Use of Lateral Flow Assays in Forensics
Abstract
1. Introduction
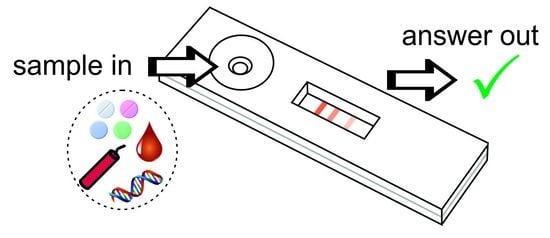
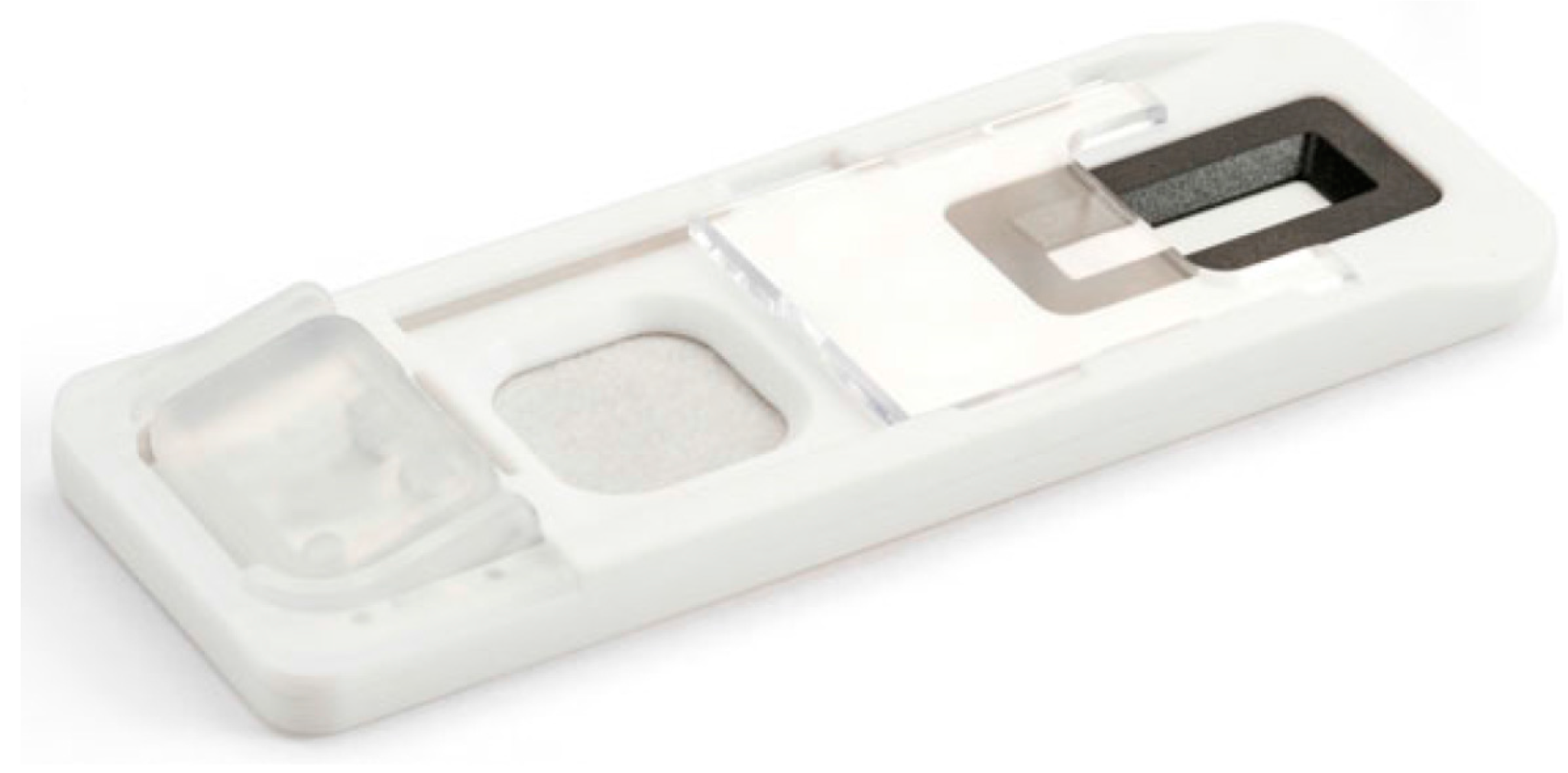
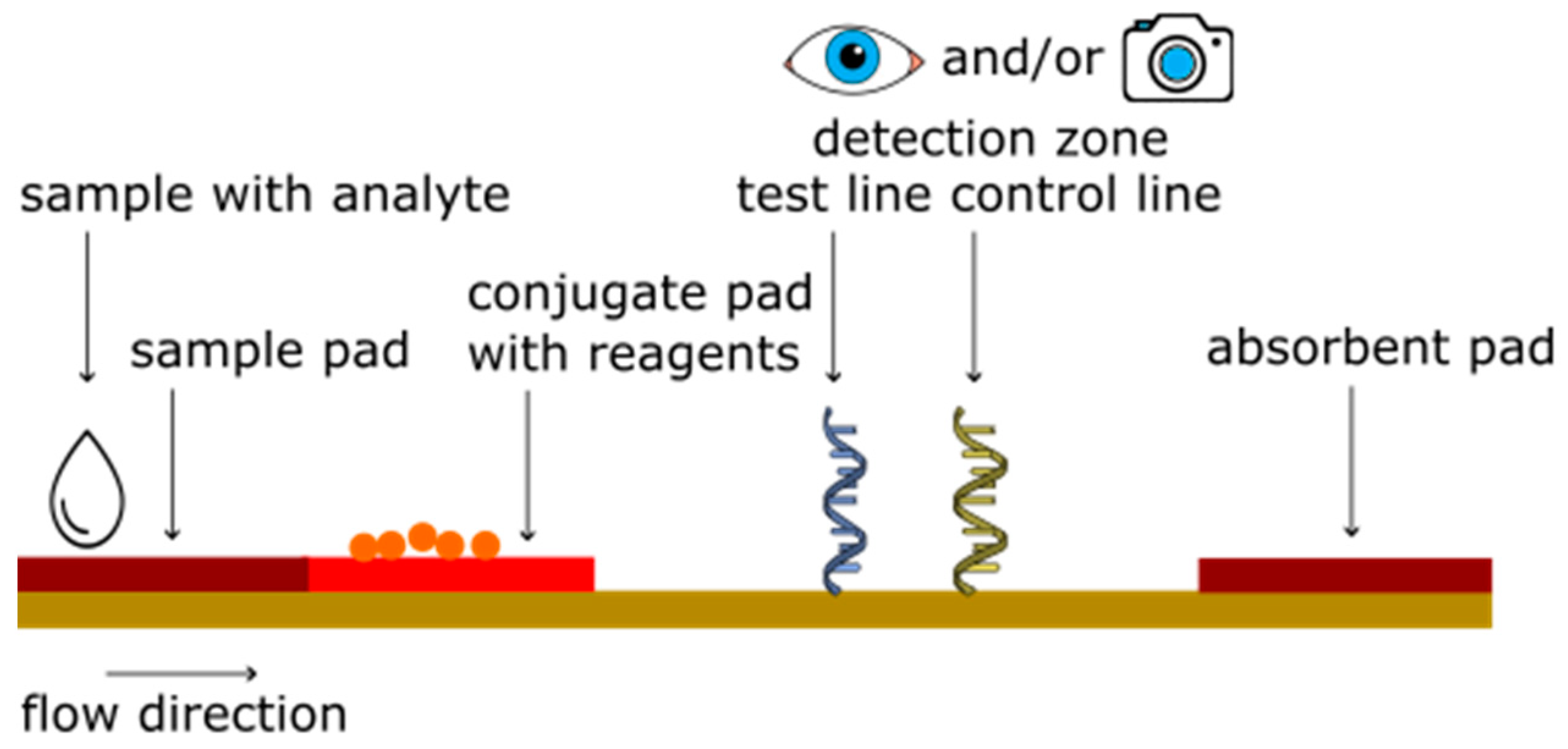
2. Principle of Lateral Flow Assays
3. Lateral Flow Assays for Biological Forensic Applications
3.1. Body Fluid Identification
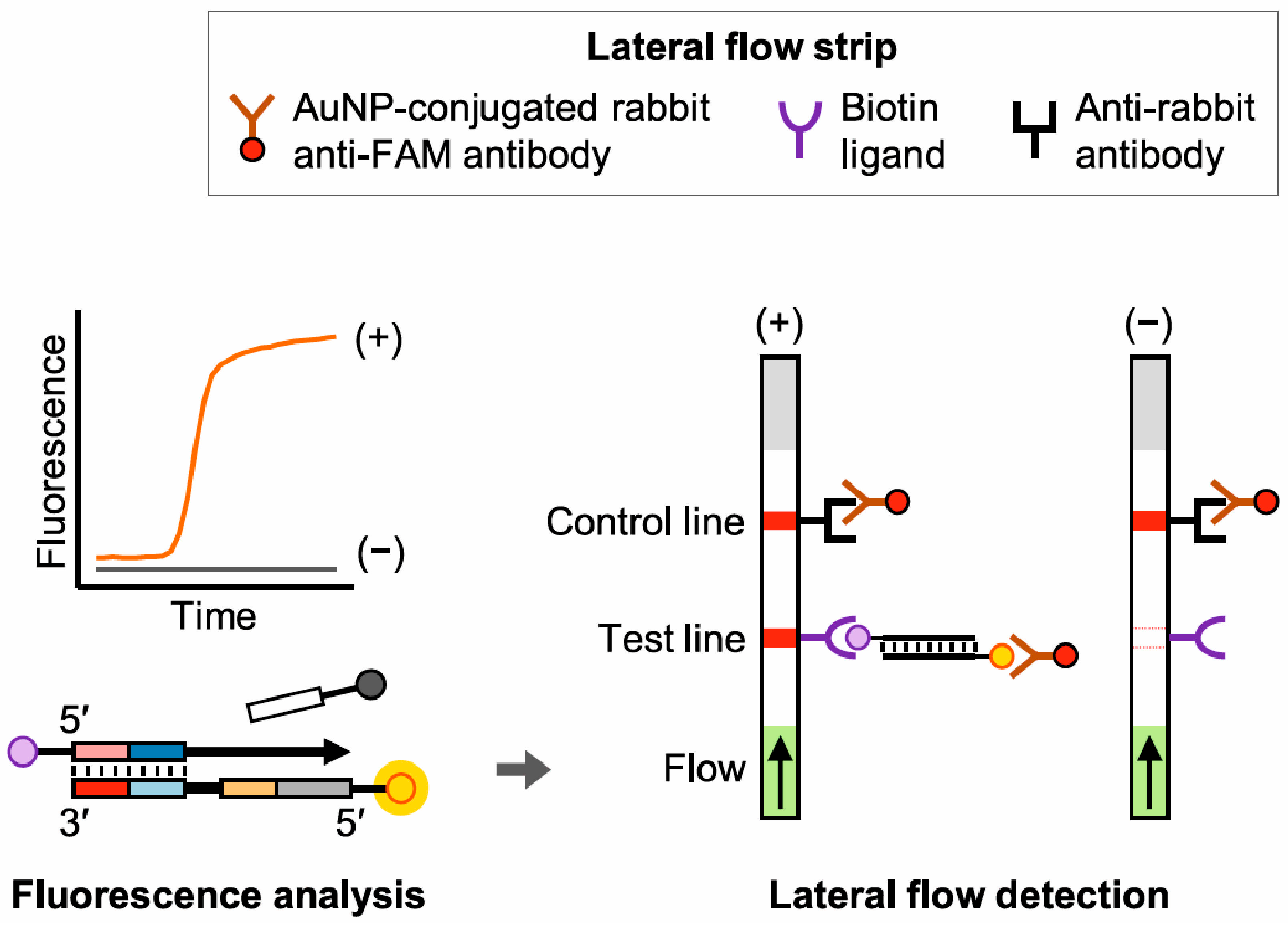
3.2. DNA
| Class of Analyte | Analyte(s) That Can Be Detected | Type of Test | LOD | Time-to-Result | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood | Glycophorin A | Lateral flow strip, RSID test | 0.05 µL blood | Extraction: 50 min Analysis: 10 min | [29,30,31,49] |
| Hemoglobin | Lateral flow strip, Seratec PMB test & Seratec HemDirect Hemoglobin test | 20 ng/mL | Extraction: 10 min Analysis: 10 min | ||
| Menstrual Blood | D-dimer | Lateral flow test, clearview rapid D-dimer test | 1:30 diluted stain | Extraction: 60 min Analysis: 20 min | [26,32,49] |
| Lateral flow test, PMB test, Seratec | 400 ng/mL 0.025 µL dried stain | Extraction: 10 min Analysis: 10 min | |||
| Dade Dimertest Latex Assay | 0.025 µL dried stain | Analysis: 10 min | |||
| Lateral flow test, OneStep D-dimer RapidCard InstaTest | 0.003125 µL dried stain | Analysis: 10 min | |||
| Saliva | α-amylase | Lateral flow strip, RSID | 1 µL saliva | Extraction: 50 min Analysis: 10 min | [26,30,33] |
| Lateral flow strip, Seratec Amylase test & CS | 1/1000 (50 mIU/mL) | Extraction: 10 min Analysis: 10 min | |||
| Semen | Semenogelin | Lateral flow strip, RSID | 1 µL semen | Extraction: 50 min Analysis: 10 min | [35,36,37,38,39,40,41,49] |
| Prostate specific antigen (PSA) | Lateral flow strip, Seratec, PSA rapid test (Atlantic International Medical), Rapid PSA (Health Tech International) | 0.5–1 ng/mL | Extraction: 50 min Analysis:10–15 min | ||
| Lateral flow strip, Bluestar, Identi-PSA | 4 ng/mL | Extraction: 10 min Analysis: 10 min | |||
| Lateral flow strip, Onestep ABAcard PSA test | 4 ng/mL | Analysis: 10 min | |||
| Urine | Tamm-Horsfall protein | Lateral flow strip, RSID | 10 µL urine | Analysis: 15 min | [42] |
| Biohazard | B. anthracis (anthrax) | Lateral flow strip, combined with NASBA | 1.5 fmol | 4 h | [44,45] |
| B. anthracis, F. tularensis (tularemia), Y. pestis (plague) | Lateral flow dipstick, combined with: | [46] | |||
| LAMP | 100–1000 genome copies | Reaction: 60 min Analysis: 15 min | |||
| tHDA | 100–1000 genome copies | Reaction: 30 min Analysis: 15 min | |||
| RPA | 100–1000 genome copies | Reaction: 90 min Analysis: 15 min | |||
| Donor profiling information | Sex typing | Lateral flow stip, combined with LAMP | 10 pg | Reaction: 30 min Analysis: 30 min | [47] |
| Opioid | M. speciosa | Lateral flow strip PCR | 0.01 pg | Reaction: <45 min Analysis: 10 min | [48] |
4. Lateral Flow Assays for Chemical Forensic Applications
4.1. Illicit Drugs
4.2. Biowarfare
4.3. Explosives
| Class of Analyte | Analyte(s) That Can Be Detected | Type of Test | LOD | Time-to-Result | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Illicit drugs | cocaine, codeine, thebaine, amphetamine, ephedrine, morphine, ketamine, MDMA and methamphetamine | Colorimetric µPAD | 1.2 to 8.7 µg (MDQ) | <5 min | [54] |
| amphetamine-type stimulants (in beverages) | Colorimetric nanofiber paper sensor | 0.3 μg/μL (DSK-1) and 0.8 μg/μL (DSK-2) | immediate | [55] | |
| scopolamine, atropine, caffeine, cocaine, morphine, ephedrine, alprazolam and dipyrone | Colorimetric µOPTO | n.d. | 20 min | [56] | |
| phenacetin (in seized cocaine) | Colorimetric paper device | 3.5 μg/mL | 1 min | [57] | |
| procaine (in seized cocaine) | Colorimetric paper device | 0.9 µmol/L | n.d. | [58] | |
| fentanyl and norfentanyl | Rapid Response Fentanyl Test Strips * | 0.25 µg/mL (fentanyl) and 0.05 µg/mL (norfentanyl) | 5–10 min | [59] | |
| ampthetamines | Cozart RapiScan System * | 1–5 ng/mL | 5 min | [60] | |
| THC, opiates, cocaine and amphetamine (in sweat) | Drug Screening Cartridge * | 68–190 pg | <10 min | [61] | |
| morphine, amphetamine, methamphetamine and BZE | Lateral flow strips (competitive assay) | 1.2–20.1 mg/mL | 10 min | [62] | |
| amphetamine, ketamine, cocaine, methamphetamine, opiates, marijuana and alcohol (in saliva) | DrugCheck SalivaScan * | 5–50 ng/mL (cut-off values) | 10 min | [63] | |
| Biowarfare | recin | Immunoassay | 50 ng/mL (with silver enhancement 100 pg/mL) | <10 min | [65] |
| botulinum neurotoxin type B | Immunoassay | 50 ng/mL (with silver enhancement 50 pg/mL) | <10 min | [65] | |
| recin | BioThreat Alert Test Strips * | 3.6 ng/mL | <20 min | [67] | |
| B. anthracis | Immunoassay | 400 pure spores | <30 min | [68] | |
| aflatoxin B1 | Dipstick aptamer (competitive assay) | 0.1 ng/mL | 30 min | [64] | |
| Explosives | TNT | LFIA and CL-LFIA | 1 µg/mL (LFIA) and 0.05 µg/mL (CL-LFIA) | 15 min | [73] |
| TNT | CL-LFIA | 0.2 µg/mL | 13 min | [74] | |
| metallic salts | Colorimetric µPAD | 0.025–0.4 µg | <10 min | [75] | |
| inorganic and military explosives | Colorimetric µPAD (2 types) | 0.39–19.8 µg | <5 min | [76] | |
| organic explosives | Colorimetric µPAD | 0.1–0.9 µg | n.d. | [77] |
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, J.R.; Yong, K.W.; Tang, R.; Gong, Y.; Wen, T.; Li, F.; Pingguan-Murphy, B.; Bai, D.; Xu, F. Advances and Challenges of Fully Integrated Paper-Based Point-of-Care Nucleic Acid Testing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 93, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Lateral Flow Assays for Viruses Diagnosis: Up-to-Date Technology and Future Prospects. Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 157, 116725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A. Lateral Flow Assays. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Yang, H.; Choi, J.R.; Gong, Y.; Hu, J.; Wen, T.; Li, X.; Xu, B.; Mei, Q.; Xu, F. Paper-Based Device with on-Chip Reagent Storage for Rapid Extraction of DNA from Biological Samples. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 2141–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B. Development of a Fully Integrated “Sample-In-Answer-Out” System for Automatic Genetic Analysis; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, S.A.; Khanlian, S.A.; Cole, L.A. Detection of Early Pregnancy Forms of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin by Home Pregnancy Test Devices. Clin. Chem. 2001, 47, 2131–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondhalekar, C.; Biela, E.; Rajwa, B.; Bae, E.; Patsekin, V.; Sturgis, J.; Reynolds, C.; Doh, I.J.; Diwakar, P.; Stanker, L.; et al. Detection of E. Coli Labeled with Metal-Conjugated Antibodies Using Lateral-Flow Assay and Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Z.; Wang, Q.; Sun, N.; Jia, X.; Wang, K.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S. Smartphone-Based Fluorescent Lateral Flow Immunoassay Platform for Highly Sensitive Point-of-Care Detection of Zika Virus Nonstructural Protein 1. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1055, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiskainen, I.; Juntunen, E.; Salminen, T.; Vuorenpää, K.; Bayoumy, S.; Vuorinen, T.; Khanna, N.; Pettersson, K.; Batra, G.; Talha, S.M. Double-Antigen Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Detection of Anti-HIV-1 and -2 Antibodies Using Upconverting Nanoparticle Reporters. Sensors 2021, 21, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukama, O.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Liang, Q.; Yi, Z.; Lu, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hussain, M.; Makafe, G.G.; et al. An Ultrasensitive and Specific Point-of-Care CRISPR/Cas12 Based Lateral Flow Biosensor for the Rapid Detection of Nucleic Acids. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, B.; Chen, Q.; Feng, Q.; Lin, L.; Sun, J. Point-of-Care-Testing of Nucleic Acids by Microfluidics. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 94, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, D.J.; Biggs, T.D.; Prugh, A.M.; Smith, J.A.; Hanburger, J.A.; Llano, B.; Avelar, R.; Ellis, A.; Lusk, B.; Malik Naanaa, A.; et al. The Use of Lateral Flow Immunoassays for the Detection of Fentanyl in Seized Drug Samples and Postmortem Urine. J. Forensic Sci. 2021, 66, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fojtíková, L.; Šuláková, A.; Blažková, M.; Holubová, B.; Kuchař, M.; Mikšátková, P.; Lapčík, O.; Fukal, L. Lateral Flow Immunoassay and Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay as Effective Immunomethods for the Detection of Synthetic Cannabinoid JWH-200 Based on the Newly Synthesized Hapten. Toxicol. Rep. 2017, 5, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Independent Forensics RSID. Available online: https://ifi-test.com/rsid/ (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- De Gruijter, M.; de Poot, C.J. The Use of Rapid Identification Information at the Crime Scene; Similarities and Differences between English and Dutch CSIs. Polic. Soc. 2018, 29, 848–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, C.; Sievers, C.; Royall, P.G.; Wolff, K. Evaluation of Latent Fingerprints for Drug Screening in a Social Care Setting. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2022, 46, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahadır, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Lateral Flow Assays: Principles, Designs and Labels. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhan, L.; Qin, Z.; Sackrison, J.; Bischof, J.C. Ultrasensitive and Highly Specific Lateral Flow Assays for Point-of-Care Diagnosis. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3593–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Kawde, A.N.; Daud, M. Designs, Formats and Applications of Lateral Flow Assay: A Literature Review. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2015, 19, 689–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, E.; Liang, T.; Spicar-Mihalic, P.; Houghtaling, J.; Ramachandran, S.; Yager, P. Two-Dimensional Paper Network Format That Enables Simple Multistep Assays for Use in Low-Resource Settings in the Context of Malaria Antigen Detection. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 4574–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beijer, R.P.; de Graaf, C.; van Weert, A.; van Leeuwen, T.G.; Aalders, M.C.G.; van Dam, A. Identification and Detection of Protein Markers to Differentiate between Forensically Relevant Body Fluids. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 290, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stravers, C.S.; Gool, E.L.; van Leeuwen, T.G.; Aalders, M.C.G.; van Dam, A. Multiplex Body Fluid Identification Using Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging with Principal Component Analysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 283, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.H.; Shin, K.J.; Yang, W.I.; Lee, H.Y. Body Fluid Identification in Forensics. BMB Rep. 2012, 45, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sijen, T. Molecular Approaches for Forensic Cell Type Identification: On MRNA, MiRNA, DNA Methylation and Microbial Markers. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2015, 18, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Steendam, K.; De Ceuleneer, M.; Dhaenens, M.; Van Hoofstat, D.; Deforce, D. Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics as a Tool to Identify Biological Matrices in Forensic Science. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2013, 127, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, L.C.; Liu, K.L.; Lin, W.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Huang, N.E.; Lee, J.C.I.; Linacre, A.; Hsieh, H.M. Evaluation of Three Commercial Kits Effective Identification of Menstrual Blood Based on the D-Dimer. Forensic Sci. Int. 2022, 338, 111389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluestar Forensic Our Products. Available online: https://www.bluestar-forensic.com/en/our-products (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- RSIDTM—Independent Forensics of IL. Available online: https://www.ifi-test.com/rsid/ (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Horjan, I.; Barbaric, L.; Mrsic, G. Applicability of Three Commercially Available Kits for Forensic Identification of Blood Stains. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2016, 290, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweers, B.A.; Old, J.; Boonlayangoor, P.W.; Reich, K.A. Developmental Validation of a Novel Lateral Flow Strip Test for Rapid Identification of Human Blood (Rapid Stain IdentificationTM-Blood). Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2008, 2, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrina, S.; Filippini, G.; Atzei, R.; Zaglia, E.; De Leo, D. Validation Studies of Rapid Stain Identification-Blood (RSID-Blood) Kit in Forensic Caseworks. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. Suppl. Ser. 2008, 1, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtkötter, H.; Dias Filho, C.R.; Schwender, K.; Stadler, C.; Vennemann, M.; Pacheco, A.C.; Roca, G. Forensic Differentiation between Peripheral and Menstrual Blood in Cases of Alleged Sexual Assault—Validating an Immunochromatographic Multiplex Assay for Simultaneous Detection of Human Hemoglobin and D-Dimer. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2018, 132, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapico, S.C.; Lascano, V.; Sadik, T.; Paromita, P.; Amaya, J.; Stadler, C.; Roca, G. The Killer Outfit and Timing: Impact of the Fabric and Time in Body Fluid Identification and DNA Profiling. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. Suppl. Ser. 2022, 8, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Old, J.B.; Schweers, B.A.; Boonlayangoor, P.W.; Reich, K.A. Developmental Validation of RSIDTM-Saliva: A Lateral Flow Immunochromatographic Strip Test for the Forensic Detection of Saliva. J. Forensic Sci. 2009, 54, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochmeister, M.N.; Budowle, B.; Rudin, O.; Gehrig, C.; Borer, U.; Thali, M.; Dirnhofer, R. Evaluation of Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Membrane Test Assays for the Forensic Identification of Seminal Fluid. J. Forensic Sci. 1999, 44, 1057–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, M.; Mitani, T.; Tsujita, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Higuchi, T.; Akane, A.; Nasu, M. Evaluation of Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Membrane Test for Forensic Examination of Semen. Leg. Med. 2001, 3, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.E.; Johnson, D.J.; Roberts, K.A.; Peterson, J.L. A Comparison of Rapid Stain Identification Test for Semen (RSID TM-Semen), Seratec® PSA Semiquant, and ABAcard® P30 Tests for the Forensic Identification of Seminal Fluid. Master’s Thesis, California State University, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kulstein, G.; Schacker, U.; Wiegand, P. Old Meets New: Comparative Examination of Conventional and Innovative RNA-Based Methods for Body Fluid Identification of Laundered Seminal Fluid Stains after Modular Extraction of DNA and RNA. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2018, 36, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, B.C.M.; Cheung, B.K.K. Identification of Human Semenogelin in Membrane Strip Test as an Alternative Method for the Detection of Semen. Forensic Sci. Int. 2007, 169, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boward, E.S.; Wilson, S.L. A Comparison of ABAcard® P30 and RSIDTM-Semen Test Kits for Forensic Semen Identification. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2013, 20, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishbaugh, J.M.; Cielski, S.; Fotusky, A.; Lighthart, S.; Maguire, K.; Quarino, L.; Conte, J. Detection of Prostate Specific Antigen and Salivary Amylase in Vaginal Swabs Using SERATEC® Immunochromatographic Assays. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 304, 109899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akutsu, T.; Watanabe, K.; Sakurada, K. Specificity, Sensitivity, and Operability of RSIDTM-Urine for Forensic Identification of Urine: Comparison with ELISA for Tamm-Horsfall Protein. J. Forensic Sci. 2012, 57, 1570–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtkötter, H.; Schwender, K.; Wiegand, P.; Peiffer, H.; Vennemann, M. Improving Body Fluid Identification in Forensic Trace Evidence—Construction of an Immunochromatographic Test Array to Rapidly Detect up to Five Body Fluids Simultaneously. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2018, 132, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, H.A.; Baeumner, A.J. Biosensor for the Specific Detection of a Single Viable B. anthracis Spore. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 376, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeumner, A.J.; Leonard, B.; McElwee, J.; Montagna, R.A. A Rapid Biosensor for Viable B. anthracis Spores. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 380, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zasada, A.A.; Zacharczuk, K.; Formińska, K.; Wiatrzyk, A.; Ziółkowski, R.; Malinowska, E. Isothermal DNA Amplification Combined with Lateral Flow Dipsticks for Detection of Biothreat Agents. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 560, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, S.; Niimi, H.; Kitajima, I. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Fluorescence Analysis and Lateral Flow Detection of Male DNA. Anal. Biochem. 2023, 664, 115029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tungphatthong, C.; Phadungcharoen, T.; Sooksawate, T.; Sukrong, S. PCR Combined with Lateral Flow Immunochromatographic Assay to Differentiate the Narcotic Mitragyna Speciosa from Related Species and Detect It in Forensic Evidence. Forensic Sci. Int. 2022, 331, 111149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SERATEC Products. Available online: https://www.seratec.com/ (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Dragan, A.-M.; Parrilla, M.; Feier, B.; Oprean, R.; Cristea, C.; De Wael, K. Analytical Techniques for the Detection of Amphetamine-Type Substances in Different Matrices: A Comprehensive Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 145, 116447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S. Forensic Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2022; ISBN 9780429804458. [Google Scholar]
- Harper, L.; Powell, J.; Pijl, E.M. An Overview of Forensic Drug Testing Methods and Their Suitability for Harm Reduction Point-of-Care Services. Harm Reduct. J. 2017, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviana, E.; Carrão, D.B.; Pratiwi, R.; Henry, C.S. Emerging Applications of Paper-Based Analytical Devices for Drug Analysis: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1116, 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musile, G.; Wang, L.; Bottoms, J.; Tagliaro, F.; McCord, B. The Development of Paper Microfluidic Devices for Presumptive Drug Detection. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 8025–8033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Son, S.U.; Kang, B.; Kim, J.; Lim, J.; Seo, S.; Kang, T.; Jung, J.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, H.; et al. Electrospun Nanofibrous Membrane-Based Colorimetric Device for Rapid and Simple Screening of Amphetamine-Type Stimulants in Drinks. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 3535–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, B.C.; Batista, A.D.; da Silveira Petruci, J.F. MOPTO: A Microfluidic Paper-Based Optoelectronic Tongue as Presumptive Tests for the Discrimination of Alkaloid Drugs for Forensic Purposes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1187, 339141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, G.O.; de Araujo, W.R.; Paixão, T.R.L.C. Portable and Low-Cost Colorimetric Office Paper-Based Device for Phenacetin Detection in Seized Cocaine Samples. Talanta 2018, 176, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.G.; De Araujo, W.R.; Muñoz, R.A.A.; Richter, E.M.; Santana, M.H.P.; Coltro, W.K.T.; Paixão, T.R.L.C. Simple and Sensitive Paper-Based Device Coupling Electrochemical Sample Pretreatment and Colorimetric Detection. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 5145–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelini, D.J.; Biggs, T.D.; Prugh, A.M.; Smith, J.A.; Hanburger, J.A.; Llano, B.; Avelar, R.; Ellis, A.; Lusk, B.; Naanaa, A.; et al. Detection of Fentanyl and Derivatives Using a Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Forensic Chem. 2021, 23, 100309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.; Jehanli, A.; Hand, C.; Cooper, G.; Smith, R. Evaluation of a Rapid Oral Fluid Point-of-Care Test for MDMA. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2007, 31, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, M.; Stuchinskaya, T.; Ramma, S.; Patel, J.; Sievers, C.; Goetz, S.; Hines, S.; Menzies, E.; Russell, D.A. Drug Screening Using the Sweat of a Fingerprint: Lateral Flow Detection of Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol, Cocaine, Opiates and Amphetamine. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2019, 43, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranova, N.A.; Byzova, N.A.; Zaiko, V.V.; Starovoitova, T.A.; Vengerov, Y.Y.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Integration of Lateral Flow and Microarray Technologies for Multiplex Immunoassay: Application to the Determination of Drugs of Abuse. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrio, A.; Sampedro, C.; Sanchez-Lopez, J.L.; Pimienta, M.; Campoy, P. Automated Low-Cost Smartphone-Based Lateral Flow Saliva Test Reader for Drugs-of-Abuse Detection. Sensors 2015, 15, 29569–29593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, W.B.; Kim, M.J.; Mun, H.; Kim, M.G. An Aptamer-Based Dipstick Assay for the Rapid and Simple Detection of Aflatoxin B1. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 62, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyu, R.H.; Shyu, H.F.; Liu, H.W.; Tang, S.S. Colloidal Gold-Based Immunochromatographic Assay for Detection of Ricin. Toxicon 2002, 40, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiao, D.J.; Shyu, R.H.; Hu, C.S.; Chiang, H.Y.; Tang, S.S. Colloidal Gold-Based Immunochromatographic Assay for Detection of Botulinum Neurotoxin Type B. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 809, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, D.R.; Prentice, K.W.; Ramage, J.G.; Prezioso, S.; Gauthier, C.; Swanson, T.; Hastings, R.; Basavanna, U.; Datta, S.; Sharma, S.K.; et al. Comprehensive Laboratory Evaluation of a Highly Specific Lateral Flow Assay for the Presumptive Identification of Ricin in Suspicious White Powders and Environmental Samples. Biosecur. Bioterror. Biodef. Strategy Pract. Sci. 2013, 11, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.B.; Tian, B.; Zhang, Z.P.; Deng, J.Y.; Cui, Z.Q.; Yang, R.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Wei, H.P.; Zhang, X.E. Rapid Detection of Bacillus Anthracis Spores Using a Super-Paramagnetic Lateral-Flow Immunological Detectionsystem. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Li, Z.; Huang, Z.; Li, K.; Lv, Y. Biosensors for Explosives: State of Art and Future Trends. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caygill, J.S.; Davis, F.; Higson, S.P.J. Current Trends in Explosive Detection Techniques. Talanta 2012, 88, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.G.; D’Souza, N.; Nicklin, S. A Review of Biosensors and Biologically-Inspired Systems for Explosives Detection. Analyst 2008, 133, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afiq Mohamed Huri, M.; Kalthom Ahmad, U.; Ibrahim, R.; Omar, M. A Review of Explosive Residue Detection from Forensic Chemistry Perspective. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2017, 21, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romolo, F.S.; Ferri, E.; Mirasoli, M.; D’Elia, M.; Ripani, L.; Peluso, G.; Risoluti, R.; Maiolini, E.; Girotti, S. Field Detection Capability of Immunochemical Assays during Criminal Investigations Involving the Use of TNT. Forensic Sci. Int. 2015, 246, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirasoli, M.; Buragina, A.; Dolci, L.S.; Guardigli, M.; Simoni, P.; Montoya, A.; Maiolini, E.; Girotti, S.; Roda, A. Development of a Chemiluminescence-Based Quantitative Lateral Flow Immunoassay for on-Field Detection of 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 721, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabaud, K.R.; Thomas, J.L.; Torres, M.N.; Oliveira, S.; McCord, B.R. Simultaneous Colorimetric Detection of Metallic Salts Contained in Low Explosives Residue Using a Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Device (MPAD). Forensic Chem. 2018, 9, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.L.; Corbin, I.; Kaufman, L.M.; Zreibe, K.; Blanes, L.; McCord, B.R. Simultaneous Colorimetric Detection of Improvised Explosive Compounds Using Microfluidic Paper-Based Analytical Devices (MPADs). Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taudte, R.V.; Beavis, A.; Wilson-Wilde, L.; Roux, C.; Doble, P.; Blanes, L. A Portable Explosive Detector Based on Fluorescence Quenching of Pyrene Deposited on Coloured Wax-Printed MPADs. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 4164–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, J.; Ruddy, A.; Domonoski, L.; Shanahan, A.; Daley, N.; McDevitt, C.; Roca, G. Recovery of DNA from SERATEC Immunochromatographic PSA and Saliva Test Strips. J. Forensic Sci. 2022, 67, 1176–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bruijns, B.; Tiggelaar, R.; Knotter, J.; van Dam, A. Use of Lateral Flow Assays in Forensics. Sensors 2023, 23, 6201. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23136201
Bruijns B, Tiggelaar R, Knotter J, van Dam A. Use of Lateral Flow Assays in Forensics. Sensors. 2023; 23(13):6201. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23136201
Chicago/Turabian StyleBruijns, Brigitte, Roald Tiggelaar, Jaap Knotter, and Annemieke van Dam. 2023. "Use of Lateral Flow Assays in Forensics" Sensors 23, no. 13: 6201. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23136201
APA StyleBruijns, B., Tiggelaar, R., Knotter, J., & van Dam, A. (2023). Use of Lateral Flow Assays in Forensics. Sensors, 23(13), 6201. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23136201