Towards Haptic-Based Dual-Arm Manipulation
Abstract
1. Approaches to Dexterous Robotic Manipulation
Contributions and Organization of Paper
2. Haptic Estimation of Point of Contact in Circular Hands
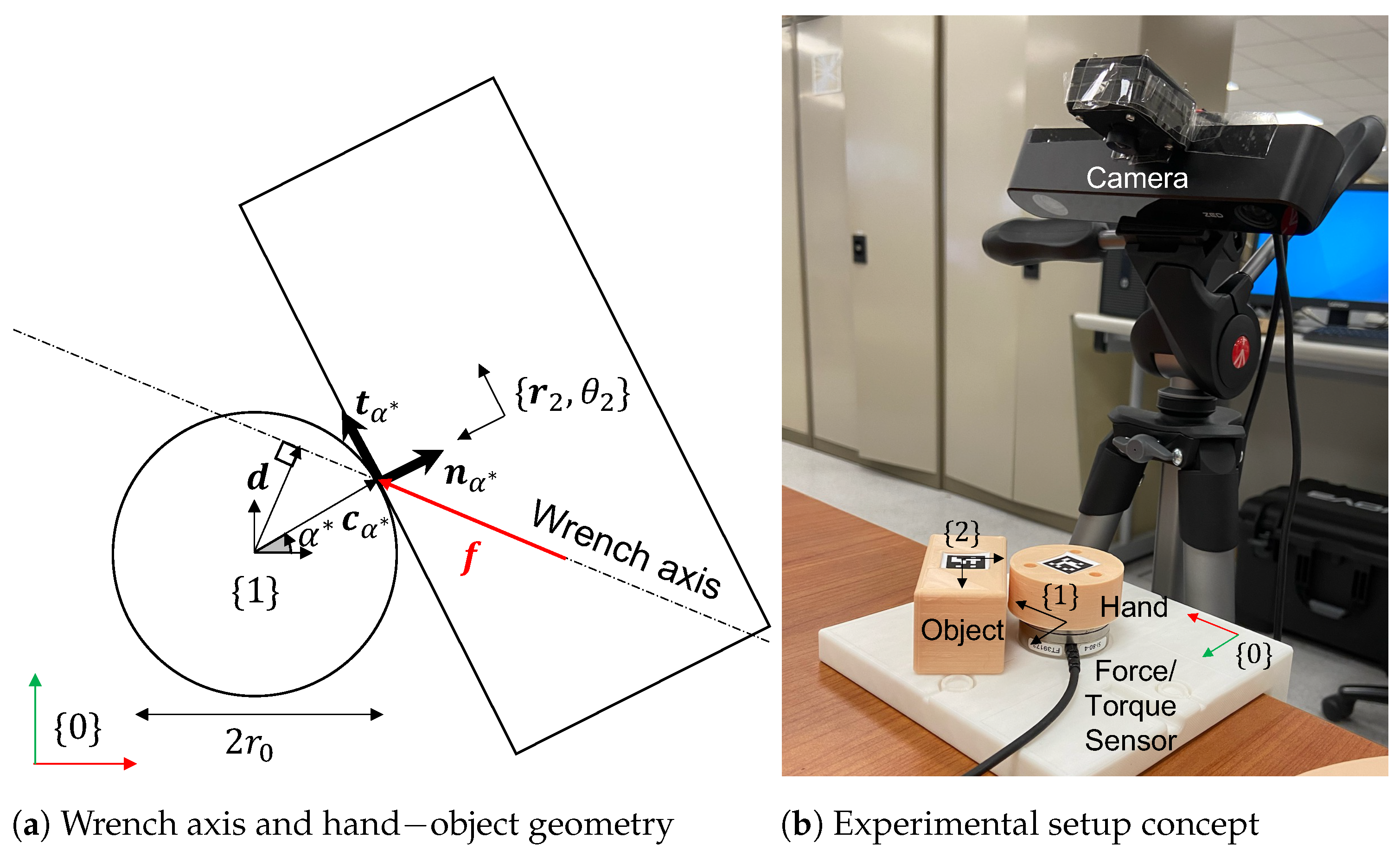
2.1. Contact Frame Estimation from Wrench Axis
2.2. Experimental Validation of Estimated Point of Contact
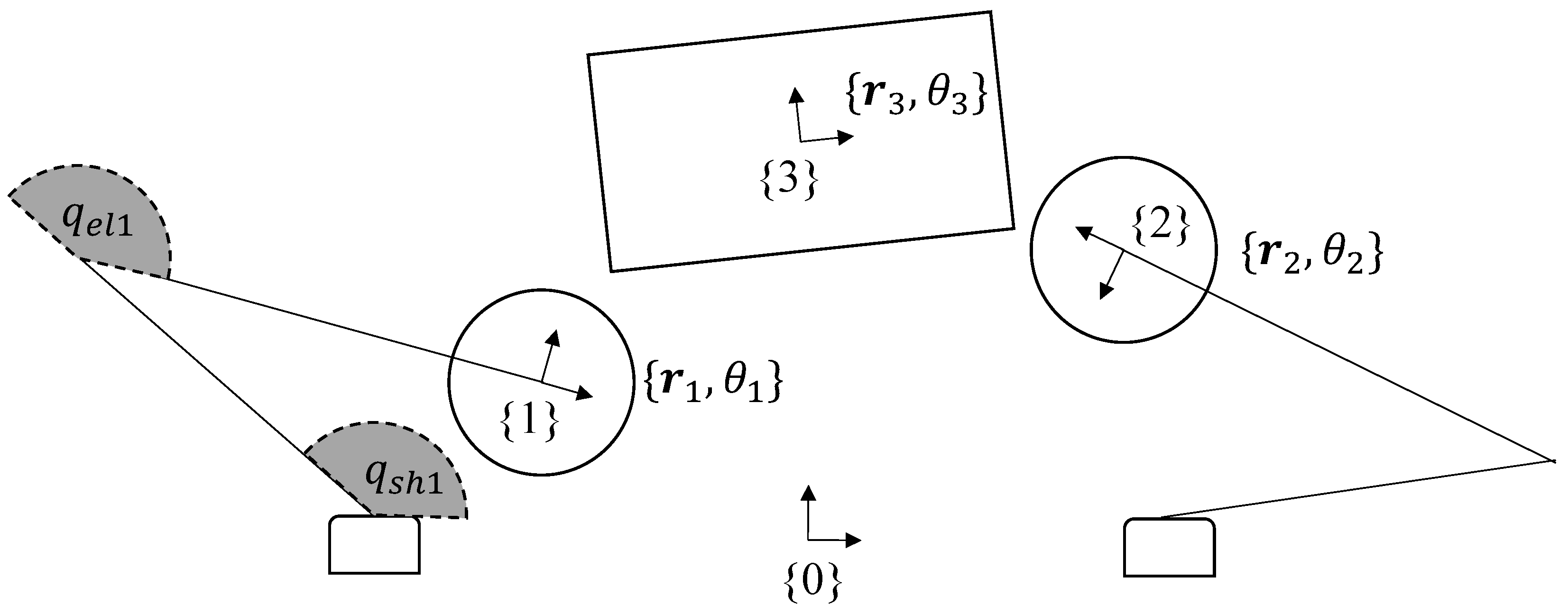
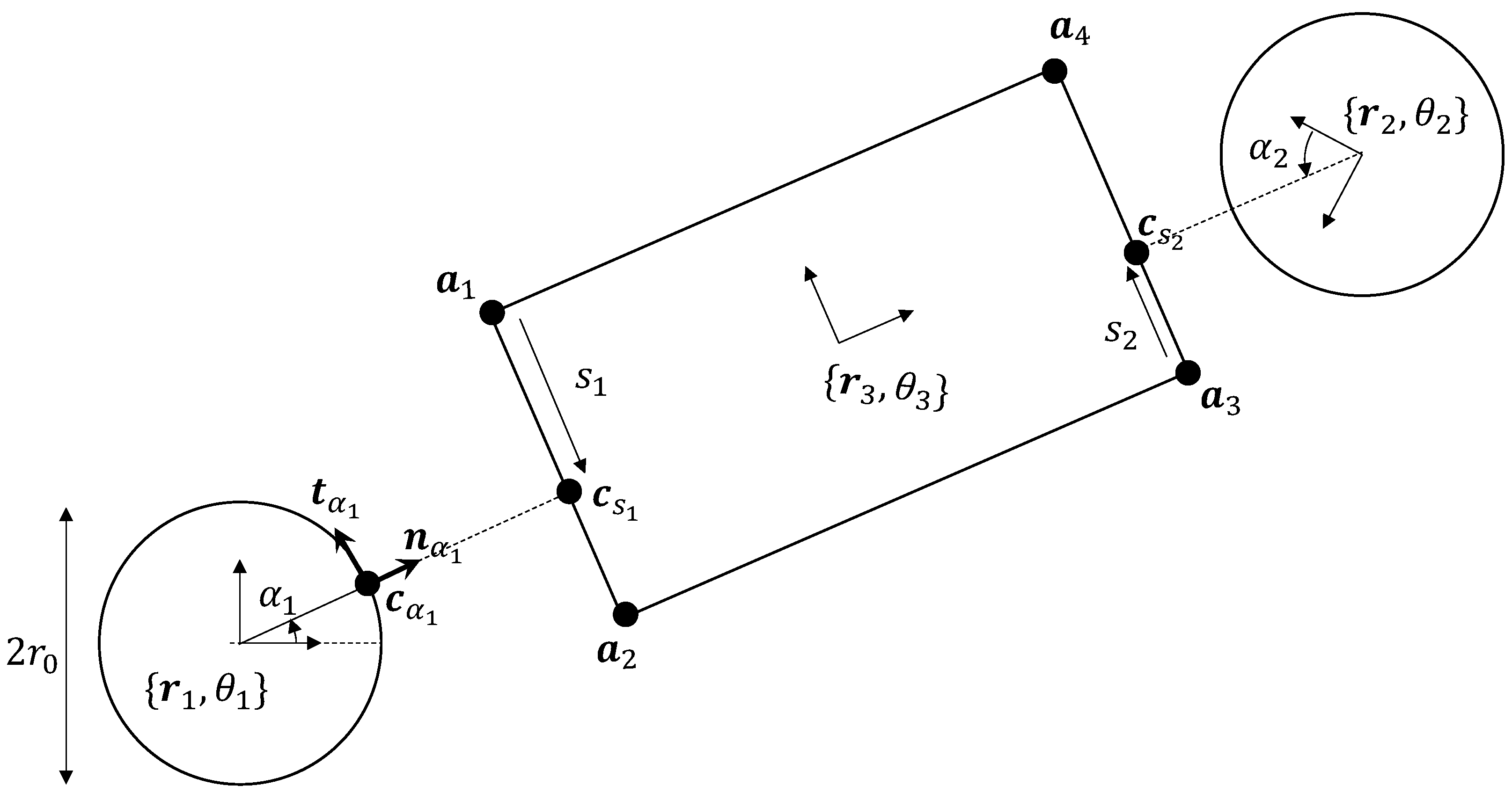
3. Kinematics of Planar Dual-Arm Manipulator
- Common frame , a fixed frame attached to the work-space (e.g., the table on which the robot is operating);
- Left-hand frame , a moving frame attached to the end-effector of robot arm 1;
- Right-hand frame , a moving frame attached to the end-effector of robot arm 2;
- Object frame , a moving frame attached to the object to be manipulated.
Hand−Object Surface Parameterization
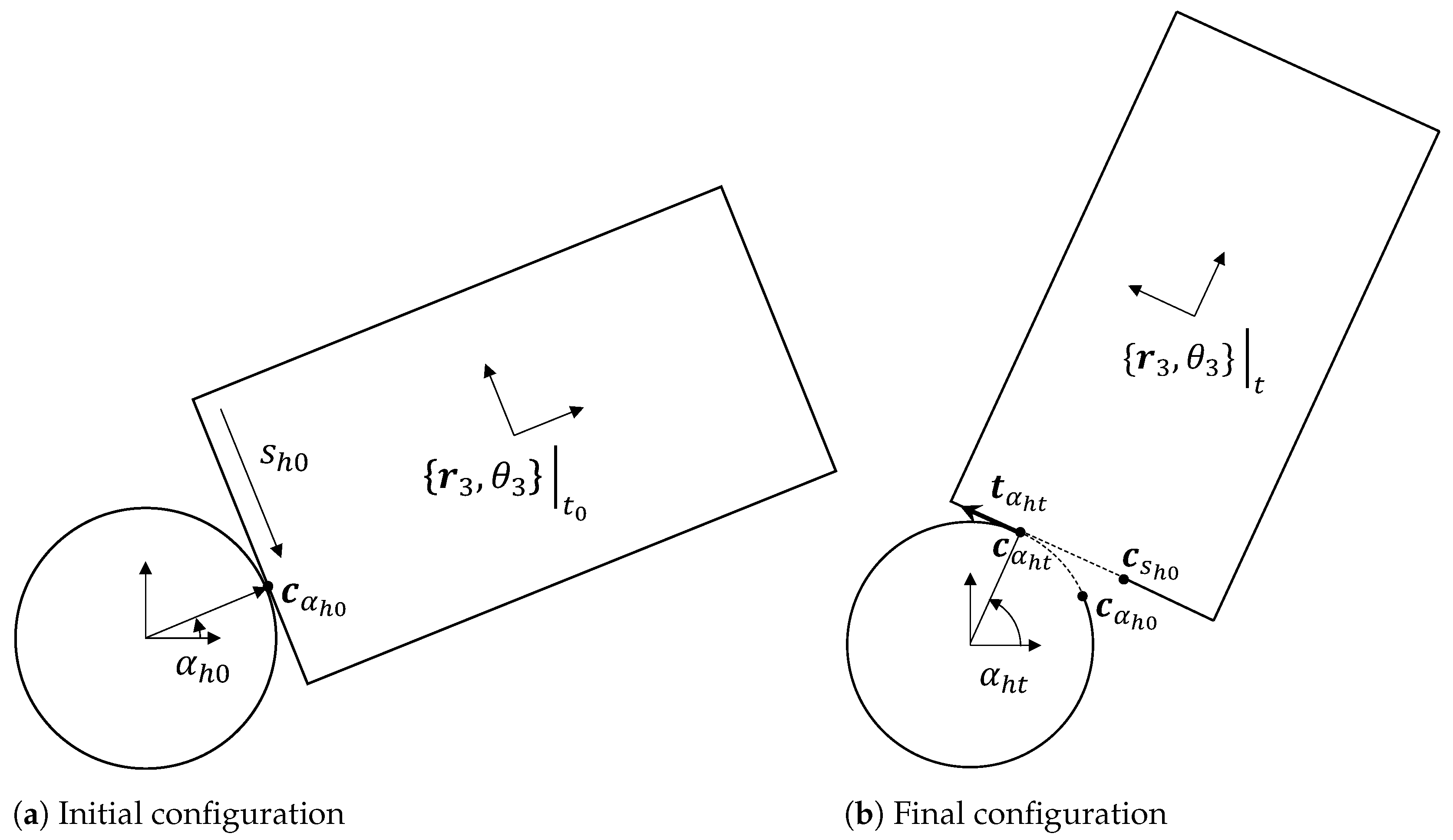
4. Haptic-Based Tracking of Object Pose
Sensor Fusion of Object Pose from Multiple Robot Arms
| Algorithm 1 Computing final configuration from (i) knowledge of initial configuration and (ii) wrench in final configuration using information from hand h. | |
| Require:, , and | ▹ (’) denotes local frame measurements |
| ▹ Rotation about hand | |
| ▹ Back-shifting along tangent | |
| ▹ Initial state | |
| ▹ Final state | |
| return | |
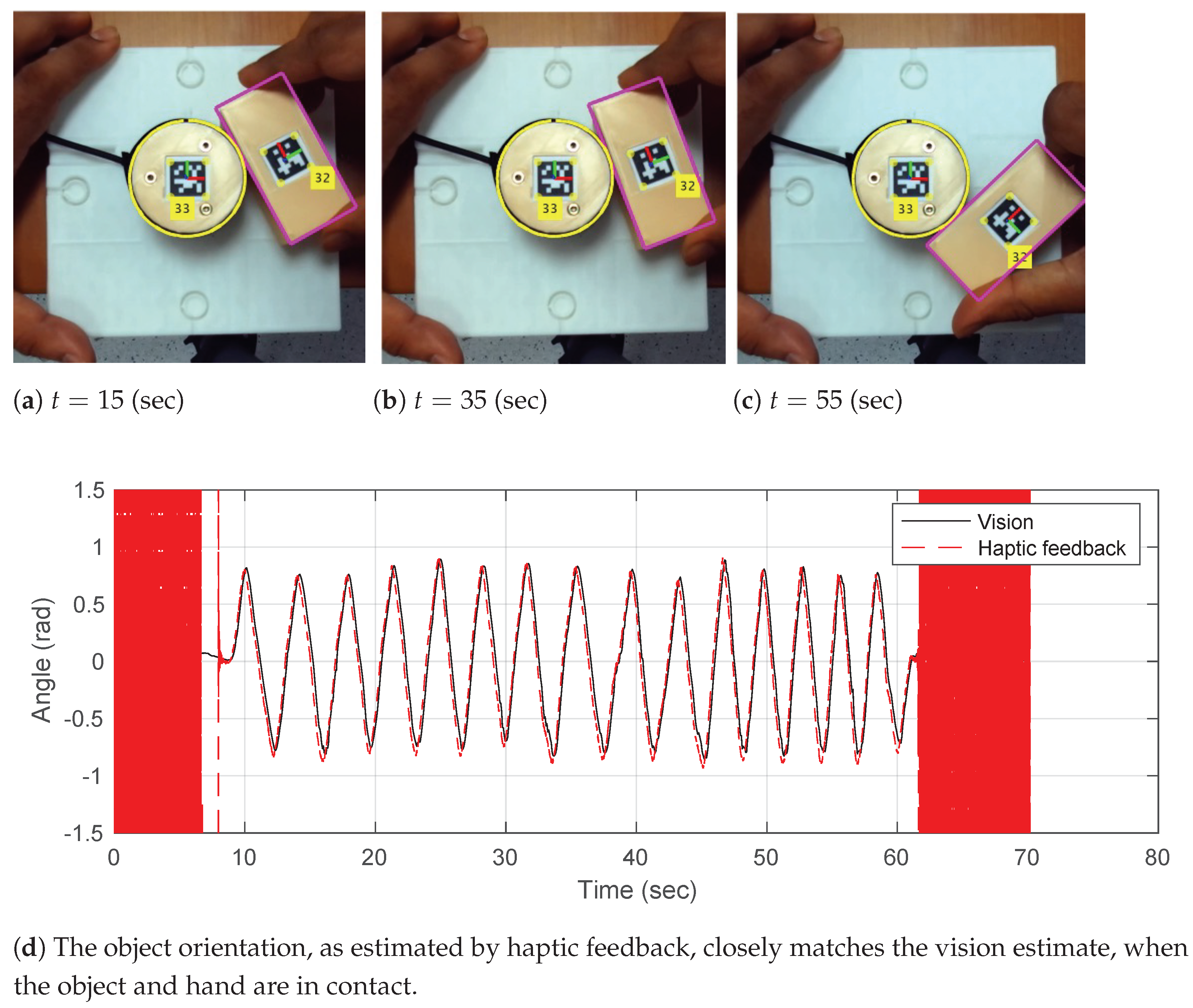
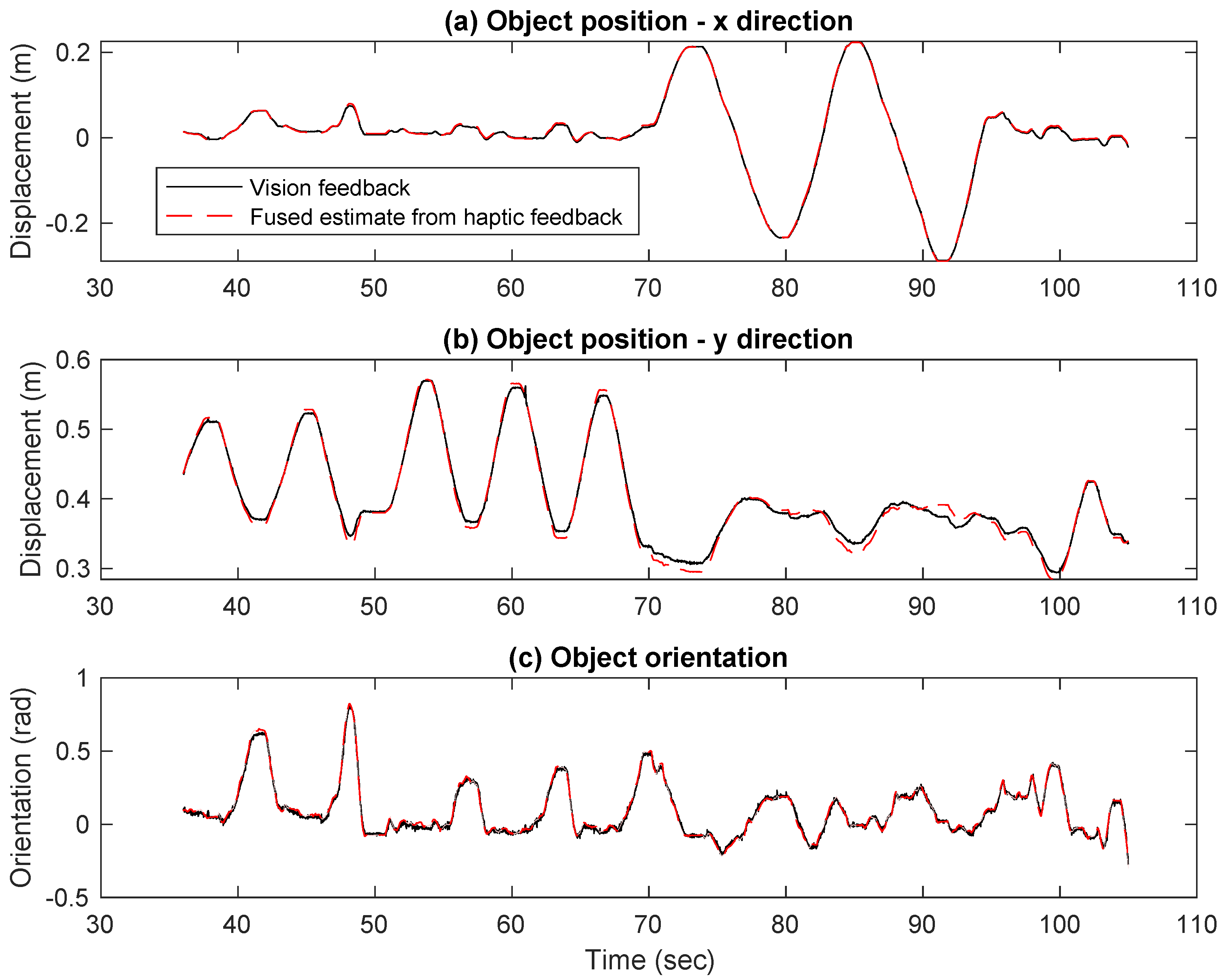
5. Object-Pose Estimation Results
Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Calibration of Force/Torque Sensors
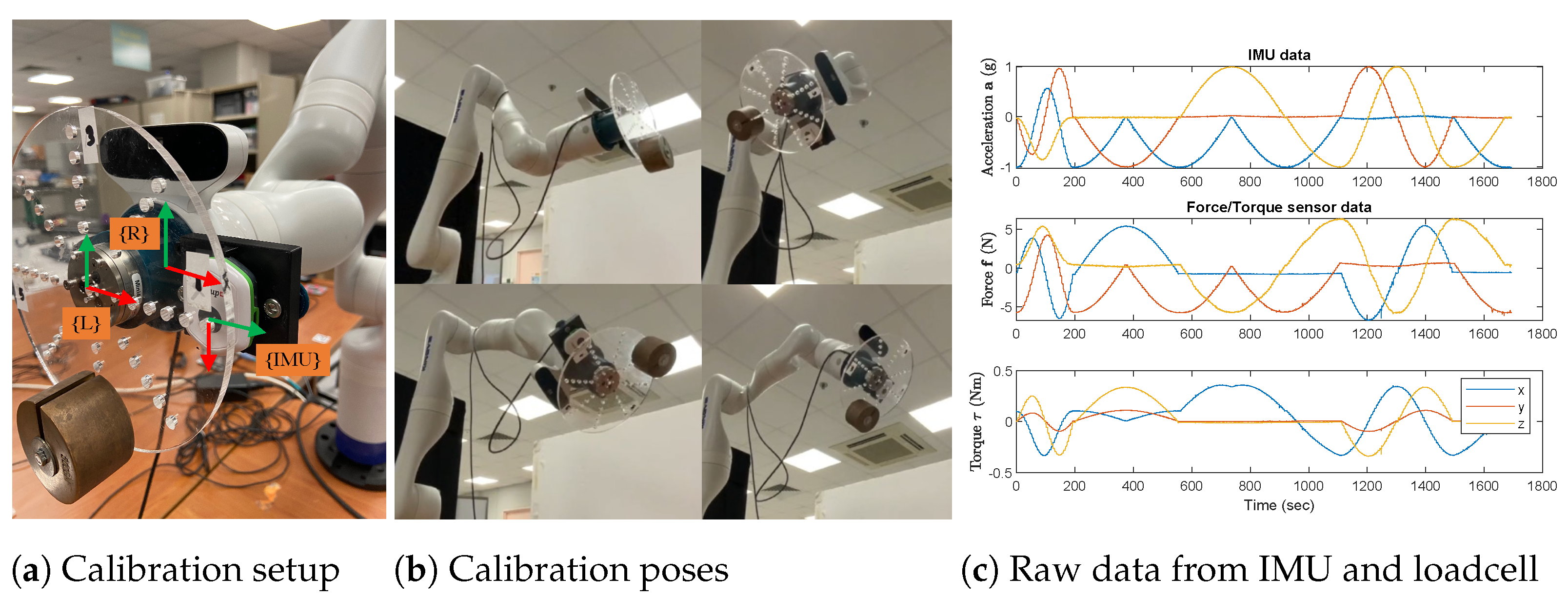
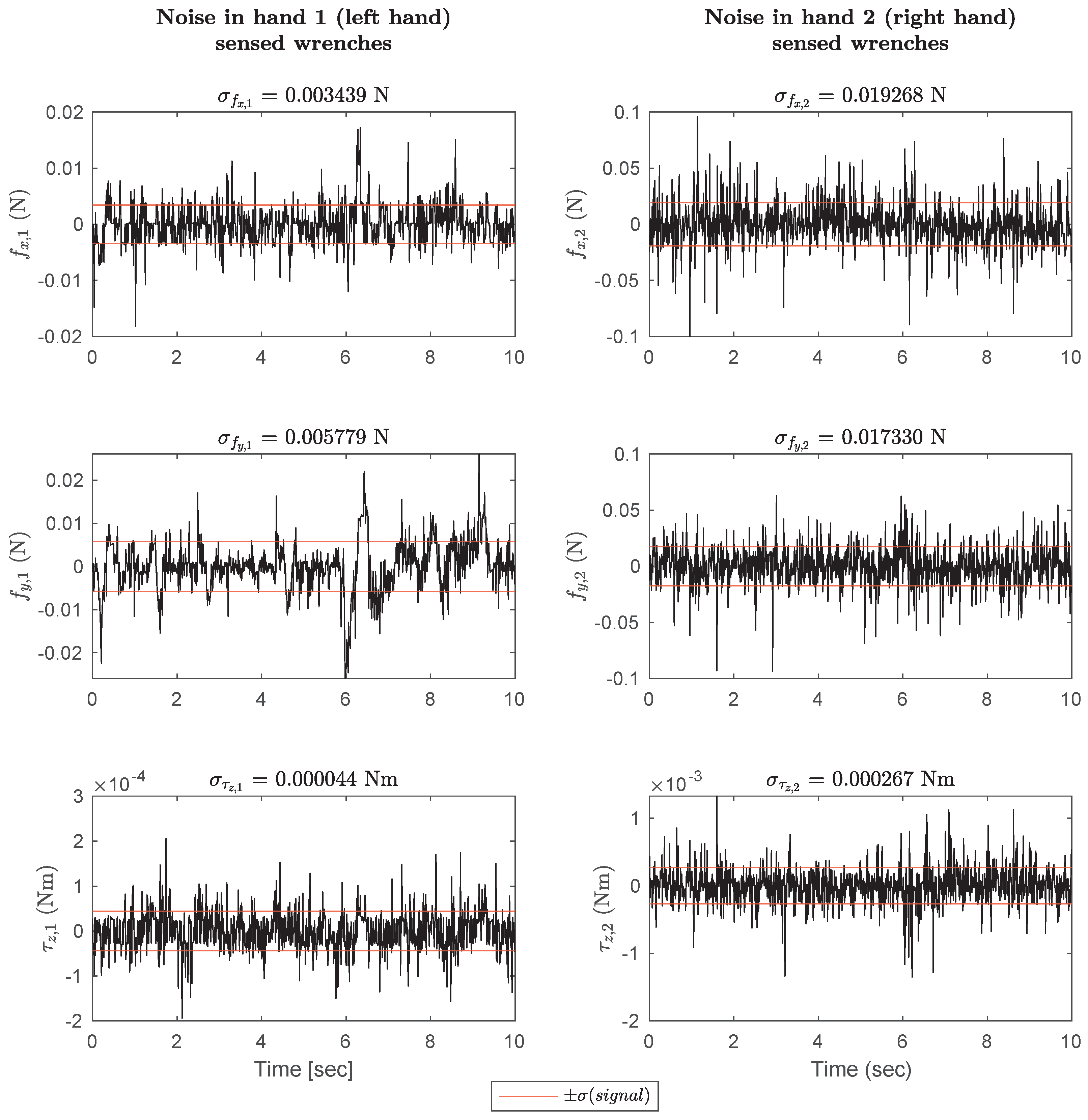
Appendix A.2. Noise in Wrenches Sensed on Both Hands
| Quantity Name | Symbol | Value and Units |
|---|---|---|
| Resolution of | res | 0.02 N |
| Resolution of | res | 0.02 N |
| Resolution of | res | 0.0005 Nm |
| SD of for hand 1 | 0.0034393 N | |
| SD of for hand 1 | 0.0057792 N | |
| SD of for hand 1 | 4.3925 × 10 Nm | |
| SD of for hand 2 | 0.019268 N | |
| SD of for hand 2 | 0.01733 N | |
| SD of for hand 2 | 0.00026706 Nm |
References
- Okamura, A.M.; Smaby, N.; Cutkosky, M.R. An overview of dexterous manipulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Symposia Proceedings (Cat. No. 00CH37065), San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 April 2000; Volume 1, pp. 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Bicchi, A. Hands for dexterous manipulation and robust grasping: A difficult road toward simplicity. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 2000, 16, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suomalainen, M.; Karayiannidis, Y.; Kyrki, V. A survey of robot manipulation in contact. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2022, 156, 104224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, C.C.; Edsinger, A.; Torres-Jara, E. Challenges for robot manipulation in human environments [grand challenges of robotics]. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2007, 14, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa, S.S.; Ferguson, D.; Helfrich, C.J.; Berenson, D.; Collet, A.; Diankov, R.; Gallagher, G.; Hollinger, G.; Kuffner, J.; Weghe, M.V. HERB: A home exploring robotic butler. Auton. Robot. 2010, 28, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Trinkle, J. Toward next-generation learned robot manipulation. Sci. Robot. 2021, 6, eabd9461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, N.; Bekris, K.E.; Berenson, D.; Brock, O.; Causo, A.; Hauser, K.; Okada, K.; Rodriguez, A.; Romano, J.M.; Wurman, P.R.; et al. Analysis and observations from the first amazon picking challenge. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2016, 15, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleeberger, K.; Bormann, R.; Kraus, W.; Huber, M.F. A Survey on Learning-Based Robotic Grasping. Curr. Robot. Rep. 2020, 1, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, R.M.; Li, Z.; Sastry, S.S. A Mathematical Introduction to Robotic Manipulation, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicchi, A.; Kumar, V. Robotic grasping and contact: A review. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2000 ICRA, Millennium Conference, Symposia Proceedings (Cat. No. 00CH37065), San Francisco, CA, USA, 24–28 April 2000; Volume 1, pp. 348–353. [Google Scholar]
- Trinkle, J.C. A quasi-static analysis of dextrous manipulation with sliding and rolling contacts. In Proceedings of the ICRA, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 14–19 May 1989; pp. 788–793. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, A.; Hauser, J.; Sastry, S. Kinematics and control of multifingered hands with rolling contact. In Proceedings of the 1988 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 24–29 April 1988; pp. 228–233. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, R.M.; Sastry, S.S. Control experiments in planar manipulation and grasping. In Proceedings of the 1989 International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 14–19 May 1989; Volume 1, pp. 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimoto, S.; Yoshida, M.; Bae, J.H.; Tahara, K. Dynamic force/torque balance of 2D polygonal objects by a pair of rolling contacts and sensory-motor coordination. J. Robot. Syst. 2003, 20, 517–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, R.; Arimoto, S.; Nakamura, S.; Bae, H.J. Control of an object with parallel surfaces by a pair of finger robots without object sensing. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2005, 21, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimoto, S. A differential-geometric approach for 2D and 3D object grasping and manipulation. Annu. Rev. Control. 2007, 31, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw-Cortez, W.; Oetomo, D.; Manzie, C.; Choong, P. Object manipulation using robotic hands with varying degrees of grasp knowledge. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2018. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw-Cortez, W.; Oetomo, D.; Manzie, C.; Choong, P. Robust object manipulation for tactile-based blind grasping. Control. Eng. Pract. 2019, 92, 104136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohg, J.; Morales, A.; Asfour, T.; Kragic, D. Data-driven grasp synthesis—A survey. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2013, 30, 289–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, N. Deep Neural Networks for Robot Vision in Evolutionary Robotics. Master’s Thesis, Nelson Mandela University, Gqeberha, South Africa, April 2021. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10948/52100 (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Hogan, F.R.; Ballester, J.; Dong, S.; Rodriguez, A. Tactile dexterity: Manipulation primitives with tactile feedback. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.03236. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.; Dong, S.; Adelson, E.H. Gelsight: High-resolution robot tactile sensors for estimating geometry and force. Sensors 2017, 17, 2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicchi, A.; Salisbury, J.K.; Brock, D.L. Contact sensing from force measurements. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1993, 12, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimura, T.; Yabuta, T. Object detection by tactile sensing method employing force/torque information. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1989, 5, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kana, S.; Tee, K.; Campolo, D. Human–robot co-manipulation during surface tooling: A general framework based on impedance control, haptic rendering and discrete geometry. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2021, 67, 102033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deisenroth, M.P.; Faisal, A.A.; Ong, C.S. Mathematics for Machine Learning; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021; p. 201. [Google Scholar]
- Kuchenbecker, K.J.; Fiene, J.; Niemeyer, G. Improving contact realism through event-based haptic feedback. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2006, 12, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kana, S.; Gurnani, J.; Ramanathan, V.; Turlapati, S.H.; Ariffin, M.Z.; Campolo, D. Fast Kinematic Re-Calibration for Industrial Robot Arms. Sensors 2022, 22, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfanne, M.; Chalon, M.; Stulp, F.; Albu-Schäffer, A. Fusing joint measurements and visual features for in-hand object pose estimation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 3497–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfanne, M.; Chalon, M.; Stulp, F.; Ritter, H.; Albu-Schäffer, A. Object-level impedance control for dexterous in-hand manipulation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 2987–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaño, A.; Suárez, R. Manipulation of unknown objects to improve the grasp quality using tactile information. Sensors 2018, 18, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, R.; Arimoto, S.; Nguyen, P.T.A.; Yoshida, M.; Bae, J.H. Manipulation of a circular object in a horizontal plane by two finger robots. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Shenyang, China, 22–26 August 2004; pp. 517–522. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.H.; Choi, M.S.; Park, H.; Jang, G.R.; Park, J.H.; Bae, J.H. Peg-in-Hole Assembly With Dual-Arm Robot and Dexterous Robot Hands. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 8566–8573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, W.S.; Oetomo, D.; Manzie, C.; Choong, P. Robust object manipulation for prosthetic hand applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 56th Annual Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 12–15 December 2017; pp. 5821–5826. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, C.; Dai, J.S. Sliding-Rolling Contact and In-Hand Manipulation; World Scientific: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Farajiparvar, P.; Ying, H.; Pandya, A. A brief survey of telerobotic time delay mitigation. Front. Robot. AI 2020, 7, 578805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATI Industrial Automation: F/T Sensor mini40. (n.d.). Available online: https://www.ati-ia.com/products/ft/ft_models.aspx?id=mini40 (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Campolo, D.; Fabris, M.; Cavallo, G.; Accoto, D.; Keller, F.; Guglielmelli, E. A novel procedure for in-field calibration of sourceless inertial/magnetic orientation tracking wearable devices. In Proceedings of the First IEEE/RAS-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Pisa, Italy, 20–22 February 2006; pp. 471–476. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turlapati, S.H.; Campolo, D. Towards Haptic-Based Dual-Arm Manipulation. Sensors 2023, 23, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010376
Turlapati SH, Campolo D. Towards Haptic-Based Dual-Arm Manipulation. Sensors. 2023; 23(1):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010376
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurlapati, Sri Harsha, and Domenico Campolo. 2023. "Towards Haptic-Based Dual-Arm Manipulation" Sensors 23, no. 1: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010376
APA StyleTurlapati, S. H., & Campolo, D. (2023). Towards Haptic-Based Dual-Arm Manipulation. Sensors, 23(1), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010376





