Fast THz-TDS Reflection Imaging with ECOPS—Point-by-Point versus Line-by-Line Scanning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. ECOPS-Based Scanner
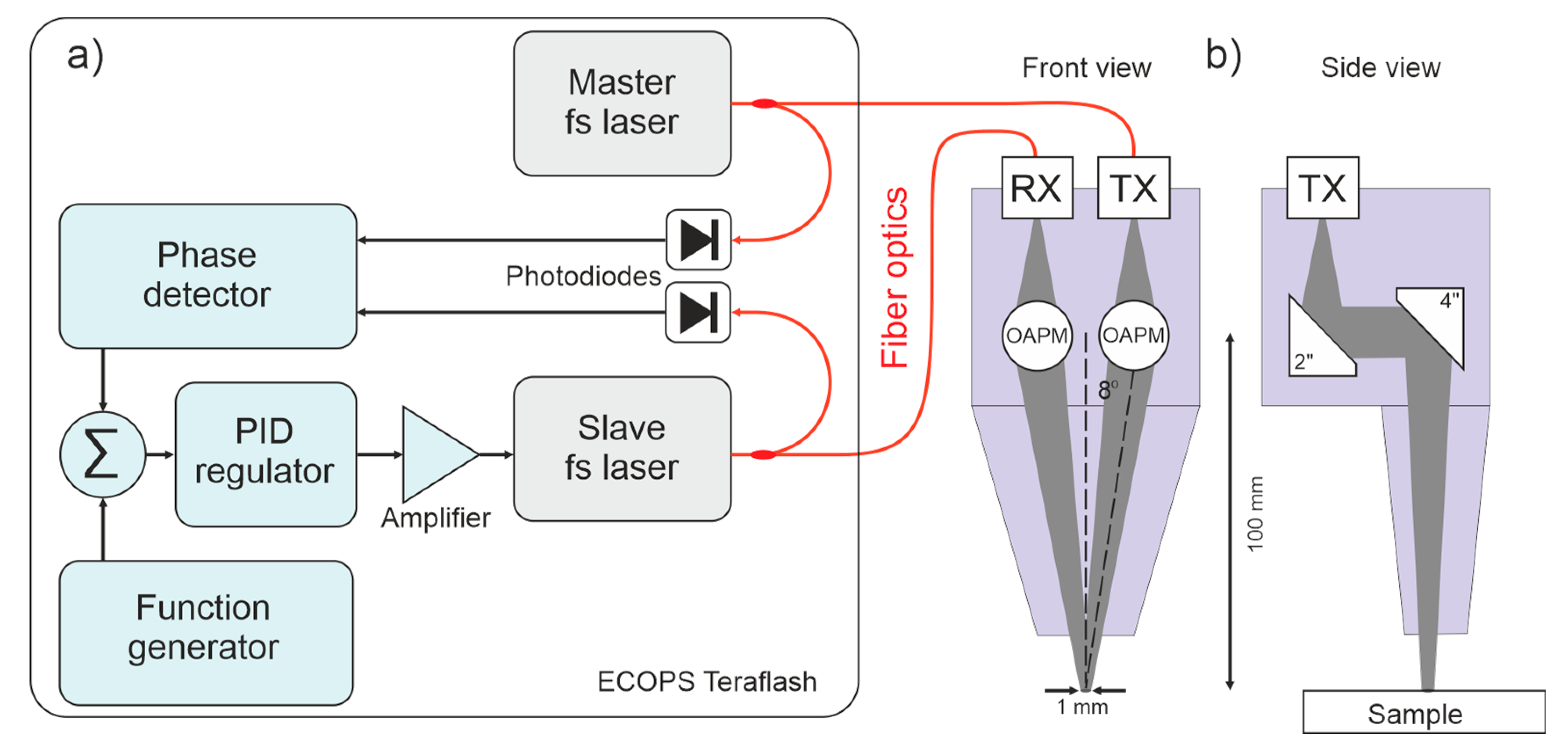
2.1. ECOPS Platform
2.2. Jitter Correction
2.3. Parameters of the Waveforms
2.4. Gantry System
2.5. Point-by-Point Scanning Scheme
2.6. Line-by-Line Scanning Scheme
3. Verification of the Synchronization
4. Scanning of the Glass Composite Sample
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neu, J.; Schmuttenmaer, C.A. Tutorial: An Introduction to Terahertz Time Domain Spectroscopy (THz-TDS). J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 124, 231101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hangyo, M.; Tani, M.; Nagashima, T. Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy of Solids: A Review. Int. J. Infrared Millim. Waves 2005, 26, 1661–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieweg, N.; Rettich, F.; Deninger, A.; Roehle, H.; Dietz, R.; Gobel, T. A Time-Domain Terahertz Spectrometer with 90 DB Dynamic Range. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves, IRMMW-THz, Tucson, AZ, USA, 14–19 September 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Camus, E.; Koch, M.; Mittleman, D.M. Recent Advances in Terahertz Imaging: 1999 to 2021. Appl. Phys. B 2021, 128, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valušis, G.; Lisauskas, A.; Yuan, H.; Knap, W.; Roskos, H.G. Roadmap of Terahertz Imaging 2021. Sensors 2021, 21, 4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoik, C.; Bohn, M.; Blackshire, J. Nondestructive Evaluation of Aircraft Composites Using Reflective Terahertz Time Domain Spectroscopy. NDT E Int. 2010, 43, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.B.; Nuss, M.C. Imaging with Terahertz Waves. Opt. Lett. 1995, 20, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palka, N.; Miedzinska, D. Detailed Non-Destructive Evaluation of UHMWPE Composites in the Terahertz Range. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2014, 46, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellrich, F.; Bauer, M.; Schreiner, N.; Keil, A.; Pfeiffer, T.; Klier, J.; Weber, S.; Jonuscheit, J.; Friederich, F.; Molter, D. Terahertz Quality Inspection for Automotive and Aviation Industries. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2020, 41, 470–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ospald, F.; Zouaghi, W.; Beigang, R.; Matheis, C.; Jonuscheit, J.; Recur, B.; Guillet, J.-P.; Mounaix, P.; Vleugels, W.; Bosom, P.V.; et al. Aeronautics Composite Material Inspection with a Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy System. Opt. Eng. 2013, 53, 031208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palka, N.; Krimi, S.; Ospald, F.; Miedzinska, D.; Gieleta, R.; Malek, M.; Beigang, R. Precise Determination of Thicknesses of Multilayer Polyethylene Composite Materials by Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2015, 36, 578–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yee, D.-S.; Kim, Y. High-Speed Terahertz Time-Domain Spectroscopy Based on Electronically Controlled Optical Sampling. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 3715–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yahyapour, M.; Jahn, A.; Dutzi, K.; Puppe, T.; Leisching, P.; Schmauss, B.; Vieweg, N.; Deninger, A. Fastest Thickness Measurements with a Terahertz Time-Domain System Based on Electronically Controlled Optical Sampling. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molter, D.; Ellenberger, K.S.; Klier, J.; Duran, S.; Jonuscheit, J.; von Freymann, G.; Vieweg, N.; Deninger, A. Kilohertz Pixel-Rate Multilayer Terahertz Imaging of Subwavelength Coatings. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosodeder, P.; Hubmer, S.; Ploier, A.; Ploier, A.; Ramlau, R.; Ramlau, R.; van Frank, S.; Rankl, C. Phase-Contrast THz-CT for Non-Destructive Testing. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 15711–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.Y.; Yee, D.-S.; Yang, H.-S.; Yahng, J.S.; Ye, J.C.; Jin, K.H. High-Speed Terahertz Reflection Three-Dimensional Imaging Using Beam Steering. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 5027–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- TeraFlash Smart. TOPTICA Photonics AG. Available online: https://www.toptica.com/products/terahertz-systems/time-domain/teraflash-smart (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Dietz, R.J.B.; Globisch, B.; Gerhard, M.; Velauthapillai, A.; Stanze, D.; Roehle, H.; Koch, M.; Göbel, T.; Schell, M. 64 ΜW Pulsed Terahertz Emission from Growth Optimized InGaAs/InAlAs Heterostructures with Separated Photoconductive and Trapping Regions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 061103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartorius, B.; Stanze, D.; Gerhard, M.; Koch, M.; Schell, M.; Dietz, R.J.B. THz Generation at 1.55 Μm Excitation: Six-Fold Increase in THz Conversion Efficiency by Separated Photoconductive and Trapping Regions. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 25911–25917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Globisch, B.; Dietz, R.J.B.; Stanze, D.; Göbel, T.; Schell, M. Carrier Dynamics in Beryllium Doped Low-Temperature-Grown InGaAs/InAlAs. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 172103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naftaly, M.; Dudley, R. Methodologies for Determining the Dynamic Ranges and Signal-to-Noise Ratios of Terahertz Time-Domain Spectrometers. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 1213–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Scanning Scheme | Measurement Time Total [min.] | Measurement Time per Line [s.] |
|---|---|---|
| Point-by-point without averaging | 208.9 | 136.3 |
| Point-by-point averaging 100 | 306.6 | 199.7 |
| Line-by-line without averaging | 2.2 | 1.4 |
| Line-by-line averaging 100 | 128.2 | 83.6 |
| Mean Distances between the Centers of Adjacent Circles | Distances between the Extreme Points | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scanning Scheme | Horizontal [mm] | Vertical [mm] | Top Line [mm] | Bottom Line [mm] |
| Point-by-point without averaging | 25.01 ± 0.11 | 25.07 ± 0.17 | 475.19 | 475.10 |
| Point-by-point averaging 100 | 25.01 ± 0.09 | 25.02 ± 0.12 | 475.04 | 475.20 |
| Line-by-line without averaging | 25.00 ± 0.12 | 25.06 ± 0.14 | 475.07 | 474.98 |
| Line-by-line averaging 100 | 25.00 ± 0.10 | 25.00 ± 0.11 | 475.10 | 475.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pałka, N.; Maciejewski, M.; Kamiński, K.; Piszczek, M.; Zagrajek, P.; Czerwińska, E.; Walczakowski, M.; Dragan, K.; Synaszko, P.; Świderski, W. Fast THz-TDS Reflection Imaging with ECOPS—Point-by-Point versus Line-by-Line Scanning. Sensors 2022, 22, 8813. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228813
Pałka N, Maciejewski M, Kamiński K, Piszczek M, Zagrajek P, Czerwińska E, Walczakowski M, Dragan K, Synaszko P, Świderski W. Fast THz-TDS Reflection Imaging with ECOPS—Point-by-Point versus Line-by-Line Scanning. Sensors. 2022; 22(22):8813. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228813
Chicago/Turabian StylePałka, Norbert, Marcin Maciejewski, Kamil Kamiński, Marek Piszczek, Przemysław Zagrajek, Elżbieta Czerwińska, Michał Walczakowski, Krzysztof Dragan, Piotr Synaszko, and Waldemar Świderski. 2022. "Fast THz-TDS Reflection Imaging with ECOPS—Point-by-Point versus Line-by-Line Scanning" Sensors 22, no. 22: 8813. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228813
APA StylePałka, N., Maciejewski, M., Kamiński, K., Piszczek, M., Zagrajek, P., Czerwińska, E., Walczakowski, M., Dragan, K., Synaszko, P., & Świderski, W. (2022). Fast THz-TDS Reflection Imaging with ECOPS—Point-by-Point versus Line-by-Line Scanning. Sensors, 22(22), 8813. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228813







