Noninvasive Assessment of Neuromechanical Coupling and Mechanical Efficiency of Parasternal Intercostal Muscle during Inspiratory Threshold Loading
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.1.1. Measurements
2.1.2. Acquisition Protocol
2.1.3. Data Preprocessing
2.2. Data Processing
2.2.1. Inspiratory Muscle Activity Estimation
2.2.2. Neuromechanical Coupling and Mechanical Efficiency
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
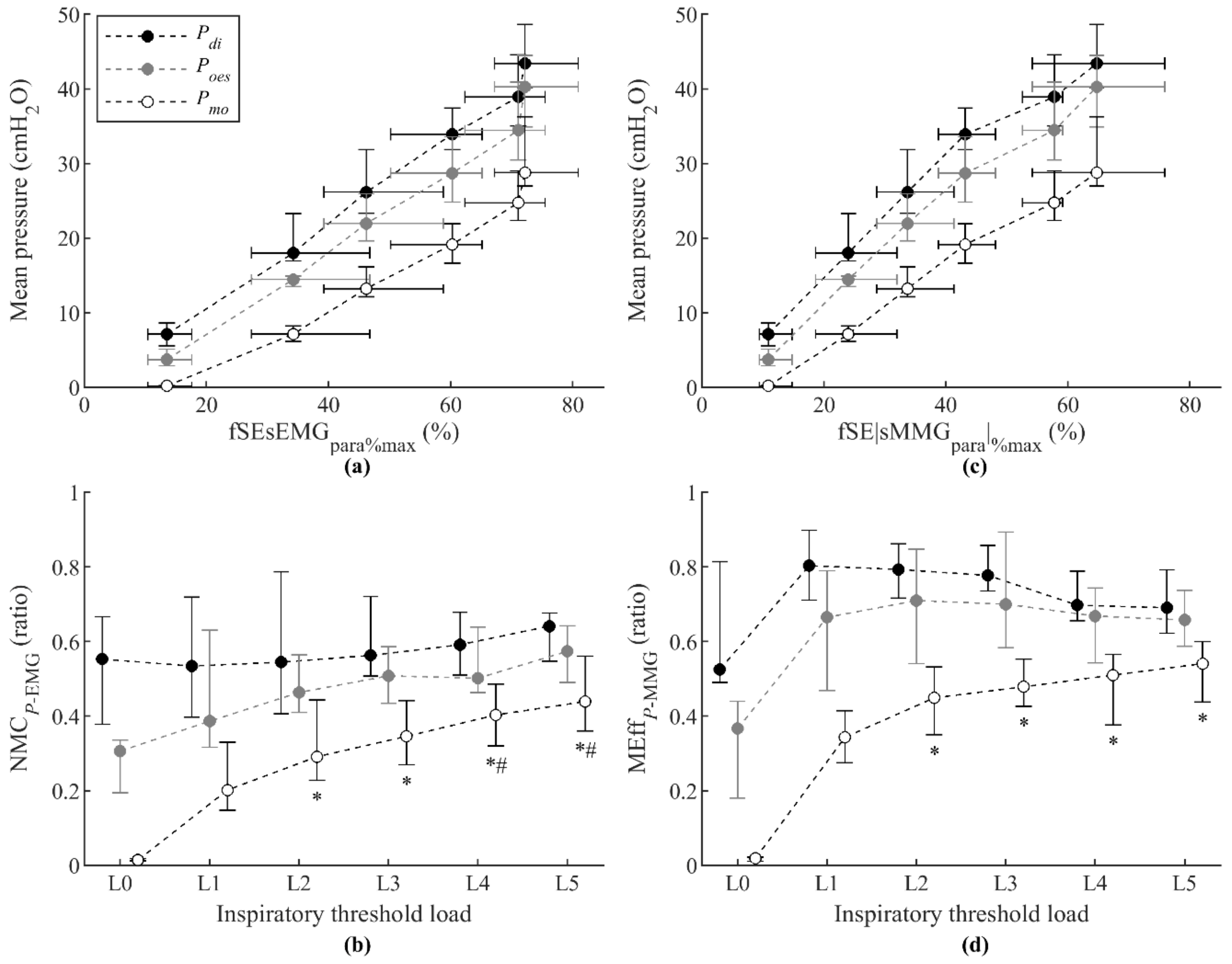
3.1. Respiratory Pressures
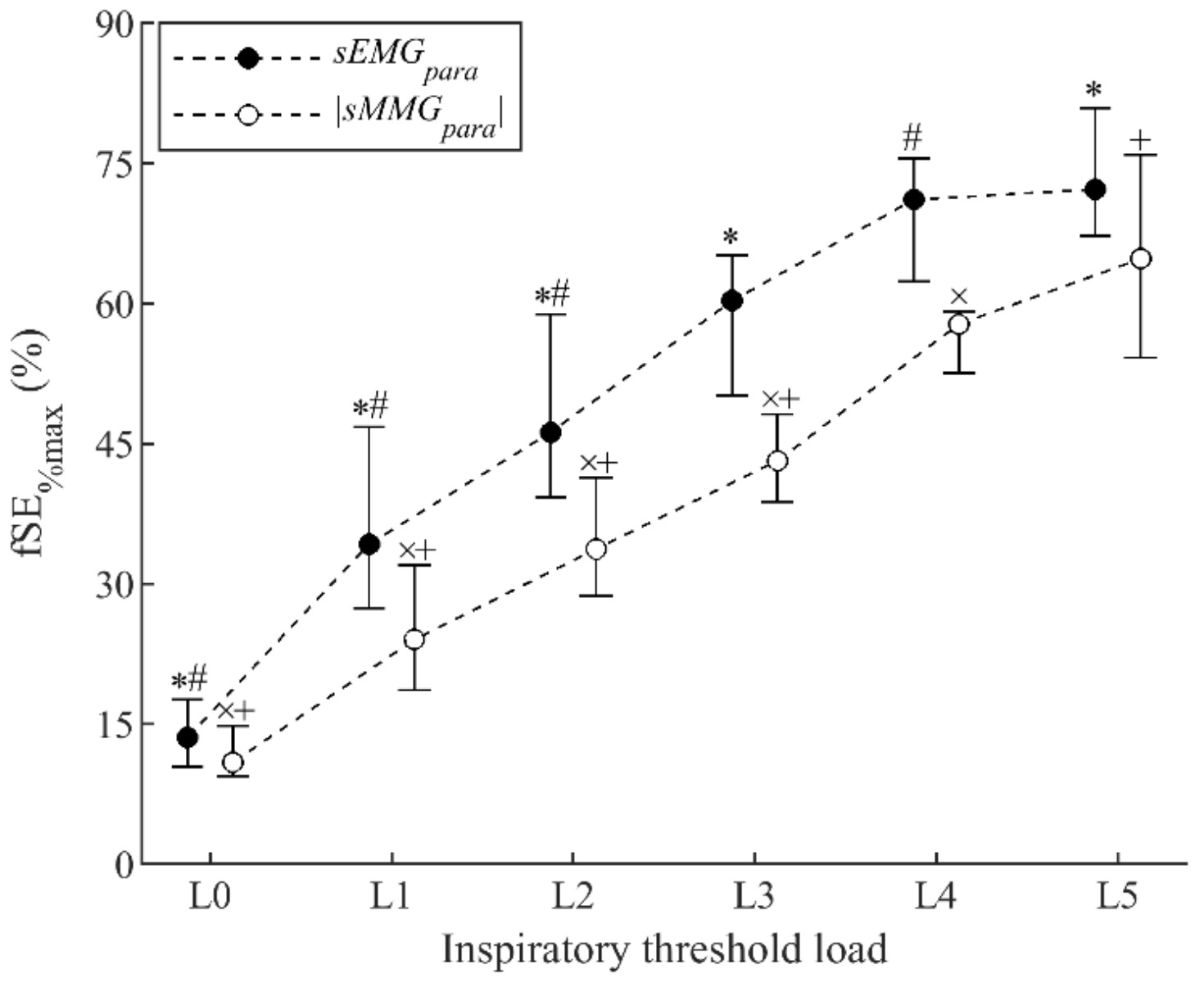
3.2. sMMG and sEMG of Parasternal Intercostal Muscles during Threshold Loading
3.3. Noninvasive Measurements of Neuromechanical Coupling and Mechanical Efficiency of Parasternal Intercostal Muscles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laveneziana, P.; Albuquerque, A.; Aliverti, A.; Babb, T.; Barreiro, E.; Dres, M.; Dubé, B.P.; Fauroux, B.; Gea, J.; Guenette, J.A.; et al. ERS statement on respiratory muscle testing at rest and during exercise. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorini, M.; Spinelli, A.; Ginanni, R.; Duranti, R.; Gigliotti, F.; Scano, G. Neural Respiratory Drive and Neuromuscular Coupling in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Chest 1990, 98, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duiverman, M.L.; de Boer, E.W.J.; van Eykern, L.A.; de Greef, M.H.G.; Jansen, D.F.; Wempe, J.B.; Kerstjens, H.A.M.; Wijkstra, P.J. Respiratory muscle activity and dyspnea during exercise in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2009, 167, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druz, W.S.; Sharp, J.T. Electrical and mechanical activity of the diaphragm accompanying body position in severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1982, 125, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, D.E.; Ora, J.; Webb, K.A.; Laveneziana, P.; Jensen, D. Mechanisms of activity-related dyspnea in pulmonary diseases. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2009, 167, 116–132. [Google Scholar]
- Lanini, B.; Misuri, G.; Gigliotti, F.; Iandelli, I.; Pizzi, A.; Romagnoli, I.; Scano, G. Perception of dyspnea in patients with neuromuscular disease. Chest 2001, 120, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, J.; Loring, S.H. Analysis of volume displacement and length changes of the diaphragm during breathing. J. Appl. Physiol. 1982, 53, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.M.; Moxham, J.; Polkey, M.I. Diaphragm electromyography using an oesophageal catheter: Current concepts. Clin. Sci. 2008, 115, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Troyer, A.; Sampson, M.G. Activation of the parasternal intercostals during breathing efforts in human subjects. J. Appl. Physiol. Respir. Environ. Exerc. Physiol. 1982, 52, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, C.C.; Jolley, C.J.; Ward, K.; MacBean, V.; Moxham, J.; Rafferty, G.F. Neural respiratory drive measured during inspiratory threshold loading and acute hypercapnia in healthy individuals. Exp. Physiol. 2013, 98, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Guan, L.; Wu, W.; Chen, R. Correlation of surface respiratory electromyography with esophageal diaphragm electromyography. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2019, 259, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, C.C.; Ward, K.; Jolley, C.J.; Lunt, A.C.; Steier, J.; Elston, C.; Polkey, M.I.; Rafferty, G.F.; Moxham, J. Neural respiratory drive, pulmonary mechanics and breathlessness in patients with cystic fibrosis. Thorax 2011, 66, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Kindler, F.; Gottfried, S.B.; Raux, M.; Hug, F.; Similowski, T.; Demoule, A. Dyspnea and surface inspiratory electromyograms in mechanically ventilated patients. Intensive Care Med. 2013, 39, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, P.B.; Kumar, A.; Reilly, C.; Jolley, C.; Walterspacher, S.; Fedele, F.; Hopkinson, N.S.; Man, W.D.-C.; Polkey, M.I.; Moxham, J.; et al. Neural respiratory drive as a physiological biomarker to monitor change during acute exacerbations of COPD. Thorax 2011, 66, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, E.-S.; Mandal, S.; Harding, R.; Ramsay, M.; Kamalanathan, M.; Henderson, K.; O’Kane, K.; Douiri, A.; Hopkinson, N.S.; Polkey, M.I.; et al. Neural respiratory drive predicts clinical deterioration and safe discharge in exacerbations of COPD. Thorax 2015, 70, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orizio, C.; Gobbo, M. Mechanomyography. In Wiley Encyclopedia of Biomedical Engineering; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Madeleine, P.; Bajaj, P.; Søgaard, K.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Mechanomyography and electromyography force relationships during concentric, isometric and eccentric contractions. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2001, 11, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebersole, K.T.; Malek, D.M. Fatigue and the electromechanical efficiency of the vastus medialis and vastus lateralis muscles. J. Athl. Train. 2008, 43, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano-Garcia, M.; Estrada-Petrocelli, L.; Moxham, J.; Rafferty, G.F.; Torres, A.; Jolley, C.J.; Jane, R. Noninvasive Assessment of Inspiratory Muscle Neuromechanical Coupling During Inspiratory Threshold Loading. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 183634–183646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlabous, L.; Torres, A.; Fiz, J.A.; Gea, J.; Martínez-Llorens, J.M.; Jané, R. Efficiency of mechanical activation of inspiratory muscles in COPD using sample entropy. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 1808–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Troyer, A.; Estenne, M.; Ninane, V.; Van Gansbeke, D.; Gorini, M. Transversus abdominis muscle function in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1990, 68, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinderby, C.; Friberg, S.; Comtois, N.; Grassino, A. Chest wall muscle cross talk in canine costal diaphragm electromyogram. J. Appl. Physiol. 1996, 81, 2312–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finucane, K.E.; Panizza, J.A.; Singh, B. Efficiency of the normal human diaphragm with hyperinflation. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 99, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finucane, K.E.; Singh, B. Human diaphragm efficiency estimated as power output relative to activation increases with hypercapnic hyperpnea. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finucane, K.E.; Singh, B. Diaphragm efficiency estimated as power output relative to activation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 113, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laghi, F.; Shaikh, H.S.; Morales, D.; Sinderby, C.; Jubran, A.; Tobin, M.J. Diaphragmatic neuromechanical coupling and mechanisms of hypercapnia during inspiratory loading. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2014, 198, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacBean, V.; Hughes, C.; Nicol, G.; Reilly, C.C.; Rafferty, G.F. Measurement of neural respiratory drive via parasternal intercostal electromyography in healthy adult subjects. Physiol. Meas. 2016, 37, 2050–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolley, C.J.; Luo, Y.M.; Steier, J.; Reilly, C.; Seymour, J.; Lunt, A.; Ward, K.; Rafferty, G.F.; Polkey, M.I.; Moxham, J. Neural respiratory drive in healthy subjects and in COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 33, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibitoye, M.O.; Hamzaid, N.A.; Zuniga, J.M.; Hasnan, N.; Wahab, A.K.A. Mechanomyographic parameter extraction methods: An appraisal for clinical applications. Sensors 2014, 14, 22940–22970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarlabous, L.; Torres, A.; Fiz, J.A.; Jané, R. Evidence towards improved estimation of respiratory muscle effort from diaphragm mechanomyographic signals with cardiac vibration interference using sample entropy with fixed tolerance values. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, L.; Torres, A.; Sarlabous, L.; Jané, R. Improvement in neural respiratory drive estimation from diaphragm electromyographic signals using fixed sample entropy. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Informatics 2016, 20, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-García, M.; Estrada, L.; Jané, R. Performance evaluation of fixed sample entropy in myographic signals for inspiratory muscle activity estimation. Entropy 2019, 21, 183. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano-García, M.; Sarlabous, L.; Moxham, J.; Rafferty, G.F.; Torres, A.; Jané, R.; Jolley, C.J. Surface mechanomyography and electromyography provide non-invasive indices of inspiratory muscle force and activation in healthy subjects. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16921. [Google Scholar]
- Demoule, A.; Verin, E.; Locher, C.; Derenne, J.P.; Similowski, T. Validation of surface recordings of the diaphragm response to transcranial magnetic stimulation in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 94, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, M.D.; Grassino, A.; Mead, J.; Sears, T.A. Mechanics of the human diaphragm during voluntary contraction: Dynamics. J. Appl. Physiol. 1978, 44, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, C.C.; Jolley, C.J.; Elston, C.; Moxham, J.; Rafferty, G.F. Measurement of parasternal intercostal electromyogram during an infective exacerbation in patients with cystic fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orizio, C.; Esposito, F.; Sansone, V.; Parrinello, G.; Meola, G.; Veicsteinas, A. Muscle surface mechanical and electrical activities in myotonic dystrophy. Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1997, 37, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barry, D.T.; Gordon, K.E.; Hinton, G.G. Acoustic and surface EMG diagnosis of pediatric muscle disease. Muscle Nerve 1990, 13, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akataki, K.; Mita, K.; Itoh, K.; Suzuki, N.; Watakabe, M. Acoustic and electrical activities during voluntary isometric contraction of biceps brachii muscles in patients with spastic cerebral palsy. Muscle Nerve 1996, 19, 1252–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, D.; Pattinson, K.; Jolley, C.J. Mechanisms of Breathlessness. In European Respiratory Society Monograph; Bausewein, C., Currow, D., Johnson, M., Eds.; European Respiratory Society Journals: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 111–113. [Google Scholar]
- Laghi, F.; Jubran, A.; Topeli, A.; Fahey, P.J.; Garrity, E.R.; Arcidi, J.M.; de Pinto, D.J.; Edwards, L.C.; Tobin, M.J. Effect of Lung Volume Reduction Surgery on Neuromechanical Coupling of the Diaphragm. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, D.E.; Bertley, J.C.; Chau, L.K.; Webb, K.A. Qualitative aspects of exertional breathlessness in chronic airflow limitation: Pathophysiologic mechanisms. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Jolley, C.J.; Luo, Y.M.; Steier, J.; Rafferty, G.F.; Polkey, M.I.; Moxham, J. Neural respiratory drive and breathlessness in COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glerant, J.C.; Mustfa, N.; Man, W.D.; Luo, Y.M.; Rafferty, G.; Polkey, M.I.; Moxham, J. Diaphragm electromyograms recorded from multiple surface electrodes following magnetic stimulation. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Reis, I.M.M.; Ohara, D.G.; Januário, L.B.; Basso-Vanelli, R.P.; Oliveira, A.B.; Jamami, M. Surface electromyography in inspiratory muscles in adults and elderly individuals: A systematic review. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2019, 44, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheeren, E.M.; Mineiro, L.; Neves, E.B.; Krueger, E.; Nogueira Neto, G.N.; Nohama, P.; Scheeren, E.M.; Mineiro, L.; Neves, E.B.; Krueger, E.; et al. Influence of subcutaneous fat on mechanomyographic signals at three levels of voluntary effort. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 32, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nordander, C.; Willner, J.; Hansson, G.-A.; Larsson, B.; Unge, J.; Granquist, L.; Skerfving, S. Influence of the subcutaneous fat layer, as measured by ultrasound, skinfold calipers and BMI, on the EMG amplitude. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 89, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ràfols-De-Urquía, M.; Estrada, L.; Estévez-Piorno, J.; Sarlabous, L.; Jané, R.; Torres, A. Evaluation of a Wearable Device to Determine Cardiorespiratory Parameters from Surface Diaphragm Electromyography. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Informatics 2019, 23, 1964–1971. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Konijnenburg, M.; Ha, H.; Van Wegberg, R.; Song, S.; Blanco-Almazán, D.; Van Hoof, C.; Van Helleputte, N. A 36 μW 1.1 mm2 Reconfigurable Analog Front-End for Cardiovascular and Respiratory Signals Recording. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2018, 12, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Konijnenburg, M.; Van Wegberg, R.; Xu, J.; Ha, H.; Sijbers, W.; Stanzione, S.; Biswas, D.; Breeschoten, A.; Vis, P.; et al. A 769 μW Battery-Powered Single-Chip SoC with BLE for Multi-modal Vital Sign Monitoring Health Patches. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2019, 13, 1506–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| ID | fSEsEMGpara%max fSE|sMMGpara|%max | fSEsEMGpara%max Mean Pdi | fSEsEMGpara%max Mean Poes | fSEsEMGpara%max Mean Pmo | fSE|sMMGpara|%max Mean Pdi | fSE|sMMGpara|%max Mean Poes | fSE|sMMGpara|%max Mean Pmo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.90 | 0.92 |
| 2 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.93 |
| 3 | 0.95 | 0.87 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.82 | 0.92 | 0.95 |
| 4 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.95 |
| 5 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.95 |
| 6 | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.92 |
| 7 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| 8 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.97 |
| 9 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| 10 | 0.91 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.94 |
| 11 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.77 | 0.74 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.96 |
| 12 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.92 | 0.92 |
| Median (IQR) | 0.93 (0.88–0.96) | 0.91 (0.88–0.95) | 0.92 (0.89–0.96) | 0.92 (0.87–0.96) | 0.92 (0.90–0.96) | 0.94 (0.92–0.96) | 0.94 (0.92–0.95) |
| ID | fSEsEMGpara%max fSE|sMMGpara|%max | fSEsEMGpara%max Mean Pdi | fSEsEMGpara%max Mean Poes | fSEsEMGpara%max Mean Pmo | fSE|sMMGpara|%max Mean Pdi | fSE|sMMGpara|%max Mean Poes | fSE|sMMGpara|%max Mean Pmo | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lin. | Exp. | Lin. | Exp. | Lin. | Exp. | Lin. | Exp. | Lin. | Exp. | Lin. | Exp. | Lin. | Exp. | |
| 1 | 0.74 | 0.69 | 0.81 | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.72 | 0.83 | 0.73 | 0.80 | 0.69 | 0.85 | 0.75 | 0.88 | 0.73 |
| 2 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 0.96 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.82 | 0.70 | 0.60 | 0.76 | 0.64 | 0.80 | 0.65 |
| 3 | 0.86 | 0.91 | 0.74 | 0.81 | 0.90 | 0.83 | 0.94 | 0.82 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.75 | 0.67 | 0.79 | 0.65 |
| 4 | 0.76 | 0.86 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.93 | 0.89 | 0.79 | 0.84 | 0.81 | 0.70 | 0.83 | 0.67 | 0.89 | 0.76 |
| 5 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.93 | 0.86 | 0.92 | 0.83 | 0.90 | 0.81 | 0.91 | 0.79 |
| 6 | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.78 | 0.74 | 0.87 | 0.79 | 0.75 | 0.67 | 0.83 | 0.78 | 0.91 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.73 |
| 7 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 0.88 | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.95 | 0.88 | 0.95 | 0.87 | 0.96 | 0.88 |
| 8 | 0.95 | 0.86 | 0.98 | 0.92 | 0.98 | 0.91 | 0.97 | 0.90 | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.92 |
| 9 | 0.84 | 0.78 | 0.82 | 0.71 | 0.81 | 0.70 | 0.86 | 0.73 | 0.87 | 0.79 | 0.84 | 0.76 | 0.89 | 0.79 |
| 10 | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.74 | 0.66 | 0.80 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.68 | 0.84 | 0.77 | 0.88 | 0.85 | 0.91 | 0.86 |
| 11 | 0.70 | 0.74 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.56 | 0.57 | 0.91 | 0.81 | 0.95 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.87 |
| 12 | 0.73 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.71 | 0.87 | 0.75 | 0.88 | 0.74 |
| Median (IQR) | 0.85 (0.75– 0.90) | 0.83 (0.77– 0.89) | 0.83 (0.77– 0.92) | 0.82 (0.76– 0.90) | 0.88 (0.80– 0.94) | 0.84 (0.74– 0.88) | 0.84 (0.77– 0.93) | 0.81 (0.71– 0.85) | 0.83 (0.80– 0.91) | 0.77 (0.71– 0.82) | 0.88 (0.84– 0.93) | 0.78 (0.71– 0.86) | 0.89 (0.85– 0.91) | 0.77 (0.73– 0.87) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lozano-García, M.; Estrada-Petrocelli, L.; Torres, A.; Rafferty, G.F.; Moxham, J.; Jolley, C.J.; Jané, R. Noninvasive Assessment of Neuromechanical Coupling and Mechanical Efficiency of Parasternal Intercostal Muscle during Inspiratory Threshold Loading. Sensors 2021, 21, 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051781
Lozano-García M, Estrada-Petrocelli L, Torres A, Rafferty GF, Moxham J, Jolley CJ, Jané R. Noninvasive Assessment of Neuromechanical Coupling and Mechanical Efficiency of Parasternal Intercostal Muscle during Inspiratory Threshold Loading. Sensors. 2021; 21(5):1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051781
Chicago/Turabian StyleLozano-García, Manuel, Luis Estrada-Petrocelli, Abel Torres, Gerrard F. Rafferty, John Moxham, Caroline J. Jolley, and Raimon Jané. 2021. "Noninvasive Assessment of Neuromechanical Coupling and Mechanical Efficiency of Parasternal Intercostal Muscle during Inspiratory Threshold Loading" Sensors 21, no. 5: 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051781
APA StyleLozano-García, M., Estrada-Petrocelli, L., Torres, A., Rafferty, G. F., Moxham, J., Jolley, C. J., & Jané, R. (2021). Noninvasive Assessment of Neuromechanical Coupling and Mechanical Efficiency of Parasternal Intercostal Muscle during Inspiratory Threshold Loading. Sensors, 21(5), 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051781








