Rethinking Sampled-Data Control for Unmanned Aircraft Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Motivating Example
3. Background
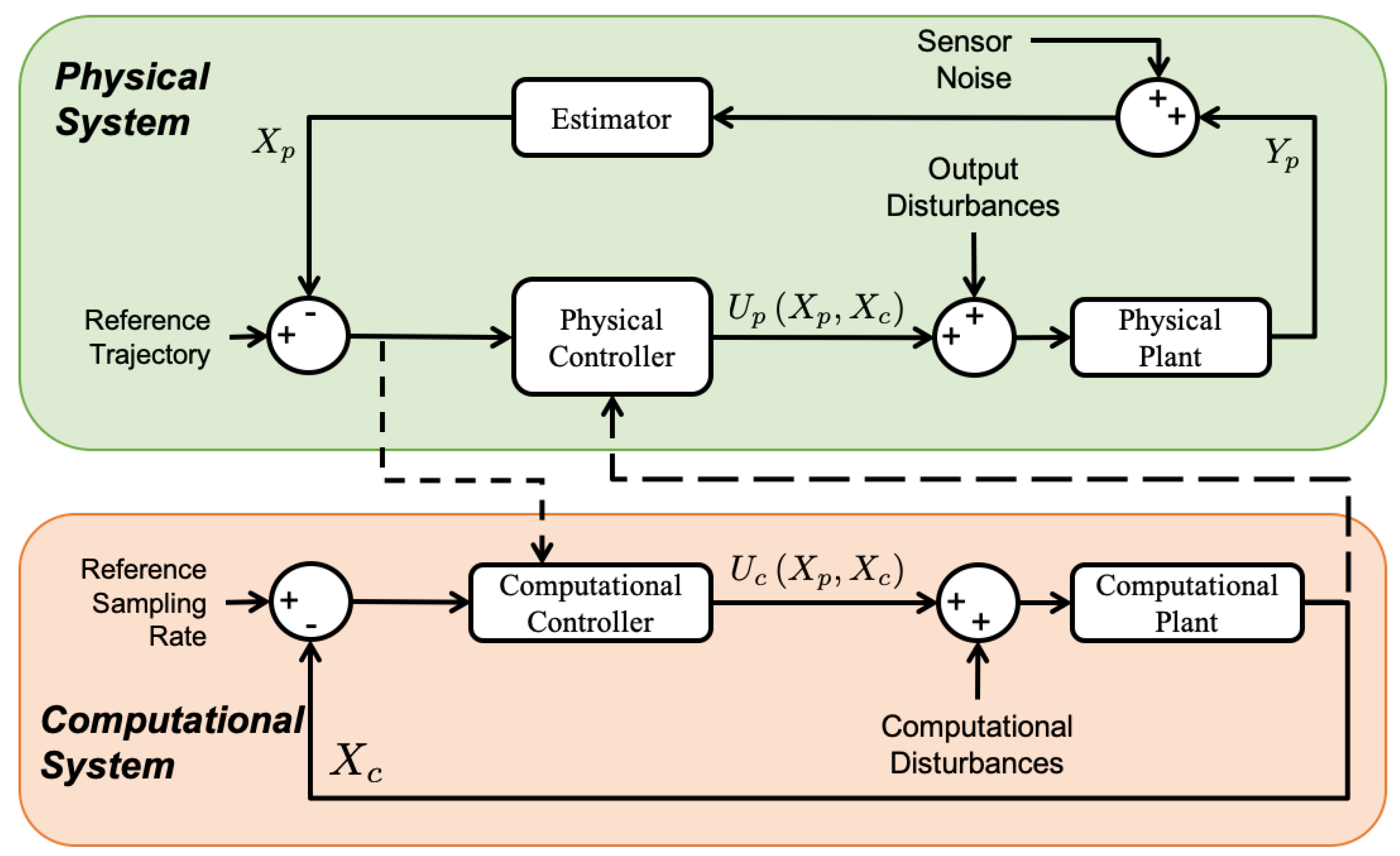
3.1. Dynamic Resource Allocation
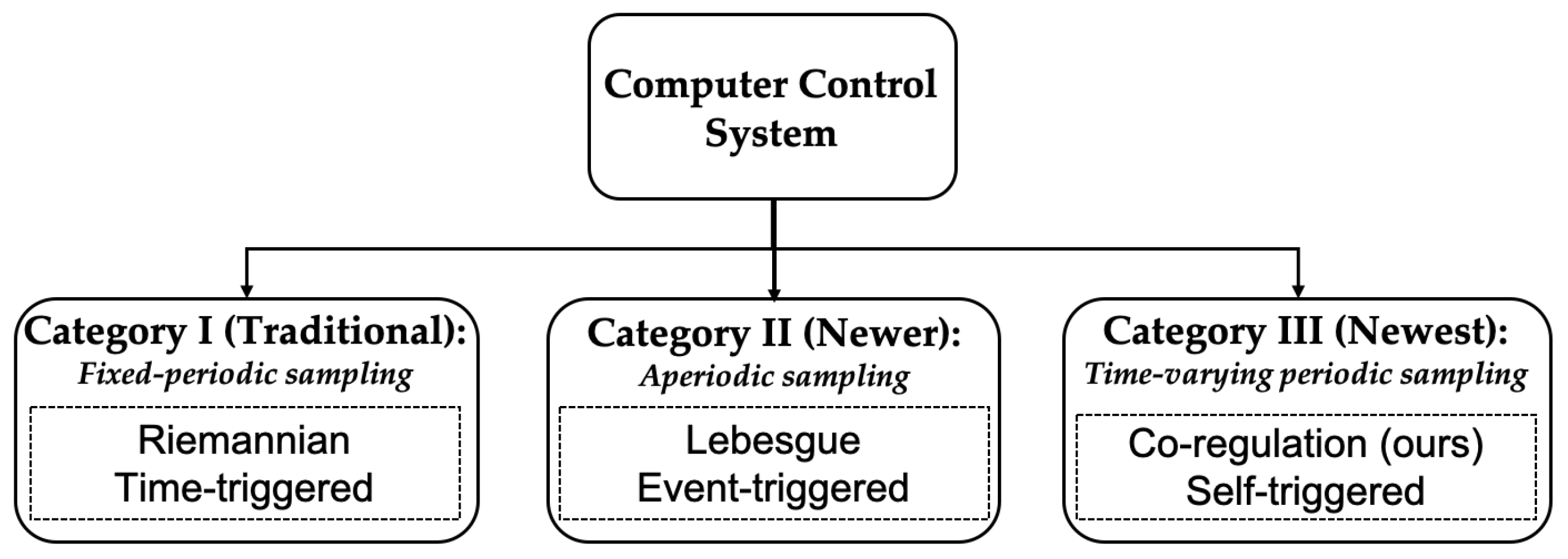
3.2. Overview of Sampling Strategies
4. Control under Different Sampling Strategies
4.1. Category I—Fixed-Periodic, or Time-Triggered Control
4.2. Category II—Event-Triggered Control
4.3. Category III—Self-Triggered Control
4.4. Cyber-Physical Co-Regulation
- Set the upper bound based on the system computational bandwidth given all other computing tasks;
- Set the lower bound to the rate where system performance degrades beyond acceptable limits, or otherwise is unstable;
- Set the resolution based on the system dynamics and application scenarios, which can guarantee system stability and accommodate performance requirements, such as disturbance rejection, dynamic response, etc.
| Algorithm 1: Cyber-physical co-regulation. |
| Result: Physical control input |
| Control task rate |
| Input: |
| Output: |
| while Algorithm is running do |
 |
5. Evaluation Metrics
5.1. Physical Evaluation Metrics
5.2. Computational Evaluation Metrics
6. Results
6.1. Simulation Setup
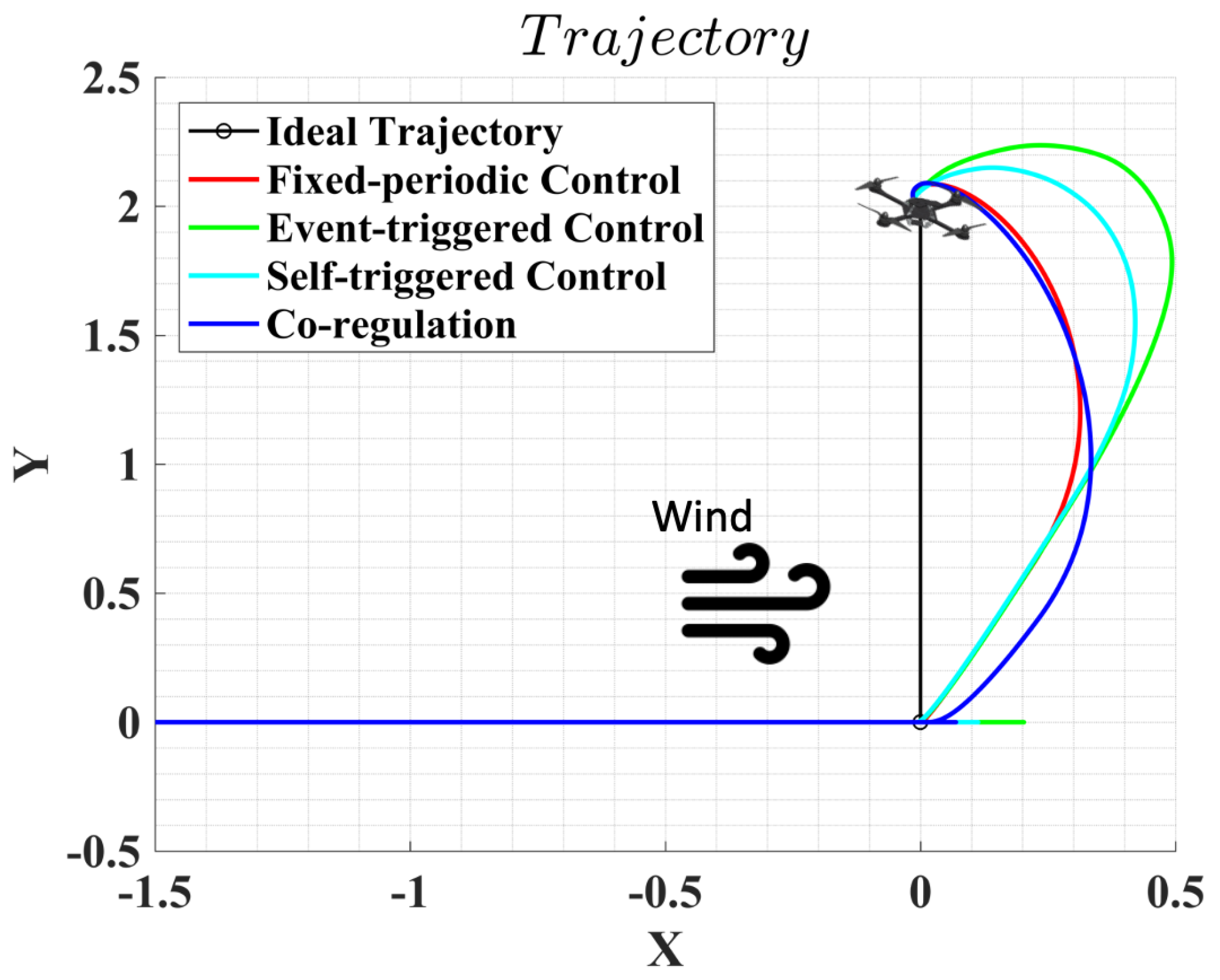
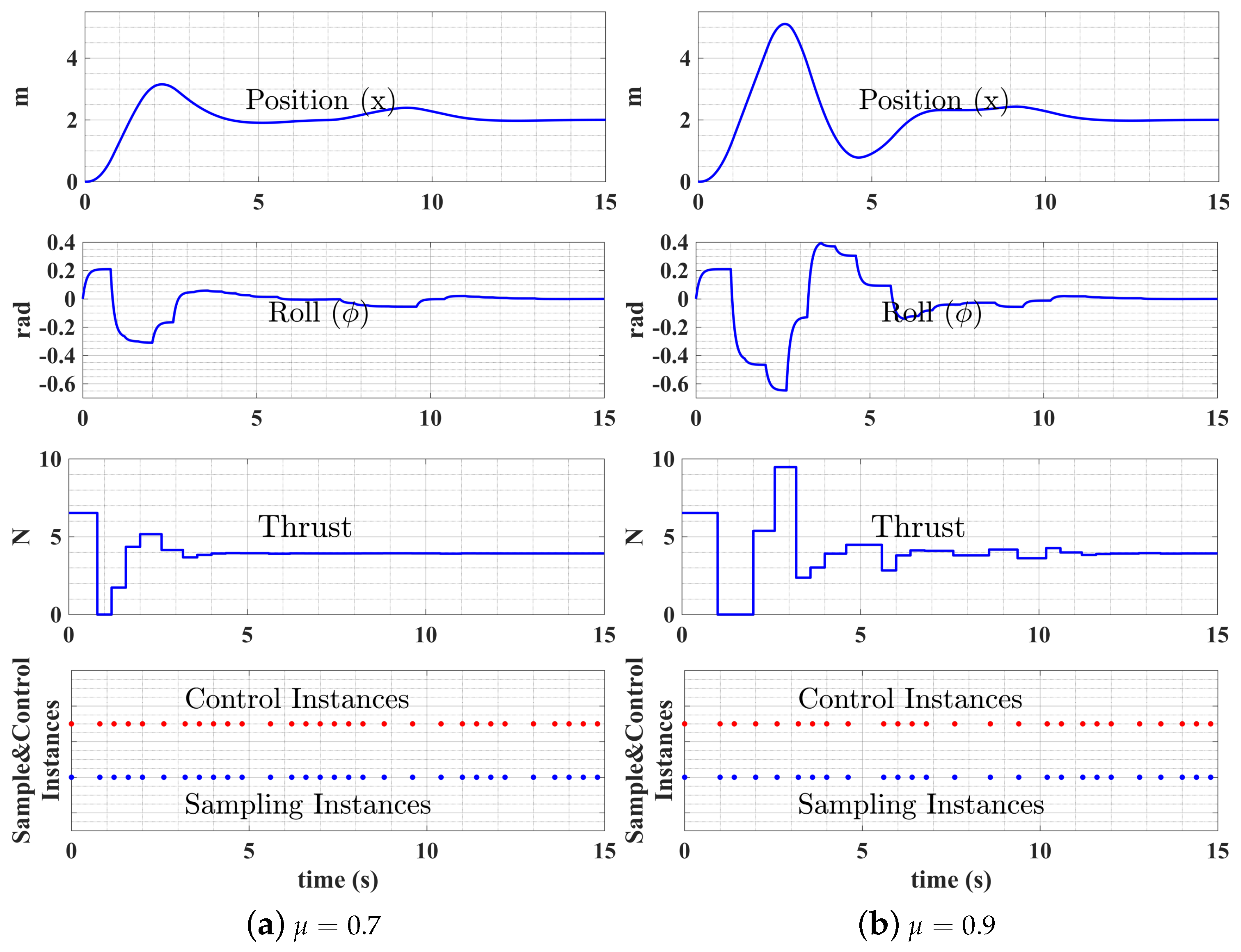
6.2. Test Results
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bradley, J.M.; Atkins, E.M. Optimization and control of cyber-physical vehicle systems. Sensors 2015, 15, 23020–23049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salhaoui, M.; Guerrero-González, A.; Arioua, M.; Ortiz, F.J.; El Oualkadi, A.; Torregrosa, C.L. Smart industrial iot monitoring and control system based on UAV and cloud computing applied to a concrete plant. Sensors 2019, 19, 3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolf, M. Computing in the real world is the grandest of challenges. Computer 2018, 51, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Khajepour, A. Cyber-physical control for energy management of off-road vehicles with hybrid energy storage systems. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 2609–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Joo, Y.H. A note on sampled-data stabilization of LTI systems with aperiodic sampling. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2015, 60, 2746–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nise, N.S. Control Systems Engineering; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Heemels, W.; Donkers, M. Model-based periodic event-triggered control for linear systems. Automatica 2013, 49, 698–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heemels, W.; Johansson, K.H.; Tabuada, P. An introduction to event-triggered and self-triggered control. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Wailea, HI, USA, 10–13 December 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 3270–3285. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, J.M.; Atkins, E.M. Coupled Cyber-Physical System Modeling and Coregulation of a CubeSat. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Doebbeling, S.; Bradley, J. Co-regulation of computational and physical effectors in a quadrotor unmanned aircraft system. In Proceedings of the 9th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems, Porto, Portugal, 11–13 April 2018; IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Bradley, J. Stability Analysis for a Class of Resource-Aware, Co-Regulated Systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Nice, France, 11–13 December 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Bradley, J. Controller Design for Time-Varying Sampling, Co-Regulated Systems. IEEE Control Syst. Lett. 2020, 5, 2132–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bradley, J. Computing for Control and Control for Computing. In Proceedings of the 2021 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Grenoble, France, 1–5 February 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 469–474. [Google Scholar]
- Åström, K.J.; Wittenmark, B. Computer-Controlled Systems: Theory and Design; Courier Corporation: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shankar, A.; Doebbeling, S.; Bradley, J. Toward a cyber-physical quadrotor: Characterizing trajectory following performance. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Miami, FL, USA, 13–16 June 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Martı, P.; Lin, C.; Brandt, S.A.; Velasco, M.; Fuertes, J.M. Draco: Efficient resource management for resource-constrained control tasks. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2009, 58, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopetz, H. Real-Time Systems: Design Principles for Distributed Embedded Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Dziurzanski, P.; Mendis, H.R.; Indrusiak, L.S. A survey and comparative study of hard and soft real-time dynamic resource allocation strategies for multi-/many-core systems. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2017, 50, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nowka, K.J.; Carpenter, G.D.; MacDonald, E.W.; Ngo, H.C.; Brock, B.C.; Ishii, K.I.; Nguyen, T.Y.; Burns, J.L. A 32-bit PowerPC system-on-a-chip with support for dynamic voltage scaling and dynamic frequency scaling. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2002, 37, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lakshmanan, K.; Rajkumar, R.R. Rhythmic tasks: A new task model with continually varying periods for cyber-physical systems. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/ACM Third International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems, Washington, DC, USA, 17–19 April 2012; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, A.; Hayes, I.J. A timeband framework for modelling real-time systems. Real-Time Syst. 2010, 45, 106–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.; Lehoezky, J.; Rajkumar, R.; Siewiorek, D. On quality of service optimization with discrete QoS options. In Proceedings of the Fifth IEEE Real-Time Technology and Applications Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2–4 June 1999; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 276–286. [Google Scholar]
- Gai, K.; Qiu, M. Optimal resource allocation using reinforcement learning for IoT content-centric services. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 70, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothukuchi, R.P.; Pothukuchi, S.Y.; Voulgaris, P.G.; Torrellas, J. Control Systems for Computing Systems: Making computers efficient with modular, coordinated, and robust control. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2020, 40, 30–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åström, K.J.; Bernhardsson, B.M. Comparison of Riemann and Lebesgue sampling for first order stochastic systems. In Proceedings of the Decision and Control, 41st IEEE Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 10–13 December 2002; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2002; Volume 2, pp. 2011–2016. [Google Scholar]
- Heemels, W.H.; Donkers, M.; Teel, A.R. Periodic event-triggered control for linear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2012, 58, 847–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eqtami, A.; Dimarogonas, D.V.; Kyriakopoulos, K.J. Event-triggered control for discrete-time systems. In Proceedings of the 2010 American Control Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 30 June–2 July 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 4719–4724. [Google Scholar]
- Sabatino, F. Quadrotor Control: Modeling, Nonlinearcontrol Design, and Simulation; KTH: Stockholm, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- AscTec Research UAVs. Available online: http://www.asctec.de (accessed on 19 January 2022).
- Hetel, L.; Fiter, C.; Omran, H.; Seuret, A.; Fridman, E.; Richard, J.P.; Niculescu, S.I. Recent developments on the stability of systems with aperiodic sampling: An overview. Automatica 2017, 76, 309–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Rate | Gain |
|---|---|
| ⋮ | ⋮ |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| g | 9.80665 m/s2 | m | 0.515 kg |
| Control Strategy | Physical | Computational | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSE | PSE | CE | W | CCT | SCT | |
| Fixed-periodic | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 3.2609 | 2.7778 |
| Event-triggered | 2.1752 | 2.4783 | 1.0917 | 1.0426 | 1.0000 | 2.7778 |
| Self-triggered | 1.7726 | 2.3041 | 1.0778 | 1.0376 | 1.3478 | 1.1481 |
| Co-regulation | 1.0031 | 1.0270 | 1.0002 | 1.0001 | 1.1739 | 1.0000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Bradley, J. Rethinking Sampled-Data Control for Unmanned Aircraft Systems. Sensors 2022, 22, 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041525
Zhang X, Bradley J. Rethinking Sampled-Data Control for Unmanned Aircraft Systems. Sensors. 2022; 22(4):1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041525
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xinkai, and Justin Bradley. 2022. "Rethinking Sampled-Data Control for Unmanned Aircraft Systems" Sensors 22, no. 4: 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041525
APA StyleZhang, X., & Bradley, J. (2022). Rethinking Sampled-Data Control for Unmanned Aircraft Systems. Sensors, 22(4), 1525. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22041525






