Dynamic Spectrum Allocation Using Multi-Source Context Information in OpenRAN Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Merging Various Information Sources
2.1. Source I: Access Point as a Source of Information about Users
2.2. Source II: Monitoring as a Source of Information about Users
2.3. Source III: Power Sensor as a Source of Information about Users
2.4. Combined Data as a Source of Information about Users
2.5. Policy Defined Dynamic Spectrum Access
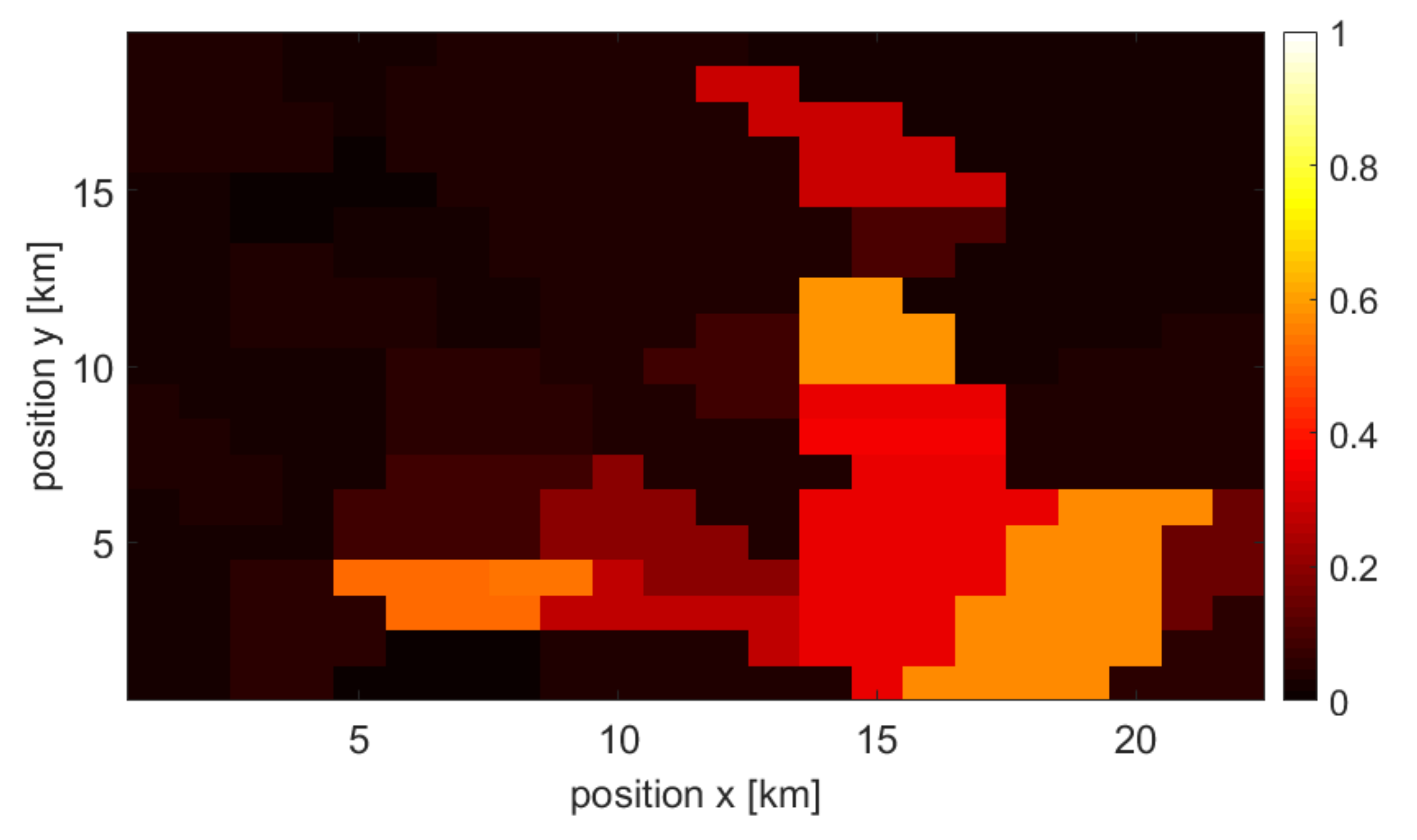
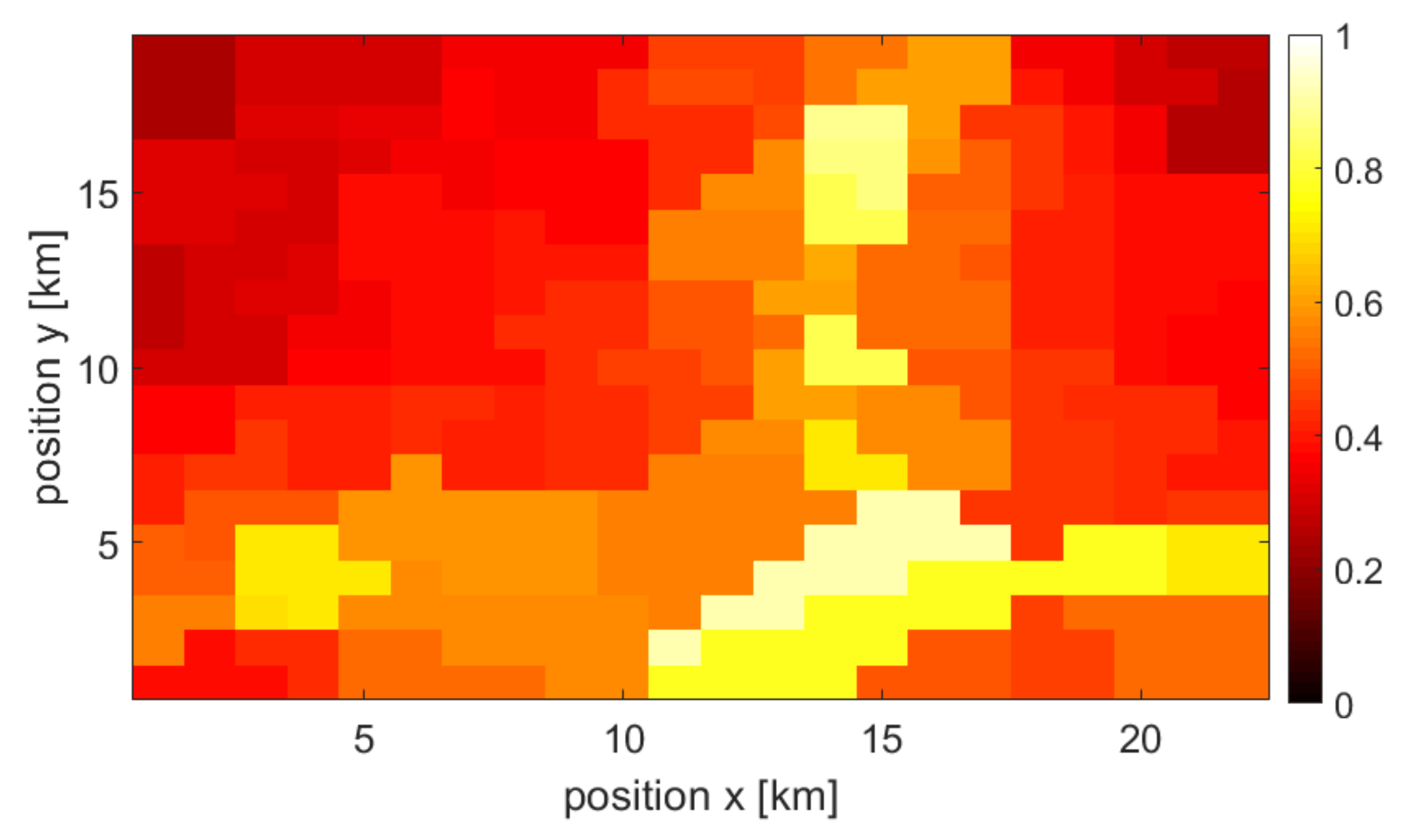
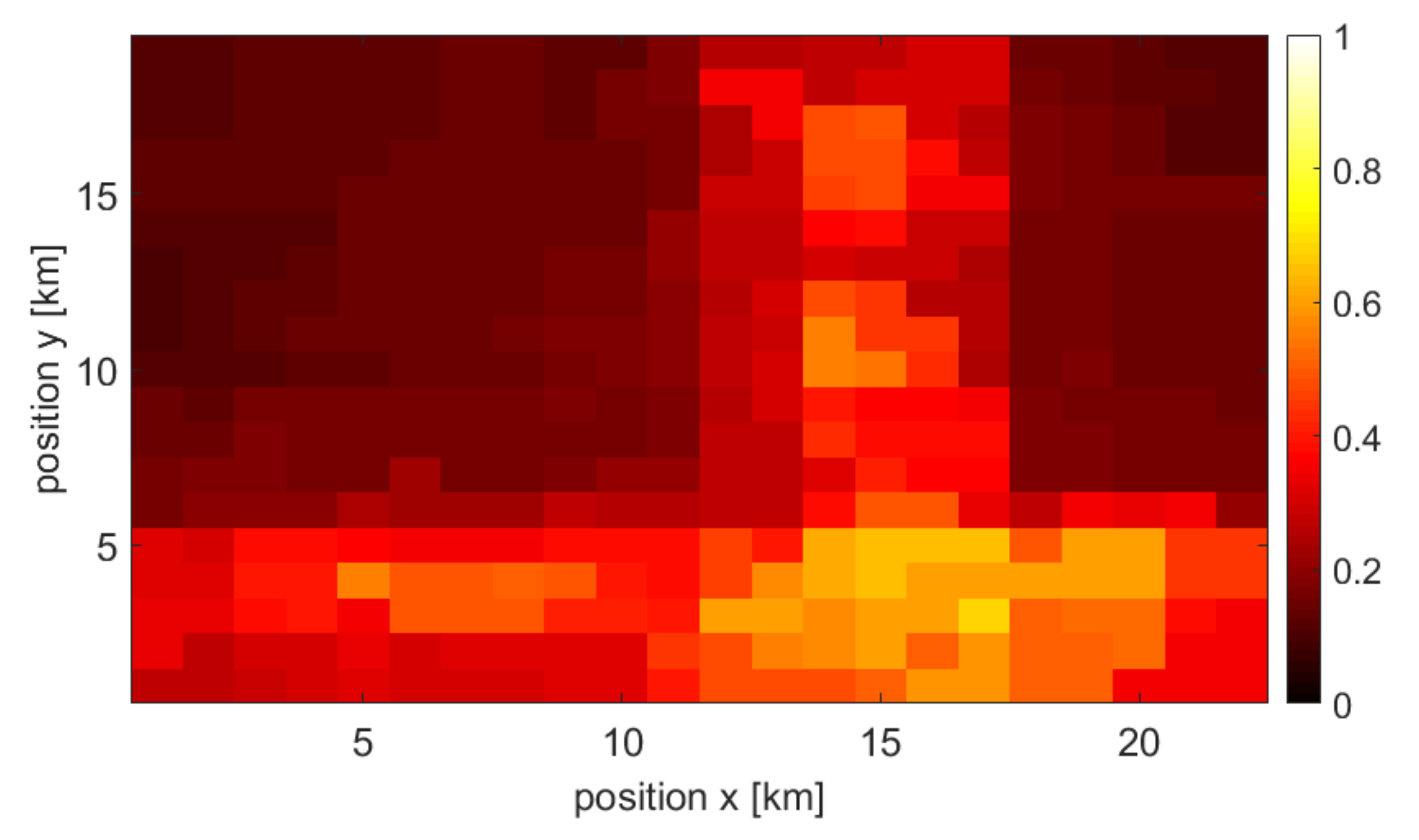
3. Evaluation Process—Combined Map Creation
3.1. Considered Scenario
3.2. Single Source and Combined Maps
3.3. Algorithm for Limiting the Available Bandwidth in Access Points
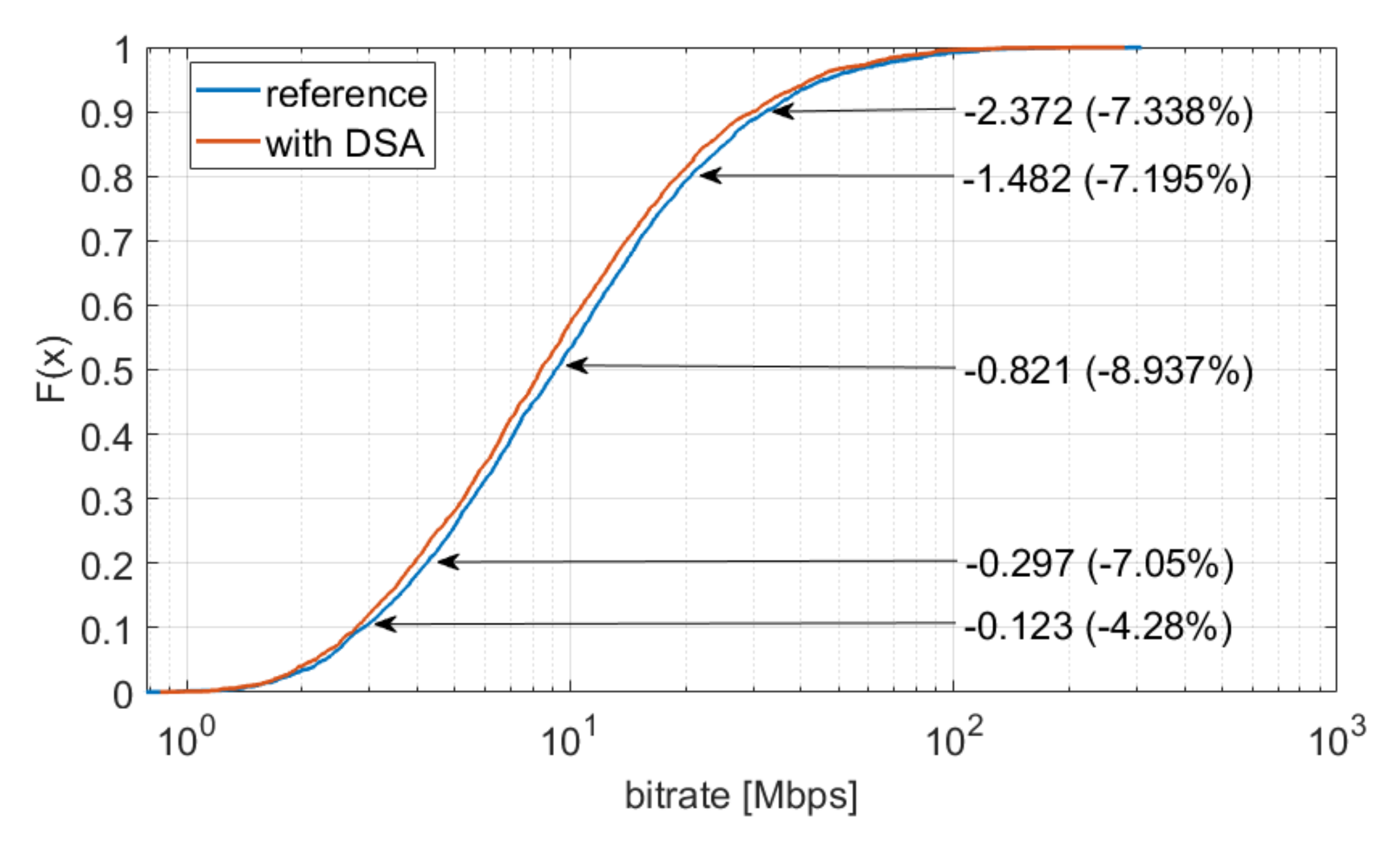
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Single Simulation Repetition
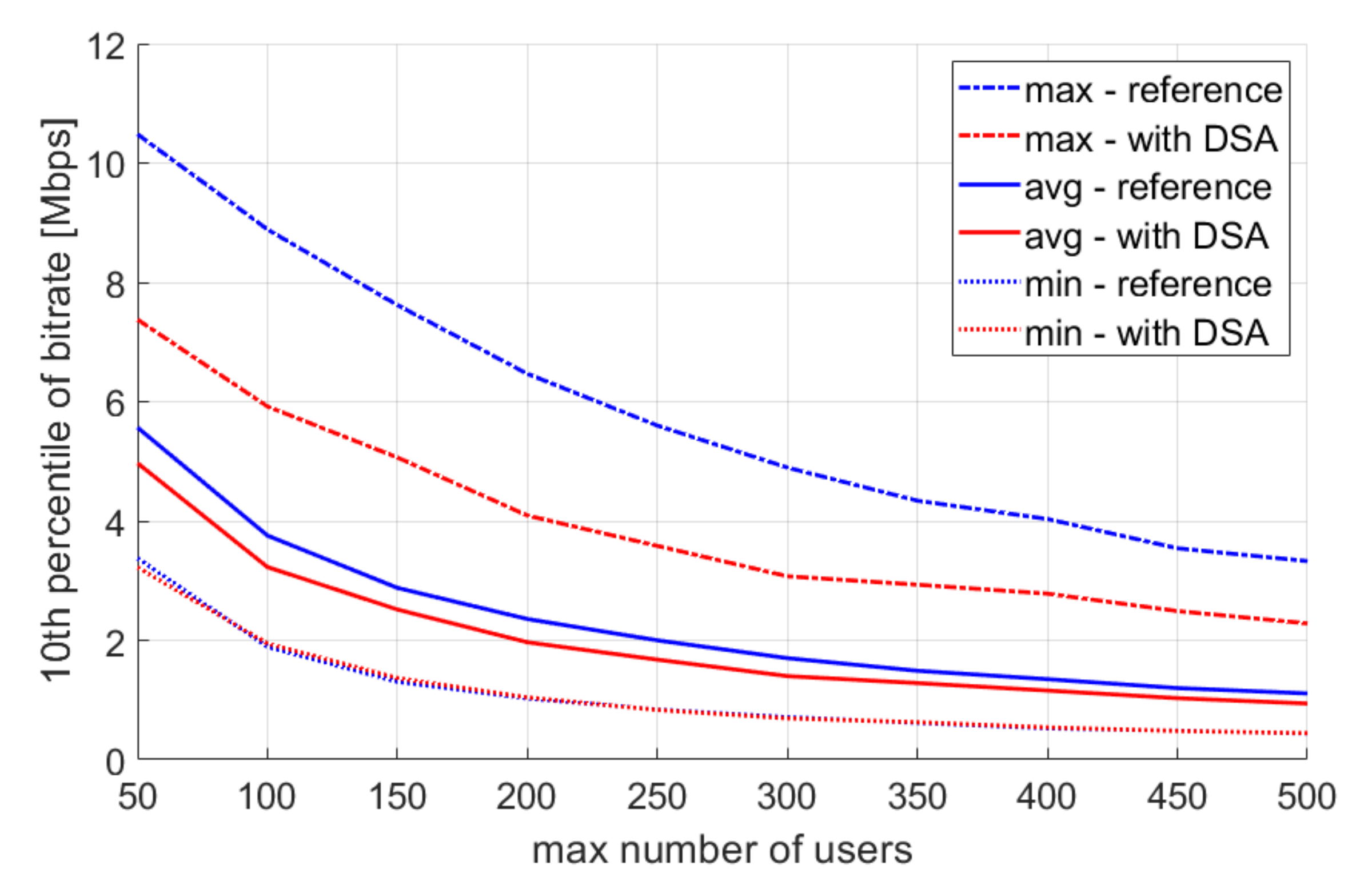
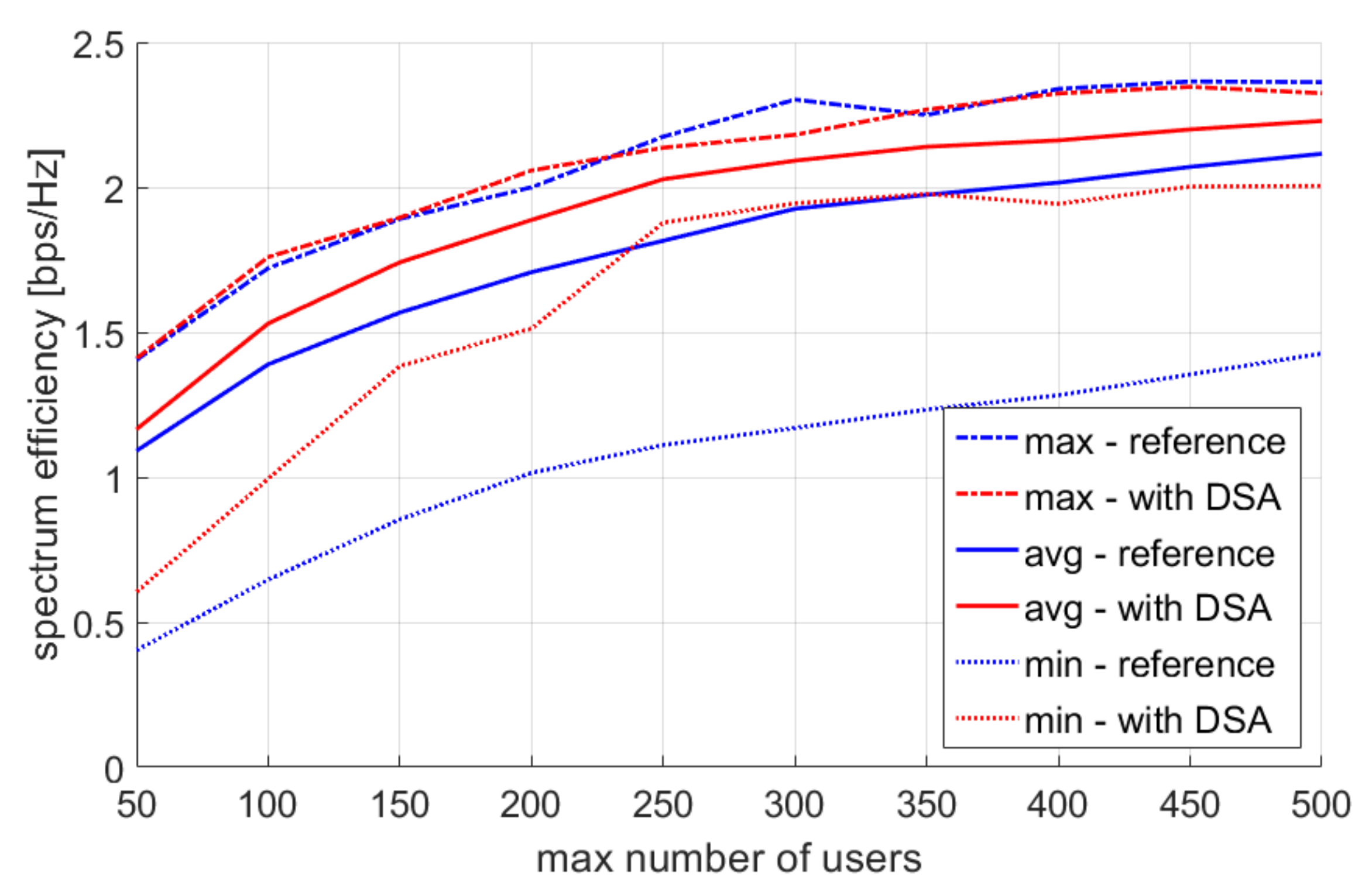
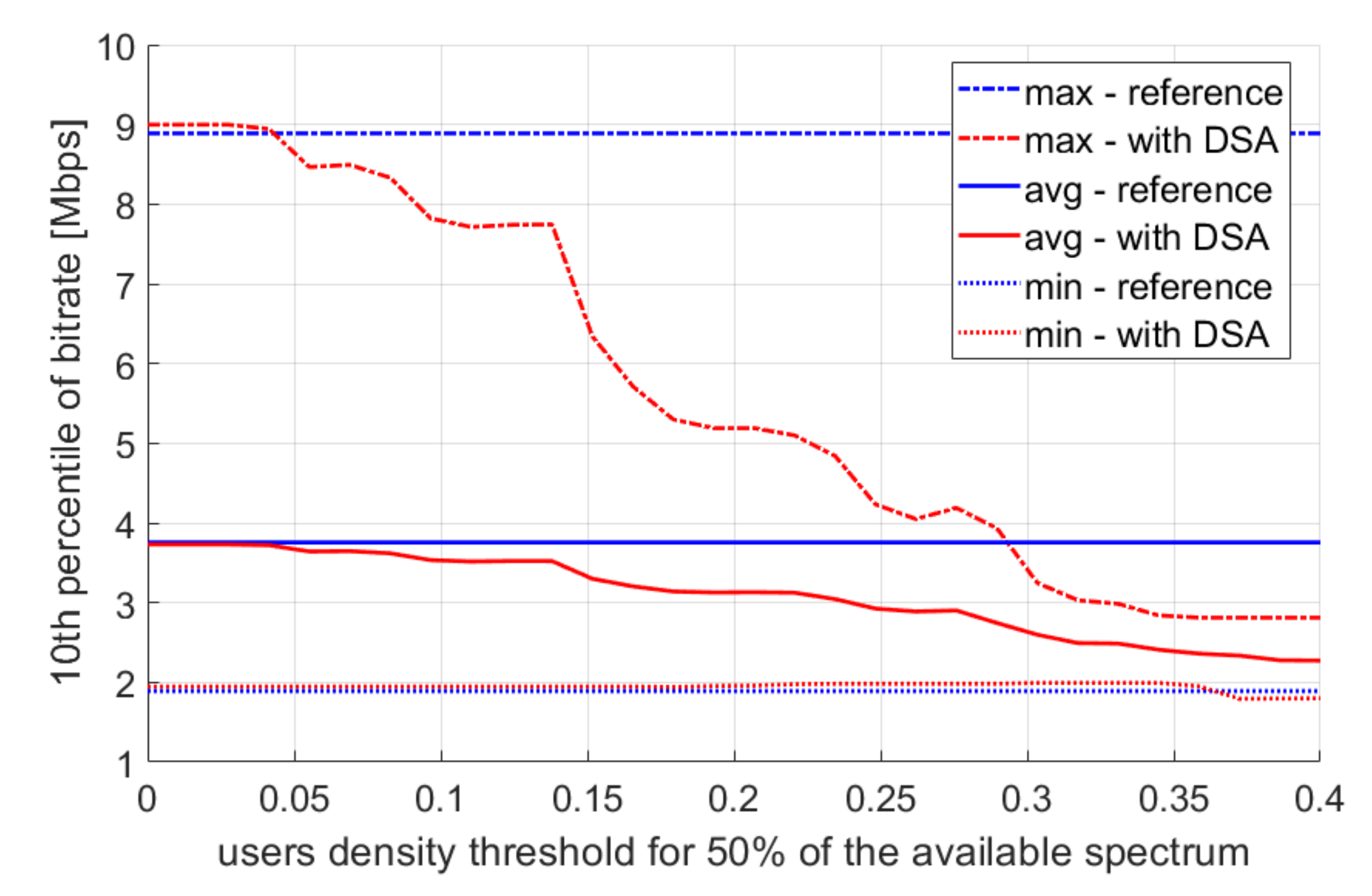
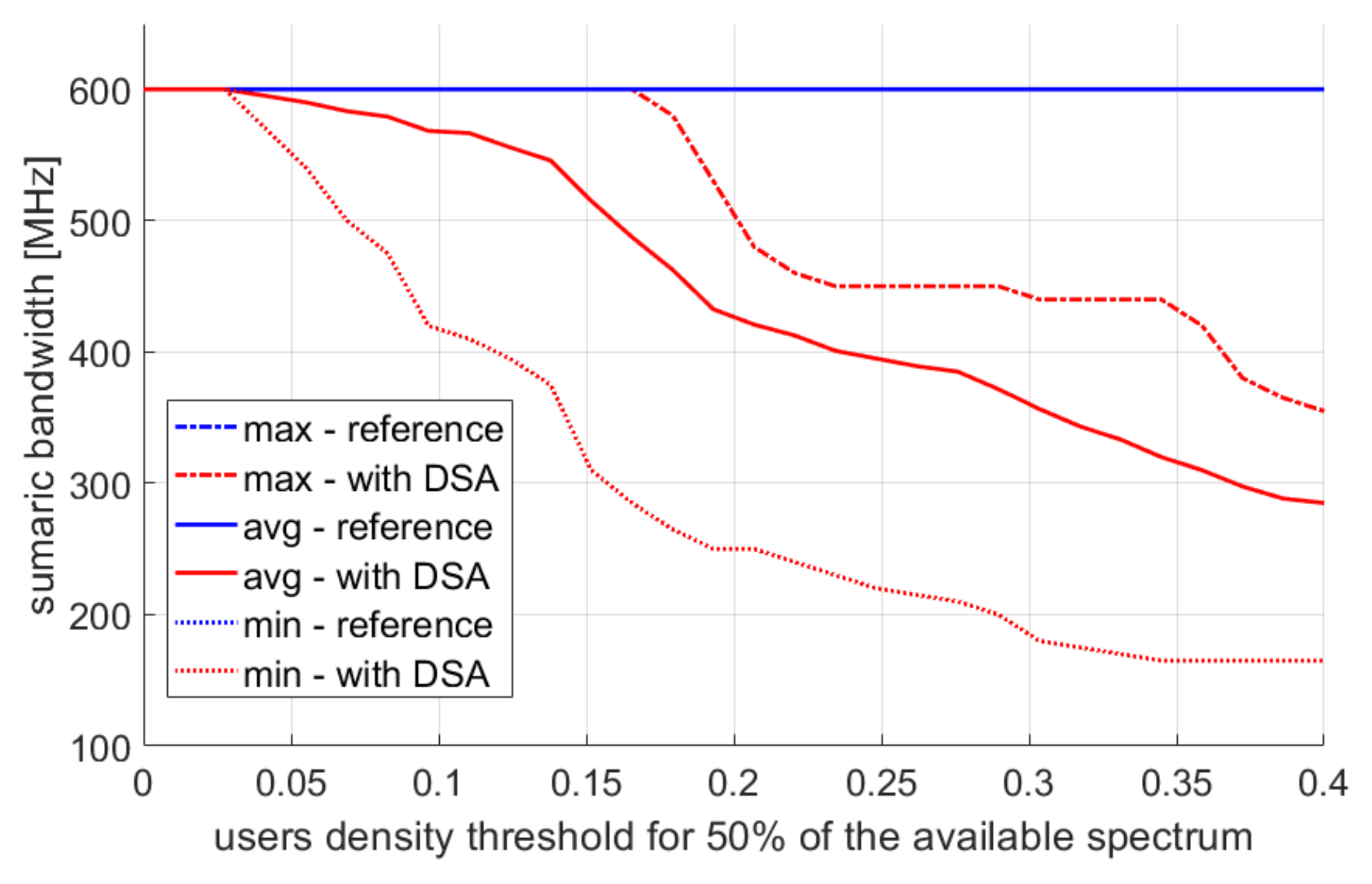
4.2. Multiple Simulation Repetitions
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DSA | Dynamic Spectrum Access |
| ORAN | Open Radio Access Networks |
| WLAN | Wireless Local Area Networks |
References
- Liu, G.; Huang, Y.; Li, N.; Dong, J.; Jin, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, N. Vision, requirements and network architecture of 6G mobile network beyond 2030. China Commun. 2020, 17, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.L.; Qin, D.; Wang, L.-C.; Sim, G.H. 6G Massive Radio Access Networks: Key Applications, Requirements and Challenges. IEEE Open J. Veh. Technol. 2021, 2, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, A.; Jafar, S.A.; Maric, I.; Srinivasa, S. Breaking Spectrum Gridlock with Cognitive Radios: An Information Theoretic Perspective. Proc. IEEE 2009, 97, 894–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Wang, Z.; Ding, G.; Li, K.; Wu, Q. 3D Compressed Spectrum Mapping with Sampling Locations Optimization in Spectrum-Heterogeneous Environment. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 21, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitola, J.; Maguire, G.Q. Cognitive radio: Making software radios more personal. IEEE Pers. Commun. 1999, 6, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arjoune, Y.; Kaabouch, N. A Comprehensive Survey on Spectrum Sensing in Cognitive Radio Networks: Recent Advances, New Challenges, and Future Research Directions. Sensors 2019, 19, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kliks, A.; Holland, O.; Basaure, A.; Matinmikko, M. Spectrum and license flexibility for 5G networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.F.; Munasinghe, K.S.; Jamalipour, A. BS Switching for Green Cellular Networks Using Energy-Aware Dynamic Traffic Offloading Schemes. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 85th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Sydney, Australia, 4–7 June 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wu, J.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, T. Energy-Efficiency Oriented Traffic Offloading in Wireless Networks: A Brief Survey and a Learning Approach for Heterogeneous Cellular Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2015, 33, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Kong, P.; Han, Y. Minimizing Energy Consumption Through Traffic Offloading in HetNets With Two-Class Traffic. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2015, 19, 1394–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liao, H. Intuitionistic Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2014, 22, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryjański, M.; Kułacz, Ł.; Kliks, A. Toward Modular and Flexible Open RAN Implementations in 6G Networks: Traffic Steering Use Case and O-RAN xApps. Sensors 2021, 21, 8173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Singh, R.; Kumbhani, B. The Evolution of Radio Access Network towards Open-RAN: Challenges and Opportunities. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE WCNCW, Seoul, Korea, 25–28 May 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pamuklu, T.; Erol-Kantarci, M.; Ersoy, C. Reinforcement Learning Based Dynamic Function Splitting in Disaggregated Green Open RANs. In Proceedings of the ICC 2021—IEEE International Conference on Communications, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–23 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilovska, L.; Rakovic, V.; Denkovski, O. From Cloud RAN to Open RAN. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 113, 1523–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonati, L.; D’Oro, S.; Polese, M.; Basagni, S.; Melodia, T. Intelligence and Learning in O-RAN for Data-Driven NextG Cellular Networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2021, 59, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter Name | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Area size | km | 21.0 × 18.0 |
| Base station spacing | km | 3.0 |
| Map grid spacing | km | 1.0 |
| Number of base stations | - | 30 |
| Max number of UEs | - | 100 |
| Max number of persons | - | 300 |
| Number of cameras | - | 50 |
| Number of WLAN APs | - | 100 |
| Number of days— | - | 50 |
| Number of time stamps | - | 6 |
| Frequency | MHz | 2400 |
| Transmit power | dBm | 20.0 |
| Max bandwidth | MHz | 20.0 |
| Interpolation method | - | nearest-neighbor |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kułacz, Ł.; Kliks, A. Dynamic Spectrum Allocation Using Multi-Source Context Information in OpenRAN Networks. Sensors 2022, 22, 3515. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093515
Kułacz Ł, Kliks A. Dynamic Spectrum Allocation Using Multi-Source Context Information in OpenRAN Networks. Sensors. 2022; 22(9):3515. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093515
Chicago/Turabian StyleKułacz, Łukasz, and Adrian Kliks. 2022. "Dynamic Spectrum Allocation Using Multi-Source Context Information in OpenRAN Networks" Sensors 22, no. 9: 3515. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093515
APA StyleKułacz, Ł., & Kliks, A. (2022). Dynamic Spectrum Allocation Using Multi-Source Context Information in OpenRAN Networks. Sensors, 22(9), 3515. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22093515







