Deep Spatiotemporal Model for COVID-19 Forecasting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
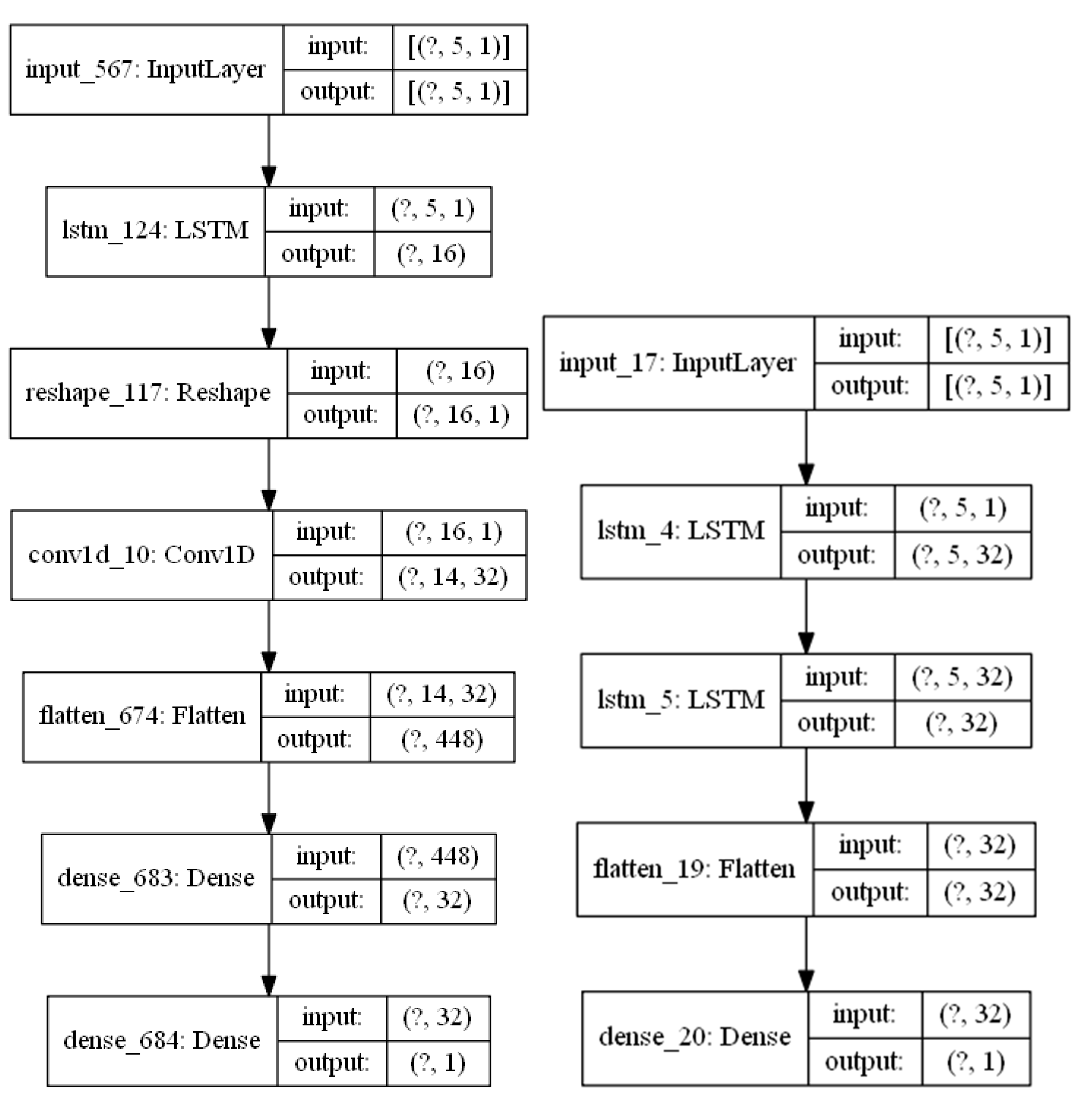
3.1. COVID-19 Forecasting Model
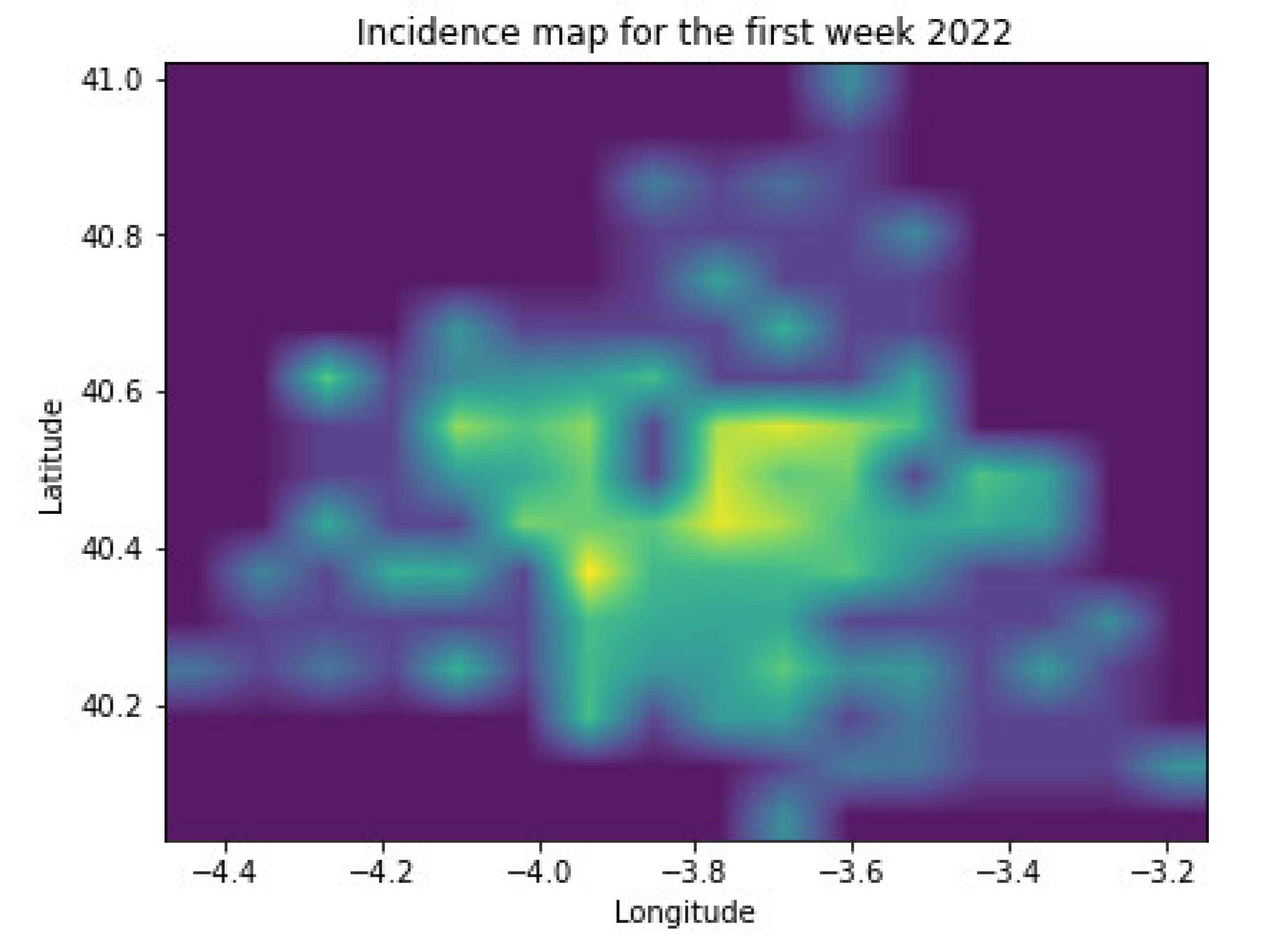
3.2. Dataset Description
4. Results
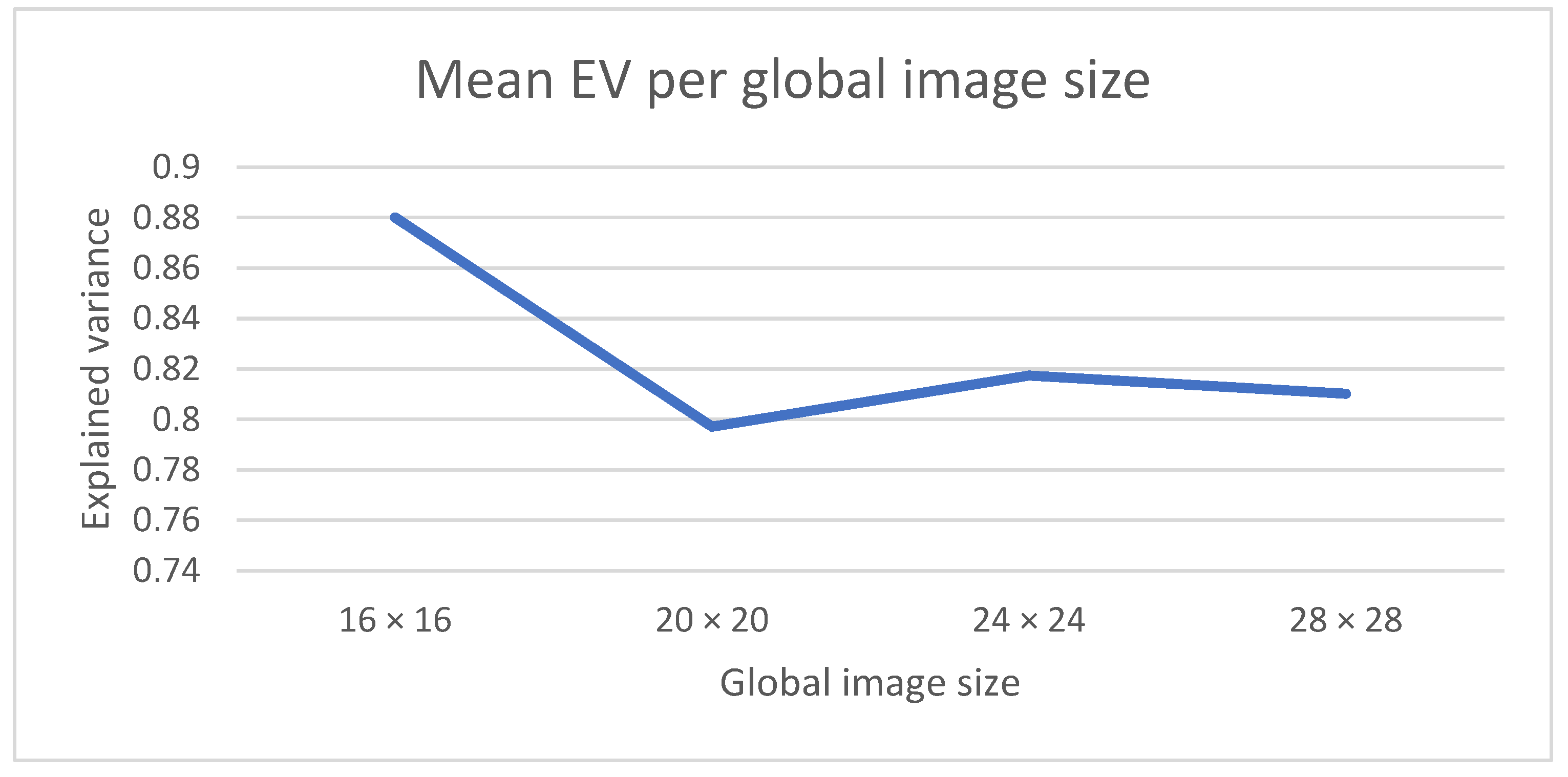
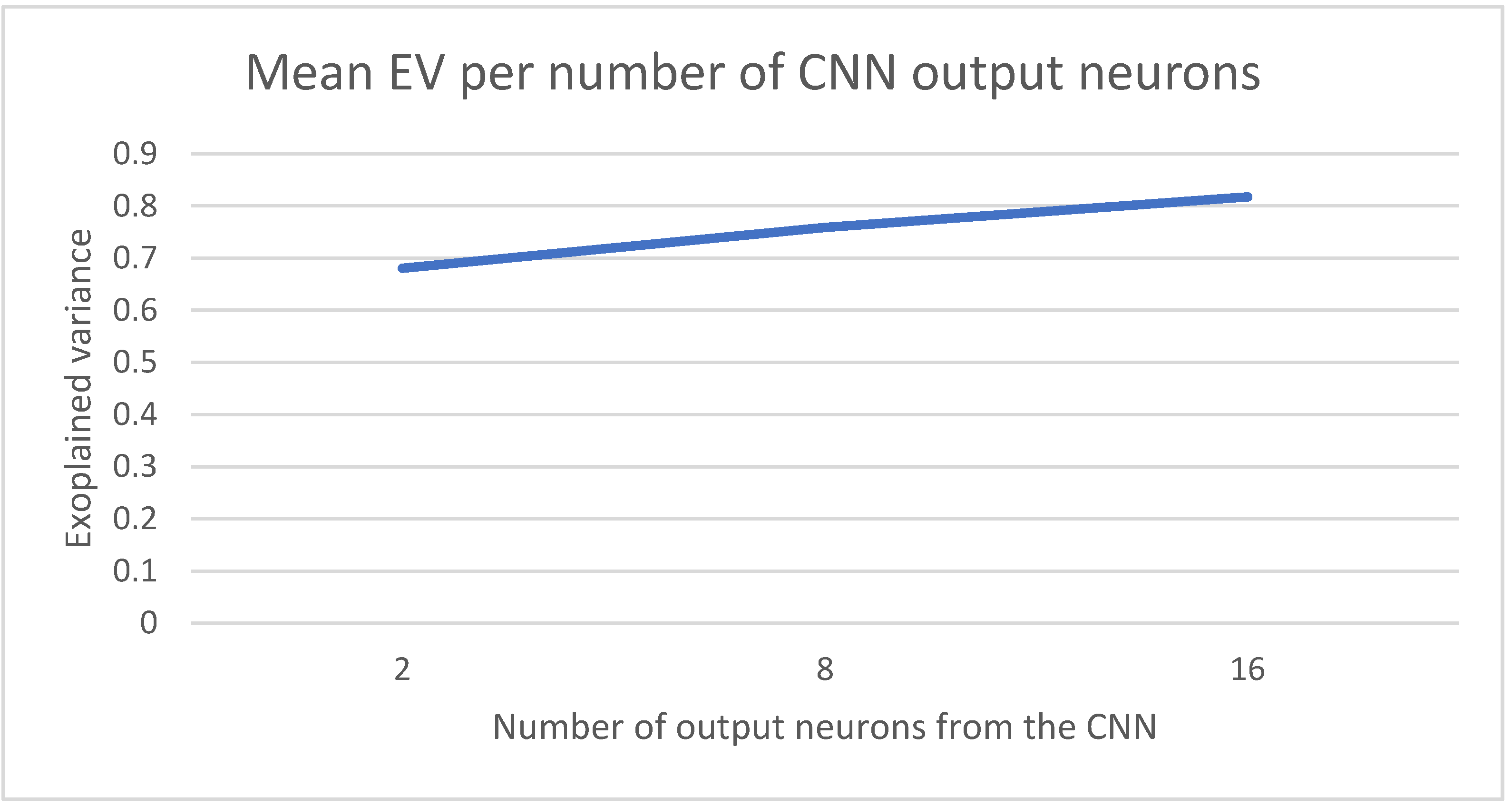
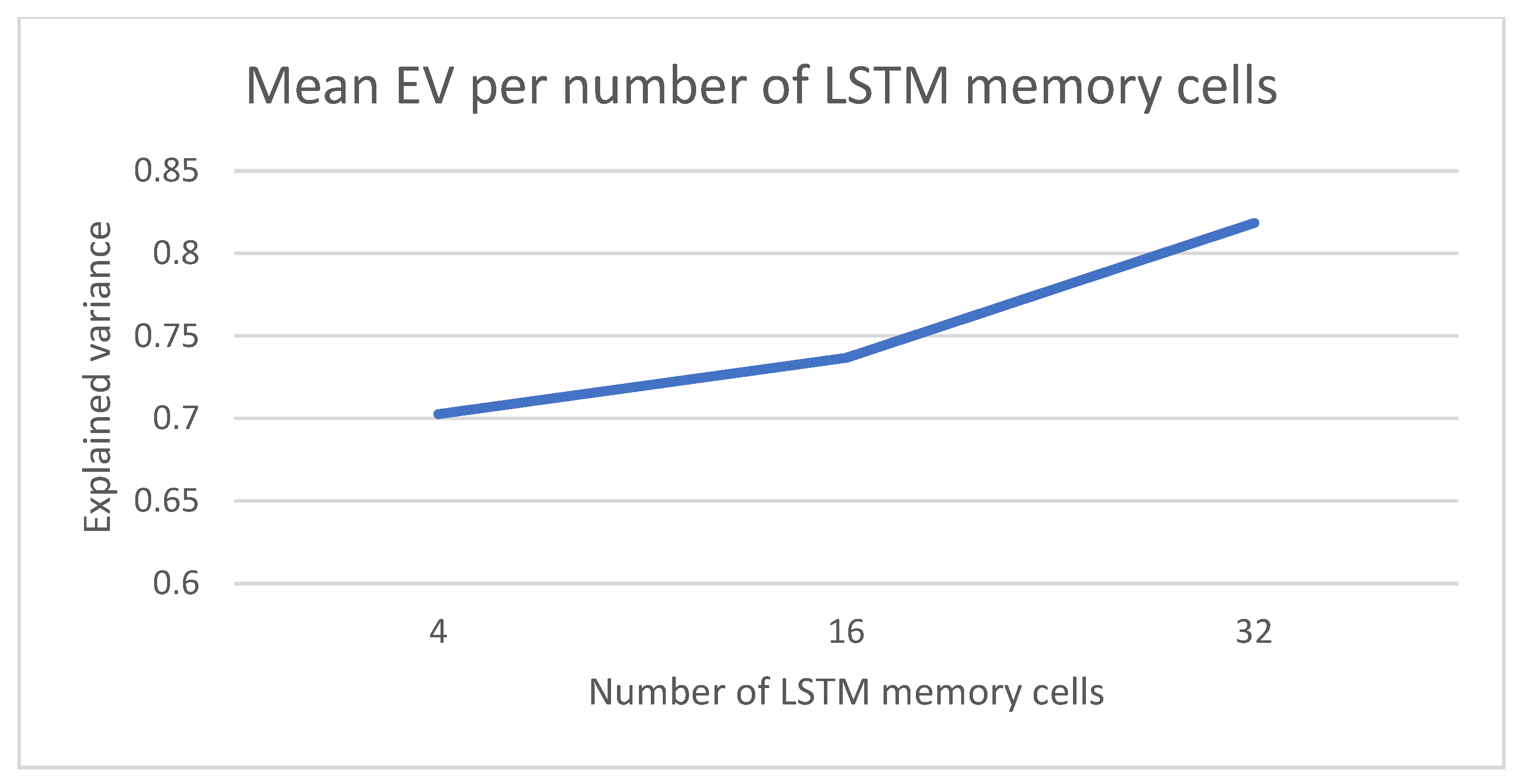
4.1. Parameter Setting for the COVID-19 Forecasting Model
- (1)
- The number of pixels or areas the Madrid region incidence map is divided into.
- (2)
- The size of the input image to the CNN (which is a set of adjacent heath units from the entire image created in the previous point).
- (3)
- The number of filters in the CNN.
- (4)
- The number of output neurons in the CNN.
- (5)
- The number of memory units in the LSTM cell.
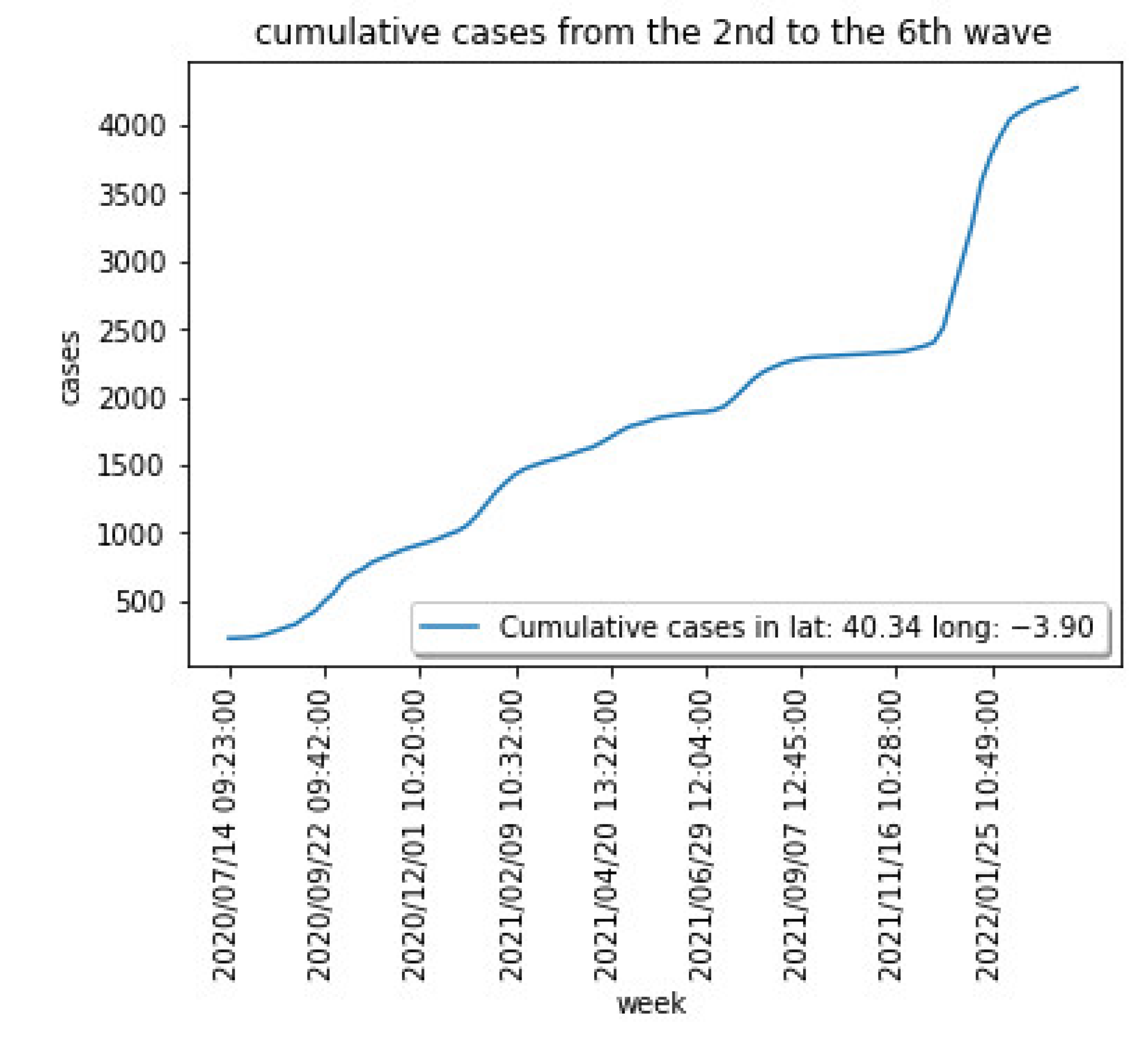
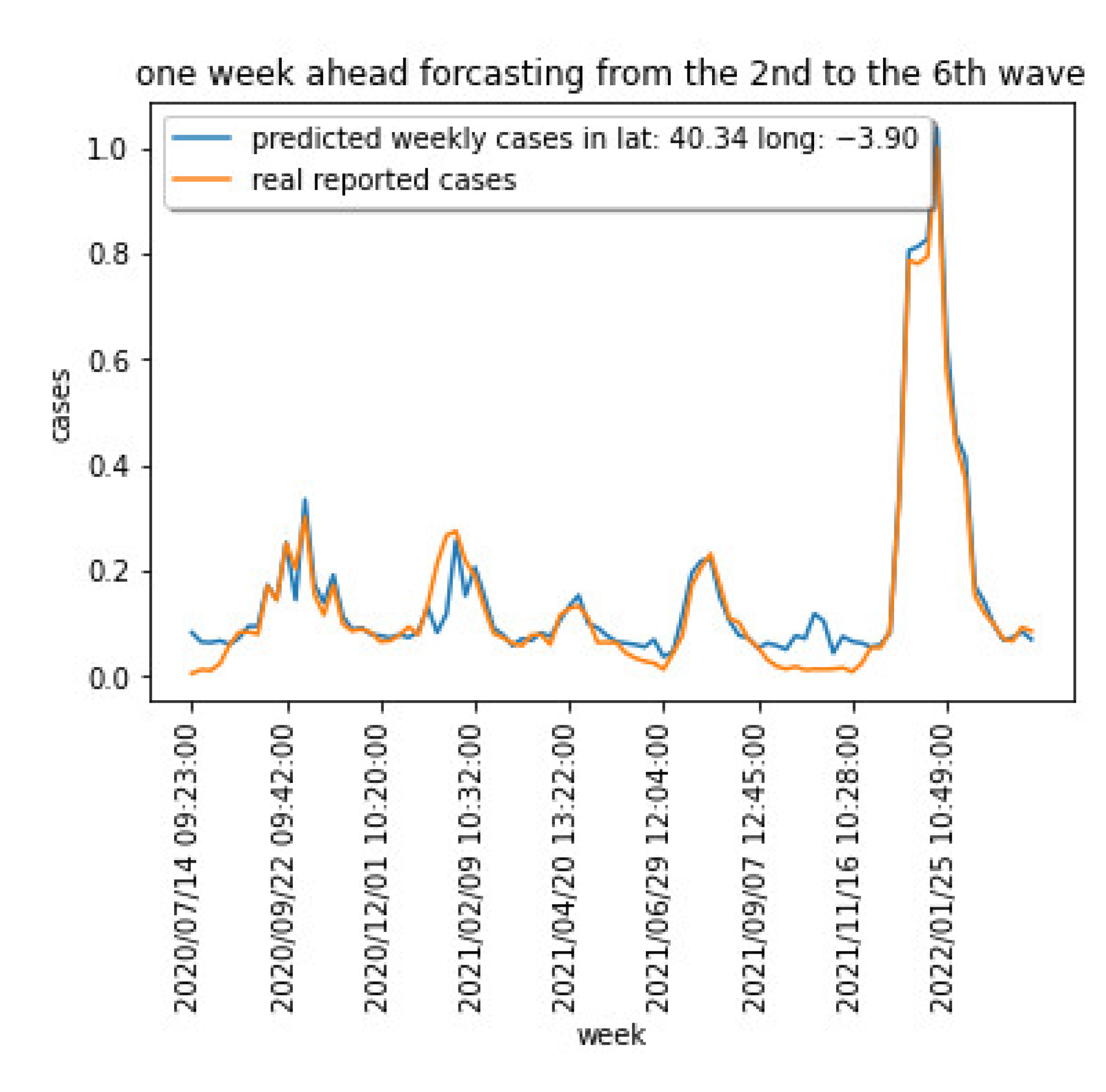
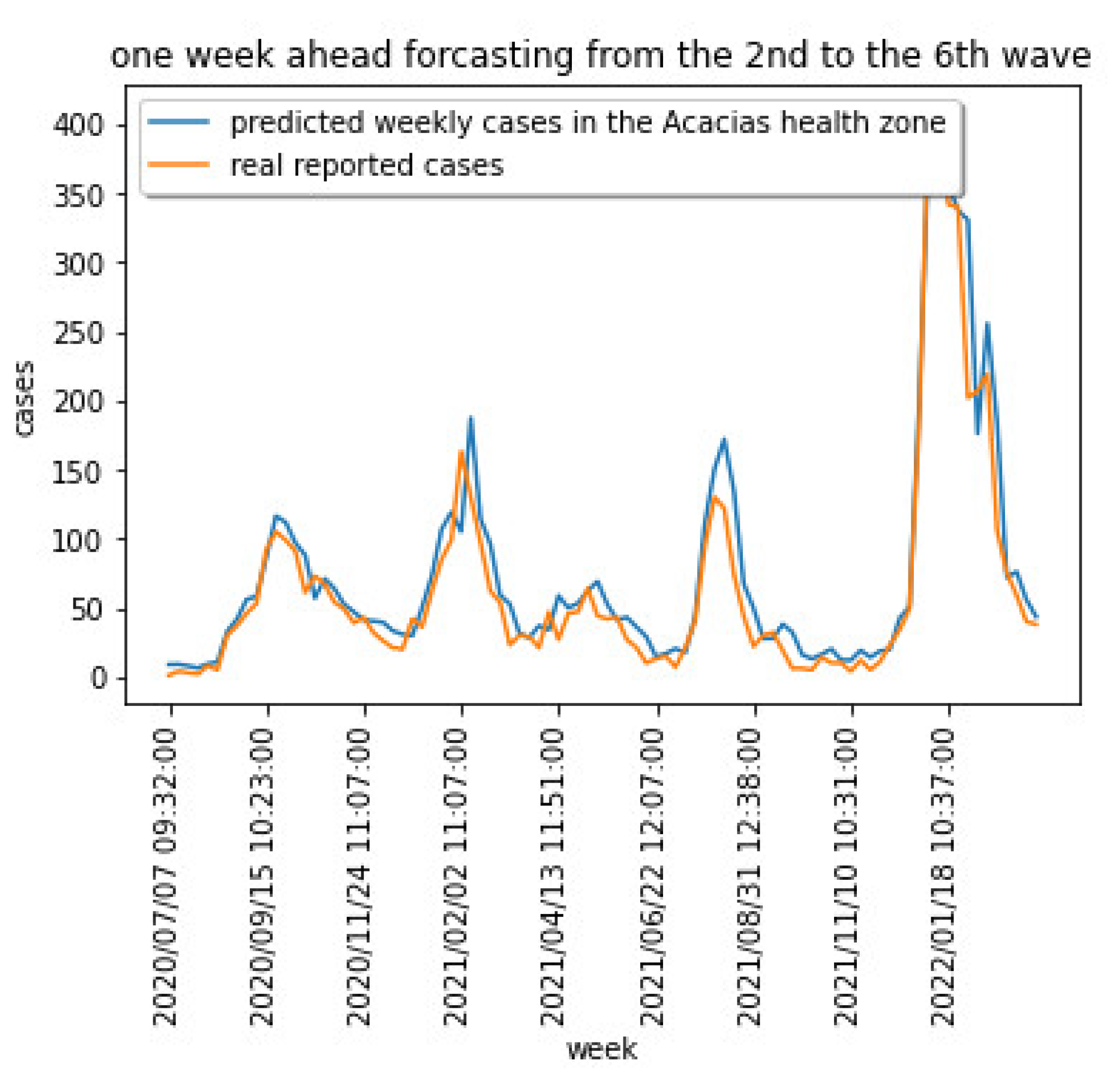
4.2. Validating the COVID-19 Forecasting Model
4.3. Comparing the COVID-19 Forecasting Model Results with Previous Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harapan, H.; Itoh, N.; Yufika, A.; Winardi, W.; Keam, S.; Te, H.; Megawati, D.; Hayati, Z.; Wagner, A.L.; Mudatsir, M. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A literature review. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, P.; Schütte, A.D.; Dietz, B.; Bauer, S. Clinical predictive models for COVID-19: Systematic study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e21439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, A.; Putri, E.R.; Susanto, H.; Nuraini, N. Data-driven modeling and forecasting of COVID-19 outbreak for public policy making. ISA Trans. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaddar, A.; Abta, A.; Alaoui, H.T. A comparison of delayed SIR and SEIR epidemic models. Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control 2011, 16, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.Q. On a statistical transmission model in analysis of the early phase of COVID-19 outbreak. Stat. Biosci. 2021, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldo, F.; Dall’Olio, L.; Ceccarelli, M.; Scheda, R.; Lombardi, M.; Borghesi, A.; Diciotti, S.; Milano, M. Deep learning for virus-spreading forecasting: A brief survey. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.02346. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Xu, T.; Stoecker, T.; Stoecker, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, K. Machine learning spatio-temporal epidemiological model to evaluate Germany-county-level COVID-19 risk. Mach. Learn. Sci. Technol. 2021, 2, 035031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Madrid, C. COVID-19 Open Data by Basic Health Care Zones. Available online: https://datos.comunidad.madrid/catalogo/dataset/covid19_tia_zonas_basicas_salud (accessed on 2 May 2022).
- Muhammad, L.J.; Algehyne, E.A.; Usman, S.S.; Ahmad, A.; Chakraborty, C.; Mohammed, I.A. Supervised machine learning models for prediction of COVID-19 infection using epidemiology dataset. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, D.; Gutman, Y.A.; Neuman, Y.; Segal, G.; Amit, S.; Gefen-Halevi, S.; Shilo, N.; Epstein, A.; Mor-Cohen, R.; Biber, A.; et al. Utilization of machine-learning models to accurately predict the risk for critical COVID-19. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2020, 15, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakus, T.B.; Turkoglu, I. Comparison of deep learning approaches to predict COVID-19 infection. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 140, 110120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazab, M.; Awajan, A.; Mesleh, A.; Abraham, A.; Jatana, V.; Alhyari, S. COVID-19 prediction and detection using deep learning. Int. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. Ind. Manag. Appl. 2020, 12, 168–181. [Google Scholar]
- Ardabili, S.; Mosavi, A.; Ghamisi, P.; Ferdinand, F.; Varkonyi-Koczy, A.; Reuter, U.; Rabczuk, T.; Atkinson, P. Covid-19 outbreak prediction with machine learning. Algorithms 2020, 13, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhi, R.; Thangeda, R.; Sugasi, R.P.; Kumar, N. Analysis and prediction of COVID-19 trajectory: A machine learning approach. J. Public Aff. 2021, 21, e2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, F.; Zameer, A.; Muneeb, M. Predictions for covid-19 with deep learning models of lstm, gru and bi-lstm. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 140, 110212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.J.; Shen, Y.; Kuo, P.H.; Chen, Y.H. Novel spatiotemporal feature extraction parallel deep neural network for forecasting confirmed cases of coronavirus disease 2019. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2020, 80, 100976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mežnar, S.; Lavrač, N.; Škrlj, B. Prediction of the effects of epidemic spreading with graph neural networks. In Complex Networks & Their Applications IX; Benito, R.M., Cherifi, C., Cherifi, H., Moro, E., Rocha, L.M., Sales-Pardo, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 420–431. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, S.; Wang, S.; Rangwala, H.; Wang, L.; Ning, Y. Cola-GNN: Cross-Location Attention Based Graph Neural Networks for Long-Term ILI Prediction; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 245–254. [Google Scholar]
- Dairi, A.; Harrou, F.; Zeroual, A.; Hittawe, M.M.; Sun, Y. Comparative study of machine learning methods for COVID-19 transmission forecasting. J. Biomed. Inform. 2021, 118, 103791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alassafi, M.O.; Jarrah, M.; Alotaibi, R. Time series predicting of COVID-19 based on deep learning. Neurocomputing 2022, 468, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhao, P.; Haitao, H.; Mansourian, A.; Axhausen, K.W. How did micro-mobility change in response to COVID-19 pandemic? A case study based on spatial-temporal-semantic analytics. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 90, 101703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lyu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yu, W.; Qu, X. DeepTSP: Deep traffic state prediction model based on large-scale empirical data. Commun. Transp. Res. 2021, 1, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wu, J.; Fu, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Shangguan, Q. Dynamic prediction of traffic incident duration on urban expressways: A deep learning approach based on LSTM and MLP. J. Intell. Connect. Veh. 2021, 4, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanat, A.B.; Mnasri, S.; Aseeri, M.; Alhazmi, K.; Cheikhrouhou, O.; Altarawneh, G.; Alrashidi, M.; Tarawneh, A.S.; Almohammadi, K.; Almoamari, H. A simulation model for forecasting covid-19 pandemic spread: Analytical results based on the current saudi covid-19 data. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Keras Library for Python. Available online: https://keras.io/ (accessed on 2 May 2022).







| Model | RMSE | EV |
|---|---|---|
| SVM 1 (France) [19] | 6560 × 106 | 0.892 |
| LR 2 (France) [19] | 5210 × 106 | 0.810 |
| RBM (France) [19] | 8540 | 0.957 |
| CNN (France) [19] | 1930 × 106 | 0.975 |
| LSTM (France) [19] | 2180 ×106 | 0.967 |
| LSTM (Madrid) | 19.71 | 0.996 |
| Time series LSTM-CNN (France) [19] | 2750 | 0.994 |
| Time series LSTM-CNN (India) [19] | 83,100 | 0.998 |
| Time series LSTM-CNN (US) [19] | 56,900 | 0.999 |
| Time series LSTM-CNN (Madrid) | 4.61 | 0.997 |
| Spatiotemporal CNN+LSTM (Madrid areas) | 1.93 | 0.998 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz-Organero, M.; Queipo-Álvarez, P. Deep Spatiotemporal Model for COVID-19 Forecasting. Sensors 2022, 22, 3519. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093519
Muñoz-Organero M, Queipo-Álvarez P. Deep Spatiotemporal Model for COVID-19 Forecasting. Sensors. 2022; 22(9):3519. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093519
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz-Organero, Mario, and Paula Queipo-Álvarez. 2022. "Deep Spatiotemporal Model for COVID-19 Forecasting" Sensors 22, no. 9: 3519. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093519
APA StyleMuñoz-Organero, M., & Queipo-Álvarez, P. (2022). Deep Spatiotemporal Model for COVID-19 Forecasting. Sensors, 22(9), 3519. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093519







