Improved Algorithms of Data Processing for Dispersive Interferometry Using a Femtosecond Laser
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principles of the Data Processing Algorithms
2.1. Proposed Algorithm 1: The Spectral Fringe Algorithm
2.2. Proposed Algorithm 2: The Combined Algorithm
3. Simulation and Experiment Results
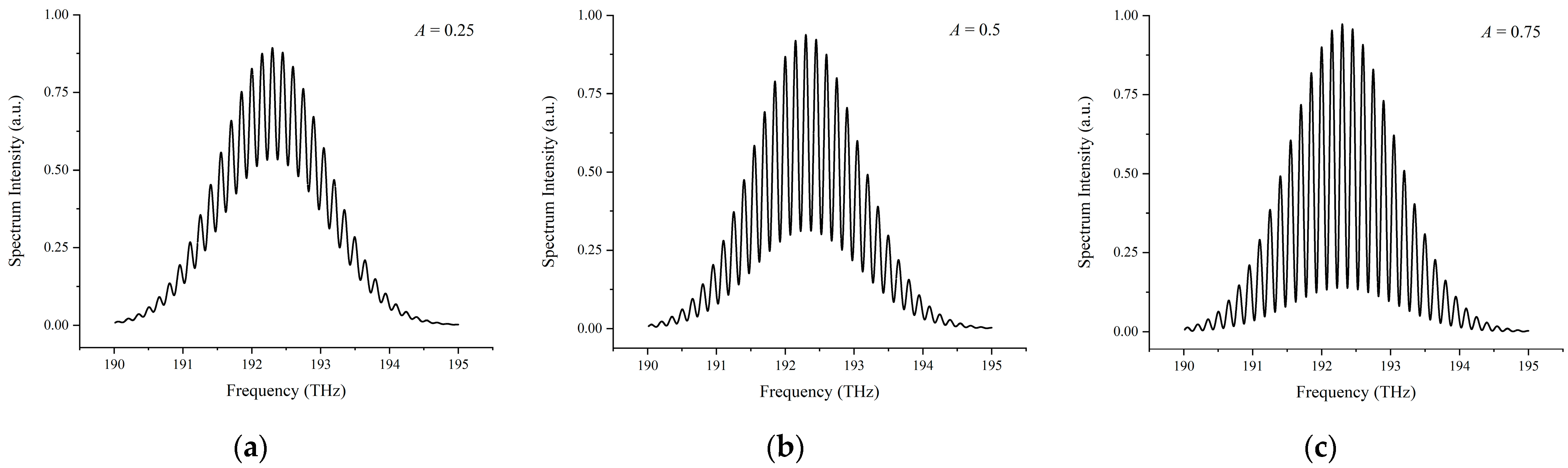
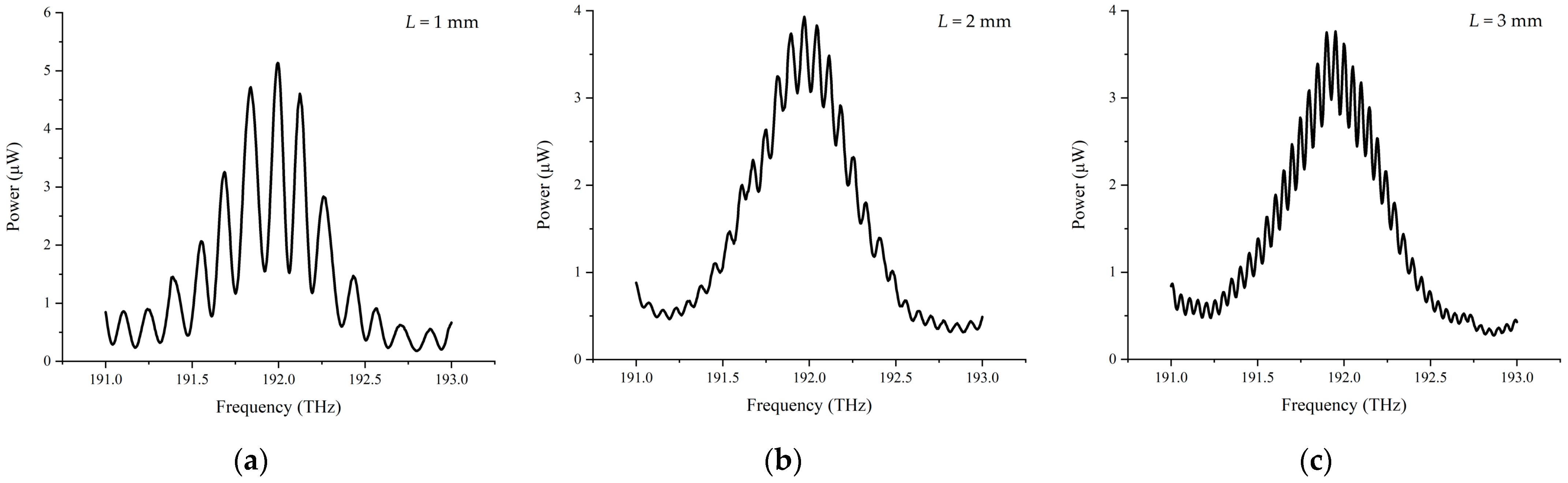
3.1. Simulation Results
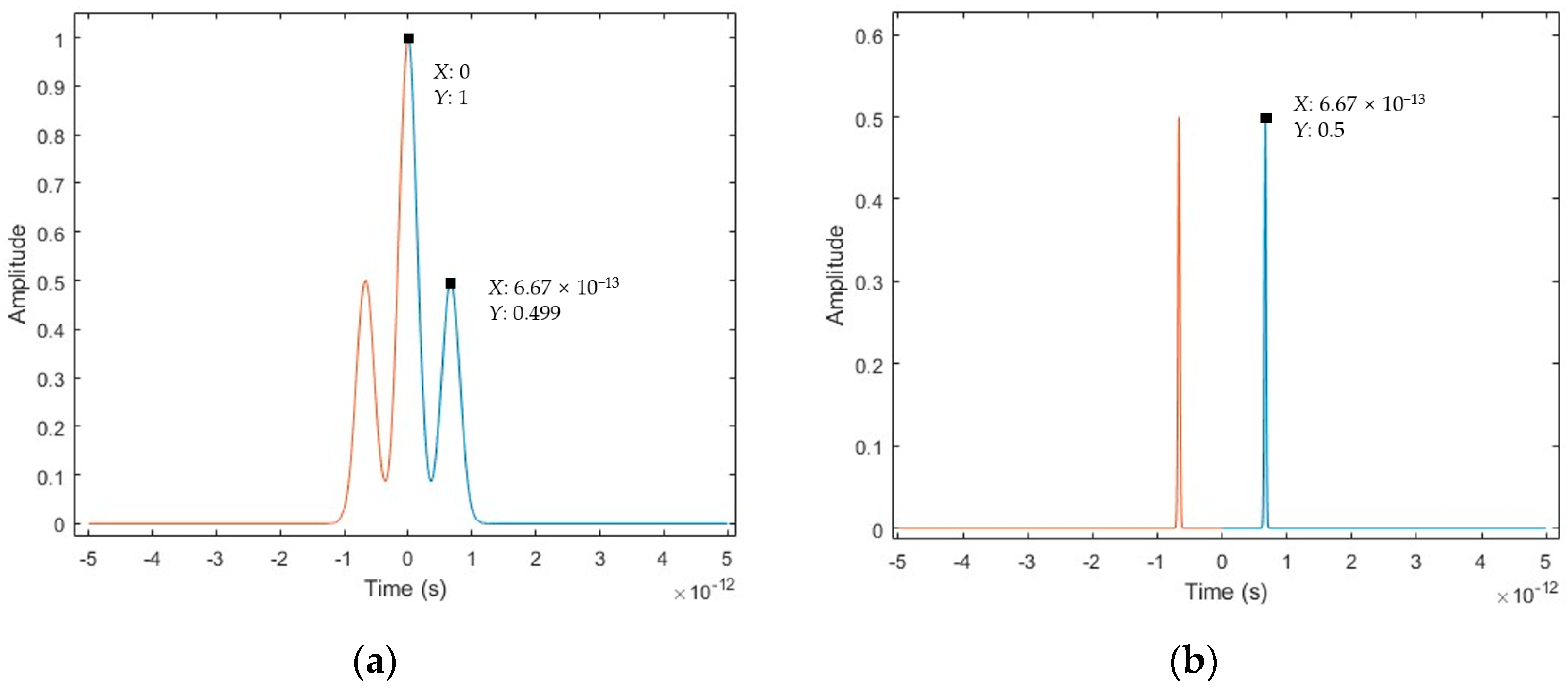
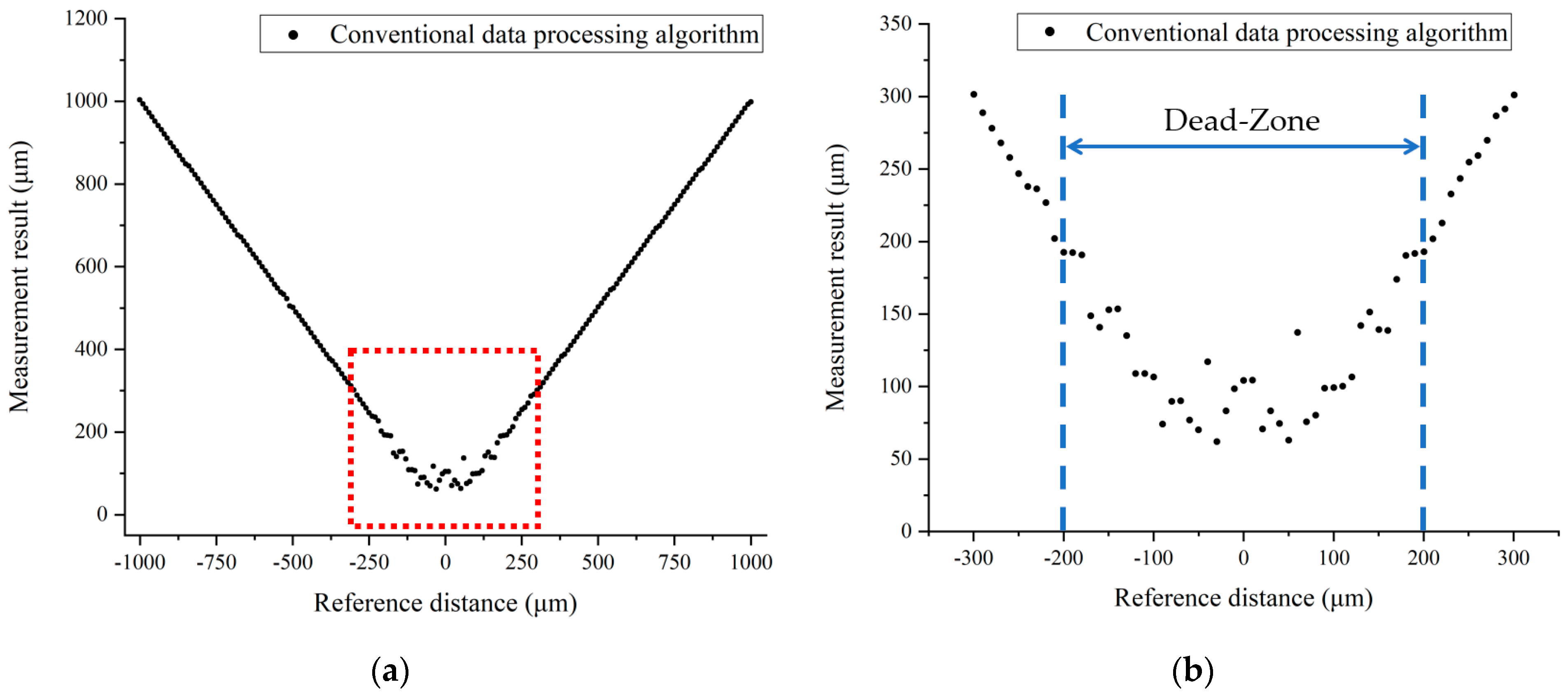
3.1.1. Simulation Results of the Conventional Data Processing Algorithm
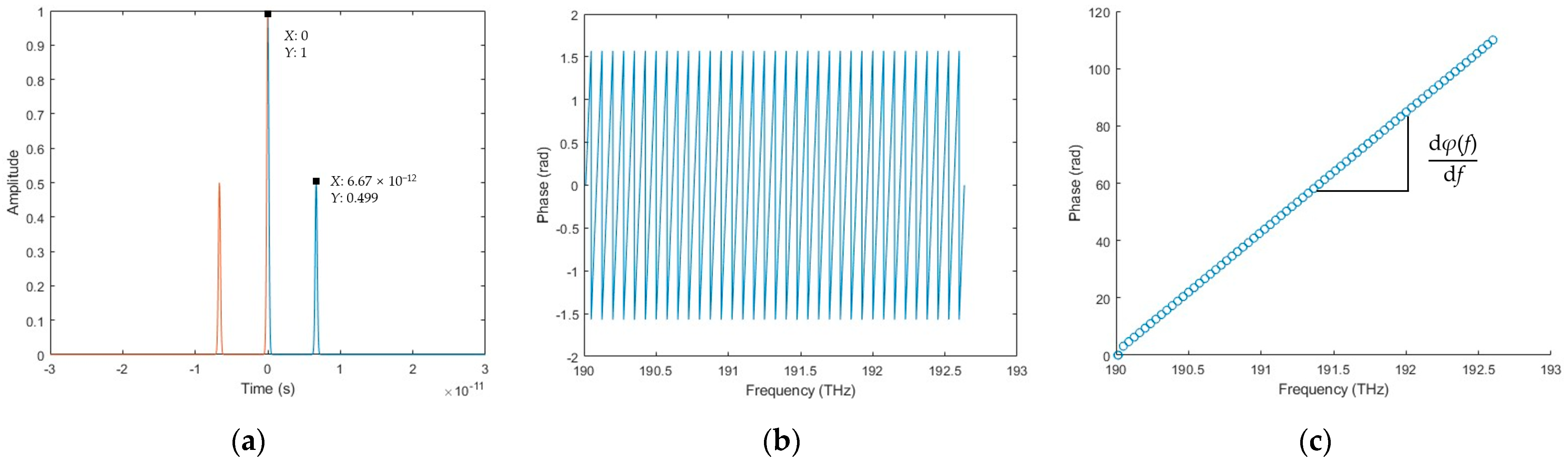
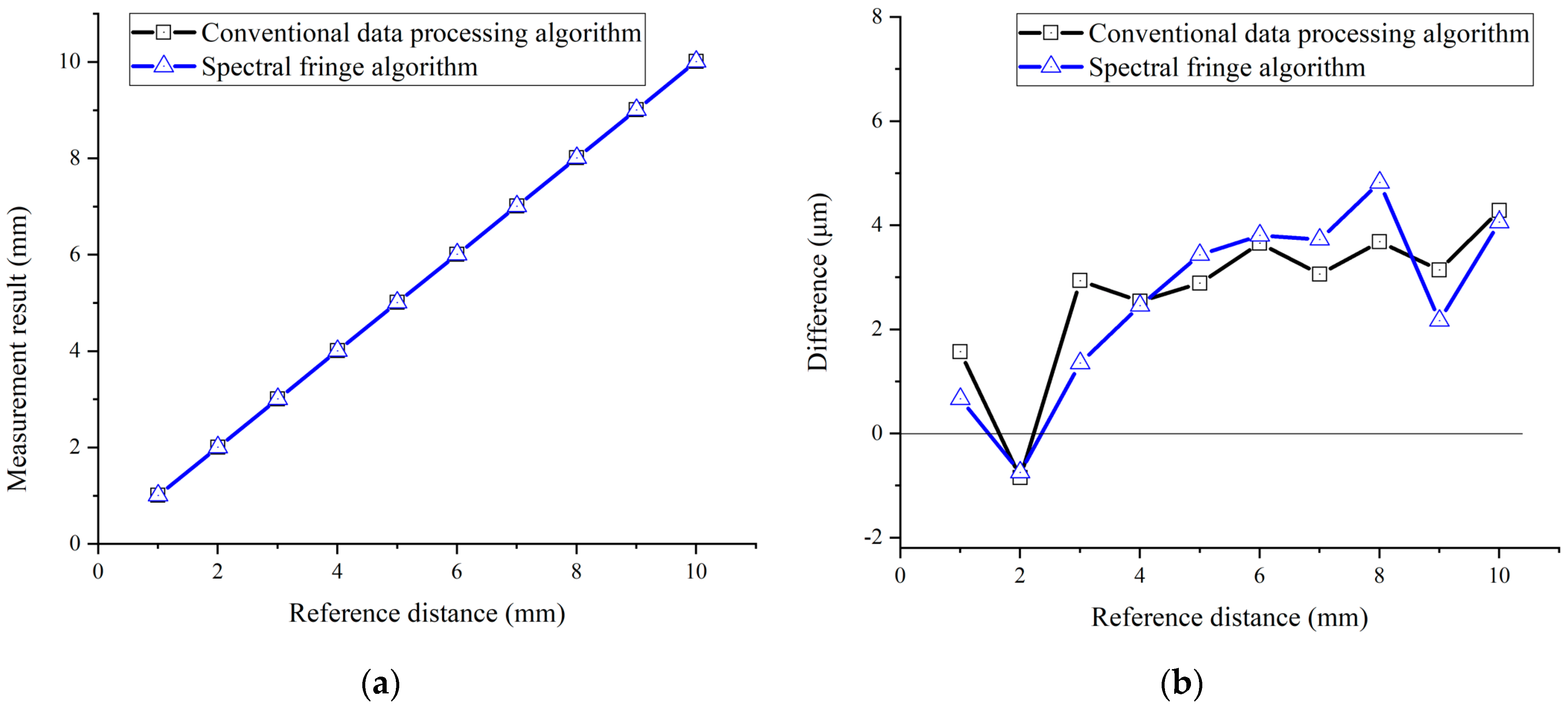
3.1.2. Simulation Results of the Spectral Fringe Algorithm
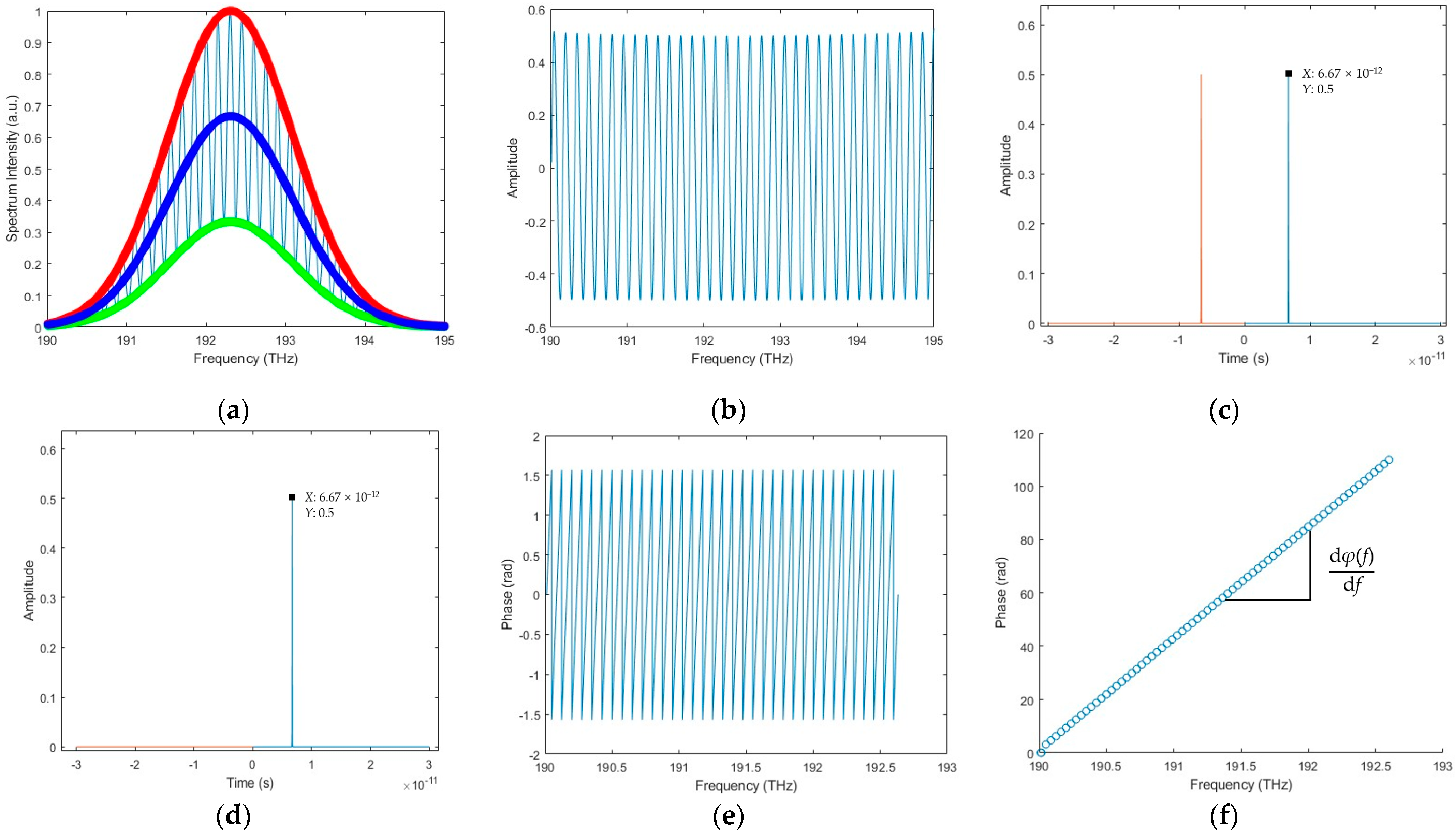
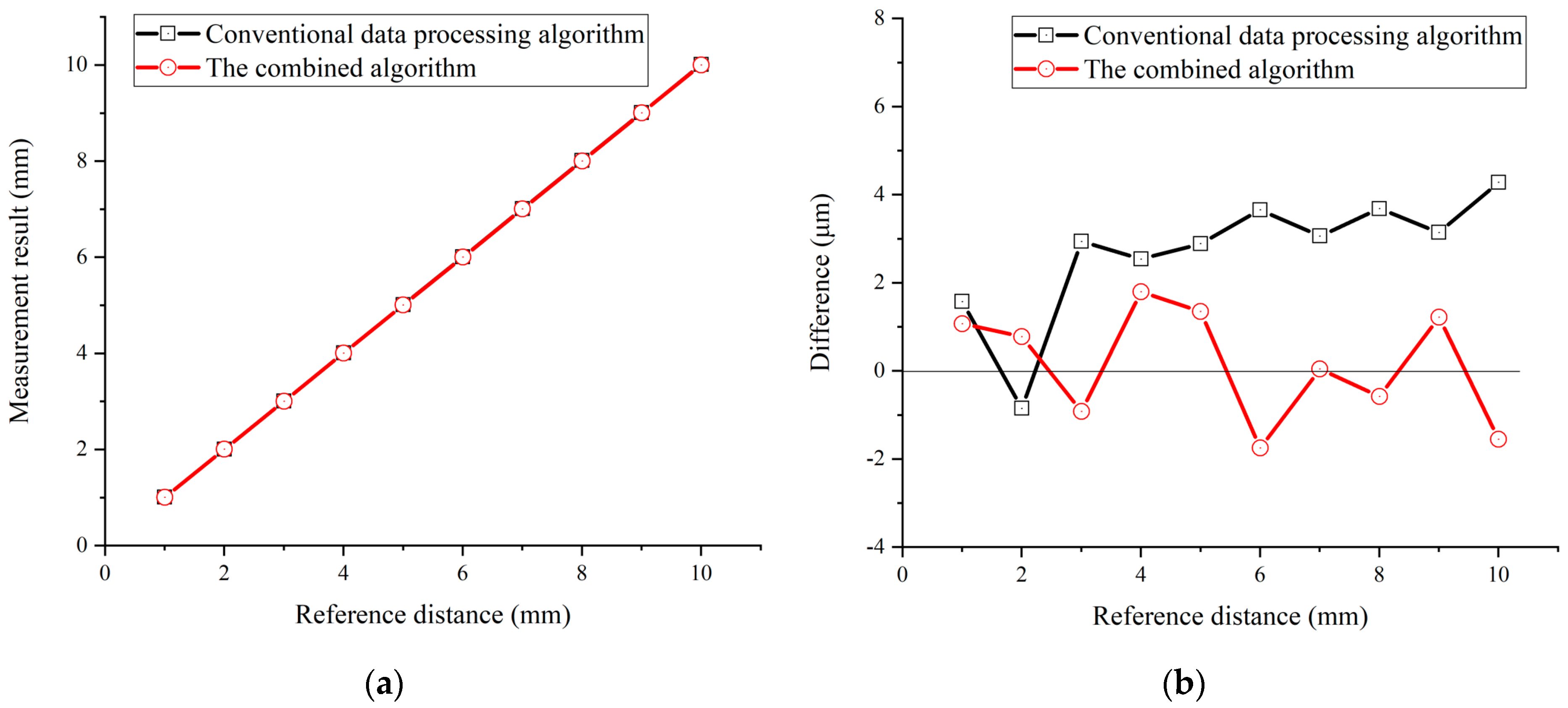
3.1.3. Simulation Results of the Combined Algorithm
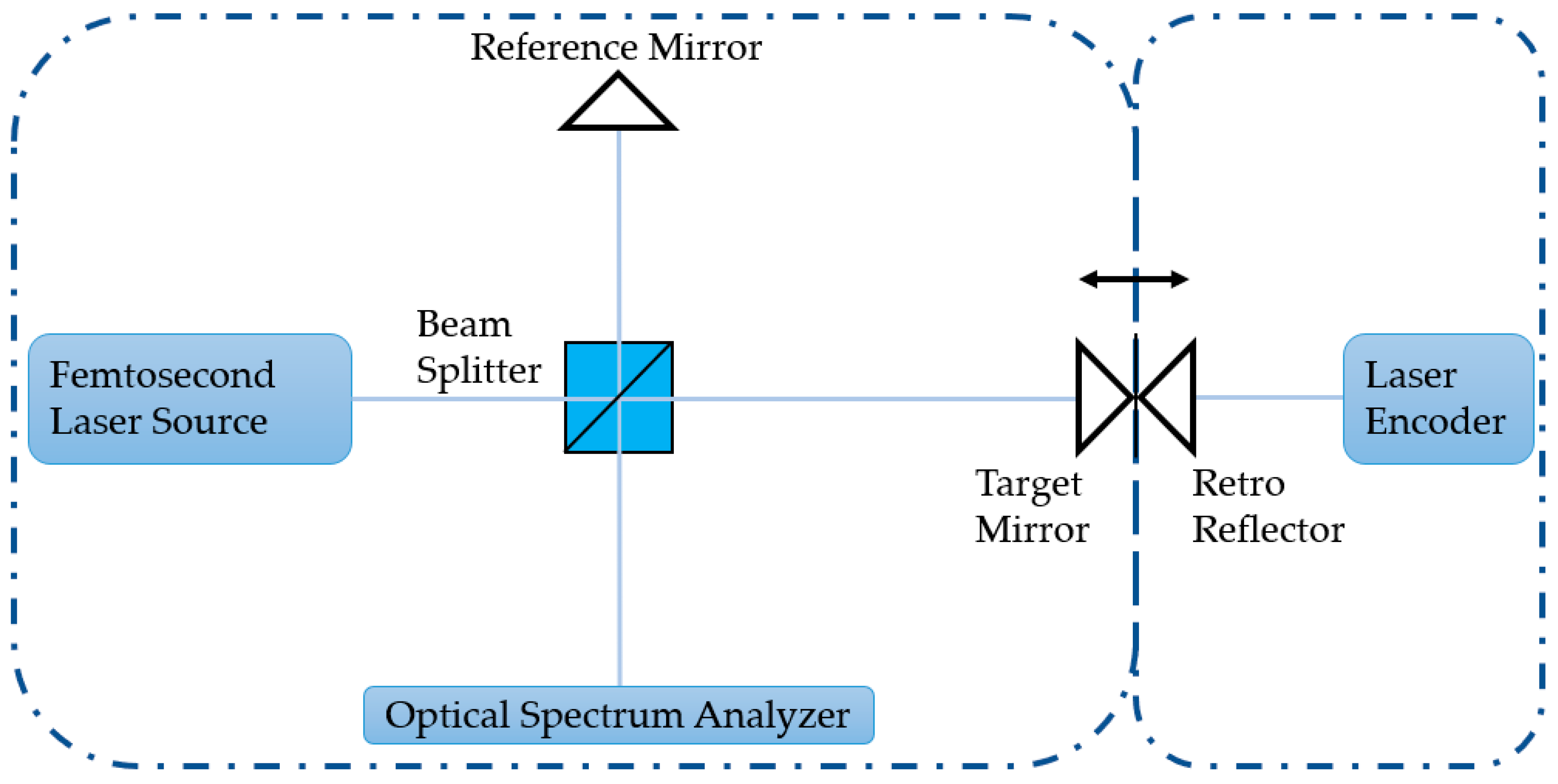
3.2. Experimental Setup
3.3. Experimental Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michelson, A.A.; Pease, F.; Pearson, F. Repetition of the Michelson-Morley experiment. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1929, 18, 181–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straube, G.; Fischer Calderón, J.S.; Ortlepp, I.; Füßl, R.; Manske, E. A Heterodyne Interferometer with Separated Beam Paths for High-Precision Displacement and Angular Measurements. Nanomanufacturing Metrol. 2021, 4, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W. Precision Nanometrology: Sensors and Measuring Systems for Nanomanufacturing, 1st ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2010; pp. 69–107. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Haitjema, H.; Fang, F.Z.; Leach, R.K.; Cheung, C.F.; Savio, E.; Linares, J.M. On-machine and in-process surface metrology for precision manufacturing. CIRP Ann. 2019, 68, 843–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W. Surface Metrology for Micro- and Nanofabrication, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2021; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Udem, T.; Holzwarth, R.; Hänsch, T.W. Optical frequency metrology. Nature 2002, 416, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.L. Nobel Lecture: Defining and measuring optical frequencies. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2006, 78, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänsch, T.W. Nobel lecture: Passion for precision. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2006, 78, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.J.; Diddams, S.A.; Ranka, J.K.; Stentz, A.; Windeler, R.S.; Hall, J.L.; Cundiff, S.T. Carrier-envelope phase control of femtosecond mode-locked lasers and direct optical frequency synthesis. Science 2000, 288, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortier, T.; Baumann, E. 20 years of developments in optical frequency comb technology and applications. Commun. Phys. 2019, 2, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddington, I.; Swann, W.C.; Newbury, N.R. Coherent multiheterodyne spectroscopy using stabilized optical frequency combs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 013902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoshima, K.; Matsumoto, H. High-accuracy measurement of 240-m distance in an optical tunnel by use of a compact femtosecond laser. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 5512–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W. Combs rule. Nat. Photonics 2009, 3, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.S.; Kim, S.W. Distance Measurements Using Mode-Locked Lasers: A Review. Nanomanufacturing Metrol. 2018, 1, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, R.; Shimizu, Y.; Shimizu, H.; Matsukuma, H.; Gao, W. Confocal probe based on the second harmonic generation for measurement of linear and angular displacements. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 11982–11993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Shimizu, Y. Optical Metrology for Precision Engineering, 1st ed.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 379–423. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.L.; Shimizu, Y.; Kudo, Y.; Ito, S.; Gao, W. Mode-locked laser autocollimator with an expanded measurement range. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 15554–15569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Kudo, Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Ito, S.; Gao, W. An optical lever by using a mode-locked laser for angle measurement. Precis. Eng. 2017, 47, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Shimizu, Y.; Tamada, J.; Kudo, Y.; Madokoro, S.; Nakamura, K.; Gao, W. Optical frequency domain angle measurement in a femtosecond laser autocollimator. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 16725–16738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.L.; Shimizu, Y.; Tamada, J.; Nakamura, K.; Matsukuma, H.; Chen, X.; Gao, W. Laser autocollimation based on an optical frequency comb for absolute angular position measurement. Precis. Eng. 2018, 54, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwi Astuti, W.; Matsukuma, H.; Nakao, M.; Li, K.; Shimizu, Y.; Gao, W. An Optical Frequency Domain Angle Measurement Method Based on Second Harmonic Generation. Sensors 2021, 21, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.W.; Matsukuma, H.; Sato, R.; Gao, W. Fabry-Perot angle sensor using a mode-locked femtosecond laser source. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 46366–46382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doloca, N.R.; Meiners-Hagen, K.; Wedde, M.; Pollinger, F.; Abou-Zeid, A. Absolute distance measurement system using a femtosecond laser as a modulator. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 115302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.S.; Lee, K.; Han, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.W. Absolute distance measurement with extension of nonambiguity range using the frequency comb of a femtosecond laser. Opt. Eng. 2014, 53, 122403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liao, L.; Xiong, S.; Li, G.; Cai, Z.; Zhu, Z. Synthetic wavelength interferometry of an optical frequency comb for absolute distance measurement. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dändliker, R.; Salvadé, Y.; Zimmermann, E. Distance measurement by multiple-wavelength interferometry. J. Opt. 1998, 29, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towers, C.E.; Towers, D.P.; Reid, D.T.; MacPherson, W.N.; Maier, R.R.; Jones, J.D. Fiber interferometer for simultaneous multiwavelength phase measurement with a broadband femtosecond laser. Opt. Lett. 2004, 29, 2722–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.W. Absolute distance measurement using the frequency comb of a femtosecond laser. CIRP Ann. 2010, 59, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvade, Y.; Schuhler, N.; Leveque, S.; Le Floch, S. High-accuracy absolute distance measurement using frequency comb referenced multiwavelength source. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 2715–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Jang, Y.S.; Hyun, S.; Chun, B.J.; Kang, H.J.; Yan, S.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, Y.J. Absolute positioning by multi-wavelength interferometry referenced to the frequency comb of a femtosecond laser. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 9121–9129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, H.Y. Absolute group refractive index measurement of air by dispersive interferometry using frequency comb. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 33597–33607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, F.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Qu, X. Absolute distance measurement with correction of air refractive index by using two-color dispersive interferometry. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 24361–24376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Q.; Song, M.; Zheng, J.; Jia, L.; Liu, J.; Ni, L.; Nian, J.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, F.; Qu, X. Improvement of Distance Measurement Based on Dispersive Interferometry Using Femtosecond Optical Frequency Comb. Sensors 2022, 22, 5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wu, T.; Lin, J.; Yang, L.; Zhu, J. Optical Frequency Comb Frequency-division Multiplexing Dispersive Interference Multichannel Distance Measurement. Nanomanuf. Metrol. 2023, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, S. Spectrometry with frequency combs. Opt. Lett. 2002, 27, 766–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wei, H.; Wu, X.; Yang, H.; Li, Y. Absolute distance measurement by dual-comb nonlinear asynchronous optical sampling. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 6597–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Xiong, S.; Ni, K.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Q. Parameter optimization of a dual-comb ranging system by using a numerical simulation method. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 32044–32053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Wu, Z.; Cao, H.; Shi, Y.; Li, R.; Tian, H.; Song, Y.; Hu, M. Dual-comb absolute distance measurement of non-cooperative targets with a single free-running mode-locked fiber laser. Opt. Commun. 2021, 482, 126566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wu, G. Dual-Comb Ranging. Engineering 2018, 4, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Absolute measurement of a long, arbitrary distance to less than an optical fringe. Opt. Lett. 2004, 29, 1153–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balling, P.; Kren, P.; Masika, P.; van den Berg, S.A. Femtosecond frequency comb based distance measurement in air. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 9300–9313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Takahashi, S.; Takamasu, K.; Matsumoto, H. Time-of-flight method using multiple pulse train interference as a time recorder. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 4881–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Matsumoto, H. Measurement accuracy of the pulse repetition interval-based excess fraction (PRIEF) method: An analogy-based theoretical analysis. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. Rapid Publ. 2012, 7, 12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, K.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, Y.J. High precision laser ranging by time-of-flight measurement of femtosecond pulses. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2012, 23, 065203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, K.N.; Kim, S.W. Absolute distance measurement by dispersive interferometry using a femtosecond pulse laser. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 5954–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, S.A.; Persijn, S.T.; Kok, G.J.; Zeitouny, M.G.; Bhattacharya, N. Many-wavelength interferometry with thousands of lasers for absolute distance measurement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 183901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Qu, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, X.; Peng, B. Absolute distance measurement based on spectral interferometry using femtosecond optical frequency comb. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2019, 120, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, P.J. Extending the unambiguous range of two-color interferometers. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 5948–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falaggis, K.; Towers, D.P.; Towers, C.E. Optimum wavelength selection for the method of excess fractions. In Proceedings of the Optical Engineering Applications, San Diego, CA, USA, 11 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, M.; Zeitouny, M.G.; Bhattacharya, N.; van den Berg, S.A.; Urbach, H.P. Long distance measurement with femtosecond pulses using a dispersive interferometer. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 6549–6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Berg, S.A.; van Eldik, S.; Bhattacharya, N. Mode-resolved frequency comb interferometry for high-accuracy long distance measurement. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, H. Revised Precision Measurement, 1st ed.; Corona Publishing: Tokyo, Japan, 1957; pp. 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Falaggis, K.; Towers, D.P.; Towers, C.E. Method of excess fractions with application to absolute distance metrology: Theoretical analysis. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, 5484–5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corporation, Y.T.M. AQ6370D Telecom Optical Spectrum Analyzer 600–1700 nm. Available online: https://tmi.yokogawa.com/solutions/products/optical-measuring-instruments/optical-spectrum-analyzer/aq6370d-optical-spectrum-analyzer/#Documents-Downloads____downloads_9 (accessed on 1 July 2022).
- Xu, Y. Study on Absolute Distance Measurement Technology Based on Femtosecond Optical Frequency Comb. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 23 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Inaba, H.; Daimon, Y.; Hong, F.L.; Onae, A.; Minoshima, K.; Schibli, T.R.; Matsumoto, H.; Hirano, M.; Okuno, T.; Onishi, M.; et al. Long-term measurement of optical frequencies using a simple, robust and low-noise fiber based frequency comb. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 5223–5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.; Wu, J.; Suzuki, A.; Sato, R.; Matsukuma, H.; Gao, W. Improved Algorithms of Data Processing for Dispersive Interferometry Using a Femtosecond Laser. Sensors 2023, 23, 4953. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104953
Liu T, Wu J, Suzuki A, Sato R, Matsukuma H, Gao W. Improved Algorithms of Data Processing for Dispersive Interferometry Using a Femtosecond Laser. Sensors. 2023; 23(10):4953. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104953
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Tao, Jiucheng Wu, Amane Suzuki, Ryo Sato, Hiraku Matsukuma, and Wei Gao. 2023. "Improved Algorithms of Data Processing for Dispersive Interferometry Using a Femtosecond Laser" Sensors 23, no. 10: 4953. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104953
APA StyleLiu, T., Wu, J., Suzuki, A., Sato, R., Matsukuma, H., & Gao, W. (2023). Improved Algorithms of Data Processing for Dispersive Interferometry Using a Femtosecond Laser. Sensors, 23(10), 4953. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104953






