Development of Electrochemical DNA Biosensor for Equine Hindgut Acidosis Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Target Identification and Capture Probe Design
2.2. Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis for DNA Hybridisation Study
2.3. Pre-Treatment of ssDNA Capture Probes
2.4. Pre-Treatment of the Gold Working Electrode
2.5. Thiol-ssDNA Probe Immobilization on the Gold Electrode Surface
2.6. Electrochemical Confirmation of DNA Hybridization
3. Results
3.1. Target Identification and Capture Probe Design
3.2. Gel Electrophoresis Study of DNA Hybridization
3.3. DNA Hybridization Study with the Unmodified Capture Probes
3.4. DNA Hybridisation Study with Thiol-Modified Capture Probes
3.5. Stripping Voltammetry Study of ssDNA-SH-Gold Bond
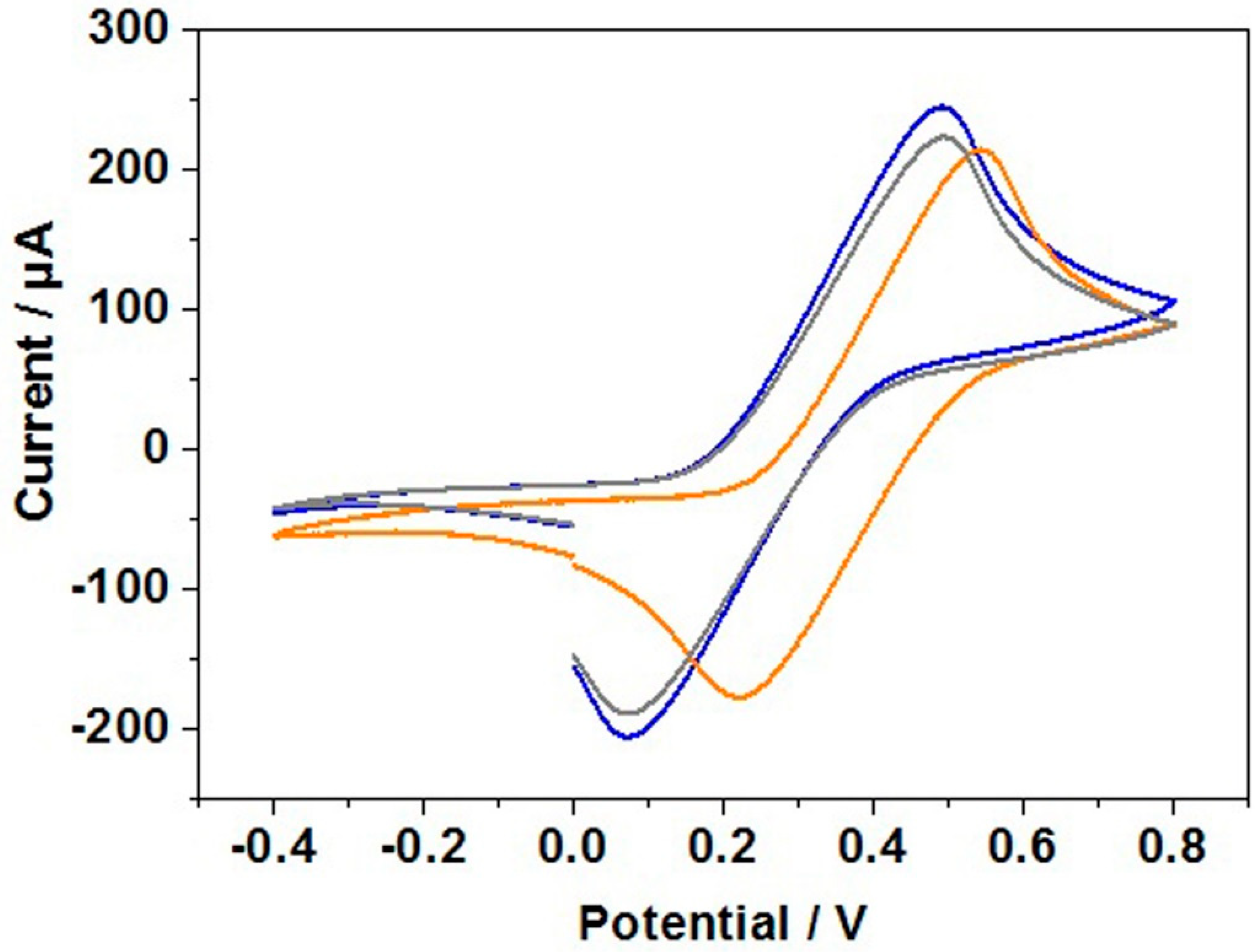
3.6. Cyclic Voltammetry Study of DNA Hybridization
3.7. EIS Confirmation of DNA Hybridization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Milinovich, G.J.; Trott, D.J.; Burrell, P.C.; van Eps, A.W.; Thoefner, M.B.; Blackall, L.L.; al Jassim, R.A.M.; Morton, J.M.; Pollitt, C.C. Changes in equine hindgut bacterial populations during oligofructose-induced laminitis. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 885–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milinovich, G.J.; Trott, D.J.; Burrell, P.C.; Croser, E.L.; al Jassim, R.A.M.; Morton, J.M.; van Eps, A.W.; Pollitt, C.C. Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis of hindgut bacteria associated with the development of equine laminitis. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2090–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecchi, C.; Costa, E.D.; Lebelt, D.; Ferrante, V.; Canali, E.; Ceciliani, F.; Stucke, D.; Minero, M. Circulating miR-23b-3p, miR-145-5p and miR-200b-3p are potential biomarkers to monitor acute pain associated with laminitis in horses. Animal 2018, 12, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocek, J.E. Bovine Acidosis: Implications on Laminitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 80, 1005–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, M.; Hoskin, S.O.; Rogers, C.W.; Grinberg, A. Fecal pH and Microbial Populations in Thoroughbred Horses During Transition from Pasture to Concentrate Feeding. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2013, 33, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougal, K.; de la Fuente, G.; Harris, P.A.; Girdwood, S.E.; Pinloche, E.; Newbold, C.J. Identification of a Core Bacterial Community within the Large Intestine of the Horse. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Jassim, R.A.M.; Scott, P.T.; Trebbin, A.L.; Trott, D.; Pollitt, C.C. The genetic diversity of lactic acid producing bacteria in the equine gastrointestinal tract. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 248, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mar, R.; Marazuela, D.; Moreno-bondi, C. Fiber-optic biosensors—An overview. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2002, 372, 664–682. [Google Scholar]
- Odenthal, K.J.; Gooding, J.J. An introduction to electrochemical DNAbiosensors. Analyst 2007, 132, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, T.G.; Hill, M.G.; Barton, J.K. Electrochemical DNA sensors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Wang, K.; Weng, S.; Lei, Y.; Lin, L.; Chen, W.; Lin, X.; Chen, Y. Development of electrochemical DNA biosensors. Trac Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Electrochemical nucleic acid biosensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 469, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palchetti, I.; Mascini, M. Nucleic acid biosensors for environmental pollution monitoring. Analyst 2008, 133, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Chen, Y.; Okhai, T.A.; Snyman, L.W. Micro optical sensors based on avalanching silicon light-emitting devices monolithically integrated on chips. Opt. Mater. Express 2019, 9, 3985–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Xu, Y.; He, P.-G.; Fang, Y.-Z. Indicator Free DNA Hybridization Detection by Impedance Measurement Based on the DNA-Doped Conducting Polymer Film Formed on the Carbon Nanotube Modified Electrode. Electroanalysis 2003, 15, 1864–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, J.; Savage, A.C.; Buckley, N.; Gwenin, C. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy biosensor for detection of active botulinum neurotoxin. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2014, 2, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, A.C.; Buckley, N.; Halliwell, J.; Gwenin, C. Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotypes Detected by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Toxins 2015, 7, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Hazmi, M.; Lima, S.A.; Ahmed, M.U. A highly sensitive electrochemical detection of human chorionic gonadotropin on a carbon nano-onions/gold nanoparticles/polyethylene glycol nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 833, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Koh, D.; Booth, M.A.; Ahmed, M.U. Combining a gold nanoparticle-polyethylene glycol nanocomposite and carbon nanofiber electrodes to develop a highly sensitive salivary secretory immunoglobulin A immunosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Elma, S.; Lim, S.A.; Ahmed, M.U. AuNPs/CNOs/SWCNTs/chitosan-nanocomposite modified electrochemical sensor for the label-free detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 107, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Nadeem, S.; Ullah, N. Entropy generation and temperature-dependent viscosity in the study of SWCNT–MWCNT hybrid nanofluid. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 5107–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Park, S.M. DNA Hybridization Sensors Based on Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy as a Detection Tool. Sensors 2009, 9, 9513–9532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.Q.; Piper, A.; Schmueser, I.; Mount, A.R.; Corrigan, D.K. Impedimetric measurement of DNA-DNA hybridisation using microelectrodes with different radii for detection of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Analyst 2017, 142, 1946–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafka, J.; Pänke, O.; Abendroth, B.; Lisdat, F. A label-free DNA sensor based on impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 7467–7474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooding, J.J. Electrochemical DNA Hybridization Biosensors. Electroanalysis 2002, 14, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Gooding, J.J.; Hibbert, D.B. Characterisation of gold electrodes modified with self-assembled monolayers of L-cysteine for the adsorptive stripping analysis of copper. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 516, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, T.; Kim, K.-N.; Lee, C.-W.; Shin, S.K.; Kang, H. Self-Assembled Monolayer of L-Cysteine on Au(111): Hydrogen Exchange between Zwitterionic L-Cysteine and Physisorbed Water. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 11674–11681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, A.; Blues, E.; Williamson, P.; Cardona, M.; Gray, L.; Corrigan, D.K. SAM Composition and Electrode Roughness Affect Performance of a DNA Biosensor for Antibiotic Resistance. Biosensors 2019, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, M.; Yoshizawa, K.; Ogawa, A.; Fujimoto, H.; Hoffmann, R. Sulfur-gold orbital interactions which determine the structure of alkanethiolate/Au(111) self-assembled monolayer systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 12727–12736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levicky, R.; Herne, T.M.; Tarlov, M.J.; Satija, S.K. Using self-assembly to control the structure of DNA monolayers on gold: A neutron reflectivity study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 9787–9792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, B. Gold, the Noble metal and the paradoxes of its toxicology. Biologicals 1998, 26, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, J.D.; Leger, L.; Workman, A.M.; Clawson, M.L.; Bulut, E.; Wang, B. Development of a multiplex real-time PCR assay using two thermocycling platforms for detection of major bacterial pathogens associated with bovine respiratory disease complex from clinical samples. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2018, 30, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, C.B.; Alonso-Hearn, M.; Juste, R.A.; Canive, M.; Iglesias, T.; Iglesias, N.; Amado, J.; Vicente, F.; Balseiro, A.; Casais, R. Detection of latent forms of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infection using host biomarker-based ELISAs greatly improves paratuberculosis diagnostic sensitivity. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, J.; Gwenin, C. A Label Free Colorimetric Assay for the Detection of Active Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A by SNAP-25 Conjugated Colloidal Gold. Toxins 2013, 5, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heeroma, A.J.; Gwenin, C. Development of Solid-Phase RPA on a Lateral Flow Device for the Detection of Pathogens Related to Sepsis. Sensors 2020, 20, 4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.-P.; Hu, Y.; Liu, P.; Deng, Y.-N.; Wang, P.; Chen, W.; Liu, A.-L.; Chen, Y.-Z.; Lin, X.-H. Label-free electrochemical DNA biosensor for rapid detection of mutidrug resistance gene based on Au nanoparticles/toluidine blue–graphene oxide nanocomposites. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.N.; Mutharasan, R. A cantilever biosensor-based assay for toxin-producing cyanobacteria microcystis aeruginosa using 16S rRNA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12333–12341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zeng, G.M.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.P.; Liu, Y.Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, M.S.; Luo, J. Electrochemical detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 16S rRNA using a biosensor based on immobilized stem-loop structured probe. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2011, 49, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.C.; Yeung, C.Y.; Chen, P.H.; Yeh, M.K.; Hou, S.Y. Salmonella detection using 16S ribosomal DNA/RNA probe-gold nanoparticles and lateral flow immunoassay. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2526–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amann, R.I.; Binder, B.J.; Olson, R.J.; Chisholm, S.W.; Devereux, R.; Stahl, D.A. Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1919–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henihan, G.; Schulze, H.; Corrigan, D.K.; Giraud, G.; Terry, J.G.; Hardie, A.; Campbell, C.J.; Walton, A.J.; Crain, J.; Pethig, R.; et al. Label- and amplification-free electrochemical detection of bacterial ribosomal RNA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoy, M.A. Insert Molecular Genetics; Academic Press Inc. (London) Ltd.: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C.; Tang, H.; Cheng, W.; Yan, L.; Zhang, D.; Ju, H.; Ding, S. A sensitive electrochemical DNA biosensor for specific detection of Enterobacteriaceae bacteria by Exonuclease III-assisted signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 48, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.A. Gene Cloning & DNA Analysis; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kasten, F.H. Cytochemical Studies with Acridine Orange and the Influence of Dye Contaminants in the Staining of Nucleic Acids. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1967, 21, 141–202. [Google Scholar]
- McMaster, G.K.; Carmichael, G.G.; Gordon, G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 4835–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerman, L.S. Structural considerations in the interaction of DNA and acridines. J. Mol. Biol. 1961, 3, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerman, L.S. The structure of the DNA-acridine complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1962, 49, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, H.A.M.; Zucolotto, V. Label-free electrochemical DNA biosensor for zika virus identification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 131, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rant, U.; Arinaga, K.; Fujita, S.; Yokoyama, N.; Abstreiter, G.; Tornow, M. Structural properties of oligonucleotide monolayers on gold surfaces probed by fluorescence investigations. Langmuir 2004, 20, 10086–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rant, U.; Arinaga, K.; Tornow, M.; Yong, W.K.; Netz, R.R.; Fujita, S.; Yokoyama, N.; Abstreiter, G. Dissimilar kinetic behaviour of electrically manipulated single- and double-stranded DNA tethered to a gold surface. Biophys. J. 2006, 90, 3666–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

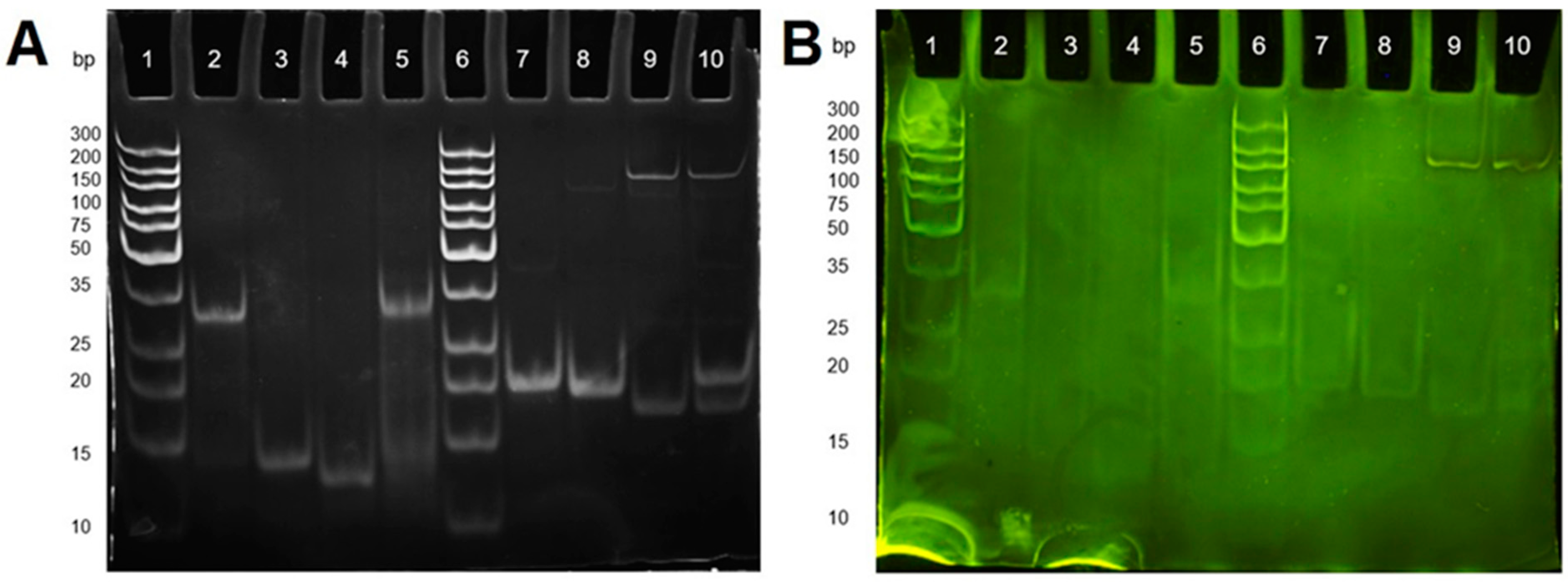



| Oligonucleotide | Position | Size (bp) | Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| SE target sequence (1) | 816–836 | 21 | GGG TCC TTT CCG GGA CTC AGT |
| SE mod target sequence (1) | 21 | GGG ACC TTT CCG GGC TTC AGT | |
| SE capture probe (1) | 21 | CCC TGG AAA GGC CCG AAG TCA | |
| SE target sequence (2) | 642–662 | 21 | AAG GGG AGA GTG GAA TTC CAT |
| SE mod target sequence (2) | 21 | AAG GGT AGA CCG GAA TTC CAT | |
| SE capture probe (2) | 21 | TTC CCA TCA GGC CTT AAG GTA | |
| MJ target sequence (1) | 650–675 | 25 | CCG TGA GGG GAT GGA AAC TAT CTT T |
| MJ mod target sequence (1) | 25 | CCG TGA GGG GAT AAA CAC TAT CTT T | |
| MJ capture probe (1) | 25 | GGC ACT CCC CTA TTT GTG ATA GAA A | |
| MJ target sequence (2) | 1180–1200 | 25 | TCC TTT GTT GCC AGC ACG CAA TGG T |
| MJ mod target sequence (2) | 25 | TCC TTT GTG CCC AGC GCG CCA TGG T | |
| MJ capture probe (2) | 25 | AGG AAA CAC GGG TCG CGC GGT ACC A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davies, J.; Thomas, C.; Rizwan, M.; Gwenin, C. Development of Electrochemical DNA Biosensor for Equine Hindgut Acidosis Detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21072319
Davies J, Thomas C, Rizwan M, Gwenin C. Development of Electrochemical DNA Biosensor for Equine Hindgut Acidosis Detection. Sensors. 2021; 21(7):2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21072319
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavies, Joshua, Carol Thomas, Mohammad Rizwan, and Christopher Gwenin. 2021. "Development of Electrochemical DNA Biosensor for Equine Hindgut Acidosis Detection" Sensors 21, no. 7: 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21072319
APA StyleDavies, J., Thomas, C., Rizwan, M., & Gwenin, C. (2021). Development of Electrochemical DNA Biosensor for Equine Hindgut Acidosis Detection. Sensors, 21(7), 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21072319







