Fluorescence Assay for Detecting Four Organophosphorus Pesticides Using Fluorescently Labeled Aptamer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
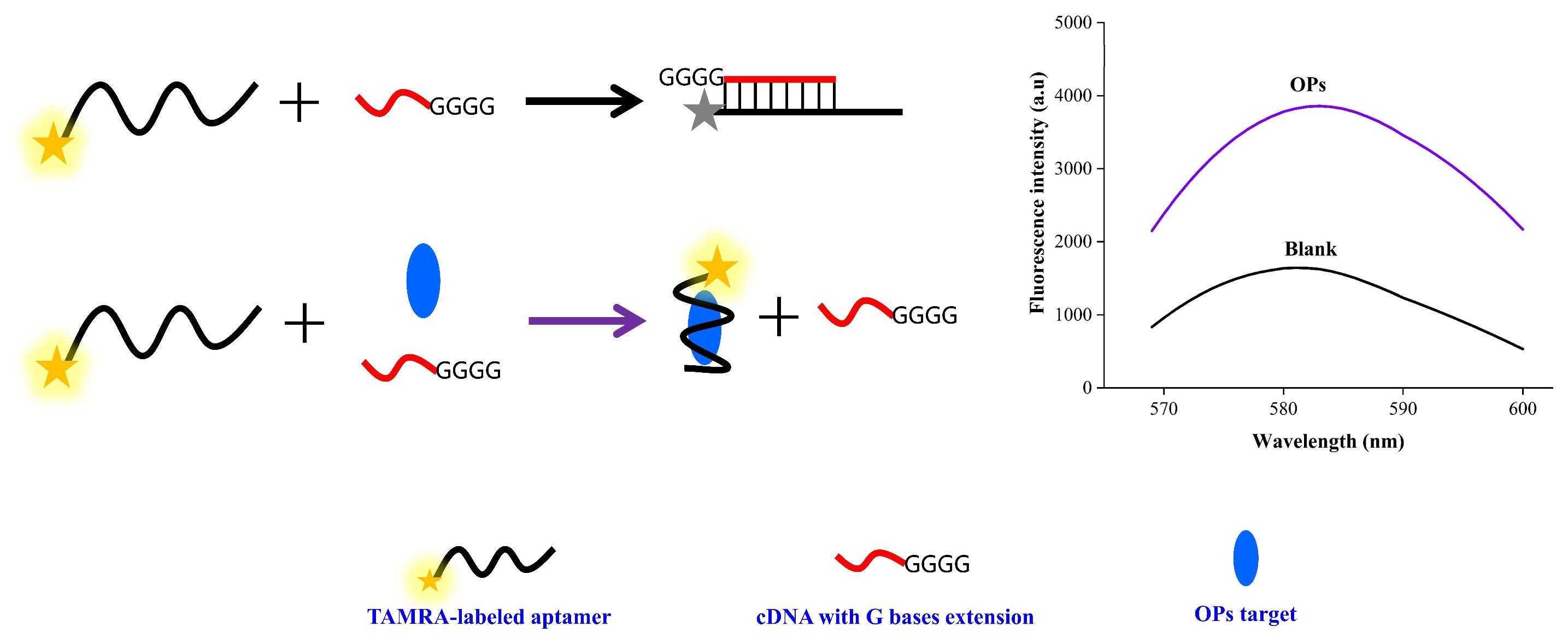
3.1. Principle of the Fluorescence Assay
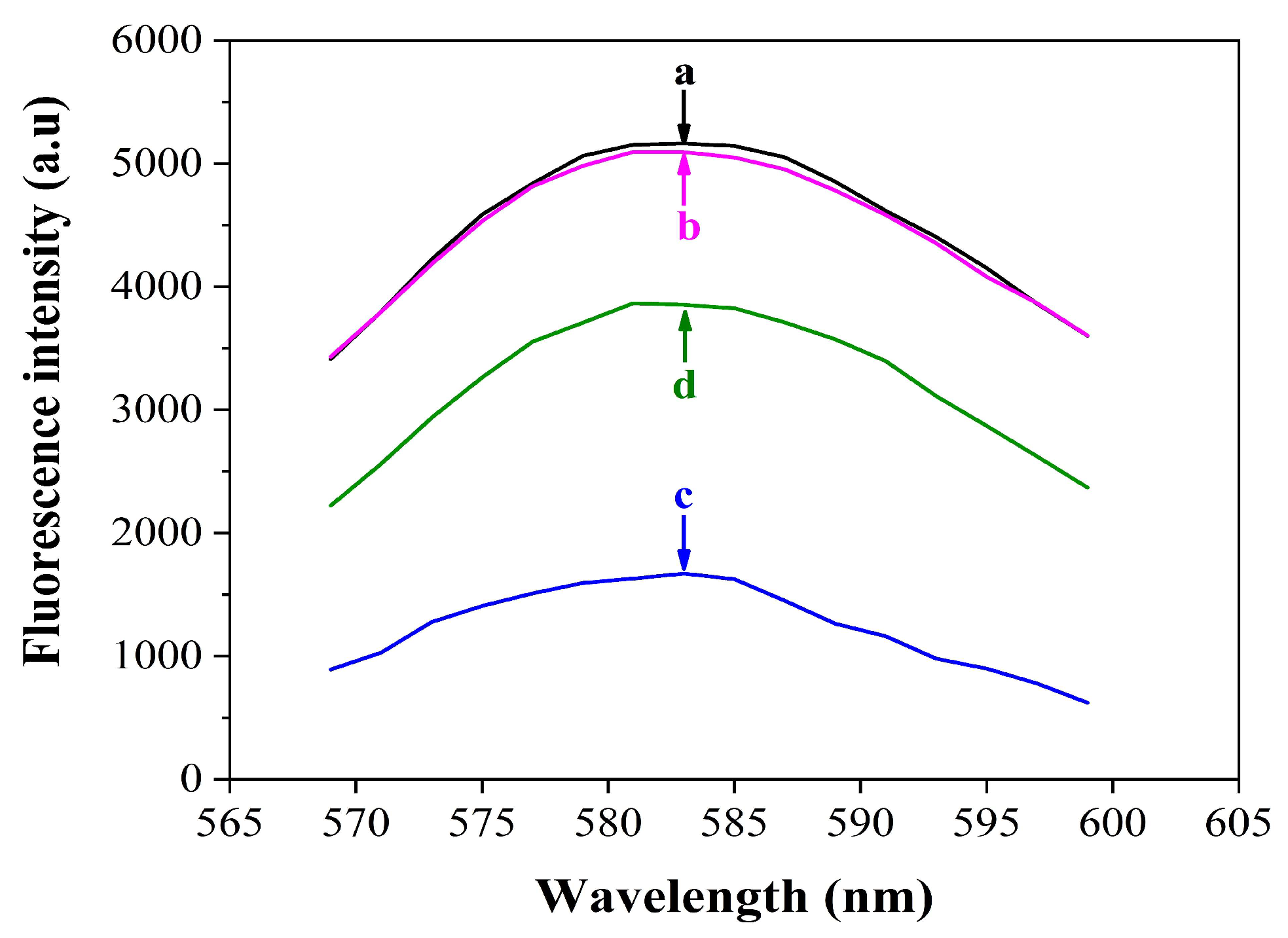
3.2. Feasibility of the Fluorescence Assay
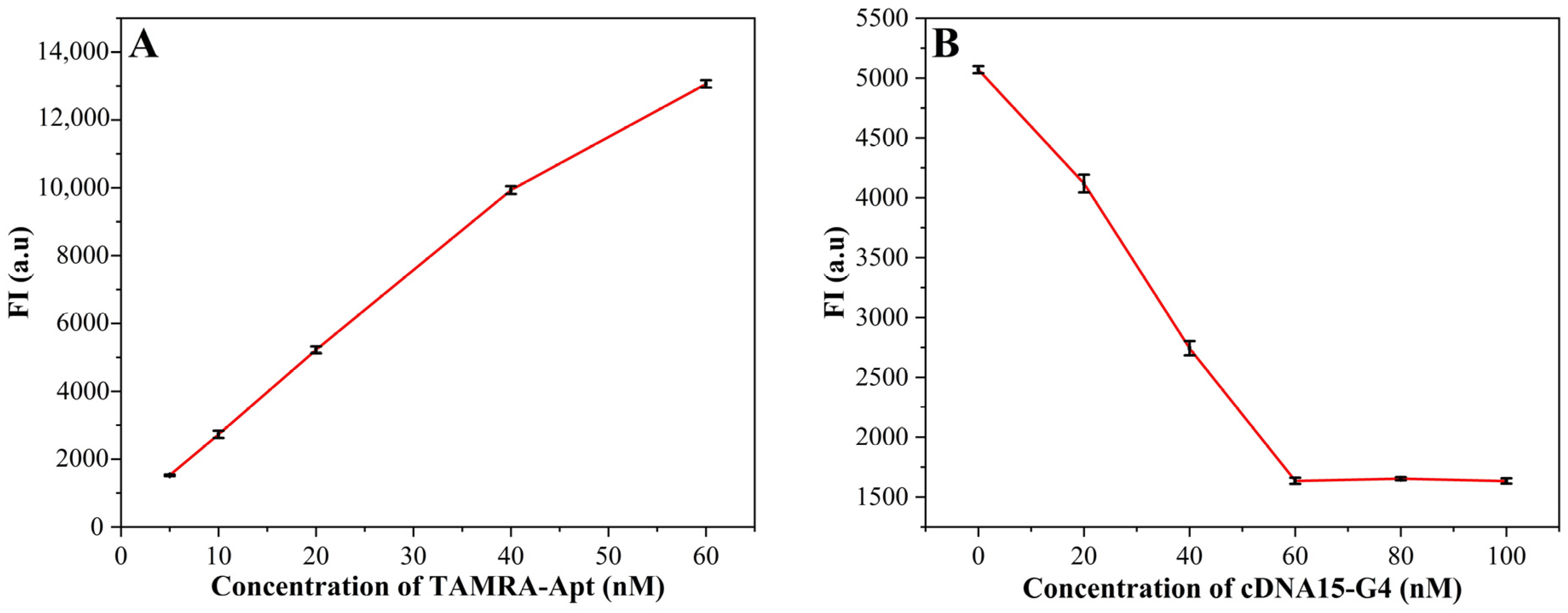
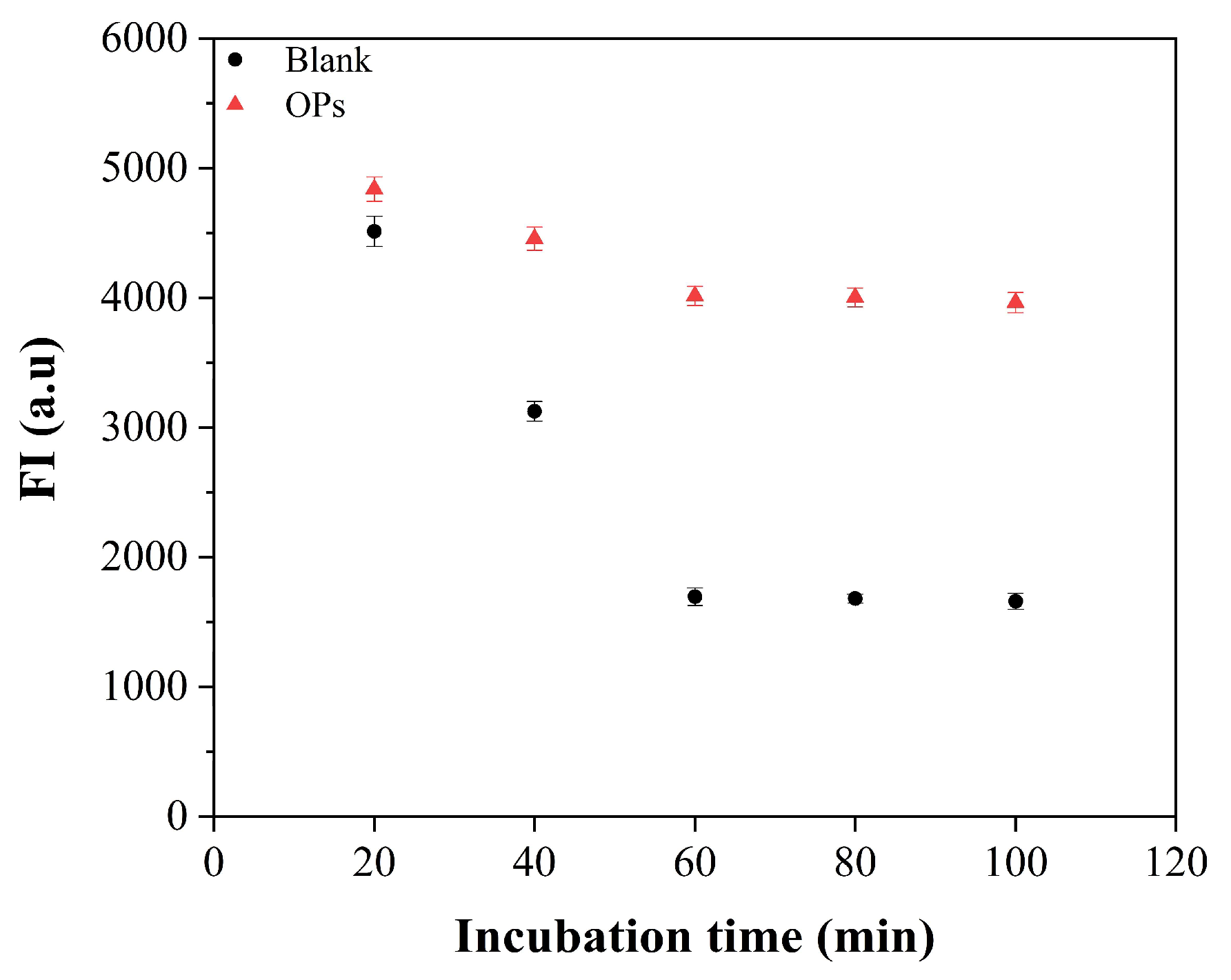
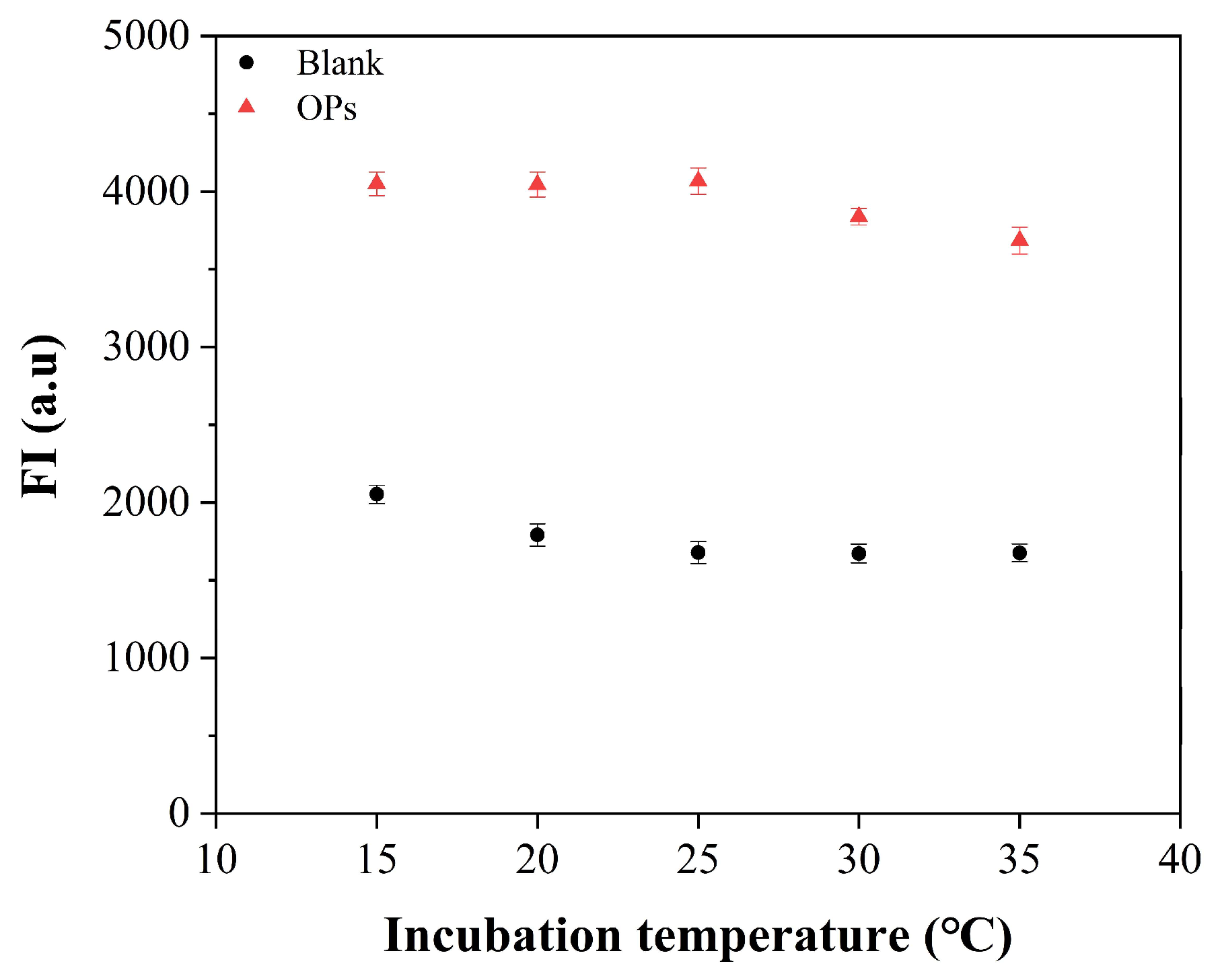
3.3. Optimizations
3.4. Quantitative Measurement
3.5. Selectivity of the Fluorescence Assay
3.6. Analysis of Actual Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TAMRA | tetramethylrhodamine |
| cDNA | complementary DNA |
| G | guanine |
| PET | photoinduced electron transfer |
| OPs | organophosphorus pesticides |
| ACh | acetylcholine |
| MRL | maximum residue limit |
| MS | mass spectrometry |
| HPLC | high performance liquid chromatography |
| LC | liquid chromatography |
| GC | gas chromatography |
| FI | fluorescence intensity (emission wavelength at 583 nm) |
| LOD | limit of detection |
| R2 | regression coefficient |
| RSD | relative standard deviation |
References
- Zhou, J.; Zou, X.; Song, S.; Chen, G. Quantum dots applied to methodology on detection of pesticide and veterinary drug residues. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1307–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, C.; Duanghathaipornsuk, S.; Goltz, M.; Kanel, S.; Kim, D.S. Peptide nanotube encapsulated enzyme biosensor for vapor phase detection of malathion, an organophosphorus compound. Sensors 2019, 19, 3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, M.; Chen, C.; He, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z. Fluorescence assay for three organophosphorus pesticides in agricultural products based on magnetic-assisted fluorescence labeling aptamer probe. Food Chem. 2020, 307, 125534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satnami, M.L.; Korram, J.; Nagwanshi, R.; Vaishanav, S.K.; Karbhal, I.; Dewangan, H.K.; Ghosh, K.K. Gold nanoprobe for inhibition and reactivation of acetylcholinesterase: An application to detection of organophosphorus pesticides. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 267, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, B.; Liu, A.; Liang, G.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y.; Wei, W.; Gou, S.; Liu, S. Multicolor sensor for organophosphorus pesticides determination based on the bi-enzyme catalytic etching of gold nanorods. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 265, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmi, H.; Jabbari, M. Development of graphene-carbon nanotube-coated magnetic nanocomposite as an efficient sorbent for HPLC determination of organophosphorus pesticides in environmental water samples. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2015, 95, 1353–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgobbi, L.F.; Machado, S.A.S. Functionalized polyacrylamide as an acetylcholinesterase-inspired biomimetic device for electrochemical sensing of organophosphorus pesticides. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Hou, J.; Jiang, J.; Ai, S. Innovative approach for the electrochemical detection of non-electroactive organophosphorus pesticides using oxime as electroactive probe. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 885, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Qin, J.; Yang, M.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Guo, W.; Ma, Z.; Kong, W. Rapid gas chromatography with flame photometric detection of multiple organophosphorus pesticides in Salvia miltiorrhizae after ultrasonication assisted one-step extraction. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1068–1069, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, P.; Fan, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L. Bamboo charcoal as solid-phase extraction adsorbent for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides in water samples by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Lett. 2012, 45, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wu, J.; Ying, Y.; She, Y.; Wang, J.; Ping, J. Carbon nanomaterial-enabled pesticide biosensors: Design strategy, biosensing mechanism, and practical application. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 106, 62–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Jiang, C.; Ping, J. Flexible freestanding graphene paper-based potentiometric enzymatic aptasensor for ultrasensitive wireless detection of kanamycin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 123, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wen, F.; Qiao, Q.; Zheng, N.; Saive, M.; Fauconnier, M.L.; Wang, J. A novel graphene oxide-based aptasensor for amplified fluorescent detection of aflatoxin M1 in milk powder. Sensors 2019, 19, 3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, R.; Jia, D.; Wen, Y.; Yu, X. Cantilever-based aptasensor for trace level detection of nerve agent simulant in aqueous matrices. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 238, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinemann, C.; Fritsch, U.F.V.; Rudolph, S.; Strehlitz, B. Generation and characterization of quinolone-specific DNA aptamers suitable for water monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotrik, M.R.; Feagin, T.A.; Csordas, A.T.; Nakamoto, M.A.; Soh, H.T. Advancements in aptamer discovery technologies. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 1903–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Dai, Z.; Tian, X.; Jiang, X. Detection of Listeria monocytogenes based on combined aptamers magnetic capture and loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Food Control 2018, 85, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Chu, G.; Guo, Y.; Sun, X. Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for kanamycin detection based on silver nanoparticle-catalyzed chemiluminescent reaction between luminol and hydrogen peroxide. Sens. Actuators B 2020, 304, 127367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Zhang, S.; Ding, X.; Mi, T.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M. Determination of enrofloxacin in bovine milk by a novel single-stranded DNA aptamer chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay. Anal. Lett. 2014, 47, 2844–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; An, X.; Yao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Sun, X. Electrochemical aptasensor based on one step co-electrodeposition of aptamer and GO-CuNPs nanocomposite for organophosphorus pesticide detection. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 287, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniyal, S.; Sharma, R. Technological advancement in electrochemical biosensor based detection of organophosphate pesticide chlorpyrifos in the environment: A review of status and prospects. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 116, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ping, J.; Ying, Y. Recent developments in carbon nanomaterial-enabled electrochemical sensors for nitrite detection. Trac Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, R.; Kumar, M.; Bansal, K.; Sharma, R.K.; Wangoo, N. Ultrasensitive aptamer biosensor for malathion detection based on cationic polymer and gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhao, G.; Liu, M.; Fan, L.; Cao, T. Aptamer-based colorimetric sensing of acetamiprid in soil samples: Sensitivity, selectivity and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Yang, B.; Zhang, X.; Cui, L.; Meng, H.; Mei, L.; Wu, C.; Ren, S.; Tan, W. Enzymatic cleavage and mass amplification strategy for small molecule detection using aptamer-based fluorescence polarization biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 879, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Lai, J.; Qiu, P.; Wang, X. An ultrasensitive fluorescent sensor for organophosphorus pesticides detection based on RB-Ag/Au bimetallic nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 263, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torimura, M.; Kurata, S.; Yamada, K.; Yokomaku, T.; Kamagata, Y.; Kanagawa, T.; Kurane, R. Fluorescence-quenching phenomenon by photoinduced electron transfer between a fluorescent dye and a nucleotide base. Anal. Sci. 2001, 17, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinlein, T.; Knemeyer, J.P.; Piestert, O.; Sauer, M. Photoinduced electron transfer between fluorescent dyes and guanosine residues in DNA-hairpins. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 7957–7964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Tao, J.; Feng, W.; Uppal, J.S.; Peng, H.; Le, X.C. Aptamer binding assays and molecular interaction studies using fluorescence anisotropy-a review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1125, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zeng, N.; Dong, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; Yang, C. High-throughput aptamer microarrays for fluorescent detection of multiple organophosphorus pesticides in food. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 3173–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Q. Aptamer structure switch fluorescence anisotropy assay for aflatoxin B1 using tetramethylrhodamine-guanine interaction to enhance signal change. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1982–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, Q. A simple fluorescence anisotropy assay for detection of bisphenol A using fluorescently labeled aptamer. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 97, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Tu, Z.; Sun, X.; He, Q.; Lei, Z.; Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; et al. Organophosphorus pesticides detection using broad-specific single-stranded DNA based fluorescence polarization aptamer assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 55, 216–219. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Shen, H.; Li, G.; Zhao, B.; Yu, A.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, H. Specific and sensitive fluorescence anisotropy sensing of guanine-quadruplex structures via a photoinduced electron transfer mechanism. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8088–8094. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Q. Aptamer-based microcantilever-array biosensor for profenofos detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1020, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tang, X.; Chen, X.; Qu, B.; Lu, L. Label-free and enzyme-free fluorescent isocarbophos aptasensor based on MWCNTs and G-quadruplex. Talanta 2018, 188, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Luo, M.; Liu, D.; Zhan, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Z. Application of a magnetic graphene nanocomposite for organophosphorus pesticide extraction in environmental water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1535, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, X.; Chu, X.; Kong, W.; Luo, J.; Yang, M. A gold-based nanobeacon probe for fluorescence sensing of organophosphorus pesticides. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 891, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| TAMRA-Apt | TAMRA-AGCTTGCTGCAGCGATTCTTGATCGCCACAGAGCT |
| cDNA15 | TCGCTGCAGCAAGCT |
| cDNA15-G4 | TCGCTGCAGCAAGCTGGGG |
| Analyte | Linear Equation | Linear Range (µg/L) | R2 | LOD (µg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phorate | ΔFI = 21.7 C + 218.24 | 1–100 | 0.9839 | 0.333 |
| Profenofos | ΔFI = 43.7 C + 273.39 | 0.5–50 | 0.9719 | 0.167 |
| Isocarbophos | ΔFI = 40.3 C + 375.57 | 0.8–50 | 0.9847 | 0.267 |
| Omethoate | ΔFI = 44.1 C + 343.16 | 1–50 | 0.9687 | 0.333 |
| Method | Pesticide | Linear Range (nM) | Detection Limit (nM) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microcantilever-array | profenofos | 13.38–2676.44 | 3.5 | [35] |
| Fluorescence | isocarbophos | 10–500 | 10 | [36] |
| Gas chromatography | profenofos | 267.64–13,382.22 | 89.21 | [37] |
| isocarbophos | 345.67–17,283.69 | 115.22 | ||
| Electrochemistry | profenofos | 0.01–100 | 0.003 | [20] |
| phorate | 1–1000 | 0.3 | ||
| isocarbophos | 0.1–1000 | 0.03 | ||
| omethoate | 1–500 | 0.3 | ||
| Fluorescence | profenofos | 268–26,800 | 134 | [38] |
| isocarbophos | 346–34,600 | 35 | ||
| Fluorescence | profenofos | 13.38–26,764.45 | 13.4 | [33] |
| isocarbophos | 17.28–34,567.63 | 17.2 | ||
| phorate | 19.2–38,405.41 | 19.2 | ||
| omethoate | 23.45–46,906.12 | 23.4 | ||
| Fluorescence | phorate | 3.84–384.05 | 1.28 | Our assay |
| profenofos | 1.34–133.82 | 0.446 | ||
| isocarbophos | 2.77–172.84 | 0.922 | ||
| omethoate | 4.69–234.53 | 1.56 |
| Sample | Spiked (µg/L) | Diluted (µg/L) | Detected (µg/L) | RSD (%) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lettuce | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| 30 | 10.516 | 31.548 | 4.91 | 105.16 | |
| 90 | 29.591 | 88.773 | 4.09 | 98.64 | |
| Cabbage | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - |
| 30 | 11.059 | 33.177 | 11.23 | 110.59 | |
| 90 | 28.925 | 86.775 | 5.41 | 96.42 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Huang, X.; Huang, J.; Bai, M.; Hu, M.; Guo, Y.; Sun, X. Fluorescence Assay for Detecting Four Organophosphorus Pesticides Using Fluorescently Labeled Aptamer. Sensors 2022, 22, 5712. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155712
Li H, Huang X, Huang J, Bai M, Hu M, Guo Y, Sun X. Fluorescence Assay for Detecting Four Organophosphorus Pesticides Using Fluorescently Labeled Aptamer. Sensors. 2022; 22(15):5712. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155712
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, He, Xue Huang, Jingcheng Huang, Mengyuan Bai, Mengjiao Hu, Yemin Guo, and Xia Sun. 2022. "Fluorescence Assay for Detecting Four Organophosphorus Pesticides Using Fluorescently Labeled Aptamer" Sensors 22, no. 15: 5712. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155712
APA StyleLi, H., Huang, X., Huang, J., Bai, M., Hu, M., Guo, Y., & Sun, X. (2022). Fluorescence Assay for Detecting Four Organophosphorus Pesticides Using Fluorescently Labeled Aptamer. Sensors, 22(15), 5712. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22155712





