Combining Low-Light Scene Enhancement for Fast and Accurate Lane Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
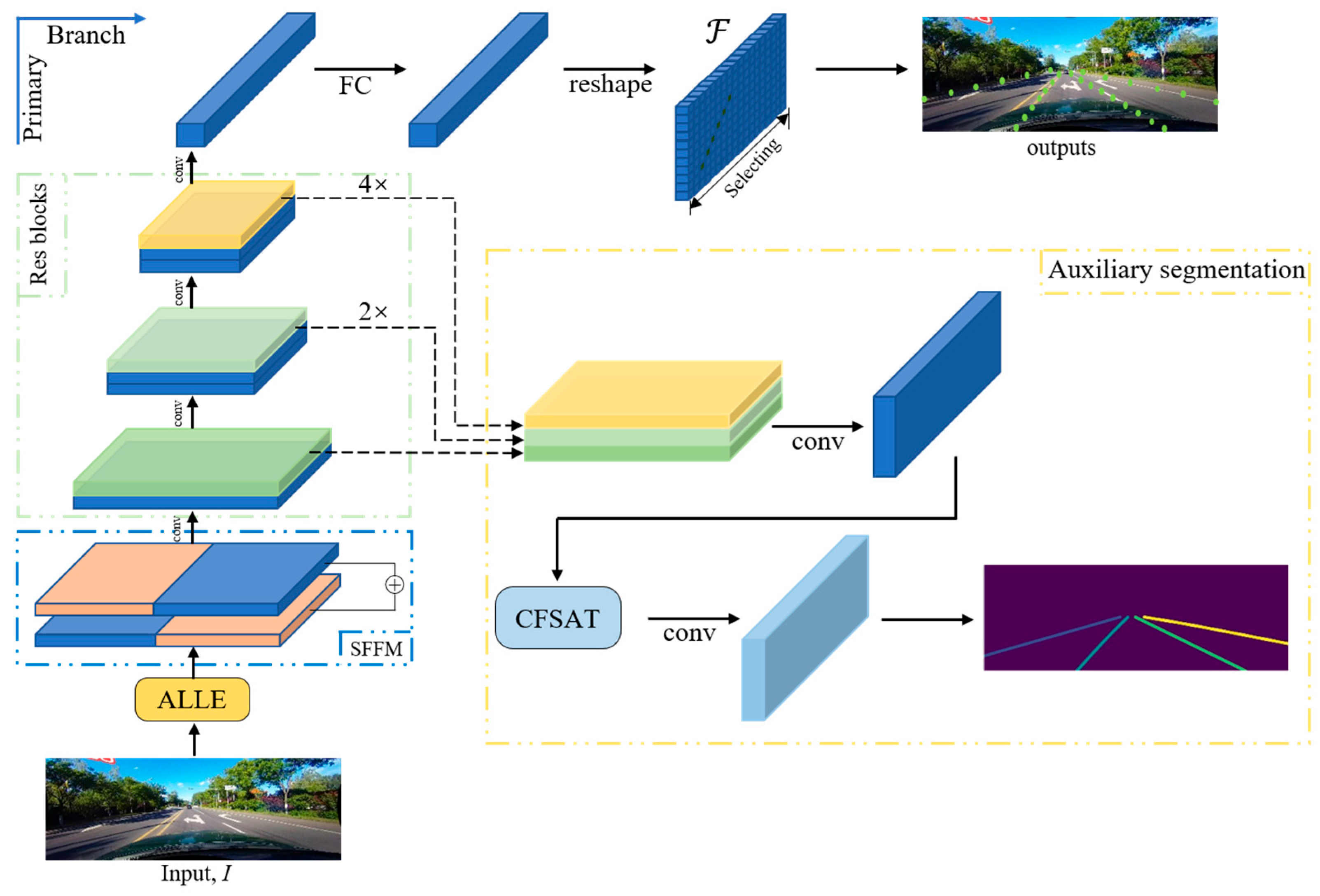
- We propose low-light enhancement fast lane detection (LLFLD), a lane detection system that combines a low-light image enhancement network (ALLE) with a lane detection network. Our approach significantly enhances the performance of the network in low-light environments while maintaining an ultra-fast detection speed.
- We propose a symmetric feature flipping module (SFFM), which refines the low-level features and gains more precise lane localization.
- We propose a channel fusion self-attention mechanism (CFSAT) in the auxiliary segmentation module, which captures and utilizes more global context information.
- We propose a novel structural loss function that leverages the inherent geometric constraints of lanes to optimize the detection results.
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Methods
2.2. Segmentation Methods
2.3. Anchor-Based Methods
2.4. Low Light Image Enhancement
3. Methodology
3.1. Overall Pipeline
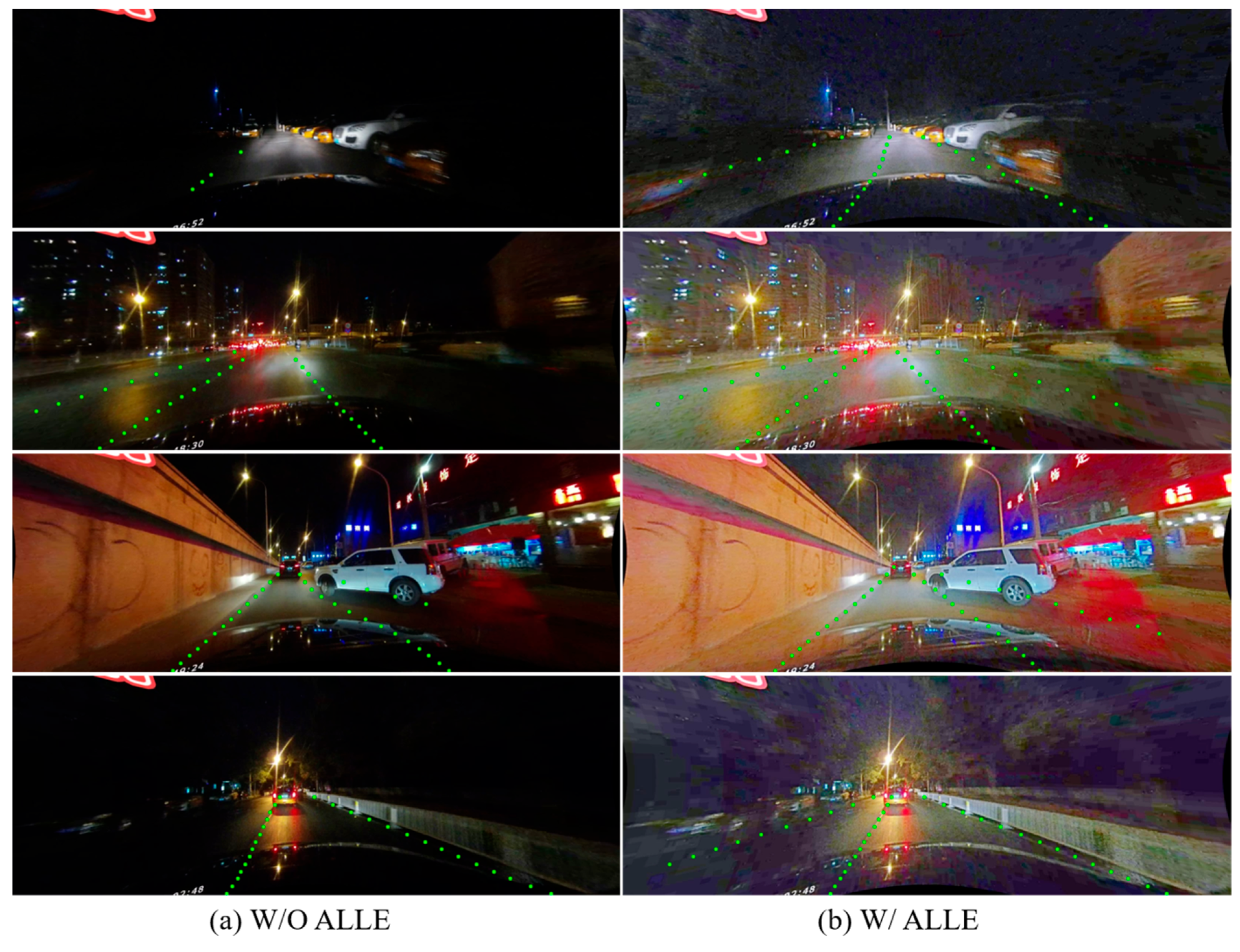
3.2. Automatic Low-Light Scene Enhancement (ALLE)
3.3. Symmetric Feature Flipping Module (SFFM)
3.4. Channel Fusion Self-Attention Mechanism (CFSAT)
3.5. A Novel Lane Structural Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Evalutaion Metrics
4.2. Implementation Details
5. Results
6. Ablation Study
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forster, M.; Frank, R.; Gerla, M.; Engel, T. A cooperative advanced driver assistance system to mitigate vehicular traffic shock waves. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2014-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Toronto, ON, Canada, 27 April–2 May 2014; pp. 1968–1976. [Google Scholar]
- Throngnumchai, K.; Nishiuchi, H.; Matsuno, Y.; Satoh, H. Application of Background Light Elimination Technique for Lane Marker Detection; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013; ISSN 0148-7191. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Shi, J.; Luo, P.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Spatial as deep: Spatial cnn for traffic scene understanding. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–3 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.; Ma, Z.; Liu, C.; Loy, C.C. Learning lightweight lane detection cnns by self attention distillation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1013–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, X. Ultra fast structure-aware deep lane detection. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 276–291. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Jain, A.K. Lane boundary detection using a multiresolution hough transform. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 26–29 October 1997; pp. 748–751. [Google Scholar]
- Canny, J. A computational approach to edge detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1986, PAMI-8, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.-Y.; Tsai, S.-J.; Chan, V. HSI color model based lane-marking detection. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference, Toronto, ON, Canada, 17–20 September 2006; pp. 1168–1172. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Shin Yoon, J.; Shin, S.; Bailo, O.; Kim, N.; Lee, T.-H.; Seok Hong, H.; Han, S.-H.; So Kweon, I. Vpgnet: Vanishing point guided network for lane and road marking detection and recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1947–1955. [Google Scholar]
- Neven, D.; De Brabandere, B.; Georgoulis, S.; Proesmans, M.; Van Gool, L. Towards end-to-end lane detection: An instance segmentation approach. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Suzhou, China, 26–30 June 2018; pp. 286–291. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Line-cnn: End-to-end traffic line detection with line proposal unit. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 21, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Guo, S.; Tan, X.; Xu, K.; Wang, M.; Ma, L. Rethinking efficient lane detection via curve modeling. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 17062–17070. [Google Scholar]
- Tabelini, L.; Berriel, R.; Paixao, T.M.; Badue, C.; De Souza, A.F.; Oliveira-Santos, T. Keep your eyes on the lane: Real-time attention-guided lane detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 294–302. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, S.; Lee, H.S.; Myeong, H.; Yun, S.; Park, H.; Cho, J.; Kim, D.H. End-to-end lane marker detection via row-wise classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 1006–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, H.; Kong, N.S.P. Brightness preserving dynamic histogram equalization for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2007, 53, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Han, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, M. Decoupled Low-Light Image Enhancement. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. (TOMM) 2022, 18, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zheng, Y. Learning to see moving objects in the dark. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7324–7333. [Google Scholar]
- Sada, A.; Kinoshita, Y.; Shiota, S.; Kiya, H. Histogram-based image pre-processing for machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 7th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), Nara, Japan, 9–12 October 2018; pp. 272–275. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Li, X.; Xiao, M.; Ma, B.; Zhao, Y. Fast expansion-bins-determination for multiple histograms modification based reversible data hiding. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2022, 29, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Evans, A.N. Improved single image dehazing methods for resource-constrained platforms. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2021, 18, 2511–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çimtay, Y.; Yilmaz, G.N. Low Light Image Enhancement on Mobile Devices by Using Dehazing. In Proceedings of the Electrical and Computer Engineering: First International Congress, ICECENG 2022, Virtual Event, 9–12 February 2022; pp. 57–67. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Guo, C.; Han, L.; Jiang, J.; Cheng, M.-M.; Gu, J.; Loy, C.C. Low-light image and video enhancement using deep learning: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 9396–9416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.04560. preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Li, C.; Guo, J.; Loy, C.C.; Hou, J.; Kwong, S.; Cong, R. Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 1780–1789. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Poynton, C.A. A Technical Introduction to Digital Video; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Hu, H.; Lin, S.; Dai, J. Deformable convnets v2: More deformable, better results. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 9308–9316. [Google Scholar]
- Mandalia, H.M.; Salvucci, M.D.D. Using support vector machines for lane-change detection. In Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting, Orlando, FL, USA, 26–30 September 2005; pp. 1965–1969. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 2006, 313, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 8024–8035. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, T.; Xiong, Z. End-to-end lane shape prediction with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2021; pp. 3694–3702. [Google Scholar]
- Philion, J. Fastdraw: Addressing the long tail of lane detection by adapting a sequential prediction network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 11582–11591. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Wang, S.; Cai, X.; Zhang, W.; Liang, X.; Li, Z. Curvelane-nas: Unifying lane-sensitive architecture search and adaptive point blending. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 689–704. [Google Scholar]





| Method | Total | Normal | Crowded | Dazzle | Shadow | No line | Arrow | Curve | Cross | Night | FPS | MACs(G) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Res50-Seg [33] | 66.70 | 87.43 | 64.10 | 54.12 | 60.70 | 38.10 | 79.00 | 59.83 | 2505 | 60.60 | - | - |
| LSTR(ResNet-18,2×) [34] | 68.72 | 86.78 | 67.34 | 56.63 | 59.82 | 40.10 | 78.66 | 56.64 | 1166 | 59.92 | - | - |
| FastDraw (ResNet-50) [35] | 67.13 | 85.90 | 63.60 | 57.00 | 59.90 | 40.60 | 79.40 | 65.20 | 7013 | 57.80 | 90.3 | - |
| SCNN [3] | 71.60 | 90.60 | 69.7 | 58.50 | 66.90 | 43.40 | 84.10 | 64.40 | 1990 | 66.10 | 7.5 | 328.4 |
| ENet-SAD [4] | 70.8 | 90.10 | 68.80 | 60.20 | 65.90 | 41.60 | 84.00 | 65.70 | 1998 | 66.00 | 75 | 7.8 |
| UFLD(ResNet-18) [5] | 68.40 | 87.70 | 66.00 | 58.40 | 62.80 | 40.20 | 81.00 | 57.90 | 1743 | 62.10 | 322.5 | - |
| UFLD(ResNet-34) [5] | 72.30 | 90.70 | 70.20 | 59.50 | 69.30 | 44.40 | 85.70 | 69.50 | 2037 | 66.70 | 175.0 | - |
| CurveLanes-NAS-M [36] | 73.50 | 90.20 | 70.50 | 65.90 | 69.30 | 48.80 | 85.70 | 67.50 | 2359 | 68.20 | - | 35.7 |
| Res18-Ours | 71.30 | 89.20 | 67.20 | 58.50 | 63.30 | 42.50 | 82.80 | 58.00 | 1819 | 66.50 | 330 | 17.4 |
| Res34-Ours | 75.20 | 91.00 | 71.80 | 65.30 | 70.20 | 47.80 | 86.20 | 69.50 | 1913 | 70.50 | 177 | 33.2 |
| Baseline | Low-Light Enhancement | Flipping Module | Attention Mechanism | Structural Loss | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| √ | 72.1 | ||||
| √ | 73.8 (+1.7) | ||||
| √ | √ | 74.3 (+2.2) | |||
| √ | √ | √ | 74.9 (+2.8) | ||
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 75.2 (+3.1) |
| W/O ALLE | W/ALLE | Shadow-F1 | Night-F1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| √ | 68.90 | 65.73 | |
| √ | 70.20 | 70.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ke, C.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D. Combining Low-Light Scene Enhancement for Fast and Accurate Lane Detection. Sensors 2023, 23, 4917. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104917
Ke C, Xu Z, Zhang J, Zhang D. Combining Low-Light Scene Enhancement for Fast and Accurate Lane Detection. Sensors. 2023; 23(10):4917. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104917
Chicago/Turabian StyleKe, Changshuo, Zhijie Xu, Jianqin Zhang, and Dongmei Zhang. 2023. "Combining Low-Light Scene Enhancement for Fast and Accurate Lane Detection" Sensors 23, no. 10: 4917. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104917
APA StyleKe, C., Xu, Z., Zhang, J., & Zhang, D. (2023). Combining Low-Light Scene Enhancement for Fast and Accurate Lane Detection. Sensors, 23(10), 4917. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104917





