Efficient Beampattern Synthesis for Sparse Frequency Diverse Array via Matrix Pencil Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
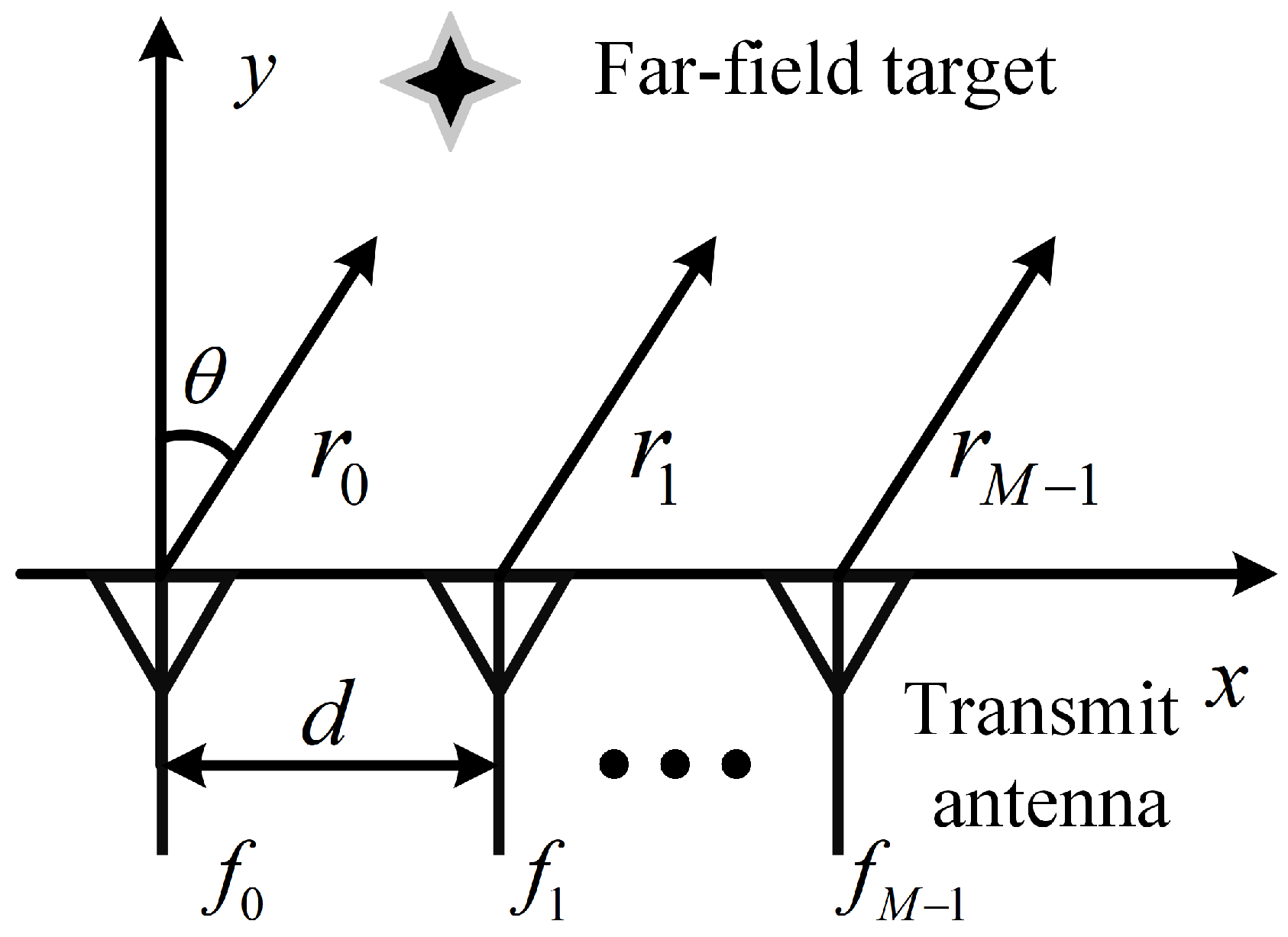
2. Array Factor of FDA
2.1. Standard FDA
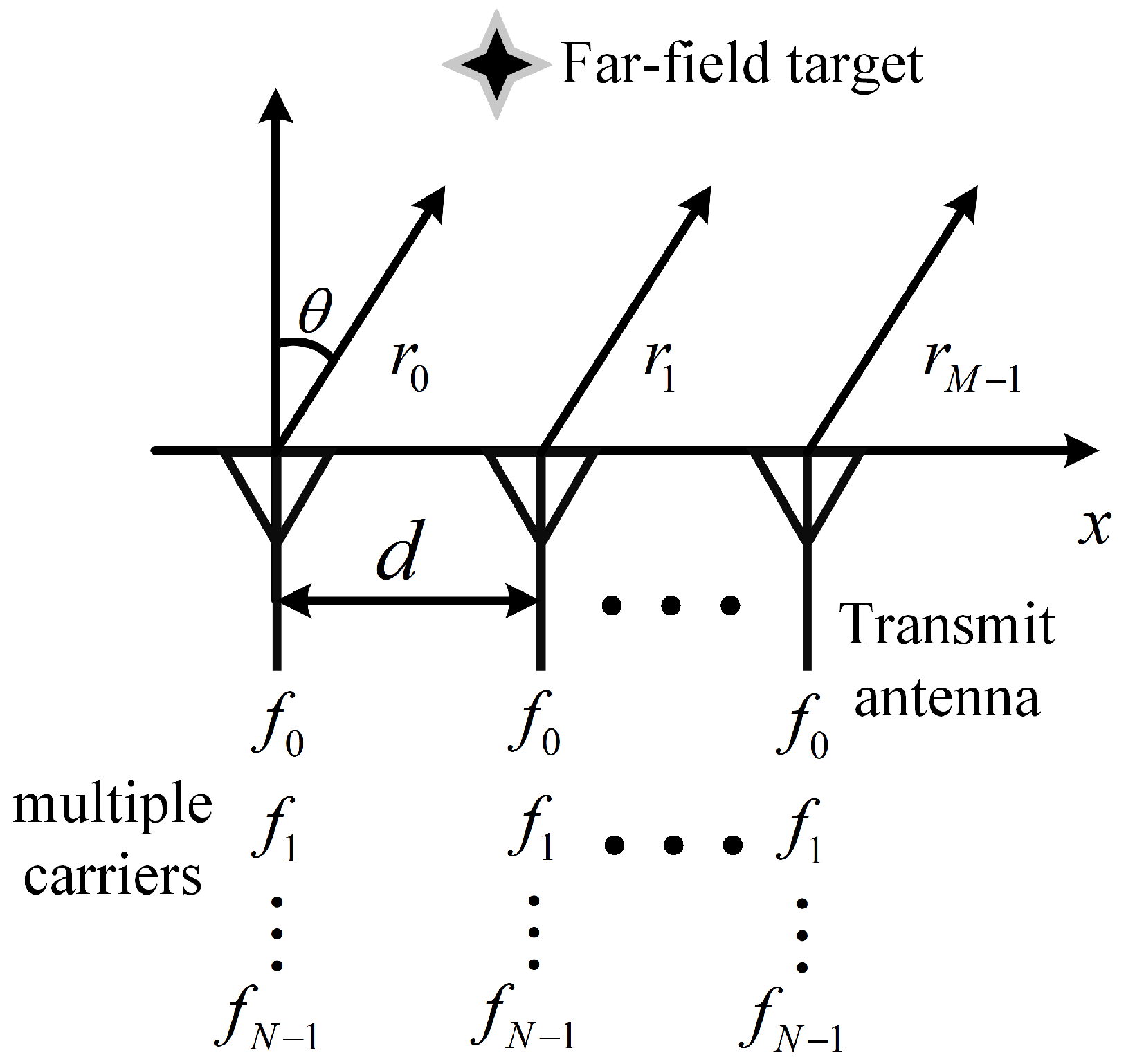
2.2. Multi-Carrier FDA
3. Proposed Synthesis Method for Sparse FDA
3.1. Proposed Synthesis Method for Sparse SFDA
| Algorithm 1: Proposed synthesis method for sparse FDA. |
| Input: |
| 1: Sample reference pattern in plane uniformly according to Equations (13) and (14), and construct the block Hankel matrix using Equations (15) and (16). |
| 2: Perform the singular value decomposition (SVD) of according to Equation (17) and calculate the singular values . |
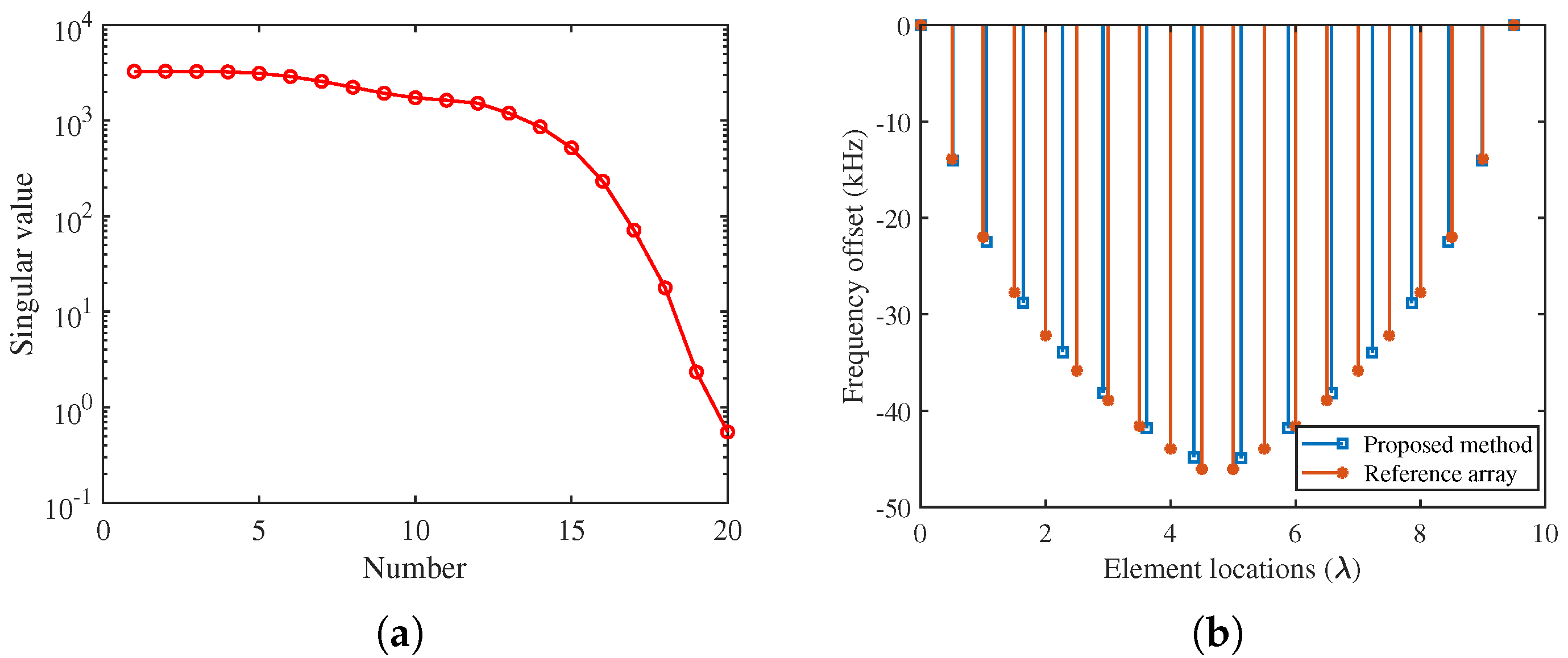
| 3: According to Equation (19), determine the minimum number of elements . |
| 4: According to Equation (21), extract the eigenvalues and , then to pair them utilizing pairing algorithm in [28]. |
| 5: Detemine frequency offsets and locations of the new sparse array with using Equations (22) and (23) |
| 6: Calculate the excitations using Equations (24)–(30). |
| Output: |
3.2. Proposed Synthesis Method for Sparse MCFDA
| Algorithm 2: Proposed synthesis method for sparse MCFDA. |
| Input: |
| 1: Sample two desired patterns and respectively, and construct the Hankel matrix and using Equations (35) and (36). |
| 2: Perform the SVD of and and determine the minimum number value and . |
| 3: According to Equation (37), extract the eigenvalues and . |
| 4: Detemine locations and carriers of the new sparse MCFDA using Equations (22) and (23) |
| 5: Calculate the excitations and using the LS method. |
| Output: |
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Example 1: Beampattern Synthesis for Sparse SFDA
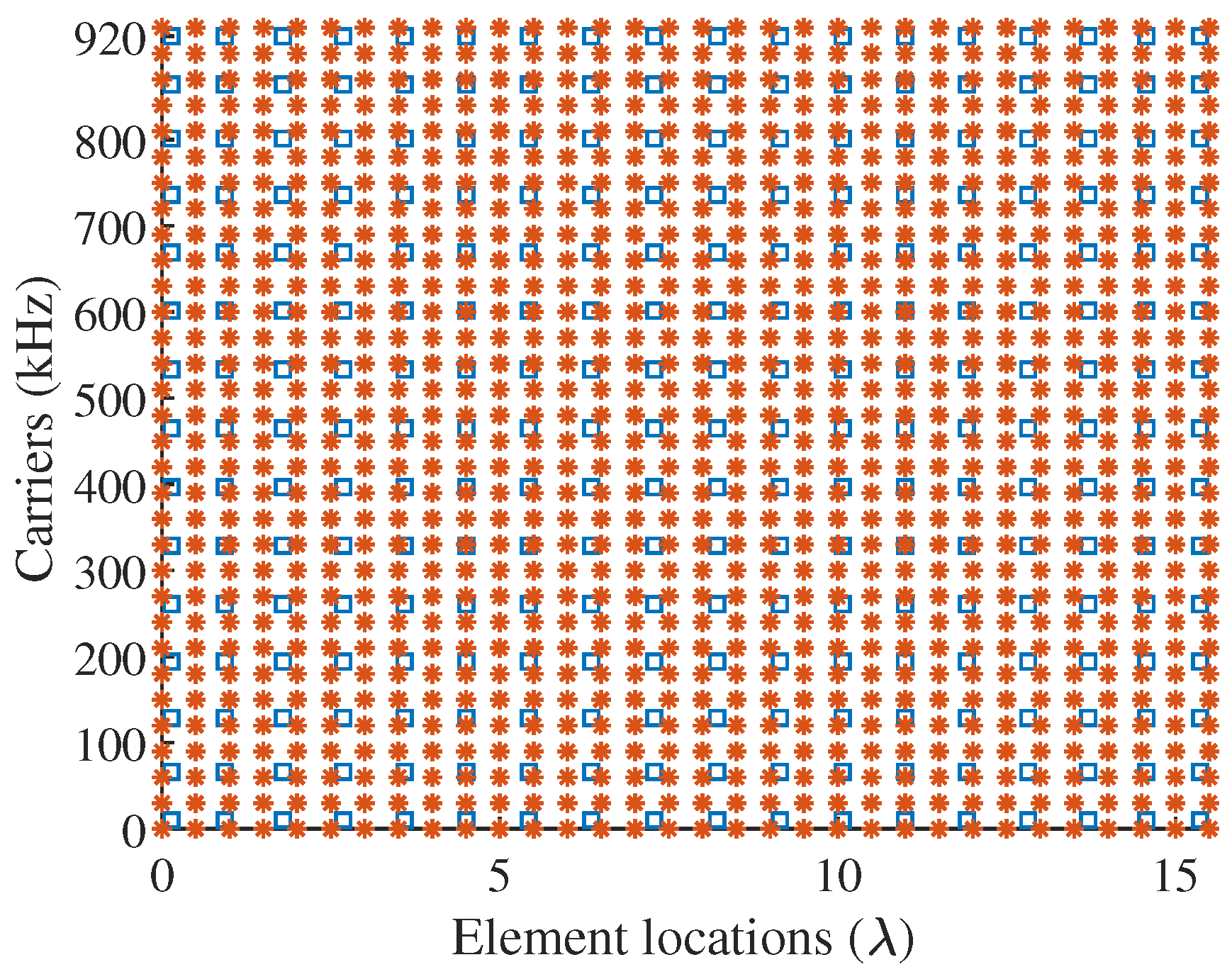
4.2. Example 2: Beampattern Synthesis for Sparse MCFDA
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antonik, P.; Wicks, M.; Griffiths, H.; Baker, C. Frequency diverse array radars. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Radar, Verona, NY, USA, 24–27 April 2006; pp. 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonik, P.; Wicks, M.C.; Griffiths, H.D.; Baker, C.J. Range-dependent beamforming using element level waveform diversity. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Waveform Diversity Design Conference, Lihue, HI, USA, 22–27 January 2006; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Q.; So, H.C.; Shao, H. Nonuniform Frequency Diverse Array for Range-Angle Imaging of Targets. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 2469–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Liao, G.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, B. Transceive Beamforming with Accurate Nulling in FDA-MIMO Radar for Imaging. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 4145–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Tang, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.Q.; Xing, M.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.H. Antenna Beampattern with Range Null Control Using Weighted Frequency Diverse Array. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 50107–50117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.; Qureshi, I.M.; Saeed, S. Frequency Diverse Array Radar with Logarithmically Increasing Frequency Offset. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shi, X.; Li, W.; Xu, J. Flat-Top Beampattern Synthesis in Range and Angle Domains for Frequency Diverse Array via Second-Order Cone Programming. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2016, 15, 1479–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, W.Q.; Shao, H.; Chen, H. Frequency Diverse Array Transmit Beampattern Optimization with Genetic Algorithm. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ruan, H.; Wang, L.; Nehorai, A. The Random Frequency Diverse Array: A New Antenna Structure for Uncoupled Direction-Range Indication in Active Sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2017, 11, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Luk, K.M. Enhanced Transmit—Receive Beamforming for Frequency Diverse Array. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 5344–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.H. Transmit Beampattern Synthesis for Frequency Diverse Array with Particle Swarm Frequency Offset Optimization. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021, 69, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Wang, W.Q.; Chen, H.; Cai, J. Transmit Beamspace Design for Multi-Carrier Frequency Diverse Array Sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 5709–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trucco, A.; Murino, V. Stochastic optimization of linear sparse arrays. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1999, 24, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; He, Z.; Han, C. A modified real GA for the sparse linear array synthesis with multiple constraints. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2006, 54, 2169–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelli, M.; Martini, A.; Massa, A. A Hybrid Approach Based on PSO and Hadamard Difference Sets for the Synthesis of Square Thinned Arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2009, 57, 2491–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinchera, D.; Migliore, M.D.; Panariello, G. Synthesis of Large Sparse Arrays Using IDEA (Inflating-Deflating Exploration Algorithm). IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 4658–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Nie, Z.; Liu, Q.H. Reducing the Number of Elements in a Linear Antenna Array by the Matrix Pencil Method. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2008, 56, 2955–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, P.; Wang, G.; Fan, Z.; Chen, R. An Efficient Approach for the Synthesis of Large Sparse Planar Array. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 7320–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caratelli, D.; Vigano, M.C. A Novel Deterministic Synthesis Technique for Constrained Sparse Array Design Problems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 4085–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Li, F. Reducing the Number of Elements in Linear and Planar Antenna Arrays with Sparseness Constrained Optimization. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 3106–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Urso, M.; Prisco, G.; Tumolo, R.M. Maximally Sparse, Steerable, and Nonsuperdirective Array Antennas via Convex Optimizations. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 3840–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchera, D.; Migliore, M.D.; Schettino, F.; Lucido, M.; Panariello, G. An Effective Compressed-Sensing Inspired Deterministic Algorithm for Sparse Array Synthesis. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2018, 66, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.Q.; Gu, S.Q.; Xu, D.L.; Quan, S.L. Optimization of Sparse Frequency Diverse Array with Time-Invariant Spatial-Focusing Beampattern. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2018, 17, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-khamy, S.E.; Korany, N.O.; Abdelhay, M.A. A Group-Sparse Compressed Sensing Approach for Thinning Multi-Carrier Frequency Diverse Arrays. In Proceedings of the 2019 URSI International Symposium on Electromagnetic Theory (EMTS), San Diego, CA, USA, 27–31 May 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shao, H.Z.; Wang, W.Q. Joint Sparsity-Based Range-Angle-Dependent Beampattern Synthesis for Frequency Diverse Array. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 15152–15161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, T.; Pereira, O. Using the matrix pencil method to estimate the parameters of a sum of complex exponentials. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 1995, 37, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua Yang, H.; Hua, Y. On rank of block Hankel matrix for 2-D frequency detection and estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1996, 44, 1046–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, M.Y.; Chen, K.S.; Wu, H.G.; Liu, X.P. Sparse planar array synthesis using matrix enhancement and matrix pencil. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2013, 2013, 147097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, H.; Wang, B.; Li, X. Shaped-Beam Pattern Synthesis of Sparse Linear Arrays Using the Unitary Matrix Pencil Method. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | Normalized Matching Error | Percentage of Saving Elements | Average Runtime |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed method | 20% | 2 s | |
| Method in [23] | 20% | 440 s |
| Index | Locations () | Frequecy Offset (kHz) | Amp. of Weights | Phase of Weights (deg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | −0.0101 | 0.6486 | −0.6086 |
| 2 | 0.5160 | −14.0468 | 0.6692 | −122.8095 |
| 3 | 1.0539 | −22.4825 | 0.7164 | 91.0485 |
| 4 | 1.6387 | −28.8050 | 0.7834 | 71.7027 |
| 5 | 2.2710 | −33.9395 | 0.8431 | 123.6288 |
| 6 | 2.9208 | −38.1580 | 0.8789 | −129.4829 |
| 7 | 3.6178 | −41.7897 | 0.9184 | 12.6200 |
| 8 | 4.3720 | −44.8412 | 1 | −170.4712 |
| 9 | 5.1280 | −44.9088 | 0.9965 | −174.5252 |
| 10 | 5.8822 | −41.8300 | 0.9190 | 10.2003 |
| 11 | 6.5792 | −38.1813 | 0.8796 | −130.8790 |
| 12 | 7.2290 | −33.9610 | 0.8435 | 122.3387 |
| 13 | 7.8616 | −28.8221 | 0.7837 | 70.6733 |
| 14 | 8.4462 | −22.4928 | 0.7176 | 90.4345 |
| 15 | 8.9841 | −14.0525 | 0.6694 | −123.1471 |
| 16 | 9.4994 | −0.0104 | 0.6486 | −0.6244 |
| Method | Normalized Matching Error | Percentage of Saving Elements | Average Runtime |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed method | 44% (antenna elements), 53% (carriers) | 0.6 s | |
| Method in [25] | 9.38% (antenna elements), 9.38% (carriers) | 4.8 s |
| Index | Locations () | Amp. of Weights | Frequency Offsets (kHz) | Amp. of Weights | Phase of Weights (deg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.1364 | 0.7847 | 10.0807 | 0.7297 | 119.9415 |
| 2 | 0.9292 | 0.9001 | 66.1003 | 0.8837 | 72.2399 |
| 3 | 1.7896 | 0.9476 | 128.7028 | 0.9423 | 103.5396 |
| 4 | 2.6805 | 0.9698 | 194.1029 | 0.9702 | 168.4138 |
| 5 | 3.5878 | 0.9829 | 260.9439 | 0.9855 | −109.4196 |
| 6 | 4.5050 | 0.9908 | 328.5951 | 0.9941 | −17.5296 |
| 7 | 5.4283 | 0.9958 | 396.6961 | 0.9986 | 79.7576 |
| 8 | 6.3553 | 0.9987 | 465.0000 | 1.0000 | 179.4811 |
| 9 | 7.2844 | 1.0000 | 533.3039 | 0.9986 | −80.7955 |
| 10 | 8.2141 | 1.0000 | 601.4049 | 0.9941 | 16.4917 |
| 11 | 9.1432 | 0.9987 | 669.0561 | 0.9855 | 108.3817 |
| 12 | 10.0703 | 0.9958 | 735.8971 | 0.9702 | −169.4516 |
| 13 | 10.9936 | 0.9908 | 801.2972 | 0.9423 | −104.5774 |
| 14 | 11.9107 | 0.9829 | 863.8997 | 0.8837 | −73.2778 |
| 15 | 12.8181 | 0.9698 | 919.9193 | 0.7297 | −120.9794 |
| 16 | 13.7090 | 0.9467 | |||
| 17 | 14.5694 | 0.9001 | |||
| 18 | 15.3622 | 0.7847 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, X.; Hu, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Xiao, M.; Xiao, Z. Efficient Beampattern Synthesis for Sparse Frequency Diverse Array via Matrix Pencil Method. Sensors 2022, 22, 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031042
Shao X, Hu T, Zhang J, Li L, Xiao M, Xiao Z. Efficient Beampattern Synthesis for Sparse Frequency Diverse Array via Matrix Pencil Method. Sensors. 2022; 22(3):1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031042
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Xiaolang, Taiyang Hu, Jinyu Zhang, Lei Li, Mengxuan Xiao, and Zelong Xiao. 2022. "Efficient Beampattern Synthesis for Sparse Frequency Diverse Array via Matrix Pencil Method" Sensors 22, no. 3: 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031042
APA StyleShao, X., Hu, T., Zhang, J., Li, L., Xiao, M., & Xiao, Z. (2022). Efficient Beampattern Synthesis for Sparse Frequency Diverse Array via Matrix Pencil Method. Sensors, 22(3), 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031042






