Condition Assessment of Industrial Gas Turbine Compressor Using a Drift Soft Sensor Based in Autoencoder
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Maintenance
1.2. Industrial Gas Turbines
1.3. Machine Learning Diagnosis
2. Materials and Methods
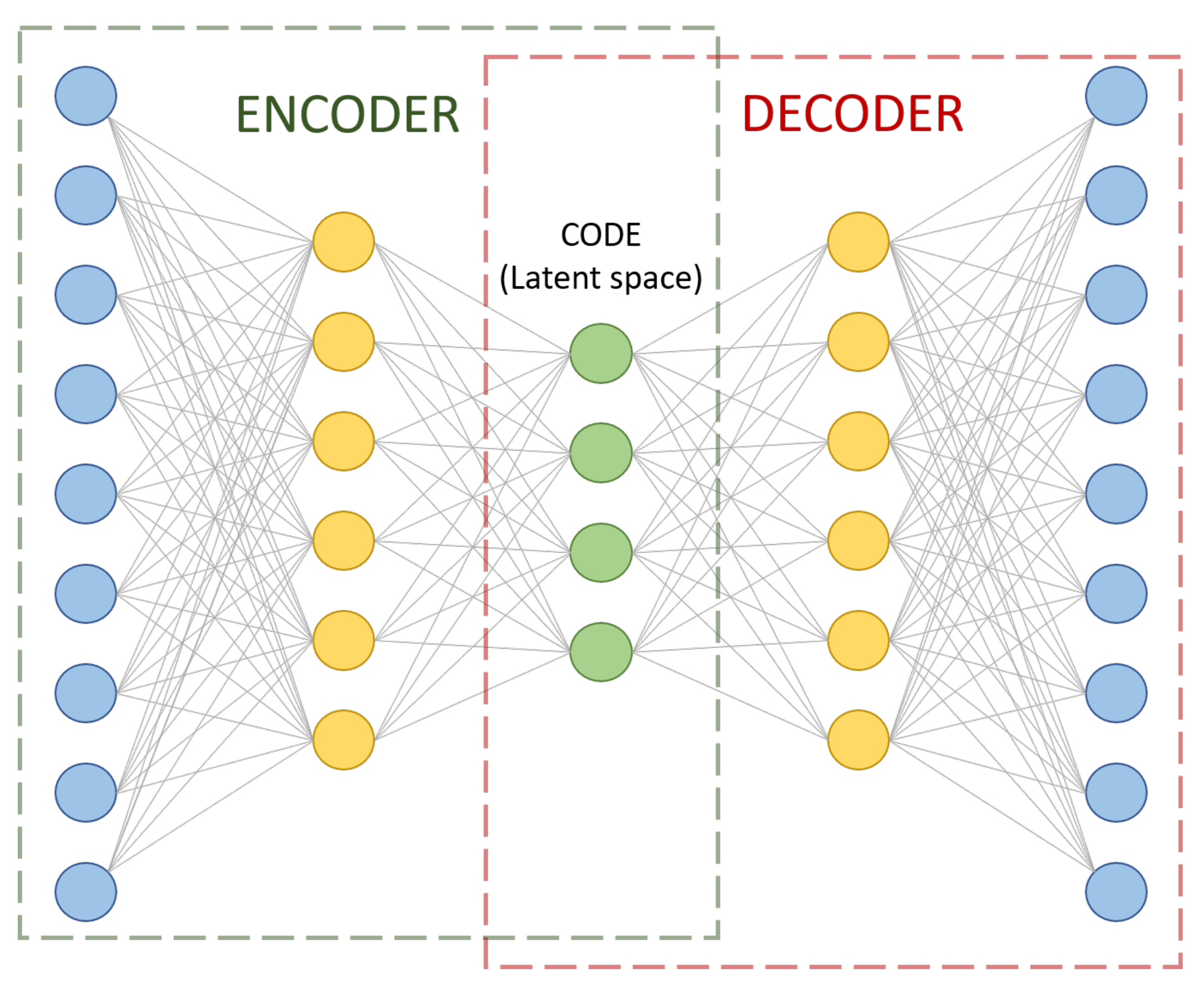
2.1. Soft Sensor Model Description
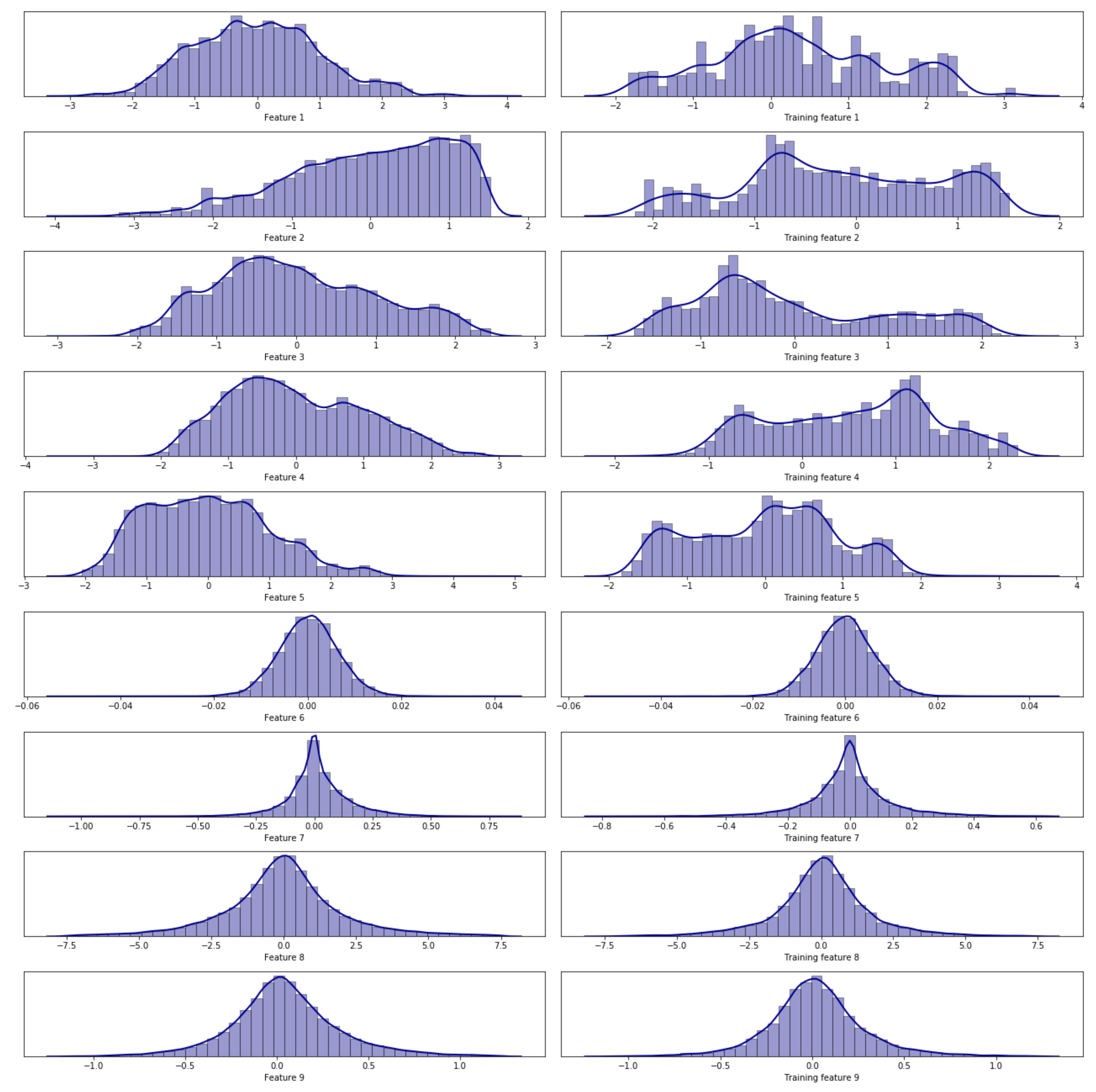
2.2. Data Processing
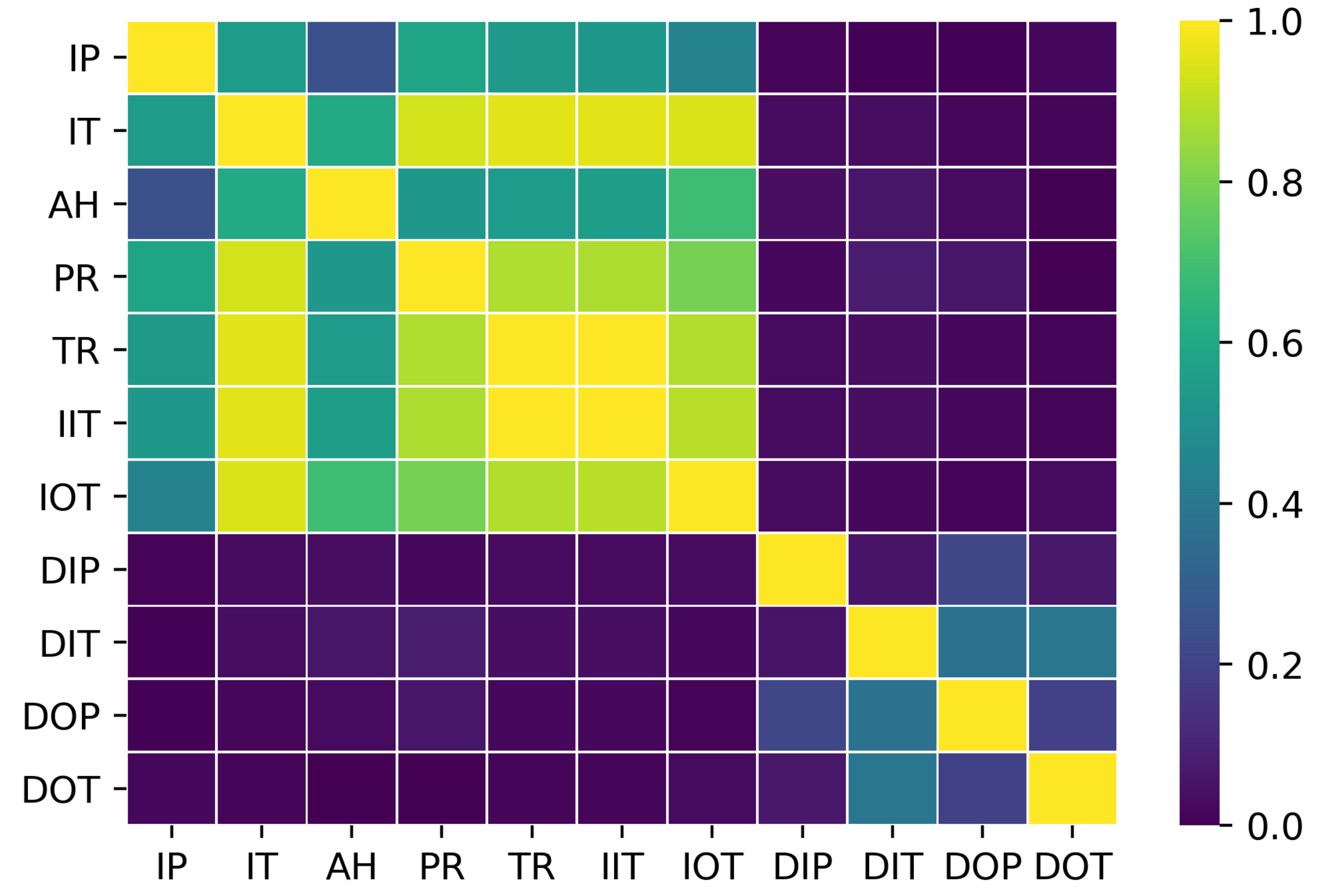
- Inlet pressure (IP),
- Inlet temperature (IT),
- Relative ambient humidity (AH),
- Pressure ratio (PR),
- Temperature ratio (TR),
- Inverse of the inlet temperature(IIT),
- Inverse of the outlet temperature (IOT),
- Inlet pressure differential (DIP),
- Input temperature differential (DIT),
- Output pressure differential (DOP),
- Output temperature differential (DOT),
2.3. Data Set
3. Results
3.1. Model Distance
3.2. Time-Window Samples Processing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tu, P.Y.; Yam, R.; Tse, P.; Sun, A. An integrated maintenance management system for an advanced manufacturing company. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2001, 17, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteli, M.; Mancarella, P. Influence of extreme weather and climate change on the resilience of power systems: Impacts and possible mitigation strategies. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2015, 127, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, K.; Komonen, K.; Oedewald, P.; Peltonen, M.; Reiman, T.; Rouhiainen, V.; Tervo, J.; Heino, P. Safety and Reliability—Technology Review; Number BTUO43-031209 in VTT Research Report; VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland: Espoo, Finland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Prakash, G.; Yuan, X.X.; Hazra, B.; Mizutani, D. Toward a big data-based approach: A review on degradation models for prognosis of critical infrastructure. J. Nondestruct. Eval. Diagn. Progn. Eng. Syst. 2021, 4, 021005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, M.P. Gas Turbine Engineering Handbook; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- de León Hijes, F.C.G.; Cartagena, J.J.R. Maintenance strategy based on a multicriterion classification of equipments. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2006, 91, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, C.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, Y. A corrective maintenance scheme for engineering equipment. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2014, 36, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, L. Linking maintenance strategies to performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2001, 70, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinga, T. Application of physical failure models to enable usage and load based maintenance. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2010, 95, 1061–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirmohammadi, A.H.; Zhang, Z.G.; Love, E. A computational model for determining the optimal preventive maintenance policy with random breakdowns and imperfect repairs. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2007, 56, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.M.; Cao, Y.; Ng, K.H. Chapter Big Data Analytics for Predictive Maintenance Strategies. In Supply Chain Management in the Big Data Era; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 50–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinga, T.; Loendersloot, R. Aligning PHM, SHM and CBM by understanding the physical system failure behaviour. In Proceedings of the European Conference on the Prognostics and Health Management Society, Nantes, France, 8–10 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lin, P.; Wen, Y.; Deng, R. A survey of predictive maintenance: Systems, purposes and approaches. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.07383. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez Muñoz, C.Q.; García Márquez, F.P.; Hernández Crespo, B.; Makaya, K. Structural health monitoring for delamination detection and location in wind turbine blades employing guided waves. Wind Energy 2019, 22, 698–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Goebel, K. Information fusion for national airspace system prognostics: A NASA ULI project. In Proceedings of the 10th Annual Conference of the Prognostics and Health Management Society, PHM, Philadelphia Center City, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 24–27 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zonta, T.; da Costa, C.A.; da Rosa Righi, R.; de Lima, M.J.; da Trindade, E.S.; Li, G.P. Predictive maintenance in the Industry 4.0: A systematic literature review. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 150, 106889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, R.; Brun, K. Degradation in Gas Turbine Systems. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2000, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqallaf, J.; Ali, N.; Teixeira, J.A.; Addali, A. Solid Particle Erosion Behaviour and Protective Coatings for Gas Turbine Compressor Blades—A Review. Processes 2020, 8, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Yang, B.; Jiang, X.; Jia, F.; Li, N.; Nandi, A.K. Applications of machine learning to machine fault diagnosis: A review and roadmap. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 138, 106587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, Z.; Luo, H.; Xie, P. A Review of Intelligent Fault Diagnosis for High-Speed Trains: Qualitative Approaches. Entropy 2021, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, J.; Peterson, J. Predictive maintenance: How big data analysis can improve maintenance. In Supply Chain Integration Challenges in Commercial Aerospace; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 267–278. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.; Wu, Q.; Ding, G.; Xu, Y.; Feng, S. A survey of machine learning for big data processing. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2016, 2016, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, F.; Lei, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhou, X.; Lu, N. Deep neural networks: A promising tool for fault characteristic mining and intelligent diagnosis of rotating machinery with massive data. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 72, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Yang, F.; Fan, X.; Huang, Z.; Tsui, K.L. Extracting degradation trends for roller bearings by using a moving-average stacked auto-encoder and a novel exponential function. Measurement 2020, 152, 107371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, H. Soft sensor based on stacked auto-encoder deep neural network for air preheater rotor deformation prediction. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2018, 36, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Hossain, M.M.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, C. Combustion stability monitoring through flame imaging and stacked sparse autoencoder based deep neural network. Appl. Energy 2020, 259, 114159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Yu, L. On accurate and reliable anomaly detection for gas turbine combustors: A deep learning approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.09238. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Tang, J.; Qiao, J.; Cui, C. Review of Concept Drift Detection Method for Industrial Process Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2020 39th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Shenyang, China, 27–29 July 2020; pp. 5754–5759. [Google Scholar]
- Tsymbal, A. The problem of concept drift: definitions and related work. Comput. Sci. Dep. Trinity Coll. Dublin 2004, 106, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Yu, D. Deep learning: methods and applications. Found. Trends Signal Process. 2014, 7, 197–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlec, P.; Gabrys, B.; Strandt, S. Data-driven soft sensors in the process industry. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2009, 33, 795–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Liao, G.; Liu, H.; Kuang, G. A review of the autoencoder and its variants: A comparative perspective from target recognition in synthetic-aperture radar images. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Mag. 2018, 6, 44–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

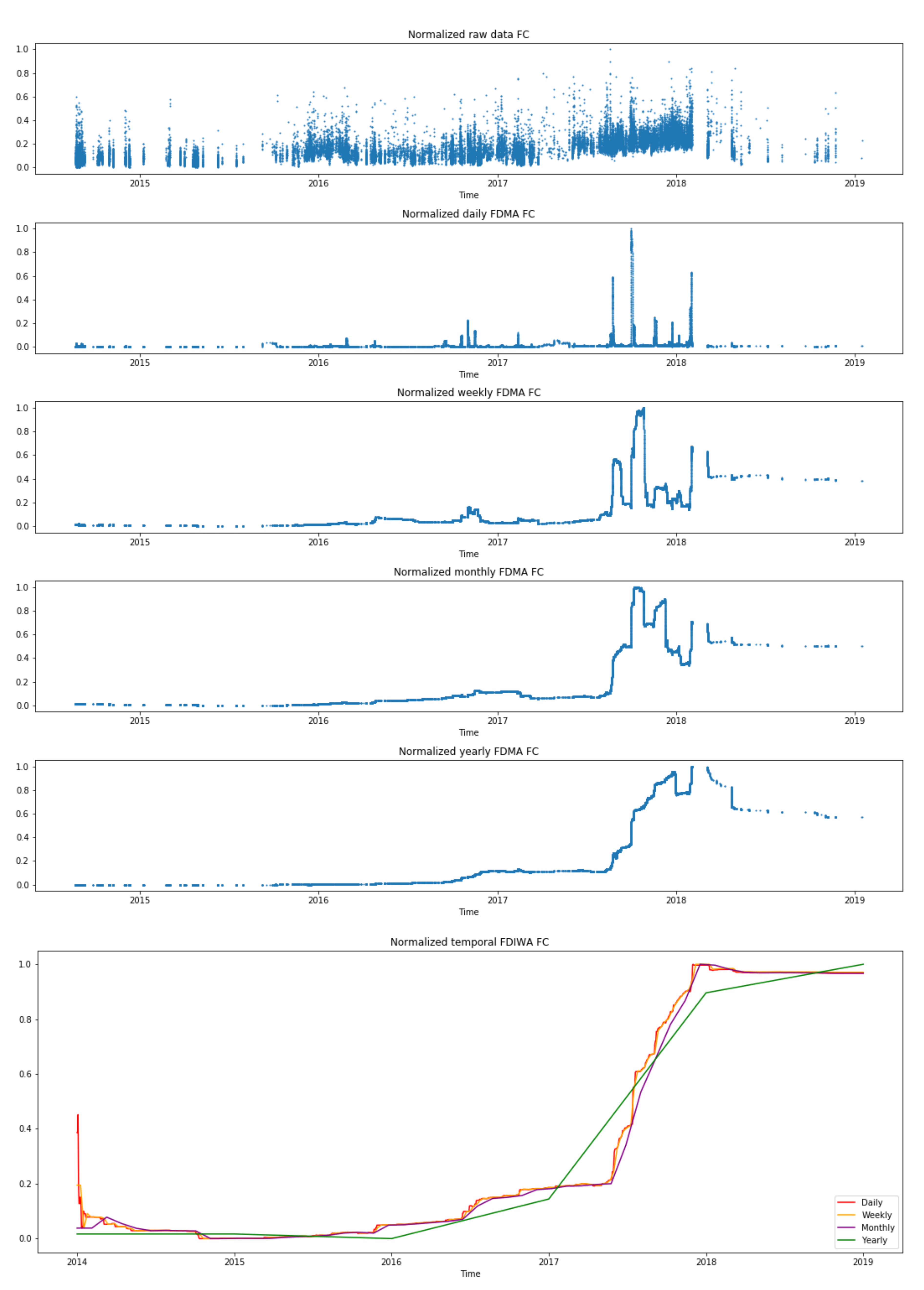
| Moving Average | Incremental Window Average | |
|---|---|---|
| Absolute Error | AEMA | FDMA |
| Fréchet distance | AEIWA | FDIWA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Castro-Cros, M.; Rosso, S.; Bahilo, E.; Velasco, M.; Angulo, C. Condition Assessment of Industrial Gas Turbine Compressor Using a Drift Soft Sensor Based in Autoencoder. Sensors 2021, 21, 2708. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082708
de Castro-Cros M, Rosso S, Bahilo E, Velasco M, Angulo C. Condition Assessment of Industrial Gas Turbine Compressor Using a Drift Soft Sensor Based in Autoencoder. Sensors. 2021; 21(8):2708. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082708
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Castro-Cros, Martí, Stefano Rosso, Edgar Bahilo, Manel Velasco, and Cecilio Angulo. 2021. "Condition Assessment of Industrial Gas Turbine Compressor Using a Drift Soft Sensor Based in Autoencoder" Sensors 21, no. 8: 2708. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082708
APA Stylede Castro-Cros, M., Rosso, S., Bahilo, E., Velasco, M., & Angulo, C. (2021). Condition Assessment of Industrial Gas Turbine Compressor Using a Drift Soft Sensor Based in Autoencoder. Sensors, 21(8), 2708. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082708







