3D Visible Light-Based Indoor Positioning System Using Two-Stage Neural Network (TSNN) and Received Intensity Selective Enhancement (RISE) to Alleviate Light Non-Overlap Zones
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. TSNN 3D VLIP Experiment and Algorithms
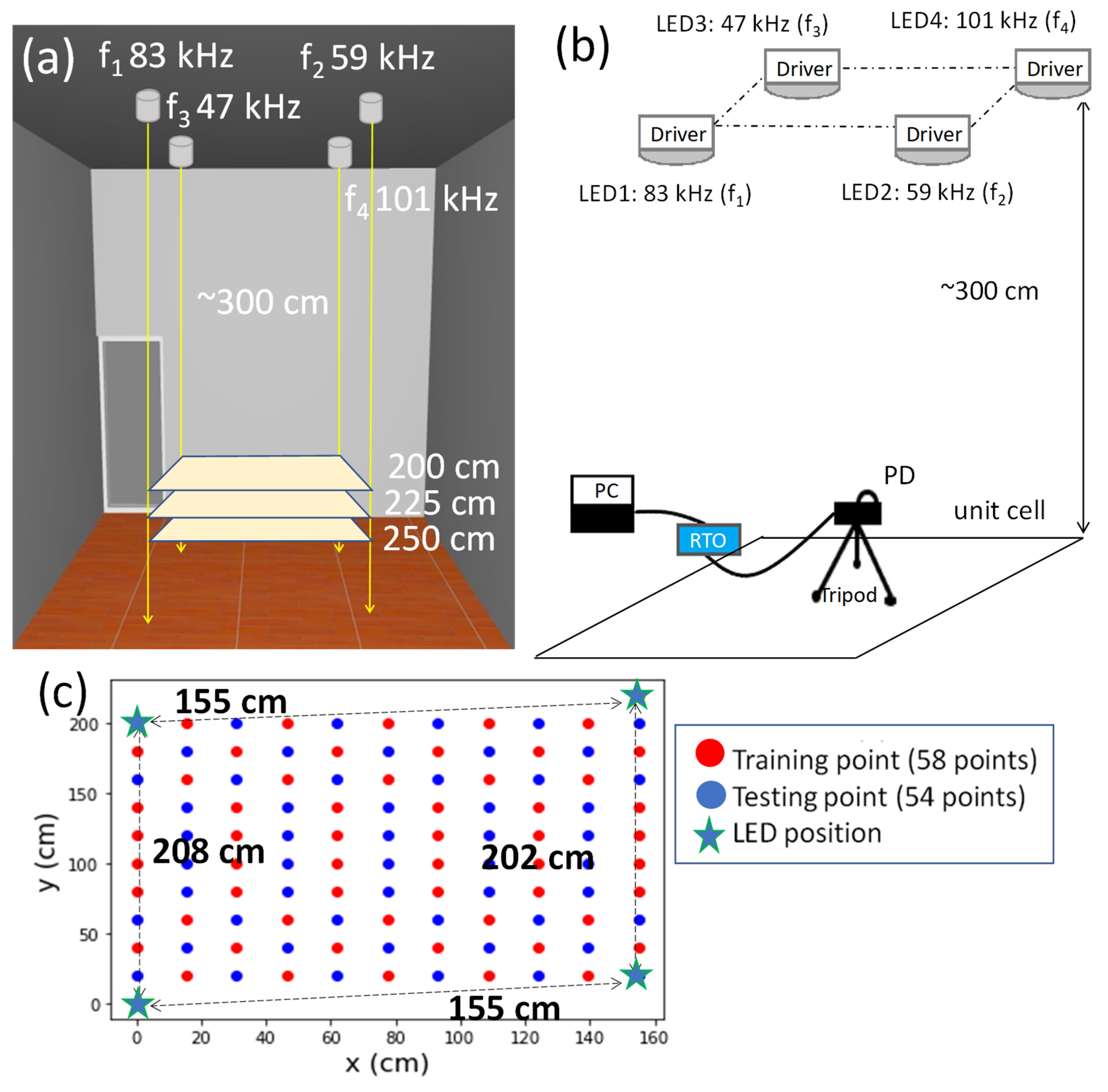
2.1. Experimental Setup
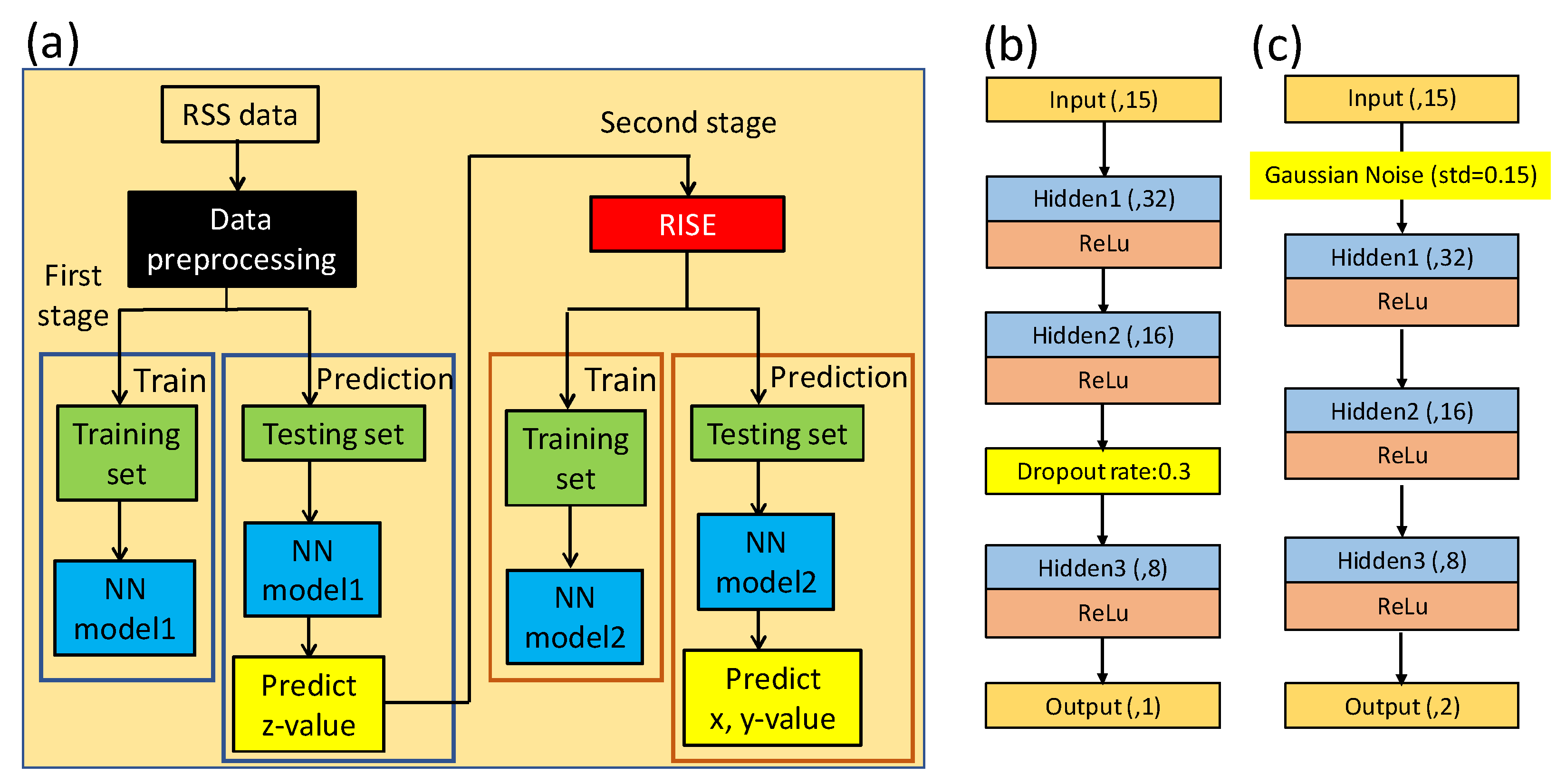
2.2. One Stage NN Model
2.3. Two Stage NN (TSNN) Model
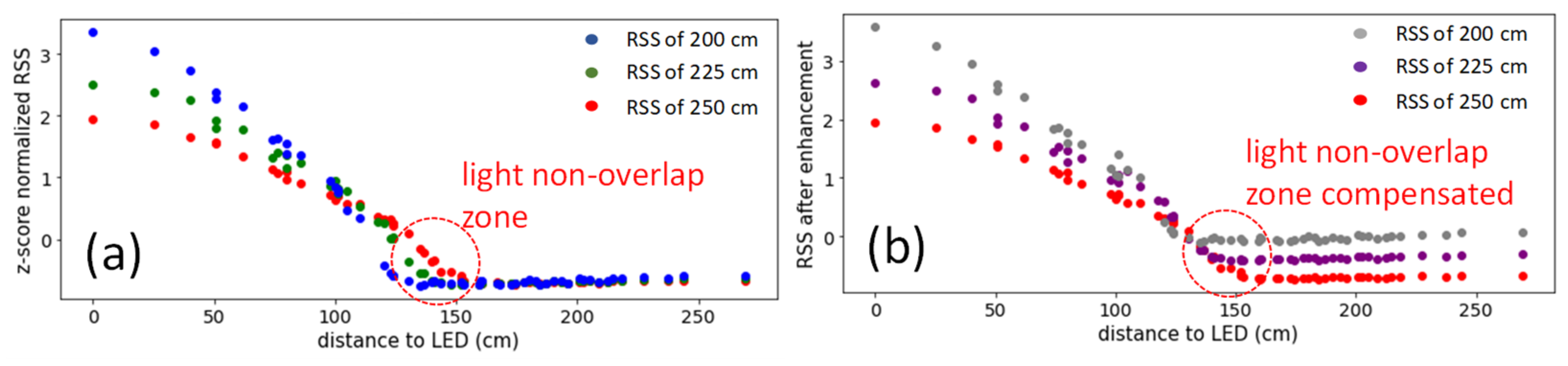
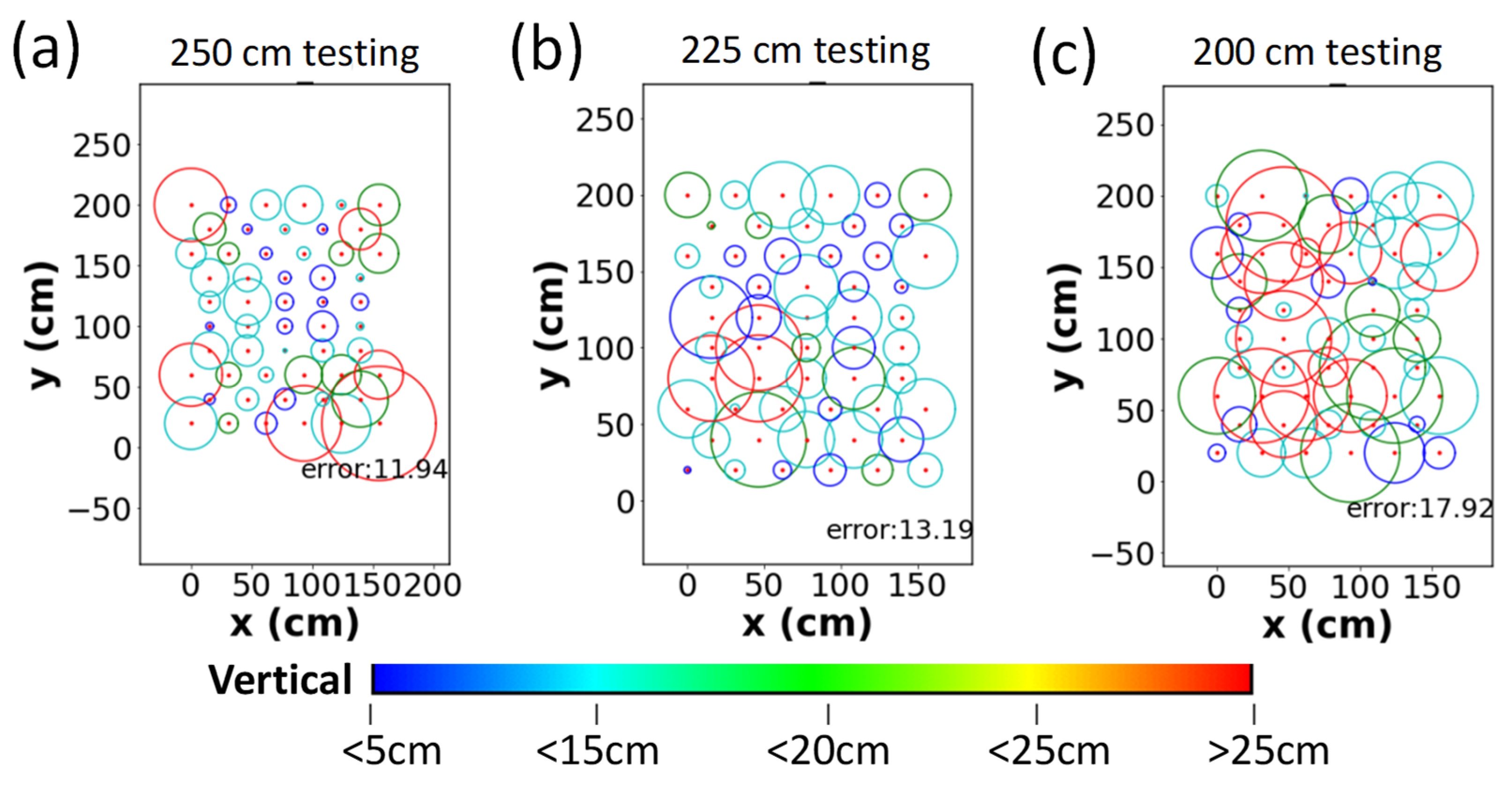
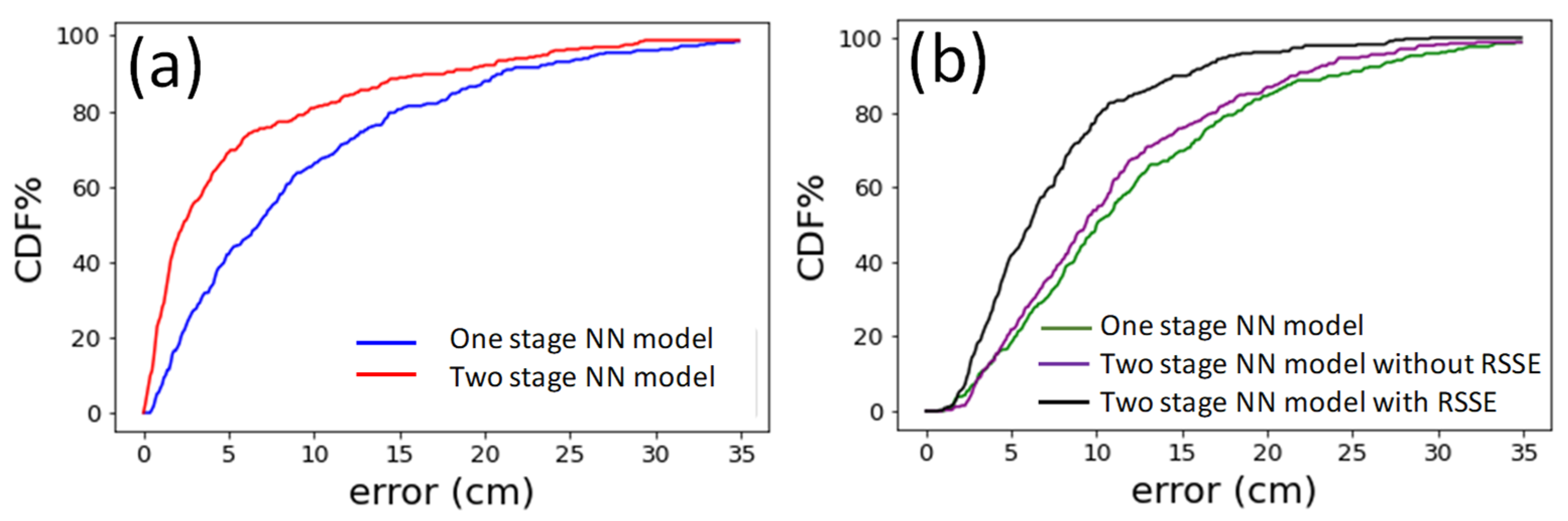
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Minh, H.L.; O’Brien, D.; Faulkner, G.; Zeng, L.; Lee, K.; Jung, D.; Oh, Y.J.; Won, E.T. 100-Mb/s NRZ visible light communications using a post-equalized white LED. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2009, 21, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, C.W.; Yeh, C.H.; Liu, Y.; Lai, Y.; Wei, L.Y.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, G.H.; Liao, X.L.; Lin, K.H. Enabling techniques for optical wireless communication systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 Optical Fiber Communications Conference and Exhibition (OFC), San Diego, CA, USA, 8–12 March 2020. paper M2F.1. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, C.T.; Cheng, C.H.; Kuo, H.C.; Lin, G.R. Toward high-speed visible laser lighting based optical wireless communications. Prog. Quant. Electron. 2019, 67, 100225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, C.L.; Lu, H.H.; Li, C.Y.; Cheng, C.J.; Peng, P.C.; Ho, W.J. 20-Gbps optical LiFi transport system. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 3276–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.; Zhang, M.; Ghassemlooy, Z.; Minh, H.L.; Tsai, H.M.; Tang, X.; Png, L.C.; Han, D. Experimental demonstration of RGB LED-based optical camera communications. IEEE Photon. J. 2015, 7, 7904212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Li, C.Y.; Lu, H.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, J.H.; Wan, Z.W.; Cheng, C.J. A 100-Gb/s multiple-input multiple-output visible laser light communication system. J. Lightw. Technol. 2014, 32, 4723–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Alkhazragi, O.; Sun, X.; Guo, Y.; Ng, T.K.; Ooi, B.S. Laser-based visible light communications and underwater wireless optical communications: A device perspective. In Proceedings of the Novel In-Plane Semiconductor Lasers XVIII, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2–7 February 2019; Volume 10939, p. 109390E. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, N.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, Y.; Hu, F. Visible light communication in 6G: Advances, challenges, and prospects. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2020, 15, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Guan, W.; Wu, Y.; Fang, L.; Cai, Y. The LED-ID detection and recognition method based on visible light positioning using proximity method. IEEE Photon. J. 2018, 10, 7902116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.Q.; Sekercioglu, Y.A.; Neild, A.; Armstrong, J. Position accuracy of time-of-arrival based ranging using visible light with application in indoor localization systems. J. Lightw. Technol. 2013, 31, 3302–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.F.; Zhang, S.; Chen, C.; Alphones, A.; Zhong, W.D. Demonstration of a low-complexity indoor visible light positioning system using an enhanced TDOA scheme. IEEE Photon. J. 2018, 10, 7905110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cincotta, S.; Neild, A.; He, C.; Armstrong, J. Visible light positioning using an aperture and a quadrant photodiode. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Singapore, 4–8 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, C.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Liu, Y.; Chow, C.W.; Yeh, C.H.; Hsu, K.L.; Lin, D.C.; Liao, X.L.; Lin, K.H.; Chen, Y.Y. Angle-of-arrival (AOA) visible light positioning (VLIP) system using solar cells with third-order regression and ridge regression algorithms. IEEE Photon. J. 2020, 12, 7902605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; You, X.; Wei, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Chen, J.; Fu, H.Y.; Yu, C. Asynchronous visible light positioning based on orthogonal pseudo-random codes. In Proceedings of the 26th Optoelectronics and Communications Conference, Hong Kong, China, 3–7 July 2021. paper S3B.3. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, D.R.; Yang, S.H.; Son, Y.H.; Han, S.K. An indoor visible light communication positioning system using a RF carrier allocation technique. J. Lightw. Technol. 2013, 31, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.W.; Wu, J.T.; Wang, H.Y.; Chow, C.W.; Lee, C.H.; Chu, M.T.; Yeh, C.H. Visible light positioning and lighting based on identity positioning and RF carrier allocation technique using a solar cell receiver. IEEE Photon. J. 2016, 8, 7905507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Hsu, K.L.; Liu, Y.; Hong, C.Y.; Chow, C.W.; Yeh, C.H.; Liao, X.L.; Lin, K.H.; Chen, Y.Y. Using linear interpolation to reduce the training samples for regression based visible light positioning system. IEEE Photon. J. 2020, 12, 7901305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.C.; Chow, C.W.; Peng, C.W.; Hung, T.Y.; Chang, Y.H.; Song, S.H.; Lin, Y.S.; Liu, Y.; Lin, K.H. Positioning unit cell model duplication with residual concatenation neural network (RCNN) and transfer learning for visible light positioning (VLP). J. Lightw. Technol. 2021, 39, 6366–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Wu, Y.; Wen, S.; Chen, H.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z. A novel three-dimensional indoor positioning algorithm design based on visible light communication. Opt. Commun. 2017, 392, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Lau, V.; Chen, Q.; Cao, Y. Simultaneous positioning and orientating for visible light communications: Algorithm design and performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Vehicular Technol. 2018, 67, 11790–11804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plets, D.; Almadani, Y.; Bastiaens, S.; Ijaz, M.; Martens, L.; Joseph, W. Efficient 3D trilateration algorithm for visible light positioning. J. Opt. 2019, 21, 05LT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plets, D.; Bastiaens, S.; Ijaz, M.; Almadani, Y.; Martens, L.; Raes, W.; Stevens, N.; Joseph, W. Three-dimensional visible light positioning: An experimental assessment of the importance of the LEDs’ locations. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Pisa, Italy, 30 September 2019–3 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Du, P.; Chen, C.; Zhong, W.-D.; Alphones, A. Robust 3D indoor VLIP system based on ANN using hybrid RSS/PDOA. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 47769–47780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Zhang, S.; Chen, C.; Yang, H.; Zhong, W.D.; Zhang, R.; Alphones, A.; Yang, Y. Experimental demonstration of 3D visible light positioning using received signal strength with low-complexity trilateration assisted by deep learning technique. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 93986–93997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Hsu, C.W.; Zhou, Q.; Tang, M.; Fu, S.; Liu, D.; Deng, L.; Chang, G.K. Demonstration of high precision 3D indoor positioning system based on two-layer ANN machine learning technique. In Proceedings of the 2019 Optical Fiber Communications Conference and Exhibition (OFC), San Diego, CA, USA, 3–7 March 2019. Paper Th3I2. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.C.; Chow, C.W.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Y.S.; Hong, C.Y.; Lin, D.C.; Song, S.H.; Yeh, C.H. Received-signal-strength (RSS) based 3D visible-light-positioning (VLIP) system using kernel ridge regression machine learning algorithm with sigmoid function data preprocessing method. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 214269–214281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, F.; Baghersalimi, G.; Ghassemlooy, Z. Effect of transmitter and receiver parameters on the output signal to noise ratio in visible light communications. In Proceedings of the 2017 Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Tehran, Iran, 2–4 May 2017; pp. 2111–2116. [Google Scholar]







| Year | Scheme [Ref.] | 2D/ 3D | Coverage (m3) | Accuracy | Light Non-Overlap Solution | Sim./ Exp’t |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | RSS/CDMA [19] | 3D | 3 × 3 × 4 | 3.18 cm (horizontal); 7.06 cm (vertical) | --- | Exp’t |
| 2018 | RSS/PASS [20] | 3D | 9 × 9 × 4 | 10 cm | --- | Sim. |
| 2019 | RSS/Trilateration + NLLS [21] | 3D | 5 × 5 × 5 | 5.8 cm | --- | Sim. |
| 2019 | RSS/Trilateration + NLLS [22] | 3D | 4 × 4 × 5 | 12.7 cm | --- | Exp’t |
| 2019 | RSS/ANN + PDOA [23] | 3D | 4 × 4 × 2.5 | 12 cm | --- | Sim. |
| 2019 | RSS/DNN [24] | 3D | 1.2 × 1.2 × 2 | 11.93 cm | --- | Exp’t |
| 2019 | RSS/ANN [25] | 3D | 1/2 × 0.9 × 1 × 0.4 | 1 cm | --- | Exp’t |
| 2020 | RSS/KRR [26] | 3D | 1/2 × 0.5 × 0.5 × 1.5 | 1.96 cm (horizontal); 2.16 cm (vertical) | --- | Exp’t |
| This work | RSS/TSNN + RISE | 3D | 2 × 1.5 × 3 | 8.91 cm (horizontal); 8.8 cm (vertical) | Yes | Exp’t |
| Schemes | Directions | Train (Mean) (cm) | Test (Mean, Std.) (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| One stage NN | z-direction | 9.02 | 11.39, 9.10 |
| xy-direction | 11.48 | 12.79, 7.99 | |
| TSNN w/o RISE | z-direction | 2.98 | 8.80, 9.90 |
| xy-direction | 9.72 | 12.56, 8.30 | |
| TSNN w/ RISE | z-direction | 2.98 | 8.80, 9.90 |
| xy-direction | 6.1 | 8.91, 5.81 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, L.-S.; Chow, C.-W.; Liu, Y.; Yeh, C.-H. 3D Visible Light-Based Indoor Positioning System Using Two-Stage Neural Network (TSNN) and Received Intensity Selective Enhancement (RISE) to Alleviate Light Non-Overlap Zones. Sensors 2022, 22, 8817. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228817
Hsu L-S, Chow C-W, Liu Y, Yeh C-H. 3D Visible Light-Based Indoor Positioning System Using Two-Stage Neural Network (TSNN) and Received Intensity Selective Enhancement (RISE) to Alleviate Light Non-Overlap Zones. Sensors. 2022; 22(22):8817. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228817
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Li-Sheng, Chi-Wai Chow, Yang Liu, and Chien-Hung Yeh. 2022. "3D Visible Light-Based Indoor Positioning System Using Two-Stage Neural Network (TSNN) and Received Intensity Selective Enhancement (RISE) to Alleviate Light Non-Overlap Zones" Sensors 22, no. 22: 8817. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228817
APA StyleHsu, L.-S., Chow, C.-W., Liu, Y., & Yeh, C.-H. (2022). 3D Visible Light-Based Indoor Positioning System Using Two-Stage Neural Network (TSNN) and Received Intensity Selective Enhancement (RISE) to Alleviate Light Non-Overlap Zones. Sensors, 22(22), 8817. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228817








