Upconversion Nanoparticles-Based Fluorescence Immunoassay for the Sensitive Detection of 2-Amino-3-methylimidazo [4,5-f] Quinoline (IQ) in Heat Processed Meat
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Apparatus
2.2. Synthesis of NaYF4: Yb, Er UCNPs
2.3. Modification NaYF4: Yb, Er UCNPs with Polyacrylic Acid
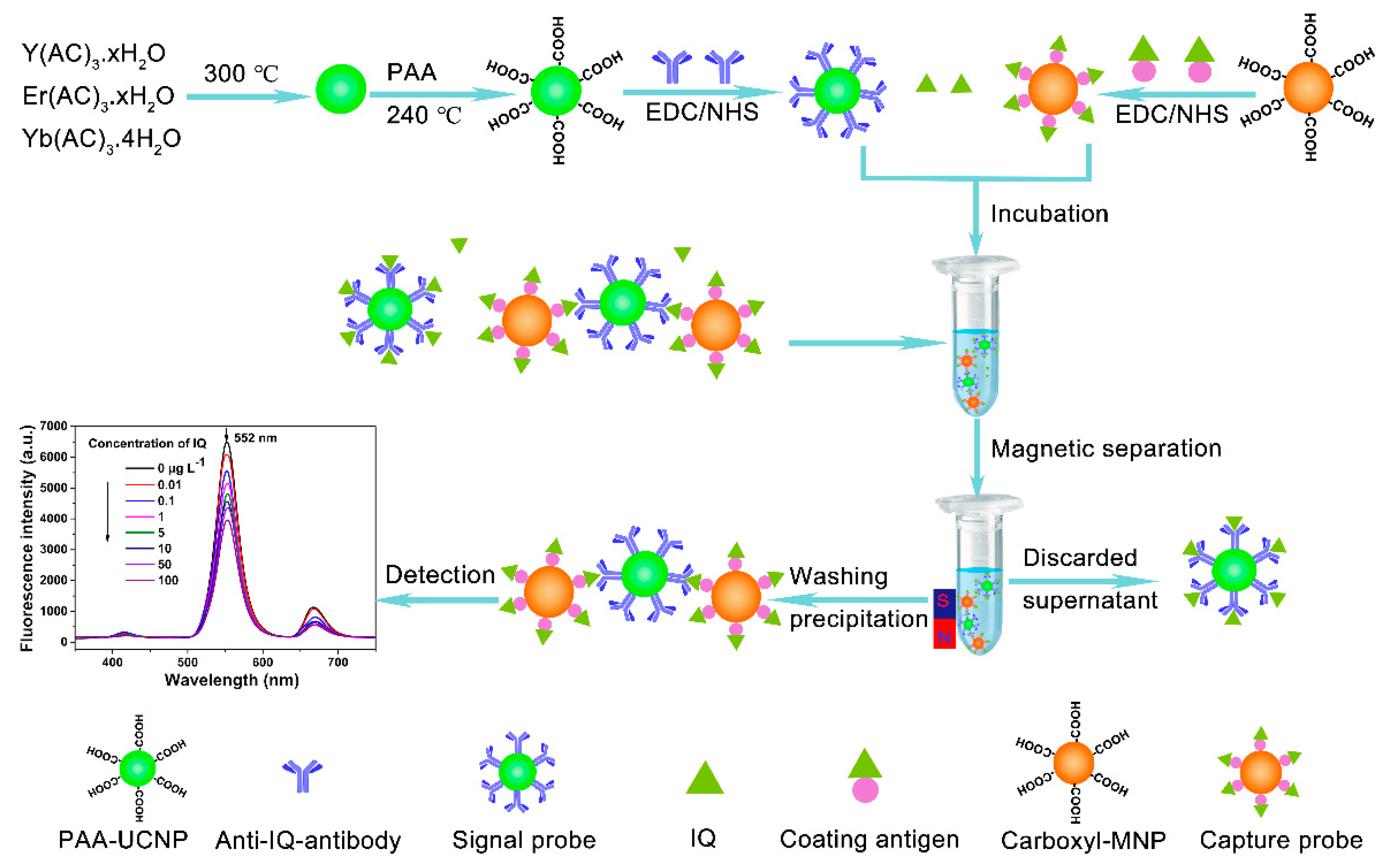
2.4. Preparation of Signal Probe
2.5. Preparation of Coating Antigen
2.6. Preparation of Capture Probe
2.7. Test Principle and Procedure of Assay
2.8. UPLC-MS/MS Analysis
2.9. Sample Preparation
3. Results and Discussions
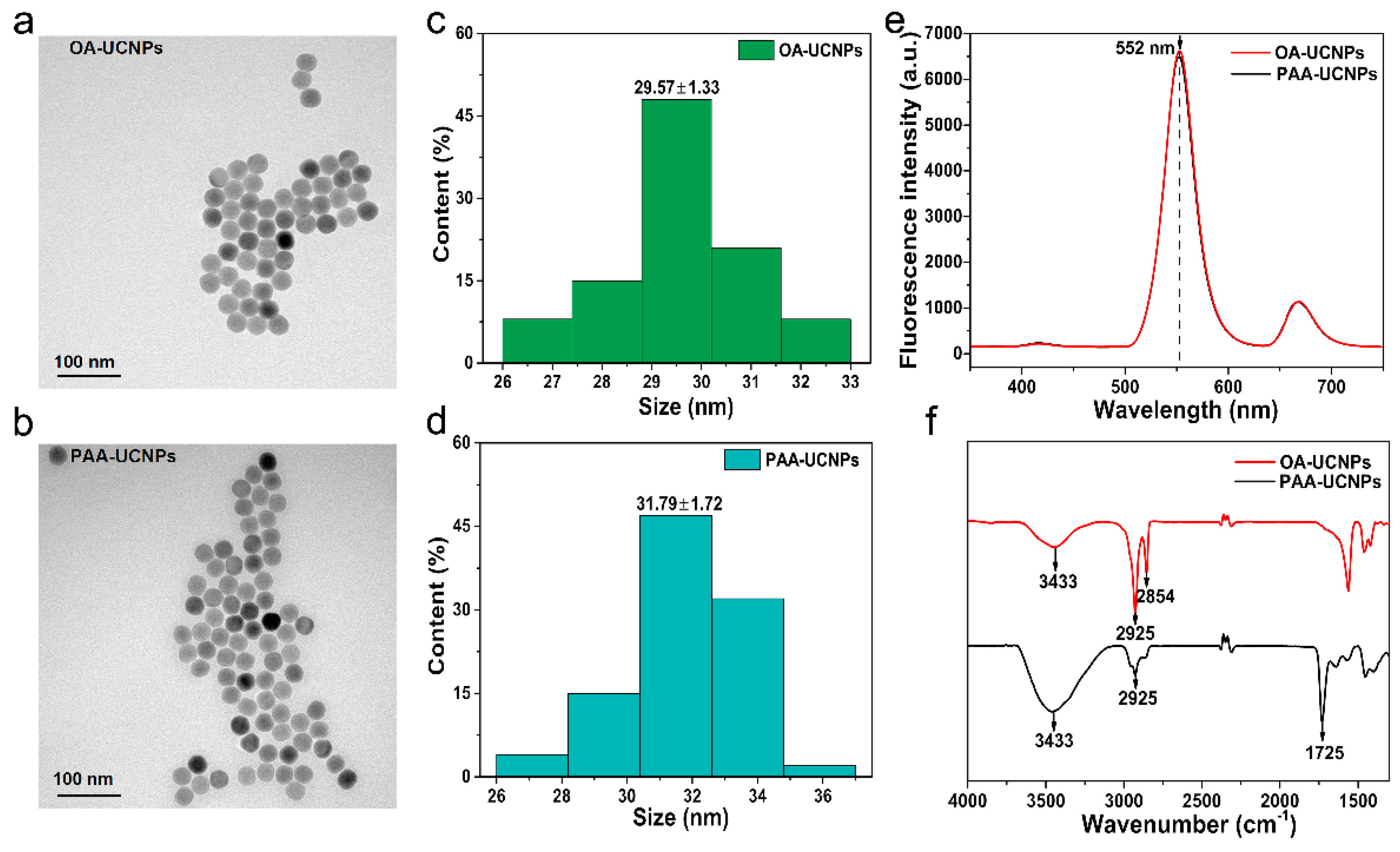
3.1. UCNPs Characterization
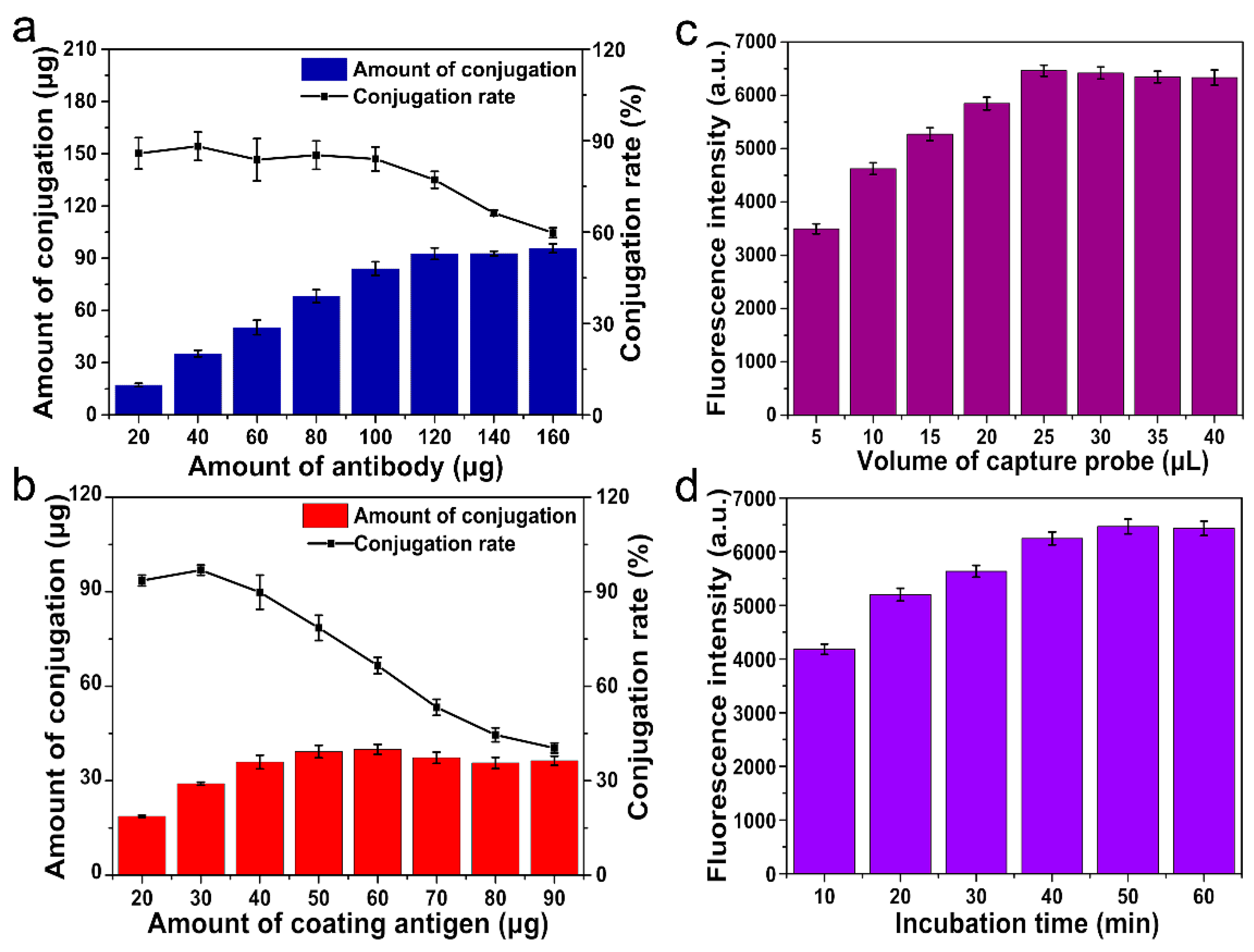
3.2. Optimization of Conditions
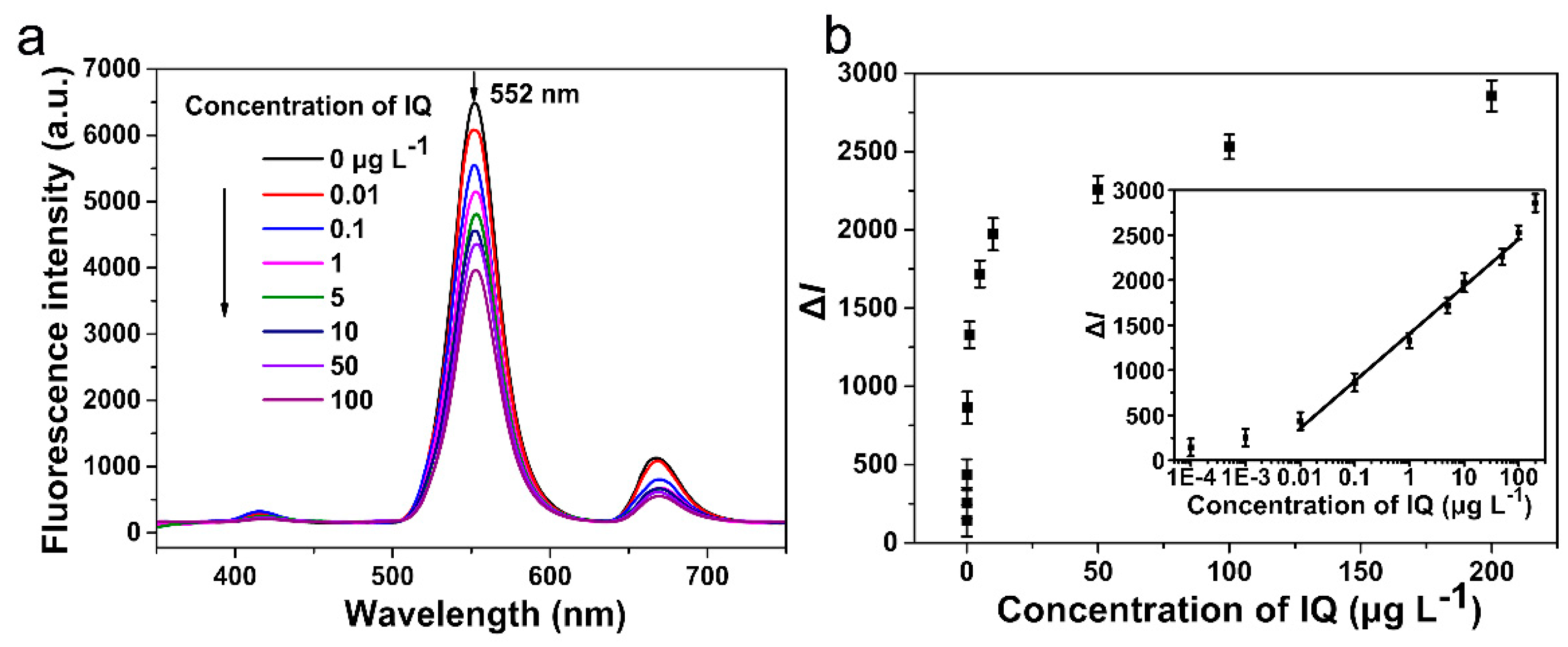
3.3. Analytical Performance
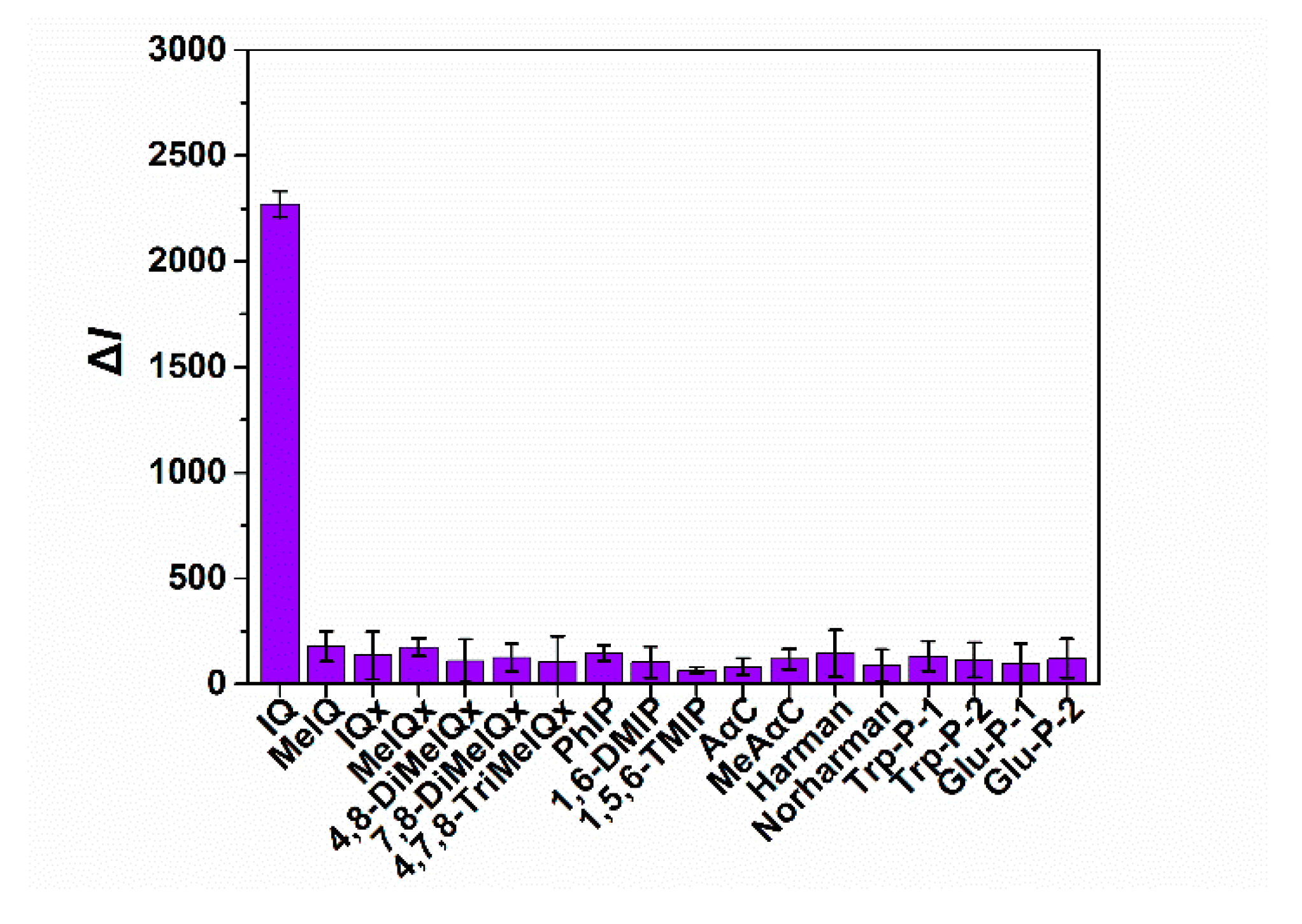
3.4. Specificity Assessment
3.5. Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
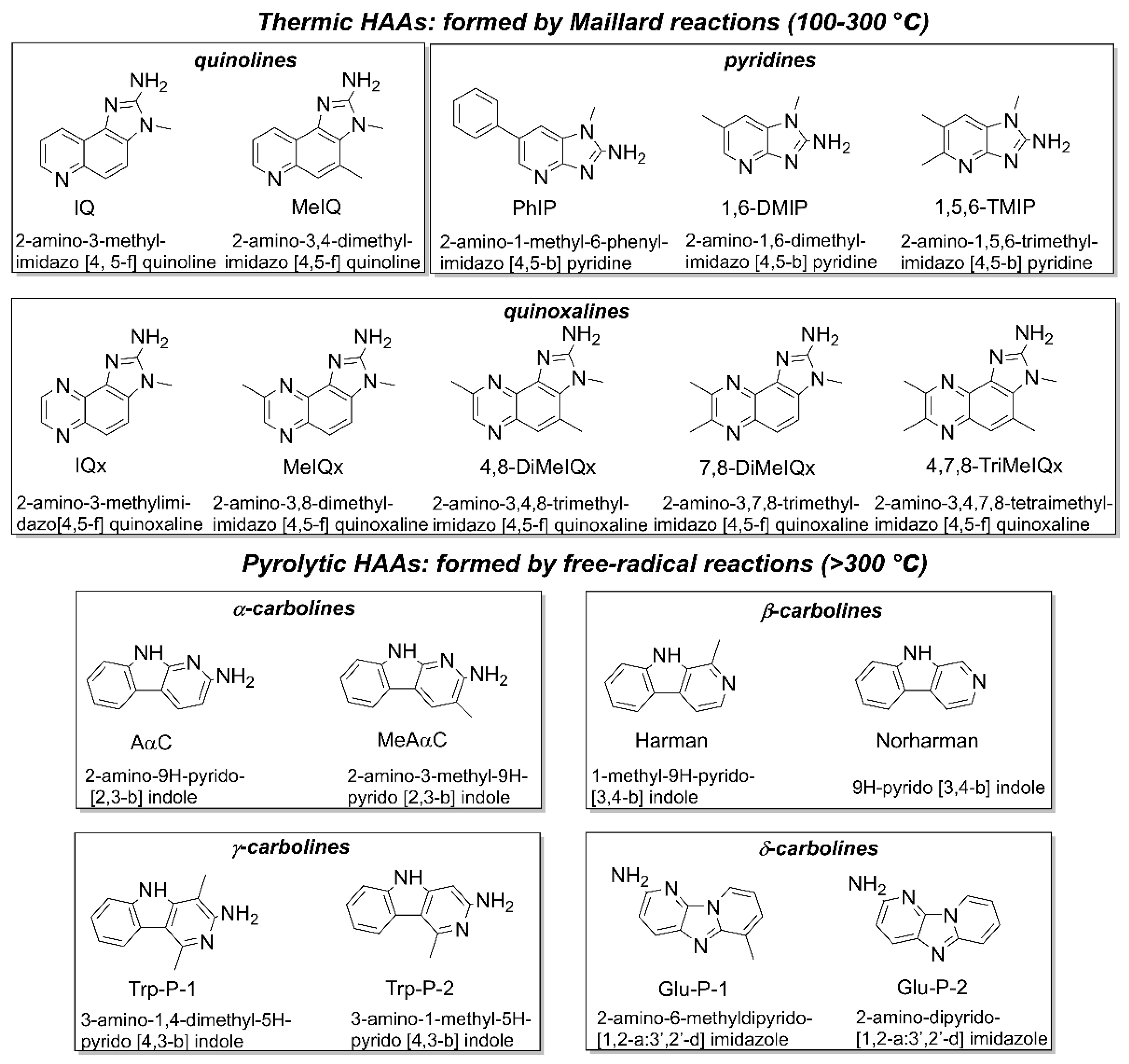
- Sugimura, T. New environmental carcinogens in daily life. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1988, 9, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatch, F.T.; Knize, M.G.; Felton, J.S.; Morgan, R.W. Quantitative structure-activity relationships of heterocyclic amine mutagens formed during the cooking of food. Environ. Mol. Mutagenesis 1991, 17, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jägerstad, M.; Skog, K.; Arvidsson, P.; Solyakov, A. Chemistry, formation and occurrence of genotoxic heterocyclic amines identified in model systems and cooked foods. Z. Lebensm.-Forsch. A 1998, 207, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimura, T. Mutagens, carcinogens, and tumor promoters in our daily food. Cancer 1982, 49, 1970–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohgaki, H.; Kusama, K.; Matsukura, N.; Morino, K.; Hasegawa, H.; Sato, S.; Takayama, S.; Sugimura, T. Carcinogenicity in mice of a mutagenic compound, 2-amino-3-methylimidazo [4,5-f] quinoline, from broiled sardine, cooked beef and beef extract. Carcinogenesis 1984, 5, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, R.H.; Takayama, S.; Sugimura, T.; Thorgeirsson, U.P. Induction of hepatocellular carcinoma in nonhuman primates by the food mutagen 2-amino-3-methylimidazo [4,5-f] quinoline. Environ. Health Perspect. 1994, 102, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- [IARC] International Agency for Research on Cancer. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Some Naturally Occurring Substances: Food Items and Constituents, Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines and Mycotoxins; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 1993; Volume 56, pp. 165–229. [Google Scholar]
- Jägerstad, M.; Reuterswärd, A.L.; Olsson, R.; Grivas, S.; Nyhammar, T.; Olsson, K.; Dahlqvist, A. Creatin(in)e and Maillard reaction products as precursors of mutagenic compounds: Effects of various amino acids. Food Chem. 1983, 12, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özsaraç, N.; Kolsarici, N.; Soncu, E.D.; Haskaraca, G. Formation of heterocyclic aromatic amines in doner kebab cooked with different methods at varying degrees of doneness. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szterk, A. Heterocyclic aromatic amines in grilled beef: The influence of free amino acids, nitrogenous bases, nucleosides, protein and glucose on HAAs content. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 40, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, G.A.; Grüter, A. Quantitation of mutagenic/carcinogenic heterocyclic aromatic amines in food products. J. Chromatogr. 1992, 592, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.C.; Li, G.K.; Xiao, X.H. Acrylamide-modified graphene for online micro-solid-phase extraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography for sensitive analysis of heterocyclic amines in food samples. Talanta 2015, 131, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzegar, F.; Omidi, N.; Kamankesh, M.; Mohammadi, A.; Ferdowsi, R.; Jazaeri, S. An advanced microwave-assisted extraction-low density solvent based on sensitive microextraction method coupled with reverse phase high-performance liquid chromatography for the simultaneous determination of heterocyclic aromatic amines in fried chicken nuggets. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudo, E.; Ruiz-Calero, V.; Puignou, L.; Galceran, M.T. Analysis of heterocyclic amines in chicken by liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 536, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Barzegar, F.; Kamankesh, M.; Khaneghah, A.M. Heterocyclic aromatic amines in doner kebab: Quantitation using an efficient microextraction technique coupled with reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, X.L.; Liu, D.M.; Gao, S.P. Seasonal variations of atmospheric heterocyclic aromatic amines in Beijing, China. Atmos. Res. 2013, 120, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidi, N.; Barzegar, F.; Abedi, A.S.; Kamankesh, M.; Ghanati, K.; Mohammadi, A. Response surface methodology of quantitative of Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines in fried fish using efficient microextraction method coupled with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography: Central composite design. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2021, 59, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H.; Hayatsu, T.; Hietsch, G.; Steinkellner, H.; Nishioka, S.; Narimatsu, S.; Knasmüller, S.; Hayatsu, H. Identification of mutagenic heterocyclic amines (IQ, Trp-P-1 and AαC) in the water of the Danube River. Mutat. Res.-Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagenesis 2000, 466, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chu, X.G.; Sun, L.; Zhao, Y.S.; Ling, Y.; Wang, X.J.; Yong, W.; Yang, M.L.; Li, X.Q. Determination of trace food-derived hazardous compounds in Chinese cooked foods using solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1209, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.Q.; Li, C.; Yu, X.D.; Chen, H.Y. Determination of heterocyclic amines by capillary electrophoresis with UV-DAD detection using on-line preconcentration. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 854, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; Ran, X.Q.; Hu, G.S.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, S. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of 2-amino-3-methylimidazo [4,5-f] quinoline (IQ) in processed foods. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Q.X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of a broad-spectrum heterocyclic aromatic amines (HAAs) antibody and its application in detection of eight HAAs in heat processed meat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 15501–15508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Kuča, K.; Bhatia, S.K.; Saini, K.; Kaushal, A.; Verma, R.; Bhalla, T.C.; Kumar, D. Applications of nanotechnology in sensor-based detection of foodborne pathogens. Sensors 2020, 20, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, B.; Malhotra, K.; Fuku, R.; Van Houten, J.; Qu, G.Y.; Piunno, P.A.E.; Krull, U.J. Recent trends in the developments of analytical probes based on lanthanide-doped upconversion nanoparticles. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 139, 116256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.A.; Parchur, A.K.; Thorat, N.D.; Chen, G.Y. New advances in pre-clinical diagnostic imaging perspectives of functionalized upconversion nanoparticle-based nanomedicine. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 440, 213971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, G.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Pan, H.Z.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.F.; Yan, C.H.; Sun, L.D.; Wang, H.J.; et al. In vivo high-contrast visualization of upconversion nanoparticle labeled virus using time-resolved approach. Nano Today 2021, 40, 101264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahata, M.K.; De, R.; Lee, K.T. Near-infrared-triggered upconverting nanoparticles for biomedicine applications. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, M.L.; Zhong, J.J.; Hong, Y.; Duan, Z.F.; Lin, M.; Xu, F. Inkjet printing upconversion nanoparticles for anti-counterfeit applications. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 4423–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.D.; Zhang, X.; Tian, G.; Yin, W.Y.; Yan, L.; Ruan, L.F.; Yang, Z.Y.; Xiao, D.B.; Gu, Z.J. A simple and efficient synthetic route for preparation of NaYF4 upconversion nanoparticles by thermo-decomposition of rare-earth oleates. CrystengComm 2014, 16, 5650–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.K.; Li, Z.P. Surface modification of hydrophobic NaYF4: Yb,Er upconversion nanophosphors and their applications for immunoassay. Sci. China Chem. 2011, 54, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 5009.243-2016, National Standards of the People’s Republic of China; Announcement of the State Administration of Public Health and Family Planning 2016 No.11; The Administrative Department of Health under the State Council: BeiJing, China, 2016.
- Liao, G.Z.; Wang, G.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Effect of cooking methods on the formation of heterocyclic aromatic amines in chicken and duck breast. Meat Sci. 2010, 85, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Fry Time (min) | This Method (μg kg−1) | UPLC-MS/MS (μg kg−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Mean ± SD) | CV (%) | (Mean ± SD) | CV (%) | ||
| Chicken | 0 | ND | - | ND | - |
| 5 | 2.11 ± 0.27 b | 12.80 | 1.95 ± 0.23 b | 11.79 | |
| 10 | 2.56 ± 0.37 b | 14.45 | 2.44 ± 0.30 ab | 12.30 | |
| 15 | 3.47 ± 0.44 a | 12.68 | 3.15 ± 0.54 a | 17.14 | |
| Fish | 0 | ND | - | ND | - |
| 3 | 1.35 ± 0.18 b | 13.33 | 1.19 ± 0.09 b | 7.56 | |
| 5 | 2.56 ± 0.21 a | 8.20 | 2.47 ± 0.15 a | 6.07 | |
| 10 | 2.85 ± 0.40 a | 14.04 | 2.82 ± 0.32 a | 11.35 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Sheng, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, B.; Huang, N.; Wang, S. Upconversion Nanoparticles-Based Fluorescence Immunoassay for the Sensitive Detection of 2-Amino-3-methylimidazo [4,5-f] Quinoline (IQ) in Heat Processed Meat. Sensors 2022, 22, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010008
Huang X, Sheng W, Chen H, Zhang B, Huang N, Wang S. Upconversion Nanoparticles-Based Fluorescence Immunoassay for the Sensitive Detection of 2-Amino-3-methylimidazo [4,5-f] Quinoline (IQ) in Heat Processed Meat. Sensors. 2022; 22(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xufang, Wei Sheng, Haonan Chen, Biao Zhang, Na Huang, and Shuo Wang. 2022. "Upconversion Nanoparticles-Based Fluorescence Immunoassay for the Sensitive Detection of 2-Amino-3-methylimidazo [4,5-f] Quinoline (IQ) in Heat Processed Meat" Sensors 22, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010008
APA StyleHuang, X., Sheng, W., Chen, H., Zhang, B., Huang, N., & Wang, S. (2022). Upconversion Nanoparticles-Based Fluorescence Immunoassay for the Sensitive Detection of 2-Amino-3-methylimidazo [4,5-f] Quinoline (IQ) in Heat Processed Meat. Sensors, 22(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22010008







