Effect of Corneal Tilt on the Determination of Asphericity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
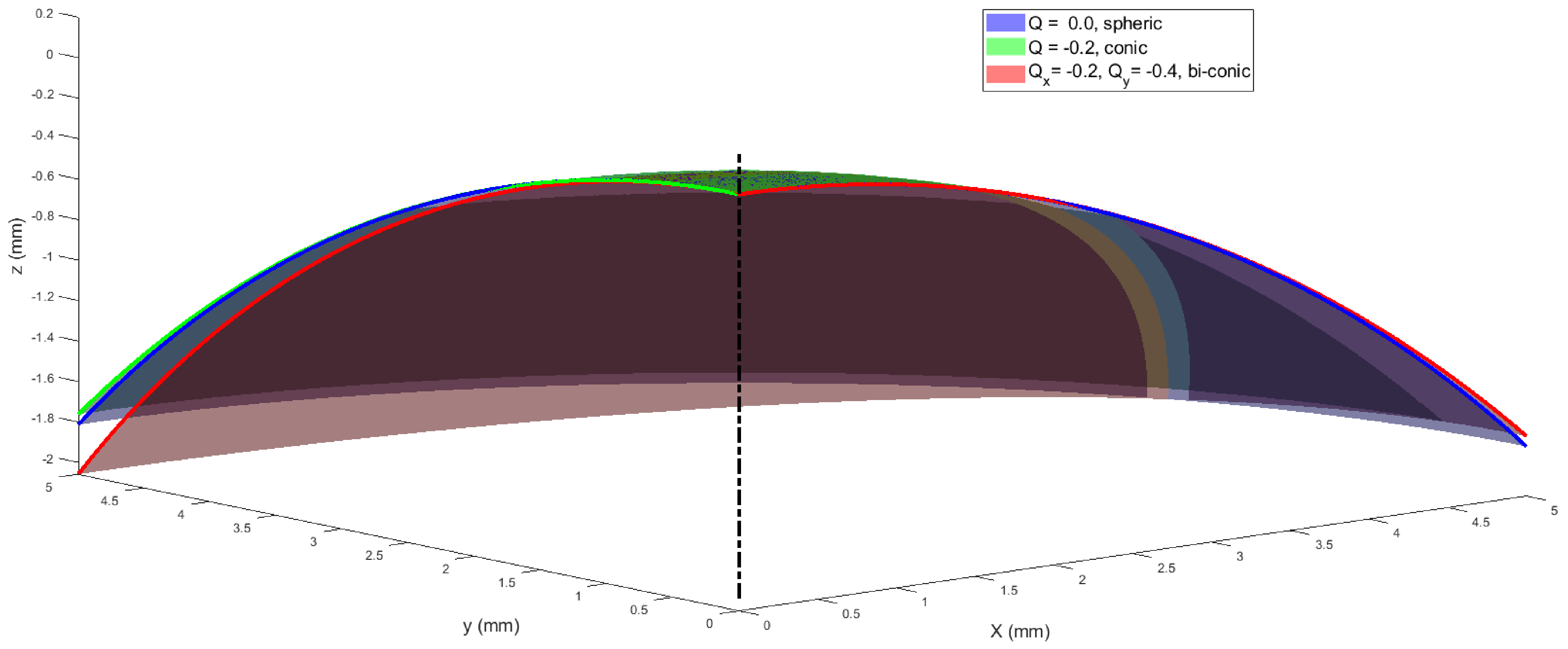
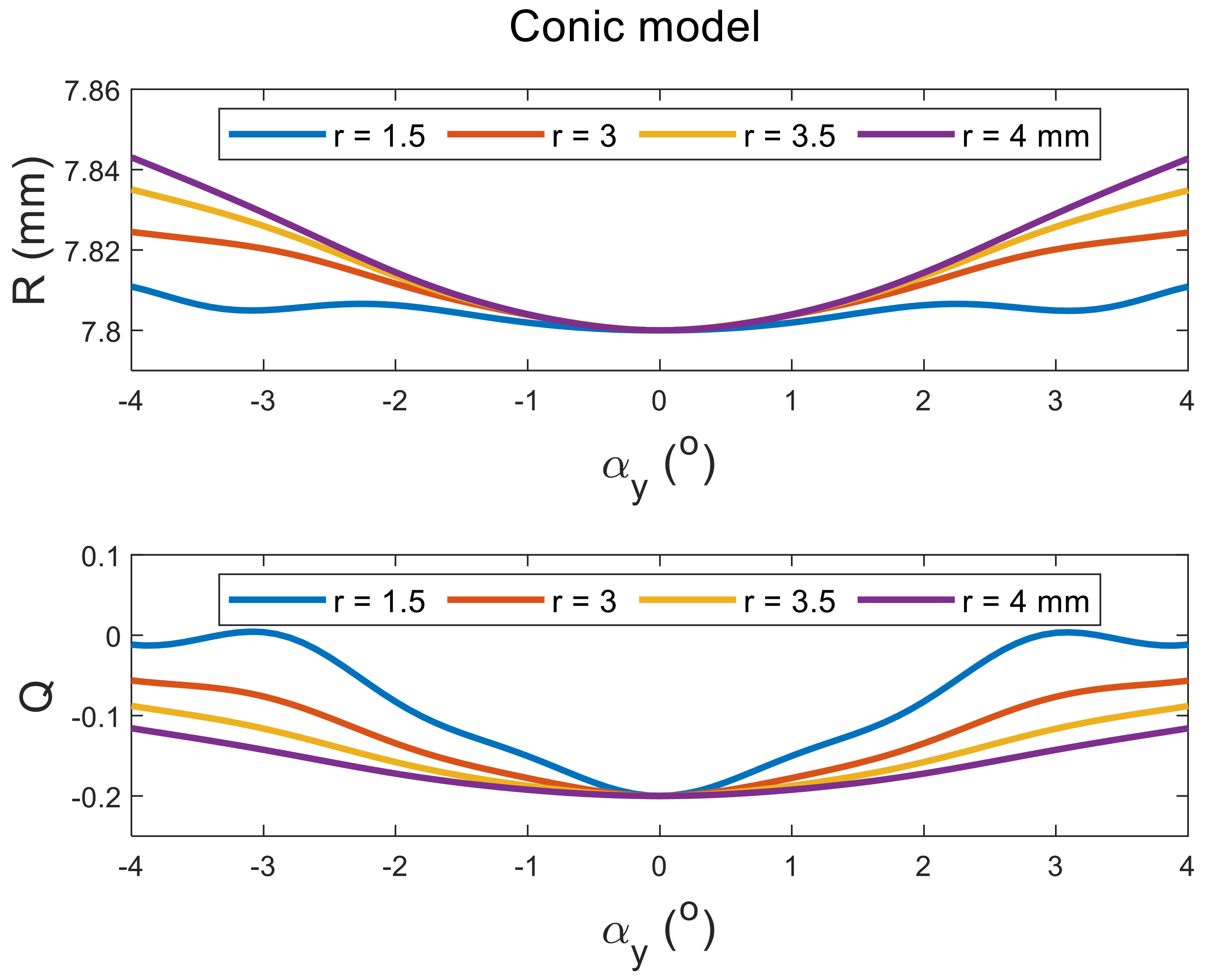
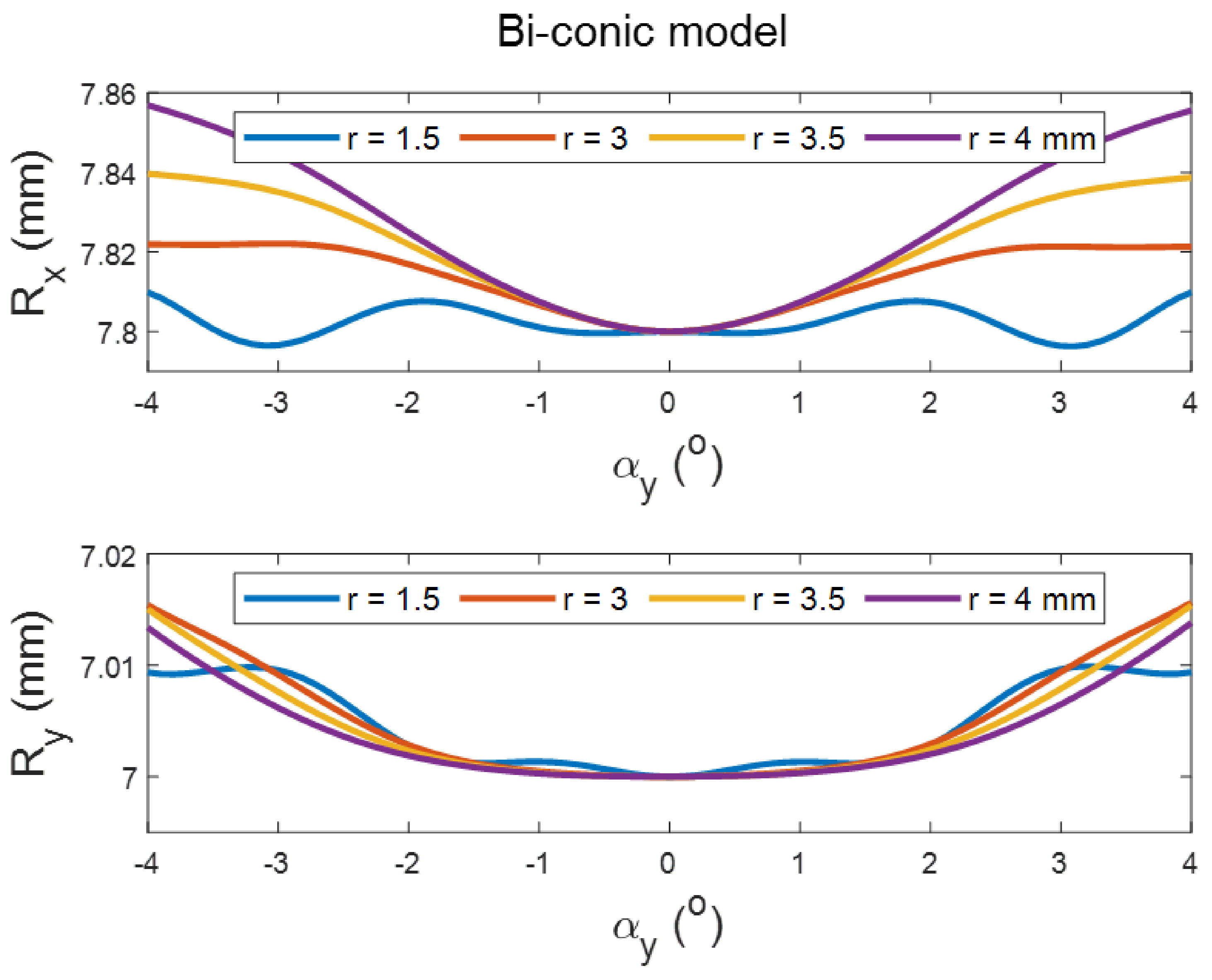
2.1. Mathematical Simulation
2.2. Clinical Data Collection and Processing
2.3. Determination of the Optical Axis from Clinical Data
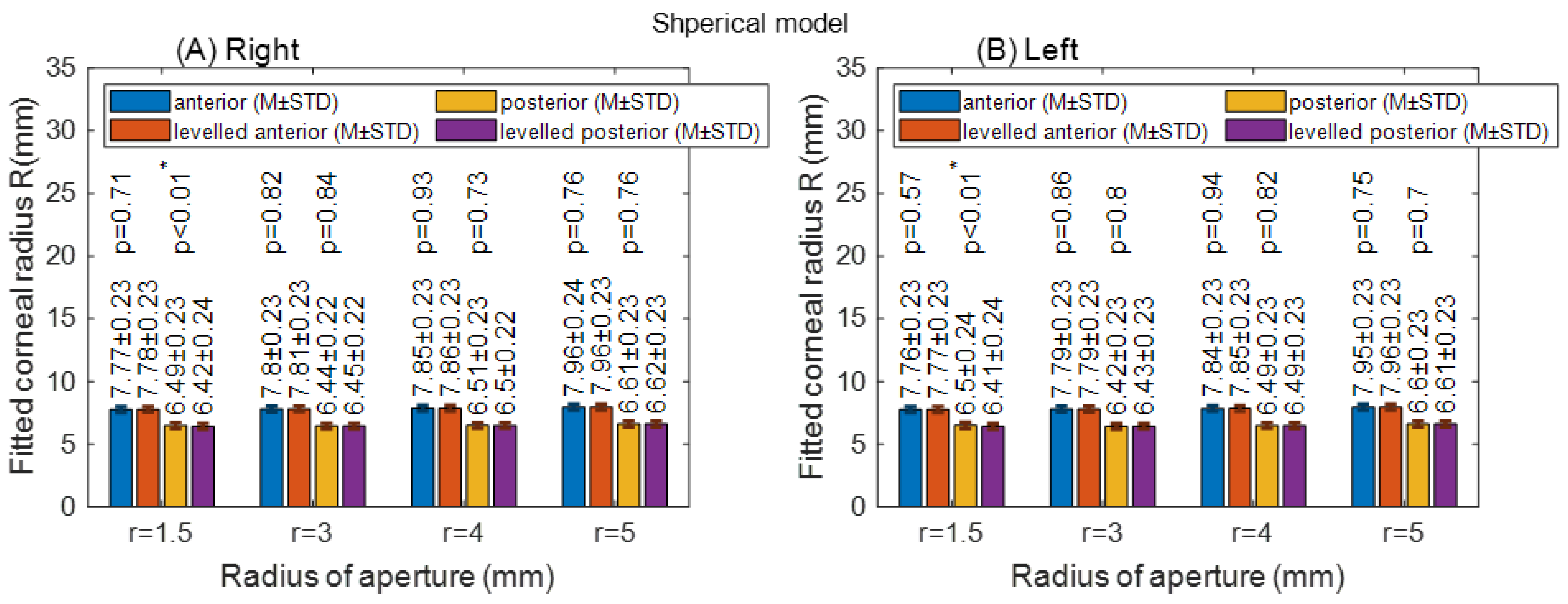
2.4. Fitting the Corneal Surface to Spherical, Conic and Biconic Models
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Simulation-Based Results
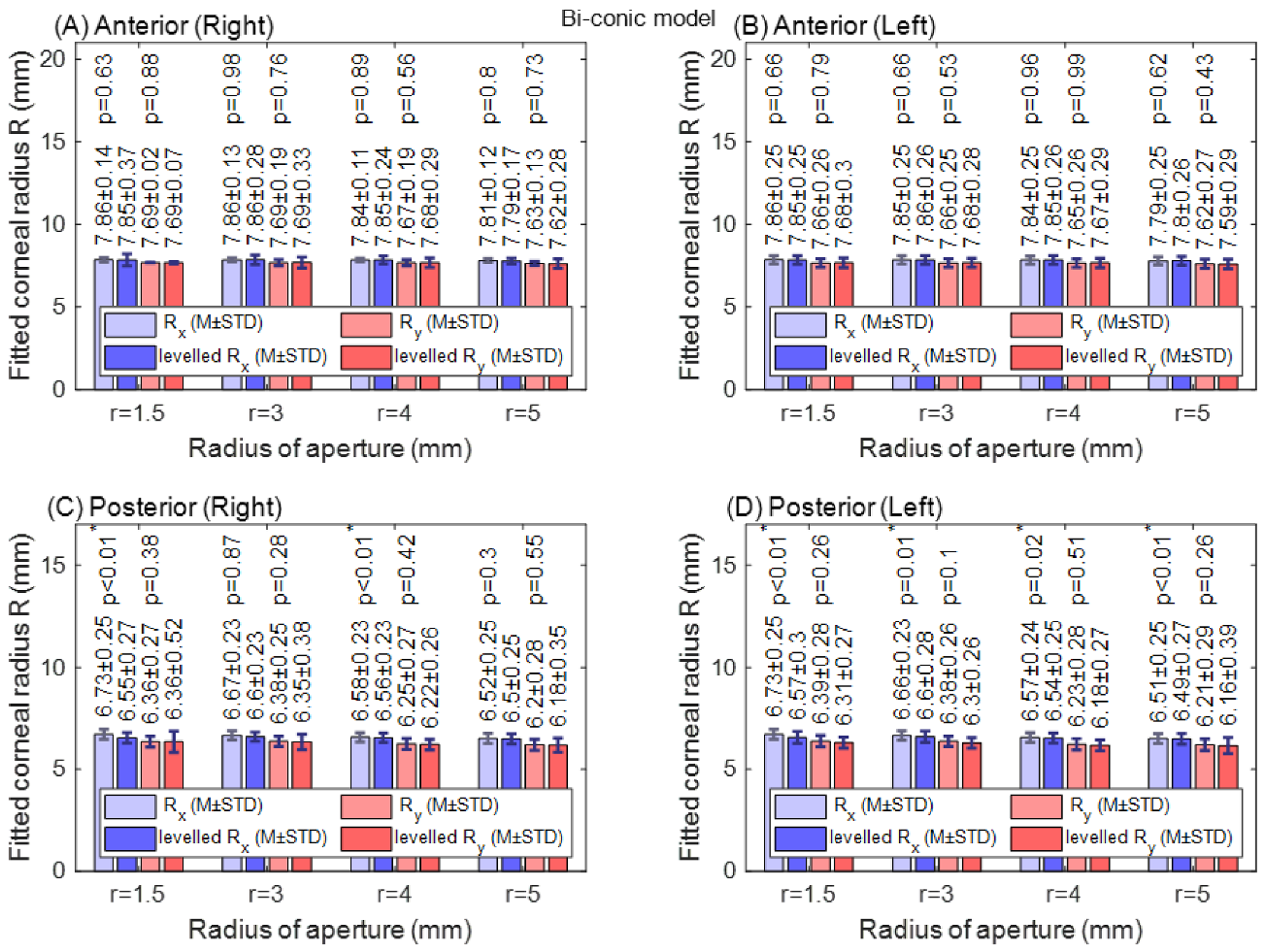
3.2. Clinical-Based Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kolb, H.F.E.; Nelson, R. Facts and Figures Concerning the Human Retina; University of Utah Health Sciences Center: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, H. Handbook of Optical Systems; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- de Castro, A.; Rosales, P.; Marcos, S. Tilt and decentration of intraocular lenses in vivo from Purkinje and Scheimpflug imaging: Validation study. J. Cataract. Refract. Surgery 2007, 33, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, A.; Vinciguerra, R.; Lopes, B.T.; Bao, F.; Vinciguerra, P.; Ambrósio, R.; Elsheikh, A. Positions of Ocular Geometrical and Visual Axes in Brazilian, Chinese and Italian Populations. Curr. Eye Res. 2018, 43, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polpitiya, A.D.; Dayawansa, W.P.; Martin, C.F.; Ghosh, B.K. Geometry and Control of Human Eye Movements. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2007, 52, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davelaar, E.J. Connectionist Models of Neurocognition and Emergent Behavior: From Theory to Applications; World Scientific Publishing Company: Singapore, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- London, A.; Benhar, I.; Schwartz, M. The retina as a window to the brain—From eye research to CNS disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, R. The Optical Design of the Human Eye: A Critical Review. J. Optom. 2009, 2, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, A.; Lopes, B.T.; Eliasy, A.; Salomao, M.; Wu, R.; White, L.; Jones, S.; Clamp, J.; Ambrósio, R., Jr.; Elsheikh, A. Artefact-free topography based scleral-asymmetry. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, A.; McMonnies, C.W.; Whitford, C.; Boneham, G.C. In vivo study of corneal responses to increased intraocular pressure loading. Eye Vis. 2015, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Elsheikh, A. Finite element modeling of corneal biomechanical behavior. J. Refract. Surg 2010, 26, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.A.G. Optics of the Human Eye; Reed Educational and Professional Publishing Ltd.: Edinburgh, UK, 2000; p. 261. [Google Scholar]
- Mutti, D.O.; Mitchell, G.L.; Jones, L.A.; Friedman, N.E.; Frane, S.L.; Lin, W.K.; Moeschberger, M.L.; Zadnik, K. Refractive astigmatism and the toricity of ocular components in human infants. Optom Vis. Sci. 2004, 81, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatinel, D.; Malet, J.; Hoang-Xuan, T.; Azar, D.T. Corneal elevation topography: Best fit sphere, elevation distance, asphericity, toricity, and clinical implications. Cornea 2011, 30, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burek, H.; Douthwaite, W.A. Mathematical models of the general corneal surface. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. J. Br. Coll. Ophthalmic Opt. 1993, 13, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainstone, J.C.; Carney, L.G.; Anderson, C.R.; Clem, P.M.; Stephensen, A.L.; Wilson, M.D. Corneal shape in hyperopia. Clin. Exp. Optom. 1998, 81, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holladay, J.T.; Dudeja, D.R.; Chang, J. Functional vision and corneal changes after laser in situ keratomileusis determined by contrast sensitivity, glare testing, and corneal topography11None of the authors has a financial interest in any device described. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 1999, 25, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douthwaite, W.A.; Hough, T.; Edwards, K.; Notay, H. The EyeSys videokeratoscopic assessment of apical radius and p-value in the normal human cornea. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 1999, 19, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes-Higgin, D.K.; Baker, P.C.; Burris, T.E.; Silvestrini, T.A. Characterization of the Aspheric Corneal Surface With Intrastromal Corneal Ring Segments. J. Refract. Surg. 1999, 15, 520–528. [Google Scholar]
- Budak, K.; Khater, T.T.; Friedman, N.J.; Holladay, J.T.; Koch, D.D. Evaluation of relationships among refractive and topographic parameters11Myrna Kahn, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, provided statistical consultation. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 1999, 25, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubbelman, M.; Weeber, H.A.; Van Der Heijde, R.G.; Völker-Dieben, H.J. Radius and asphericity of the posterior corneal surface determined by corrected Scheimpflug photography. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 2002, 80, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, J.R.J.; Anera, R.G.; Jimnez, R.; Salas, C. Impact of interocular differences in corneal asphericity on binocular summation. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 135, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manns, F.; Fernandez, V.; Zipper, S.; Sandadi, S.; Hamaoui, M.; Ho, A.; Parel, J.-M. Radius of curvature and asphericity of the anterior and posterior surface of human cadaver crystalline lenses. Exp. Eye Res. 2004, 78, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somani, S.; Tuan, K.A.; Chernyak, D. Corneal asphericity and retinal image quality: A case study and simulations. J. Refract. Surg. 2004, 20, S581–S585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorente, L.; Barbero, S.; Cano, D.; Dorronsoro, C.; Marcos, S. Myopic versus hyperopic eyes: Axial length, corneal shape and optical aberrations. J. Vis. 2004, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, W.R.; Raasch, T.W.; Mitchell, G.L.; Mutti, D.O.; Zadnik, K. Corneal Asphericity and Apical Curvature in Children: A Cross-sectional and Longitudinal Evaluation. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubbelman, M.; Sicam, V.A.D.P.; Van der Heijde, G.L. The shape of the anterior and posterior surface of the aging human cornea. Vis. Res. 2006, 46, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Méijome, J.M.; Villa-Collar, C.; Montés-Micó, R.; Gomes, A. Asphericity of the anterior human cornea with different corneal diameters. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2007, 33, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto-Bona, A.; Lorente-Velázquez, A.; Mòntes-Micó, R. Relationship between anterior corneal asphericity and refractive variables. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2009, 247, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñero, D.P.; Alió, J.L.; Alesón, A.; Vergara, M.E.; Miranda, M. Corneal volume, pachymetry, and correlation of anterior and posterior corneal shape in subclinical and different stages of clinical keratoconus. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2010, 36, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottos, K.M.; Leite, M.T.; Aventura-Isidro, M.; Bernabe-Ko, J.; Wongpitoonpiya, N.; Ong-Camara, N.H.; Purcell, T.L.; Schanzlin, D.J. Corneal asphericity and spherical aberration after refractive surgery. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2011, 37, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Niu, W.; Ma, M.; Jiang, K.; Zhu, P.; Ke, B. Corneal asphericity and its related factors in 1052 Chinese subjects. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2011, 88, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, F.; Chen, H.; Yu, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Elsheikh, A. Evaluation of the shape symmetry of bilateral normal corneas in a Chinese population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, R.; Rozema, J.J.; Tassignon, M.J. Optical changes of the human cornea as a function of age. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2013, 90, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKendrick, A.M.; Brennan, N.A. Distribution of astigmatism in the adult population. J. Opt. Soc. America. A Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 1996, 13, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, J.; Wang, B.; Shi, M. Anterior corneal asphericity calculated by the tangential radius of curvature. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 075005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, B.T.; Eliasy, A.; Elhalwagy, M.; Vinciguerra, R.; Bao, F.; Vinciguerra, P.; Ambrósio, R.; Elsheikh, A.; Abass, A. Determination of Optic Axes by Corneal Topography among Italian, Brazilian, and Chinese Populations. Photonics 2021, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyamu, E.; Iyamu, J.; Obiakor, C.I. The role of axial length-corneal radius of curvature ratio in refractive state categorization in a nigerian population. ISRN Ophthalmol. 2011, 2011, 138941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, A.; Lopes, B.T.; Eliasy, A.; Wu, R.; Jones, S.; Clamp, J.; Ambrósio, R., Jr.; Elsheikh, A. Three-dimensional non-parametric method for limbus detection. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvo, J. Fast random rotation matrices. In Graphics Gems III.; David, K., Ed.; Academic Press Professional, Inc.: Burlington, MA, USA, 1992; pp. 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Schwiegerling, J.T. Eye axes and their relevance to alignment of corneal refractive procedures. J. Refract. Surg 2013, 29, 515–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, G.; Atchison, D.A. The Eye and Visual Optical Instruments; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Vojnikovi, B.O.; Tamajo, E. Gullstrand’s Optical Schematic System of the Eye Modified by Vojnikovi & Tamajo. Coll. Antropol. 2013, 37, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Anderson, B.L.; Koch, D.D.; Roberts, C.J. Total corneal power estimation: Ray tracing method versus gaussian optics formula. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 1716–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welford, W.T. Aberrations of Optical Systems; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Arba Mosquera, S.; Verma, S.; McAlinden, C. Centration axis in refractive surgery. Eye Vis. 2015, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyon, F.; Riche, R.L. Least Squares Parameter Estimation and the Levenberg-Marquardt Algorithm: Deterministic Analysis, Sensitivities and Numerical Experiments; INSA de Rouen: Rouen, France, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- BjÓrck, A. Numerical Methods for Least Squares Problems; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996; Volume 51, p. 408. [Google Scholar]
- Massey, F.J. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test for Goodness of Fit. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1951, 46, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.H. Table of Percentage Points of Kolmogorov Statistics. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1956, 51, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsaglia, G.; Tsang, W.W.; Wang, J. Evaluating Kolmogorov’s Distribution. J. Stat. Softw. 2003, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, D.G.; Soni, P.S.; Vyas, N.; Himebaugh, N.L. Longitudinal Changes in Corneal Asphericity in Myopia. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2000, 77, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatinel, D.; Hoang-Xuan, T.; Azar, D.T. Determination of Corneal Asphericity after Myopia Surgery with the Excimer Laser: A Mathematical Model. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 1736–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan, M.; Douthwaite, W. Corneal asphericity and refractive error. Ophthal. Physiol. Opt. 1989, 9, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, J.R.; Anera, R.G.; Barco, L.J.d. Equation for Corneal Asphericity After Corneal Refractive Surgery. J. Refract. Surg. 2003, 19, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calossi, A. Corneal Asphericity and Spherical Aberration. J. Refract. Surg. 2007, 23, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anera, R.G.; Jiménez, J.R.; Jiménez del Barco, L.; Bermúdez, J.; Hita, E. Changes in corneal asphericity after laser in situ keratomileusis. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2003, 29, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holladay, J.T.; Janes, J.A. Topographic changes in corneal asphericity and effective optical zone after laser in situ keratomileusis. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2002, 28, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, N.; Klyce, S.D.; Hamano, H. Alteration of corneal asphericity in rigid gas permeable contact lens induced warpage. CLAO J. Off. Publ. Contact Lens Assoc. Ophthalmol. Inc. 1994, 20, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, D.G.; Alperin, D. Variations in Corneal Asphericity (Q Value) between African-Americans and Whites. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2013, 90, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbali, F.; Yeung, K.K.; Maloney, R.K. Topographic Determination of Corneal Asphericity and Its Lack of Effect on the Refractive Outcome of Radial Keratotomy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1995, 119, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wa, D. Application of linear regression to videokeratoscope data for tilted surfaces. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2002, 22, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Douthwaite, W.A. The asphericity, curvature and tilt of the human cornea measured using a videokeratoscope human cornea measured using a videokeratoscope. Ophthal. Physiol. Opt. 2003, 23, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, G. Wavefront Optics for Vision Correction; Dai, G.-M., Ed.; Society of Photo Optical: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chaurasia, B.D.; Mathur, B.B. Eyedness. Acta Anat 1976, 96, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, M.R. Ocular dominance: Some family data. Laterality 1997, 2, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenstein, W.H.; Arnold-Schulz-Gahmen, B.E.; Jaschinski, W. Eye preference within the context of binocular functions. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2005, 243, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eser, I.; Durrie, D.S.; Stahl, J.E. Association between ocular dominance and refraction. J. Refract. Surg. 2008, 24, 685–689. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, A.; Sapru, H.N. Essential Neuroscience; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, E. Advances and Challenges in Multisensor Data and Information Processing; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; p. 401. [Google Scholar]
- Barro, S.; Marin, R. Fuzzy Logic In Medicine; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.; Marshall, J.; Fitzke, F.W. Shape and radius of posterior corneal surface. Refract. Corneal Surg. 1993, 9, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickson-Curran, S.; Brennan, N.A.; Igarashi, Y.; Young, G. Comparative evaluation of Asian and white ocular topography. Optom Vis. Sci 2014, 91, 1396–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickson-Curran, S.; Young, G.; Brennan, N.; Hunt, C. Chinese and Caucasian ocular topography and soft contact lens fit. Clin. Exp. Optom 2016, 99, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, D.D.; Jenkins, R.B.; Weikert, M.P.; Yeu, E.; Wang, L. Correcting astigmatism with toric intraocular lenses: Effect of posterior corneal astigmatism. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2013, 39, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preussner, P.R.; Hoffmann, P.; Wahl, J. Impact of Posterior Corneal Surface on Toric Intraocular Lens (IOL) Calculation. Curr Eye Res. 2015, 40, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAlinden, C.; Khadka, J.; Pesudovs, K. A Comprehensive Evaluation of the Precision (Repeatability and Reproducibility) of the Oculus Pentacam HR. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 7731–7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Consejo, A.; Fathy, A.; Lopes, B.T.; Ambrósio, R., Jr.; Abass, A. Effect of Corneal Tilt on the Determination of Asphericity. Sensors 2021, 21, 7636. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227636
Consejo A, Fathy A, Lopes BT, Ambrósio R Jr., Abass A. Effect of Corneal Tilt on the Determination of Asphericity. Sensors. 2021; 21(22):7636. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227636
Chicago/Turabian StyleConsejo, Alejandra, Arwa Fathy, Bernardo T. Lopes, Renato Ambrósio, Jr., and Ahmed Abass. 2021. "Effect of Corneal Tilt on the Determination of Asphericity" Sensors 21, no. 22: 7636. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227636
APA StyleConsejo, A., Fathy, A., Lopes, B. T., Ambrósio, R., Jr., & Abass, A. (2021). Effect of Corneal Tilt on the Determination of Asphericity. Sensors, 21(22), 7636. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227636






