A Hierarchical Approach for Traffic Sign Recognition Based on Shape Detection and Image Classification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Traffic Image Database
2.2. Image Classification
2.3. Object Detection
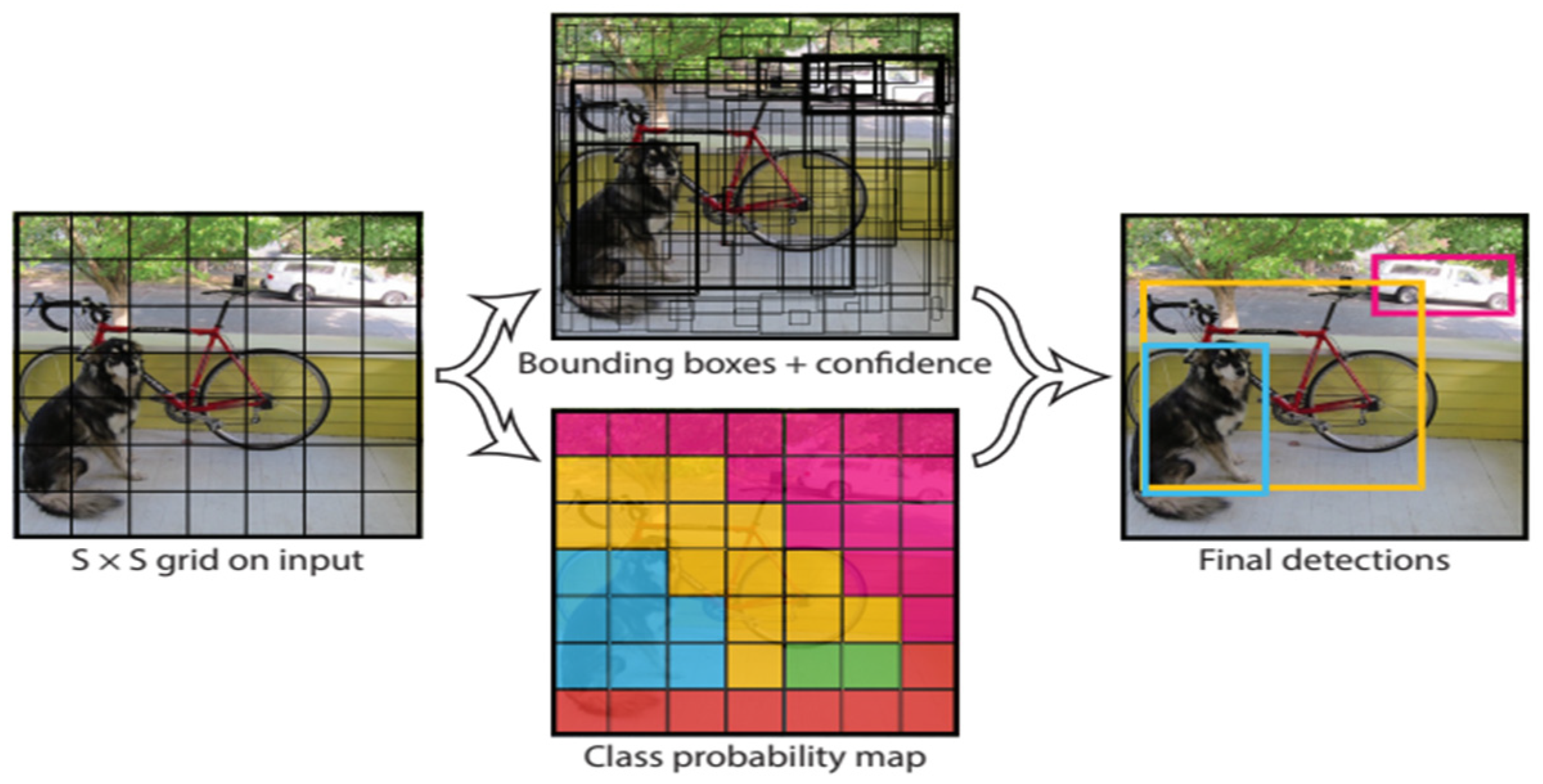
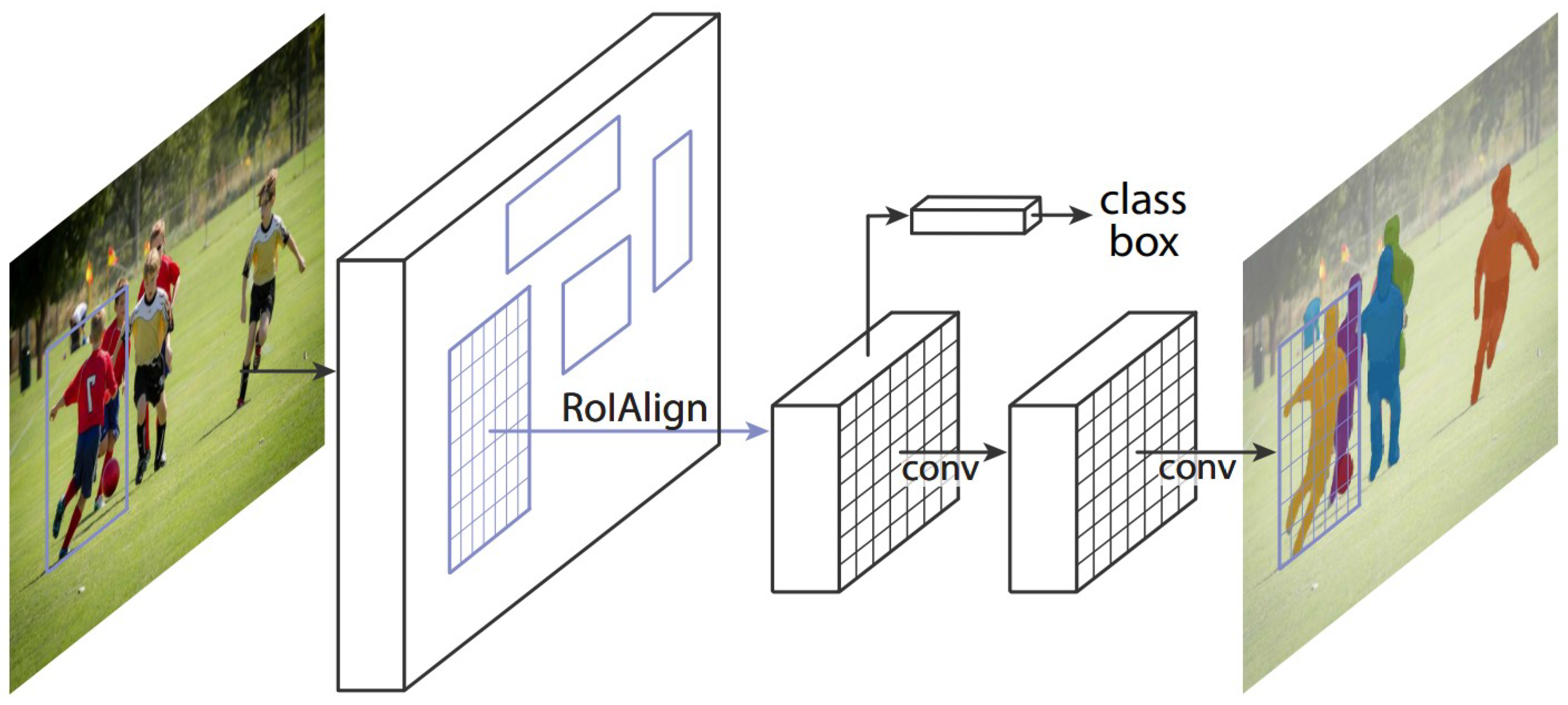
3. Methodology
3.1. Dataset Creation and Annotation
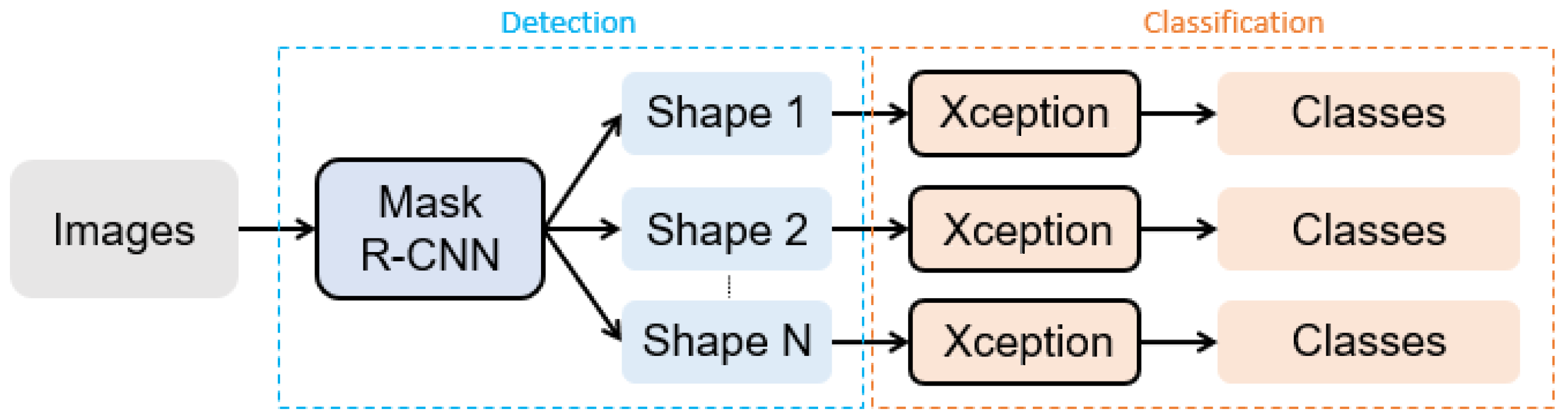
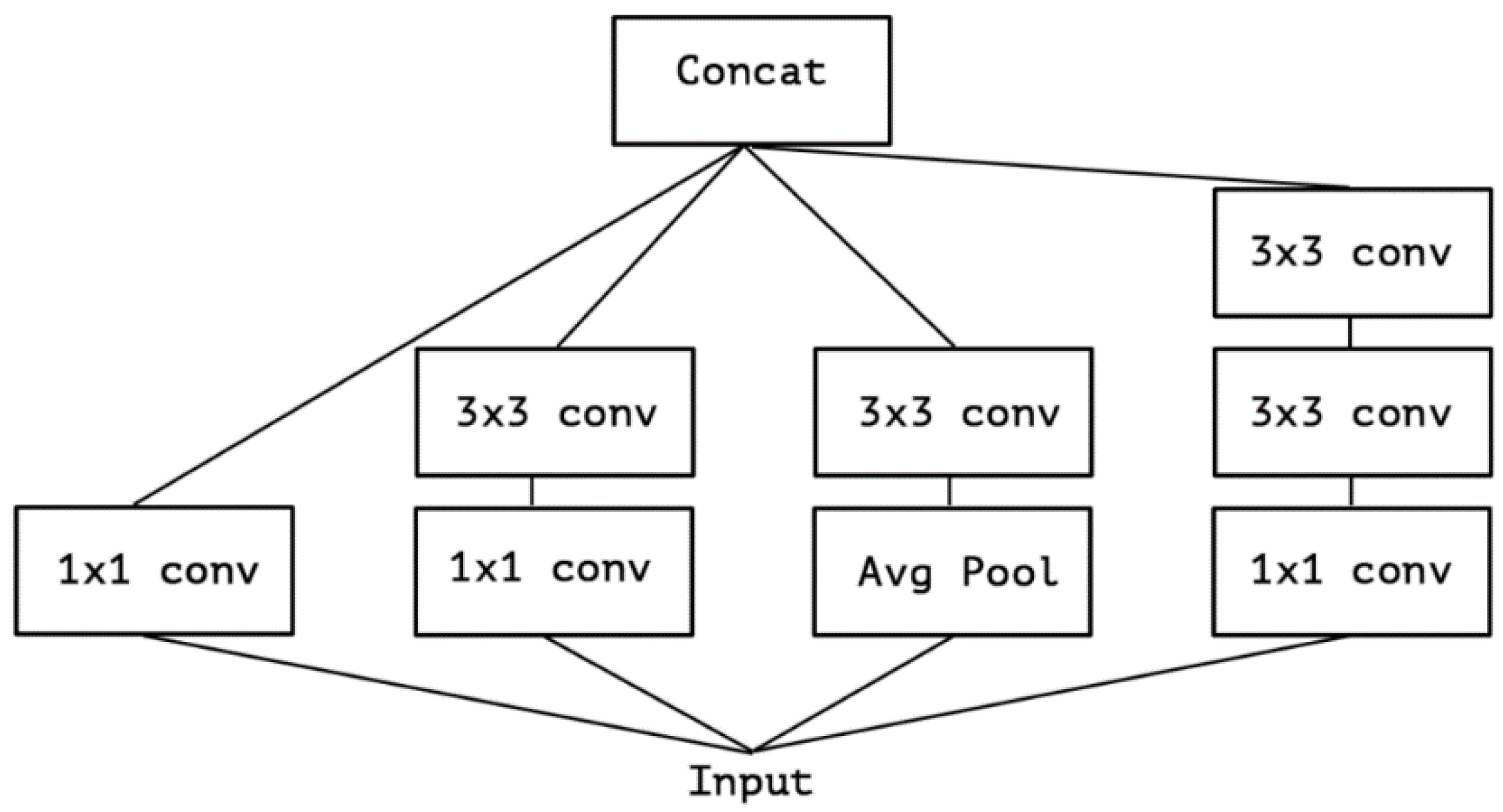
3.2. Our Approach
4. Experimental Evaluation
4.1. Experimental Settings
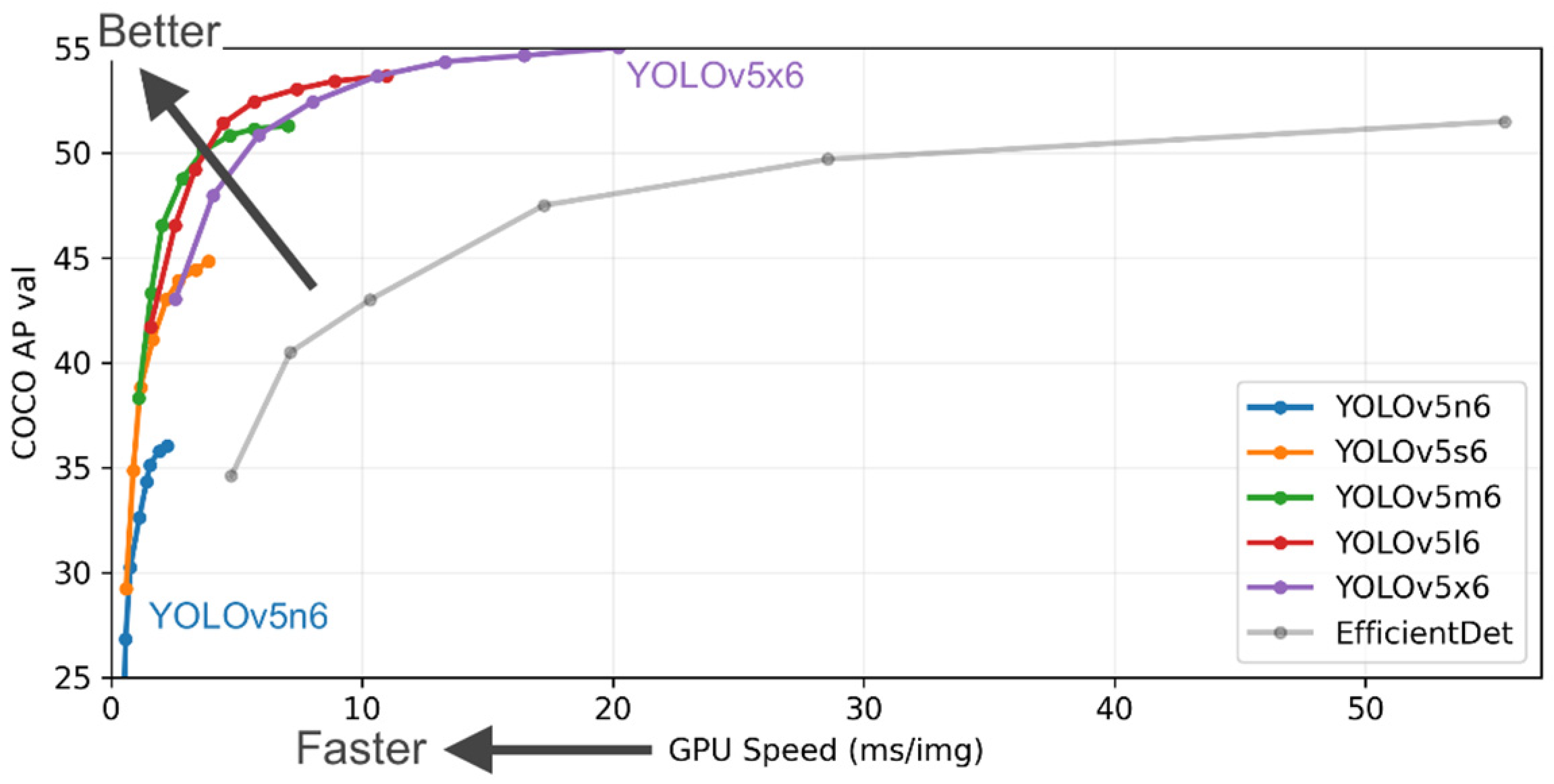
4.2. Performance Comparison
4.3. Model Robustness
4.4. Details of Our Approach
4.5. Impact of Training Data Size
4.6. Impact of Image Resolution
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jamson, S.; Carsten, O.; Cholrton, K.; Fowkes, M. Literature Review and Scoping Study; The University of Leeds and MIRA Ltd.: Leeds, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kloeden, C.N.; McLean, A.J.; Moore, V.M.; Ponte, G. Traveling Speed and the Risk of Crash Involvement; NHMRC Road Accident Research Unit, The University of Adelaide: Singapore, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Arem, G.; Walker, E.; Murdoch, C.; Graham, A.; Fernandes, R.; Job, R.F. Is a focus on low level speeding justified? Objective determination of the relative contributions of low and high level speeding to the road toll. In Proceedings of the Australasian Road Safety Research, Policing and Education Conference; Monash University: Canberra, ACT, Australia, 2010; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- Faulks, I.J.; Paine, M.; Paine, D.; Irwin, J.D. (Eds.) ISA in Australia: Workplace safety, road safety and the commercialisation of intelligent speed adaptation. In Proceedings of the 1st Australian Conference on Intelligent Speed Adaptation, Held at Parliament House, Sydney, Australasian College of Road Safety, Canberra, ACT, Australia, 1 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Paine, M.; Paine, D.; Faulks, I.J. Speed limiting trials in Australia. In Proceedings of the 21st International Technical Conference on the Enhanced Safety of Vehicles, Stuttgart, Germany, 15–18 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Li, Y.; He, K.; Sun, J. R-FCN: Object detection via region-based fully convolutional networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1605.06409. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.01497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single shot multibox detector. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Path to Autonomy: Self-driving Car Levels 0 to 5 Explained—Car and Driver. Available online: https://www.caranddriver.com/features/a15079828/autonomous-self-driving-car-levels-car-levels/ (accessed on 3 October 2017).
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1610.02357v3. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G. YOLOv5 Documentation. Available online: https://docs.ultralytics.com/ (accessed on 18 May 2020).
- Liu, Z.; Qi, M.; Shen, C.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, X. Cascade saccade machine learning network with hierarchical classes for traffic sign detection. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 67, 102700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sichkar, V.N. Real Time detection and classification of traffic signs based on yolo version 3 algorithm. J. Sci. Tech. Inf. Technol. Mech. Opt. 2020, 20, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, S.K.; Dewi, C.; Chen, R.C.; Liu, Y.T.; Jiang, X.; Yu, H. Deep learning for traffic sign recognition based on spatial pyramid pooling with scale analysis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7263–7271. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiqiang, X. YOLOv5s-GTB: Light-weighted and improved YOLOv5s for bridge crack detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.01498. [Google Scholar]
- Snegireva, D.; Perkova, A. Traffic sign recognition application using yolov5 architecture. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Russian Automation Conference (RusAutoCon), Sochi, Russian, 5–11 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Uijlings, J.R.; Van De Sande, K.E.; Gevers, T.; Smeulders, A.W. Selective search for object recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2013, 104, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabernik, D.; Skočaj, D. Deep learning for large-scale traffic-sign detection and recognition. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 21, 1427–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, J.; Shekhar, S. Road damage detection and classification in smartphone captured images using Mask R-CNN. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.04535. [Google Scholar]
- Malbog, M.A. MASK R-CNN for pedestrian crosswalk detection and instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 6th International Conference on Engineering Technologies and Applied Sciences (ICETAS), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 20–21 December 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Wang, G.; Yan, S.; Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Dai, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, L. Fast vehicle and pedestrian detection using improved Mask R-CNN. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 5761414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chang, X.; Bian, S.B. Vehicle-damage-detection segmentation algorithm based on improved mask RCNN. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 6997–7004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




 No entry |  Max vehicle weight |  Max vehicle width |  Max vehicle height |  Max vehicle length |
 Speed limit |  Minimum speed |  Road-designated vehicles | ||
 Forked road (1) |  Forked road (2) |  Forked road (3) |  Forked road (4) |  Forked road (5) |
 Forked road (6) |  Forked road (7) |  Forked road (8) |  Forked road (9) |  Entering roadway merge (right) |
 Entering roadway merge (left) |  Divided lanes |  Careful, cyclists |  Careful, strong winds |  Safe orientation guidance |
| Model | Precision | Recall | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mask R-CNN | 78.40 | 29.57 | 28.64 |
| YOLOv5 | 55.49 | 73.44 | 71.12 |
| Our Approach | 88.13 | 85.27 | 81.99 |
| Mask R-CNN | Precision | Recall | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fold 1 | 78.24 | 39.42 | 37.15 |
| Fold 2 | 77.39 | 39.23 | 36.42 |
| Fold 3 | 69.82 | 32.55 | 31.67 |
| Fold 4 | 78.31 | 40.67 | 38.25 |
| Fold 5 | 72.47 | 35.74 | 31.65 |
| Average | 75.25 | 37.52 | 35.03 |
| Standard Deviation | 3.47 | 2.98 | 2.81 |
| YOLOv5 | Precision | Recall | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fold 1 | 56.22 | 74.17 | 72.81 |
| Fold 2 | 55.40 | 73.92 | 72.04 |
| Fold 3 | 54.82 | 73.36 | 71.94 |
| Fold 4 | 55.27 | 74.03 | 72.14 |
| Fold 5 | 54.98 | 73.45 | 72.48 |
| Average | 55.34 | 73.78 | 72.28 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.48 | 0.32 | 0.32 |
| Our Approach | Precision | Recall | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fold 1 | 88.93 | 83.95 | 81.39 |
| Fold 2 | 84.05 | 86.86 | 83.62 |
| Fold 3 | 88.13 | 85.27 | 81.99 |
| Fold 4 | 81.17 | 86.43 | 83.15 |
| Fold 5 | 80.73 | 84.98 | 81.48 |
| Average | 84.60 | 85.50 | 82.33 |
| Standard Deviation | 3.41 | 1.04 | 0.90 |
| Model | Device | Precision | Recall | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mask R-CNN | Gopro | 80.25 | 25.49 | 21.24 |
| Phone | 75.72 | 34.69 | 32.70 | |
| YOLOv5 | Gopro | 54.49 | 77.45 | 71.19 |
| Phone | 58.21 | 75.63 | 72.04 | |
| Our Approach | Gopro | 71.49 | 66.86 | 61.05 |
| Phone | 82.54 | 83.45 | 77.92 |
| Model | Train/Test | Precision | Recall | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mask R-CNN | Phone/Gopro | 60.45 | 25.48 | 22.58 |
| Gopro/Phone | 43.73 | 17.76 | 14.74 | |
| YOLOv5 | Phone/Gopro | 38.66 | 44.50 | 42.38 |
| Gopro/Phone | 48.29 | 54.84 | 50.47 | |
| Our Approach | Phone/Gopro | 79.94 | 62.32 | 58.34 |
| Gopro/Phone | 76.81 | 79.11 | 72.13 |
| Model | Precision | Recall | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mask R-CNN (Shape) | 94.91 | 89.59 | 92.86 |
| Xception (circle) | 99.73 | 99.73 | - |
| Xception (triangle) | 98.45 | 98.30 | - |
| Model | Number of Training Images | Precision | Recall | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mask R-CNN | 2000 | 77.31 | 39.89 | 35.94 |
| 4000 | 81.37 | 46.22 | 43.32 | |
| 6000 | 77.30 | 38.65 | 35.25 | |
| 8000 | 86.47 | 45.27 | 43.18 | |
| 10,000 | 80.53 | 28.98 | 24.08 | |
| YOLOv5 | 2000 | 49.56 | 61.87 | 58.72 |
| 4000 | 72.19 | 80.42 | 77.91 | |
| 6000 | 77.59 | 86.46 | 85.73 | |
| 8000 | 84.58 | 90.35 | 88.28 | |
| 10,000 | 92.24 | 96.94 | 94.63 | |
| Our Approach | 2000 | 58.09 | 78.58 | 72.51 |
| 4000 | 84.64 | 83.36 | 80.82 | |
| 6000 | 86.46 | 84.39 | 81.56 | |
| 8000 | 78.24 | 86.15 | 82.64 | |
| 10,000 | 92.53 | 89.73 | 88.72 |
| Mask R-CNN | Xception | Precision | Recall | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1024 × 1024 | 224 × 224 | 88.13 | 85.27 | 81.99 |
| 512 × 512 | 112 × 112 | 66.06 | 57.00 | 47.17 |
| 1536 × 1536 | 336 × 336 | 76.50 | 91.12 | 84.34 |
| Resolution | Precision | Recall | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 416 × 416 | 55.49 | 73.44 | 71.12 |
| 208 × 208 | 39.74 | 56.12 | 52.44 |
| 624 × 624 | 82.64 | 88.91 | 87.22 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, E.H.-C.; Gozdzikiewicz, M.; Chang, K.-H.; Ciou, J.-M. A Hierarchical Approach for Traffic Sign Recognition Based on Shape Detection and Image Classification. Sensors 2022, 22, 4768. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22134768
Lu EH-C, Gozdzikiewicz M, Chang K-H, Ciou J-M. A Hierarchical Approach for Traffic Sign Recognition Based on Shape Detection and Image Classification. Sensors. 2022; 22(13):4768. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22134768
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Eric Hsueh-Chan, Michal Gozdzikiewicz, Kuei-Hua Chang, and Jing-Mei Ciou. 2022. "A Hierarchical Approach for Traffic Sign Recognition Based on Shape Detection and Image Classification" Sensors 22, no. 13: 4768. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22134768
APA StyleLu, E. H.-C., Gozdzikiewicz, M., Chang, K.-H., & Ciou, J.-M. (2022). A Hierarchical Approach for Traffic Sign Recognition Based on Shape Detection and Image Classification. Sensors, 22(13), 4768. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22134768






