Multi-Task Partial Offloading with Relay and Adaptive Bandwidth Allocation for the MEC-Assisted IoT
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We investigate the heterogeneity in transmission rates and suggest using a relay to help nodes far from the AP and combine it with adaptive bandwidth allocation to achieve fine-grained resource allocation.
- We propose an evolutionary algorithm for joint optimization of radio resources (bandwidth) and computation resources. This not only improves the performance of nodes using relays but also reduces the delay of other nodes.
2. Related Work
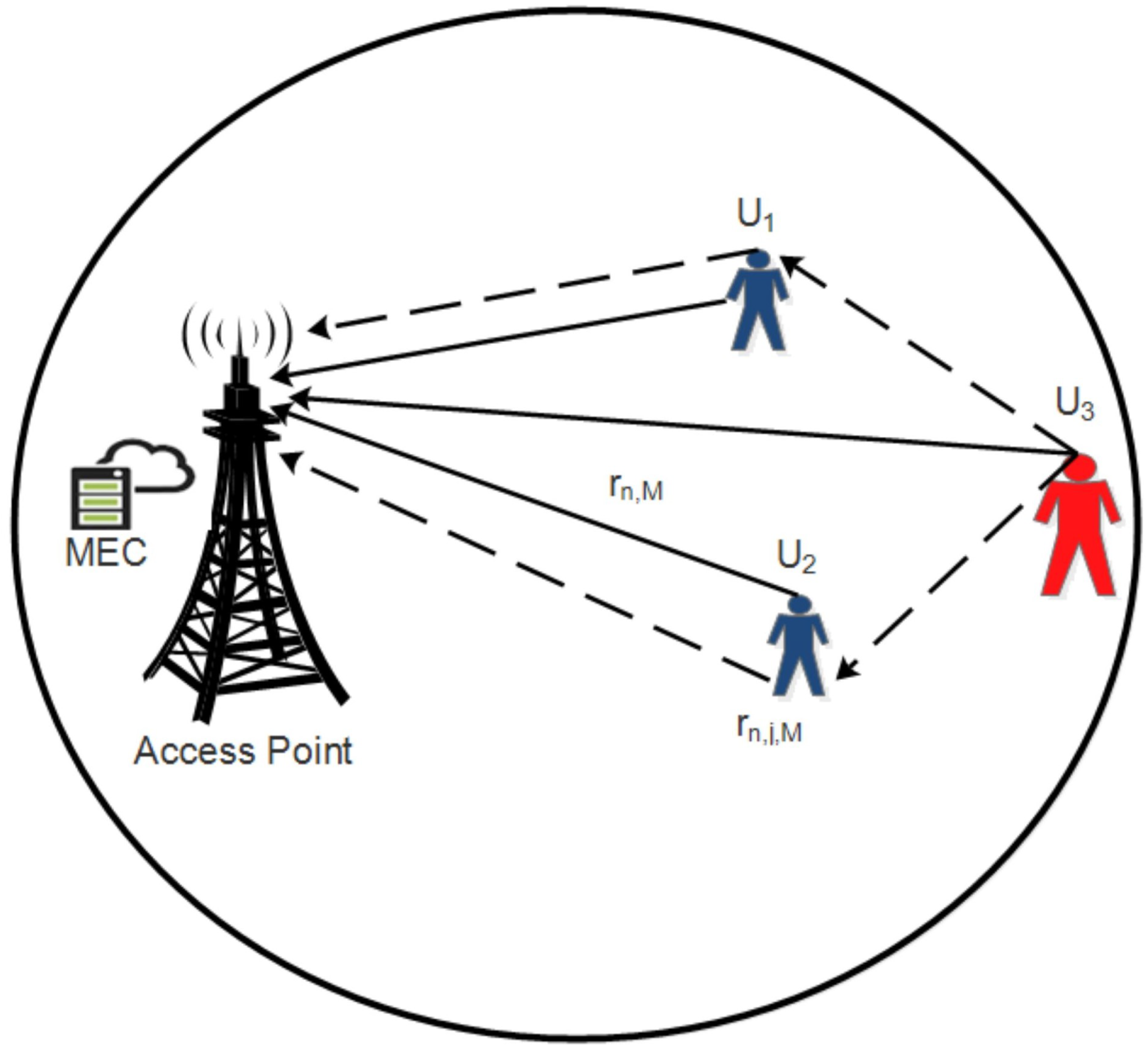
3. System Model
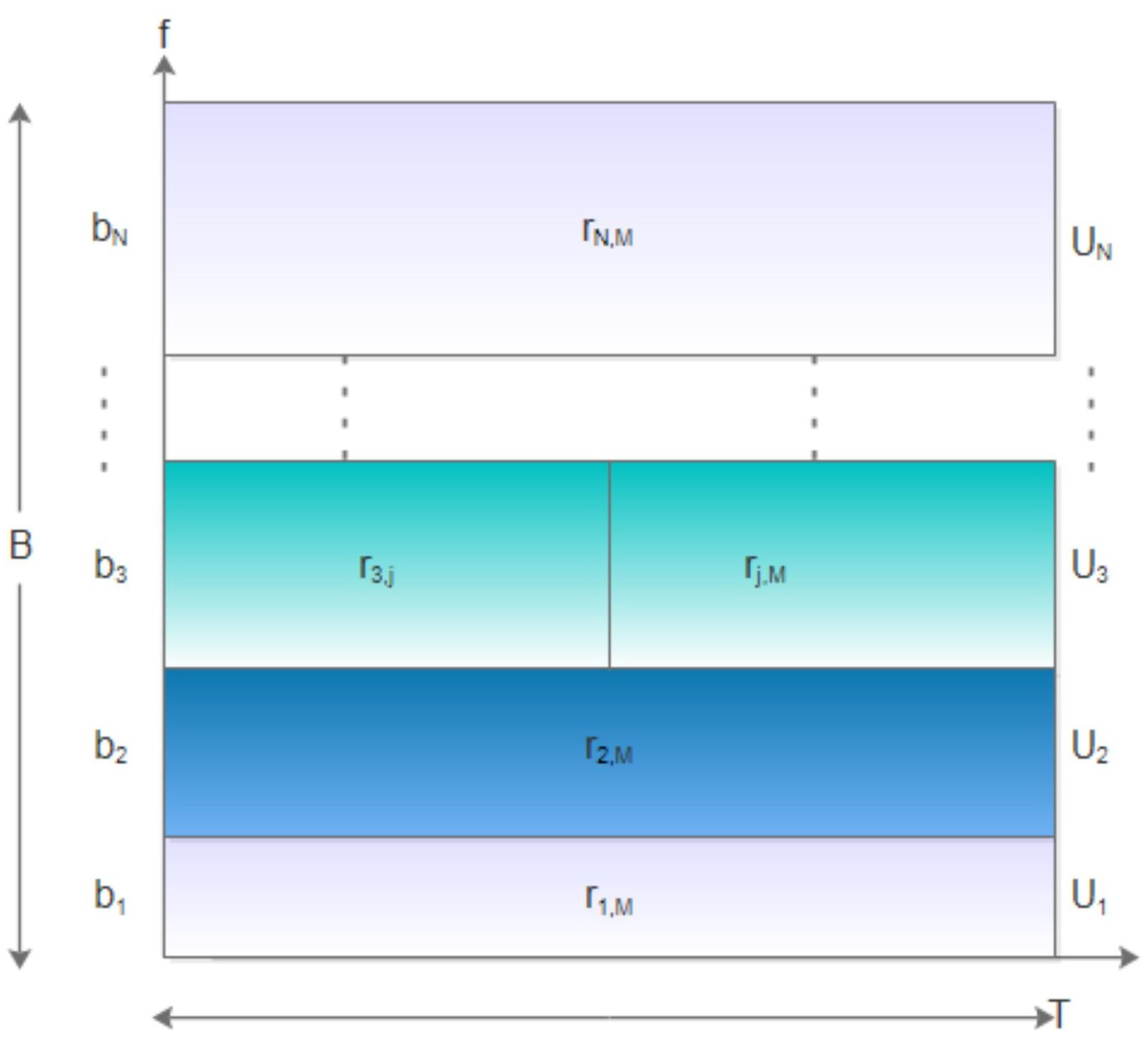
3.1. Relay Model and Adaptive Bandwidth Allocation
3.2. Computation Time
3.3. Problem Formulation
4. Proposed Method
4.1. Optimal Calculation of
4.2. Optimal Resource Allocation
| Algorithm 1: Partial Offloading with Relay and Adaptive Bandwidth Allocation (PORAB) |
 |
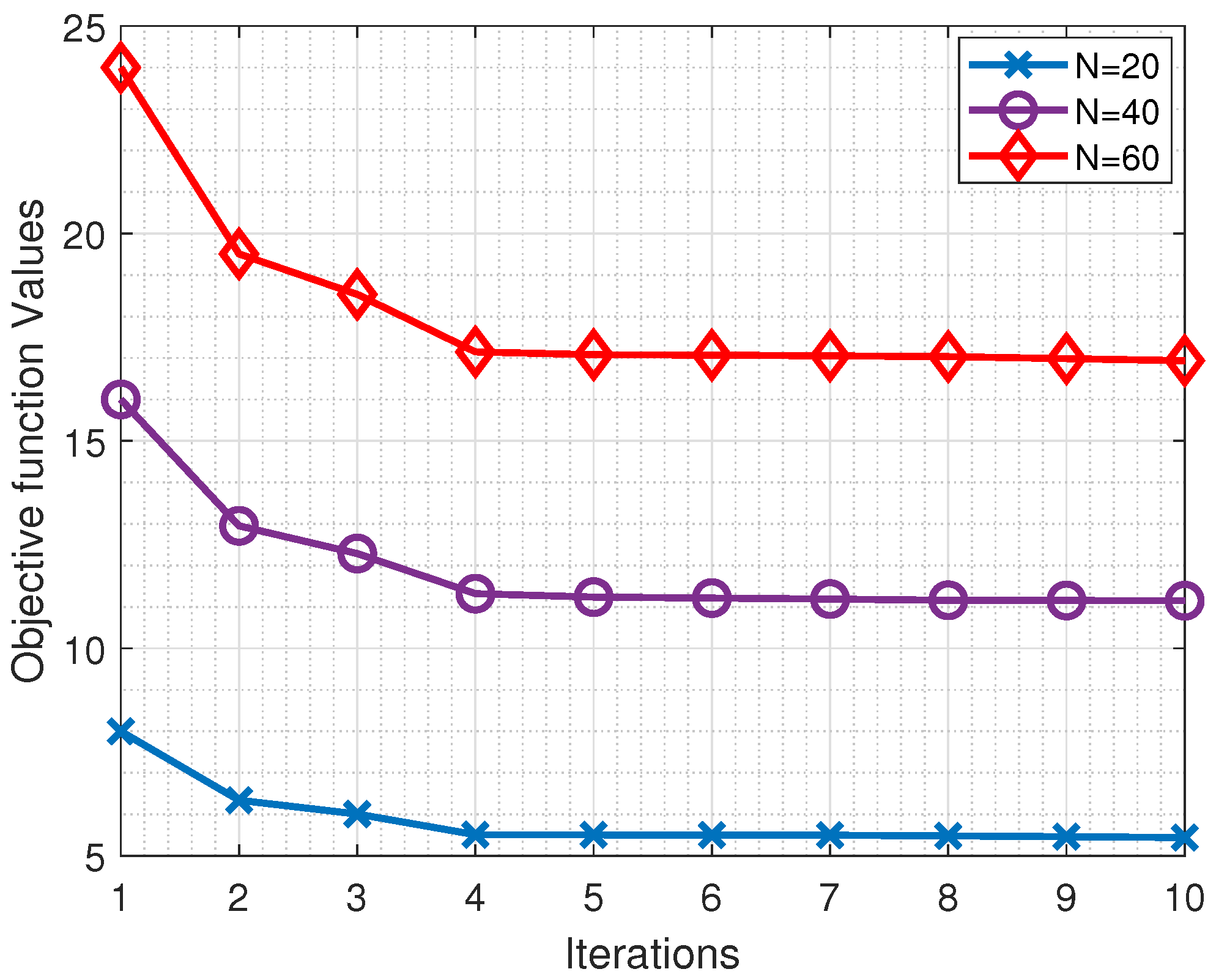
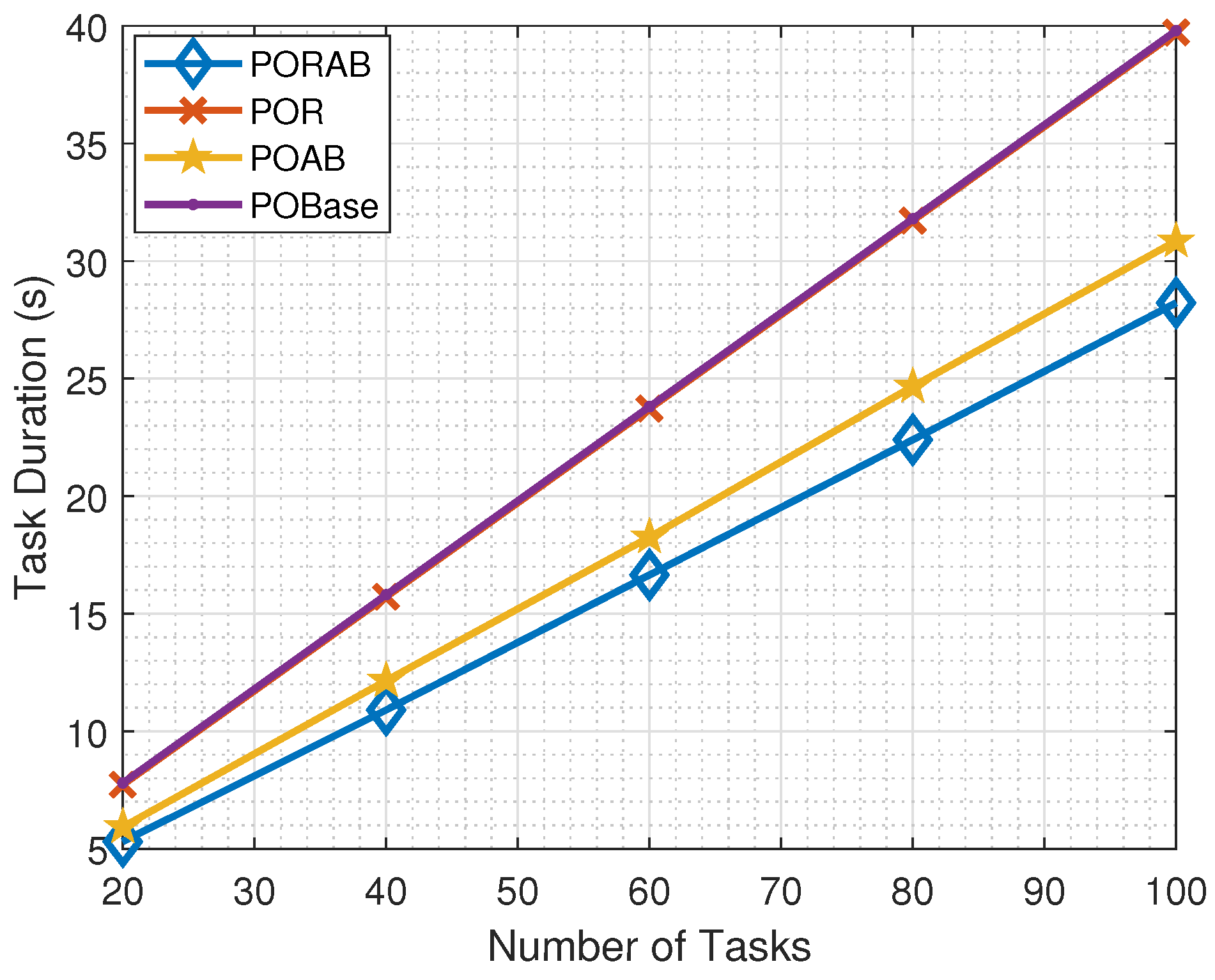
5. Simulation Evaluation
5.1. Simulation Setting
5.2. Simulation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almutairi, A.F.; Alshargabi, A.A. Using Deep Learning Technique to Protect Internet Network from Intrusion in IoT Environment. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Smart Technologies and Applications (eSmarTA), Ibb, Yemen, 25–26 October 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ourad, A.Z.; Belgacem, B.; Salah, K. Using blockchain for iot access control and authentication man- agement. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Internet of Things, Seattle, WA, USA, 25–30 June 2018; pp. 150–164. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, H.; Zahoor, E.; Akhtar, S.; Olivier, P. A blockchain-based approach for secure data migration from the cloud to the decentralized storage systems. Int. Web Serv. Res. (IJWSR) 2022, 19, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, X.; Chen, M. In-edge ai: Intelligentizing mobile edge computing, caching and communication by federated learning. IEEE Netw. 2019, 33, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Shuai, B. A predictive and trajectory-aware edge service allocation approach in a mobile computing environ- ment. Int. J. Web Serv. Res. (IJWSR) 2022, 19, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Jin, S.; Zhang, S. Computation offloading in untrusted mec-aided mobile blockchain iot systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 8333–8347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Kato, N. Optimal edge resource allocation in iot-based smart cities. IEEE Netw. 2019, 33, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, D. Mobile Cloud Computing: Architectures, Algorithms and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Keat, L.C.; Fong, A.T.; Chong, C.Y.; Tew, Y. (offloading) qoe-aware application mapping and energy- aware module placement in fog computing+ offloading. Inter-Natl. J. Web Serv. Res. (IJWSR) 2022, 19, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobari, H.; Du, Z.; Wu, C.; Yoshinaga, T.; Bao, W. A reinforcement learning based edge cloud collaboration. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Disaster Management (ICT-DM), Hangzhou, China, 3–5 December 2021; pp. 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kai, C.; Zhou, H.; Yi, Y.; Huang, W. Collaborative cloud-edge-end task offloading in mobile-edge computing networks with limited communication capability. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2021, 7, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Qingyang Hu, R. Computation efficiency maximization in ofdma-based mobile edge computing networks. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2019, 24, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, F.; Xu, J.; Zhang, R.; Shuguang, C. Joint computation and communication cooperation for energy-efficient mobile edge computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 6, 4188–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Letaief, K.B. Joint Subcarrier and CPU Time Allocation for Mobile Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Washington, DC, USA, 4–8 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sheng, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Mobile-edge computing: Partial computation offloading using dynamic voltage scaling. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2016, 64, 4268–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.Q.; Al-Shatri, H.; Klein, A. Efficient resource allocation in mobile-edge computation offloading: Com- pletion time minimization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), Aachen, Germany, 25–30 June 2017; pp. 2513–2517. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Yu, G.; Cai, Y.; He, Y.; Qu, F. Partial offloading for latency minimization in mobile-edge computing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference, Singapore, 4–8 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Li, R.; Jiao, P. Green Parallel Online Offloading for DSCI-Type Tasks in IoT-Edge Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 7955–7966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, Y.; Tachibana, T. Optimal task allocation algorithm based on queueing theory for future internet application in mobile edge computing platform. Sensors 2022, 22, 4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lan, X.; Ren, J.; Cai, L. Efficient computing resource sharing for mobile edge-cloud computing networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2020, 28, 1227–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Bi, S.; Zhang, Y.A. Deep reinforcement learning for online computation offloading in wireless powered mobile-edge computing networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2019, 19, 2581–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Hao, Y. Task offloading for mobile edge computing in software defined ultra-dense network. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2018, 36, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Ahmed, A.; Naeem, M.; Hong, Y. Partial offloading in energy harvested mobile edge computing: A direct search approach. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 36757–36763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wolter, K.; Jiao, P.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, M. Eedto: An energy-efficient dynamic task offloading algorithm for blockchain-enabled iot-edge-cloud orchestrated computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 2163–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Edge-cloud collaborative computation offloading model based on improved partical swarm optimization in mec. In Proceedings of the IEEE 25th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems (ICPADS), Tianjin, China, 4–6 December 2019; pp. 959–962. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, R.; Lai, S.; Dan, Z.; Xia, J.; Fan, L. Intelligent offloading strategy design for relaying mobile edge computing networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 35127–35135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Hong, Y.; Ehsan, M.K.; Mumtaz, S. Optimal resource allocation and task segmentation in iot enabled mobile edge cloud. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 13294–13303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Wu, H.; Li, R.; Jiao, P. Dmro: A deep meta reinforcement learning-based task offloading frame- work for edge-cloud computing. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2021, 18, 3448–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Ahmed, A.; Naeem, M.; Amirzada, M.R.; Al-Dweik, A. Weighted utility aware computational overhead minimization of wireless power mobile edge cloud. Comput. Commun. 2022, 190, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Valdez, M.; Márquez, R.; Trujillo, L.; Merelo, J.J. Random selection of parameters in asyn- chronous pool-based evolutionary algorithms. In Proceedings of the IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Kraków, Poland, 28 June–1 July 2021; pp. 2531–2538. [Google Scholar]
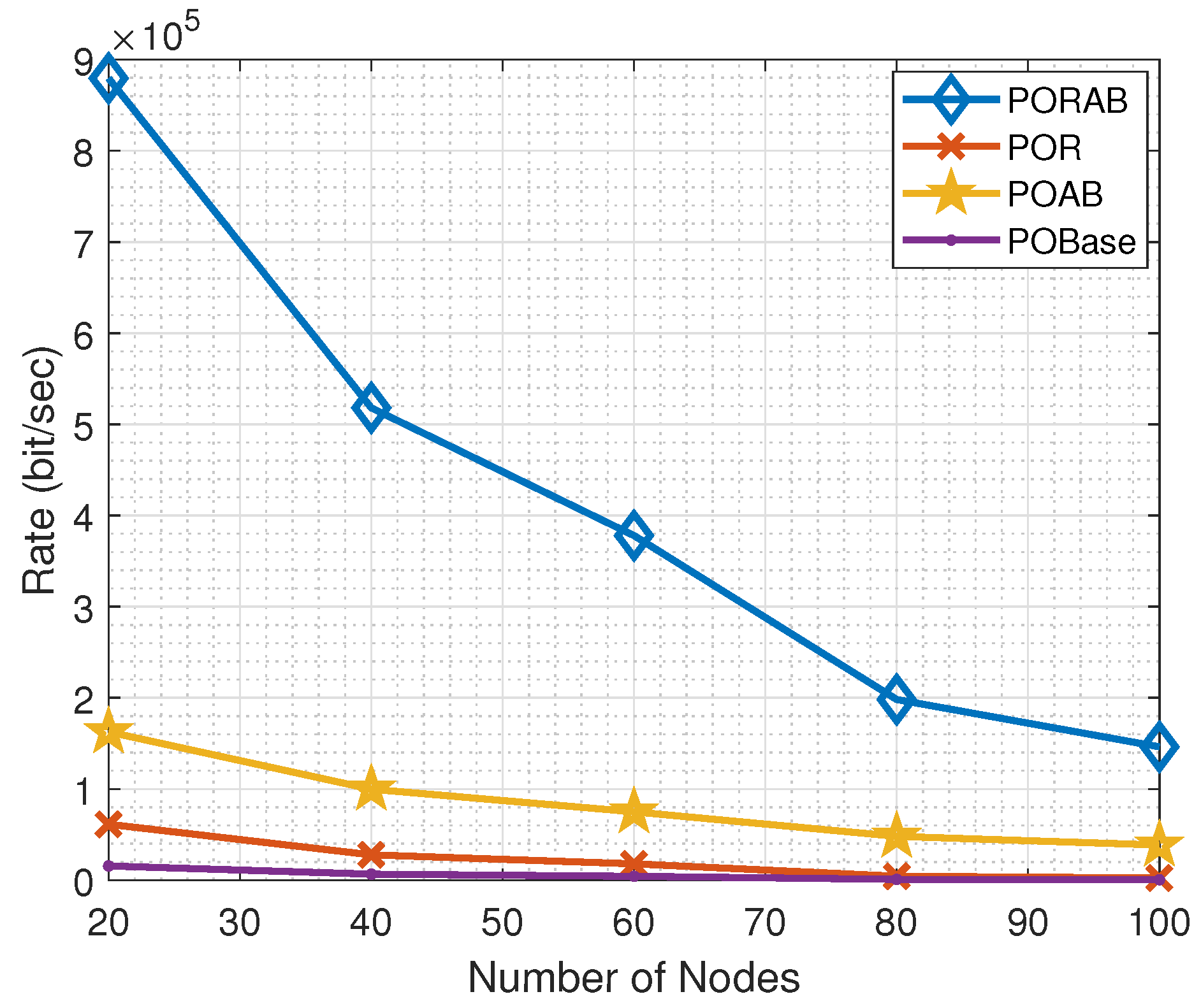
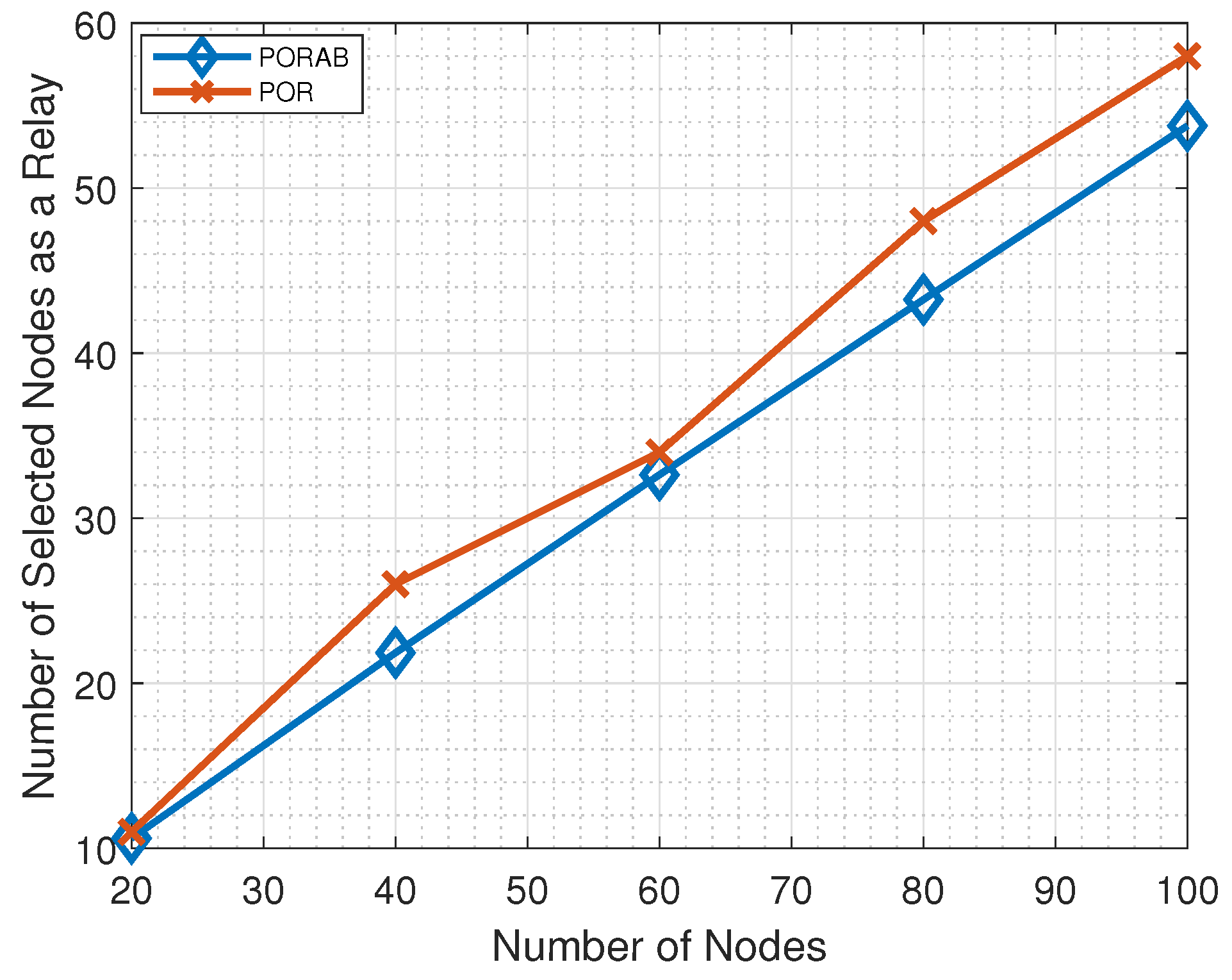
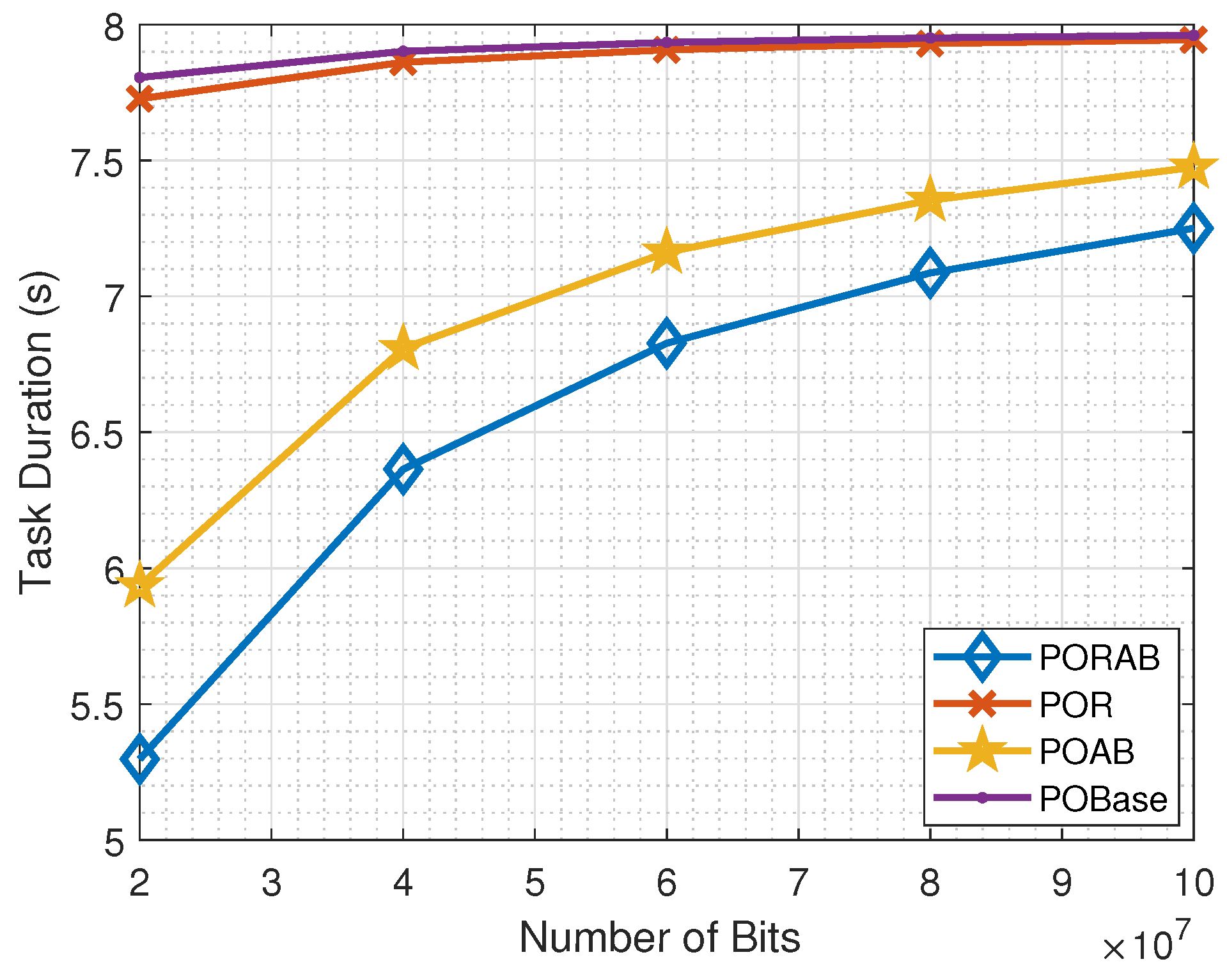
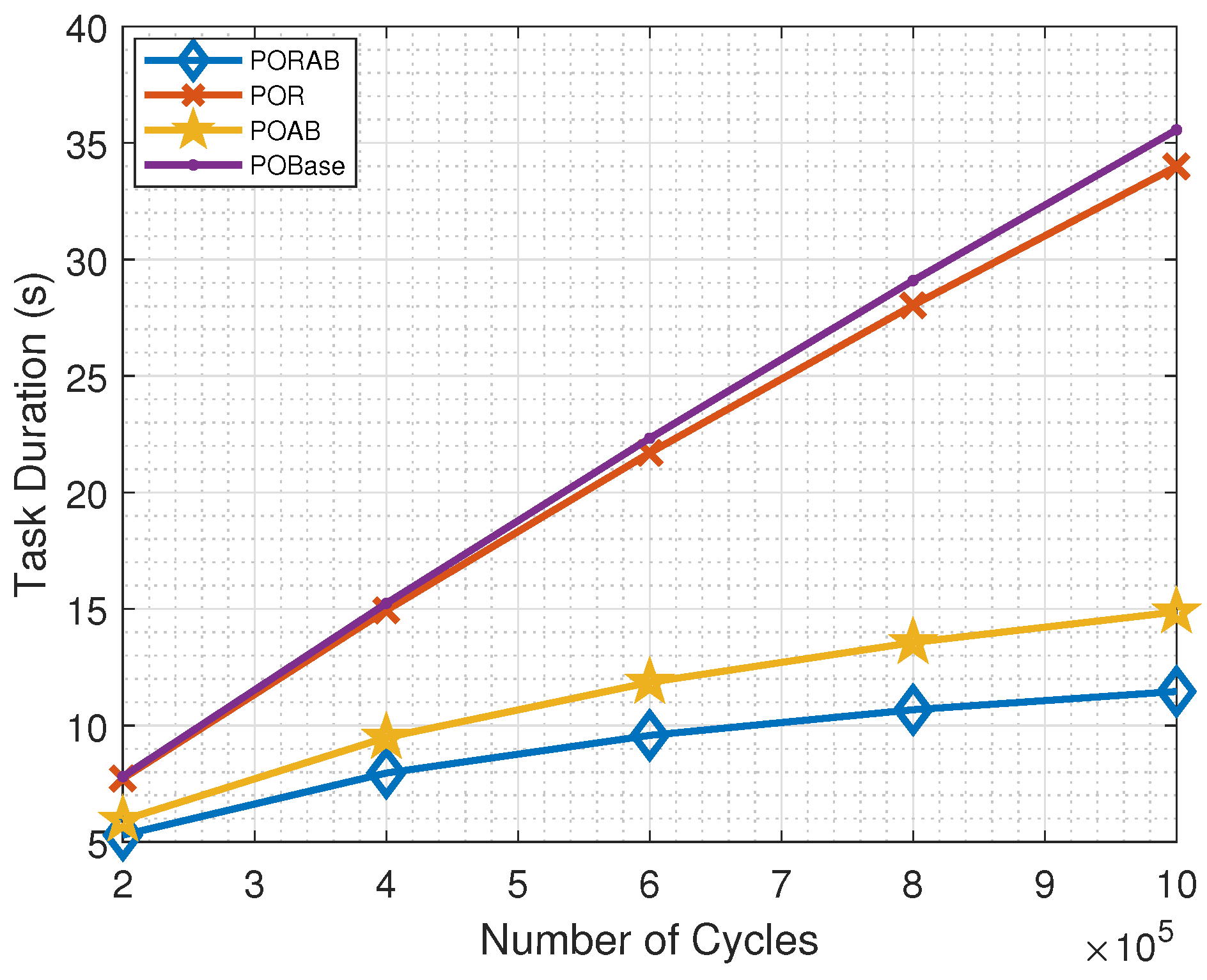
| Parameters | Descriptions | Values |
|---|---|---|
| N | Number of nodes | 100 |
| B | Overall bandwidth | 2 MHz |
| Percentage of bandwidth for task n | By algorithm | |
| Number of processing cycles of task n | M cycles | |
| Data size of task n | M bits | |
| Comp. resource of node n for task n | 1 M cycle/sec | |
| Comp. resource for task n at MEC server | By algorithm | |
| Overall comp. resource at MEC server | 25 M cycle/sec | |
| Percentage of task n for local processing | By algorithm | |
| Maximum energy of a node | 2 joules |
| N | 20 | 40 | 80 | 100 |
| POR | 11 | 26 | 48 | 58 |
| PORAB | 10 | 22 | 43 | 53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Imtiaz, H.H.; Tang, S. Multi-Task Partial Offloading with Relay and Adaptive Bandwidth Allocation for the MEC-Assisted IoT. Sensors 2023, 23, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010190
Imtiaz HH, Tang S. Multi-Task Partial Offloading with Relay and Adaptive Bandwidth Allocation for the MEC-Assisted IoT. Sensors. 2023; 23(1):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010190
Chicago/Turabian StyleImtiaz, Hafiz Hasnain, and Suhua Tang. 2023. "Multi-Task Partial Offloading with Relay and Adaptive Bandwidth Allocation for the MEC-Assisted IoT" Sensors 23, no. 1: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010190
APA StyleImtiaz, H. H., & Tang, S. (2023). Multi-Task Partial Offloading with Relay and Adaptive Bandwidth Allocation for the MEC-Assisted IoT. Sensors, 23(1), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010190






