Validity of Hip and Ankle Worn Actigraph Accelerometers for Measuring Steps as a Function of Gait Speed during Steady State Walking and Continuous Turning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
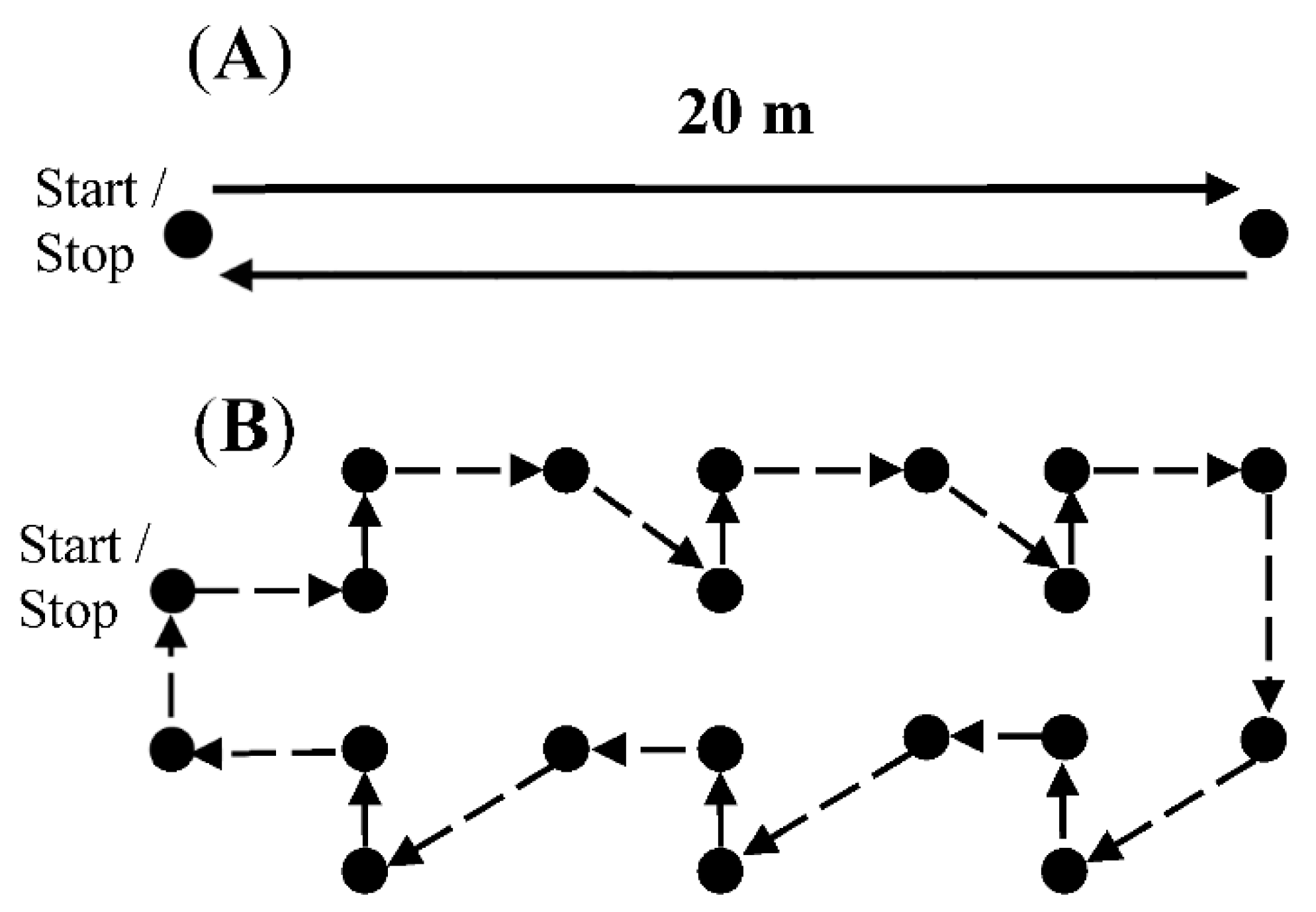
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Number of Steps and Time Spent in Each Gait Speed Group for Straight Walking and Walking with Continuous Turning
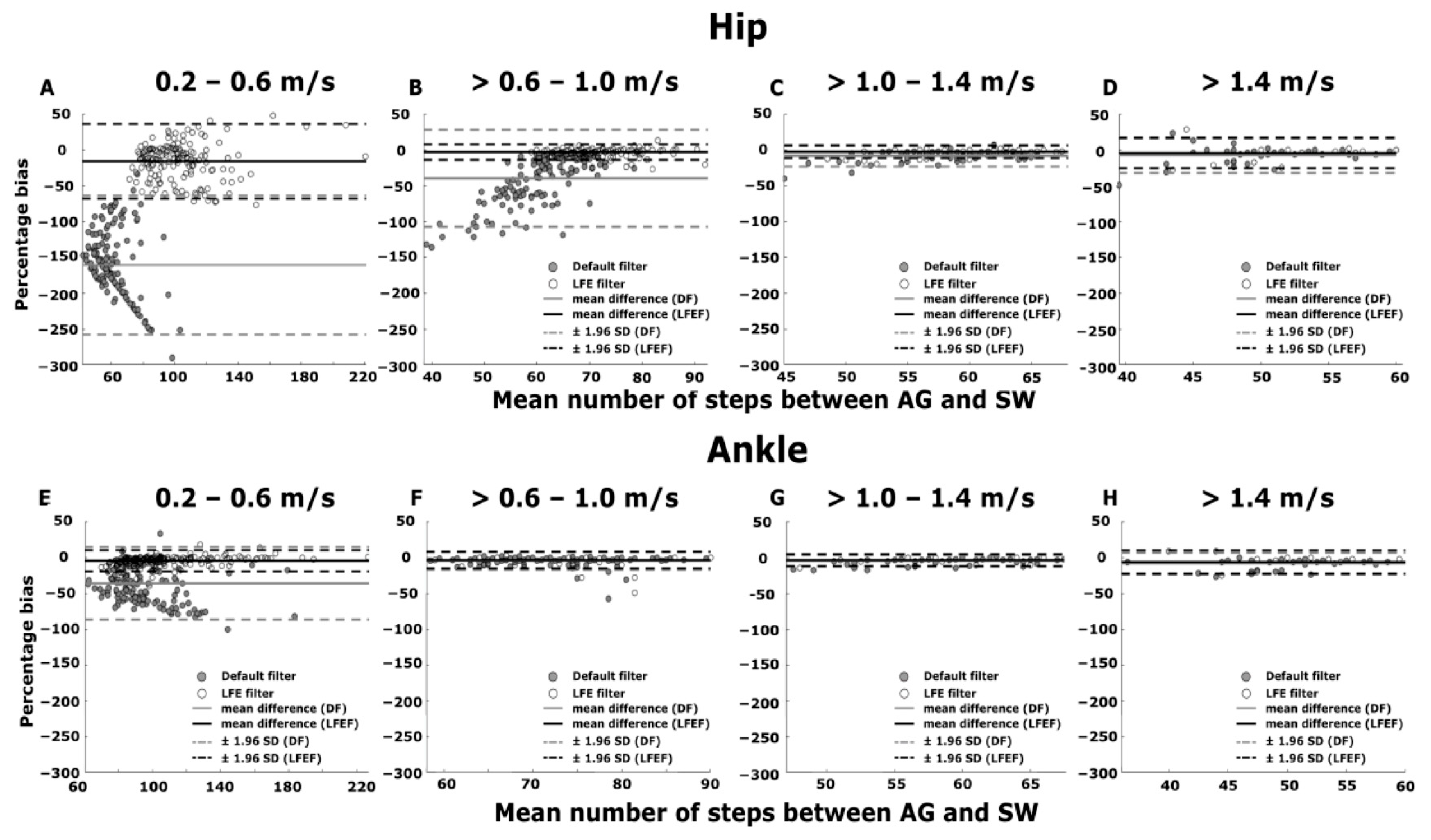
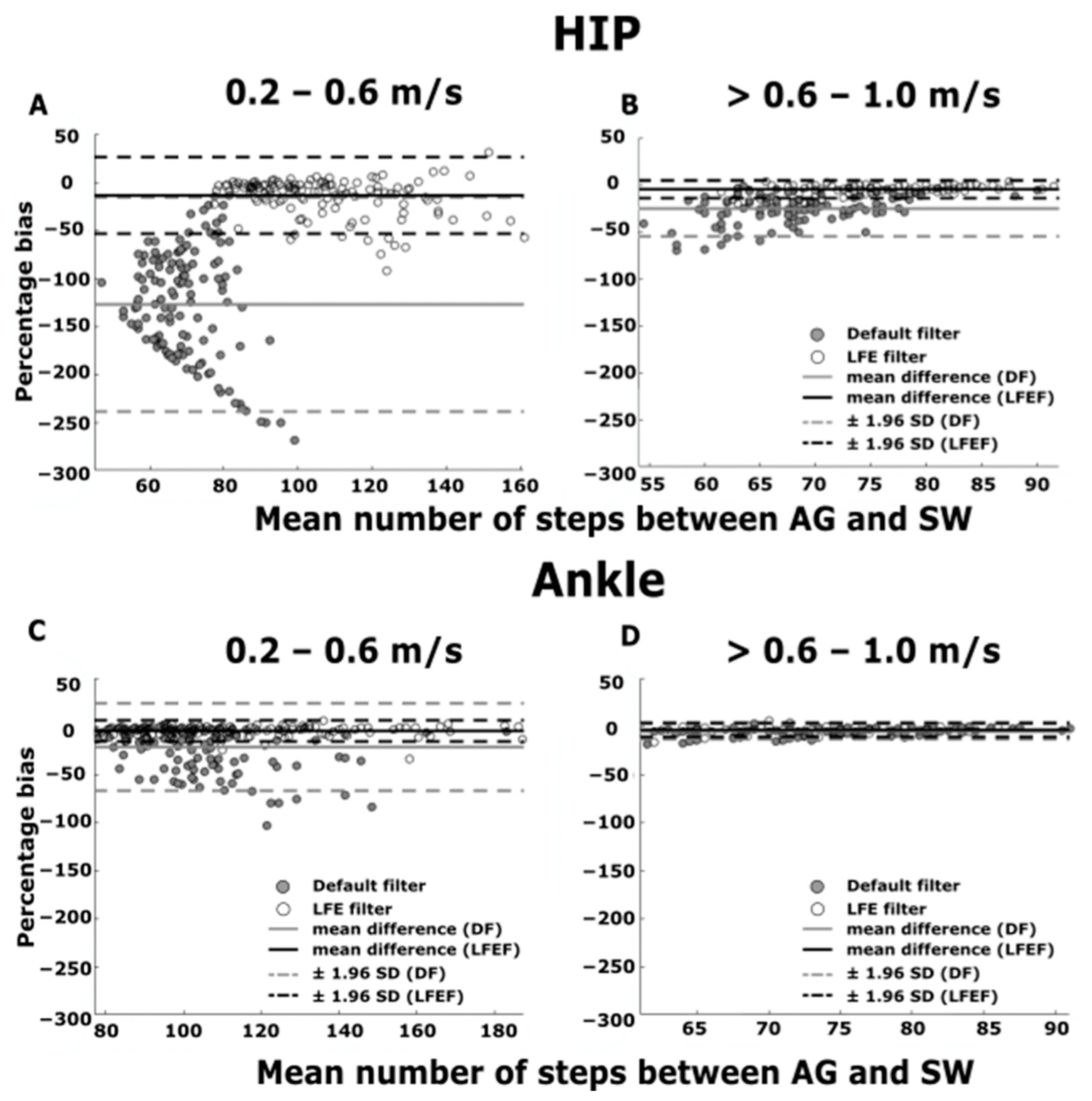
3.2. Straight Walking
3.3. Walking with Continuous Turning
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hergenroeder, A.L.; Gibbs, B.B.; Kotlarczyk, M.P.; Kowalsky, R.J.; Perera, S.; Brach, J.S. Accuracy of Objective Physical Activity Monitors in Measuring Steps in Older Adults. Gerontol. Geriatr. Med. 2018, 4, 2333721418781126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudor-Locke, C.; Craig, C.L.; Aoyagi, Y.; Bell, R.C.; A Croteau, K.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Ewald, B.; Gardner, A.W.; Hatano, Y.; Lutes, L.D.; et al. How many steps/day are enough? For older adults and special populations. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, A.; Fritz, S.L.; Lusardi, M. Walking speed: The functional vital sign. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2015, 23, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karas, M.; Bai, J.; Strączkiewicz, M.; Harezlak, J.; Glynn, N.W.; Harris, T.; Zipunnikov, V.; Crainiceanu, C.; Urbanek, J.K. Accelerometry Data in Health Research: Challenges and Opportunities. Stat. Biosci. 2019, 11, 210–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storti, K.L.; Pettee, K.K.; Brach, J.S.; Talkowski, J.B.; Richardson, C.R.; Kriska, A.M. Gait Speed and Step-Count Monitor Accuracy in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.; DePaul, V.G.; Knorr, S.; Wong, J.S.; Mansfield, A.; Patterson, K.K. Validity of the ActiGraph activity monitor for individuals who walk slowly post-stroke. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2018, 25, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, D.; Morton, A.; Arguello, D.; Lyden, K.; Bassett, D. “What Is a Step?” Differences in How a Step Is Detected among Three Popular Activity Monitors That Have Impacted Physical Activity Research. Sensors 2018, 18, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, S.C.; John, P.D.S. Comparison of ActiGraph GT3X+ and StepWatch Step Count Accuracy in Geriatric Rehabilitation Patients. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2016, 24, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treacy, D.; Hassett, L.; Schurr, K.; Chagpar, S.; Paul, S.S.; Sherrington, C. Validity of Different Activity Monitors to Count Steps in an Inpatient Rehabilitation Setting. Phys. Ther. 2017, 97, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingebrigtsen, J.; Stemland, I.; Christiansen, C.; Skotte, J.; Hanisch, C.; Krustrup, P.; Holtermann, A. Validation of a Commercial and Custom Made Accelerometer-Based Software for Step Count and Frequency during Walking and Running. J. Ergon. 2013, 3, 1000119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugade, V.; Fortune, E.; Morrow, M.; Kaufman, K. Validity of using tri-axial accelerometers to measure human movement—Part I: Posture and movement detection. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, P.M.; Dall, P.M.; Mitchell, S.L.; Granat, M.H. Activity-Monitor Accuracy in Measuring Step Number and Cadence in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2008, 16, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feito, Y.; Bassett, D.R.; Thompson, D.L. Evaluation of Activity Monitors in Controlled and Free-Living Environments. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2012, 44, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feito, Y.; Garner, H.R.; Bassett, D.R. Evaluation of ActiGraph’s Low-Frequency Filter in Laboratory and Free-Living Environments. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandroff, B.M.; Motl, R.W.; Pilutti, L.A.; Learmonth, Y.C.; Ensari, I.; Dlugonski, D.; Klaren, R.E.; Balantrapu, S.; Riskin, B.J. Accuracy of StepWatch™ and ActiGraph Accelerometers for Measuring Steps Taken among Persons with Multiple Sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orendurff, M.S. How humans walk: Bout duration, steps per bout, and rest duration. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2008, 45, 1077–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaister, B.C.; Bernatz, G.C.; Klute, G.K.; Orendurff, M.S. Video task analysis of turning during activities of daily living. Gait Posture 2007, 25, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallén, M.B.; Nero, H.; Franzén, E.; Hagströmer, M. Comparison of two accelerometer filter settings in individuals with Parkinson’s disease. Physiol. Meas. 2014, 35, 2287–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, L.P.; Park, S.; Springer, C.M.; Feyerabend, M.D.; Steeves, J.A.; Bassett, D.R. Video-Recorded Validation of Wearable Step Counters under Free-living Conditions. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klassen, T.D.; Simpson, L.A.; Lim, S.B.; Louie, D.R.; Parappilly, B.; Sakakibara, B.M.; Zbogar, D.; Eng, J.J. “Stepping Up” Activity Poststroke: Ankle-Positioned Accelerometer Can Accurately Record Steps During Slow Walking. Phys. Ther. 2016, 96, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svarre, F.R.; Jensen, M.M.; Nielsen, J.; Villumsen, M. The validity of activity trackers is affected by walking speed: The criterion validity of Garmin Vivosmart((R)) HR and StepWatch() 3 for measuring steps at various walking speeds under controlled conditions. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brønd, J.C.; Andersen, L.B.; Arvidsson, D. Generating ActiGraph Counts from Raw Acceleration Recorded by an Alternative Monitor. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 2351–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryon, W.W.; Williams, R. Fully proportional actigraphy: A new instrument. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 1996, 28, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feito, Y.; Hornbuckle, L.M.; Reid, L.A.; Crouter, S.E. Effect of ActiGraph’s low frequency extension for estimating steps and physical activity intensity. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, S.; Lusardi, M. White paper: “walking speed: The sixth vital sign”. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2009, 32, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobak, C.A.; Barr, P.J.; O’Malley, A.J. Estimation of an inter-rater intra-class correlation coefficient that overcomes common assumption violations in the assessment of health measurement scales. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2018, 18, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giavarina, D. Understanding Bland Altman analysis. Biochem. Med. 2015, 25, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrini, F.; Gasperini, G.; Guanziroli, E.; Vitale, J.A.; Banfi, G.; Molteni, F. Using an Accelerometer-Based Step Counter in Post-Stroke Patients: Validation of a Low-Cost Tool. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpan, S.M.; Schafer, J.L.; Wilson, K.C.; Webber, S.C. Effect of ActiGraph GT3X+ Position and Algorithm Choice on Step Count Accuracy in Older Adults. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2015, 23, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreira, T.V.; Brouillette, R.M.; Foil, H.C.; Keller, J.N.; Tudor-Locke, C. Comparison of Older Adults’ Steps per Day Using an NL-1000 Pedometer and Two GT3X+ Accelerometer Filters. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2013, 21, 402–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galna, B.; Lord, S.; Rochester, L. Is gait variability reliable in older adults and Parkinson’s disease? Towards an optimal testing protocol. Gait Postur. 2013, 37, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Straight Walking | Continuous Turning | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gait Speed (m/s) | Ankle | Hip | Ankle | Hip | ||||
| DF | LFEF | DF | LFEF | DF | LFEF | DF | LFEF | |
| 0.2–0.6 | 71 (19) | 96 (7) | 12 (17) | 87 (22) | 82 (17) | 96 (5) | 25 (23) | 88 (15) |
| >0.6–1.0 | 96 (5) | 97 (5) | 69 (25) | 97 (5) | 95 (4) | 97 (4) | 78 (13) | 96 (5) |
| >1.0–1.4 | 96 (4) | 97 (4) | 92 (7) | 97 (4) | - | - | - | - |
| >1.4 | 92 (8) | 94 (8) | 94 (12) | 96 (11) | - | - | - | - |
| Straight Ahead Walking | Continuous Turning | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gait Speed (m/s) | Ankle | Hip | Ankle | Hip | ||||
| DF | LFEF | DF | LFEF | DF | LFEF | DF | LFEF | |
| 0.2–0.6 | 0.29 | 0.97 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.28 | 0.97 | 0.00 | 0.58 |
| >0.6–1.0 | 0.79 | 0.83 | 0.00 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.12 | 0.88 |
| >1.0–1.4 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.58 | 0.87 | - | - | - | - |
| >1.4 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.42 | 0.57 | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bezuidenhout, L.; Thurston, C.; Hagströmer, M.; Moulaee Conradsson, D. Validity of Hip and Ankle Worn Actigraph Accelerometers for Measuring Steps as a Function of Gait Speed during Steady State Walking and Continuous Turning. Sensors 2021, 21, 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21093154
Bezuidenhout L, Thurston C, Hagströmer M, Moulaee Conradsson D. Validity of Hip and Ankle Worn Actigraph Accelerometers for Measuring Steps as a Function of Gait Speed during Steady State Walking and Continuous Turning. Sensors. 2021; 21(9):3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21093154
Chicago/Turabian StyleBezuidenhout, Lucian, Charlotte Thurston, Maria Hagströmer, and David Moulaee Conradsson. 2021. "Validity of Hip and Ankle Worn Actigraph Accelerometers for Measuring Steps as a Function of Gait Speed during Steady State Walking and Continuous Turning" Sensors 21, no. 9: 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21093154
APA StyleBezuidenhout, L., Thurston, C., Hagströmer, M., & Moulaee Conradsson, D. (2021). Validity of Hip and Ankle Worn Actigraph Accelerometers for Measuring Steps as a Function of Gait Speed during Steady State Walking and Continuous Turning. Sensors, 21(9), 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21093154






