An Exploration of Recent Intelligent Image Analysis Techniques for Visual Pavement Surface Condition Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pavement Surface Types and Distress Assessment Indicators
2.1. Pavement Surface and Distress
2.2. Pavement Assessment Indicators
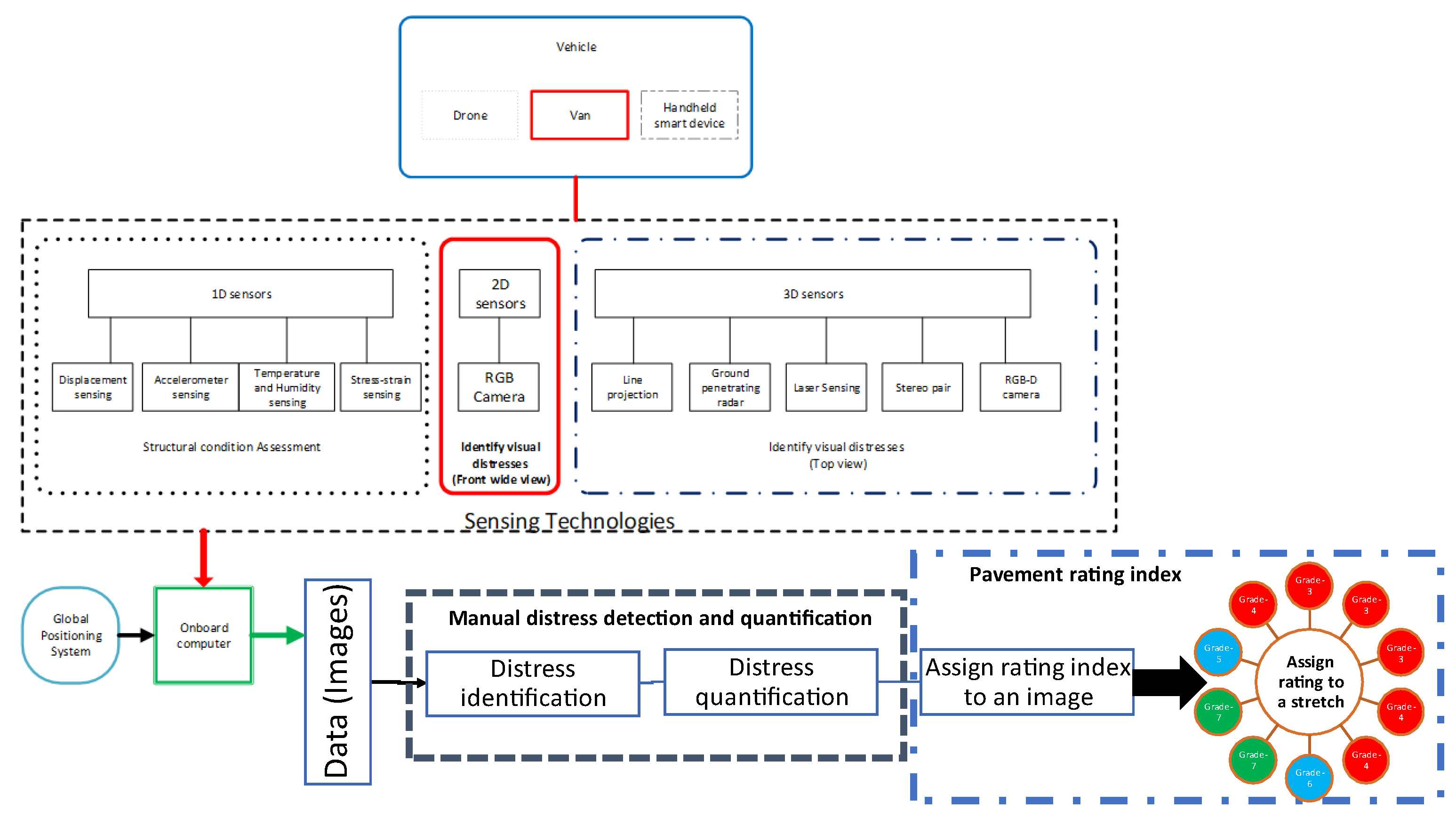
3. Data Acquisition Process and Commercial Practices
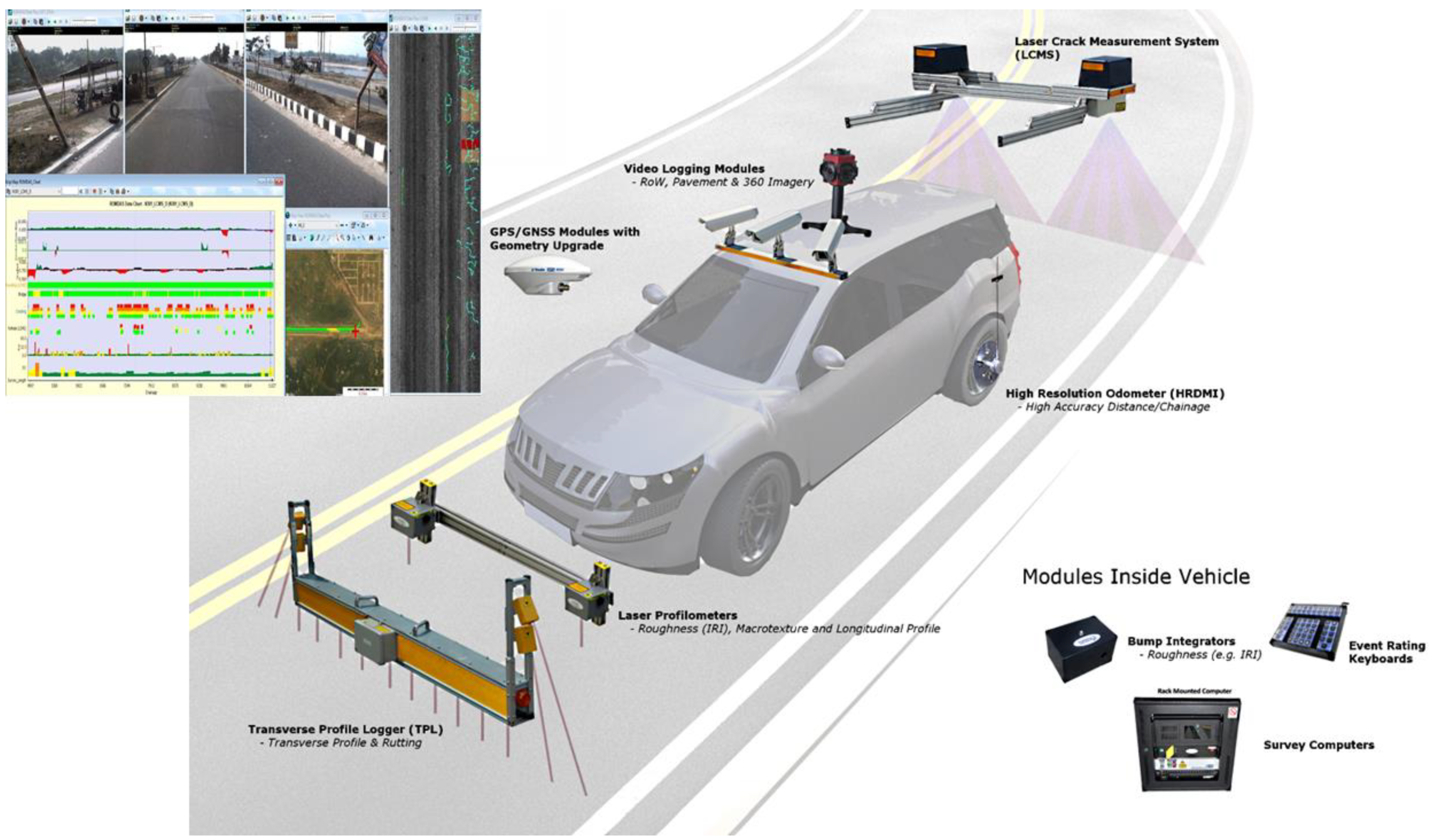
3.1. Data Acquisition Process
3.2. Current Commercial Practices
4. Literature Review on Automated Visual Pavement Condition Rating Systems
4.1. Evolution of Machine Learning in Computer Vision
4.2. Automated Distress Detection and Identification
4.2.1. Publicly Available Datasets
4.2.2. Image Processing Techniques
4.2.3. Classical Machine Learning Techniques
4.2.4. Deep Learning Techniques
Classification Approaches to Distress Detection
Pixel Segmentation Approaches to Distress Detection
Object Detection Approach to Distress Detection
| S. No | Year | Country | Dataset | Architecture | Learning Method | Input Size | View | Channel | Distress | Size of Training Patches | F1-Score (or Accuracy *) of Test Data | Method -Type | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2018 | Germany | GAPs/ ICIP | SqueezeNet | Scratch | 64 × 64 64 × 64 | top-view | Intensity | cracks, potholes | 1,600,000/1,300,000 | 0.73/0.90 | object detection | [139] |
| 2 | 2018 | China | private (China) | Faster RCNN | Transfer | - | frontal view | RGB | cracks, potholes | 3200 | 0.88 | object detection | [146] |
| 3 | 2018 | Timor Leste | private (Timor Leste) | Custom CNN | Scratch | 200 × 200 | frontal view | color | potholes detection | 15,500 | 0.96 | object detection | [147] |
| 4 | 2019 | China | private (China) | Faster RCNN | Scratch | 1024 × 1024 | top-view | RGB | crack pothole, bleeding, surface dots, | 6498 | 0.89 | object detection | [148] |
| 5 | 2019 | India | private (India) | ResNet50 + YOLO | Transfer | 224 × 224 | frontal view | RGB | pothole, pumps | 5283 | 0.54 | object detection | [140] |
| 6 | 2020 | China | LIST | YoloV3 | Transfer | - | frontal view | RGB | crack, patch-crack, pothole, patch-pothole, net, patch-net, manhole | 30,000 | 0.747 (excluding utility hole) | object detection | [141] |
| 7 | 2020 | USA | Paris-Saclay | YoloV2 for detection | Transfer | 640 × 640 | frontal view | RGB | longitudinal cracks, transverse cracks, alligator cracks, potholes, block cracks, reflective cracks, | 5789 | 0.84 | object detection | [142] |
| 8 | 2020 | South Africa | IBM-Hackathon | Custom 2-stage (LCNN object detection and PCNN for classification) | Transfer | 352 × 224 | frontal view | RGB | potholes | 5000 | 0.936 | object detection and classification | [143] |
| 9 | 2020 | China | private (China-Baidu) | Yolo3 | Transfer | 1024 × 512 | frontal view | RGB | potholes, net-crack, cracks, patches | 20,886 | - | object detection | [144] |
| 10 | 2020 | USA | private (USA) - Google | Yolo2 | Transfer | 640 × 640 | frontal view | RGB | reflective crack, transverse cracks, block crack, longitudinal crack, alligator crack, pothole | 7237 | 0.84 | object detection | [142] |
| 11 | 2021 | China | private (China) | Faster RCNN | Scratch | - | top-view | Laser 3D images | crack, pothole, patch | 2208 | 0.95 * (MIOU) | object detection | [45] |
| 12 | 2021 | China | private (China) | YoloV5 | Transfer | 640 × 640 | top-view | RGB | low-medium-high severity cracks | 70,000 | 0.5 | object detection | [45] |
| 13 | 2021 | India | private (India) | Custom CNN | Scratch | 64 × 64 | handheld | RGB | potholes detection | 3424 | 0.97 | object detection | [52] |
| 14 | 2022 | Lebanon | private (Lebanon) | YoloV3 | Transfer | 416 × 416 | frontal view | RGB | pothole | 344 | 0.6 | object detection | [145] |
4.2.5. Automated Direct Pavement Condition Rating
4.3. Benchmarking and State-of-the-Art Models
4.4. Limitations of AI-Based Automated Pavement Rating Systems
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roads in Ireland—Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Roads_in_Ireland (accessed on 16 September 2022).
- PASER Asphalt Roads Pavement Surface Evaluation and Rating PASER Manual Asphalt Roads. 2002. Available online: http://tic.engr.wisc.edu (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- Peraka, N.S.P.; Biligiri, K.P. Pavement asset management systems and technologies: A review. Autom. Constr. 2020, 119, 103336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholevar, N.; Golroo, A.; Esfahani, S.R. Machine learning techniques for pavement condition evaluation. Autom. Constr. 2022, 136, 104190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government of Ireland. Local Authority Budgets 2021. 2021. Available online: https://assets.gov.ie/139273/8554c7e7-d87c-4185-8cc1-32c8bf51c5c3.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Huang, J.; Rathod, V.; Sun, C.; Zhu, M.; Korattikara, A.; Fathi, A.; Fischer, I.; Wojna, Z.; Song, Y.; Guadarrama, S.; et al. Speed/accuracy trade-offs for modern convolutional object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3296–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Yuan, J.; Xiao, F.; Hettiarachchi, C. Application of image technology on pavement distress detection: A review. Measurement 2021, 184, 109900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Liu, Q.; He, Z. Review of Pavement Defect Detection Methods. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 14531–14544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragnoli, A.; De Blasiis, M.R.; Benedetto, A. Di Pavement Distress Detection Methods: A Review. Infrastructures 2018, 8, 14531–14544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coenen, T.B.J.; Golroo, A. A review on automated pavement distress detection methods. Cogent Eng. 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.; Georgieva, K.; Kasireddy, V.; Akinci, B.; Fieguth, P. A review on computer vision based defect detection and condition assessment of concrete and asphalt civil infrastructure. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2015, 29, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Lu, G.; Ye, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Cao, D. The State-of-the-Art Review on Applications of Intrusive Sensing, Image Processing Techniques, and Machine Learning Methods in Pavement Monitoring and Analysis. Engineering 2021, 7, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, D.; Maeda, H.; Ghosh, S.K.; Toshniwal, D.; Mraz, A.; Kashiyama, T.; Sekimoto, Y. Transfer Learning-based Road Damage Detection for Multiple Countries. 2020. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2008.13101 (accessed on 25 October 2021).
- Rateke, T.; Justen, K.A.; Chiarella, V.F.; Sobieranski, A.C.; Comunello, E.; Von Wangenheim, A. Passive vision region-based road detection: A literature review. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 52, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Ortiz, S.; Pascual-Muñoz, P.; Castro-Fresno, D. Machine learning algorithms for monitoring pavement performance. Autom. Constr. 2022, 139, 104309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Road Pavement Surface Types. Available online: https://interpro.wisc.edu/tic/?csis-search-options=site-search&s=paser&submit=Search (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- Miller, J.S.; Bellinger, W.Y. Distress Identification Manual for the Long-Term Pavement performance Program. Georgetown Pike, May 2014. Available online: https://highways.dot.gov/sites/fhwa.dot.gov/files/docs/research/long-term-pavement-performance/products/1401/distress-identification-manual-13092.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2022).
- Mulry, B.; McCarthy, J. A Simplified System for Assessing the Condition of Irish Regional and Local Roads. Civ. Eng. Res. Irel. 2016, 2016, 1–7. Available online: https://ceri2016.exordo.com/files/papers/97/final_draft/097.pdf (accessed on 14 March 2022).
- Standard Practice for Roads and Parking Lots Pavement Condition Index Surveys. Available online: https://www.astm.org/d6433-09.html (accessed on 16 February 2022).
- Gandhi, J.R.; Jaliya, U.K.; Thakore, D.G. A Review Paper on Pothole Detection Methods. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, J.R.; Kanuganti, S.; Bhanegaonkar, P.N.; Sarkar, A.K.; Arkatkar, S. Development of Relationship between Roughness (IRI) and Visible Surface Distresses: A Study on PMGSY Roads. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 104, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- ASTM D5340-12; Standard Test Method for Airport Pavement Condition Index Surveys. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020; Volume 4, pp. 1–55.
- Mccarthy, J.; Fitzgerald, L.; Mclaughlin, J.; Mulry, B.; O’brien, D.; Dowling, K. Rural Flexible Roads Manual—Pavement Surface Condition Index; Department of Transport, Toursim and Sports: Dublin, Ireland, 2014; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Network Condition & Geography Statistics Branch Department for Transport, Technical Note: Road Condition and Maintenance, London, November 2021. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/1032372/technical-guide-to-road-conditions.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2022).
- Carey, W.N.; Irick, P.E. Highway Research Board, The Pavement Serviceability-Performance Concept. 1960. Available online: http://onlinepubs.trb.org/Onlinepubs/hrbbulletin/250/250-003.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2022).
- Mulry, B.; Feighan, K.; McCarthy, J. Development and Implementation of a Simplified System for Assessing the Condition of Irish Regional and Local Roads. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Managing Pavement Assets, Washington, DC, USA, 18–21 May 2015; pp. 1–17. Available online: https://vtechworks.lib.vt.edu/handle/10919/56413 (accessed on 14 March 2022).
- Federal Lands Transportation Program Instructions for FY 2019-2020 Investment Strategy (Competition). 2018. Available online: http://fltp-2019-2020-investment-strategy-guidance-2018.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- New Zealand, T. RAMM road condition rating and roughness manual (Manual No. PFM6). Available online: https://nzta.govt.nz/ (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Kazuyuki, K. Pavement Maintenance in Japan. Available online: https://www.road.or.jp/international/pdf/32_AM6.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Japan International Cooperation Agency, Pavement Inspection Guideline. Available online: https://openjicareport.jica.go.jp/pdf/12286001_01.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Eisenbach, M.; Stricker, R.; Seichter, D.; Amende, K.; Debes, K.; Sesselmann, M.; Ebersbach, D.; Stoeckert, U.; Gross, H.M. How to get pavement distress detection ready for deep learning? A systematic approach. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Anchorage, AK, USA, 14–19 May 2017; pp. 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rateke, T.; Justen, K.A.; Von Wangenheim, A. Road Surface Classification with Images Captured from Low-cost Camera-Road Traversing Knowledge (RTK) Dataset. Revista De Informática Teórica E Aplicada 2019, 26, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, J.; Laurent, J. Pavemetrics LCMS-Laser Crack Measurement System. Available online: https://www.pavemetrics.com/applications/road-inspection/lcms2-en/ (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- FHWA. Practical Guide for Quality Management of Pavement Condition Data Collection; U.S. Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, X. Monitoring Asphalt Pavement Aging and Damage Conditions from Low-Altitude UAV Imagery Based on a CNN Approach. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 47, 432–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappo, N.; Mavrouli, O.; Nex, F.; van Westen, C.; Gambillara, R.; Michetti, A.M. Use of UAV-based photogrammetry products for semi-automatic detection and classification of asphalt road damage in landslide-affected areas. Eng. Geol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inzerillo, L.; Di Mino, G.; Roberts, R. Image-based 3D reconstruction using traditional and UAV datasets for analysis of road pavement distress. Autom. Constr. 2018, 96, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.M.; Tahar, K.N. Identification of rut and pothole by using multirotor unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2019, 137, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhong, J.; Ma, T.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y. Pavement distress detection using convolutional neural networks with images captured via UAV. Autom. Constr. 2022, 133, 103991. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0926580521004428 (accessed on 26 October 2021). [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Qurishee, M.A.; Owino, J.; Fomunung, I.; Onyango, M.; Atolagbe, B. Coupling Deep Learning and UAV for Infrastructure Condition Assessment Automation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2), Kansas City, MO, USA, 16–19 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Biçici, S.; Zeybek, M. An approach for the automated extraction of road surface distress from a UAV-derived point cloud. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outay, F.; Mengash, H.A.; Adnan, M. Applications of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) in road safety, traffic and highway infrastructure management: Recent advances and challenges. Transp. Res. Part A: Policy Pract. 2020, 141, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riid, A.; Lõuk, R.; Pihlak, R.; Tepljakov, A.; Vassiljeva, K. Pavement Distress Detection with Deep Learning Using the Orthoframes Acquired by a Mobile Mapping System. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, R.; Eisenbach, M.; Sesselmann, M.; Debes, K.; Gross, H.M. Improving Visual Road Condition Assessment by Extensive Experiments on the Extended GAPs Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Budapest, Hungary, 14–19 July 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, J.; Gao, J.; Gao, Z.; Chen, Z. Combination of pixel-wise and region-based deep learning for pavement inspection and segmentation. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 23, 3011–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Lau, S.; Wang, X.; Luo, S.; Lee, V.C.S.; Ding, L. Automated pavement crack detection and segmentation based on two-step convolutional neural network. Comput. Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2020, 35, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyan, J.; Li, W.; Tighe, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhai, J. CrackU-net: A novel deep convolutional neural network for pixelwise pavement crack detection. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2020, 27, e2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, D.; Maeda, H.; Ghosh, S.K.; Toshniwal, D.; Mraz, A.; Kashiyama, T.; Sekimoto, Y. Deep learning-based road damage detection and classification for multiple countries. Autom. Constr. 2021, 132, 103935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegazzo, J.; von Wangenheim, A. Road surface type classification based on inertial sensors and machine learning: A comparison between classical and deep machine learning approaches for multi-contextual real-world scenarios. Computing 2021, 103, 2143–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouma, Y.O.; Hahn, M. Pothole detection on asphalt pavements from 2D-colour pothole images using fuzzy c-means clustering and morphological reconstruction. Autom. Constr. 2017, 83, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, L.; Yu, S.; Prokhorov, D.; Mei, X.; Ling, H. Feature Pyramid and Hierarchical Boosting Network for Pavement Crack Detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, S.; Middya, A.I.; Roy, S. PotSpot: Participatory sensing based monitoring system for pothole detection using deep learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 25171–25195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitale, P.A.; Kekre, K.Y.; Shenai, H.R.; Karani, R.; Gala, J.P. Pothole Detection and Dimension Estimation System using Deep Learning (YOLO) and Image Processing. In Proceedings of the 2020 35th International Conference on Image and Vision Computing New Zealand (IVCNZ), Wellington, New Zealand, 25–27 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ROMDAS System | Road Survey Vehicle, Pavement Data Collection. Available online: https://romdas.com/romdas-system.html (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Automatische Detektion von Substanzschäden mit Smart Phone und Künstlicher Intelligenz (KI)—Lehmann & Partner aus Erfurt. Available online: https://www.lehmann-partner.de/automatische-detektion-von-substanzschaeden-mit-smart-phone-und-kuenstlicher-intelligenz-ki/ (accessed on 26 August 2022).
- Video Survey | PMSUSC. Available online: https://www.pms.ie/video-survey (accessed on 8 November 2022).
- Road Surface Inspection System | Global | Ricoh. Available online: https://www.ricoh.com/technology/tech/104_road_surface_monitoring (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- Roadway by RoadBotics. Available online: https://roadway.demo.roadbotics.com/map/wPJQ8Zc82QxFHBbswpYs/?assessmentType=normal (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E. 4TH EDITION Digital Image Processing; Pearson: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 9780133356724. [Google Scholar]
- Altman, N.S. An introduction to kernel and nearest-neighbor nonparametric regression. Am. Stat. 1992, 46, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V.N. Support-Vector Networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, F. The perceptron: A probabilistic model for information storage and organization in the brain. Psychol. Rev. 1958, 65, 386–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, M.; Kleinberg, J.; Schölkopf, B. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D.G. Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1999; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Rublee, E.; Rabaud, V.; Konolige, K.; Bradski, G. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Alcantarilla, P.F.; Nuevo, J.; Bartoli, A. Fast Explicit Diffusion for Accelerated Features in Nonlinear Scale Spaces. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), Bristol, UK, 9–13 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidhuber, J. Deep Learning in Neural Networks: An Overview. Neural Netw. 2015, 61, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convolutional Neural Network—Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Convolutional_neural_network#cite_note-:0-2 (accessed on 9 March 2022).
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5999–6009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Tang, W. Pavement crack segmentation algorithm based on local optimal threshold of cracks density distribution. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Hong Kong, China, 25–27 November 2011; pp. 298–302. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Qin, G.; Wang, X. Improvement of canny algorithm based on pavement edge detection. In Proceedings of the 2010 3rd International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Yantai, China, 16–18 October 2010; Volume 2, pp. 964–967. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, Z.; Abdullah, A.; Kasmin, F.; Ahmad, S.S.S. Road crack detection using adaptive multi resolution thresholding techniques. Telkomnika 2019, 17, 1874–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Cui, L.; Qi, Z.; Meng, F.; Chen, Z. Automatic road crack detection using random structured forests. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 3434–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Chao, W.; Shuangmiao, L.; Baocai, F. Research on crack detection method of airport runway based on twice-threshold segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2015 Fifth International Conference on Instrumentation and Measurement, Computer, Communication and Control (IMCCC), Qinhuangdao, China, 18–20 September 2015; pp. 1716–1720. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, I.H.; Ismael, M.Q. Automated Pavement Distress Detection Using Image Processing Techniques. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2021, 11, 7702–7708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.; Correia, P.L. CrackIT—An image processing toolbox for crack detection and characterization. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Wang, K.C.P.; Li, B.; Yang, E.; Dai, X.; Peng, Y.; Fei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.Q.; Chen, C. Automated Pixel-Level Pavement Crack Detection on 3D Asphalt Surfaces Using a Deep-Learning Network. Comput. Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2017, 32, 805–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Shimada, K.; Ichihara, M.; Hamamoto, Y. A method based on machine learning using hand-crafted features for crack detection from asphalt pavement surface images. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Quality Control by Artificial Vision 2017, Tokyo, Japan, 14 May 2017; Volume 10338, p. 103380. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Qiu, S.; Wang, W.; Xiao, D.; Wang, K.C.P. Cracking classification using minimum rectangular cover--based support vector machine. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2017, 31, 4017027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, A.; Preeja, V. Automatic road distress detection and analysis. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2014, 101, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Zhao, Y.; Pop-Stefanov, B.; Chatterjee, A. Automatically detect and classify asphalt pavement raveling severity using 3D technology and machine learning. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wu, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, W. Automatic Pavement Crack Detection Based on Structured Prediction with the Convolutional Neural Network. February 2018. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1802.02208 (accessed on 2 March 2022).
- Zou, Q.; Cao, Y.; Li, Q.; Mao, Q.; Wang, S. CrackTree: Automatic crack detection from pavement images. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2012, 33, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CRACK500—Google Drive. Available online: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1oJ-yoOaUf2TPbUB1LznrHOas_7imd68o (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- CrackForest. Available online: https://github.com/cuilimeng/CrackForest-dataset (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- Agile-RN and Amhaz Dataset. Available online: https://www.irit.fr/~Sylvie.Chambon/Crack_Detection_Database.html (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- German Asphalt Pavement Distress Dataset—GAPs | Technische Universität Ilmenau. Available online: https://www.tu-ilmenau.de/en/university/departments/department-of-computer-science-and-automation/profile/institutes-and-groups/institute-of-computer-and-systems-engineering/group-for-neuroinformatics-and-cognitive-robotics/data-sets-code/german-asphalt-pavement-distress-dataset-gaps (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- Arya, D.; Maeda, H.; Ghosh, S.K.; Toshniwal, D.; Sekimoto, Y. RDD2020: An annotated image dataset for automatic road damage detection using deep learning. Data Br. 2021, 36, 107133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, D.; Maeda, H.; Ghosh, S.K.; Toshniwal, D. RDD2022: A multi—National image dataset for automatic Road Damage Detection, 2020, pp. 1–16. Available online: https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/2209/2209.08538.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Mei, Q.; Gül, M.; Azim, M.R. Densely connected deep neural network considering connectivity of pixels for automatic crack detection. Autom. Constr. 2020, 110, 103018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoch0d/Road-Quality-Classification. Available online: https://github.com/lenoch0d/road-quality-classification (accessed on 29 August 2022).
- Ma, K.; Hoai, M.; Samaras, D. Large-scale continual road inspection: Visual infrastructure assessment in the wild. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2017, London, UK, 4–7 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Street Pavement Rating | NYC Open Data. Available online: https://data.cityofnewyork.us/Transportation/Street-Pavement-Rating/2cav-chmn/data#revert (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- Pavement Condition Index (PCI). Available online: https://www.arcgis.com/apps/dashboards/5d844eacab5f40598fcd0e45376d785f (accessed on 30 August 2022).
- Browse the State-of-the-Art in Machine Learning | Papers with Code. Available online: https://paperswithcode.com/sota (accessed on 9 March 2022).
- Hong, D.; Gao, L.; Yao, J.; Zhang, B.; Plaza, A.; Chanussot, J. Graph Convolutional Networks for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 5966–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Meng, D.; Zhao, Q.; Cao, W.; Xu, Z. Nonconvex-Sparsity and Nonlocal-Smoothness-Based Blind Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 2991–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Kashiyama, T.; Sekimoto, Y.; Seto, T.; Omata, H. Generative adversarial network for road damage detection. Comput. Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2021, 36, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.A.; Tsai, Y. Automated asphalt pavement raveling detection and classification using convolutional neural network and macrotexture analysis. Transp. Res. Rec. 2021, 2675, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, K.; Khaitan, S.K.; Choudhary, A.; Agrawal, A. Deep convolutional neural networks with transfer learning for computer vision-based data-driven pavement distress detection. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 157, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, F.; Daniel Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.J. Road crack detection using deep convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 3708–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, Y.; Rai, R.; Gupta, V.; Aggarwal, N.; Akula, A. Convolutional neural networks based potholes detection using thermal imaging. J. King Saud Univ. Inf. Sci. 2019, 34, 578–588. [Google Scholar]
- Yusof, N.A.M.; Ibrahim, A.; Noor, M.H.M.; Tahir, N.M.; Yusof, N.M.; Abidin, N.Z.; Osman, M.K. Deep convolution neural network for crack detection on asphalt pavement. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2019, 1349, 12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llopis-Castelló, D.; Paredes, R.; Parreño-Lara, M.; García-Segura, T.; Pellicer, E. Automatic Classification and Quantification of Basic Distresses on Urban Flexible Pavement through Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2021, 147, 04021063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.-C.; Jahanshahi, M.R. NB-CNN: Deep learning-based crack detection using convolutional neural network and Na{\"\i}ve Bayes data fusion. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 4392–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorafshan, S.; Thomas, R.J.; Coopmans, C.; Maguire, M. Deep learning neural networks for sUAS-assisted structural inspections: Feasibility and application. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Dallas, TX, USA, 12–15 June 2018; pp. 874–882. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wang, K.C.P.; Zhang, A.; Yang, E.; Wang, G. Automatic classification of pavement crack using deep convolutional neural network. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2018, 21, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, X. Image-based concrete crack detection using convolutional neural network and exhaustive search technique. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 6520620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.H.; Le, T.H.; Perry, S.; Nguyen, T.T. Pavement crack detection using convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology, Da Nang City, Vietnam, 6–7 December 2018; pp. 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjbar, S.; Nejad, F.M.; Zakeri, H. An image-based system for asphalt pavement bleeding inspection. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, M.D.; Carr, T.A.; Iglesias, M.I.; Buggy, T.; Morison, G. A deep convolutional neural network for semantic pixel-wise segmentation of road and pavement surface cracks. In Proceedings of the 2018 26th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Roma, Italy, 3–7 September 2018; pp. 2120–2124. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, Y.-A.; Tsai, Y.J. Machine Learning for Crack Detection: Review and Model Performance Comparison. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2020, 34, 04020038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, W.; Zhu, X. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. IEEE Access 2015, 9, 16591–16603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Qi, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S. Deepcrack: Learning hierarchical convolutional features for crack detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 1498–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. Computer vision-based concrete crack detection using U-net fully convolutional networks. Autom. Constr. 2019, 104, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Jia, G.; Zhu, H.; Jia, D.; Gao, L. Automated pavement crack damage detection using deep multiscale convolutional features. J. Adv. Transp. 2020, 2020, 6412562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9351, pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. Available online: https://github.com/hszhao/PSPNet (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, A.A.; Luo, L.; Wang, G.; Yang, E. Pixel-level pavement crack segmentation with encoder-decoder network. Measurement 2021, 184, 109914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhat-Duc, H.; Nguyen, Q.L.; Tran, V.D. Automatic recognition of asphalt pavement cracks using metaheuristic optimized edge detection algorithms and convolution neural network. Autom. Constr. 2018, 94, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, S.; Park, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, H. Encoder–decoder network for pixel-level road crack detection in black-box images. Comput. Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2019, 34, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Q.; Gül, M. A cost effective solution for pavement crack inspection using cameras and deep neural networks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 256, 119397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.X.; Hu, B.L.; Yang, Z.; Huang, L.; Li, P. Pavement Crack Detection Method Based on Deep Learning Models. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2021, 2021, 5573590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, M.; Peel, H.; Cohn, A.G.; Fuentes, R. Combining block-based and pixel-based approaches to improve crack detection and localisation. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Wang, K.C.P.; Fei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, G.; Li, J.Q.; Yang, E.; Qiu, S. Automated Pixel-Level Pavement Crack Detection on 3D Asphalt Surfaces with a Recurrent Neural Network. Comput. Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2019, 34, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konig, J.; Jenkins, M.D.; Barrie, P.; Mannion, M.; Morison, G. A Convolutional Neural Network for Pavement Surface Crack Segmentation Using Residual Connections and Attention Gating. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing, ICIP, Taipei, Taiwan, 22–25 September 2019; pp. 1460–1464. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Song, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, B. Automatic Pavement Crack Detection by Multi-Scale Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 20, 2025–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Wang, K.C.P.; Zhang, A.; Chen, C.; Li, J.Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Li, B. Pixel-Level Cracking Detection on 3D Asphalt Pavement Images through Deep-Learning- Based CrackNet-V. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 21, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Di Mascio, P.; Chen, X.; Zhu, G.; Loprencipe, G. Ensemble of deep convolutional neural networks for automatic pavement crack detection and measurement. Coatings 2020, 10, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zong, J.; Nie, J.; Wu, Z.; Han, H. Pavement crack detection algorithm based on densely connected and deeply supervised network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 11835–11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Su, C. Deep Learning-Based Real-Time Crack Segmentation for Pavement Images. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 25, 4495–4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single shot multibox detector. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2016; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 9905, pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, A.; Redmon, J. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. In Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 1804. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, P.; Yang, X.; Gao, Z. A Deep Learning Approach for Street Pothole Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Sixth International Conference on Big Data Computing Service and Applications (BigDataService), Oxford, UK, 3–6 August 2020; pp. 198–204. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, S.; Gupta, S.; Darbari, V.; Kohli, S. Crack-pot: Autonomous Road Crack and Pothole Detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Canberra, ACT, Australia, 10–13 December 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Deshmukh, C. Pothole and Bump detection using Convolution Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference (ITEC-India), Bengaluru, India, 17–19 December 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Pan, N.; Xu, Z.; Deng, F.; Shen, Y.; Kang, H. Pavement distress detection and classification based on YOLO network. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 22, 1659–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidifard, H.; Jin, P.; Adu-Gyamfi, Y.; Buttlar, W.G. Pavement Image Datasets: A New Benchmark Dataset to Classify and Densify Pavement Distresses. Transp. Res. Rec. 2020, 2674, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yao, M.; Gu, Q. Pothole detection using location-aware convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2020, 11, 899–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Liu, C.; Li, L.; Wang, G. Automated Pavement Distress Detection and Deterioration Analysis Using Street View Map. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 76163–76172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yik, Y.K.; Alias, N.E.; Yusof, Y.; Isaak, S. A real-time pothole detection based on deep learning approach. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.; Wang, K. Pavement Distress Detection Based on Transfer Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 5th International Conference on Systems and Informatics (ICSAI), Nanjing, China, 10–12 November 2018; pp. 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.; Tamura, S.; Hayamizu, S.; Fukai, H. A Deep Learning-Based Approach for Road Pothole Detection in Timor Leste. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Service Operations and Logistics, and Informatics (SOLI), Singapore, 31 July–2 August 2018; pp. 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Wang, X. Faster region convolutional neural network for automated pavement distress detection. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2021, 22, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, D.; Gupta, V.; Sambyal, N. Detection and localization of potholes in thermal images using deep neural networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 26265–26284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Sekimoto, Y.; Seto, T.; Kashiyama, T.; Omata, H. Road Damage Detection and Classification Using Deep Neural Networks with Smartphone Images. Comput. Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 33, 1127–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidifard, H.; Adu-Gyamfi, Y.; Buttlar, W.G. Deep machine learning approach to develop a new asphalt pavement condition index. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 247, 118513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rateke, T.; von Wangenheim, A. Road surface detection and differentiation considering surface damages. Auton. Robots 2021, 45, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinzato, P.Y.; Dos Santos, T.C.; Rosero, L.A.; Ridel, D.A.; Massera, C.M.; Alencar, F.; Batista, M.P.; Hata, A.Y.; Osório, F.S.; Wolf, D.F. CaRINA dataset: An emerging-country urban scenario benchmark for road detection systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 19th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1–4 November 2016; pp. 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, J.; Kuhnl, T.; Geiger, A. A new performance measure and evaluation benchmark for road detection algorithms. In Proceedings of the 16th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC 2013), The Hague, The Netherlands, 6–9 October 2013; pp. 1693–1700. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, W.S.; Power, D.; Joseph, M.; Brian, M.; Kieran, F.; Dympna, O.S. Learning pavement surface condition ratings through visual cues using a deep learning classification approach. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Intelligent Computer Communication and Processing (ICCP 2022), Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 22–24 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Road-Segmentation-Adas-0001—OpenVINO Toolkit. Available online: https://docs.openvino.ai/2018_R5/_docs_Transportation_segmentation_curbs_release1_caffe_desc_road_segmentation_adas_0001.html (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. V EfficientNetV2: Smaller Models and Faster Training. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/google/ (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Machine Learning Datasets | Papers with Code. Available online: https://paperswithcode.com/datasets (accessed on 9 March 2022).
- ImageNet Benchmark (Image Classification) | Papers with Code. Available online: https://paperswithcode.com/sota/image-classification-on-imagenet?tag_filter=104%2C171%2C105 (accessed on 21 February 2022).
- The Latest in Machine Learning | Papers with Code. Available online: https://paperswithcode.com/ (accessed on 9 March 2022).
- Andrew Ng: Unbiggen AI—IEEE Spectrum. Available online: https://spectrum.ieee.org/andrew-ng-data-centric-ai#toggle-gdpr (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Raji, I.D.; Bender, E.M.; Paullada, A.; Denton, E.; Research, G.; Hanna, A. AI and the Everything in the Whole Wide World Benchmark. AI and the Everything in the Whole Wide World Benchmark. Available online: https://trec.nist.gov (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Mathavan, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Stonecliffe-Janes, M.; Kamal, K. Pavement raveling detection and measurement from synchronized intensity and range images. Transp. Res. Rec. 2014, 2457, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, S.; Moghadas Nejad, F.; Zakeri, H. Asphalt pavement bleeding evaluation using deep learning and wavelet transform. Amirkabir J. Civ. Eng. 2022, 53, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.; O’sullivan, D.; Mckeever, S.; Power, D.; Mcgowan, R.; Feighan, K. Detecting Patches on Road Pavement Images Acquired with 3D Laser Sensors using Object Detection and Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 17th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications, Online, 6–8 February 2022; Volume 2, pp. 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Surface Distress Group | Asphalt Rural Flexible | Asphalt Urban Flexible | Joined Portland Concrete | Continuously Concrete Reinforced |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cracks | Alligator cracking | Fatigue cracking | Durability cracking | Durability Cracking |
| Block cracking | ||||
| Edge cracking | Edge cracking | Corner breakups | Corner breakups and shattered slabs | |
| Reflection cracking at joints | Reflection cracking at joints | |||
| Longitudinal cracking | Longitudinal cracking (wheel path and non-wheel path) | Longitudinal cracking | Longitudinal cracking | |
| Transverse cracking | Transverse cracking | Transverse cracking | Transverse cracking | |
| Meander and slippage | Meander and slippage | |||
| Surface Openings | Patches | Patches and utility patches | Patches and utility patches | Patches and utility patches |
| Potholes | Potholes | Blow-ups | Blow-ups | |
| Surface disintegration | Utility hole defects | Utility hole defects | Utility hole defects | |
| Surface Deformation | Rutting | Rutting | -- | -- |
| Depression and bumps | Shoving, depressions, bumps, sags, and heave | |||
| Surface Defects | Raveling | Raveling | Wearing | Wearing |
| Bleeding | Bleeding | Polish aggregate | Polish aggregate | |
| Miscellaneous Distresses | Lane-to-shoulder drop off | Lane-to-shoulder drop off | Lane-to-shoulder drop-off and separation | Lane-to-shoulder drop-off and separation |
| Water bleeding and pumping | Water bleeding and pumping | Water bleeding and pumping | Water bleeding and pumping | |
| Joint Deficiencies | --- | --- | Joint seal damage (longitudinal and transverse) | Joint seal damage (longitudinal and transverse) |
| Spalling of longitudinal and transverse joints | Spalling of longitudinal and transverse joints |
| Type of Indicators | Granularity | Measurement Criteria | Standard Developing Body |
|---|---|---|---|
| Present Serviceability Index (PSI) | 5 (Excellent)—0 (Essentially impassable) | A mathematical formula based on the severity of surface roughness, cracking, deflection | Illinois, Minnesota, and Indiana—AASHO Road Test (1961) |
| Integer value | |||
| Pavement Condition Index (PCI) | 100–85 (Good)—0–10 (Failed) | A mathematical formula based on the occurrence, and severity of distresses, mainly crack and IRI | ASTM D6433—11 |
| Pavement Condition Rating (PCR) | Alabama Department of Transport | ||
| Pavement Structural Condition (PSC) | Washington Department of Transport | ||
| Surface Condition Rating (SCR) | Georgia Department of Transport | ||
| Pavement Surface Evaluation and Rating (PASER) | 10 (Excellent)—1 (failed) | A direct rating based on visual distresses | Wisconsin Transportation Information Center, University of Wisconsin Madison, USA |
| Integer value | |||
| Pavement Surface Condition Index (PSCI) | 10 (Perfect)—1 (No surface) | A direct rating based on visual distresses | Road Management Office, Ireland |
| Integer value | |||
| Unified Pavement Distress Index for Managing Flexible Pavements (UPDI) | 0 (Failed)—1 (Perfect) | A mathematical formula based on six visual distress | Civil Engineering Department, Clemson University, USA |
| Pavement Distress Index (PDI) | Good/Fair/Poor | IRI, rutting, cracking, and faulting are used to estimate PDI | Arizona Department of Transport |
| Pavement Performance Levels | Good/Fair/Poor | IRI, rutting, cracking, and faulting are used to estimate PDI | Kansas Department of Transport |
| Pavement Quality Index (PQI) | 0 (Fail)—4.0 (Good) | A square root of the product of roughness quality index (RQI) and visual surface rating (SR) | Government Accounting Standards Board, Standard 34 (GASB 34). Minnesota |
| Condition Rating Score (CR) | 1–59 (Very poor)—90–100 (Very good) | Mathematical combination of distress and ride quality (roughness) | Texas Department of Transport |
| Pavement Condition Index -2 | 1–100 (same as PCI) | A mathematical formula based on cracking index, riding index, and rutting/faulting index | IOWA STATE University Institute for Transportation |
| Pavement Condition | Good/Fair/Poor/Very/Poor | A pavement condition based on the international roughness index | New Hampshire Department of Transportation |
| Remaining Service Life (RSL) | Good/Fair/Poor | A superset rating is calculated based on PCI rating (0–100) | Colorado Department of Transportation |
| Chinese Pavement Condition Index | 100–85 (Good)—0–10 (Failed) | A mathematical formula based on the occurrence, and severity of distresses, mainly crack and IRI | China |
| Maintenance Control Index (MCI) | 10 (Good)—0–1 (Failed) | A mathematical formula based on cracking Ratio, Rutting Depth, and roughness | Japan (Until 2005) |
| Repair Requirement Index (RRI) | 0-5 New – More than 12 (Lifetime over) | A mathematical formula based on International Roughness Index, crack rate coefficient, and pothole rank coefficient | Japan (after 2005) Tajikistan |
| Road Condition Index | 1 (poor)—4 (Good) | A mathematical formula based on the occurrence and severity of visual distresses and roughness index | UK |
| Pavement Distress Condition Rating | Good/Fair/Poor | A rating is based on maintenance strategy and is a function of cracks, patches, and potholes | India |
| Condition Index (CI) | 0 (Excellent)—100 (Failed) | A mathematical formula based on visually measured condition defects | New Zealand |
| RMA | 1 (Poor)—4 (Good) | A mathematical formula based on the occurrence and severity of visual distresses and roughness index | Germany |
| S.No | Name | Distress | Ground Truth | Device | No. of Images | Resolution | Ch | View | Country | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Crack Forest Dataset (CFD) | crack | pixel-level | hand-held static | 329 | 480 × 320 | 3 | Top | China | https://bit.ly/3PMFWhl accessed on 20 October 2022 |
| 2 | Amhaz Crack Dataset (Aigle_RN + ESAR + LCMS + LRIS = TEMPEST2) | cracks | pixel-level | vehicle with 5 sensors | 66 (38 + 15 + 5 + 3 + 5) | 991 × 462 + 311 × 462 + 768 × 512 + 700 × 1000 + 3249 × 1576 + 1127 × 1598 | 1 | Top | France | https://bit.ly/3TdmOfB |
| 3 | CRACK500 and CRACK-500-B | cracks | pixel-level | hand-held static | 500 + 1896 | 2560 × 1440 640 × 360 | 3 | Top | China | https://bit.ly/3QPeAsx |
| 4 | GAPs-10m | 22 classes | pixel-level | JAI Pulnix TM2030 monochrome cameras (vehicle) | 20 | 5030 × 11,505 | 1 | Top | Germany | https://bit.ly/3cnqI4X |
| 5 | GAPs | crack, pothole, inlaid patch, applied patch, open joint, bleeding | bounding box | JAI Pulnix TM2030 monochrome cameras (vehicle) | 2468 | 1920 × 1080 | 1 | Top | Germany | https://bit.ly/3cnqI4X |
| 6 | Paris-Saclay | pavement rating (1–3) | image | Google Streetview | 700,000 | 640 × 640 | 3 | Frontal | New York, USA | https://bit.ly/3pNlYc4 |
| 7 | RDD2019 | pothole, longitudinal crack, transverse crack, alligator crack, line markings | bounding box | mobile device moving vehicle | 10,561 | 600 × 600 | 3 | Frontal | Japan | https://bit.ly/3cqCKun |
| 8 | RDD2020 (excluding Japan) | pothole, longitudinal crack, transverse crack, alligator crack | bounding box | mobile device moving vehicle | 11,000 | 720 × 720 (India) 600 × 600 (Czech) | 3 | Frontal | India Czech Republic | |
| 9 | RDD2022 (excluding RDD2020) | pothole, longitudinal crack, transverse crack, alligator crack | bounding box | mobile device moving vehicle | 17,500 | 3650 × 2044 (Norway) 640 × 640 (USA) 512 × 512 (China) | 3 | frontal/top | Norway USA China | |
| 10 | DatasetCrackDeepa2022 | cracks | pixel-level | hand-held static | 3000 | 800 × 600 | 1 | Top | https://bit.ly/3coASSY | |
| 11 | RQ Dataset | pavement rating (1–6) | image | Google Streetview | 7247 | 640 × 480 | 3 | frontal | Czech | https://bit.ly/3pMYofi |
| 12 | CrackIT | crack | pixel-level | hand-held static | 56 | 1536 × 2048 | 3 | Top | Portugal | https://bit.ly/3RajLCR |
| 13 | EdmCrack600 | crack | pixel-level | camera mounted on vehicle | 600 | 1920 × 1080 | 3 | Back | Canada | https://bit.ly/3ThzDW8 |
| 14 | FHWA-LTPP | aligator, transverse crack, longitudinal cracks, deflection, IRI | image | camera mounted on vehicle (top and frontal) | - | 2048 × 3072 | 3 | frontal and top | USA Canada | https://bit.ly/3CzyNOO |
| 15 | bim-hackathon | potholes | bounding box | mobile camera mounted on vehicle | 5676 | 3680 × 2760 | 3 | frontal | South Africa | https://bit.ly/3RNGSDV |
| 16 | LIST | crack, patch-crack, pothole, patch-pothole, net, patch-net, manhole | - | camera on a moving vehicle | 30,000 | - | 3 | frontal | China | https://bit.ly/3qchLPd |
| 17 | CrackTree200 | cracks | images | hand-held static | 260 | 512 × 512 | 1 | Top | China | https://bit.ly/3ARIEg6 |
| 18 | CRKWH100 | crack | images | hand-held static | 100 | 512 × 512 | 1 | Top | China | https://bit.ly/3QcPdzL |
| 19 | CrackLS315 | crack | images | hand-held static | 315 | 512 × 513 | 1 | Top | China | https://bit.ly/3QcPdzL |
| 20 | APR | cracks | pixel-level | camera on a moving robot | 19 + 14 | 1200 × 900 + 2040 × 2048 | 2 | Top | China | https://bit.ly/3RwZF6y |
| S.No | Year | Country | Dataset | Architecture | Learning Method | Input Size | View | Channel | Distress | Size of Training Patches | F1-SCORE (or Accuracy *) of Test Data | Method-Type | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2019 | Itlay | private (Italy) | ResNet101 | Transfer | 224 × 224 | Top | RGB | 9 distresses (e.g., longitudinal cracks, transverse cracks, alligator cracks, potholes, patches, | 12,728 | 0.92 | patch-based classification for sliding window | [43] |
| 2 | 2019 | Germany | GAPs (Germany) | RestNet34 | Transfer | 160 × 160 | Top | Intensity | cracks applied patches, inlaid patches, open joints, potholes | 50,000 | 0.9041 | patch-based classification for sliding window | [44] |
| 3 | 2020 | China | private (China) | customized (RCNN + FCN) | Scratch | 75 × 75 | Top | Laser 3D images | cracks, pothole, patch | 2208 | 0.87 | semantic segmentation | [45] |
| 4 | 2020 | China | private (China) + CFD | YoloV3 + UNET with ResNet34 | Transfer | 128 × 128 + 256 × 256 + 320 × 320 | Top | RGB | longitudinal and transverse cracks, block crack, alligator and linear crack | 16,780 | 0.906 (detection) 0.957 (segmentation) | instance detection and segmentation | [46] |
| 5 | 2020 | Canada | private (Canada) | customized U-Net | Scratch | 1024 × 1024 | Top | RGB | transverse and longitudinal cracks, alligator cracks, and block cracks | 3000 | 0.984 | semantic segmentation | [47] |
| 6 | 2021 | Iran | private (Iran) | SqueezeNet | Transfer | 224 × 224 | Frontal | RGB | bleeding detection and severity classification | 800 | 0.98 | image classification | [110] |
| 7 | 2021 | USA | private (USA) | ResNet18 | Transfer | 520 × 417 | Top | Laser 3D images | raveling detection and classification | 2500 | 0.915 | image classification | [99] |
| S.No | Year | Country | Dataset | Architecture | Learning Method | Input Size | View | Channel | Size of Input Patch | F1-Score (or Accuracy *) | Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2018 | USA | LTPP-FHWA | VGG16 | Transfer | 2072 × 2048 | Top | Intensity | 760 | 0.9 | image classification | [100] |
| 2 | 2018 | Vietnam | custom (Similar to CrackIT) | custom CNN | Scratch | 100 × 100 | Top | RGB | 12,500 | 0.91 | patch-based classification for sliding window | [109] |
| 3 | 2018 | China | private (China) | custom CNN | Scratch | 256 × 256 | Top | Laser 3D images | 4000 | 0.98 * | patch-based classification for sliding window | [107] |
| 4 | 2018 | Vietnam | private (Vietnam) | custom CNN | Scratch | 150 × 150 | Top | Intensity | 400 | 0.907 | patch-based classification for sliding window | [123] |
| 5 | 2018 | France | Amhaz Crack dataset + CFD | custom CNN | Scratch | 27 × 27 | Top | RGB | 898,764 | 0.8954 + 0.9244 | patch-based classification for sliding window | [94] |
| 6 | 2019 | USA | private (USA) | custom CNN (encoder + decoder) | Scratch | 1024 × 512 | Top | Laser 3D images | 3800 | 0.94 | semantic segmentation | [128] |
| 7 | 2019 | USA | crackTree CRKWH100 CrackLS315 | custom UNET (DeepCrack) | Transfer | 512 × 512 | Top | RGB + Laser | 260 | 0.95 + 0.84 + 0.85 | semantic segmentation | [115] |
| 8 | 2019 | China | CrackForest | U-Net with patch training | Scratch | 48 × 48 | Top | Intensity | 20,000 | 0.874 | semantic segmentation | [111] |
| 9 | 2019 | China | CrackForest + Aigle_RN | U-Net with residual block, attention Unit, and patch training | Scratch | 48 × 49 | Top | Intensity | 142,000 | 0.92 | semantic segmentation | [129] |
| 10 | 2019 | Korea | private (Korea) | custom CNN (ResNet +decoder) | Transfer | 1920 × 1080 | Front | RGB | 427 | 0.74 | semantic segmentation | [124] |
| 11 | 2019 | China | Aigle_RN + crackForest + APR | multi-scale fusion (unsupervised) learning | Scratch | - | Top | RGB | 118 + 38 + 33 | 0.698 + 0.88 + 0.87 | semantic segmentation | [130] |
| 12 | 2019 | USA | crack500-B + GAPs + Cracktree200 + CrackForest + Amhaz Crack | feature pyramid hierarchical boosting network | Scratch | - | Top | RGB + Laser | - | 0.60 + 0.22 + 0.51 + 0.68 + 0.49 | semantic segmentation | [51] |
| 13 | 2020 | China | crackForest + Crack500 | customized U-Net | Scratch | 320 × 320 | Top | Intensity | 72 + 1896 | 0.955 + 0.7327 | semantic segmentation | [46] |
| 14 | 2020 | Canada | EdmCrack600 + CrackForest | 121-layer custom CNN | Transfer | 256 × 256 | Back | RGB | - | 0.77 + 0.92 | semantic segmentation | [125] |
| 15 | 2020 | USA | custom + CrackForest | custom CNN (encoder + decoder) crackNet-V | Scratch | 512 × 256 | Top | Laser 3D images | 6000 | 0.871 + 0.891 | semantic segmentation | [131] |
| 16 | 2020 | USA | Aigle_RN + crackForest | custom CNN (encoder +decoder) | Scratch | 48 × 48 | Top | RGB | 142,000 + 84,000 | 0.923 + 0.9533 | semantic segmentation | [132] |
| 17 | 2021 | Iran | private (Iran) | faster RCNN + SSD | Scratch | - | Top | RGB-D | 2085 | 0.97 * | object detection | [126] |
| 18 | 2021 | China | Aigle_RN + cracktree200 + crack500-B | customized U-Net with dense connection and deep supervision module | Scratch | 800 × 800 | Top | RGB | 58 + 1896 + 206 | 0.65 + 0.67 + 0.64 | semantic segmentation | [133] |
| 19 | 2021 | China | crack500-B | custom CNN model | Scratch | 512 × 512 | Top | RGB | 1896 | 0.827 | semantic segmentation | [134] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qureshi, W.S.; Hassan, S.I.; McKeever, S.; Power, D.; Mulry, B.; Feighan, K.; O’Sullivan, D. An Exploration of Recent Intelligent Image Analysis Techniques for Visual Pavement Surface Condition Assessment. Sensors 2022, 22, 9019. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22229019
Qureshi WS, Hassan SI, McKeever S, Power D, Mulry B, Feighan K, O’Sullivan D. An Exploration of Recent Intelligent Image Analysis Techniques for Visual Pavement Surface Condition Assessment. Sensors. 2022; 22(22):9019. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22229019
Chicago/Turabian StyleQureshi, Waqar S., Syed Ibrahim Hassan, Susan McKeever, David Power, Brian Mulry, Kieran Feighan, and Dympna O’Sullivan. 2022. "An Exploration of Recent Intelligent Image Analysis Techniques for Visual Pavement Surface Condition Assessment" Sensors 22, no. 22: 9019. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22229019
APA StyleQureshi, W. S., Hassan, S. I., McKeever, S., Power, D., Mulry, B., Feighan, K., & O’Sullivan, D. (2022). An Exploration of Recent Intelligent Image Analysis Techniques for Visual Pavement Surface Condition Assessment. Sensors, 22(22), 9019. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22229019









