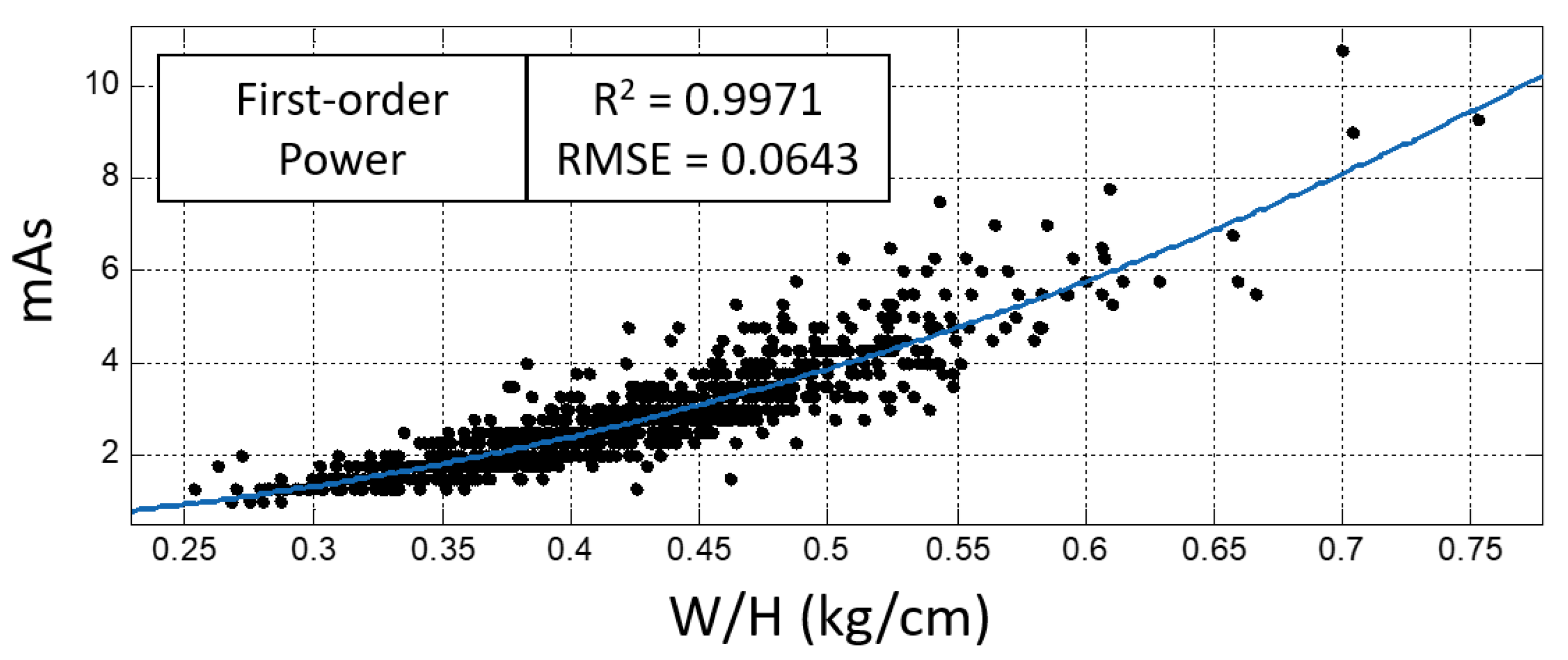
| W/H | 0.9971 | 0.0643 |
| Age (Years) | Height (cm) | Weight (kg) | BMI (kg/m2) | Thickness (cm) | Exposure Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30.8 ± 11.9 | 174.1 ± 5.3 | 78.5 ± 14.9 | 28.9 ± 4.7 | 20.3 ± 4.5 | 151.9 ± 23.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, J.-R.; Cheng, I.-H.; Liang, Y.-S.; Li, J.-J.; Tsai, J.-M.; Wang, M.-T.; Lin, T.-P.; Huang, S.-L.; Chou, M.-C. Investigation of the Relationship between Body Parameters and mAs Using Non-Contact Two-Dimensional Thickness Measurement in Chest Digital Radiography. Sensors 2023, 23, 7169. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167169
Lin J-R, Cheng I-H, Liang Y-S, Li J-J, Tsai J-M, Wang M-T, Lin T-P, Huang S-L, Chou M-C. Investigation of the Relationship between Body Parameters and mAs Using Non-Contact Two-Dimensional Thickness Measurement in Chest Digital Radiography. Sensors. 2023; 23(16):7169. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167169
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Jia-Ru, I-Hao Cheng, Yu-Syuan Liang, Jyun-Jie Li, Jen-Ming Tsai, Min-Tsung Wang, Te-Pao Lin, Su-Lan Huang, and Ming-Chung Chou. 2023. "Investigation of the Relationship between Body Parameters and mAs Using Non-Contact Two-Dimensional Thickness Measurement in Chest Digital Radiography" Sensors 23, no. 16: 7169. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167169
APA StyleLin, J.-R., Cheng, I.-H., Liang, Y.-S., Li, J.-J., Tsai, J.-M., Wang, M.-T., Lin, T.-P., Huang, S.-L., & Chou, M.-C. (2023). Investigation of the Relationship between Body Parameters and mAs Using Non-Contact Two-Dimensional Thickness Measurement in Chest Digital Radiography. Sensors, 23(16), 7169. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167169






