Remote Photoplethysmography for Evaluation of Cutaneous Sensory Nerve Fiber Function †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
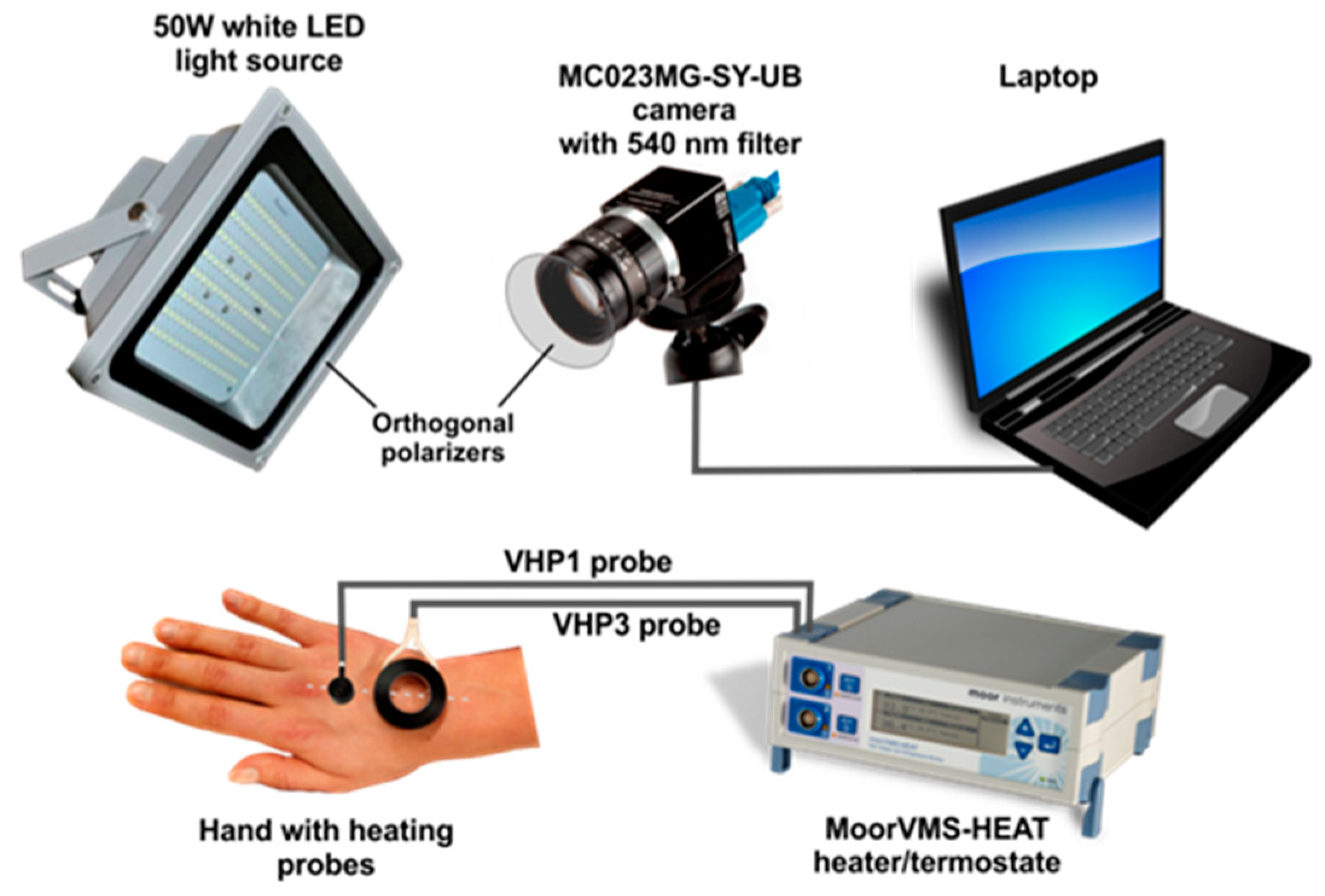
2.1. Remote Photoplethysmography Setup
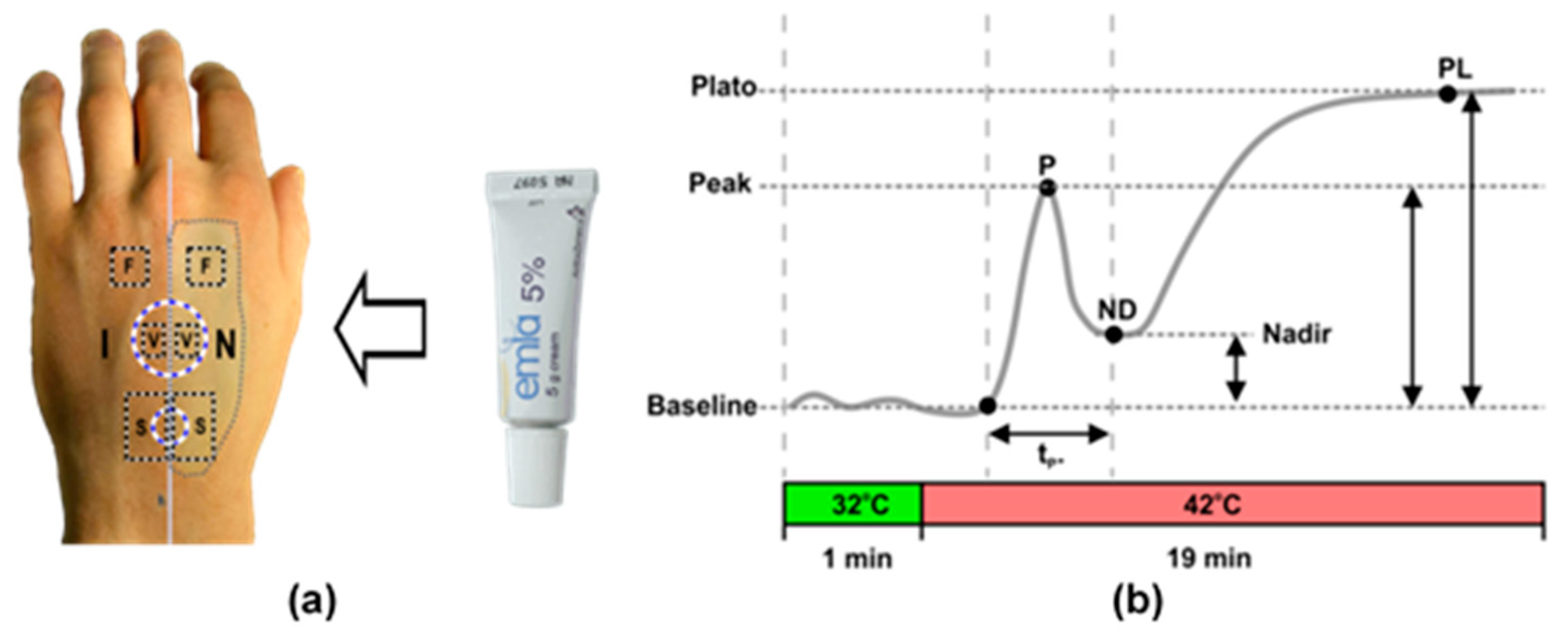
2.2. Measurement Protocol
2.3. Signal Processing
2.4. Analyses of Cutaneous Perfusion Data
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
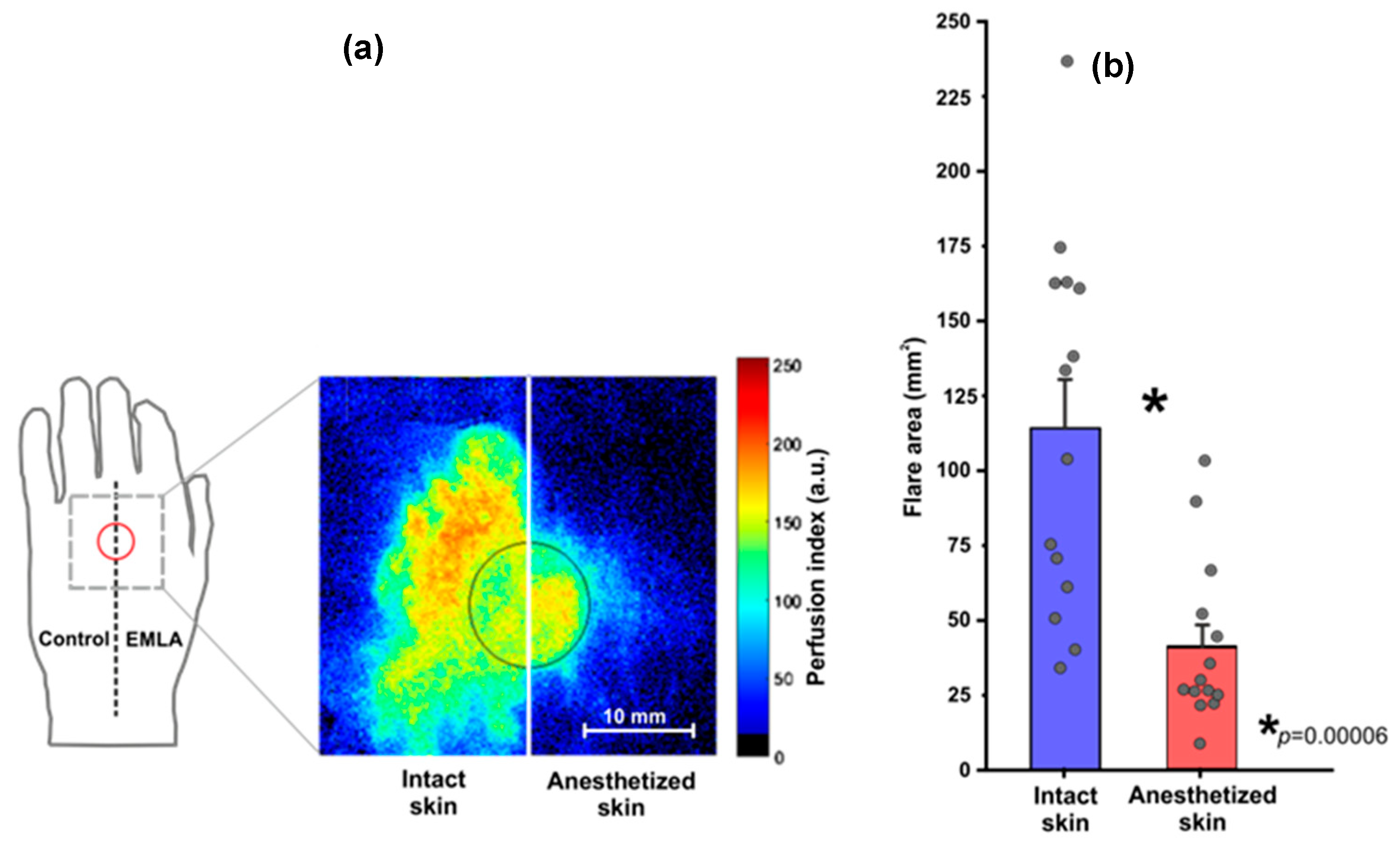
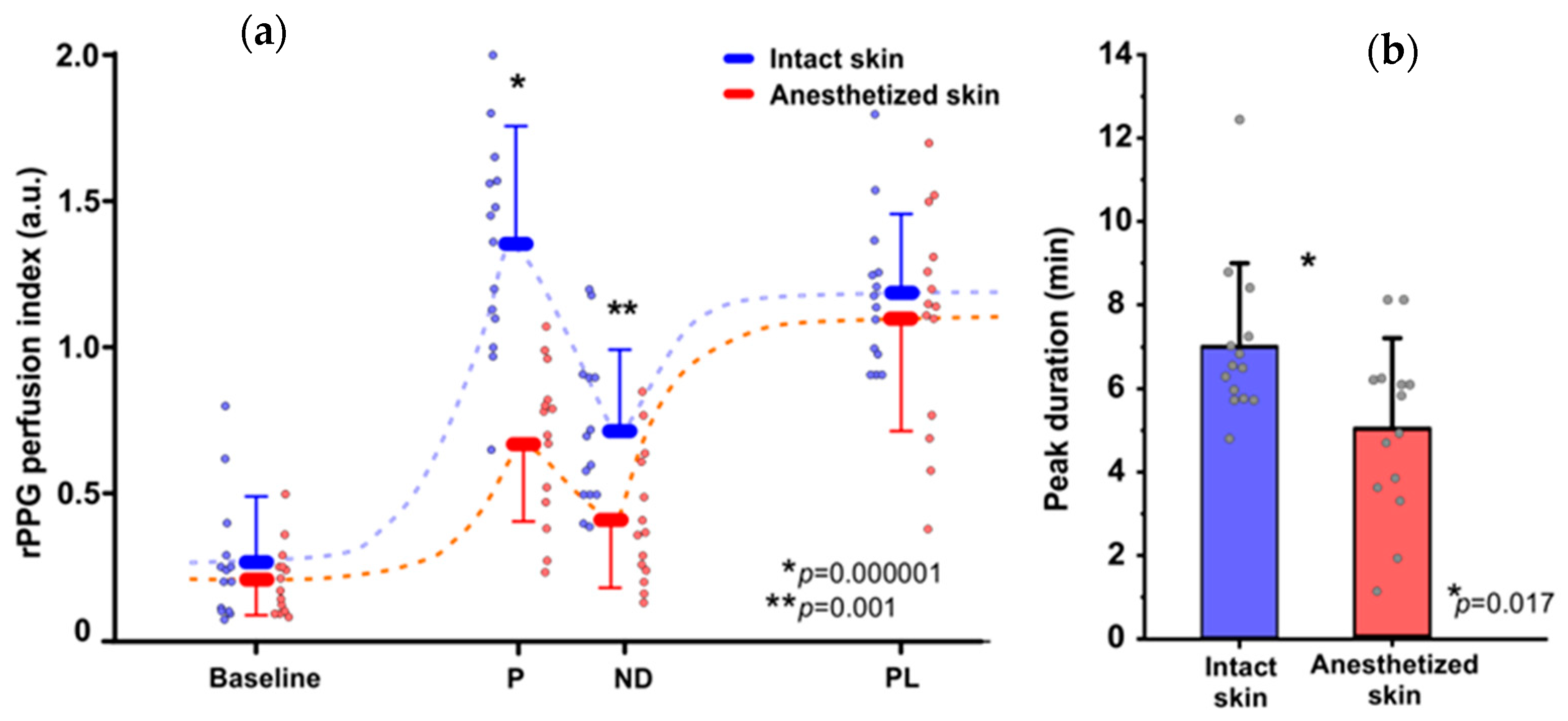
3.1. Topical Heating Induced Flare Response
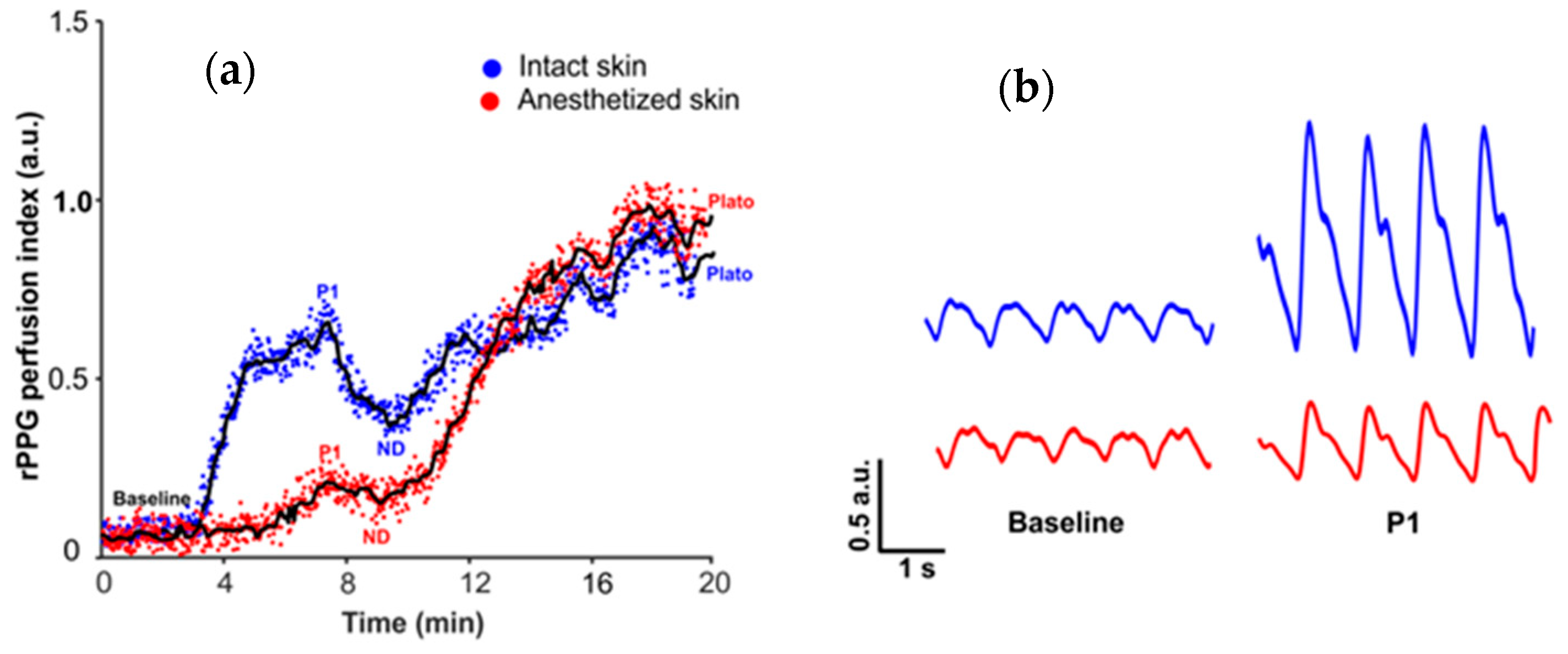
3.2. Topical Heating Induced Vasomotor Response Trend
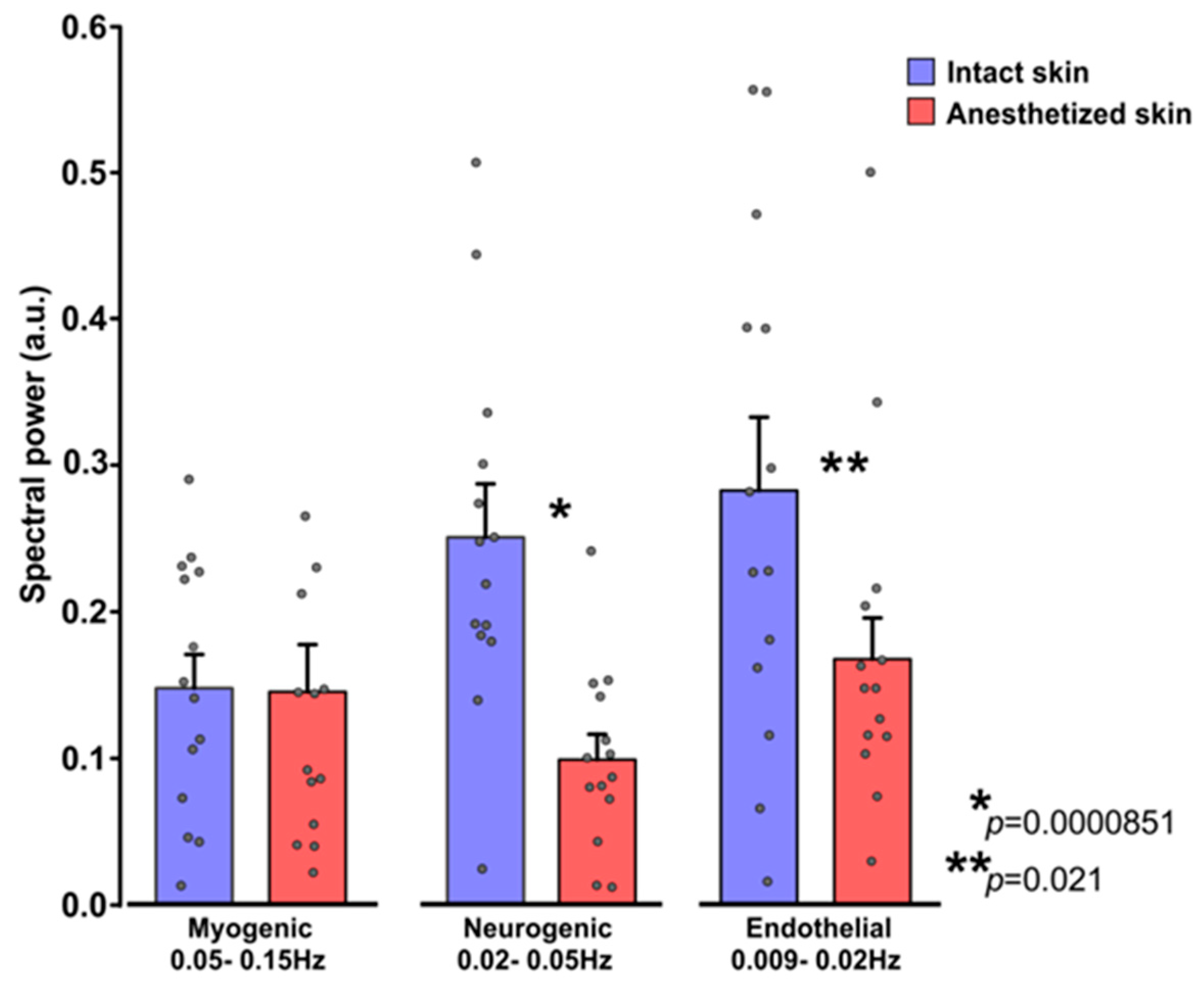
3.3. Influence of EMLA on Cutaneous Flowmotions
4. Discussion
4.1. Vasomotor Responses
4.2. Cutaneous Flowmotions
4.3. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Shekhlee, A.; Chelimsky, T.C.; Preston, D.C. Review: Small-fiber neuropathy. Neurologist 2002, 8, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovaguimian, A.; Gibbons, C.H. Diagnosis and treatment of pain in small-fiber neuropathy. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2011, 15, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truini, A. A Review of Neuropathic Pain: From Diagnostic Tests to Mechanisms. Pain Ther. 2017, 6, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, B.C.; Price, R.S.; Feldman, E.L. Distal Symmetric Polyneuropathy: A Review. JAMA 2015, 314, 2172–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koralnik, I.J.; Tyler, K.L. COVID-19: A Global Threat to the Nervous System. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahiri, D.; Ardila, A. COVID-19 Pandemic: A Neurological Perspective. Cureus 2020, 12, e7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsivgoulis, G.; Palaiodimou, L.; Katsanos, A.H.; Caso, V.; Köhrmann, M.; Molina, C.; Cordonnier, C.; Fischer, U.; Kelly, P.; Sharma, V.K.; et al. Neurological manifestations and implications of COVID-19 pandemic. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaslansky, R.; Yarnitsky, D. Clinical applications of quantitative sensory testing (QST). J. Neurol. Sci. 1998, 153, 215–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, B.G.; Hsieh, S.T.; Stocks, A.; Hauer, P.; Macko, C.; Cornblath, D.R.; Griffin, J.W.; McArthur, J.C. Cutaneous innervation in sensory neuropathies: Evaluation by skin biopsy. Neurology 1995, 45, 1848–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.I.; Peltier, A.C. Uses of skin biopsy for sensory and autonomic nerve assessment. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2013, 13, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roosterman, D.; Goerge, T.; Schneider, S.W.; Bunnett, N.W.; Steinhoff, M. Neuronal Control of Skin Function: The Skin as a Neuroimmunoendocrine Organ. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 1309–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Wortsman, J.; Paus, R.; Elias, P.M.; Tobin, D.J.; Feingold, K.R. Skin as an endocrine organ: Implications for its function. Drug Discov. Today. Dis. Mech. 2008, 5, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigopoulos, D.; Larios, G.; Katsambas, A. Skin signs of systemic diseases. Clin. Dermatol. 2011, 29, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashkatov, A.N.; Genina, E.A.; Kochubey, V.I.; Tuchin, V. V Optical properties of human skin, subcutaneous and mucous tissues in the wavelength range from 400 to 2000 nm. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, 2543–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, M.; Duchnik, E.; Maleszka, R.; Marchlewicz, M. Structural and biophysical characteristics of human skin in maintaining proper epidermal barrier function. Postep. Dermatol. Alergol. 2016, 33, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignon, C.; Tobin, D.J.; Zeitouny, M.; Uzunbajakava, N.E. Shedding light on the variability of optical skin properties: Finding a path towards more accurate prediction of light propagation in human cutaneous compartments. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 852–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.C.; Kuo, C.D.; Chi, L.Y.; Lin, H.D.; Wei, S.H.; Chen, C.S. Microcirculatory vasomotor changes are associated with severity of peripheral neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2013, 10, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizeva, I.; Di Maria, C.; Frick, P.; Podtaev, S.; Allen, J. Quantifying the correlation between photoplethysmography and laser Doppler flowmetry microvascular low-frequency oscillations. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 37007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltier, A.; Smith, A.G.; Russell, J.W.; Sheikh, K.; Bixby, B.; Howard, J.; Goldstein, J.; Song, Y.; Wang, L.; Feldman, E.L.; et al. Reliability of quantitative sudomotor axon reflex testing and quantitative sensory testing in neuropathy of impaired glucose regulation. Muscle Nerve 2009, 39, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ysihai, R. Abnormal LDIflare but Normal Quantitative Sensory Testing and Dermal Nerve Fiber Density in Patients with Painful Diabetic Neuropathy. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sharma, S.; Venkitaraman, R.; Vas, P.R.J.; Rayman, G. Assessment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy using the LDIFLARE technique: A novel technique to detect neural small fiber dysfunction. Brain Behav. 2015, 5, e00354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namer, B.; Pfeffer, S.; Handwerker, H.O.; Schmelz, M.; Bickel, A. Axon reflex flare and quantitative sudomotor axon reflex contribute in the diagnosis of small fiber neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 2013, 47, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubasch, M.L.; Kubasch, A.S.; Torres Pacheco, J.; Buchmann, S.J.; Illigens, B.M.-W.; Barlinn, K.; Siepmann, T. Laser Doppler Assessment of Vasomotor Axon Reflex Responsiveness to Evaluate Neurovascular Function. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.Q.; Krishnan, S.T.; Rayman, G. C-fiber function assessed by the laser doppler imager flare technique and acetylcholine iontophoresis. Muscle Nerve 2009, 40, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hop, M.J.; Stekelenburg, C.M.; Hiddingh, J.; Kuipers, H.C.; Middelkoop, E.; Nieuwenhuis, M.K.; Polinder, S.; van Baar, M.E. Cost-Effectiveness of Laser Doppler Imaging in Burn Care in The Netherlands: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 137, 166e–176e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Papin, C.; Azorin-Peris, V.; Kalawsky, R.; Greenwald, S.; Hu, S. Use of ambient light in remote photoplethysmographic systems: Comparison between a high-performance camera and a low-cost webcam. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 037005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubins, U.; Spigulis, J.; Miscuks, A. Application of Colour Magnification Technique for Revealing Skin Microcirculation Changes Under Regional Anaesthetic Input. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference “Biophotonics Riga 2013”, Riga, Latvia, 26–31 August 2013; Volume 9032, p. 903203. [Google Scholar]
- Marcinkevics, Z.; Rubins, U.; Zaharans, J.; Miscuks, A.; Urtane, E.; Ozolina-Moll, L. Imaging photoplethysmography for clinical assessment of cutaneous microcirculation at two different depths. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 35005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubins, U.; Marcinkevics, Z.; Logina, I.; Grabovskis, A.; Kviesis-Kipge, E. Imaging photoplethysmography for assessment of chronic pain patients. In Optical Diagnostics and Sensing XIX: Toward Point-of-Care Diagnostics; Coté, G.L., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019; Volume 10885, p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Marcinkevics, Z.; Rubins, U.; Aglinska, A.; Caica, A.; Grabovskis, A. Remote photoplethysmography for skin perfusion monitoring using narrowband illumination. In Clinical and Preclinical Optical Diagnostics II; Brown, J.Q., van Leeuwen, T.G., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2019; Volume 11073, p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Kamshilin, A.; Belaventseva, A.; Romashko, R.; Kulchin, Y.; Mamontov, O. Local Thermal Impact on Microcirculation Assessed by Imaging Photoplethysmography. Biol. Med. 2016, 8, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volynsky, M.A.; Margaryants, N.B.; Mamontov, O.V.; Kamshilin, A.A. Contactless Monitoring of Microcirculation Reaction on Local Temperature Changes. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubins, U.; Miscuks, A.; Lange, M. Simple and convenient remote photoplethysmography system for monitoring regional anesthesia effectiveness. IFMBE Proc. 2016, 65, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191. [CrossRef]
- Kastrup, J.; Bülow, J.; Lassen, N.A. Vasomotion in human skin before and after local heating recorded with laser Doppler flowmetry. A method for induction of vasomotion. Int. J. Microcirc. Clin. Exp. 1989, 8, 205–215. [Google Scholar]
- Söderström, T.; Stefanovska, A.; Veber, M.; Svensson, H. Involvement of sympathetic nerve activity in skin blood flow oscillations in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2003, 284, H1638–H1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvernmo, H.D.; Stefanovska, A.; Kirkeboen, K.A.; Kvernebo, K. Oscillations in the human cutaneous blood perfusion signal modified by endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent vasodilators. Microvasc. Res. 1999, 57, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvandal, P.; Stefanovska, A.; Veber, M.; Kvernmo, H.D.; Kirkebøen, K.A. Regulation of human cutaneous circulation evaluated by laser Doppler flowmetry, iontophoresis, and spectral analysis: Importance of nitric oxide and prostaglandines. Microvasc. Res. 2003, 65, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkevics, Z.; Aglinska, A.; Rubins, U.; Mikale, A.; Grabovskis, A. Imaging photoplethysmography for evaluation of cutaneous sensory nerve fiber function. In Biophotonics—Riga 2020; Spigulis, J., Ed.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020; Volume 11585, pp. 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, S.T.M.; Rayman, G. The LDIflare: A novel test of C-fiber function demonstrates early neuropathy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2930–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzler-Wilson, K.; Kellie, L.A.; Tomc, C.; Simpson, C.; Sammons, D.; Wilson, T.E. Differential vasodilatory responses to local heating in facial, glabrous and hairy skin. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2012, 32, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieuwenhoff, M.D.; Wu, Y.; Huygen, F.J.P.M.; Schouten, A.C.; van der Helm, F.C.T.; Niehof, S.P. Reproducibility of axon reflex-related vasodilation assessed by dynamic thermal imaging in healthy subjects. Microvasc. Res. 2016, 106, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciplak, M.; Pasche, A.; Heim, A.; Haeberli, C.; Waeber, B.; Liaudet, L.; Feihl, F.; Engelberger, R. The vasodilatory response of skin microcirculation to local heating is subject to desensitization. Microcirculation 2009, 16, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, Z.T.; Shannon, C.A.; Kistler, B.M.; Nagelkirk, P.R.; Del Pozzi, A.T. Effect of Sex and Menstrual Cycle on Skin Sensory Nerve Contribution to Local Heating. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2019, 12, 1265–1279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Wang, S.; Tsai, Y. Axon reflex-related hyperemia induced by short local heating is reproducible. Microvasc. Res. 2012, 84, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marche, P.; Dubois, S.; Abraham, P.; Gascoin, L. Neurovascular microcirculatory vasodilation mediated by C-fibers and Transient receptor potential vanilloid-type-1 channels (TRPV 1) is impaired in type 1 diabetes. Nat. Publ. Gr. 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, B.J.; Hollowed, C.G. Current concepts of active vasodilation in human skin. Temperature 2017, 4, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijazi, M.M.; Buchmann, S.J.; Sedghi, A.; Illigens, B.M.; Reichmann, H.; Schackert, G.; Siepmann, T. Assessment of cutaneous axon-reflex responses to evaluate functional integrity of autonomic small nerve fibers. Neurol. Sci. Off. J. Ital. Neurol. Soc. Ital. Soc. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 41, 1685–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arildsson, M.; Nilsson, G.E.; Strömberg, T. Effects on skin blood flow by provocation during local analgesia. Microvasc. Res. 2000, 59, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caselli, A.; Uccioli, L.; Khaodhiar, L.; Veves, A. Local anesthesia reduces the maximal skin vasodilation during iontophoresis of sodium nitroprusside and heating. Microvasc. Res. 2003, 66, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, D.J.; McLeod, G.A.; Khan, F.; Belch, J.J.F. Mechanisms influencing the vasoactive effects of lidocaine in human skin. Anaesthesia 2007, 62, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, A.K.; Herrick, A.L.; King, T.A. Laser Doppler imaging: A developing technique for application in the rheumatic diseases. Rheumatology 2004, 43, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamshilin, A.A.; Nippolainen, E.; Sidorov, I.S.; Vasilev, P.V.; Erofeev, N.P.; Podolian, N.P.; Romashko, R.V. A new look at the essence of the imaging photoplethysmography. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, M.V.; Margaryants, N.B.; Potemkin, A.V.; Volynsky, M.A.; Gurov, I.P.; Mamontov, O.V.; Kamshilin, A.A. Video capillaroscopy clarifies mechanism of the photoplethysmographic waveform appearance. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.; Bento, M.; Vieira, H.; Monteiro Rodrigues, L. Comparing the spectral components of laser Doppler flowmetry and photoplethysmography signals for the assessment of the vascular response to hyperoxia. J. Biomed. Biopharm. Res. 2017, 14, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minson, C.T.; Berry, L.T.; Joyner, M.J. Nitric oxide and neurally mediated regulation of skin blood flow during local heating. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 91, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, S.J.; Hodges, G.J. Sensory and sympathetic nerve contributions to the cutaneous vasodilator response from a noxious heat stimulus. Exp. Physiol. 2011, 96, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, C.; Schmidt, R.; Schmelz, M.; Torebjork, H.E.; Handwerker, H.O. Action potential conduction in the terminal arborisation of nociceptive C-fibre afferents. J. Physiol. 2003, 547, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickel, A.; Heyer, G.; Senger, C.; Maihöfner, C.; Maihoefner, C.; Heuss, D.; Hilz, M.J.; Namer, B. C-fiber axon reflex flare size correlates with epidermal nerve fiber density in human skin biopsies. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2009, 14, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illigens, B.M.W.; Siepmann, T.; Roofeh, J.; Gibbons, C.H. Laser Doppler imaging in the detection of peripheral neuropathy. Auton. Neurosci. Basic Clin. 2013, 177, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalkjær, C.; Boedtkjer, D.; Matchkov, V. Vasomotion—What is currently thought? Acta Physiol. 2011, 202, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.M.; Rocha, C.; Ferreira, H.; Silva, H. Different lasers reveal different skin microcirculatory flowmotion-data from the wavelet transform analysis of human hindlimb perfusion. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Carpi, A.; Galetta, F.; Franzoni, F.; Santoro, G. The investigation of skin blood flowmotion: A new approach to study the microcirculatory impairment in vascular diseases? Biomed. Pharmacother. 2006, 60, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, G.J.; Mallette, M.M.; Tew, G.A.; Saxton, J.M.; Moss, J.; Ruddock, A.D.; Klonizakis, M. Effect of age on cutaneous vasomotor responses during local skin heating. Microvasc. Res. 2017, 112, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edvinsson, M.-L.; Andersson, S.E.; Xu, C.-B.; Edvinsson, L. Cigarette smoking leads to reduced relaxant responses of the cutaneous microcirculation. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesselaar, E.; Nezirevic Dernroth, D.; Farnebo, S. Acute effects of coffee on skin blood flow and microvascular function. Microvasc. Res. 2017, 114, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glazachev, O.S.; Dudnik, E.N. The microcirculatory blood flow and autonomic regulation’s functional state in young people with different levels of subjectively experienced psychological stress. Fiziol. Cheloveka 2012, 38, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, G.H.; Wong, B.J.; Holowatz, L.A.; Kenney, W.L. Changes in the control of skin blood flow with exercise training: Where do cutaneous vascular adaptations fit in? Exp. Physiol. 2011, 96, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrofsky, J.; Lee, H.; Khowailed, I.A. Sudomotor and vasomotor activity during the menstrual cycle with global heating. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2017, 37, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minson, C.T.; Tew, G.A.; Klonizakis, M.; Moss, J.; Ruddock, A.D.; Saxton, J.M.; Gary, J. Thermal provocation to evaluate microvascular reactivity in human skin Mechanisms and Modulators of Temperature Regulation Thermal provocation to evaluate microvascular reactivity in human skin. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 109, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marcinkevics, Z.; Aglinska, A.; Rubins, U.; Grabovskis, A. Remote Photoplethysmography for Evaluation of Cutaneous Sensory Nerve Fiber Function. Sensors 2021, 21, 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041272
Marcinkevics Z, Aglinska A, Rubins U, Grabovskis A. Remote Photoplethysmography for Evaluation of Cutaneous Sensory Nerve Fiber Function. Sensors. 2021; 21(4):1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041272
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarcinkevics, Zbignevs, Alise Aglinska, Uldis Rubins, and Andris Grabovskis. 2021. "Remote Photoplethysmography for Evaluation of Cutaneous Sensory Nerve Fiber Function" Sensors 21, no. 4: 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041272
APA StyleMarcinkevics, Z., Aglinska, A., Rubins, U., & Grabovskis, A. (2021). Remote Photoplethysmography for Evaluation of Cutaneous Sensory Nerve Fiber Function. Sensors, 21(4), 1272. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041272




