A Comprehensive Review of Blockchain Technology-Enabled Smart Manufacturing: A Framework, Challenges and Future Research Directions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Search
3. Critical Issues in Smart Manufacturing
3.1. Data Security Issues
3.2. Data Sharing Issues
3.3. Trust Mechanism Issues
3.4. System Coordination Issues
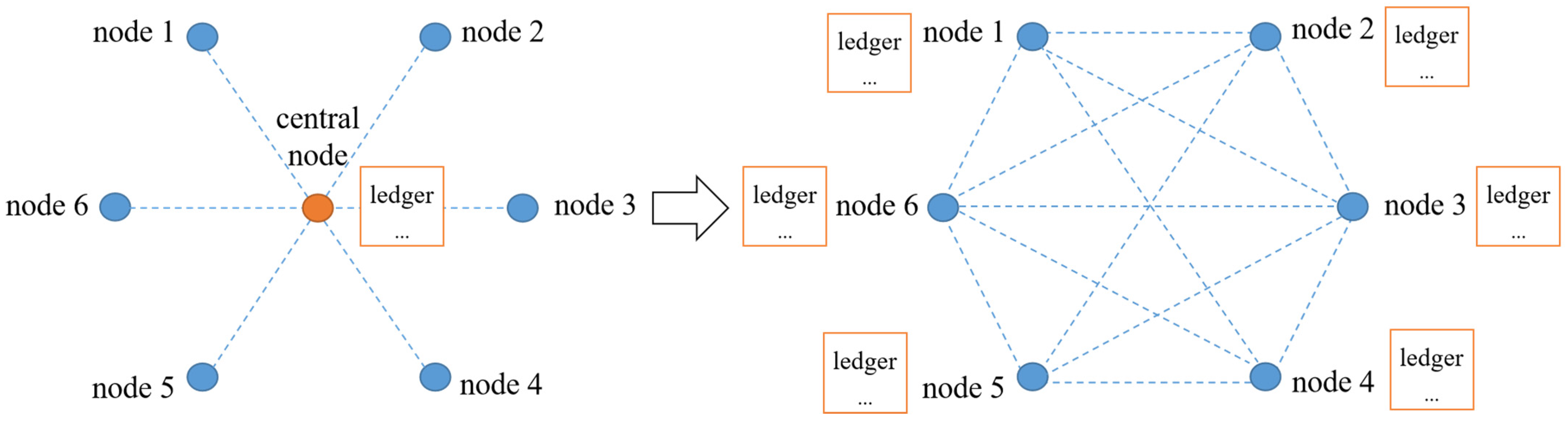
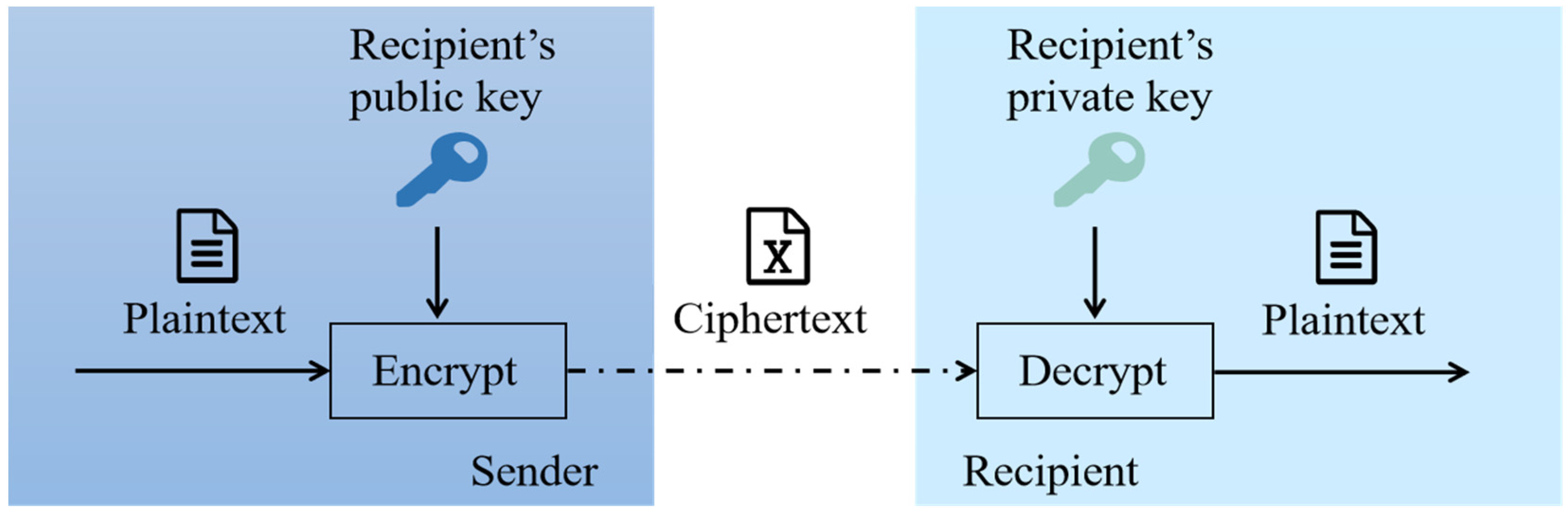
4. Blockchain and Its Advantages in the Manufacturing System
4.1. Key Technologies of Blockchain
4.2. Blockchain Solutions to Critical Issues in Smart Manufacturing
5. Application of Blockchain Technology in Smart Manufacturing
5.1. Research on Data Sharing and Data Security in Smart Manufacturing
5.2. Research on Traceability and Trust Mechanisms in Smart Manufacturing
5.3. Research on System Construction and Performance Optimization in Smart Manufacturing
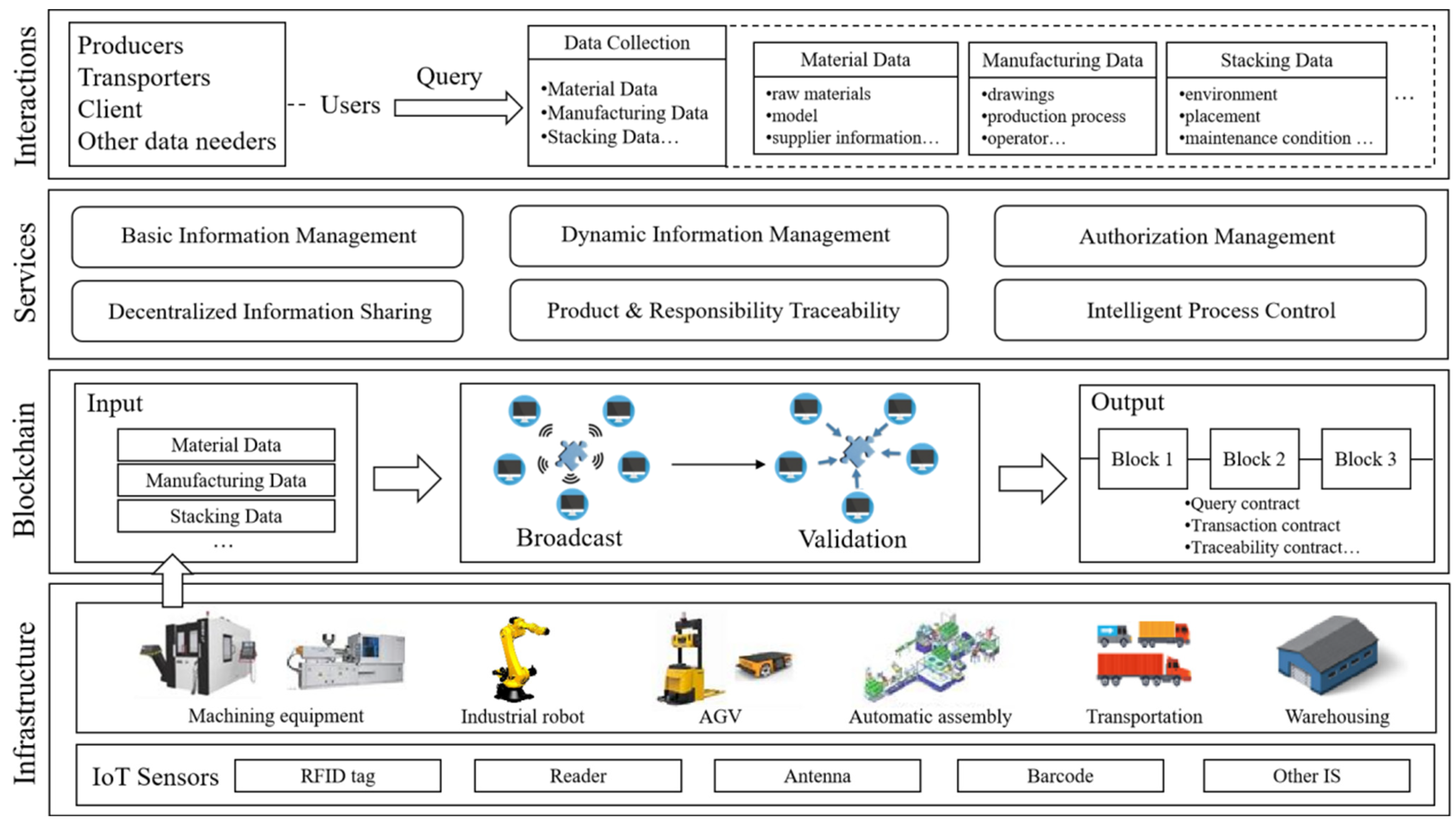
6. Reference Framework of Blockchain Technology-Enabled Smart Manufacturing
7. Challenges and Future Research
- (1)
- System integration
- (2)
- Privacy protection
- (3)
- System scalability
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zuo, Y. Making smart manufacturing smarter—A survey on blockchain technology in Industry 4.0. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2020, 15, 1323–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Khan, M.A.; Romero, D.; Wuest, T. Building Blocks for Adopting Smart Manufacturing. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 34, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Ye, S.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, J.L.; Liu, Q.; Guo, W.; Cao, W.; Fu, L. Blockchain-Secured Smart Manufacturing in Industry 4.0: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2020, 51, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Ruan, G.; Jiang, P.; Xu, K.; Xiu, Q.; Zhou, X.; Liu, C. Blockchain-empowered sustainable manufacturing and product lifecycle management in industry 4.0: A survey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 132, 110112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, S. Bitcoin: A Peer to Peer Electronic Cash System. 2009. Available online: https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- Crosby, M.; Pattanayak, P.; Verma, S.; Kalyanaraman, V. Blockchain Technology: Beyond Bitcoin. Appl. Innov. 2016, 2, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ahram, T.; Sargolzaei, A.; Sargolzaei, S.; Daniels, J.; Amaba, B. Blockchain technology innovations. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Technology & Engineering Management Conference (TEMSCON), Santa Clara, CA, USA, 8–10 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga-Lamas, P.; Fernández-Caramés, T.M. A review on blockchain technologies for an advanced and cyber-resilient automotive industry. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 17578–17598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorri, A.; Luo, F.; Kanhere, S.S.; Jurdak, R.; Dong, Z.Y. SPB: A Secure Private Blockchain-Based Solution for Distributed Energy Trading. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2019, 57, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; He, D.; Huang, X.; Choo, K.-K.R.; Vasilakos, A.V. BSeIn: A blockchain-based secure mutual authentication with fine-grained access control system for industry 4.0. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2018, 116, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Mumtaz, S.; Zhou, Z.; Peng, M. When Internet of Things Meets Blockchain: Challenges in Distributed Consensus. IEEE Netw. 2019, 33, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fc, A.; Tkd, B.; Cp, A. A systematic literature review of blockchain-based applications: Current status, classification and open issues—Sciencedirect. Telemat. Inform. 2019, 36, 55–81. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Jaroodi, J.; Mohamed, N. Blockchain in Industries: A Survey. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 36500–36515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanfar, A.; Iranmanesh, M.; Ghobakhloo, M.; Senali, M.; Fathi, M. Applications of Blockchain Technology in Sustainable Manufacturing and Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, R.; Dhib, E.; Ben Said, A.; Krichen, M.; Fetais, N.; Zaidan, E.; Barkaoui, K. Blockchain Technology for Intelligent Transportation Systems: A Systematic Literature Review. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 20995–21031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.J.; Ming, X.G.; Liu, Z.W.; Zhang, X.Y.; Hou, Z.T. Smart manufacturing systems: State of the art and future trends. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 3751–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culot, G.; Orzes, G.; Sartor, M.; Nassimbeni, G. The future of manufacturing: A Delphi-based scenario analysis on Industry 4.0. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 157, 120092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, S.; Nowostawski, M.; Jameel, R.; Mourya, A. Security Aspects of Blockchain Technology Intended for Industrial Applications. Electronics 2021, 10, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, J.; Ruj, S.; Das Bit, S. A Comprehensive Survey on Attacks, Security Issues and Blockchain Solutions for IoT and IIoT. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2019, 149, 102481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElMamy, S.; Mrabet, H.; Gharbi, H.; Jemai, A.; Trentesaux, D. A Survey on the Usage of Blockchain Technology for Cyber-Threats in the Context of Industry 4.0. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervais, A.; Karame, G.O.; Wüst, K.; Glykantzis, V.; Ritzdorf, H.; Capkun, S. On the Security and Performance of Proof of Work Blockchains. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Vienna, Austria, 25–27 October 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Masud, M.; Hossain, M.S.; Kaur, A. Cross-domain secure data sharing using blockchain for industrial IoT. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2021, 156, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J. Blockchain adoption for information sharing: Risk decision-making in spacecraft supply chain. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2019, 15, 1070–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaqty, M.I.S.; Gao, Y.; Hu, X.; Ning, Z.; Leung, V.C.M.; Wen, Q.; Chen, Y. Private-Blockchain-Based Industrial IoT for Material and Product Tracking in Smart Manufacturing. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, N.; Al-Jaroodi, J.; Lazarova-Molnar, S. Leveraging the capabilities of industry 4.0 for improving energy efficiency in smart factories. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 18008–18020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Carames, T.M.; Fraga-Lamas, P. A review on the application of blockchain for the next generation of cybersecure industry 4.0 smart factories. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 45201–45218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; El, A.; Woo, T.; Pan, Y.; Park, J.H. Deepblockscheme: A deep learning-based blockchain driven scheme for secure smart city. Hum. Cent. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2021, 11, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Dolgui, A.; Ivanov, D.; Potryasaev, S.; Sokolov, B.; Ivanova, M.; Werner, F. Blockchain-oriented dynamic modelling of smart contract design and execution in the supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 58, 2184–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Shao, Q.; Xiao, R. A supply chain prototype system based on blockchain, smart contract and internet of things. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2017, 35, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Ølnes, S.; Ubacht, J.; Janssen, M. Blockchain in government: Benefits and implications of distributed ledger technology for information sharing. Gov. Inf. Q. 2017, 34, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, P.G.; Efstathios, P. Understanding modern banking ledgers through blockchain technologies: Future of transaction processing and smart contracts on the internet of money. SSRN Electron. J. 2015, 239–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workie, H.; Jain, K. Distributed ledger technology: Implications of blockchain for the securities industry. J. Secur. Oper. Custody 2017, 9, 347–355. [Google Scholar]
- Ostern, N. Typology of Distributed Ledger Based Business Models; Publications of Darmstadt Technical University, Institute for Business Studies (BWL): Darmstadt, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bartoletti, M.; Lande, S.; Pompianu, L.; Bracciali, A. A general framework for blockchain analytics. In 1st Workshop on Scalable and Resilient Infrastructures for Distributed Ledgers; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pilkington, M. Blockchain Technology: Principles and Applications. In Research Handbook on Digital Transformations; Edward Elgar Publishing: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofer, M.; Gomber, P.; Hinz, O.; Schiereck, D. Blockchain. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2017, 59, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Guo, Z.; Xu, M. Bitmessage Plus: A Blockchain-Based Communication Protocol with High Practicality. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 21618–21626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashkari, B.; Musilek, P. A Comprehensive Review of Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 43620–43652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hoang, D.T.; Hu, P.; Xiong, Z.; Niyato, D.; Wang, P.; Wen, Y.; Kim, D.I. A Survey on Consensus Mechanisms and Mining Strategy Management in Blockchain Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 22328–22370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, M.; Chen, S.; Ma, C.; Gong, Q. An improved DPoS consensus mechanism in blockchain based on PLTS for the smart autonomous multi-robot system. Inf. Sci. 2021, 575, 528–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamar, J.; Patel, H. An Extensive Survey on Consensus Mechanisms for Blockchain Technology. In Data Science and Intelligent Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Fujimura, S.; Nakadaira, A.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kishigami, J.J. Blockchain contract: A complete consensus using blockchain. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 4th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), Osaka, Japan, 27–30 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mourouzis, T.; Tandon, J. Introduction to decentralization and smart contracts. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.04806. [Google Scholar]
- Christidis, K.; Devetsikiotis, M. Blockchains and Smart Contracts for the Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 2292–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosba, A.; Miller, A.; Shi, E.; Wen, Z.; Papamanthou, C. Hawk: The Blockchain Model of Cryptography and Privacy-Preserving Smart Contracts. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Jose, CA, USA, 22–26 May 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, L.; Chu, D.-H.; Olickel, H.; Saxena, P.; Hobor, A. Making Smart Contracts Smarter. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference, Vienna, Austria, 24–28 October 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, P.; Chen, T.; Luo, X.; Wen, Q. A survey on the security of blockchain systems. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 107, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmolino, K.; Arnett, M.; Kosba, A.; Miller, A.; Shi, E. Step by Step towards Creating a Safe Smart Contract: Lessons and Insights from a Cryptocurrency Lab. In International Conference on Financial Cryptography and Data Security; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rathee, G.; Ahmad, F.; Sandhu, R.; Kerrache, C.A.; Azad, M.A. On the design and implementation of a secure blockchain-based hybrid framework for Industrial Internet-of-Things. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Jeong, Y.S.; Park, J.H. A deep learning-based iot-oriented infrastructure for secure smart city. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 60, 102252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhader, W.; Alkaabi, N.; Salah, K.; Jayaraman, R.; Arshad, J.; Omar, M. Blockchain-Based Traceability and Management for Additive Manufacturing. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 188363–188377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, H.R.; Salah, K.; Jayaraman, R.; Ahmad, R.W.; Yaqoob, I.; Omar, M. Blockchain-Based Solution for the Traceability of Spare Parts in Manufacturing. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 100308–100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Tan, L.; Aloqaily, M.; Yang, H.; Jararweh, Y. Blockchain-Enhanced Data Sharing with Traceable and Direct Revocation in IIoT. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 7669–7678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, P. A blockchain-driven cyber-credit evaluation approach for establishing reliable cooperation among unauthentic MSMEs in social manufacturing. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2020, 121, 724–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, R.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Q.; Qin, J. Optimization of dynamic data traceability mechanism in Internet of Things based on consortium blockchain. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2018, 14, 1550147718819072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, A.; Lu, Q.; Tao, F. Blockchain-based trust mechanism for iot-based smart manufacturing system. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2019, 6, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhou, B. Trusted transaction method of manufacturing services based on blockchain. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2019, 25, 3247–3257. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.C.; Ghose, S.; Kim, A.; Kang, M.A.; Chung, K. BlockChain based Trust Process for Smart Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference for Small & Medium Business 2018 (ICSMB2018), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 18 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Barenji, R.V. A blockchain technology based trust system for cloud manufacturing. J. Intell. Manuf. 2021, 33, 1451–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Dai, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Chao, L.I.; Wang, X. Data governance collaborative method based on blockchain. J. Comput. Appl. 2018, 38, 2500. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, J.; Yan, D.; Liu, Q.; Xu, K.; Zhao, J.L.; Shi, R.; Wei, L.; Zhang, D.; Chen, X. ManuChain: Combining Permissioned Blockchain with a Holistic Optimization Model as Bi-Level Intelligence for Smart Manufacturing. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2019, 50, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Dixon, J.; Guin, U.; Dimase, D. A Blockchain-Based Framework for Supply Chain Provenance. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 157113–157125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Kumar, N.; Park, J.H. Blockchain-Based Distributed Framework for Automotive Industry in a Smart City. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 15, 4197–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Starly, B. Decentralized cloud manufacturing-as-a-service (CMaaS) platform architecture with configurable digital assets. J. Manuf. Syst. 2020, 56, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiskanen, A. The technology of trust: How the Internet of Things and blockchain could usher in a new era of construction productivity. Constr. Res. Innov. 2017, 8, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Kong, L.; Dai, H.-N.; Ding, W.; Cheng, L.; Chen, G.; Jin, X.; Zeng, P. Blockchain-Based Mobile Crowd Sensing in Industrial Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 6553–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Li, J.; Imran, M.; Li, D.; Amin, F.E. A Blockchain-Based Solution for Enhancing Security and Privacy in Smart Factory. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 3652–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, Z.; Byun, Y.-C. Integration of Blockchain, IoT and Machine Learning for Multistage Quality Control and Enhancing Security in Smart Manufacturing. Sensors 2021, 21, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Souri, A. Blockchain technology for energy-aware mobile crowd sensing approaches in internet of things. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2021, 11, e4217. [Google Scholar]
- Vangala, A.; Das, A.K.; Kumar, N.; Alazab, M. Smart secure sensing for iot-based agriculture: Blockchain perspective. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 17591–17607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tian, Y.; Ma, T.; Al-Nabhan, N. Intelligent manufacturing security model based on improved blockchain. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2020, 17, 5633–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Abhishek, K.; Nerurkar, P.; Ghalib, M.R.; Shankar, A.; Cheng, X. Secure smart contracts for cloud-based manufacturing using Ethereum blockchain. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2020, 33, e4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kho, J.S.; Jeong, J. HACCP-based Cooperative Model for Smart Factory in South Korea. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 175, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barenji, A.V.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.M.; Huang, G.Q.; Guerra-Zubiaga, D.A. Blockchain-based ubiquitous manufacturing: A secure and reliable cyber-physical system. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 58, 2200–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, F.; Chis, A.E.; Caton, S.; González–Vélez, H.; García–Gómez, J.M.; Durá, M.; Sánchez–García, A.; Sáez, C.; Karageorgos, A.; Gerogiannis, V.C.; et al. Smart Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Ensuring End-to-End Traceability and Data Integrity in Medicine Production. Big Data Res. 2021, 24, 100172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, F. Trusted resource scheduling scheme in cloud manufacturing system based on blockchain. Appl. Res. Comput. 2021, 6, 1626–1630+1636. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, S.K.; Satapathy, S.C. Drug traceability and transparency in medical supply chain using blockchain for easing the process and creating trust between stakeholders and consumers. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2021, 29, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.M.; Huo, Y.Z.; Zhang, S.Z.; Ng, K.K.H. Design of a Smart Manufacturing System with the Application of Multi-Access Edge Computing and Blockchain Technology. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 28659–28667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcinkaya, E.; Maffei, A.; Onori, M. Blockchain Reference System Architecture Description for the ISA95 Compliant Traditional and Smart Manufacturing Systems. Sensors 2020, 20, 6456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Zhu, H.; Tan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Da Xu, L.; Guo, K. A novel service level agreement model using blockchain and smart contract for cloud manufacturing in industry 4.0. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2021, 16, 1939426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Hu, M.; Liu, M.; Wang, J. BPIIoT: A Light-Weighted Blockchain-Based Platform for Industrial IoT. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 58381–58393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, Z.; Byun, Y.-C. Smart Manufacturing Real-Time Analysis Based on Blockchain and Machine Learning Approaches. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Jiang, X.; Yu, S.; Yang, C. Blockchain-based shared manufacturing in support of cyber physical systems: Concept, framework, and operation. Robot. Comput. Manuf. 2020, 64, 101931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, Z.; Byun, Y.-C. Improving Transactional Data System Based on an Edge Computing–Blockchain–Machine Learning Integrated Framework. Processes 2021, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Ma, X.; Zhang, S. Performance Analysis of the Raft Consensus Algorithm for Private Blockchains. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 50, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Peng, M.; Li, Y. Performance analysis and comparison of PoW, PoS and DAG based blockchains. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2020, 6, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Shi, Z.; Nixon, M.; Han, S. ChainSplitter: Towards Blockchain-Based Industrial IoT Architecture for Supporting Hierarchical Storage. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Blockchain (Blockchain), Atlanta, GA, USA, 14–17 July 2019; pp. 166–175. [Google Scholar]
- Bandara, E.; Tosh, D.; Foytik, P.; Shetty, S.; Ranasinghe, N.; Zoysa, K.D. Tikiri-towards a lightweight blockchain for iot. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 119, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuli, S.; Mahmud, R.; Tuli, S.; Buyya, R. Fogbus: A blockchain-based lightweight framework for edge and fog computing. J. Syst. Softw. 2019, 154, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolaki, M.; Zohar, A.; Vanbever, L. Hijacking bitcoin: Routing attacks on cryptocurrencies. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Jose, CA, USA, 22–26 May 2017; pp. 375–392. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Jha, S.; Hu, W. LoRa-key: Secure key generation system for LoRa-based network. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 6, 6404–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botello, J.V.; Mesa, A.P.; Rodríguez, F.A.; Díaz-López, D.; Nespoli, P.; Mármol, F.G. BlockSIEM: Protecting smart city services through a blockchain-based and distributed SIEM. Sensors 2020, 20, 4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, M.; Kumar, E.S.; Lal, C.; Ruj, S. A survey on security and privacy issues of bitcoin. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 3416–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorri, A.; Kanhere, S.S.; Jurdak, R. MOF-BC: A memory optimized and flexible blockchain for large scale networks. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 92, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CrCroman, K.; Decker, C.; Eyal, I.; Gencer, A.E.; Juels, A.; Kosba, A.; Miller, A.; Saxena, P.; Shi, E.; Gün Sirer, E.; et al. On scaling decentralized blockchains. In International Conference on Financial Cryptography and Data Security; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 106–125. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Long, C.; Xu, H.; Peng, S. A Review on Scalability of Blockchain. In Proceedings of the ICBCT’20: 2020 The 2nd International Conference on Blockchain Technology, Hilo, HI, USA, 12–14 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, S.; Reichert, S.; Schmid, J.; Strüker, J.; Neumann, D.; Fridgen, G. Dynamics of blockchain implementation-a case study from the energy sector. In Proceedings of the 51st Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Waikoloa Village, HI, USA, 3–6 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Luu, L.; Narayanan, V.; Zheng, C.; Baweja, K.; Gilbert, S.; Saxena, P. A secure sharding protocol for open blockchains. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Vienna, Austria, 25–27 October 2016; pp. 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Huang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Bian, J. Solutions to Scalability of Blockchain: A Survey. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 16440–16455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Yu, F.R.; Huang, T.; Xie, R.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. A Survey on the Scalability of Blockchain Systems. IEEE Netw. 2019, 33, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D. Toward next generation of blockchain using improvized bitcoin-ng. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2021, 99, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halgamuge, M.N.; Mapatunage, S.P. Fair Rewarding Mechanism for Sharding-based Blockchain Networks with Low-powered Devices in the Internet of Things. Proceedings of 2021 IEEE 16th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Chengdu, China, 1–4 August 2021. [Google Scholar]

| PoW | PoS | DPoS | PBFT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application | Bitcoin, Ethereum, LiteCoin, Dogecoin | Ethereum, Peercoin, Nxt | BitShares, Steemit, EOS, Lisk, Ark | Hyperledger Fabric, Stellar, Ripple, Dispatch |
| Classification | Competitive consensus | Competitive consensus | Collaborative consensus | Collaborative consensus |
| Advantages | Easy to implement, high security and difficult to attack | Low computing resource consumption, high efficiency | High throughput, fast operation speed | High-speed and scalable |
| Disadvantages | Huge energy consumption; low operating efficiency | Complex protocol, high network requirements | Slightly centralized, easy to cause collusion attacks | Only used for private and consortium blockchain |
| Function | Literature | Addressed Issues | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data sharing and data security | [67] | C1, C2 | The proposed multi-center partially decentralized IIoT architecture uses blockchain to enhance security and privacy |
| [68] | C1 | The study applies the integrated methods of blockchain and machine learning to solve data security and management issues in smart manufacturing | |
| [69] | C1, C2 | The utilized blockchain technology to improve the privacy and security of data transmission and communications in IoT | |
| [70] | C1 | The proposed generalized architecture applies blockchain technology in smart agriculture to provide security goals | |
| [71] | C1, C2, C3 | The proposed intelligent manufacturing security model supported by the blockchain can effectively enhance security, privacy and non-tamperability | |
| [72] | C1, C2 | The proposed use case of a blockchain framework is aim to avoid fraud scenarios and secure logistics trade | |
| Traceability and trust mechanism | [56] | C1, C2, C3 | The blockchain-based trust mechanism for quality assurance promotes the transparency, security and efficiency of transactions |
| [73] | C1 | The study applies blockchain technology to enhance the security of data in smart factories | |
| [74] | C1, C2, C3 | The proposed platform uses blockchain to provide a peer-to-peer communication network between the end user and the service provider | |
| [75] | C1, C2, C3 | The proposed system in a pharmaceutical environment takes advantage of blockchain properties and smart contracts to ensure data authenticity, transparency and immutability | |
| [76] | C3, C4 | The study utilizes blockchain technology to solve the trust problem and resource scheduling efficiency problem in a cloud manufacturing system | |
| [77] | C1, C3 | The study applies a blockchain platform to maintain a decentralized medical supply chain and promote the traceability of the overall system | |
| System construction and performance optimization | [78] | C1, C2 | The proposed system utilizes blockchain technology to promote both device-level data transmission and manufacturing service transaction |
| [79] | C1, C2 | The proposed blockchain reference system architecture promotes applicability and consistency across enterprise infrastructure | |
| [80] | C2, C3 | The study applies blockchain technologies and smart contracts to address trust issues while ensuring the effectiveness and efficiency of business services | |
| [24] | C1, C2 | The proposed private-blockchain-based IIoT is aimed to bridge the need for product and material tracking information exchange while ensuring confidentiality | |
| [81] | C1, C2 | The proposed blockchain-based platform for Industrial Internet of Things (BPIIoT) applies blockchain network to process all transactions, including digital signature and programmable permission | |
| [82] | C1, C2 | The proposed smart manufacturing conceptual scenario applies blockchain technology to strengthen data integrity and decrease data transmission risk | |
| [83] | C3, C4 | The proposed Blockchain-based Shared Manufacturing (BSM) framework is applied to support Cyber Physical Systems (CPS) | |
| [61] | C2, C4 | The proposed ManuChain takes advantage of blockchain-driven smart contracts to proactively decentralize task execution and make the results available for optimization | |
| [84] | C1, C2 | The proposed smart manufacturing conceptual scenario applies blockchain technology to strengthen data integrity and decrease data transmission risk |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y. A Comprehensive Review of Blockchain Technology-Enabled Smart Manufacturing: A Framework, Challenges and Future Research Directions. Sensors 2023, 23, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010155
Guo X, Zhang G, Zhang Y. A Comprehensive Review of Blockchain Technology-Enabled Smart Manufacturing: A Framework, Challenges and Future Research Directions. Sensors. 2023; 23(1):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010155
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xin, Geng Zhang, and Yingfeng Zhang. 2023. "A Comprehensive Review of Blockchain Technology-Enabled Smart Manufacturing: A Framework, Challenges and Future Research Directions" Sensors 23, no. 1: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010155
APA StyleGuo, X., Zhang, G., & Zhang, Y. (2023). A Comprehensive Review of Blockchain Technology-Enabled Smart Manufacturing: A Framework, Challenges and Future Research Directions. Sensors, 23(1), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010155





