A Resilient Method for Visual–Inertial Fusion Based on Covariance Tuning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Principles
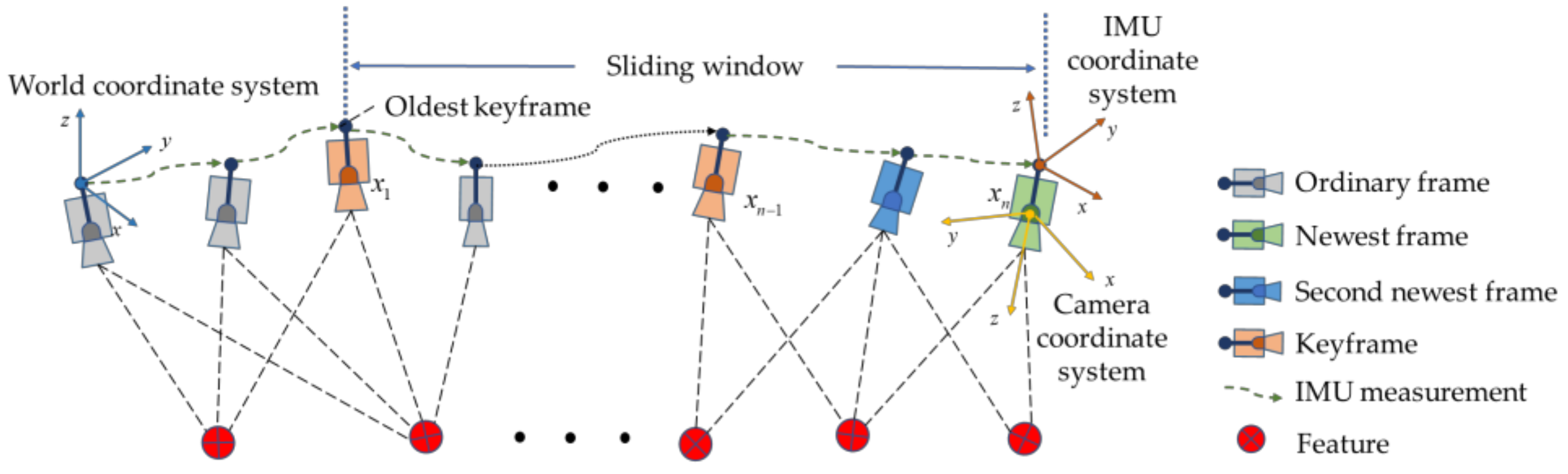
2.1. Construction of the Factor Graph
2.2. Visual Reprojection Factor
2.3. IMU Preintegration Factor
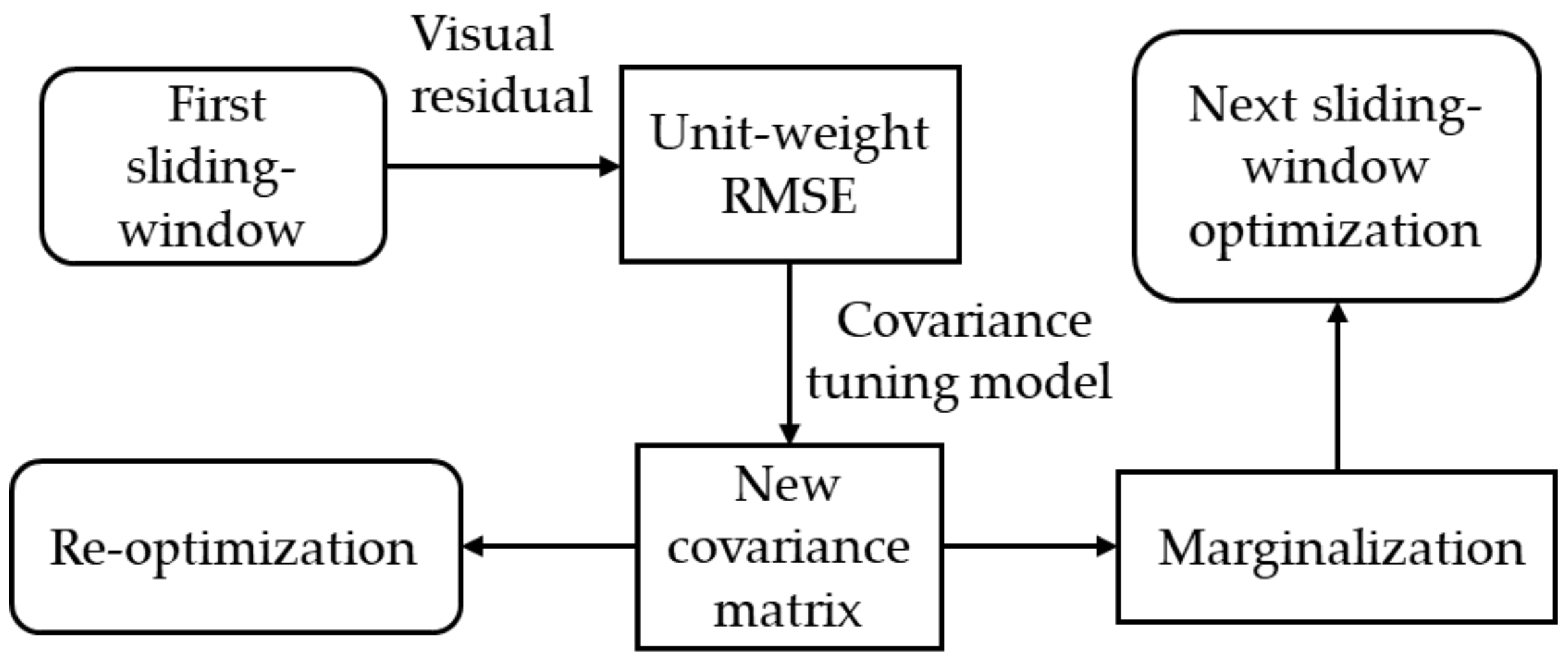
2.4. Covariance Tuning Based on Unit-Weight RMSE
2.5. Re-Optimization
3. Experiments and Analysis
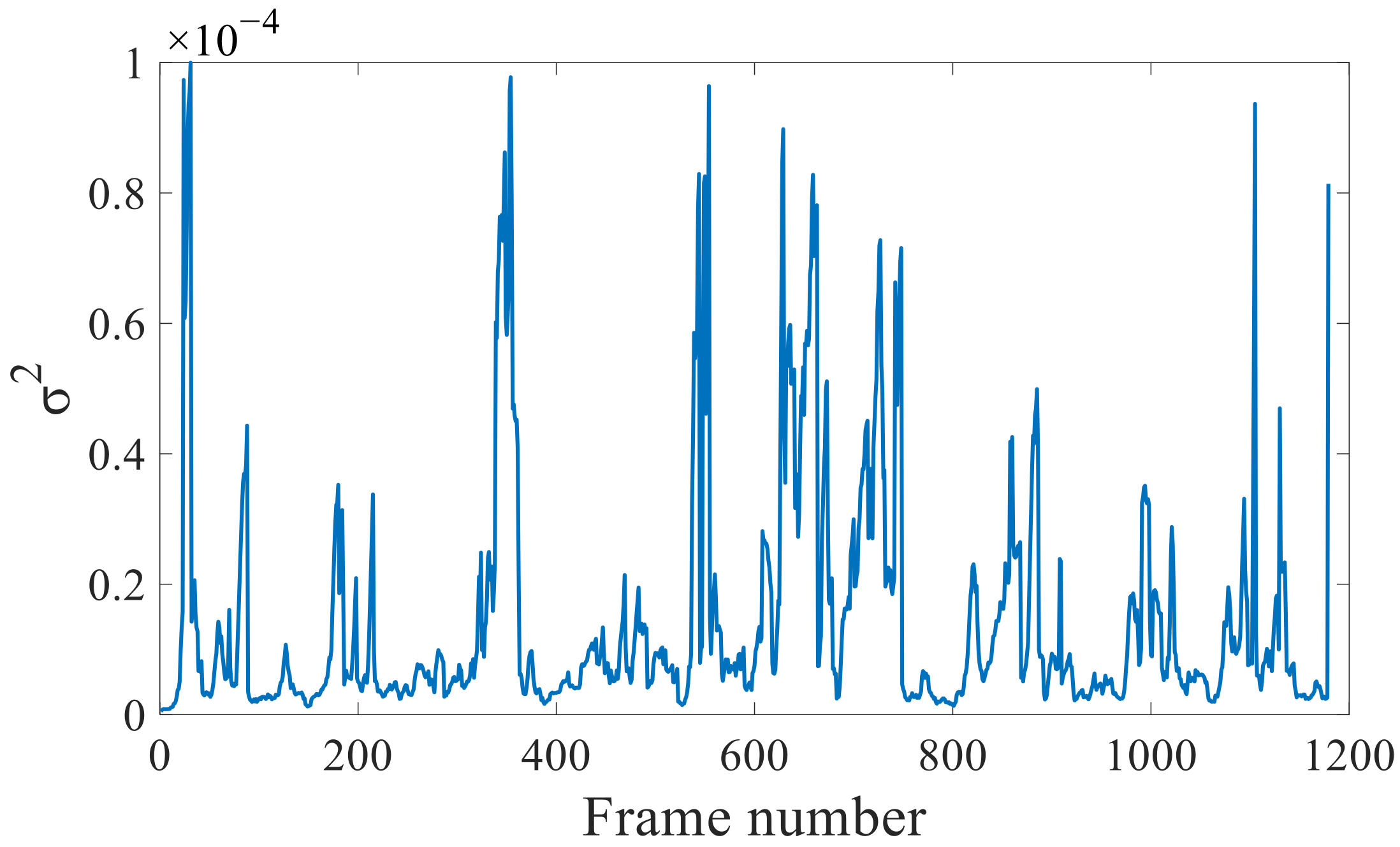
3.1. Effectiveness of Covariance Tuning
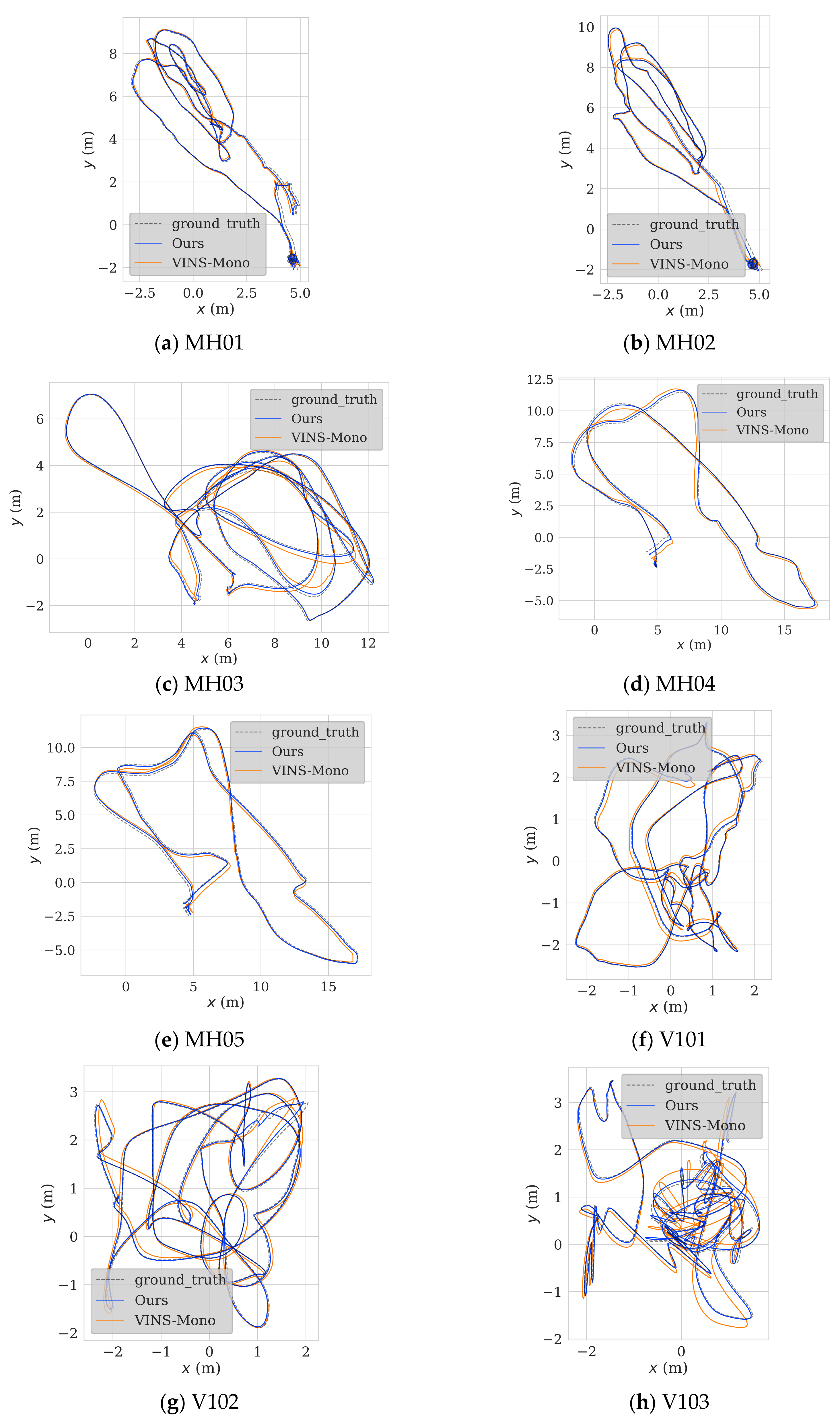
3.2. Experimental Analysis of the Resilient Covariance Tuning-Based Visual–Inertial Fusion Algorithm
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| viSLAM | Visual–inertial simultaneous localization and mapping |
| RMSE | Root-mean-square error |
| PNT | Positioning navigation and time |
| VINS | Visual–inertial navigation systems |
| SLAM | Simultaneous localization and mapping |
| VSLAM | Visual simultaneous localization and mapping system |
| VO | Visual odometry |
| LIBVISO | Library for visual odometry |
| SVO | Semi-direct monocular visual odometry |
| DSO | Direct sparse odometry |
| BA | Bundle adjustment |
| PTAM | Parallel tracking and mapping |
| IMUs | Inertial measurement units |
| FGO | Factor graph optimization |
| MSCKF | Multi-state constraint Kalman filter |
| UKF | Unscented Kalman filter |
| EKF | Extended Kalman filter |
| MAP | Maximum-a-posteriori |
| RMSEs | Root-mean-square errors |
| GFTT | Good Features To Track |
| SfM | Structure from motion |
| EPnP | efficient perspecitve-n-point |
| UAV | Unmanned aerial vehicle |
| ROS | Robot Operating System |
| RMS-APE | Root-mean-square absolute pose error |
References
- Yang, Y. Concepts of comprehensive PNT and related key technologies. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2016, 45, 505. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. Resilient PNT concept fame. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2018, 47, 893–898. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G. Visual-inertial Navigation: A Concise Review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 9572–9582. [Google Scholar]
- Kitt, B.; Geiger, A.; Lategahn, H. Visual Odometry Based on Stereo Image Sequences with RANSAC-Based Outlier Rejection Scheme. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, La Jolla, CA, USA, 21–24 June 2010; pp. 486–492. [Google Scholar]
- Forster, C.; Pizzoli, M.; Scaramuzza, D. SVO: Fast Semi-direct Monocular Visual Odometry. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Engel, J.; Koltun, V.; Cremers, D. Direct sparse odometry. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison, A.J.; Reid, I.D.; Molton, N.D.; Stasse, O. MonoSLAM: Real-Time Single Camera SLAM. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 1052–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, G.; Murray, D. Parallel Tracking and Mapping for Small AR Workspaces. In Proceedings of the 6th IEEE and ACM International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality, Nara, Japan, 13–16 November 2007; pp. 225–234. [Google Scholar]
- Strasdat, H.; Montiel, J.M.; Davison, A.J. Real-time monocular SLAM: Why filter? In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010; pp. 2657–2664. [Google Scholar]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Montiel, J.M.M.; Tardos, J.D. ORB-SLAM: A Versatile and Accurate Monocular SLAM System. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 1147–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, J.; Schöps, T.; Cremers, D. LSD-SLAM: Large-scale direct monocular slam. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis. 2014, 8690, 834–849. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, S.; Michael, N.; Kumar, V. Tightly-coupled monocular visual-inertial fusion for autonomous flight of rotorcraft MAVs. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 5303–5310. [Google Scholar]
- Mourikis, A.I.; Roumeliotis, S.I. A Multi-state Constraint Kalman Filter for Vision-Aided Inertial Navigation. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Rome, Italy, 10–14 April 2007; pp. 3565–3572. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.J.; Ahmed, A.M.; Georgiou, G.A.; Roumeliotis, S.I. A Square Root Inverse Filter for Efficient Vision-aided Inertial Navigation on Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems, Rome, Italy, 13–17 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, M.K.; Wu, K.; Hesch, J.A.; Nerurkar, E.D.; Roumeliotis, S.I. A Comparative Analysis of Tightly-coupled Monocular, Binocular, and Stereo VINS. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.S.; Chen, M.Y. A Sliding-window Visual-IMU Odometer Based on Tri-focal Tensor Geometry. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 3963–3968. [Google Scholar]
- Bloesch, M.; Omari, S.; Hutter, M.; Siegwart, R. Robust Visual Inertial Odometry Using a Direct EKF-Based Approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE Publications/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 298–304. [Google Scholar]
- Huai, Z.; Huang, G. Robocentric Visual–Inertial Odometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 6319–6326. [Google Scholar]
- Geneva, P.; Eckenhoff, K.; Lee, W.; Yang, Y.; Huang, G. OpenVINS: A Research Platform for Visual–Inertial Estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 4666–4672. [Google Scholar]
- Kaess, M.; Johannsson, H.; Roberts, R.; Ila, V.; Leonard, J.J.; Dellaert, F. iSAM2: Incremental smoothing and mapping using the Bayes tree. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2011, 31, 216–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Tardos, J.D. Visual-Inertial Monocular SLAM With Map Reuse. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutenegger, S.; Lynen, S.; Bosse, M.; Siegwart, R.; Furgale, P. Keyframe-based visual–inertial odometry using nonlinear optimization. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2015, 34, 314–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Li, P.; Shen, S. VINS-Mono: A Robust and Versatile Monocular Visual-Inertial State Estimator. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2018, 34, 1004–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.; Elvira, R.; Rodriguez, J.J.G.; Montiel, J.M.M.; Tardos, J.D. ORB-SLAM3: An Accurate Open-Source Library for Visual, Visual–Inertial, and Multimap SLAM. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 37, 1874–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupton, T.; Sukkarieh, S. Visual-Inertial-Aided Navigation for High-Dynamic Motion in Built Environments Without Initial Conditions. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2011, 28, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, C.; Carlone, L.; Dellaert, F.; Scaramuzza, D. On-Manifold Preintegration for Real-Time Visual--Inertial Odometry. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2016, 33, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; He, H.; Xu, G. Adaptively robust filtering for kinematic geodetic positioning. J. Geod. 2001, 75, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Gao, W.G. Integrated navigation based on robust estimation outputs of multi-sensor measurements and adaptive weights of dynamic model information. Geom. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2004, 29, 885–888. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.X.; Gao, W.G. Integrated navigation by using variance component estimates of multi-sensor measurements and adaptive weights of dynamic model information. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2004, 33, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Burri, M.; Nikolic, J.; Gohl, P.; Schneider, T.; Rehder, J.; Omari, S.; Achtelik, M.W.; Siegwart, R. The EuRoC micro aerial vehicle datasets. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2016, 35, 1157–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.B.; Tomasi, C. Good Features to Track. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 21–23 June 1994; pp. 593–600. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, B.D.; Kanade, T. An Iterative Image Registration Technique with an Application to Stereo Vision. In Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 August 1981; pp. 674–679. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, T.; Shen, S. Robust Initialization of Monocular Visual—Inertial Estimation on Aerial Robots. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 4225–4232. [Google Scholar]
- Lepetit, V.; Moreno-Noguer, F.; Fua, P. EPnP: An Accurate O(n) Solution to the PnP Problem. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2008, 81, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, G.; Matthies, L.; Sukhatme, G. Sliding window filter with application to planetary landing. J. Field Robot. 2010, 27, 587–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sub-Dataset | Quantity of Segments | Difficulty | Traveled Distance/m |
|---|---|---|---|
| MH01–MH05 | 5 | E/E/M/D/D | 80.6/73.5/130.9/91.7/97.6 |
| V101–V103 | 3 | E/M/D | 58.6/75.9/79.0 |
| V201–V203 | 3 | E/M/D | 36.5/83.2/86.1 |
| Sub-Dataset | Difficulty | Our Algorithm | VINS-Mono | R-VIO | OKVIS | Improvement in Precision Compared to VINS-Mono |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MH01 | Easy | 0.101233 | 0.157314 | 0.328240 | 0.331345 | 35.65% |
| MH02 | Easy | 0.131429 | 0.178440 | 0.639892 | 0.387684 | 26.35% |
| MH03 | Medium | 0.174250 | 0.195266 | 0.233700 | 0.268468 | 10.76% |
| MH04 | Hard | 0.315295 | 0.439647 | 1.297599 | 0.287485 | 28.28% |
| MH05 | Hard | 0.221533 | 0.303964 | 0.521598 | 0.393153 | 27.12% |
| V101 | Easy | 0.079860 | 0.088830 | 0.098709 | 0.095340 | 10.10% |
| V102 | Medium | 0.106666 | 0.111855 | 0.134505 | 0.148746 | 4.64% |
| V103 | Hard | 0.159576 | 0.187750 | 0.151586 | 0.211350 | 15.01% |
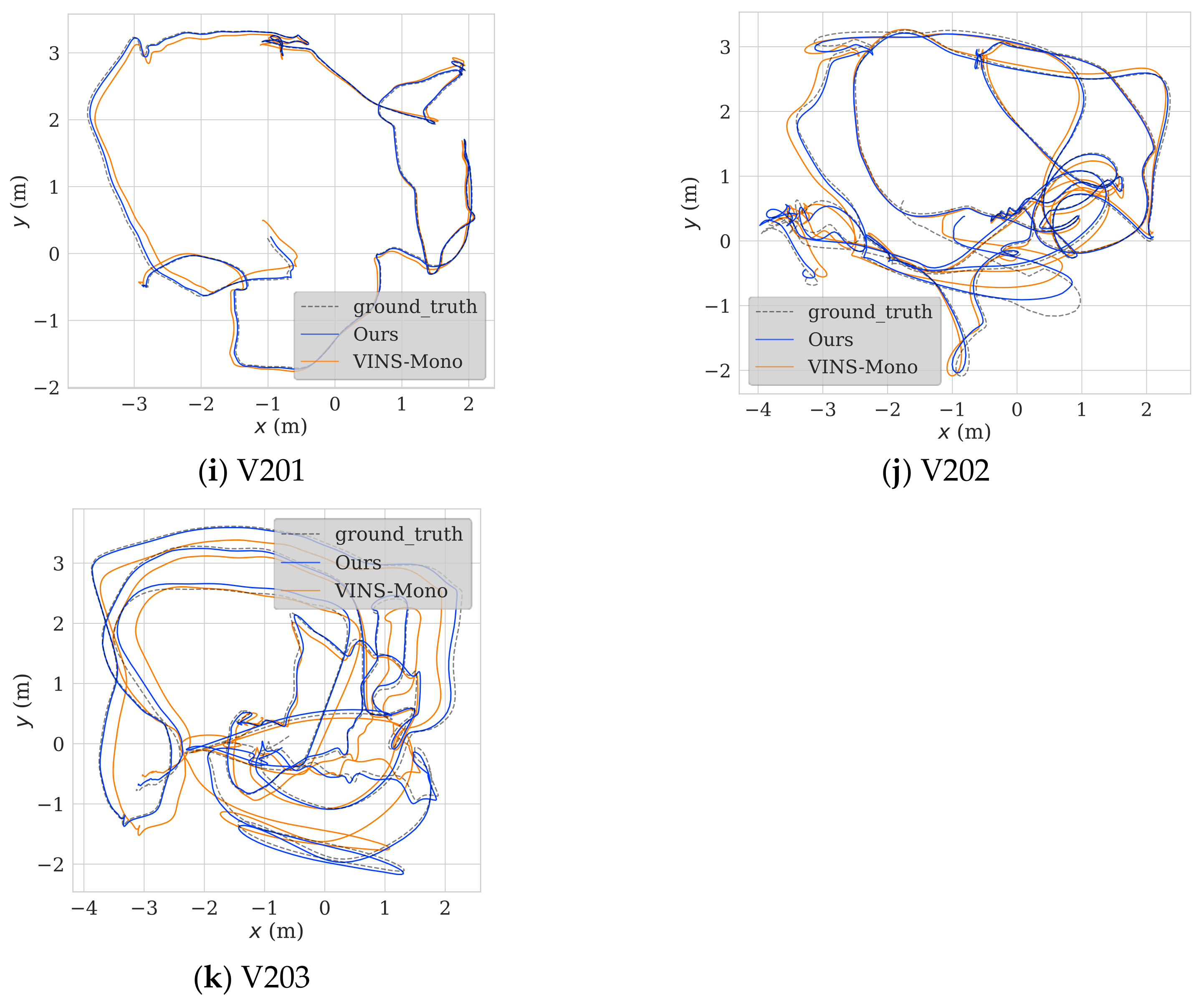
| V201 | Easy | 0.074389 | 0.094752 | 0.123188 | 0.099128 | 21.49% |
| V202 | Medium | 0.137455 | 0.168498 | 0.169666 | 0.176457 | 18.42% |
| V203 | Hard | 0.280010 | 0.286872 | 0.837517 | 0.237462 | 2.39% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, K.; Li, J.; Wang, A.; Luo, H.; Li, X.; Yang, Z. A Resilient Method for Visual–Inertial Fusion Based on Covariance Tuning. Sensors 2022, 22, 9836. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22249836
Li K, Li J, Wang A, Luo H, Li X, Yang Z. A Resilient Method for Visual–Inertial Fusion Based on Covariance Tuning. Sensors. 2022; 22(24):9836. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22249836
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Kailin, Jiansheng Li, Ancheng Wang, Haolong Luo, Xueqiang Li, and Zidi Yang. 2022. "A Resilient Method for Visual–Inertial Fusion Based on Covariance Tuning" Sensors 22, no. 24: 9836. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22249836
APA StyleLi, K., Li, J., Wang, A., Luo, H., Li, X., & Yang, Z. (2022). A Resilient Method for Visual–Inertial Fusion Based on Covariance Tuning. Sensors, 22(24), 9836. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22249836





