Affective Recommender System for Pet Social Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
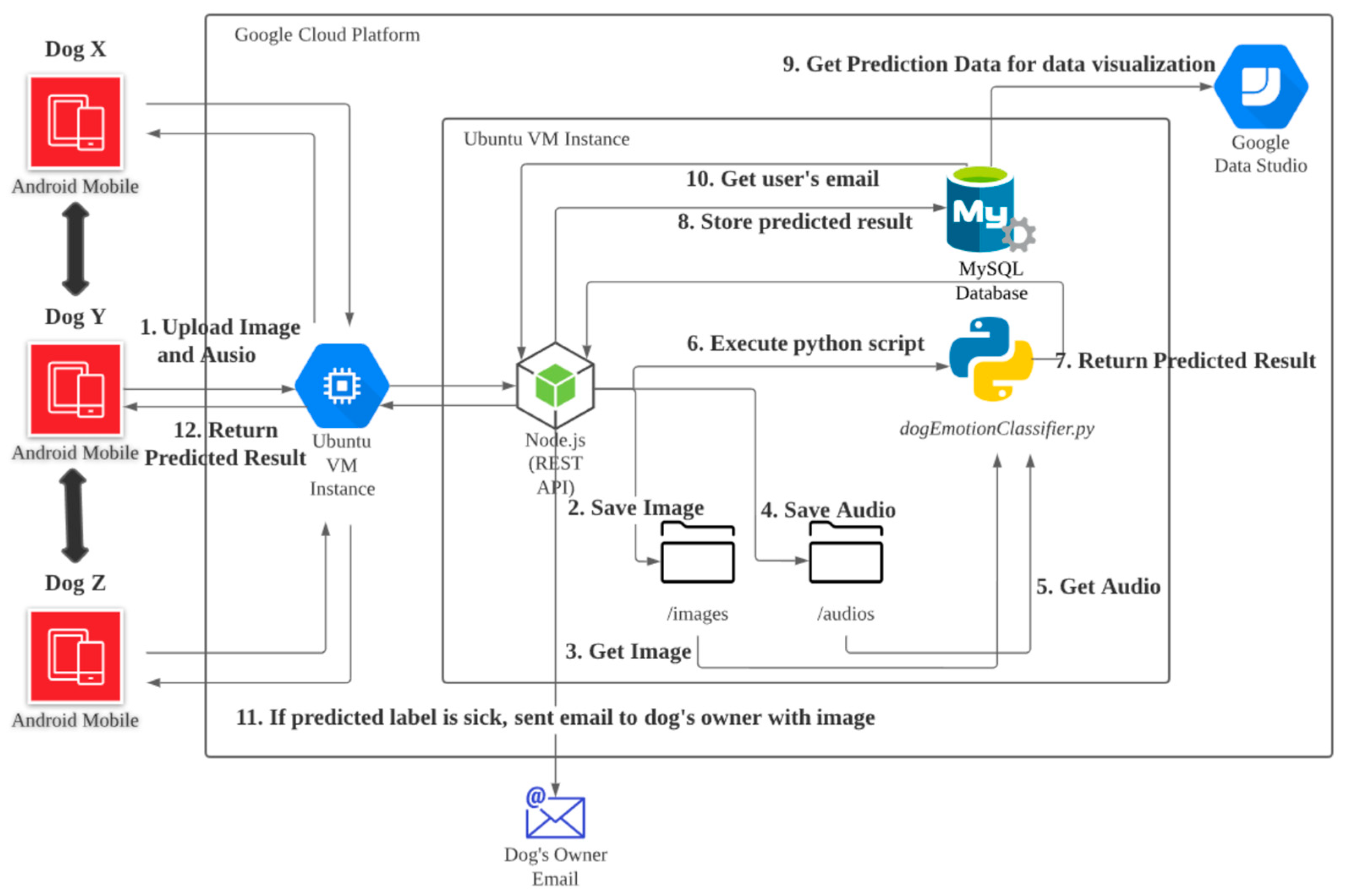
3. Dogs’ Social Network Architecture
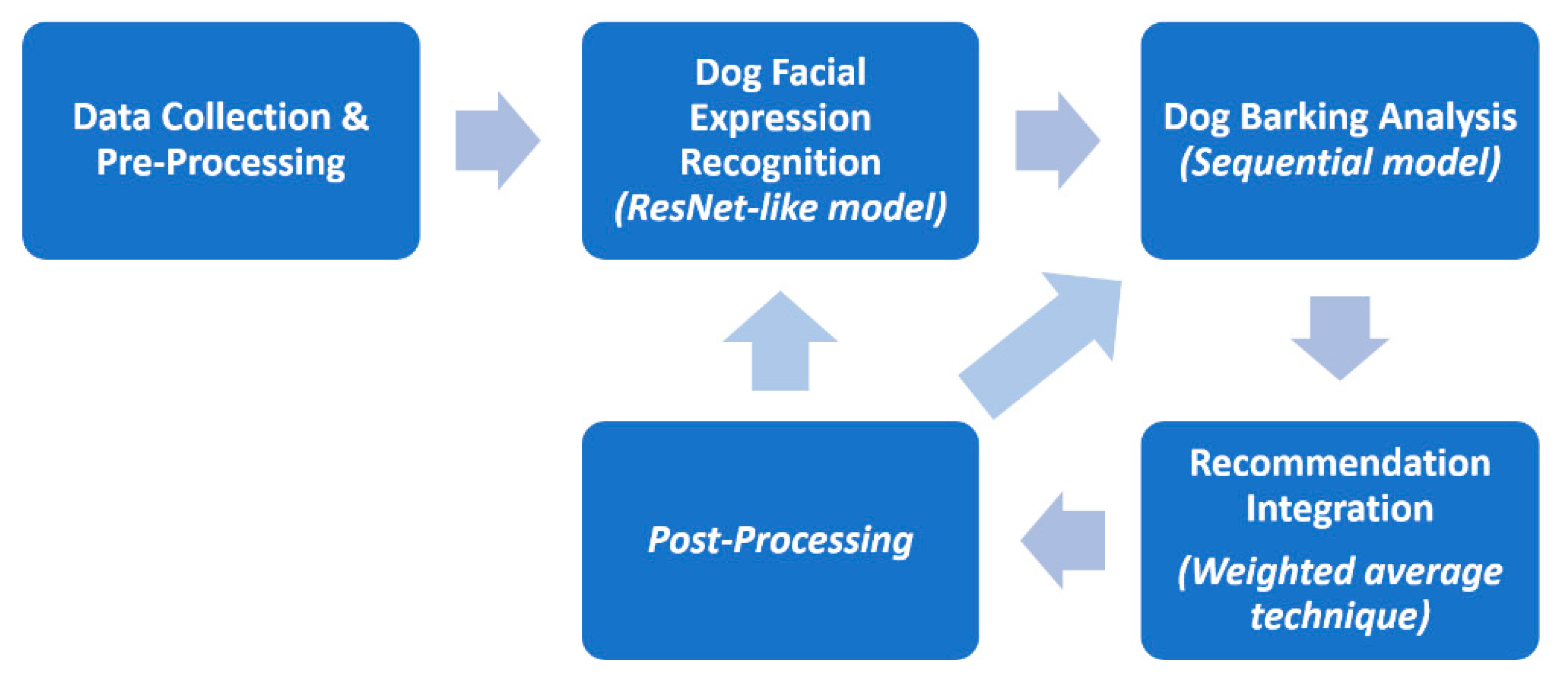
4. Affective Recommender Framework
4.1. Data Collection and Pre-Processing
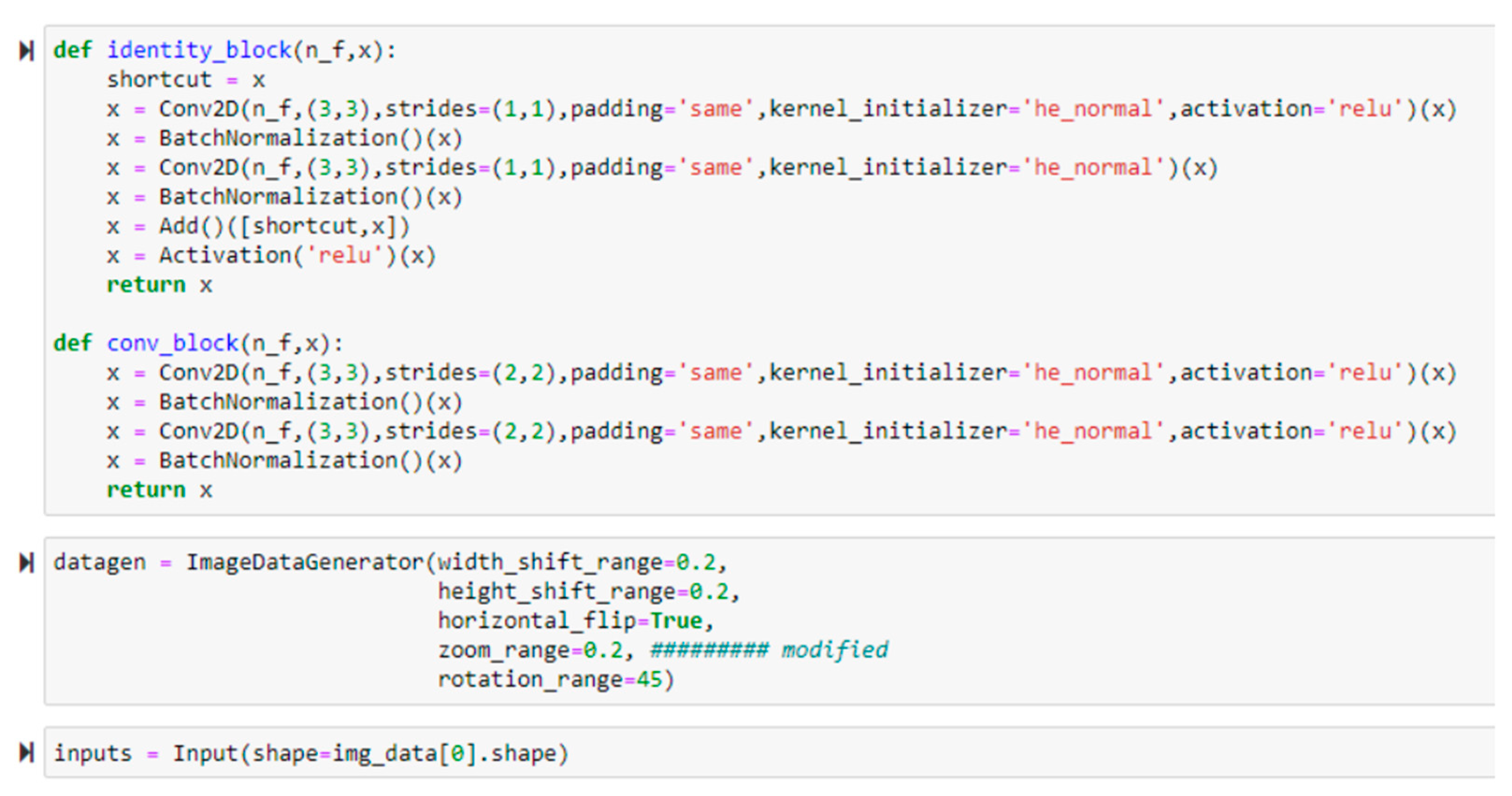
4.2. Dogs’ Facial Expression Recognition
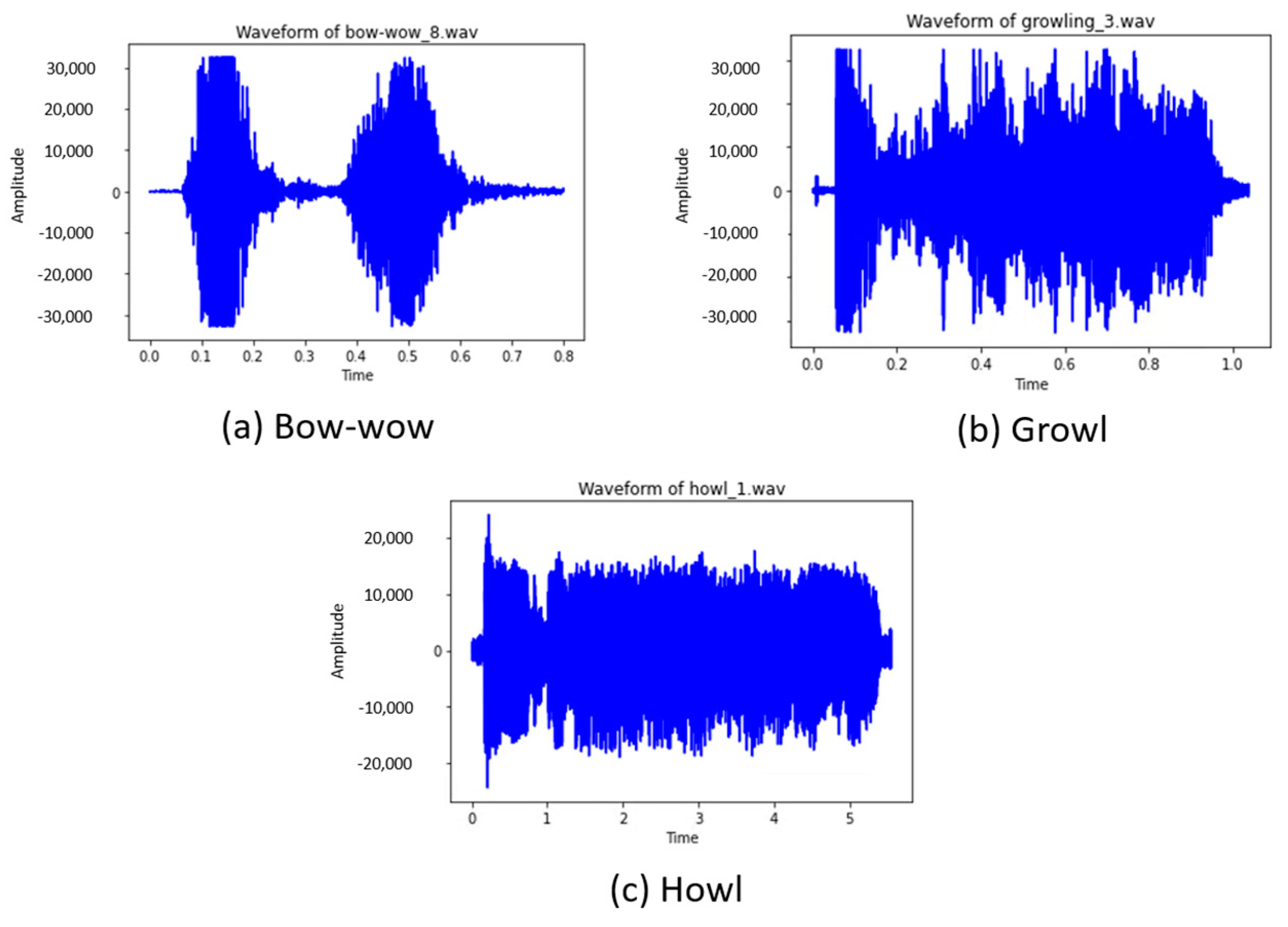
4.3. Dog Barking Analysis
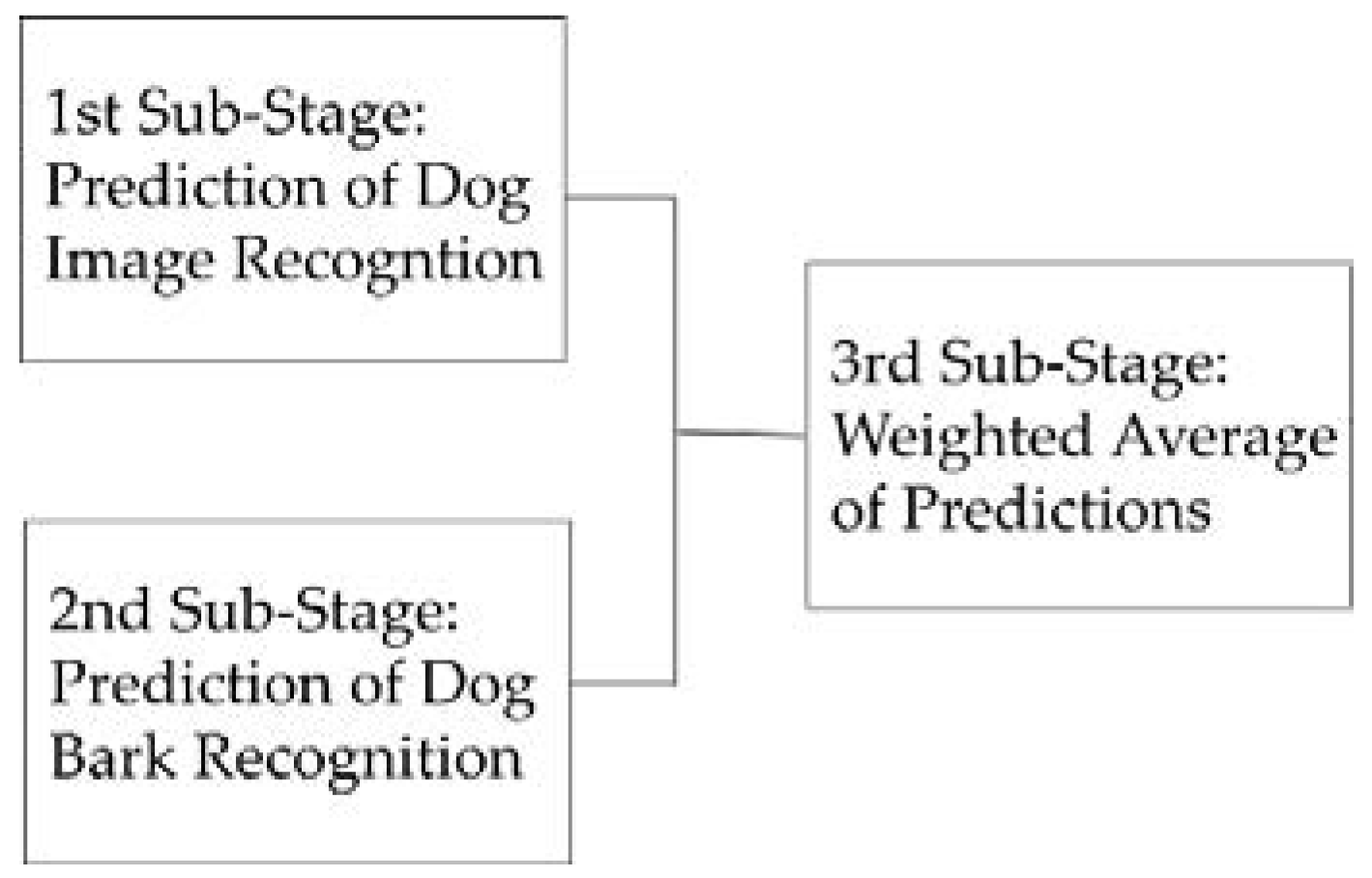
4.4. Recommendation Integration and Post-Processing
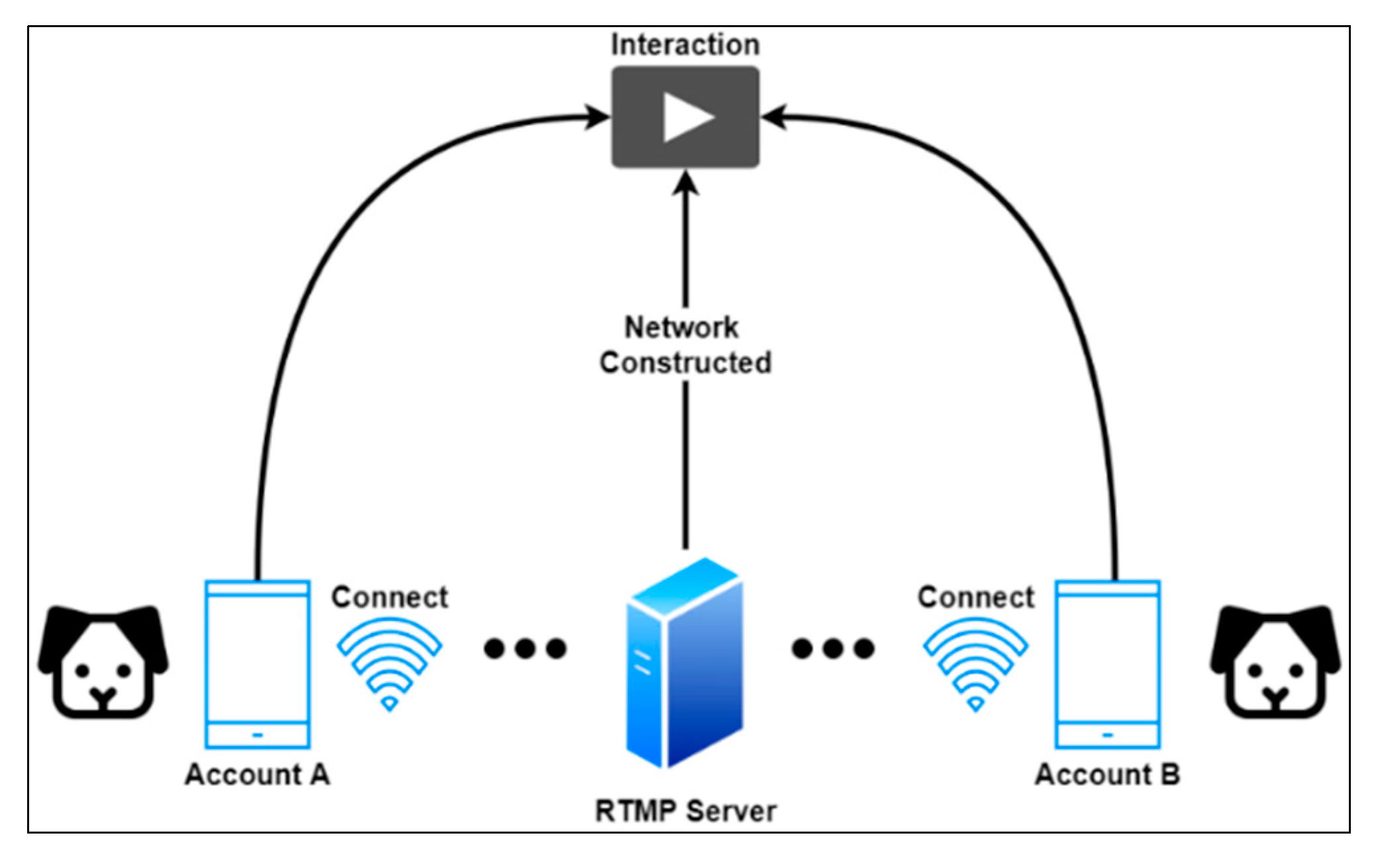
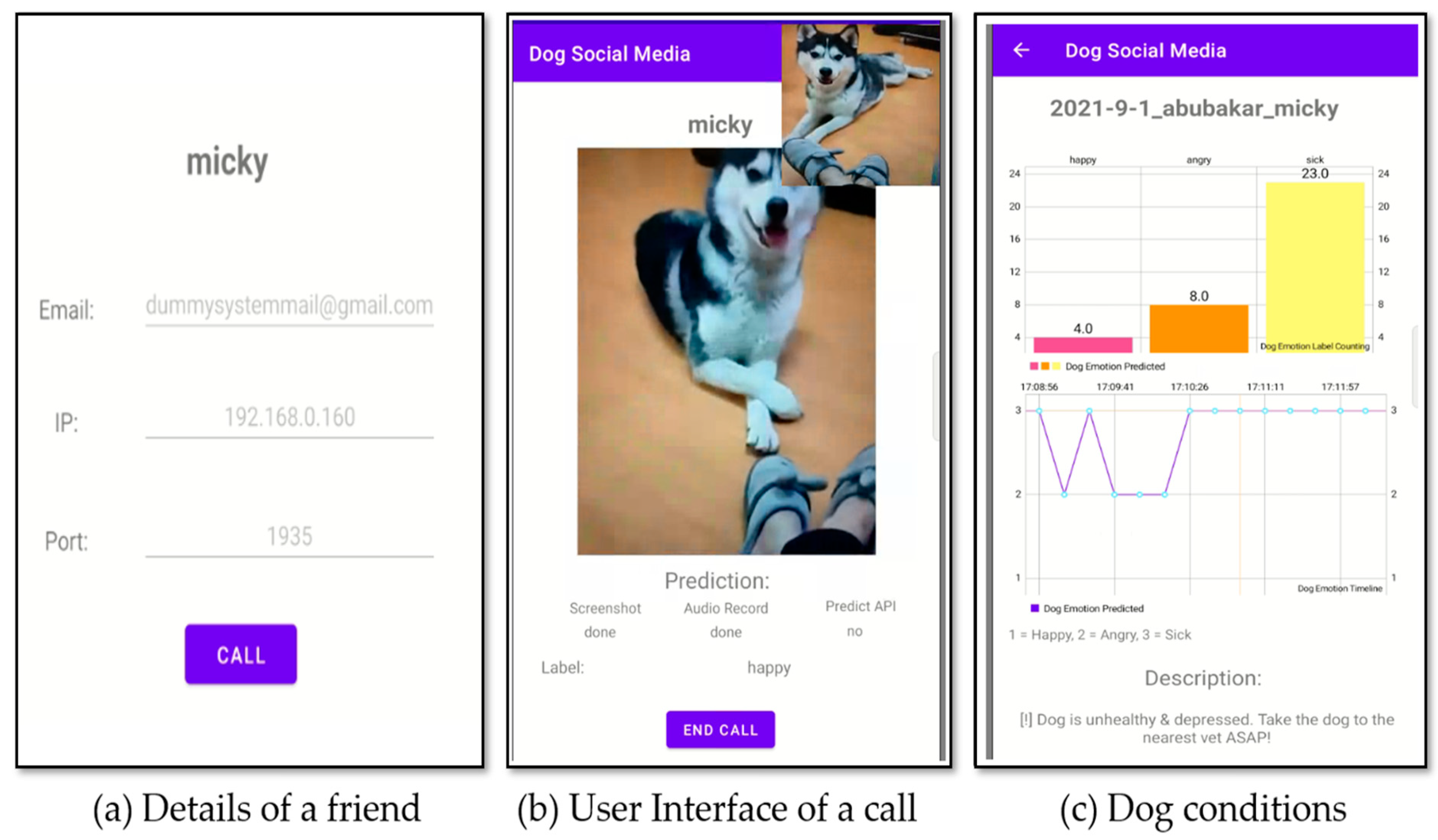
4.5. Building Dogs’ Social Network
5. Testing and Discussion
5.1. Dog’s Emotion Recognition
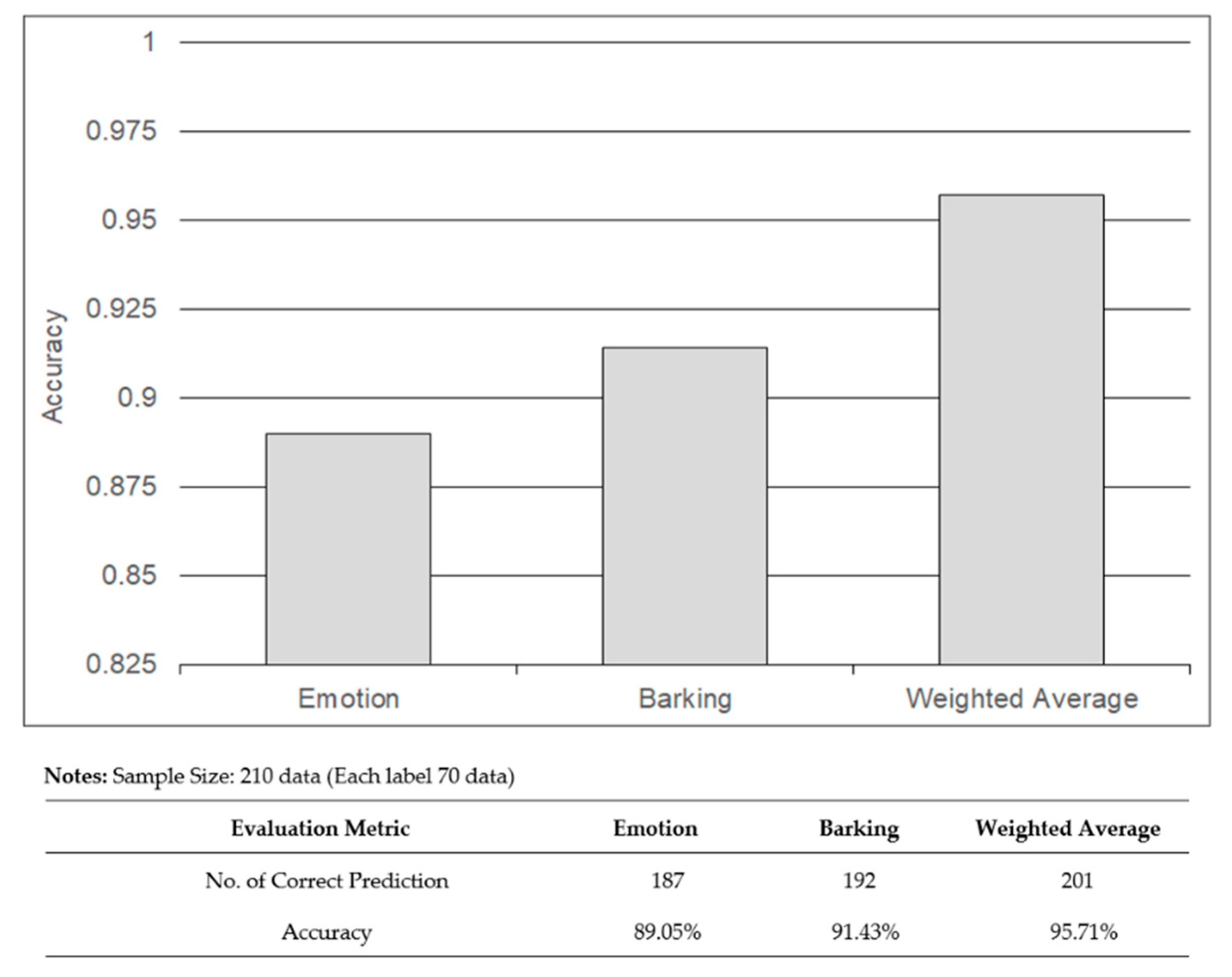
5.2. Dog Barking Emotion Recognition and Weighted Average for Dogs’ Behavior Prediction
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasch, K. An Unsupervised Recommender System for Smart Homes. J. Ambient Intell. Smart Environ. 2014, 6, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojagh, S.; Malek, M.R.; Saeedi, S.; Liang, S. A Location-Based Orientation-Aware Recommender System Using IoT Smart Devices and Social Networks. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 108, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Gudla, S.K.; ShanBhag, A.D.; Bose, J. Alternate Action Recommender System Using Recurrent Patterns of Smart Home Users. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th Annual Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 10–13 January 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gladence, L.M.; Anu, V.M.; Rathna, R.; Brumancia, E. Recommender System for Home Automation Using IoT and Artificial Intelligence. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altulyan, M.; Yao, L.; Wang, X.; Huang, C.; Kanhere, S.S.; Sheng, Q.Z. A Survey on Recommender Systems for Internet of Things: Techniques, Applications and Future Directions. Comput. J. 2021, 65, 2098–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zheng, C.; Li, D.; Shen, X.; Lin, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, N.N. EDMF: Efficient Deep Matrix Factorization with Review Feature Learning for Industrial Recommender System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 18, 4361–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zheng, C.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, K.; Shen, X.; Xiong, N.N.; Wang, J. Multi-Perspective Social Recommendation Method with Graph Representation Learning. Neurocomputing 2022, 468, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, K.; Fang, S.; Li, Z.; Xiong, N.N. CARM: Confidence-Aware Recommender Model via Review Representation Learning and Historical Rating Behavior in the Online Platforms. Neurocomputing 2021, 455, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Fernández, M.; Cortés García, A.; González Alonso, I.; Zalama Casanova, E. Using the Big Data Generated by the Smart Home to Improve Energy Efficiency Management. Energy Effic. 2016, 9, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Rahman, M.A.; Muhammad, G. Cyber–Physical Cloud-Oriented Multi-Sensory Smart Home Framework for Elderly People: An Energy Efficiency Perspective. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2017, 103, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lye, G.X.; Cheng, W.K.; Tan, T.B.; Hung, C.W.; Chen, Y.-L. Creating Personalized Recommendations in a Smart Community by Performing User Trajectory Analysis through Social Internet of Things Deployment. Sensors 2020, 20, 2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.; Kang, X. Edge and Cloud Collaborative Entity Recommendation Method towards the IoT Search. Sensors 2020, 20, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.K.; Ileladewa, A.A.; Tan, T.B. A Personalized Recommendation Framework for Social Internet of Things (SIoT). In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Green and Human Information Technology (ICGHIT), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 15–17 January 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, B. A Review and Analysis of the Use of ‘Habit’in Understanding, Predicting and Influencing Health-Related Behaviour. Health Psychol. Rev. 2015, 9, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsalemi, A.; Sardianos, C.; Bensaali, F.; Varlamis, I.; Amira, A.; Dimitrakopoulos, G. The Role of Micro-Moments: A Survey of Habitual Behavior Change and Recommender Systems for Energy Saving. IEEE Syst. J. 2019, 13, 3376–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lee, W.; Lee, H. IoT Smart Home Adoption: The Importance of Proper Level Automation. J. Sens. 2018, 2018, 6464036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrave, E.A. Diagnostic Criteria for Separation Anxiety in the Dog. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 1991, 21, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Atif, O.; Tian, J.; Lee, J.; Park, D.; Chung, Y. Multi-Level Hierarchical Complex Behavior Monitoring System for Dog Psychological Separation Anxiety Symptoms. Sensors 2022, 22, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pet Ownership in Asia. Available online: https://insight.rakuten.com/pet-ownership-in-asia/ (accessed on 17 August 2022).
- How to Manage Anti-Social Behavior in Your Pandemic Dog. Available online: https://www.nextavenue.org/separation-anxiety-in-dog/ (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- 6 Ways To Ease Post-Pandemic Separation Anxiety in Pets|Mars, Incorporated. Available online: https://www.mars.com/news-and-stories/articles/6-ways-ease-post-pandemic-separation-anxiety-pets (accessed on 27 August 2022).
- Shannon, L. Dog Gone: How to Handle Your Pet’s Post—Covid Separation Anxiety; The Guardian: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Rashidi, P.; Cook, D.J.; Holder, L.B.; Schmitter-Edgecombe, M. Discovering Activities to Recognize and Track in a Smart Environment. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2010, 23, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belghini, N.; Gouttaya, N.; Bouab, W.; Sayouti, A. Pervasive Recommender System for Smart Home Environment. Int. J. Appl. Inf. Syst. 2016, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Han, C.Y. A Context-Driven Complex Activity Framework for Smart Home. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 9th Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (IEMCON), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1–3 November 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 801–806. [Google Scholar]
- Felfernig, A.; Polat-Erdeniz, S.; Uran, C.; Reiterer, S.; Atas, M.; Tran, T.N.T.; Azzoni, P.; Kiraly, C.; Dolui, K. An Overview of Recommender Systems in the Internet of Things. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2019, 52, 285–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corujo, L.A.; Kieson, E.; Schloesser, T.; Gloor, P.A. Emotion Recognition in Horses with Convolutional Neural Networks. Future Internet 2021, 13, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorend, R.W.A. Deep Unsupervised Representation Learning For Animal Activity Recognition; University of Twente: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ladha, C.; Hammerla, N.; Hughes, E.; Olivier, P.; Ploetz, T. Dog’s Life: Wearable Activity Recognition for Dogs. In Proceedings of the 2013 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, Zurich, Switzerland, 8–12 September 2013; pp. 415–418. [Google Scholar]
- Iwashita, Y.; Takamine, A.; Kurazume, R.; Ryoo, M.S. First-Person Animal Activity Recognition from Egocentric Videos. In Proceedings of the 2014 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Stockholm, Sweden, 24–28 August 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 4310–4315. [Google Scholar]
- Pons, P.; Jaen, J.; Catala, A. Developing a Depth-Based Tracking System for Interactive Playful Environments with Animals. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Advances in Computer Entertainment Technology, Iskandar, Malaysia, 16–19 November 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kamminga, J.W.; Bisby, H.C.; Le, D.V.; Meratnia, N.; Havinga, P.J. Generic Online Animal Activity Recognition on Collar Tags. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing and Proceedings of the 2017 ACM International Symposium on Wearable Computers, Maui, HI, USA, 11–15 September 2017; pp. 597–606. [Google Scholar]
- Casella, E.; Khamesi, A.R.; Silvestri, S. Smartwatch Application for Horse Gaits Activity Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing (SMARTCOMP), Washington, DC, USA, 12–15 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Siniscalchi, M.; Quaranta, A.; Rogers, L.J. Hemispheric Specialization in Dogs for Processing Different Acoustic Stimuli. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaranta, A.; d’Ingeo, S.; Amoruso, R.; Siniscalchi, M. Emotion Recognition in Cats. Animals 2020, 10, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totakura, V.; Janmanchi, M.K.; Rajesh, D.; Hussan, M.T. Prediction of Animal Vocal Emotions Using Convolutional Neural Network. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2020, 9, 6007–6011. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.K.; Dua, T.; Sharma, D.P.; Changare, A.A. Animal Emotion Detection and Application. In Data Driven Approach towards Disruptive Technologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 449–460. [Google Scholar]
- Caeiro, C.; Guo, K.; Mills, D. Dogs and Humans Respond to Emotionally Competent Stimuli by Producing Different Facial Actions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yang, B.; Liu, H.; Ju, J.; Tang, J.; Subramanian, S.; Zhang, Z. GMDL: Toward Precise Head Pose Estimation via Gaussian Mixed Distribution Learning for Students’ Attention Understanding. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 122, 104099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Lin, K.; Wang, J. MFDNet: Collaborative Poses Perception and Matrix Fisher Distribution for Head Pose Estimation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 24, 2449–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Yang, B.; Li, Y. ARHPE: Asymmetric Relation-Aware Representation Learning for Head Pose Estimation in Industrial Human–Computer Interaction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 7107–7117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yao, L.; Sun, A.; Tay, Y. Deep Learning Based Recommender System: A Survey and New Perspectives. ACM Comput. Surv. CSUR 2019, 52, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Uddin, M.Z.; Mohamed, A.; Almogren, A. A Robust Human Activity Recognition System Using Smartphone Sensors and Deep Learning. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 81, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamminga, J.W.; Le, D.V.; Havinga, P.J.M. Towards Deep Unsupervised Representation Learning from Accelerometer Time Series for Animal Activity Recognition. In Proceedings of the 6th Workshop on Mining and Learning from Time Series, MiLeTS, San Diego, CA, USA, 24 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bocaj, E.; Uzunidis, D.; Kasnesis, P.; Patrikakis, C.Z. On the Benefits of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks on Animal Activity Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Smart Systems and Technologies (SST), Osijek, Croatia, 14–16 October 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Ferres, K.; Schloesser, T.; Gloor, P.A. Predicting Dog Emotions Based on Posture Analysis Using DeepLabCut. Future Internet 2022, 14, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethirajan, S. Happy Cow or Thinking Pig? Wur Wolf—Facial Coding Platform for Measuring Emotions in Farm Animals. AI 2021, 2, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota-Rojas, D.; Marcet-Rius, M.; Ogi, A.; Hernández-Ávalos, I.; Mariti, C.; Martínez-Burnes, J.; Mora-Medina, P.; Casas, A.; Domínguez, A.; Reyes, B. Current Advances in Assessment of Dog’s Emotions, Facial Expressions, and Their Use for Clinical Recognition of Pain. Animals 2021, 11, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumrosen, G.; Hawellek, D.; Pesaran, B. Towards Automated Recognition of Facial Expressions in Animal Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2810–2819. [Google Scholar]
- Hantke, S.; Cummins, N.; Schuller, B. What Is My Dog Trying to Tell Me? The Automatic Recognition of the Context and Perceived Emotion of Dog Barks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 5134–5138. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:14126980. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:14091556. [Google Scholar]
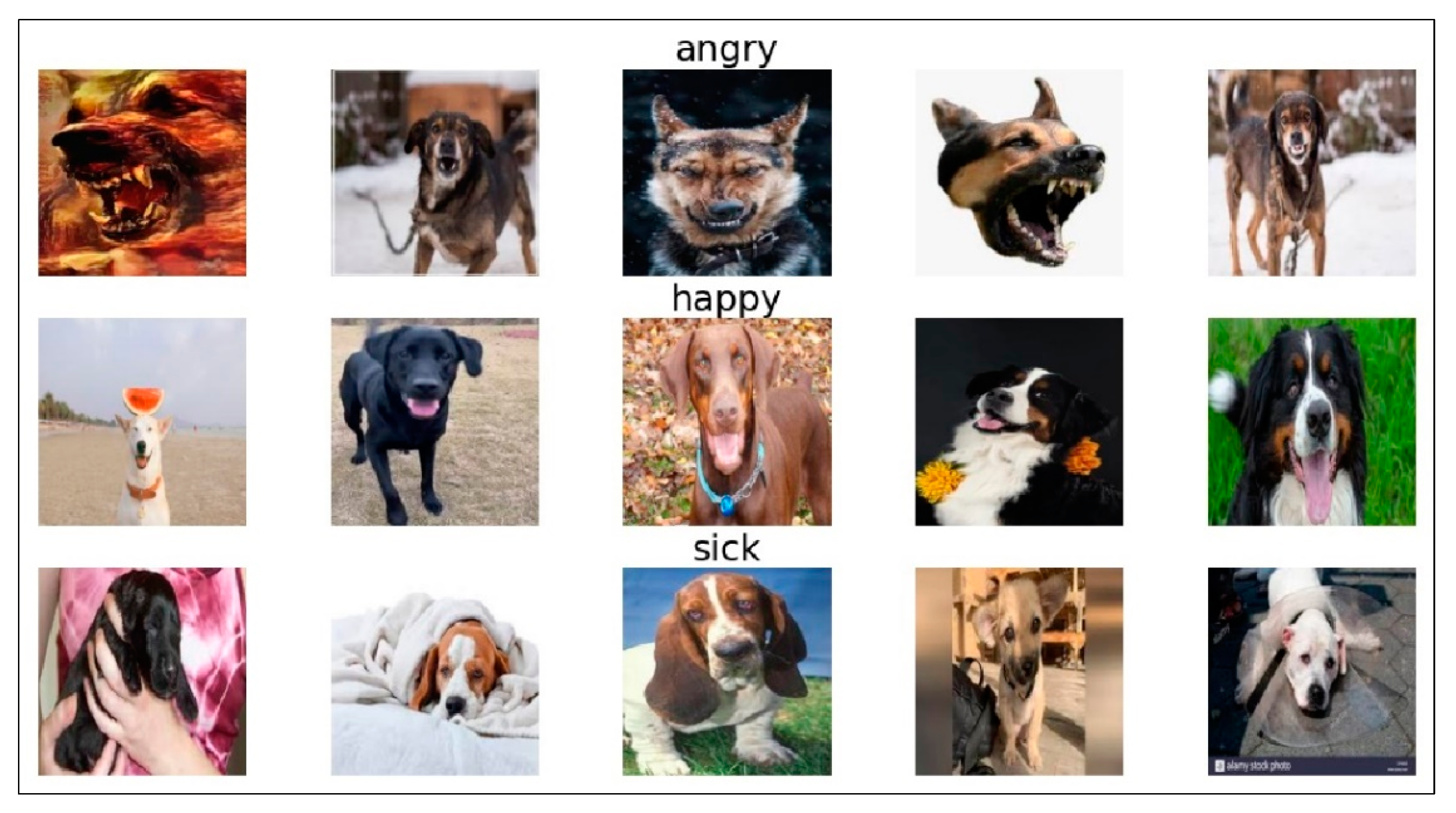








| Facial Expression | Eyes | Ears | Mouth/Teeth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Happy | Wide open, merry looking, raised eyebrows | Perked-up and forward, or relaxed | Mouth relaxed and slightly open, teeth covered, excited panting, possible lip-licking |
| Angry | Narrow or staring challengingly | Forward or back, close to head | Lips open, drawn back to expose teeth bared in a snarl, possible jaw snapping |
| Sick | Eyelids semi-closed with tearing, raised eyebrows, simulating large eyes, sad gaze | Distance between ears tends to widen | Contracted, giving the appearance of wrinkles on the face |
| Evaluation Metric | Less Data Sample Size | More Data Sample Size | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Training | Accuracy | 70.83% | 73.75% |
| Loss | 0.8192 | 0.8289 | |
| Validation | Accuracy | 66.67% | 72.50% |
| Loss | 0.8482 | 0.6038 | |
| Test | Accuracy | 33.33% | 53.75% |
| Loss | 0.8482 | 0.6038 |
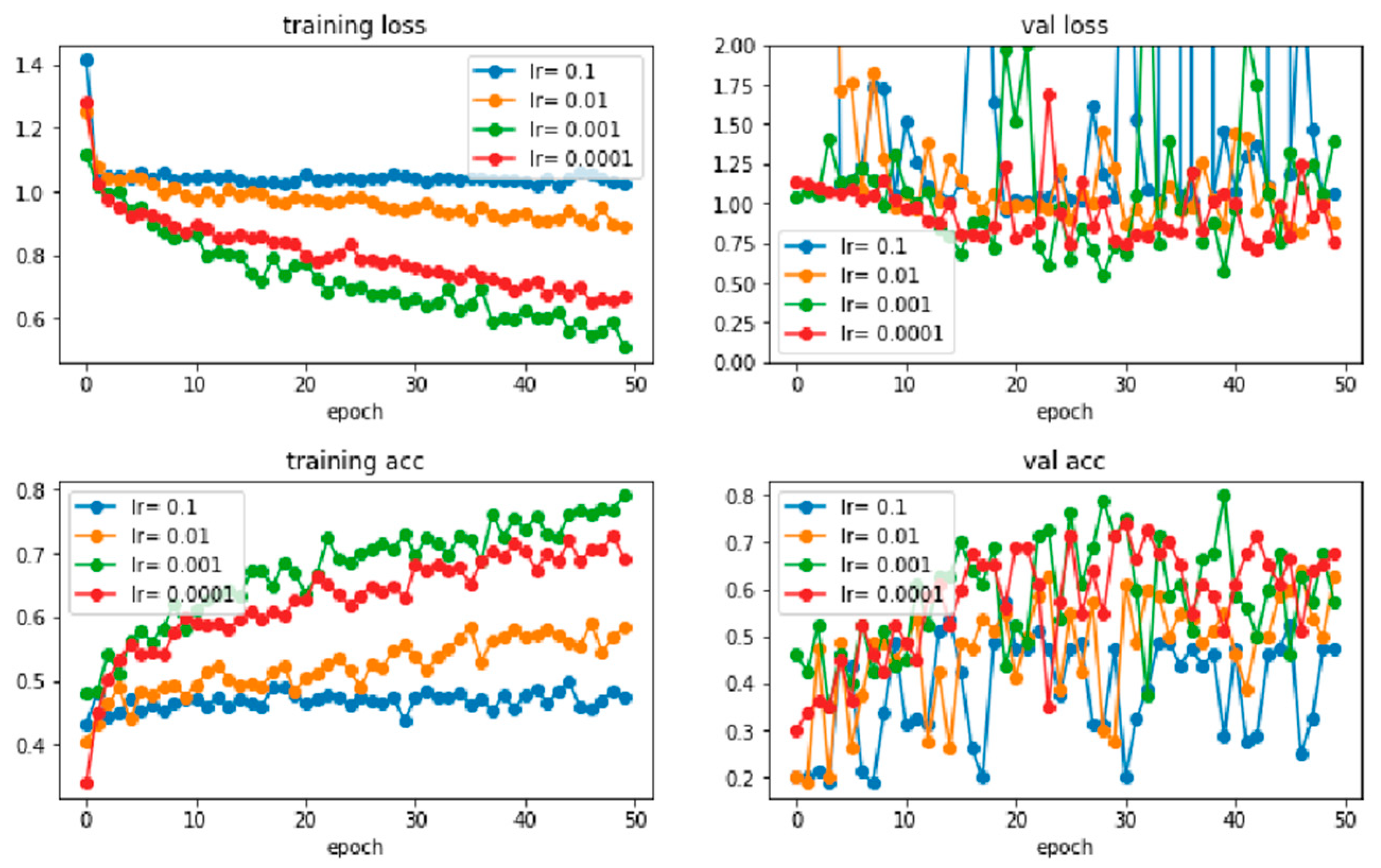
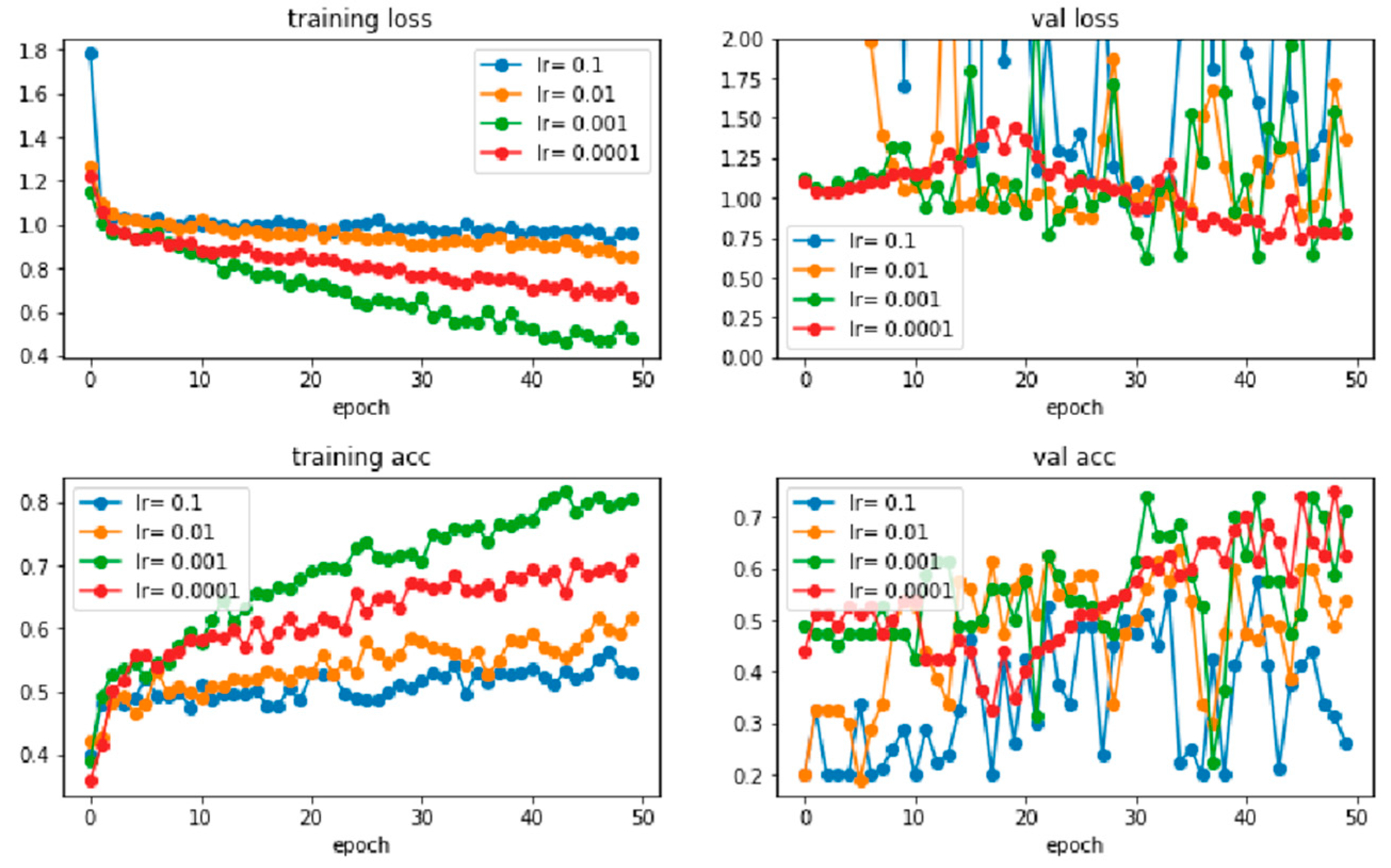
| Learning Rate | Batch Size of 16 | Batch Size of 32 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 50 epochs | 200 epochs | 50 epochs | 200 epochs |
| 0.01 | ||||
| 0.001 | ||||
| 0.0001 | ||||
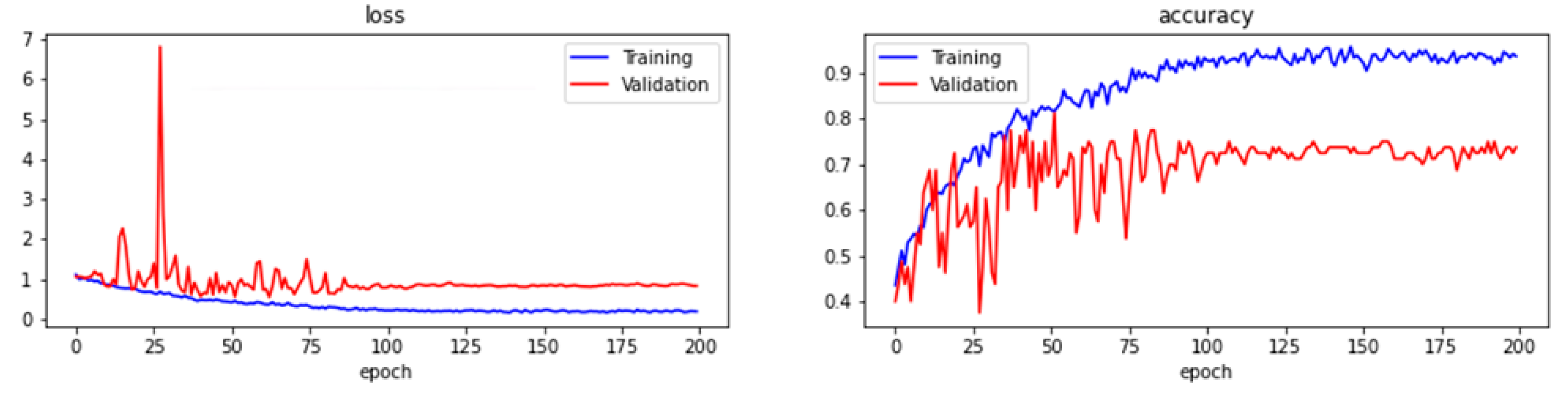
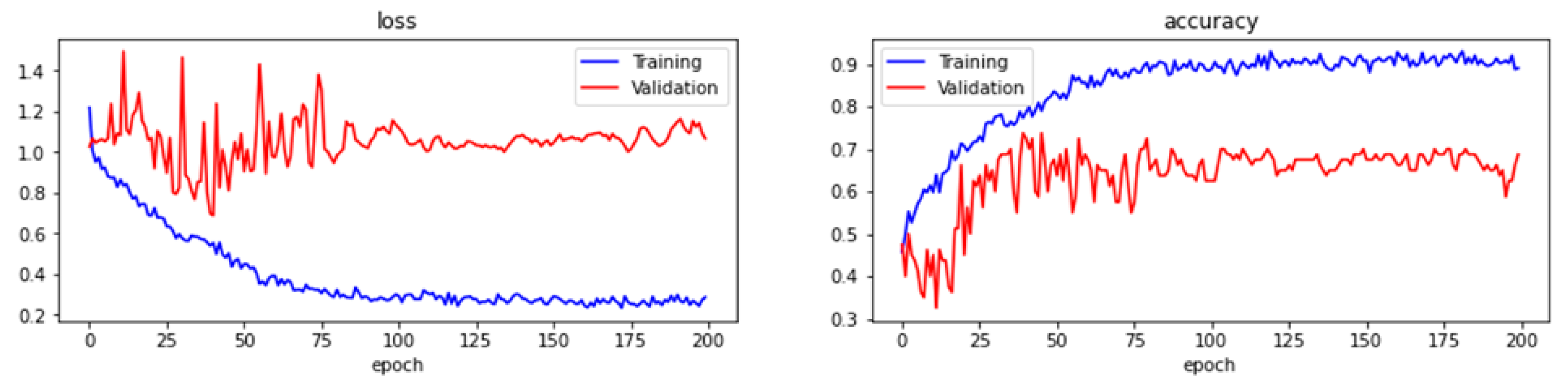
| Hyper-Parameter | Evaluation Metric | ResNet-like | VGG16 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | Accuracy | 73.75% | 47.50% | |
| Loss | 0.8289 | 1.0408 | ||
| Batch 16 | Validation | Accuracy | 72.50% | 47.50% |
| Loss | 0.6038 | 1.0408 | ||
| Test | Accuracy | 53.75% | 35.27% | |
| Loss | 0.6038 | 1.0408 | ||
| Training | Accuracy | 68.75% | 47.50% | |
| Loss | 1.0672 | 1.0408 | ||
| Batch 32 | Validation | Accuracy | 72.50% | 47.50% |
| Loss | 0.6629 | 1.0408 | ||
| Test | Accuracy | 43.75% | 38.16% | |
| Loss | 0.6629 | 1.0408 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, W.K.; Leong, W.C.; Tan, J.S.; Hong, Z.-W.; Chen, Y.-L. Affective Recommender System for Pet Social Network. Sensors 2022, 22, 6759. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22186759
Cheng WK, Leong WC, Tan JS, Hong Z-W, Chen Y-L. Affective Recommender System for Pet Social Network. Sensors. 2022; 22(18):6759. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22186759
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Wai Khuen, Wai Chun Leong, Joi San Tan, Zeng-Wei Hong, and Yen-Lin Chen. 2022. "Affective Recommender System for Pet Social Network" Sensors 22, no. 18: 6759. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22186759
APA StyleCheng, W. K., Leong, W. C., Tan, J. S., Hong, Z.-W., & Chen, Y.-L. (2022). Affective Recommender System for Pet Social Network. Sensors, 22(18), 6759. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22186759







