Adaptive High-Resolution Imaging Method Based on Compressive Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theory
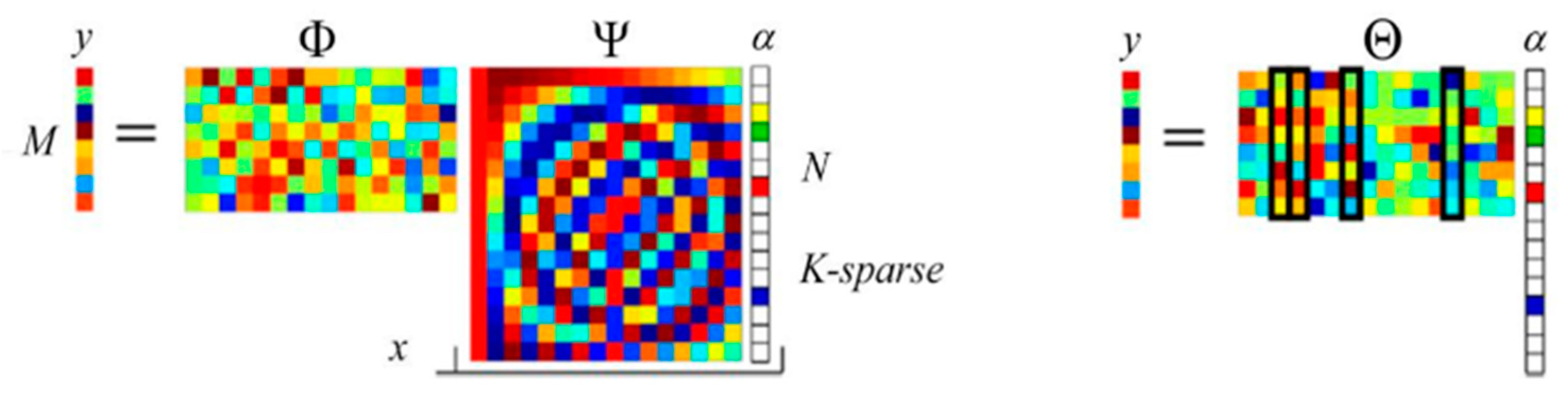
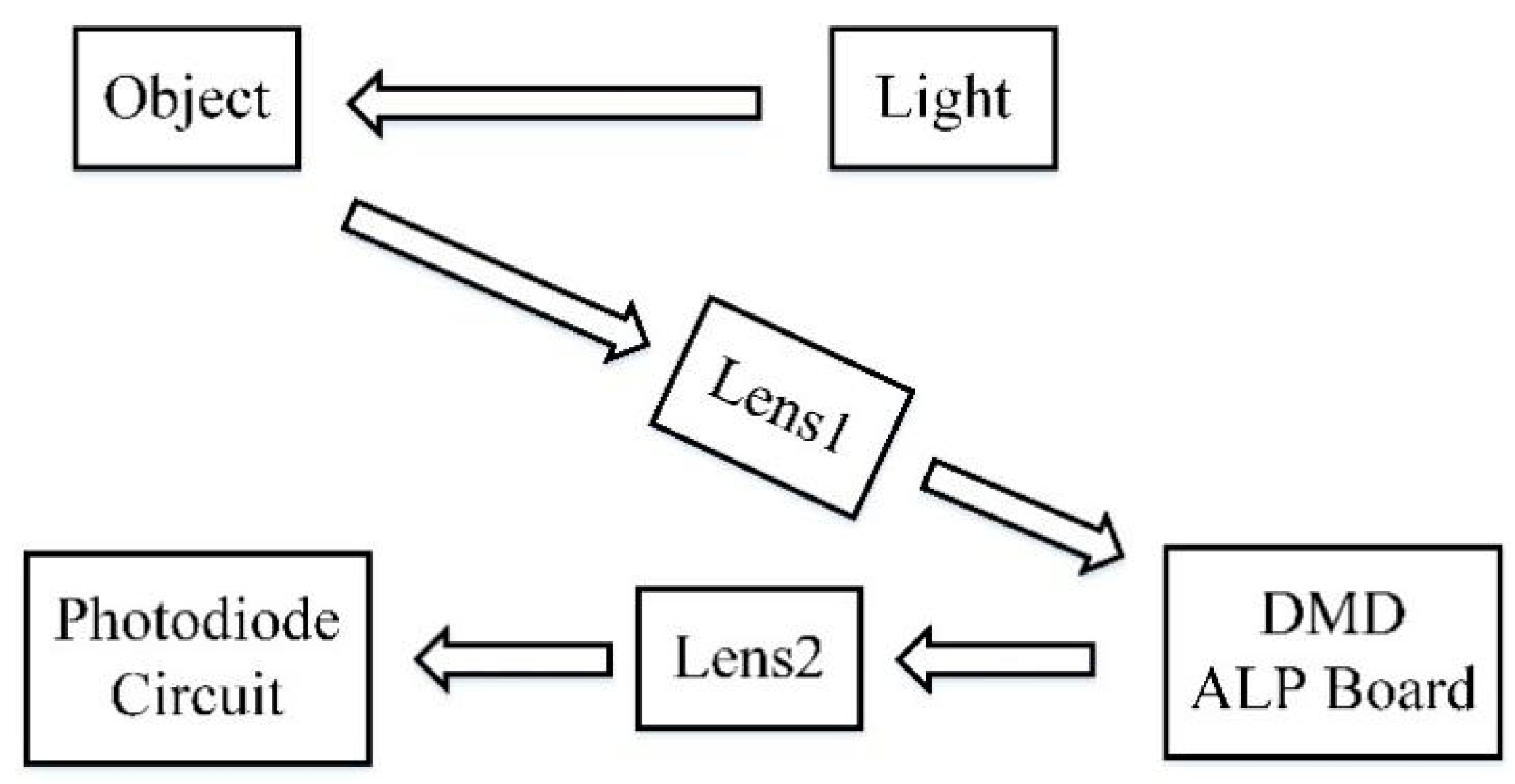
2.1. CS and Single-Pixel Camera
2.2. Problem
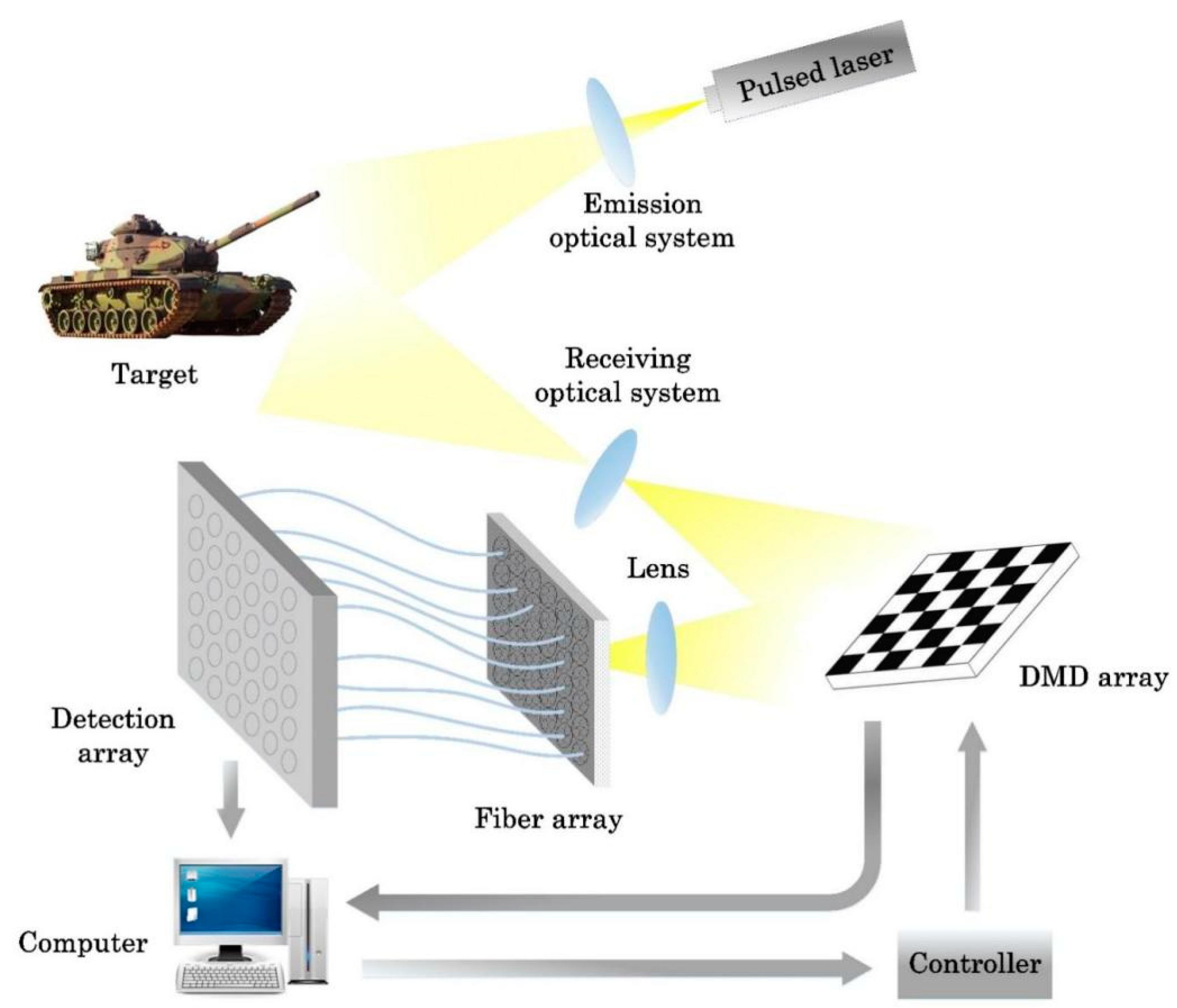
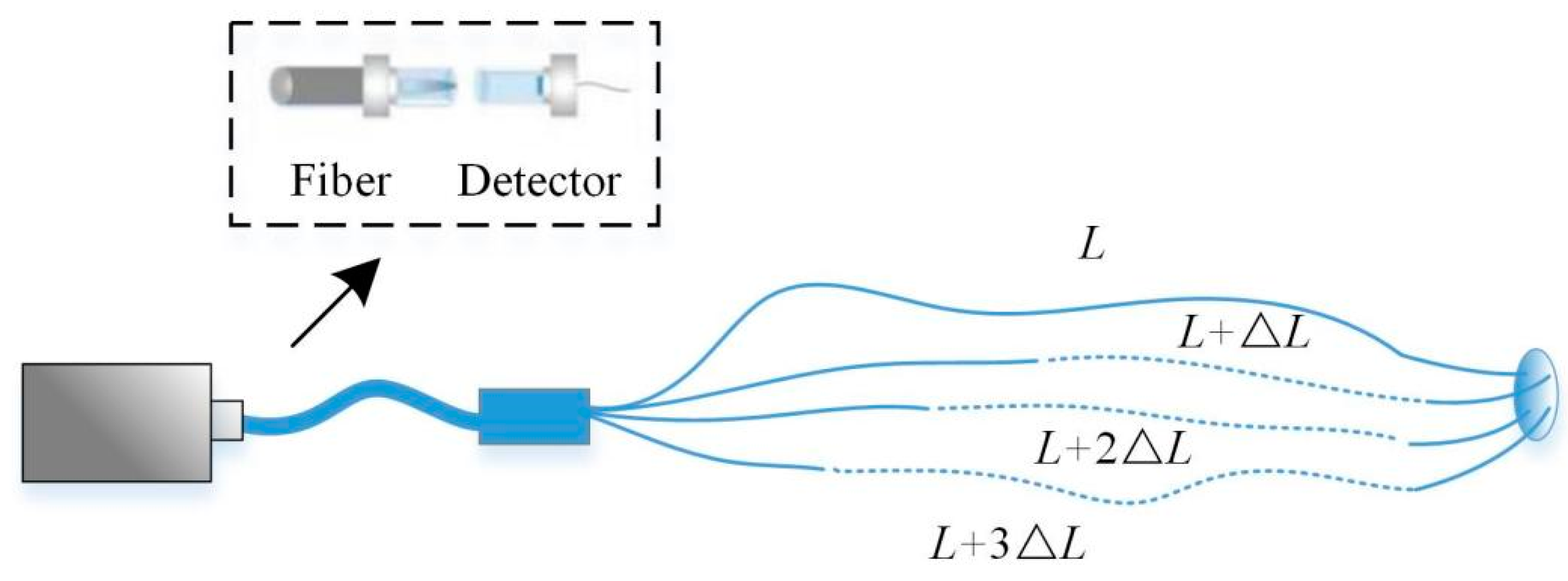
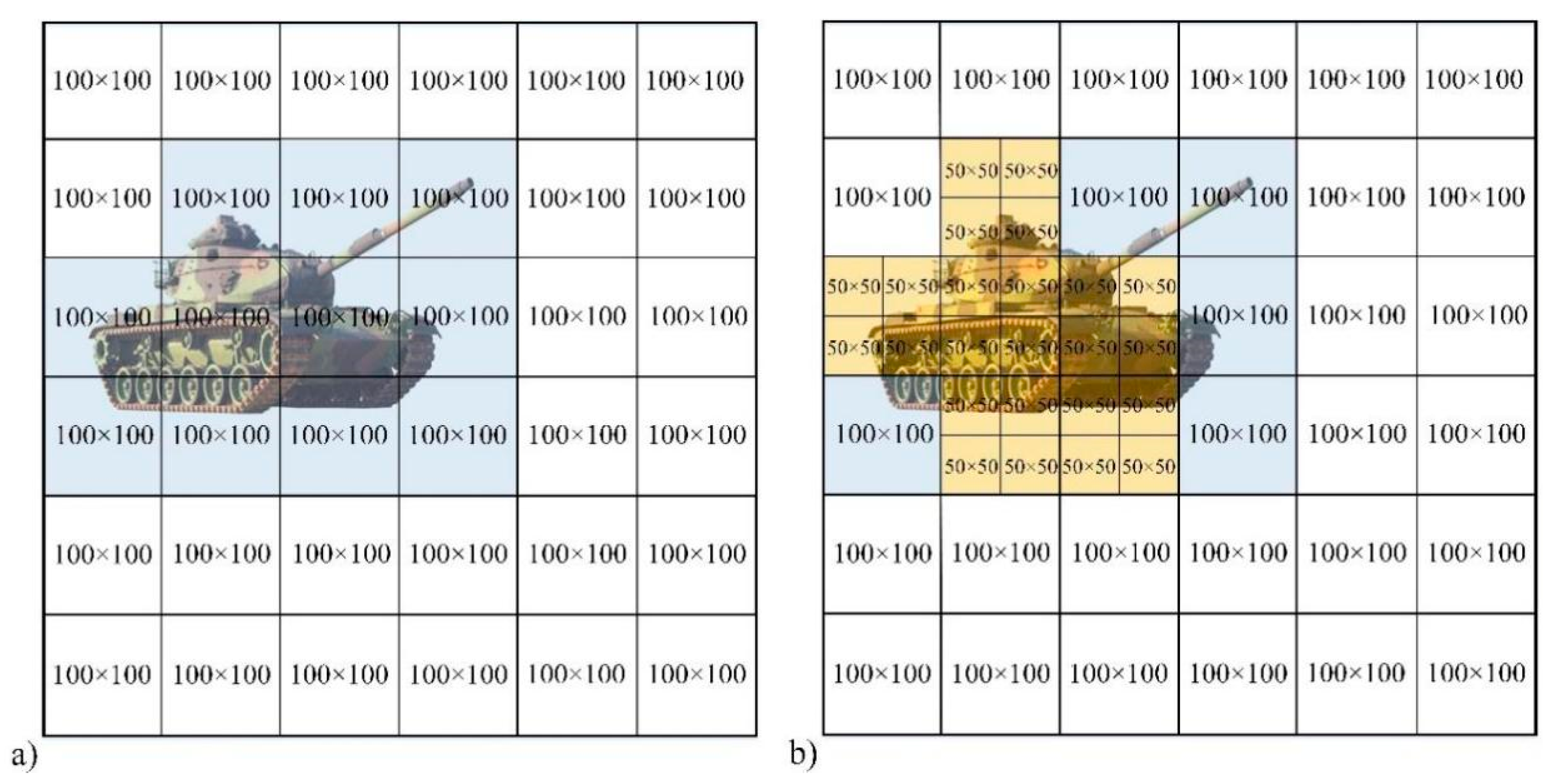
2.3. Proposed System
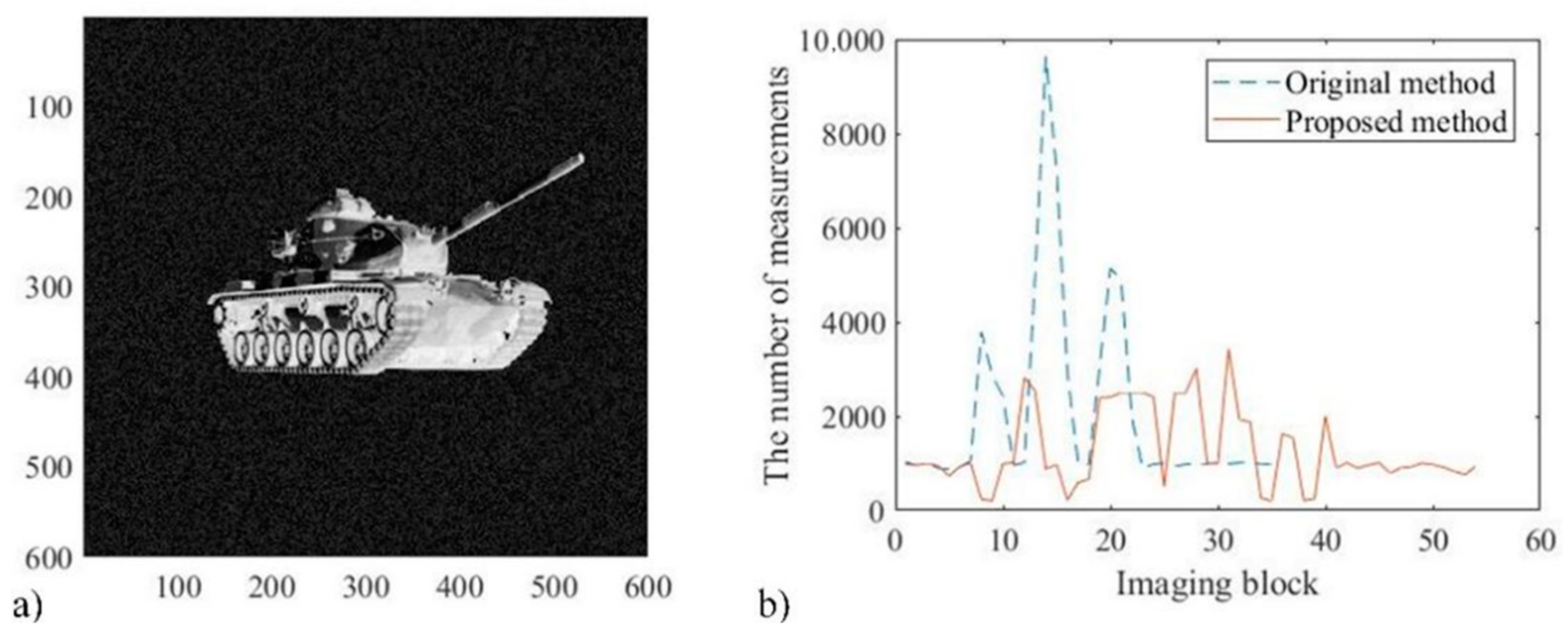
3. Comparative Experiment
4. Threshold Selection
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donoho, D.L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 2006, 52, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candès, E.J.; Tao, T. Near optimal signal recovery from random projections: Universal encoding strategies? IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 2006, 52, 5406–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Candès, E.J. Compressive sampling. Proc. Int. Cong. Math. 2006, 3, 1433–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Baraniuk, R.G. Compressive sensing. IEEE Signal Proc. Mag. 2007, 24, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candès, E.J.; Wakin, M.B. An introduction to compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Proc. Mag. 2008, 25, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, R.M.; Marcia, R.F.; Nichols, J.M. Compressed sensing for practical optical imaging systems: A tutorial. Opt. Eng. 2011, 50, 07260. [Google Scholar]
- MDuarte, F.; Davenport, M.A.; Takbar, D.; Laska, J.N. Single-pixel imaging via compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Proc. Mag. 2008, 25, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lahbib, N.D.; Cherif, M.; Hizem, M.; Bouallegue, R. Channel Estimation for TDD Uplink Massive MIMO Systems Via Compressed Sensing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference, Tangier, Morocco, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 1680–1684. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.F.; Jia, X.S.; Bai, H.J.; Wang, G.L.; Liu, G.Z.; Guo, C.M. A new fault diagnosis method using deep belief network and compressive sensing. J. Vibro Eng. 2020, 22, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takhar, D.; Laska, J.N.; Wakin, M.B.; Duarte, M.F.; Baron, D.; Sarvotham, S.; Kelly, K.F.; Baraniuk, R.G. A new compressive imaging camera architecture using optical-domain compression. Proc. Comput. Imaging IV 2006, 6065, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.W.; Jung, Y.H.; Lee, M.J.; Lee, W.Y. Compressive Sensing-Based SAR Image Reconstruction from Sparse Radar Sensor Data Acquisition in Automotive FMCW Radar System. Sensors 2021, 21, 7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graff, C.G.; Sidky, E.Y. Compressive Sensing in Medical Imaging. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, C23–C44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ke, J.; Alieva, T.; Oktem, F.S.; Silveira, P.E.; Wetzstein, G.; Willomitzer, F. Computational Optical Sensing and Imaging 2021: Introduction to the feature issue. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, COSI1–COSI4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.T.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.P.; Xu, F. Compressed sensing for active non-line-of-sight imaging. Opt. Exp. 2021, 29, 1749–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiguo, X.; Zhisong, P.; Pengqiang, M. Video Compressive sensing reconstruction using unfolded LSTM. Sensors 2022, 22, 7172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.Y.; Han, S.K.; Liu, F.; Zhai, Y.; Xia, W.Z. Research on the high pixels ladar imaging system based on compressive sensing. Opt. Eng. 2019, 58, 013103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Ju, Z.; Zhang, X.; Meng, Z.; Yin, F.; Xu, K. High-speed multimode fiber imaging system based on conditional generative adversarial network. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2021, 19, 081101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.X.; Shen, G.Y.; Li, Z.H.; Wu, E.; Chen, X.L.; Wu, G. Single-photon imaging system with a fiber optic taper. Optoelectron. Lett. 2018, 14, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraniuk, R.; Steeghs, P. Compressive Radar Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Radar Conference, Waltham, MA, USA, 17–20 April 2007; pp. 128–133. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, D.R.; Stephen, C.C. Direct-Detection LADAR Systems; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2009; pp. 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, W.Z.; Han, S.K.; Ullah, N.; Cao, J.Y.; Wang, L.; Cao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, H.Y. Design and modeling of three-dimensional laser imaging system based on streak tube. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| laser power (J) | 1 |
| fiber diameter (μm) | 125 |
| atmospheric transmission | 1 |
| laser dispersion angular | 0.012 |
| detector dark current (A) | 10−9 |
| CCD pixels | 800 × 800 |
| optics transmission | 1 |
| detector quantum efficiency | 0.75 |
| width of laser pulse (ns) | 6 |
| background power (w/m2) | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Duan, X.; Cao, J. Adaptive High-Resolution Imaging Method Based on Compressive Sensing. Sensors 2022, 22, 8848. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228848
Wang Z, Gao Y, Duan X, Cao J. Adaptive High-Resolution Imaging Method Based on Compressive Sensing. Sensors. 2022; 22(22):8848. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228848
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zijiao, Yufeng Gao, Xiusheng Duan, and Jingya Cao. 2022. "Adaptive High-Resolution Imaging Method Based on Compressive Sensing" Sensors 22, no. 22: 8848. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228848
APA StyleWang, Z., Gao, Y., Duan, X., & Cao, J. (2022). Adaptive High-Resolution Imaging Method Based on Compressive Sensing. Sensors, 22(22), 8848. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228848




