Determination of Peak Purity in HPLC by Coupling Coulometric Array Detection and Two-Dimensional Correlation Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Material Source
2.2. Extraction of Chili Powder
2.3. Chili Extract Analysis by HPLC–ECD
2.4. Two-Dimensional Correlation Analysis
2.5. Conditions for Chromatographic Separation of the First Peak
2.6. Characterization of the Chromatographic Signals by HPLC–MS
3. Results and Discussion
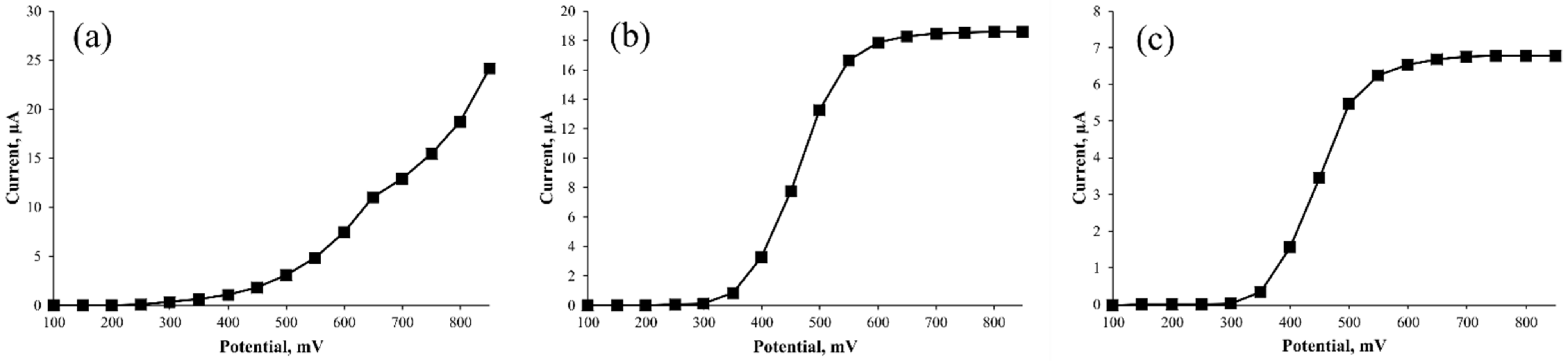
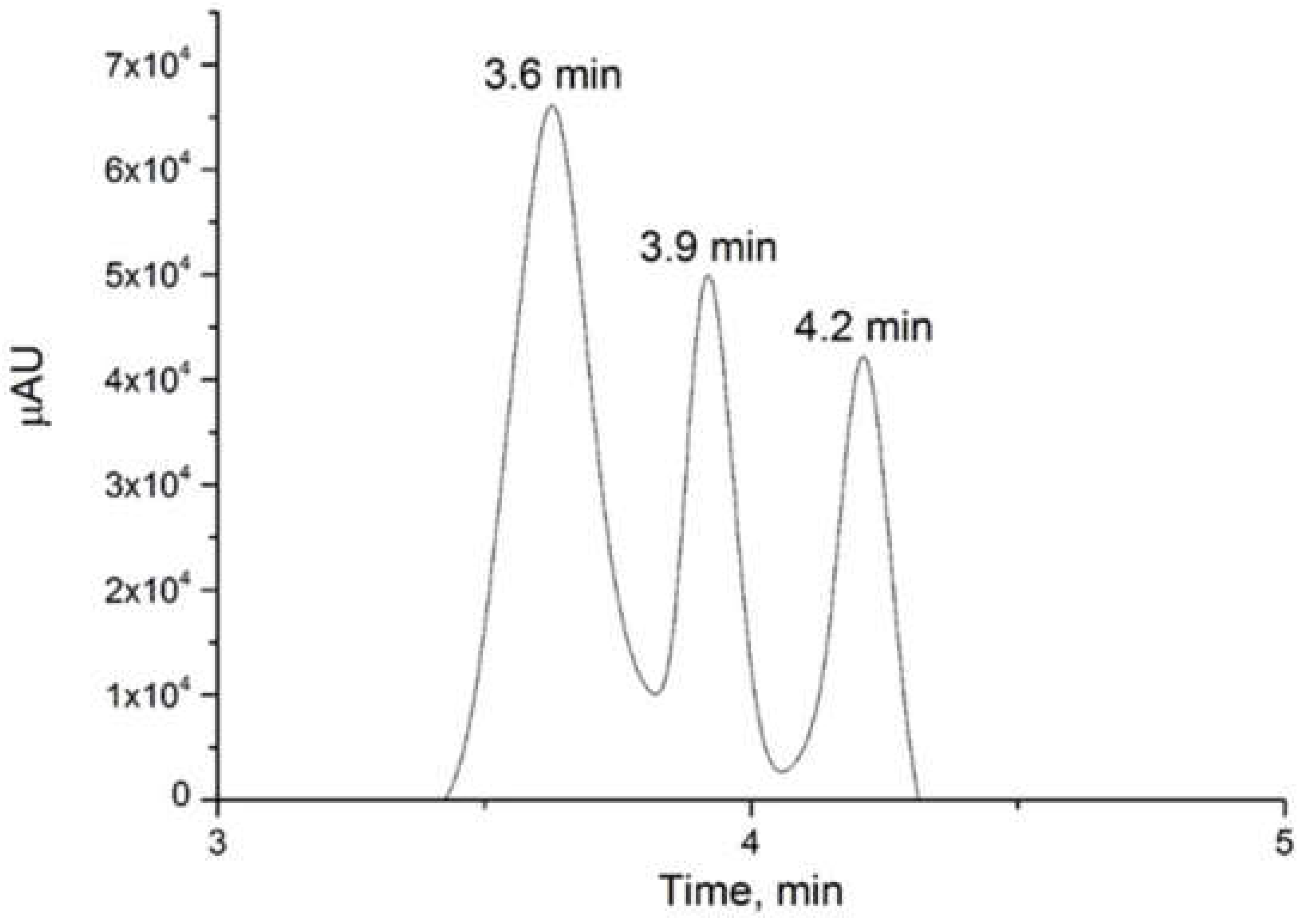
3.1. Analysis by HPLC–ECD
3.2. Two-Dimensional Correlation Analysis
3.3. Identification of Peaks by HPLC–MS
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Compound | tr | k′ | N | H |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quinic acid | 3.59 | 6.98 | 307 | 0.33 |
| Ascorbic acid | 3.94 | 7.76 | 1480 | 0.07 |
| Phenylalanine | 4.23 | 8.40 | 1192 | 0.08 |
| Selectivity Factor (α) | Resolution Factor (Rs) | |
|---|---|---|
| Quinic acid–ascorbic acid | 1.11 | 0.57 |
| Ascorbic acid–phenylalanine | 1.08 | 0.64 |
Appendix B

References
- Stahl, M. Peak purity analysis in HPLC and CE using diode-array technology. Agil. Technol. 2003, 8, 5988–8647. [Google Scholar]
- King, T.; Cole, M.; Farber, J.M.; Eisenbrand, G.; Zabaras, D.; Fox, E.M.; Hill, J.P. Food safety for food security: Relationship between global megatrends and developments in food safety. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 68, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinholds, I.; Bartkevics, V.; Silvis, I.C.; Van Ruth, S.M.; Esslinger, S. Analytical techniques combined with chemometrics for authentication and determination of contaminants in condiments: A review. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2015, 44, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, B.; Örnemark, U. Eurachem Guide: The Fitness for Purpose of Analytical Methods, 2nd ed. A Laboratory Guide to Method Validation and Related Topics. 2014. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2%3A948751&dswid=7736 (accessed on 6 June 2021).
- Papadoyannis, I.N.; Gika, H.G. Peak purity determination with a diode array detector. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2004, 27, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, B.; Müller, K.P.; Komenda, M.; Koppmann, R.; Schaub, A. A new mathematical procedure to evaluate peaks in complex chromatograms. J. Chromatogr. A. 2005, 1071, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, K.; Frederiksen, S.S.; Leuenhagen, C.; Bro, R. Chemometric quality control of chromatographic purity. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 6503–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, I. Two-Dimensional Infrared (2D IR) Spectroscopy: Theory and Applications. Appl. Spectrosc. 1990, 44, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, I. Graphical representation of two-dimensional correlation in vector space. Vib. Spectrosc. 2004, 36, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Rong, L.; Wang, J. Integrative two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy (i2DCOS) for the intuitive identification of adulterated herbal materials. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1163, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, I.; Dowrey, A.E.; Marcott, C.; Story, G.M.; Ozaki, Y. Generalized two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2000, 54, 236A–248A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Dong, G.; Sun, X.; Yu, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W. Synchronous-asynchronous two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy for the discrimination of adulterated milk. Anal. Methods. 2015, 7, 4302–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, D.; Mei, X.; Ran, W.; Xu, Y.; Yu, G. Functional groups determine biochar properties (pH and EC) as studied by two-dimensional 13C NMR correlation spectroscopy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, D.; Cynkar, W.; Dambergs, R.; Smith, P. Two-dimensional correlation analysis of the effect of temperature on the fingerprint of wines analysed by mass spectrometry electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 145, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. Application of two-dimensional correlation UV-Vis spectroscopy in Chinese liquor Moutai discrimination. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 6, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashilov, V.A.; Lednev, I.K. Two-dimensional correlation Raman spectroscopy for characterizing protein structure and dynamics. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2009, 40, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Pan, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Yuan, Y. BOIN: An R Package for Designing Single-Agent and Drug-Combination Dose-Finding Trials Using Bayesian Optimal Interval Designs. J. Stat. Softw. 2019, 94, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongwong, P.; Morozova, K.; Ferrentino, G.; Poonlarp, P.; Scampicchio, M. Rapid Determination of the Antioxidant Capacity of Lettuce by an E-Tongue Based on Flow Injection Coulometry. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontag, G.; Pinto, M.I.; Noronha, J.P.; Burrows, H.D. Analysis of food by high performance liquid chromatography coupled with coulometric detection and related techniques: A review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4113–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozova, K.; Rodríguez-Buenfil, I.; López-Domínguez, C.; Ramírez-Sucre, M.; Ballabio, D.; Scampicchio, M. Capsaicinoids in Chili Habanero by Flow Injection with Coulometric Array Detection. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oney-Montalvo, J.E.; Morozova, K.; Ferrentino, G.; Ramirez-Sucre, M.O.; Rodriguez-Buenfil, I.M.; Scampicchio, M. Effects of local environmental factors on the spiciness of Habanero chili peppers (Capsicum chinense Jacq.) by coulometric electronic tongue. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ren, Y.F.; Dong, G.M.; Yang, R.J.; Liu, H.X.; Du, Y.H.; Zhang, W.Y. Determination of methanol in alcoholic beverages by two-dimensional near-infrared correlation spectroscopy. Anal. Lett. 2016, 49, 2279–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyuni, Y.; Ballester, A.R.; Sudarmonowati, E.; Bino, R.J.; Bovy, A.G. Secondary metabolites of Capsicum species and their importance in the human diet. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sá Mendes, N.; Branco de Andrade Gonçalves, É.C. The role of bioactive components found in peppers. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denev, P.; Todorova, V.; Ognyanov, M.; Georgiev, Y.; Yanakieva, I.; Tringovska, I.; Grozeva, S.; Kostova, D. Phytochemical composition and antioxidant activity of 63 Balkan pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) accessions. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 2510–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas-Espinola, F.M.; Castro-Concha, L.A.; Vázquez-Flota, F.A.; Miranda-Ham, M.L. Capsaicin synthesis requires in situ phenylalanine and valine formation in in vitro maintained placentas from Capsicum chinense. Molecules 2016, 21, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Concha, L.A.; Baas-Espinola, F.M.; Ancona-Escalante, W.R.; Vázquez-Flota, F.A.; Miranda-Ham, M.L. Phenylalanine biosynthesis and its relationship to accumulation of capsaicinoids during Capsicum chinense fruit development. Biol. Plant 2016, 60, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 Auto-peaks located along the main diagonal.
Auto-peaks located along the main diagonal.  Peaks with a positive sign.
Peaks with a positive sign.  Peaks with a negative sign.
Peaks with a negative sign.
 Auto-peaks located along the main diagonal.
Auto-peaks located along the main diagonal.  Peaks with a positive sign.
Peaks with a positive sign.  Peaks with a negative sign.
Peaks with a negative sign.


| Time (Minutes) | Phase A (%) | Phase B (%) | Flow (mL min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 95 | 5 | 0.2 |
| 5 | 95 | 5 | 0.3 |
| 6 | 0 | 100 | 0.6 |
| 20 | 0 | 100 | 0.6 |
| 22 | 95 | 5 | 0.2 |
| 35 | 95 | 5 | 0.2 |
| Molecule | Formula | Retention Time (Minutes) | Molecular Weight | Theoretical m/z | Measured m/z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quinic acid | C7H12O6 | 3.593 | 192.06369 | 191.05611 | 191.05646 |
| Ascorbic acid | C6H8O6 | 3.943 | 176.12410 | 175.02481 | 175.02480 |
| Phenylalanine | C9H11NO2 | 4.229 | 165.07933 | 164.07170 | 164.07203 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oney-Montalvo, J.E.; Morozova, K.; Ramírez-Sucre, M.O.; Scampicchio, M.; Rodríguez-Buenfil, I.M. Determination of Peak Purity in HPLC by Coupling Coulometric Array Detection and Two-Dimensional Correlation Analysis. Sensors 2022, 22, 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22051794
Oney-Montalvo JE, Morozova K, Ramírez-Sucre MO, Scampicchio M, Rodríguez-Buenfil IM. Determination of Peak Purity in HPLC by Coupling Coulometric Array Detection and Two-Dimensional Correlation Analysis. Sensors. 2022; 22(5):1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22051794
Chicago/Turabian StyleOney-Montalvo, Julio Enrique, Ksenia Morozova, Manuel Octavio Ramírez-Sucre, Matteo Scampicchio, and Ingrid Mayanin Rodríguez-Buenfil. 2022. "Determination of Peak Purity in HPLC by Coupling Coulometric Array Detection and Two-Dimensional Correlation Analysis" Sensors 22, no. 5: 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22051794
APA StyleOney-Montalvo, J. E., Morozova, K., Ramírez-Sucre, M. O., Scampicchio, M., & Rodríguez-Buenfil, I. M. (2022). Determination of Peak Purity in HPLC by Coupling Coulometric Array Detection and Two-Dimensional Correlation Analysis. Sensors, 22(5), 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22051794









