An Assessment of Balance through Posturography in Healthy about Women: An Observational Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
2.2. Participants
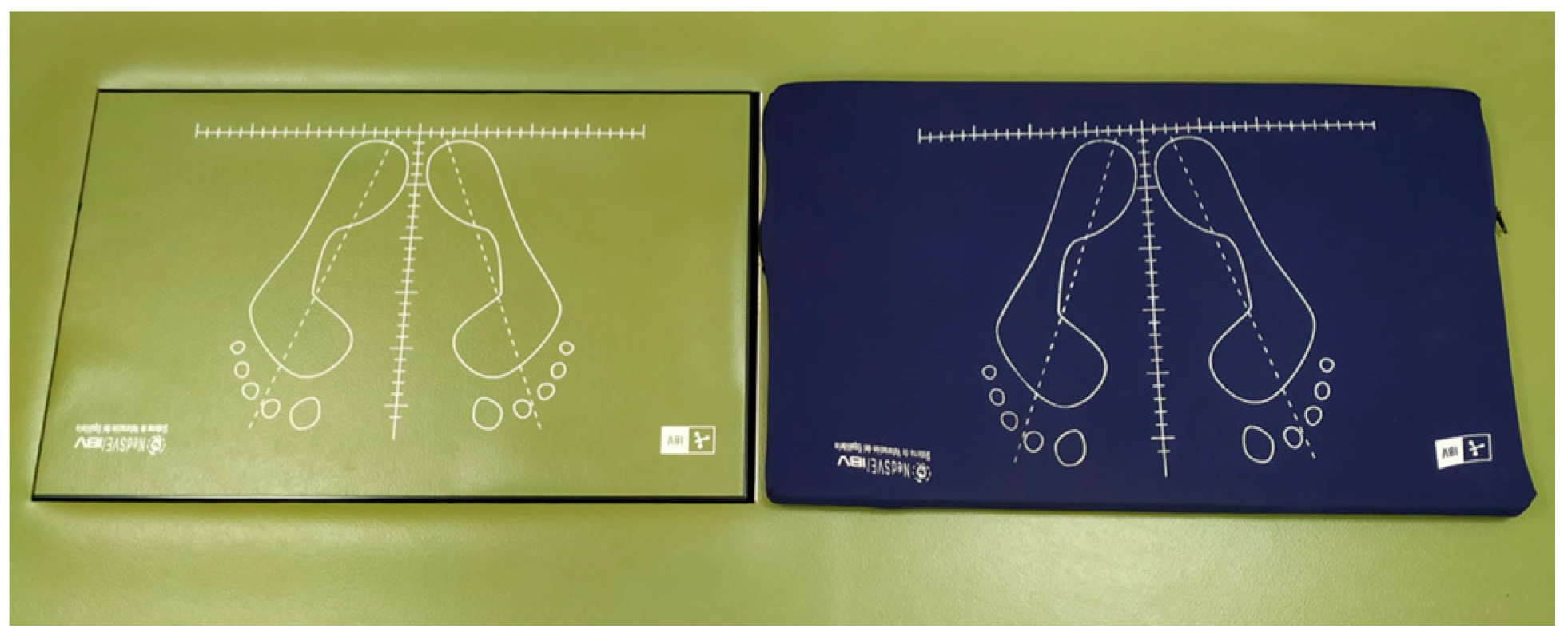
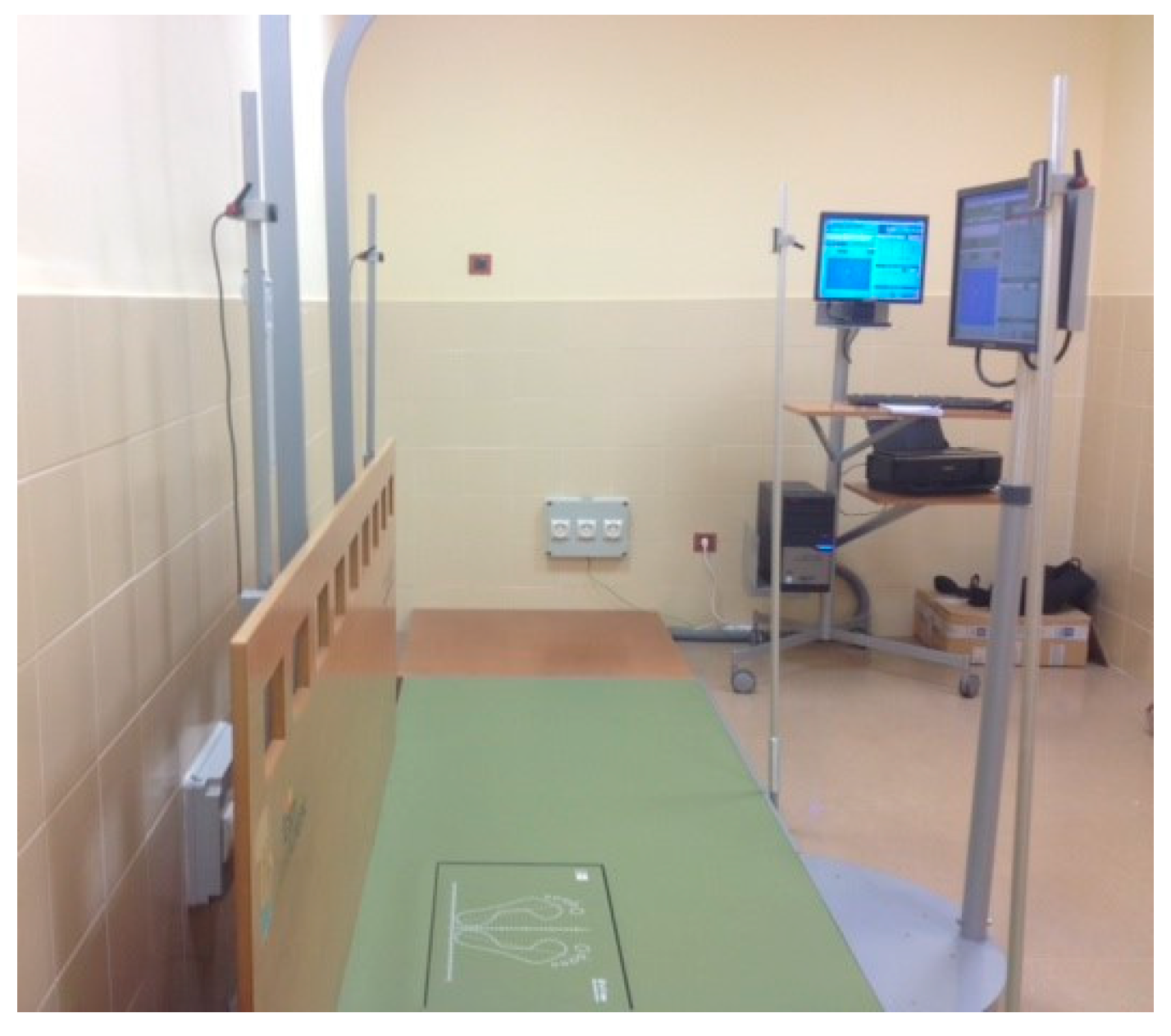
2.3. Data Collection Protocol
- −
- Body sway area (mm2): approximate area in which the subject’s balance takes place. To obtain this calculation, the software application determines an ellipse that encompasses a group of points that represent the subject’s trajectory during the duration of the test.
- −
- Maximum anteroposterior (AP) and mediolateral (ML) displacement (mm): these represent the furthest point reached by the centers of pressure in the anteroposterior and mediolateral axes during the recording time.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ambrose, A.F.; Paul, G.; Hausdorff, J.M. Risk factors for falls among older adults: A review of the literature. Maturitas 2013, 75, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Trisan, R. Balance problems and fall risks in the elderly. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 28, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrella-Castillo, D.F.; Euán-Paz, A.; Pinto-Loría, M.L.; Sánchez-Escobedo, P.A.; Rubio-Zapata, H.A. Alteraciones del equilibrio como predictoras de caídas en una muestra de adultos mayores de Mérida Yucatán, México. Rehabilitación 2011, 4, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, N.S.; Martins, A.C.G.; Machado, D.C.D.; Dias, K.P.; Nader, S.; Bastos, V.H. The influence of vision-foot axis in morphoe-static balance regulation in elderly. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 20, 320–327. [Google Scholar]
- Gama, Z.A.S.; Gómez-Conesa, A. Factores de riesgo de las caídas en ancianos: Revisión sistemática. Rev. Saúde Pública 2008, 42, 946–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sampedro, J.; Meléndez, A.; Ruiz, P. Análisis comparativo de la relación entre el número de caídas anual y baterías de pruebas de equilibrio y agilidad en personas mayores. Retos Nuevas Tend. Educ. Física Deporte Recreación 2010, 17, 115–117. [Google Scholar]
- Era, P.; Sainio, P.; Koskinen, S.; Haavisto, P.; Vaara, M.; Aromaa, A. Postural balance in a random sample of 7979 subjects aged 30 years and over. Gerontology 2006, 52, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piirtola, M.; Era, P. Force platform measurements as predictors of falls among older people: A review. Gerontology 2006, 52, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lázaro-Del Nogal, M. Fall among older persons. Med. Clin. 2009, 133, 147–153. [Google Scholar]
- Bear, M.F.; Connors, B.; Paradiso, M. Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz, E.M.; Guzmán, R.B.; Cerverón, C.C.; Baydal, J.M. Análisis de la interacción visuo-vestibular y la influencia visual en el control postural. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Española 2004, 55, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachman, A.; Marszałek, W.; Kamieniarz, A.; Michalska, J.; Pawłowski, M.; Akbas, A.; Juras, G. The Effects of Exergaming Training on Balance in Healthy Elderly Women—A Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, D.C.; Walsh, G.S.; Arkesteijn, M. Effectiveness of Exercise Interventions to Improve Postural Control in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses of Centre of Pressure Measurements. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chittrakul, J.; Siviroj, P.; Sungkarat, S.; Sapbamrer, R. Multi-System Physical Exercise Intervention for Fall Prevention and Quality of Life in Pre-Frail Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maki, B.E.; Sibley, K.M.; Jaglal, S.B.; Bayley, M.; Brooks, D.; Fernie, G.R.; Flint, A.J.; Gage, W.; Liu, B.A.; McIlroy, W.E.; et al. Reducing fall risk by improving balance control: Development, evaluation and knowledge-translation of new approaches. J. Saf. Res. 2011, 42, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, R.L.; Ruiz, M.C.L. Stabilometry and quality of life in the spinal pain. An analytic transversal study. Fisioterapia 2005, 27, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, J.E.; Carpenter, M.G.; Van der Kooij, H.; Bloem, B.R. The clinical utility of posturography. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 2424–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J. Strobe: Annals of internal medicine academia and clinic the strengthening the reporting of observational studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for reporting. Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, C.; Tomas-Carus, P.; Bravo, J.; Pereira, C.; Mendes, F. Understanding fall risk factors in community-dwelling older adults: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Older People Nurs. 2020, 15, e12294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, D.; Wadhwa, S.; Singh, U.; Yadav, S.L.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Sindhu, V. Age related changes in postural stability. Indian J. Phisiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 51, 395–404. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Amat, A.; Hita-Contreras, F.; Lomas-Vega, R.; Caballero-Martínez, I.; Alvarez, P.J.; Martínez-López, E. Effects of 12-week proprioception training program on postural stability, gait, and balance in older adults: A controlled clinical trial. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 2180–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espejo-Antúnez, L.; Pérez-Mármol, J.M.; Cardero-Durán, M.A.; Toledo-Marhuenda, J.V.; Albornoz-Cabello, M. The Effect of Proprioceptive Exercises on Balance and Physical Function in Institutionalized Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 101, 1780–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourey, F. Los pies y el envejecimiento: Efectos sobre el equilibrio y la deambulación. EMC-Podología 2011, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baydal-Bertomeu, J.M.; Viosca-Herrero, E.; Ortuño-Cortés, M.A.; Quinza-Valero, V.; Garrido-Jaén, D.; Vivas-Broseta, M.J. Estudio de la eficacia y fiabilidad de un sistema de Posturografía en comparación con la escala de Berg. Rehabilitación 2010, 44, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshima, N.; Islam, M.M.; Rogers, M.E.; Koizumi, D.; Tomiyama, N.; Narita, M.; Rogers, N.L. Pattern of age-associated de-cline of static and dynamic balance in community-dwelling older women. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2014, 14, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howcroft, J.; Lemaire, E.D.; Kofman, J.; William, E.; McIlroy, W.E. Elderly fall risk prediction using static posturography. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, A.; Zemp, D.; Zanda, E.; Rocchi, S.; Meroni, F.; Tettamanti, M.; Recchia, A.; Lucca, U.; Quadri, P. Postural stability and history of falls in cognitively able older adults: The Canton Ticino study. Gait Posture 2012, 36, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olchowik, G.; Czwalik, A.; Kowalczyk, B. The Changes in Postural Stability of Women in Early Old Age. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2020, 24, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Borges, A.P.; Oliveira-Carneiro, J.A.; Zaia, J.E.; Oliveira-Carneiro, A.A.; Massaiti-Takayanagui, O. Evaluation of pos-tural balance in mild cognitive impairment through a three-dimensional electromagnetic system. Braz. J. Otorrinolaringol. 2016, 82, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, B.M.; Han, S.J.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, J.E.; Fregni, F.J. Effect of mild cognitive impairment on balance. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 305, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalheiro, G.; Almeida, M.; Pereira, A.; Andrade, A. Study of age-related changes in postural control during quiet standing through linear discriminant analysis. BioMed. Eng. OnLine 2009, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortuño-Cortés, M.A.; Martín-Sanz, E.; Barona-de Guzmán, R. Static posturography versus clinical tests in elderly people with vestibular pathology. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2008, 59, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Sanz, E.; Barona De Guzmán, R.; Comeche-Cerverón, R.; Baydal, J.M. Analysis of the interaction between visual and vestibular influence in postural control. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2004, 55, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ramírez, A.; Lázaro del NogaL, M.; Ribera-Casado, J.M. Valoración de los sistemas de control postural en ancianos con caídas de repetición. Rev. Esp. Geriatr. Gerontol. 2008, 43, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmali, F.; Bermúdez-Rey, M.C.; Clark, T.K.; Wang, W.; Merfeld, D.M. Multivariate Analyses of Balance Test Performance, Vestibular Thresholds, and Age. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domènech-Vadillo, E.; Montes-Jovellar, L.; Rey-Martínez, J.; Pérez-Fernández, N. Normal and vestibular patterns in dynamic posturography in patients with Meniere’s disease. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2010, 61, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibeneme, S.C.; Exanem, C.; Ezuma, A.; LLoanus, I.N.; Lasebikian, N.; Lasebikian, O.; Oboh, O.C. Walking balance is mediated by muscle strength and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women: An observational study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 15, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Mean ± SD | Minimum | Maximum | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 62.84 ± 7.77 | 50 | 78 |
| Weigh | 65.07 ± 9.05 | 40.6 | 78.1 |
| Heigh | 157.94 ± 5.7 | 143 | 168 |
| IMC | 26.08 ± 3.57 | 19.68 | 35.73 |
| ROA | ROC | RGA | RGC | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body sway area (mm2) | 29.81 ± 18.27 | 43.15 ± 28.64 | 48.70 ± 37.57 | 143.07 ± 115.35 | 0.001 |
| AP displacement (mm) | 18.15± 8.39 | 23.30 ± 10.03 | 22.27 ± 7.93 | 38.03 ± 14.89 | 0.001 |
| ML displacement (mm) | 10.06 ± 3.09 | 13.84 ± 6.71 | 15.60 ± 12.45 | 24.56 ± 13.31 | 0.001 |
| ROA | ROC | RGA | RGC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r/rho | p | r/rho | p | rho | p | rho | p | |
| Body sway area | −0.009 | 0.95 | 0.09 | 0.54 | 0.23 | 0.88 | 0.16 | 0.26 |
| AP displacement | −0.09 ** | 0.54 | 0.27 ** | 0.85 | −0.001 | 0.99 | 0.15 | 0.30 |
| ML displacement | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.12 | 0.40 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Escamilla-Martínez, E.; Gómez-Maldonado, A.; Gómez-Martín, B.; Castro-Méndez, A.; Díaz-Mancha, J.A.; Fernández-Seguín, L.M. An Assessment of Balance through Posturography in Healthy about Women: An Observational Study. Sensors 2021, 21, 7684. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227684
Escamilla-Martínez E, Gómez-Maldonado A, Gómez-Martín B, Castro-Méndez A, Díaz-Mancha JA, Fernández-Seguín LM. An Assessment of Balance through Posturography in Healthy about Women: An Observational Study. Sensors. 2021; 21(22):7684. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227684
Chicago/Turabian StyleEscamilla-Martínez, Elena, Ana Gómez-Maldonado, Beatriz Gómez-Martín, Aurora Castro-Méndez, Juan Antonio Díaz-Mancha, and Lourdes María Fernández-Seguín. 2021. "An Assessment of Balance through Posturography in Healthy about Women: An Observational Study" Sensors 21, no. 22: 7684. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227684
APA StyleEscamilla-Martínez, E., Gómez-Maldonado, A., Gómez-Martín, B., Castro-Méndez, A., Díaz-Mancha, J. A., & Fernández-Seguín, L. M. (2021). An Assessment of Balance through Posturography in Healthy about Women: An Observational Study. Sensors, 21(22), 7684. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227684






