Infrasonic Earthquake Detectability Investigated in Southern Part of Japan, 2019
Abstract
1. Introduction
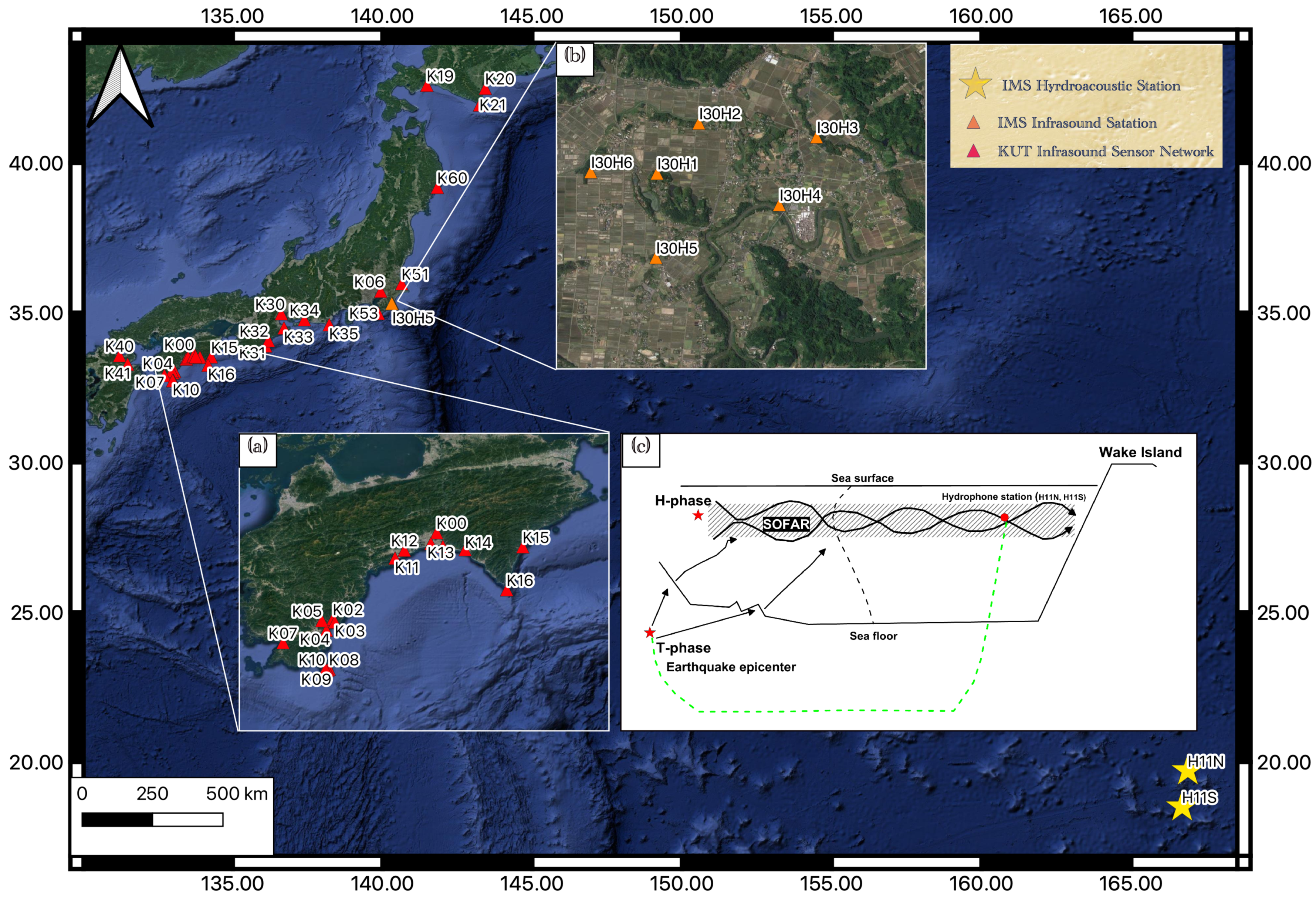
2. Data Sets and Method
2.1. Infrasound Data
2.2. Hydroacoustic Data
2.3. Infrasound Analysis Method
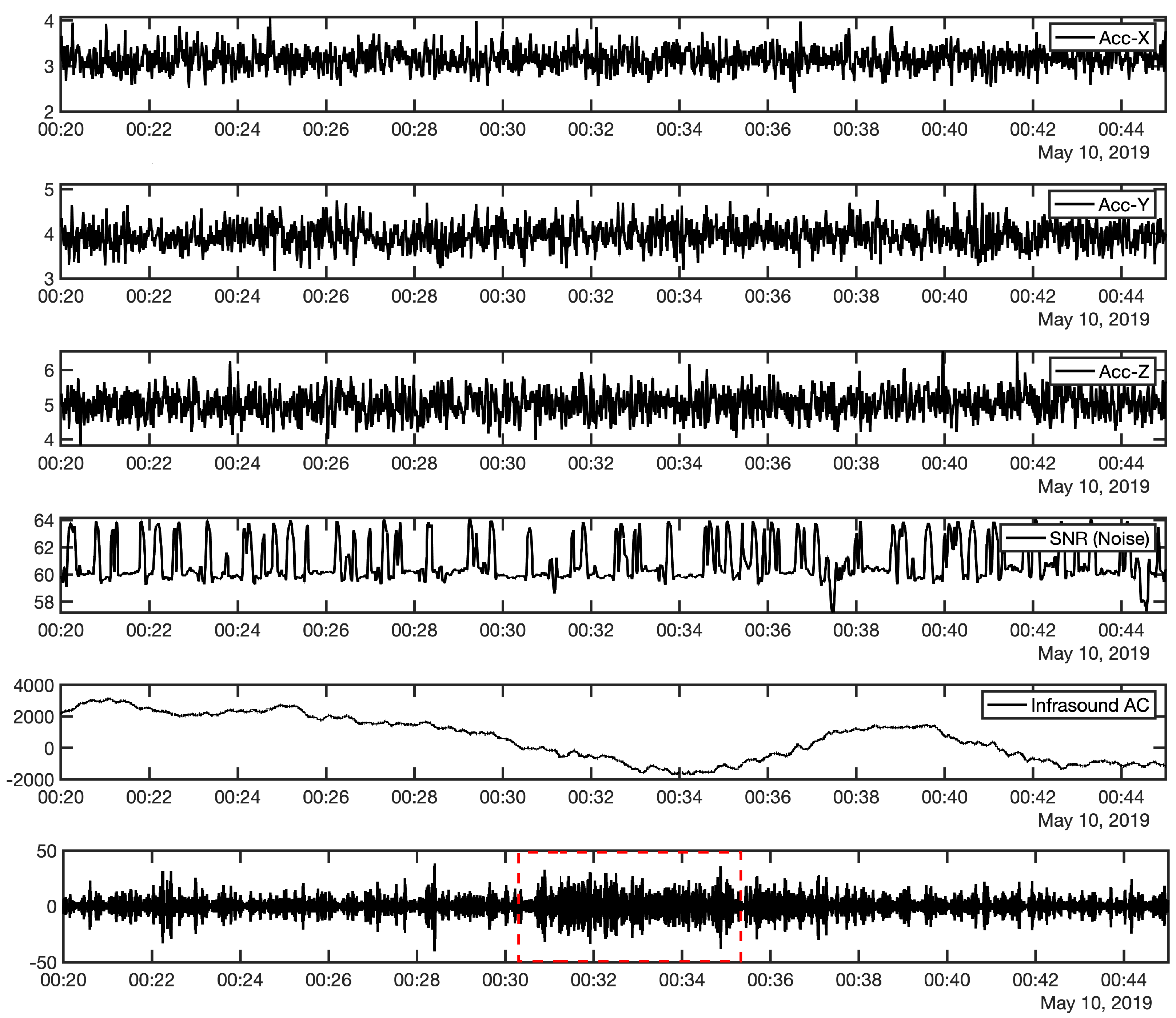
3. Observations
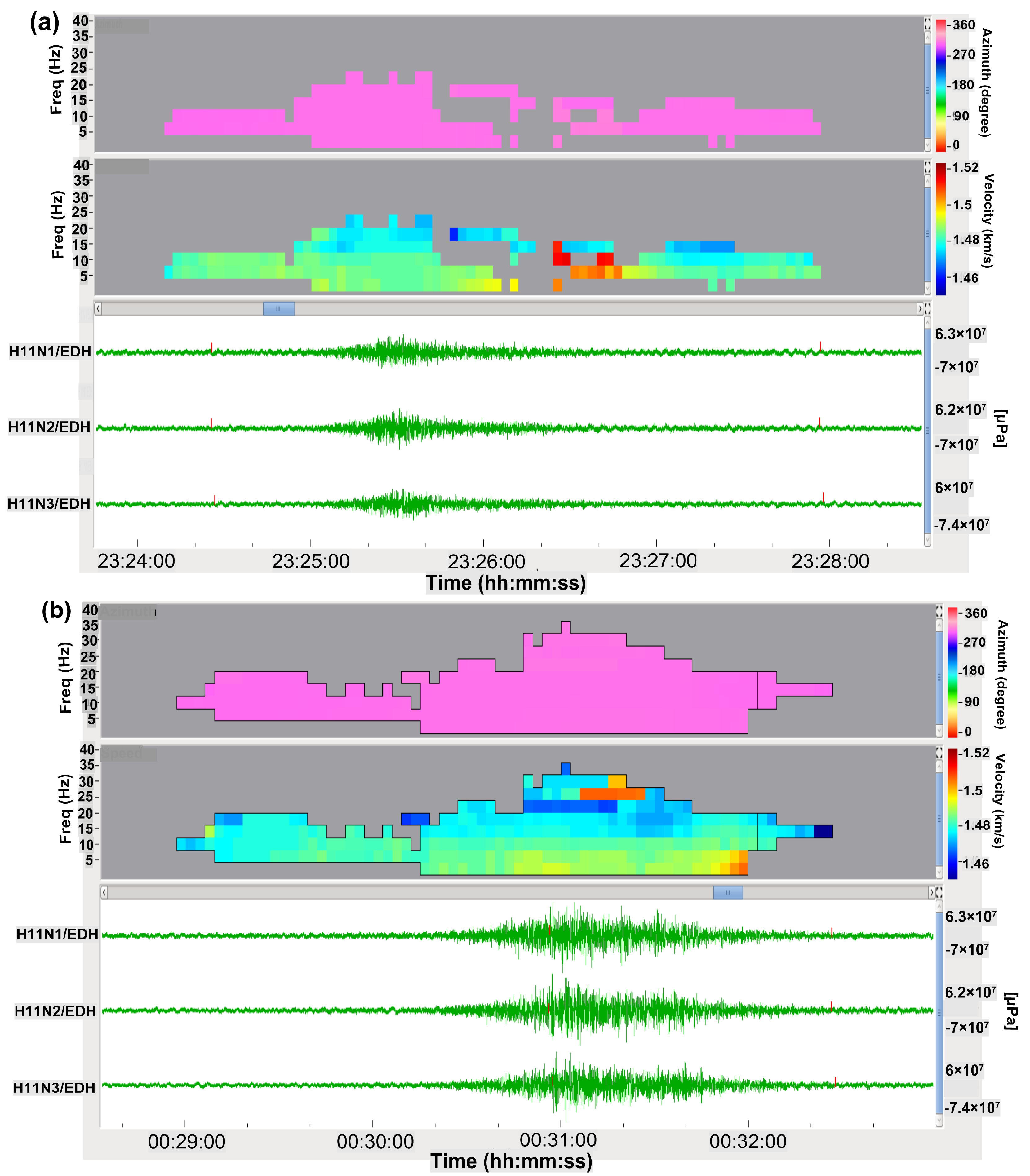
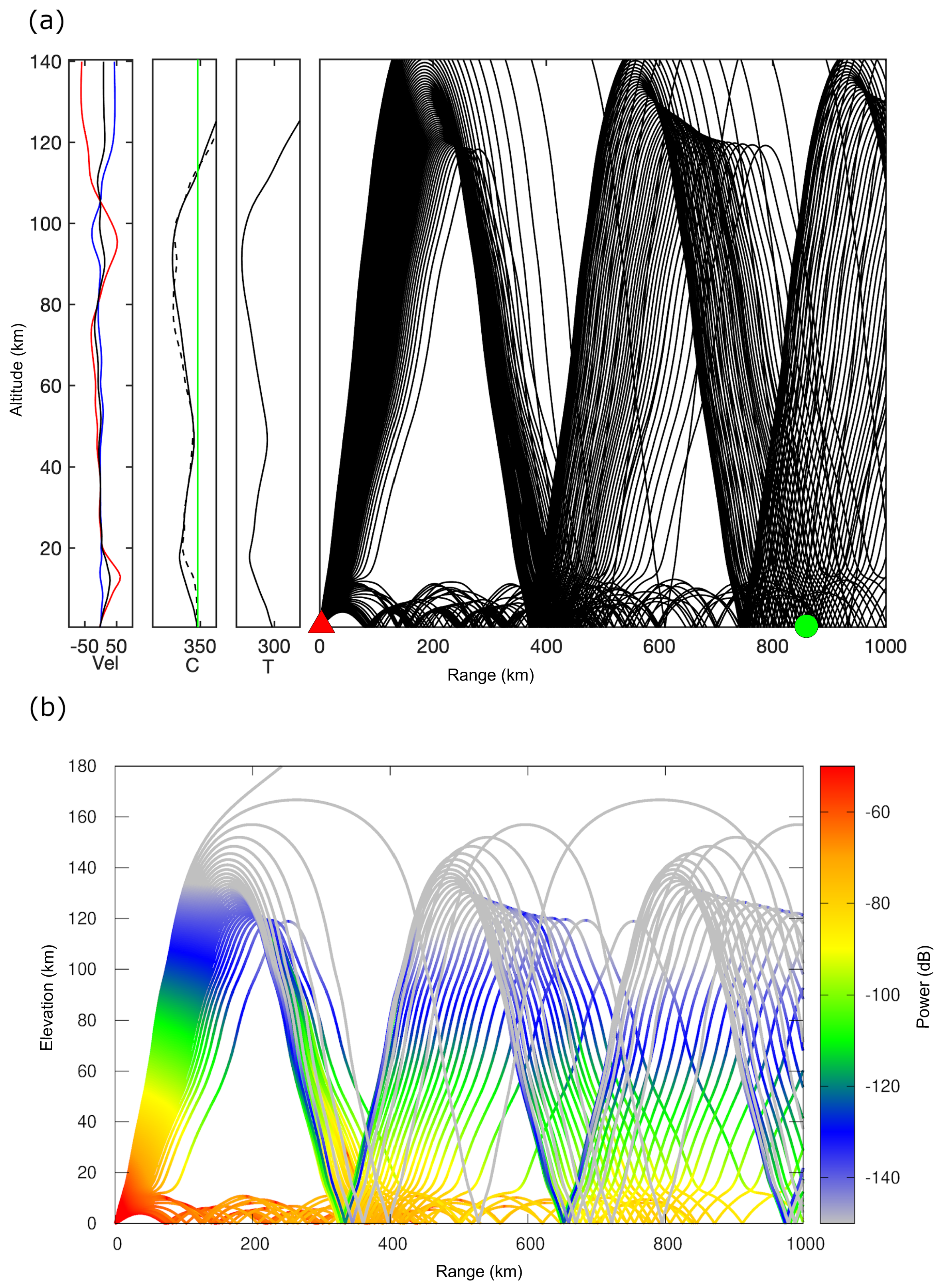
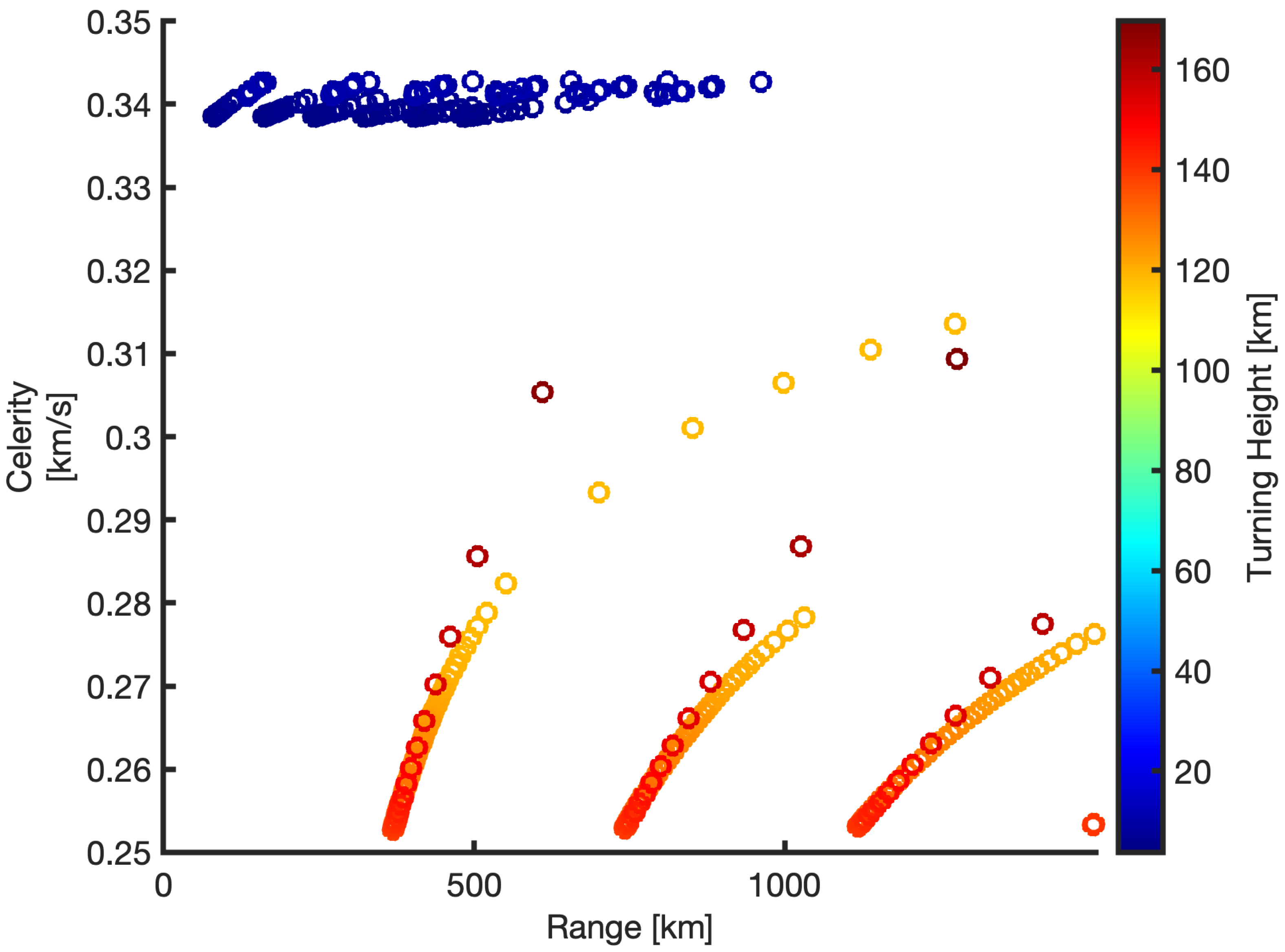
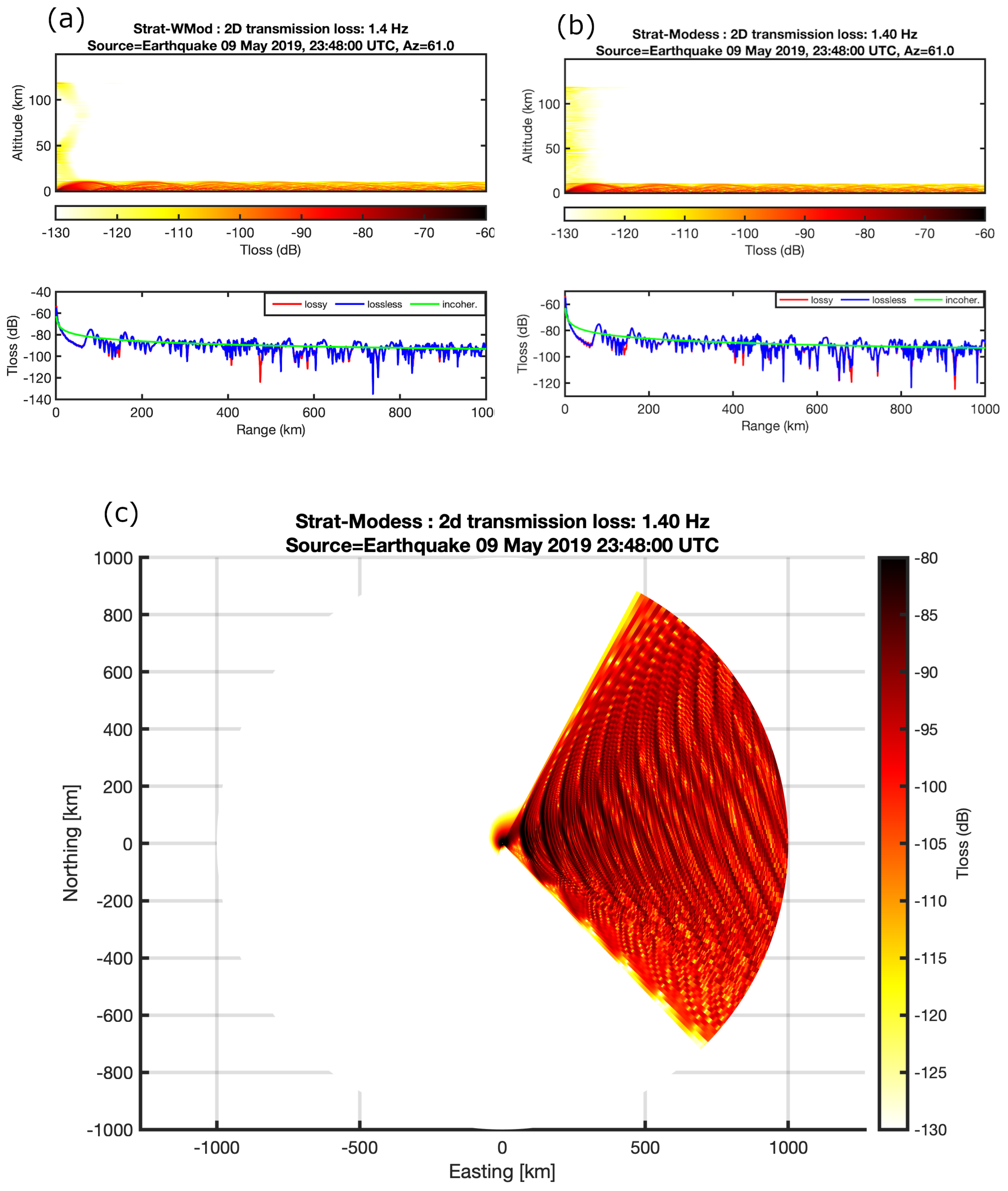
4. Infrasound Propagation Analysis and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ElGabry, M.N.; Korrat, I.M.; Hussein, H.M.; Hamama, I.H. Infrasound detection of meteors. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 2019, 6, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Garces, M.; Le Pichon, A. Infrasound from Earthquakes, Tsunamis and Volcanoes. In Extreme Environmental Events: Complexity in Forecasting and Early Warning; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 35, pp. 663–679. ISBN 978-1-4419-7695-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikumo, T. Atmospheric Pressure Waves and Tectonic Deformation Associated with the Alaskan Earthquake of March 28, 1964. J. Phys. Earth 1968, 16, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, I.-Y.; Lee, H.-I.; Jeon, J.-S.; Kang, T.-S. An analysis of the infrasound signal from the Miyagi-Oki earthquake in Japan on 16 August 2005. Earth Planets Space 2007, 59, e9–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mutschlecner, J.P.; Whitaker, R.W. Infrasound from earthquakes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, B.; Le Pichon, A.; Vergoz, J.; Herry, P.; Ceranna, L.; Pilger, C.; Marchetti, E.; Ripepe, M.; Bossu, R. Estimating the Ground-Motion Distribution of the 2016 Mw 6.2 Amatrice, Italy, Earthquake Using Remote Infrasound Observations. Seismol. Res. Lett. 2018, 89, 2227–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.S. Local infrasound signals from the Tokachi-Oki earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pichon, A.; Guilbert, J.; Vega, A.; Garcés, M.; Brachet, N. Ground-coupled air waves and diffracted infrasound from the Arequipa earthquake of June 23, 2001. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 33-31–33-34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, L.G.; Brown, D.; Heaney, K.D.; Assink, J.D.; Smets, P.S.M.; Snellen, M. Evanescent wave coupling in a geophysical system: Airborne acoustic signals from the Mw 8.1 Macquarie Ridge earthquake. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot-Hedlin, C.D.; Orcutt, J.A. Excitation of T-phases by seafloor scattering. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2001, 109, 1944–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, K.; Kimura, S. Seismicity Characteristics in Shikoku in Relation to the Great Nankaido Earthquakes. J. Phys. Earth 1979, 27, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batubara, M.; Yamamoto, M.-Y. Infrasound Observations of Atmospheric Disturbances Due to a Sequence of Explosive Eruptions at Mt. Shinmoedake in Japan on March 2018. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cansi, Y. An automatic seismic event processing for detection and location: The P.M.C.C. Method. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cansi, Y.; Pichon, A.L. Infrasound Event Detection Using the Progressive Multi-Channel Correlation Algorithm. In Handbook of Signal Processing in Acoustics; Havelock, D., Kuwano, S., Vorländer, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 1425–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilger, C.; Gaebler, P.; Ceranna, L.; Le Pichon, A.; Vergoz, J.; Perttu, A.; Tailpied, D.; Taisne, B. Infrasound and seismoacoustic signatures of the 28 September 2018 Sulawesi super-shear earthquake. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 19, 2811–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelly, D.R.; Beroza, G.C.; Ide, S.; Nakamula, S. Low-frequency earthquakes in Shikoku, Japan, and their relationship to episodic tremor and slip. Nature 2006, 442, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip Stephen, B.; Omar Eduardo, M.; Garrett Gene, E. InfraPy: Python-Based Signal Analysis Tools for Infrasound; National Nuclear Security Administration: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, G.V. Geometrical theory of sound propagation in the atmosphere. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1955, 7, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drob, D.P.; Picone, J.M.; Garcés, M. Global morphology of infrasound propagation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingevitch, J.F.; Collins, M.D.; Dacol, D.K.; Drob, D.P.; Rogers, J.C.W.; Siegmann, W.L. A wide angle and high Mach number parabolic equation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 111, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxler, R.M.; Assink, J.D.; Hetzer, C.; Velea, D. NCPAprop—A software package for infrasound propagation modeling. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 141, 3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drob, D.P.; Emmert, J.T.; Meriwether, J.W.; Makela, J.J.; Doornbos, E.; Conde, M.; Hernandez, G.; Noto, J.; Zawdie, K.A.; McDonald, S.E.; et al. An update to the Horizontal Wind Model (HWM): The quiet time thermosphere. Earth Space Sci. 2015, 2, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picone, J.M.; Hedin, A.E.; Drob, D.P.; Aikin, A.C. NRLMSISE-00 empirical model of the atmosphere: Statistical comparisons and scientific issues. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2002, 107, SIA 15-1–SIA 15-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaiger, H.F.; Iezzi, A.M.; Fee, D. AVO-G2S: A modified, open-source Ground-to-Space atmospheric specification for infrasound modeling. Comput. Geosci. 2019, 125, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
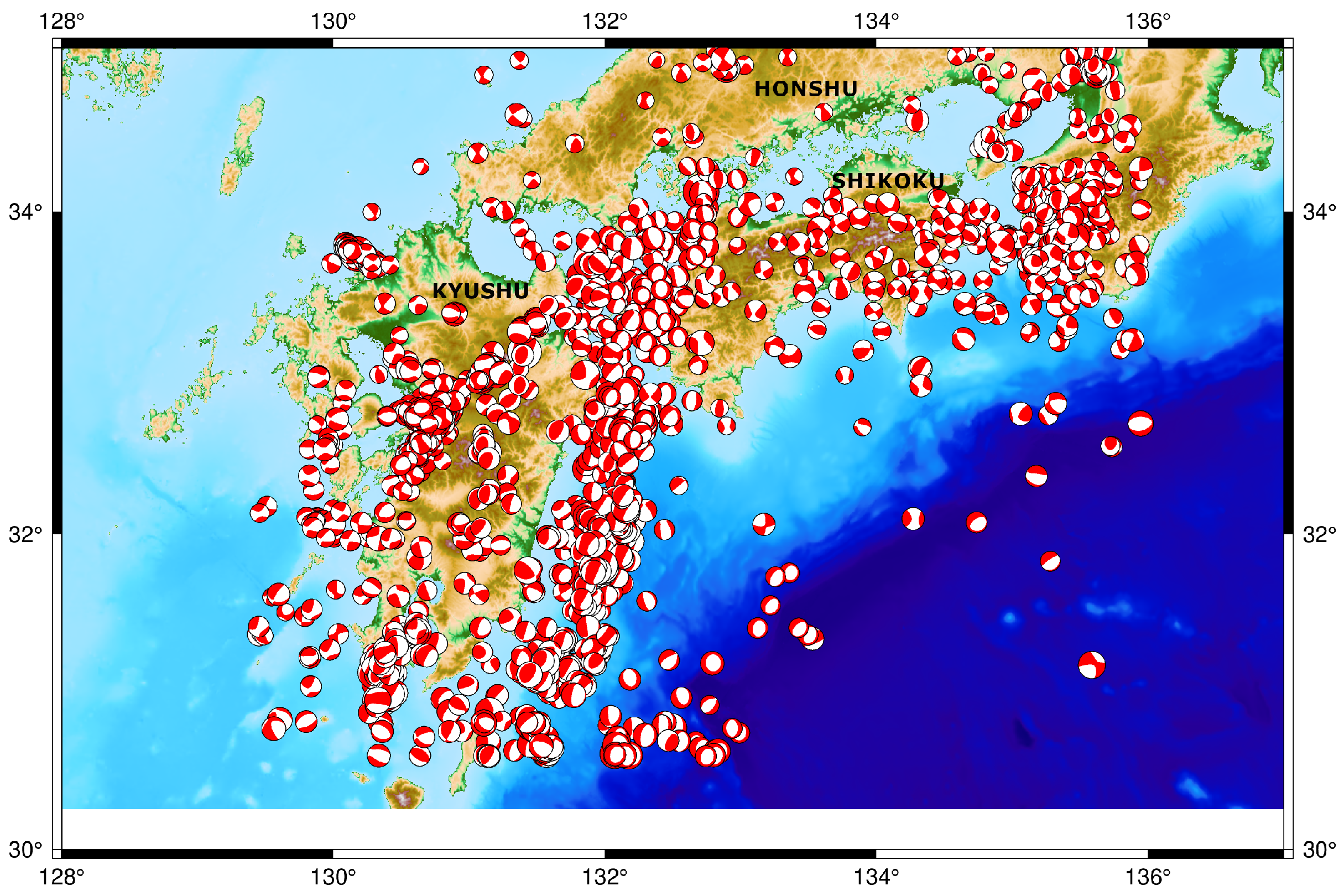
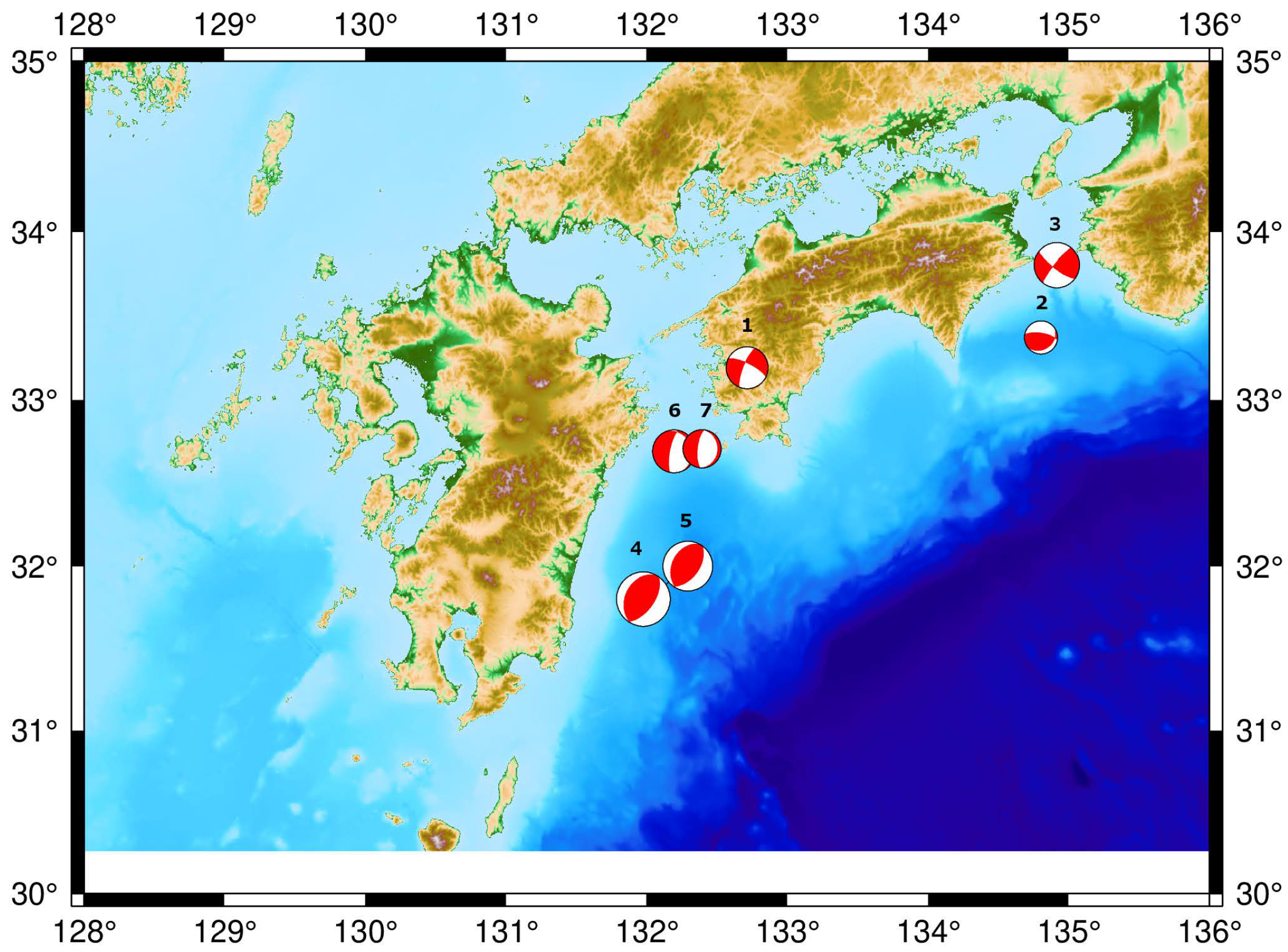






| No. | Date | Event Time UTC | Mag. (mb) | Lon. E | Lat. N | Depth (km) | Source Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7 Mar 2019 | 02:20:34.57 | 4.4 mb | 134.79 | 33.3703 | 31.61 | Reverse |
| 2 | 11 Mar 2019 | 06:37:51.27 | 4.9 mb | 132.71 | 33.1903 | 38.13 | Strike-Slip |
| 3 | 13 Mar 2019 | 04:48:48.78 | 5.1 mb | 134.91 | 33.8010 | 43.05 | Strike-Slip |
| 4 | 9 May 2019 | 22:43:21.23 | 5.8 mb | 131.99 | 31.7850 | 25.35 | Reverse |
| 5 | 9 May 2019 | 23:48:41.68 | 6.0 mb | 131.97 | 31.8012 | 25.46 | Reverse |
| 6 | 10 May 2019 | 23:59:40.05 | 5.0 mb | 132.29 | 32.6903 | 36.34 | Normal |
| 7 | 12 May 2019 | 06:07:43.73 | 4.7 mb | 132.29 | 32.7053 | 36.66 | Normal |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamama, I.; Yamamoto, M.-y. Infrasonic Earthquake Detectability Investigated in Southern Part of Japan, 2019. Sensors 2021, 21, 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21030894
Hamama I, Yamamoto M-y. Infrasonic Earthquake Detectability Investigated in Southern Part of Japan, 2019. Sensors. 2021; 21(3):894. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21030894
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamama, Islam, and Masa-yuki Yamamoto. 2021. "Infrasonic Earthquake Detectability Investigated in Southern Part of Japan, 2019" Sensors 21, no. 3: 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21030894
APA StyleHamama, I., & Yamamoto, M.-y. (2021). Infrasonic Earthquake Detectability Investigated in Southern Part of Japan, 2019. Sensors, 21(3), 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21030894






