A Fast Shape-from-Focus-Based Surface Topography Measurement Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
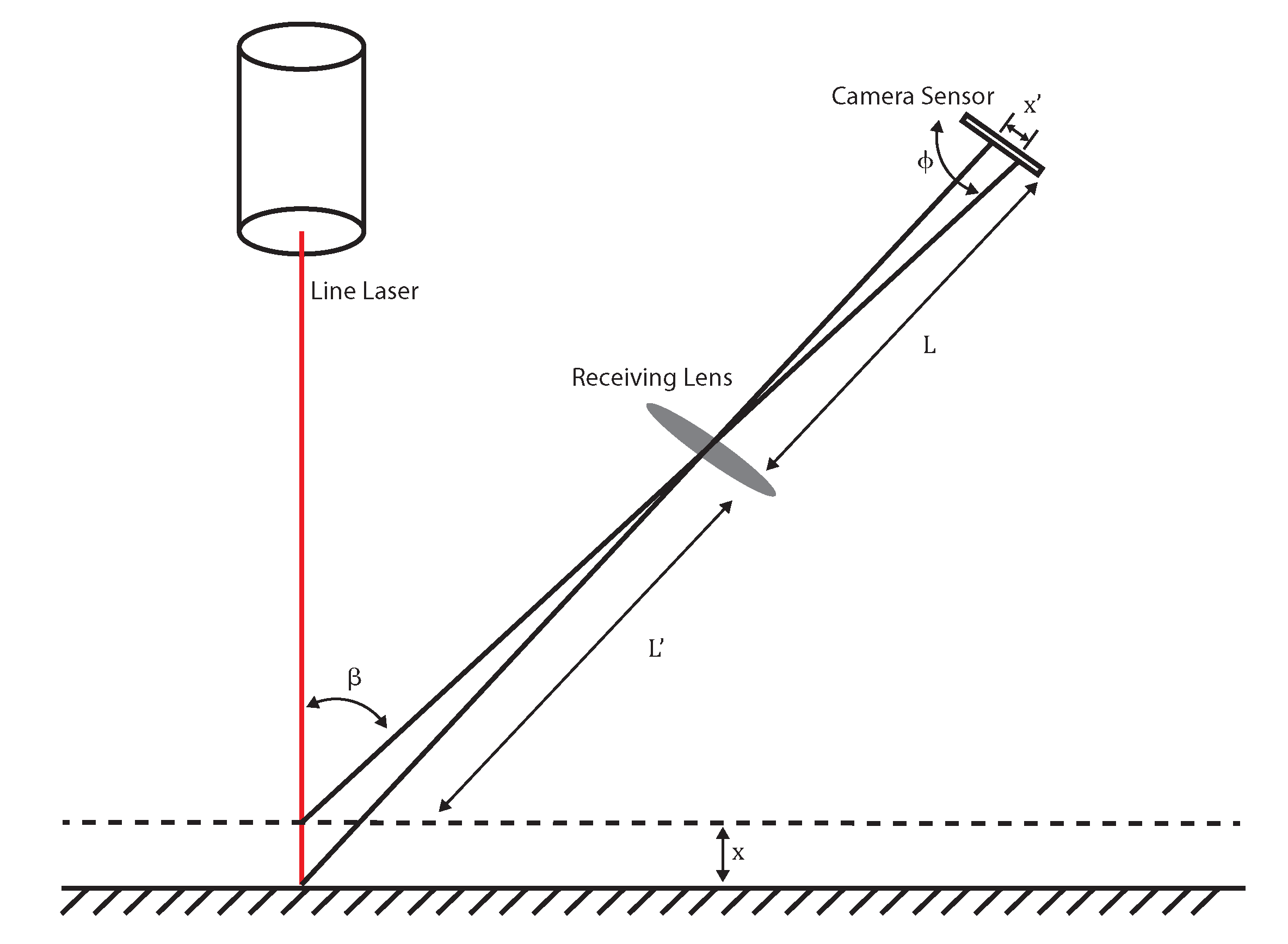
2. Methodology
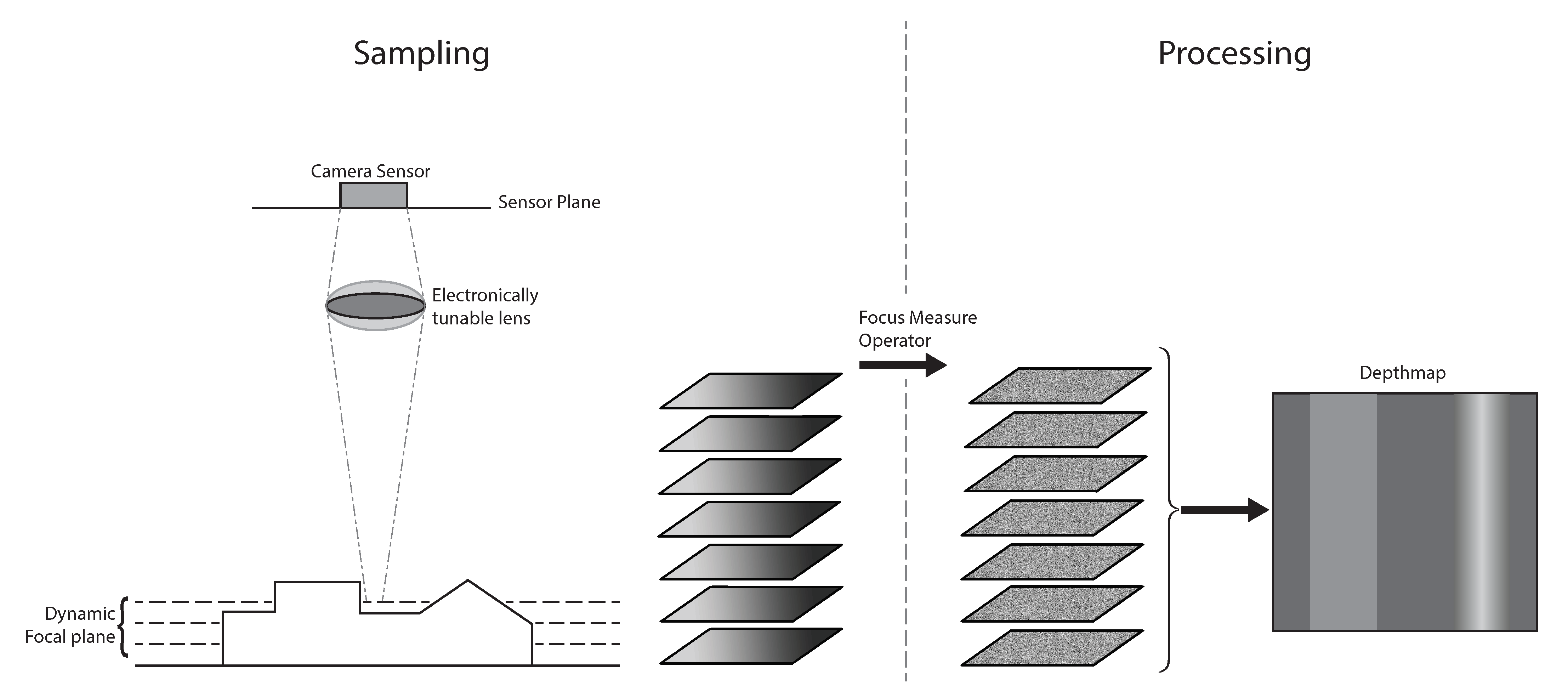
2.1. Traditional Shape from Focus
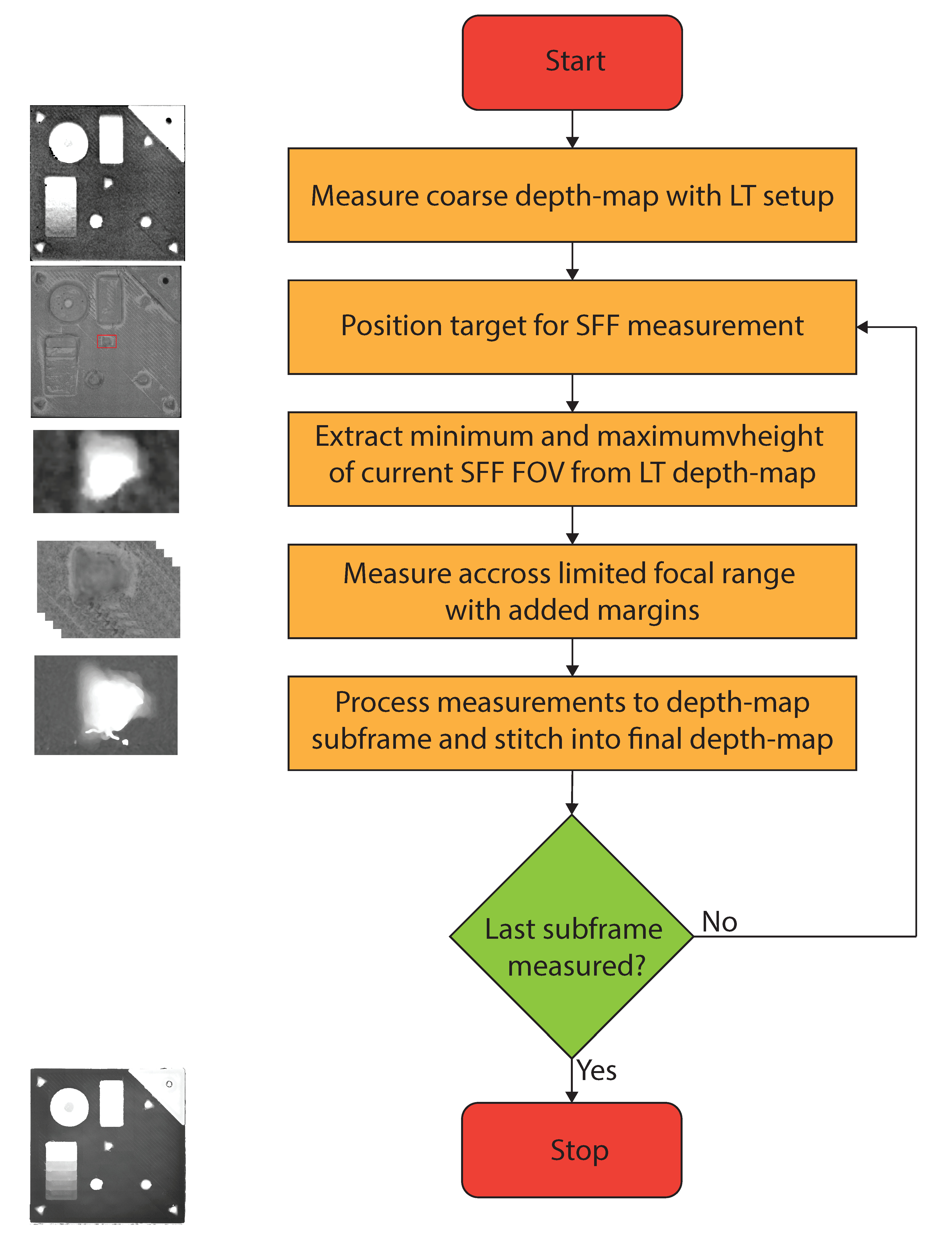
2.2. Two-Step Shape from Focus
Process Parameters
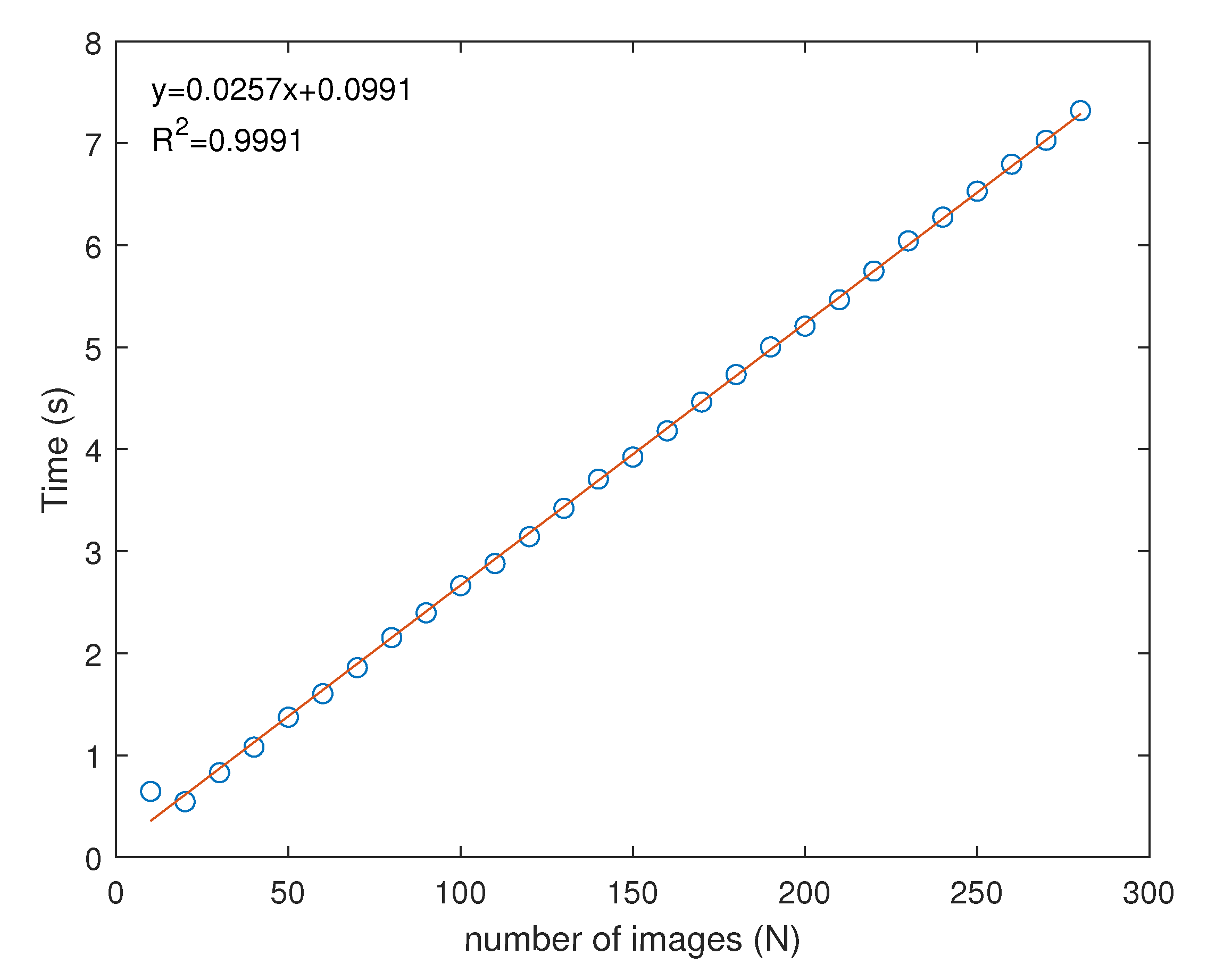
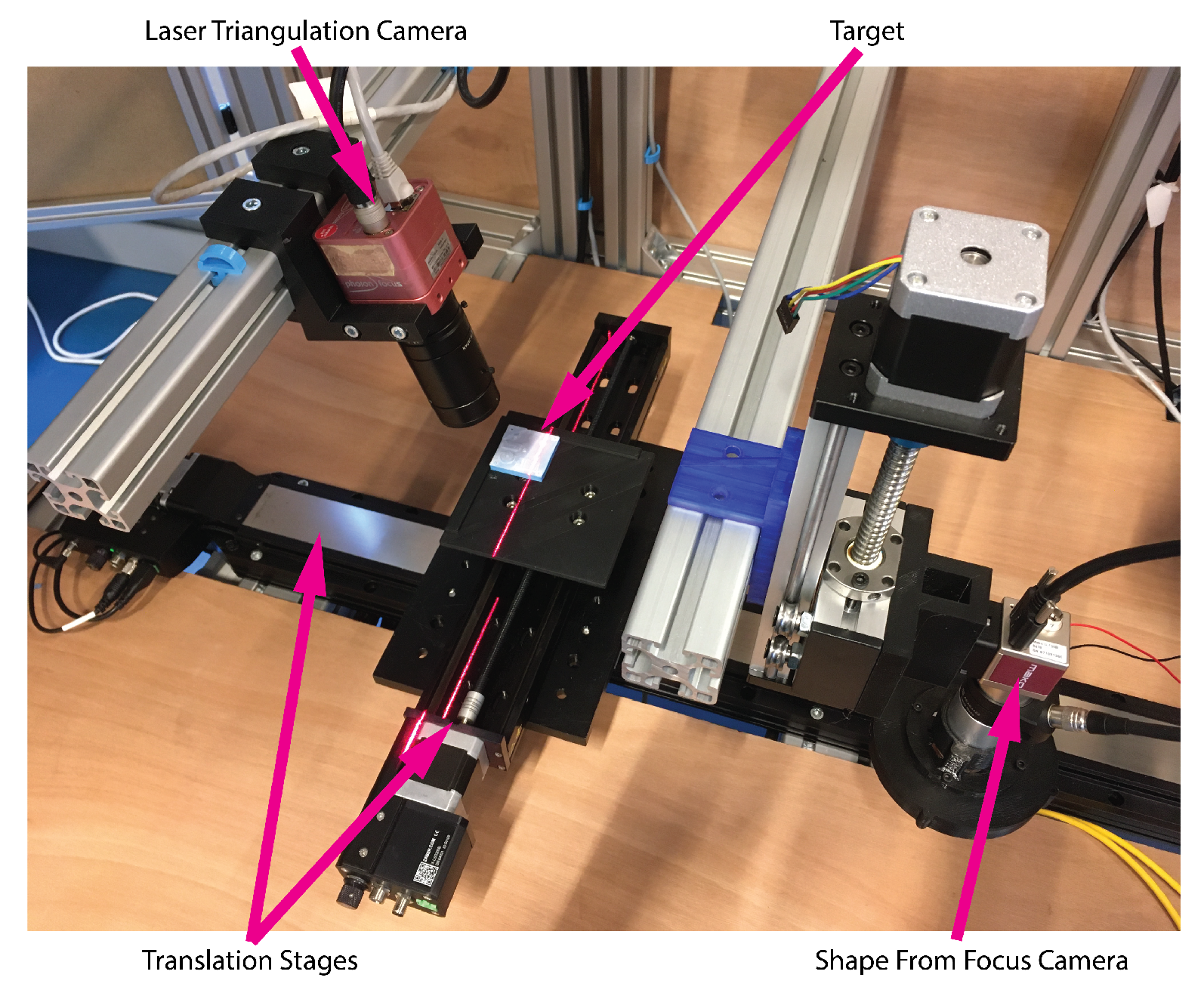
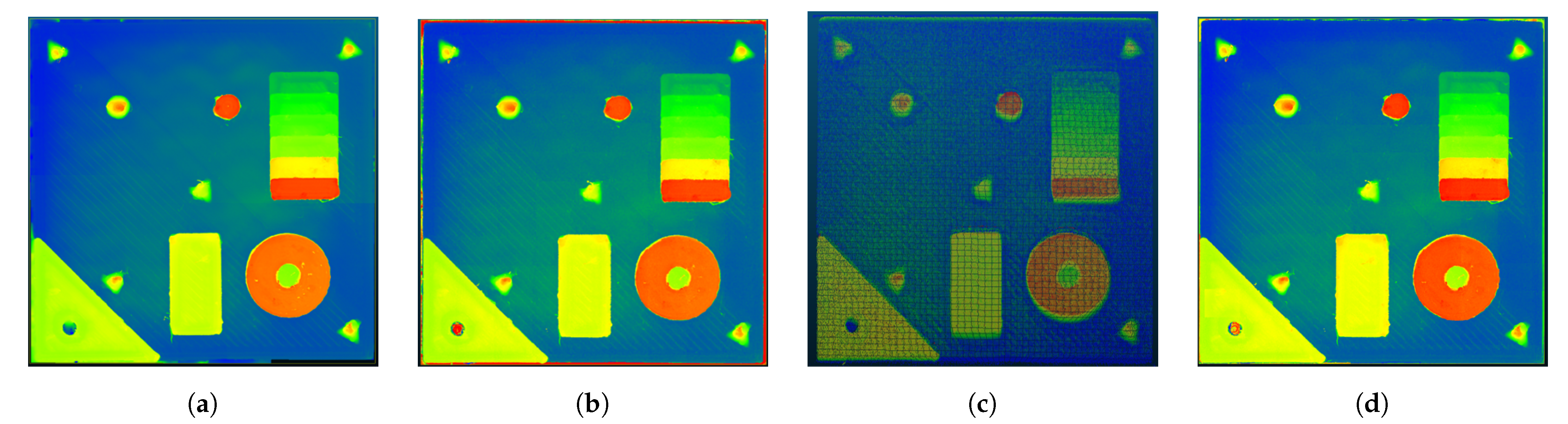
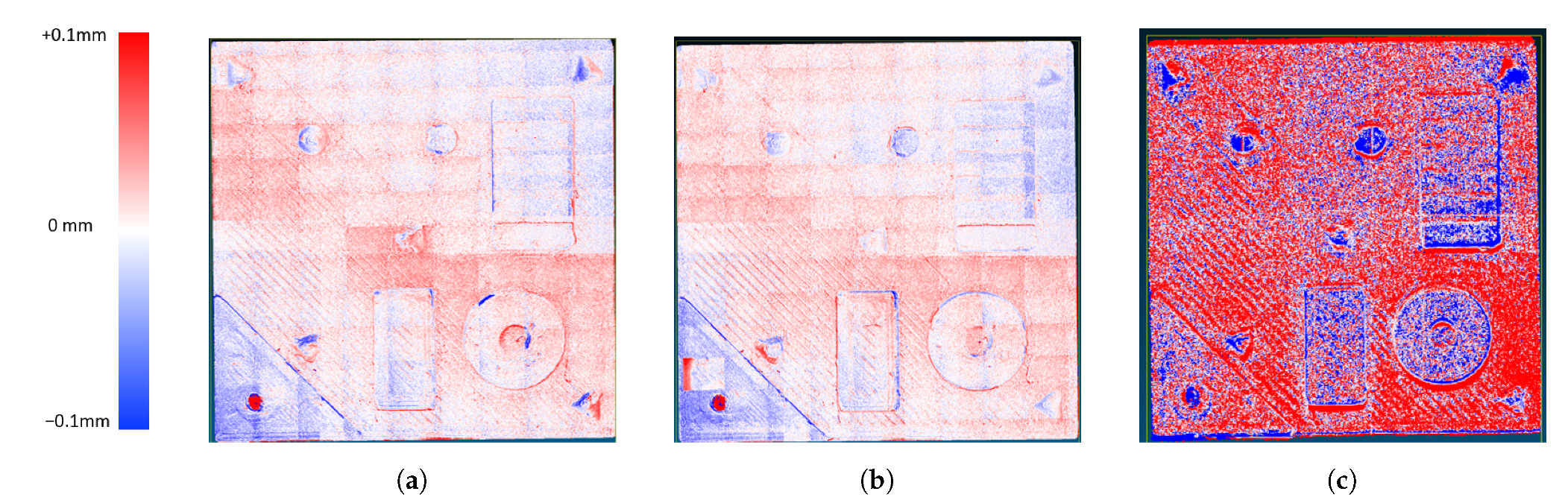
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3D | Three Dimensional |
| DFF | Depth From Focus |
| DOF | Depth Of Field |
| ETL | Electronically Tunable Lens |
| FMO | Focus Measure Operator |
| FOV | Field Of View |
| GLVM | Modified Gray Level Variance |
| GPU | Graphical Processing Unit |
| LT | Laser Triangulation |
| ICP | Iterative Closest Points |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| ICP | Iterative Closest Points |
| PTC | Portable Calibration Target |
| SFF | Shape From Focus |
| STL | Stereo Lithography |
References
- Newton, L.; Senin, N.; Gomez, C.; Danzl, R.; Helmli, F.; Blunt, L.; Leach, R. Areal topography measurement of metal additive surfaces using focus variation microscopy. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 25, 365–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angot-Petit, L.J. Small scale surface profile recovery using a tunable lens based System. Electron. Imaging 2017, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flack, D.; Hannaford, J. Fundamental Good Practice in Dimensional Metrology; National Physical Laboratory: Teddington, UK, 2009; p. 227. [Google Scholar]
- Kienle, P.; Batarilo, L.; Akgül, M.; Köhler, M.H.; Wang, K.; Jakobi, M.; Koch, A.W. Optical Setup for Error Compensation in a Laser Triangulation System. Sensors 2020, 20, 4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genta, G.; Minetola, P.; Barbato, G. Calibration procedure for a laser triangulation scanner with uncertainty evaluation. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2016, 86, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehler, W.; Marbs, A. Investigating Laser Scanner Accuracy. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2003, 34, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liao, H.; Zhang, X. Telecentric stereo micro-vision system: Calibration method and experiments. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2014, 57, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calì, M.; Ambu, R. Advanced 3D photogrammetric surface reconstruction of extensive objects by UAV camera image acquisition. Sensors 2018, 18, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosed, F.J.; Aguilar, J.J.; Santolaria, J.; Lázaro, R. Geometrical Verification based on a Laser Triangulation System in Industrial Environment. Effect of the Image Noise in the Measurement Results. In Procedia Engineering; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 132, pp. 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swojak, N.; Wieczorowski, M.; Jakubowicz, M. Assessment of selected metrological properties of laser triangulation sensors. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2021, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Feng, S.; Zuo, C. Microscopic fringe projection profilometry: A review. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 135, 106192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentland, A.P. A New Sense for Depth of Field. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1987, PAMI-9, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, M.; Benning, M.; Schönlieb, C.; Cremers, D. Variational Depth from Focus Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 5369–5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, F.; Mahmood, M.T.; Iqbal, J. 3-D shape recovery from image focus using no-reference sharpness metric based on inherent sharpness. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems, Jeju, Korea, 18–21 October 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Optotune. Fast Electrically Tunable Lens EL-10-30 Series. 2019. Available online: https://www.optotune.com/s/Optotune-EL-10-30.pdf (accessed on 19 September 2019).
- Pertuz, S.; Puig, D.; Garcia, M.A. Analysis of focus measure operators for shape-from-focus. Pattern Recognit. 2013, 46, 1415–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazirbas, C.; Soyer, S.G.; Staab, M.C.; Leal-Taixé, L.; Cremers, D. Deep Depth from Focus. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV 2018), Perth, WA, Australia, 2–6 December 2018; pp. 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialka, O.; Čadík, M. FFT and convolution performance in image filtering on GPU. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Information Visualisation (IV 2006), London, UK, 5–7 July 2006; pp. 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qiu, Y.; Yi, H. Implementation and performance of image filtering on GPU. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing (ICICIP 2013), Beijing, China, 9–11 June 2013; pp. 514–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertuz, S. Shape from Focus. 2019. Available online: https://nl.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/55103-shape-from-focus (accessed on 24 July 2019).
- Movimed. What Is Laser Triangulation? 2020. Available online: https://www.movimed.com/knowledgebase/what-is-laser-triangulation/ (accessed on 7 August 2020).
- Sun, B.; Li, B. A rapid method to achieve aero-engine blade form detection. Sensors 2015, 15, 12782–12801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girardeau-Montaut, D.; Roux, M.; Marc, R.; Thibault, G. Change detection on points cloud data acquired with a ground laser scanner. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. ISPRS Arch. 2005, 36, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendra, Y.D.; Mehrotra, S.C.; Kale, K.V.; Manza, R.R.; Dhumal, R.K.; Nagne, A.D.; Vibhute, D.; Ramanujan, S.; Chair, G. Evaluation of Partially Overlapping 3D Point Cloud’s Registration by Using ICP Variant and Cloudcompare. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Measurement | Total Number of Images | Imaging Time (s) | Processing Time on CPU (s) | Total Measurement Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Shape from focus method | 25,350 | 507 | 844 | 1350 |
| Two-step Shape from focus method | 14,411 | 288 | 436 | 724 |
| Measurement | Mean Deviation from Reference (mm) | Standard Deviation (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional Shape from focus | 0.033 | |
| Proposed Two-step approach | 0.026 | |
| Laser Triangulation Measurement | 0.120 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gladines, J.; Sels, S.; Blom, J.; Vanlanduit, S. A Fast Shape-from-Focus-Based Surface Topography Measurement Method. Sensors 2021, 21, 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082574
Gladines J, Sels S, Blom J, Vanlanduit S. A Fast Shape-from-Focus-Based Surface Topography Measurement Method. Sensors. 2021; 21(8):2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082574
Chicago/Turabian StyleGladines, Jona, Seppe Sels, Johan Blom, and Steve Vanlanduit. 2021. "A Fast Shape-from-Focus-Based Surface Topography Measurement Method" Sensors 21, no. 8: 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082574
APA StyleGladines, J., Sels, S., Blom, J., & Vanlanduit, S. (2021). A Fast Shape-from-Focus-Based Surface Topography Measurement Method. Sensors, 21(8), 2574. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082574







