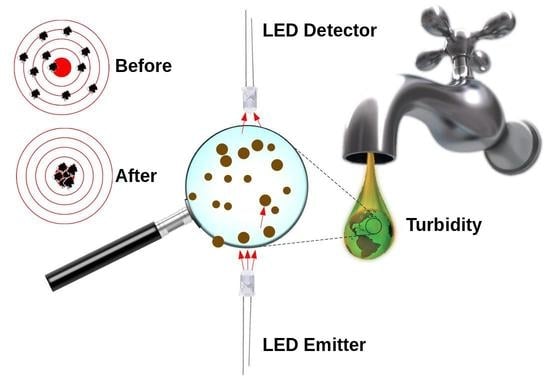
LED PEDD Discharge Photometry: Effects of Software Driven Measurements for Sensing Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
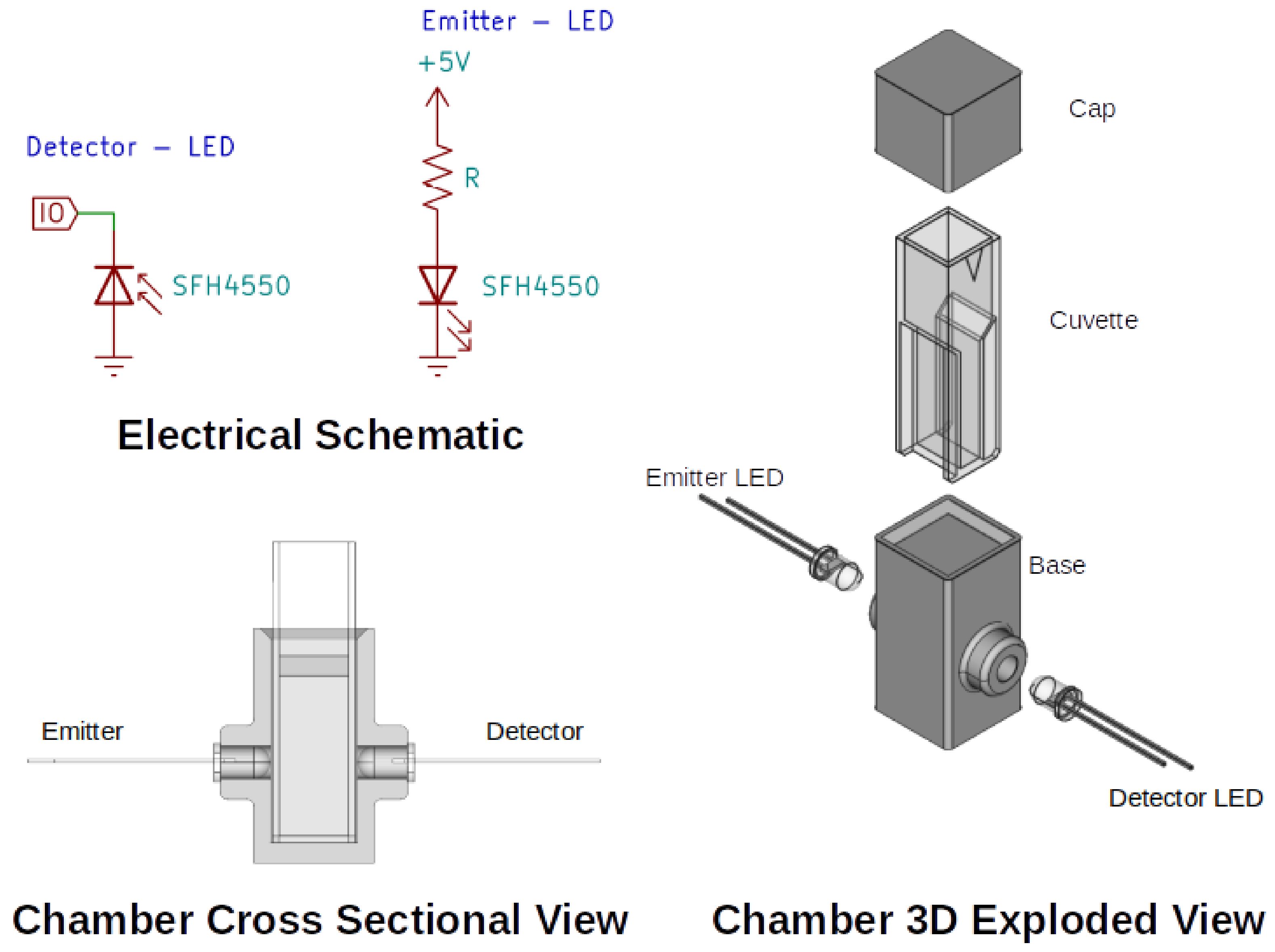
2.1. Components and Characterization
2.2. System Setup and Design
2.3. LED Detection Principle
2.4. Turbidity Measurement
2.5. Embedded Software Implementations
3. Results
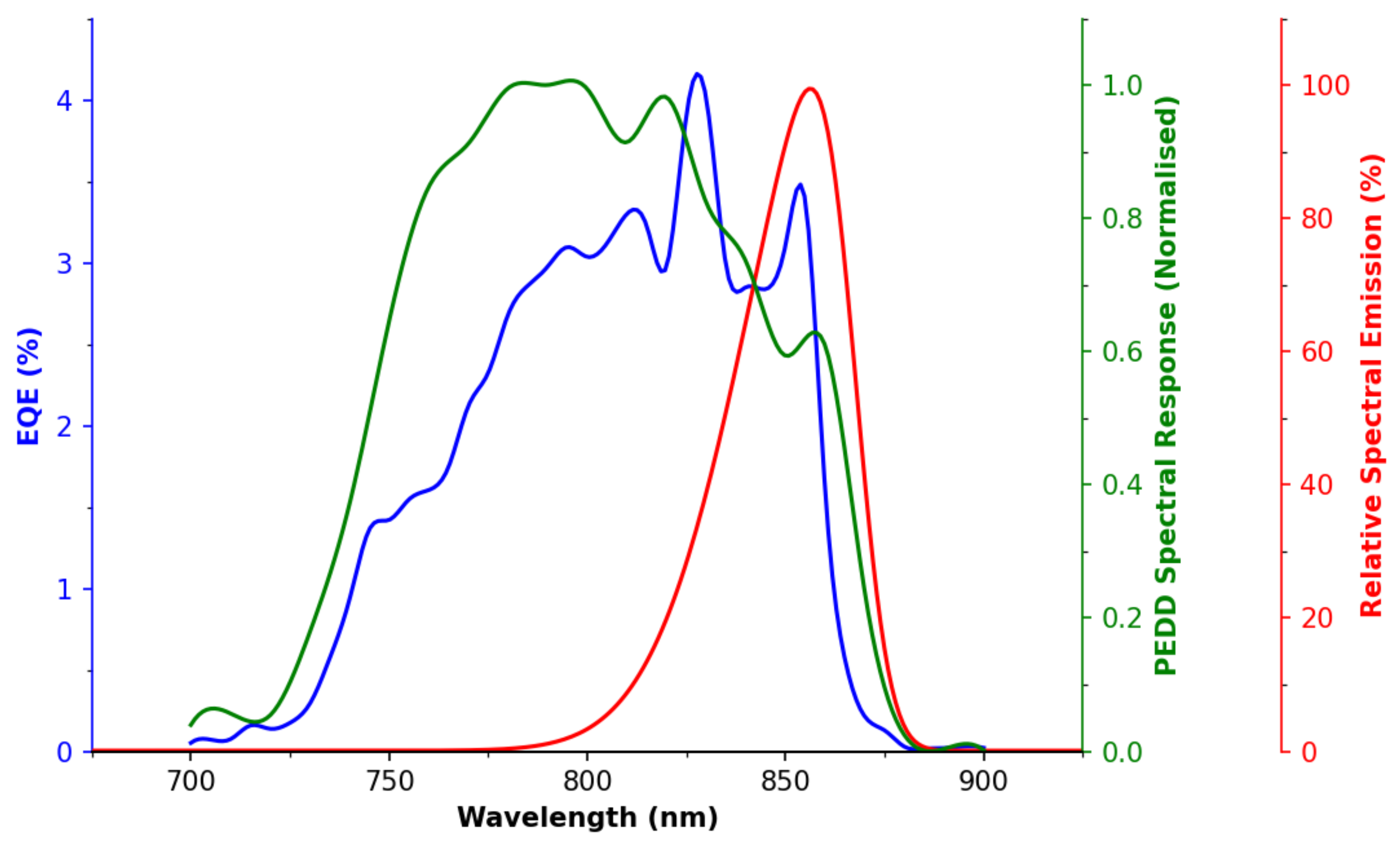
3.1. LED Spectral Sensitivity
3.2. Turbidity Measurements
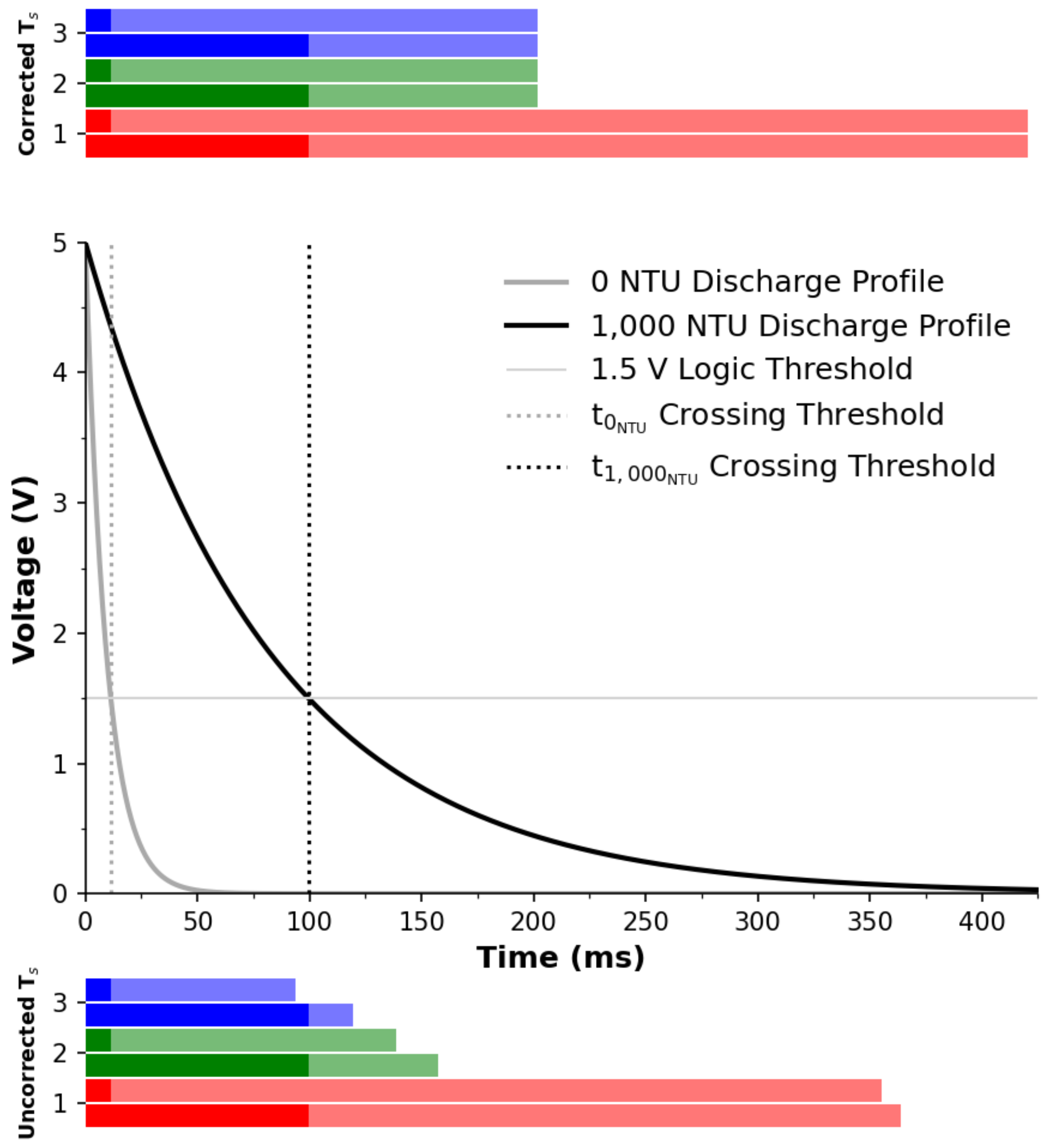
3.2.1. Literature Derived Method (Uncorrected )
3.2.2. Proposed Method (Corrected )
3.2.3. Quantitative Comparison
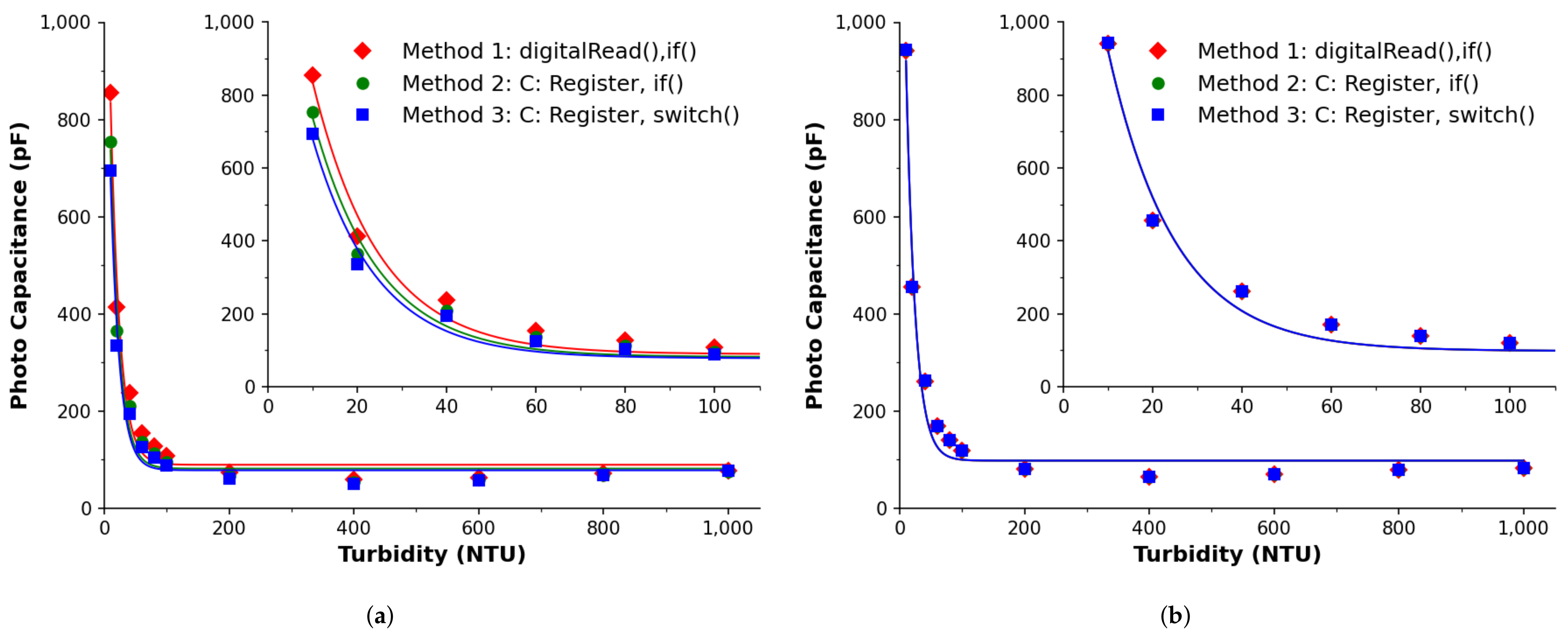
3.2.4. Comparison via Photo-Capacitance
3.2.5. Graphical Comparison
3.3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PEDD | Paired Emitter-Detector Diode |
| LED | Light Emitting Diode |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| NTU | Nephelometric Turbidity Unit |
| EQE | External Quantum Efficiency |
| CAD | Computer Aided Design |
| nm | nanometer |
| ESI | Electronic Supplementary Information |
Appendix A. LED JV Curve

Appendix B. LED Spectral Response

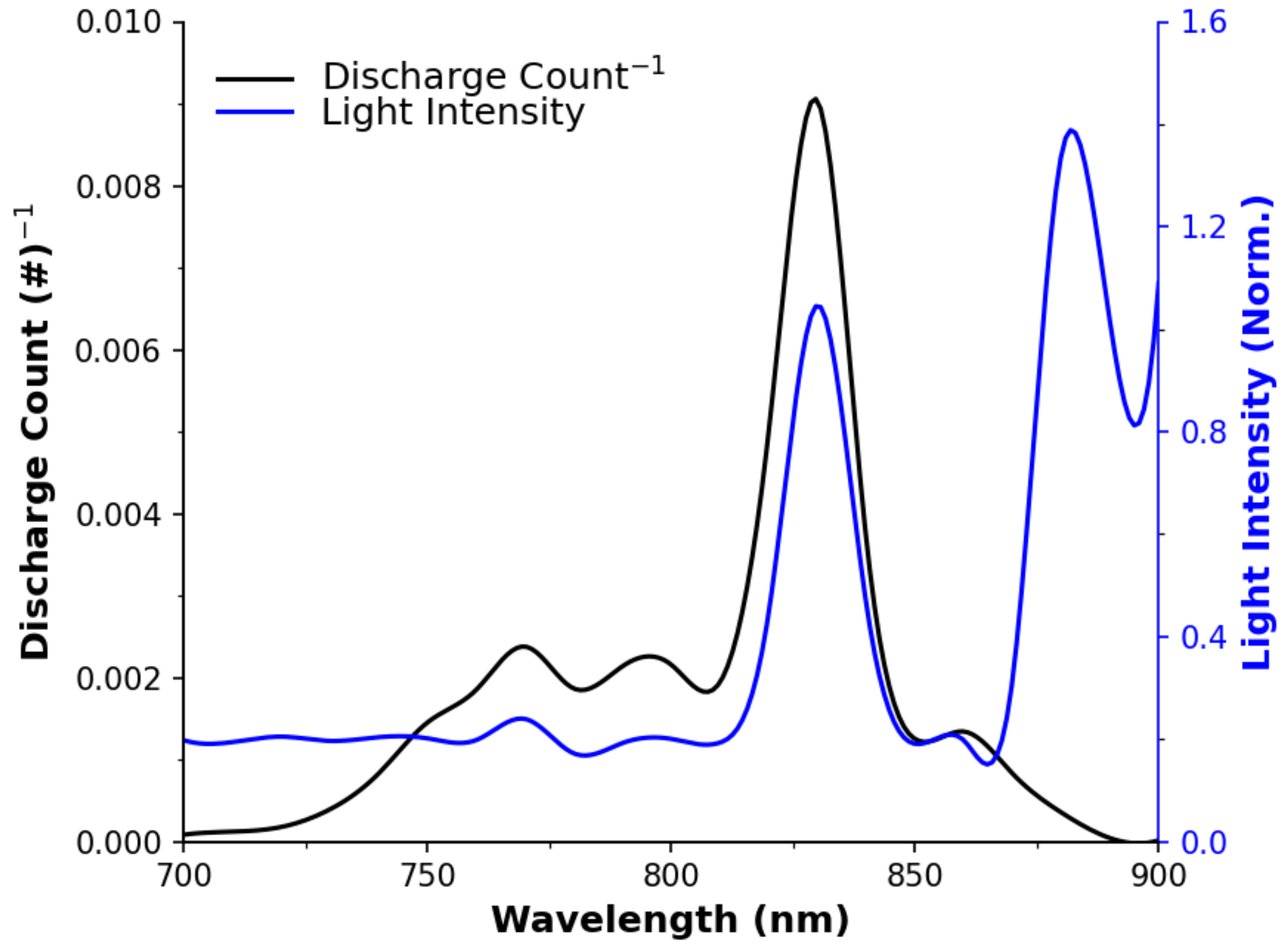

References
- Dietz, P.; Yerazunis, W.; Leigh, D. Very Low-Cost Sensing and Communication Using Bidirectional LEDs. In UbiComp 2003: Ubiquitous Computing; Dey, A.K., Schmidt, A., McCarthy, J.F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.; Baldwin, S.; Shepherd, R.; Dietz, P.; Yerzunis, W.; Diamond, D. Novel fused-LEDs devices as optical sensors for colorimetric analysis. Talanta 2004, 63, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, R.; Yerazunis, W.; Lau, K.T.; Diamond, D. Novel surface mount LED ammonia sensors. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE SENSORS, Vienna, Austria, 24–27 October 2004; Volume 2, pp. 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, S.; Lau, K.; Shepherd, R.; Yerazunis, W.; Diamond, D. Colorimetric detection of iron (II) using novel paired emitter detector diode (PEDD) based optical system: Special section on recent progress in organic molecular electronics. IEICE Trans. Electron. 2004, 87, 2099–2102. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, K.T.; McHugh, E.; Baldwin, S.; Diamond, D. Paired emitter-detector light emitting diodes for the measurement of lead(II) and cadmium(II). Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 569, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.T.; Shepherd, R.; Diamond, D.; Diamond, D. Solid State pH Sensor Based on Light Emitting Diodes (LED) As Detector Platform. Sensors 2006, 6, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orpen, D.; Beirne, S.; Fay, C.; Lau, K.; Corcoran, B.; Diamond, D. The optimisation of a paired emitter-detector diode optical pH sensing device. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 153, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, M.; Lau, K.T.; Shepherd, R.; Slater, C.; Diamond, D. Determination of phosphate using a highly sensitive paired emitter-detector diode photometric flow detector. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 597, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, M.; Shepherd, R.; Lau, K.T.; Diamond, D. Detection of nitrite by flow injection analysis using a novel paired emitter-detector diode (PEDD) as a photometric detector. In Advanced Environmental, Chemical, and Biological Sensing Technologies V; International Society for Optics and Photonics; Vo-Dinh, T., Lieberman, R.A., Gauglitz, G., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2007; Volume 6755, pp. 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czugala, M.; Fay, C.; O’Connor, N.; Corcoran, B.; Benito-Lopez, F.; Diamond, D. Portable integrated microfluidic analytical platform for the monitoring and detection of nitrite. Talanta 2013, 116, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Sansalvador, I.P.D.; Fay, C.; Phelan, T.; Ferndndez-Ramos, M.; Capitan-Vallvey, L.; Diamond, D.; Benito-Lopez, F. A new light emitting diode-light emitting diode portable carbon dioxide gas sensor based on an interchangeable membrane system for industrial applications. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 699, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez De Vargas-Sansalvador, I.; Fay, C.; Fernandez-Ramos, M.; Diamond, D.; Benito-Lopez, F.; Capitan-Vallvey, L. LED-LED portable oxygen gas sensor. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 2851–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogan, D.; Cleary, J.; Phelan, T.; McNamara, E.; Bowkett, M.; Diamond, D. Integrated flow analysis platform for the direct detection of nitrate in water using a simplified chromotropic acid method. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 4798–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kraikaew, P.; Pluangklang, T.; Ratanawimarnwong, N.; Uraisin, K.; Wilairat, P.; Mantim, T.; Nacapricha, D. Simultaneous determination of ethanol and total sulfite in white wine using on-line cone reservoirs membraneless gas-liquid separation flow system. Microchem. J. 2019, 149, 104007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.; Schazmann, B.; Wu, Y.; Coyle, S.; Brady, S.; Hayes, J.; Slater, C.; Fay, C.; Lau, K.T.; Wallace, G.; et al. Wearable sensors for monitoring sports performance and training. In Proceedings of the 2008 5th International Summer School and Symposium on Medical Devices and Biosensors, Hong Kong, China, 1–3 June 2008; pp. 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.; Schazmann, B.; Wu, Y.; Coyle, S.; Brady, S.; Fay, C.; Hayes, J.; Lau, K.T.; Wallace, G.; Diamond, D. Wearable technology for bio-chemical analysis of body fluids during exercise. In Proceedings of the 2008 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–24 August 2008; pp. 5741–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.; Schazmann, B.; Wu, Y.; Fay, C.; Beirne, S.; Slater, C.; Lau, K.T.; Wallace, G.; Diamond, D. Wearable technology for the real-time analysis of sweat during exercise. In Proceedings of the 2008 First International Symposium on Applied Sciences on Biomedical and Communication Technologies, Aalborg, Denmark, 25–28 October 2008; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieczkowska, E.; Koncki, R.; Tymecki, L. Hemoglobin determination with paired emitter detector diode. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 3293–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strzelak, K.; Koncki, R.; Tymecki, L. Serum alkaline phosphatase assay with paired emitter detector diode. Talanta 2012, 96, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tymecki, L.; Korszun, J.; Strzelak, K.; Koncki, R. Multicommutated flow analysis system for determination of creatinine in physiological fluids by Jaffe method. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 787, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiedoruk-Pogrebniak, M.; Koncki, R. Multicommutated flow analysis system based on fluorescence microdetectors for simultaneous determination of phosphate and calcium ions in human serum. Talanta 2015, 144, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokrzywnicka, M.; Tymecki, L.; Koncki, R. Low-cost optical detectors and flow systems for protein determination. Talanta 2012, 96, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelak, K.; Wisniewska, A.; Bobilewicz, D.; Koncki, R. Multicommutated flow analysis system for determination of total protein in cerebrospinal fluid. Talanta 2014, 128, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocovi-Solberg, D.J.; Miro, M.; Cerda, V.; Pokrzywnicka, M.; Tymecki, L.; Koncki, R. Towards the development of a miniaturized fiberless optofluidic biosensor for glucose. Talanta 2012, 96, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libecki, B.; Kalinowski, S. Application of the PEDD flow detector for analysis of natural dissolved organic substances in coloured water. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 68, 29–35. Available online: https://iwaponline.com/wst/article-pdf/68/1/29/439985/29.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2022). [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Strzelak, K.; Koncki, R. Nephelometry and turbidimetry with paired emitter detector diodes and their application for determination of total urinary protein. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 788, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrzywnicka, M.; Koncki, R.; Tymecki, L. Towards optoelectronic urea biosensors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewinska, I.; Tymecki, L.; Michalec, M. An alternative, single-point method for creatinine determination in urine samples with optoelectronic detector. Critical comparison to Jaffe method. Talanta 2019, 195, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwankire, C.E.; Czugala, M.; Burger, R.; Fraser, K.J.; O’Connell, T.M.; Glennon, T.; Onwuliri, B.E.; Nduaguibe, I.E.; Diamond, D.; Ducree, J. A portable centrifugal analyser for liver function screening. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 56, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seetasang, S.; Kaneta, T. Development of a miniaturized photometer with paired emitter-detector light-emitting diodes for investigating thiocyanate levels in the saliva of smokers and non-smokers. Talanta 2019, 204, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fay, C.D.; Nattestad, A. Optical Measurements using LED Discharge Photometry (PEDD Approach): Critical Timing Effects Identified & Corrected. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, C.D.; Nattestad, A. Advances in Optical Based Turbidity Sensing Using LED Photometry (PEDD). Sensors 2022, 22, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilotta, G.; Brazier, R. Understanding the influence of suspended solids on water quality and aquatic biota. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2849–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, T.; Karmo, O. The influence of suspended solids on oxygen transfer in aeration systems. Water Res. 1974, 8, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E. Water Quality; Chapter Solar Radiation and Water Temperature; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, A.; Anastasova, S.; Fay, C.; Diamond, D.; Bobacka, J.; Lewenstam, A. Low cost, calibration-free sensors for in situ determination of natural water pollution. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE SENSORS, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 1–4 November 2010; pp. 1487–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, C.; Anastasova, S.; Slater, C.; Buda, S.T.; Shepherd, R.; Corcoran, B.; O’Connor, N.E.; Wallace, G.G.; Radu, A.; Diamond, D. Wireless Ion-Selective Electrode Autonomous Sensing System. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 2374–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Liao, Q.; Titi, H.H.; Li, J. Turbidity of Stormwater Runoff from Highway Construction Sites. J. Environ. Eng. 2018, 144, 04018061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatten, D.A.; Habel, M.; Babinski, Z.; Obodovskyi, O. The Impact of Bridges on the Process of Water Turbidity on the Example of Large Lowland Rivers. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogan, D.; Cleary, J.; Fay, C.; Rickard, A.; Jankowski, K.; Phelan, T.; Bowkett, M.; Diamond, D. The development of an autonomous sensing platform for the monitoring of ammonia in water using a simplified Berthelot method. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 7606–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelemy, J.; Amirghasemi, M.; Arshad, B.; Fay, C.; Forehead, H.; Hutchison, N.; Iqbal, U.; Li, Y.; Qian, Y.; Perez, P. Problem-Driven and Technology-Enabled Solutions for Safer Communities. In Handbook of Smart Cities; Augusto, J.C., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez de Vargas Sansalvador, I.M.; Fay, C.D.; Cleary, J.; Nightingale, A.M.; Mowlem, M.C.; Diamond, D. Autonomous reagent-based microfluidic pH sensor platform. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 225, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, A.; Tam, C.; Higgins, C.; Rodrigues, L. The association between drinking water turbidity and gastrointestinal illness: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2007, 7, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roos, A.; Gurian, P.; Robinson, L.; Rai, A.; Zakeri, I.; Kondo, M. Review of epidemiological studies of drinking-water turbidity in relation to acute gastrointestinal illness. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muoio, R.; Caretti, C.; Rossi, L.; Santianni, D.; Lubello, C. Water safety plans and risk assessment: A novel procedure applied to treated water turbidity and gastrointestinal diseases. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 223, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Chen, F.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yuan, F.; Kuang, D.; Jia, Z.; Yuan, Z. Microbial Indicators and Their Use for Monitoring Drinking Water Quality—A Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuth. Water Quality—Determination of Turbidity (ISO 7027,1999). Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/30123.html (accessed on 21 January 2022). [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.T.; Baldwin, S.; O’Toole, M.; Shepherd, R.; Yerazunis, W.J.; Izuo, S.; Ueyama, S.; Diamond, D. A low-cost optical sensing device based on paired emitter-detector light emitting diodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 557, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymecki, L.; Pokrzywnicka, M.; Koncki, R. Paired emitter detector diode (PEDD)-based photometry—An alternative approach. Analyst 2008, 133, 1501–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, D.A.; Hauser, P.C. Analytical devices based on light-emitting diodes—A review of the state-of-the-art. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 853, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh Bui, D.; Hauser, P.C. Absorbance measurements with light-emitting diodes as sources: Silicon photodiodes or light-emitting diodes as detectors? Talanta 2013, 116, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Pandharipande, A. LED-Based Color Sensing and Control. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 6116–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymecki, L.; Brodacka, L.; Rozum, B.; Koncki, R. UV-PEDD photometry dedicated for bioanalytical uses. Analyst 2009, 134, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, K.T.; Yerazunis, W.S.; Shepherd, R.L.; Diamond, D. Quantitative colorimetric analysis of dye mixtures using an optical photometer based on LED array. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 114, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.T.; Shepherd, R.L.; Yerazunis, B.; Diamond, D. Low Cost Optical Array Sensing Platform. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE SENSORS, Daegu, Korea, 22–25 October 2006; pp. 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czugala, M.; Gorkin, R., III; Phelan, T.; Gaughran, J.; Curto, V.F.; Ducree, J.; Diamond, D.; Benito-Lopez, F. Optical sensing system based on wireless paired emitter detector diode device and ionogels for lab-on-a-disc water quality analysis. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 5069–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, D.; Pry, T. Limit of Blank, Limit of Detection and Limit of Quantitation. Clin. Biochem. Rev. Aust. Assoc. Clin. Biochem. 2008, 29 (Suppl. 1), S49–S52. [Google Scholar]
- Dietz, P.H.; Alford, J.G. LEDs as Sensors. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2019 Studio; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, M.L.; Saraiva, M.L.M. Detection in UV-visible spectrophotometry: Detectors, detection systems, and detection strategies. Measurement 2019, 135, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macka, M.; Piasecki, T.; Dasgupta, P.K. Light-Emitting Diodes for Analytical Chemistry. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2014, 7, 183–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneta, T.; Alahmad, W.; Varanusupakul, P. Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices with instrument-free detection and miniaturized portable detectors. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2019, 54, 117–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Pandharipande, A.; Willems, F.M.J. Two-Way Visible Light Communication and Illumination with LEDs. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2017, 65, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, B.; Xu, Z. LED Receiver Impedance and Its Effects on LED-LED Visible Light Communications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Kansas City, MO, USA, 20–24 May 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahri, F.A.; Umrani, F.A.; Baqai, A.; Mangrio, H.B. Design and implementation of LED-LED indoor visible light communication system. Phys. Commun. 2020, 38, 100981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, M.; Lau, K.T.; Diamond, D. Photometric detection in flow analysis systems using integrated PEDDs. Talanta 2005, 66, 1340–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Measurement | Method | Function | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uncorrected | Counter | 1 | uncorrectedCounterMethod1() |
| 2 | uncorrectedCounterMethod2() | ||
| 3 | uncorrectedCounterMethod3() | ||
| Timer | 1 | uncorrectedTimerMethod1() | |
| 2 | uncorrectedTimerMethod2() | ||
| 3 | uncorrectedTimerMethod3() | ||
| Corrected | Counter | 1 | correctedCounterMethod1() |
| 2 | correctedCounterMethod2() | ||
| 3 | correctedCounterMethod3() | ||
| Timer | 1 | correctedTimerMethod1() | |
| 2 | correctedTimerMethod2() | ||
| 3 | correctedTimerMethod3() |
| Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Style | Wiring | C Bitwise | C Bitwise |
| Operation | digitalRead() | PIND & PD2 | PIND & PD2 |
| Statement | if | if | switch |
| Coeff. | Counter | Timer | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Uncorrected | A | 5504 | 12,568 | 16,906 | 3118 | 7115 | 9566 |
| 756 | 761 | 756 | 757 | 761 | 756 | ||
| −3810 | −8733 | −11,706 | 352,200 | 131,036 | 84,035 | ||
| 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | ||
| Corrected | A | 5144 | 10,721 | 10,671 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 759 | 758 | 755 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| −3566 | −7433 | −7382 | 420,286 | 201,908 | 201,907 | ||
| 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.327 | 0.039 | 0.006 | ||
| Ts Approach | Characteristic | Method | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Uncorrected | Sensitivity ( s/NTU) | 40.51 | 42.13 | 46.01 |
| LOD (NTU) | 1.61 | 1.17 | 0.46 | |
| Range (ms) | 85 | 82.3 | 81.3 | |
| Corrected | Sensitivity ( s/NTU) | 50.26 | 50.37 | 50.41 |
| LOD (NTU) | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.12 | |
| Range (ms) | 88.1 | 88.4 | 88.6 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fay, C.D.; Nattestad, A. LED PEDD Discharge Photometry: Effects of Software Driven Measurements for Sensing Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041526
Fay CD, Nattestad A. LED PEDD Discharge Photometry: Effects of Software Driven Measurements for Sensing Applications. Sensors. 2022; 22(4):1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041526
Chicago/Turabian StyleFay, Cormac D., and Andrew Nattestad. 2022. "LED PEDD Discharge Photometry: Effects of Software Driven Measurements for Sensing Applications" Sensors 22, no. 4: 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041526
APA StyleFay, C. D., & Nattestad, A. (2022). LED PEDD Discharge Photometry: Effects of Software Driven Measurements for Sensing Applications. Sensors, 22(4), 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041526