Investigation of Advanced Robotized Polymer Sheet Incremental Forming Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Numerical Investigation of Polymer Sheet Forming Parameters
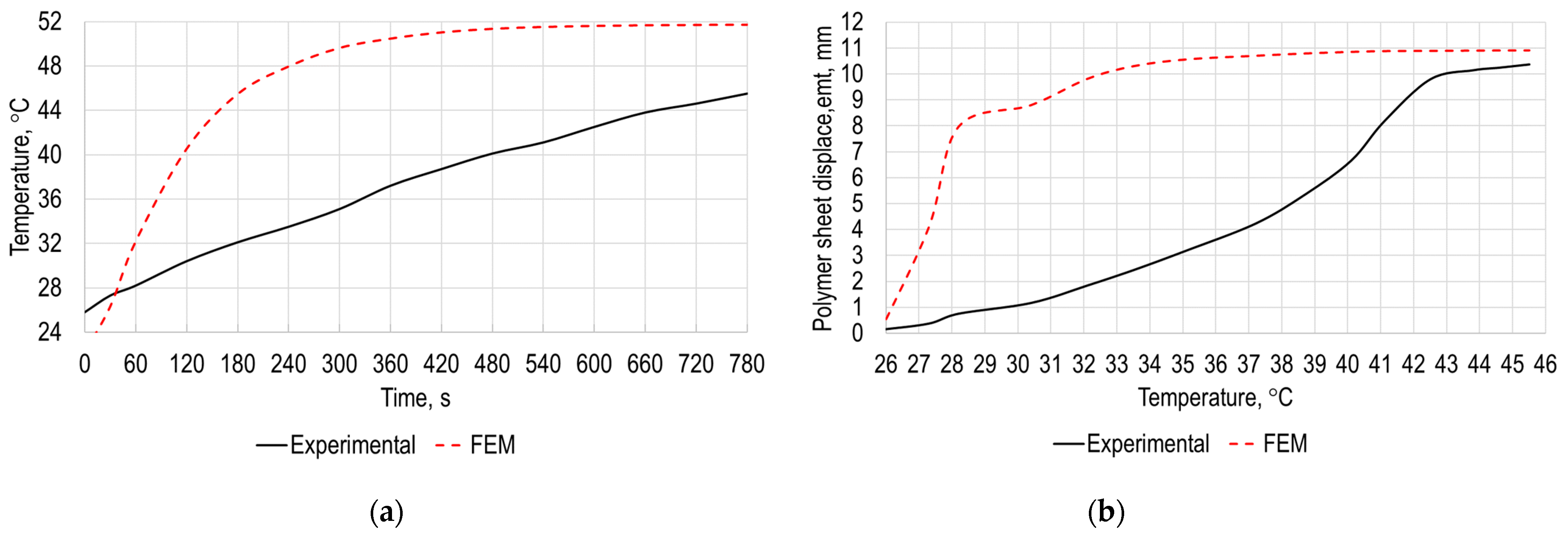
3. Validation of Numerical Simulation Results
4. Investigation of the Polymer Sheet Advanced Heating Device
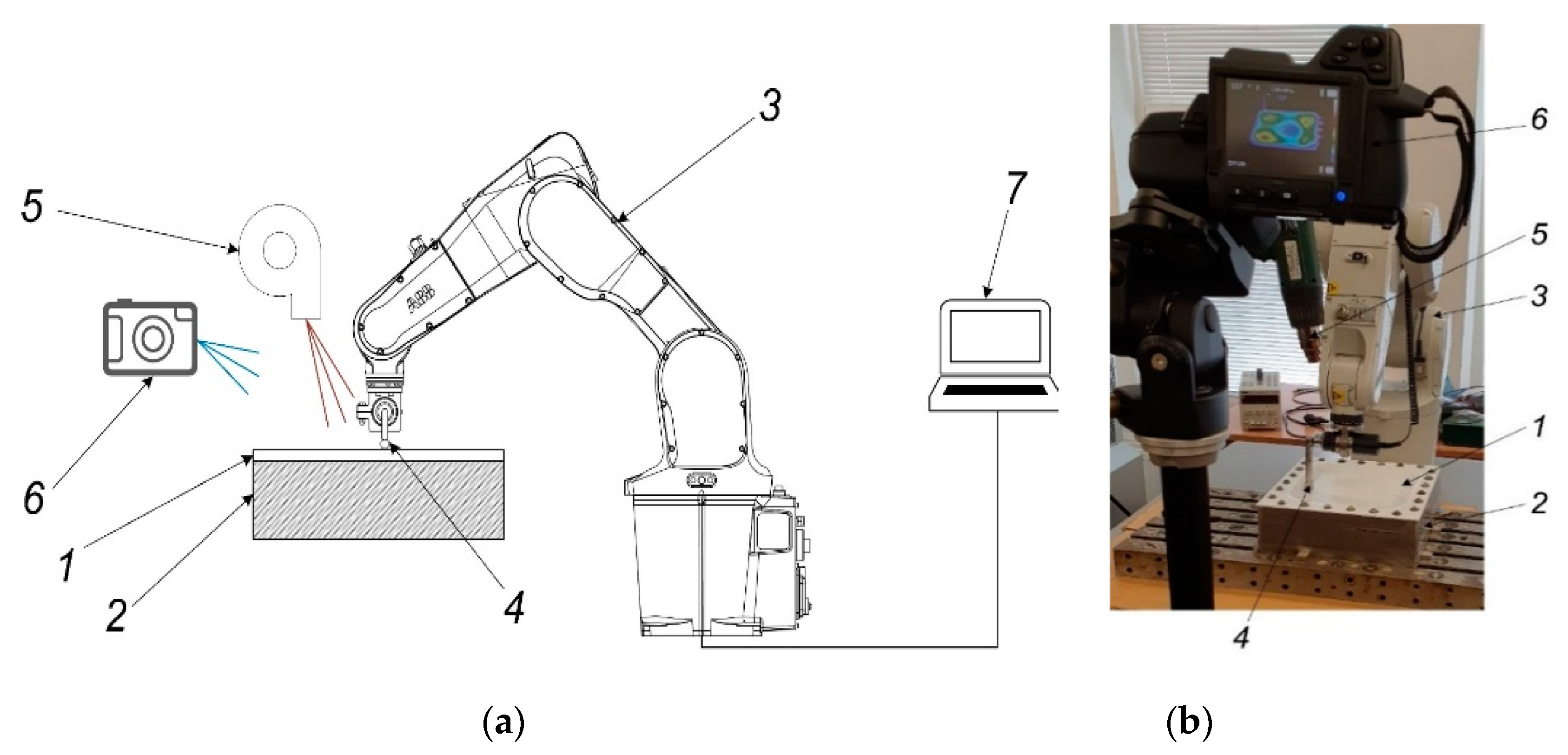
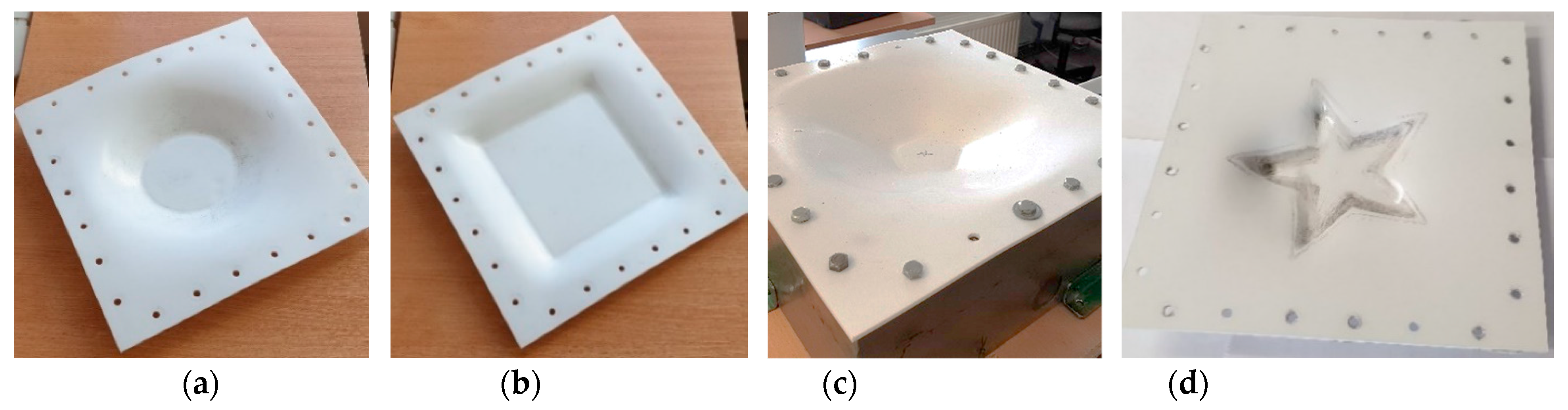
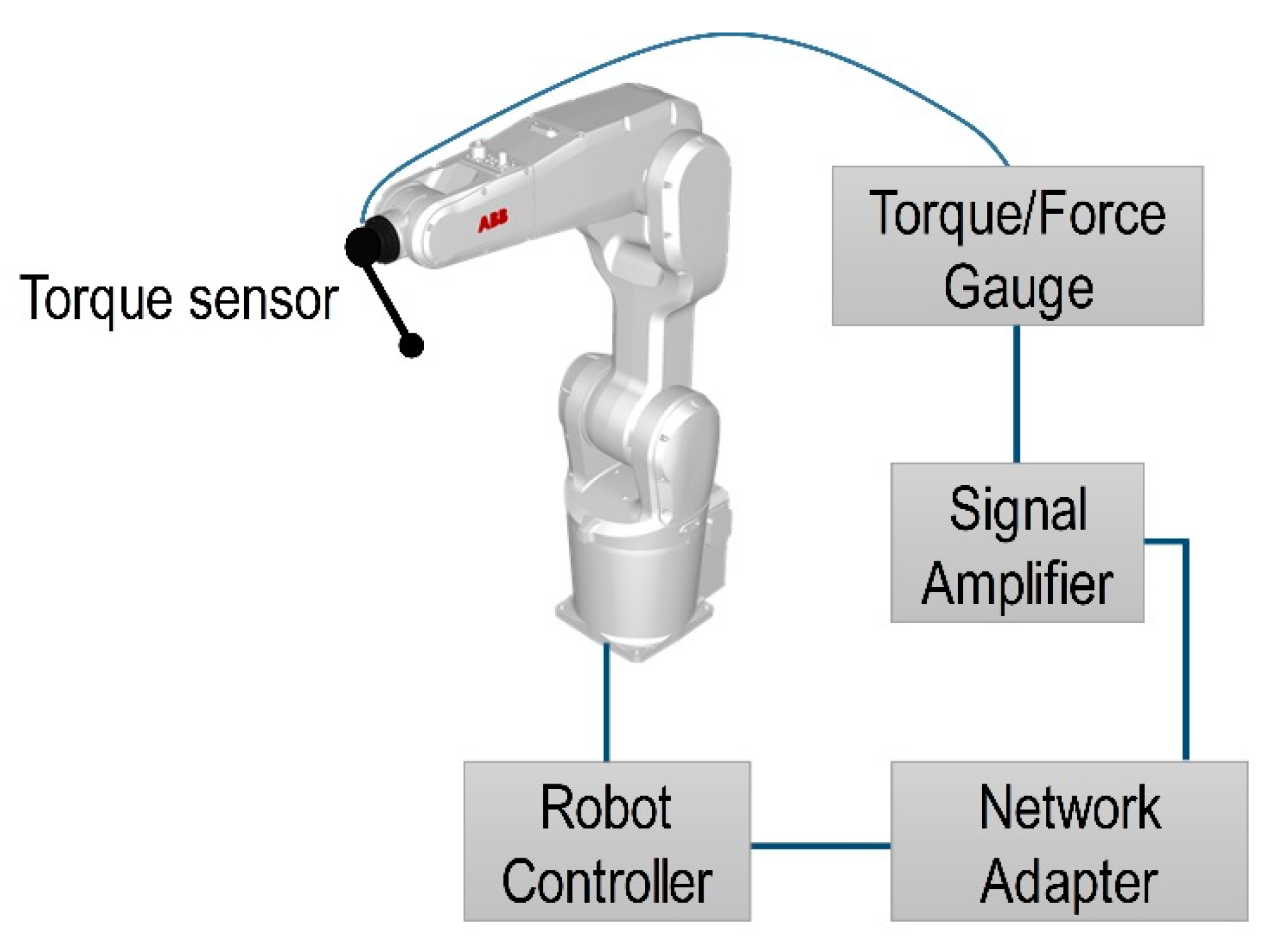
5. Experimental Investigation of Polymer Sheet SPIF Parameters
6. Polymer Sheet Robotized SPIF Tests with Different Tools
- Forming tool with Ø17 mm freely rotating sphere.
- Forming tool with Ø10 mm rotating sphere, supported by a ring-shaped magnetic holder.
- Forming tool with Ø10 mm rotating sphere, supported by a ring-shaped magnetic holder and heated to 46 °C.
7. Conclusions
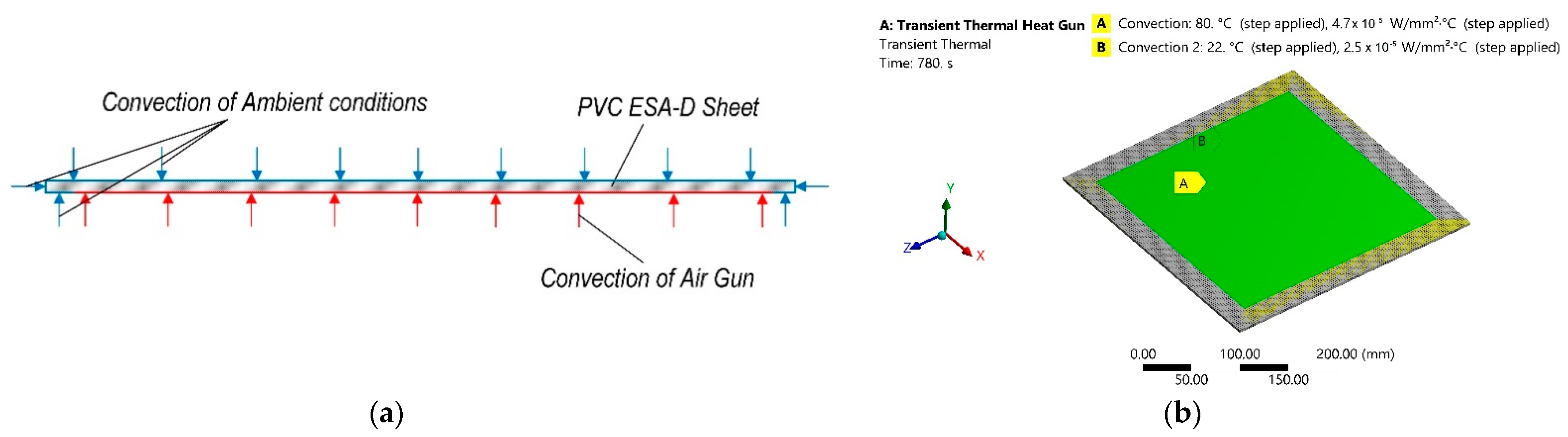
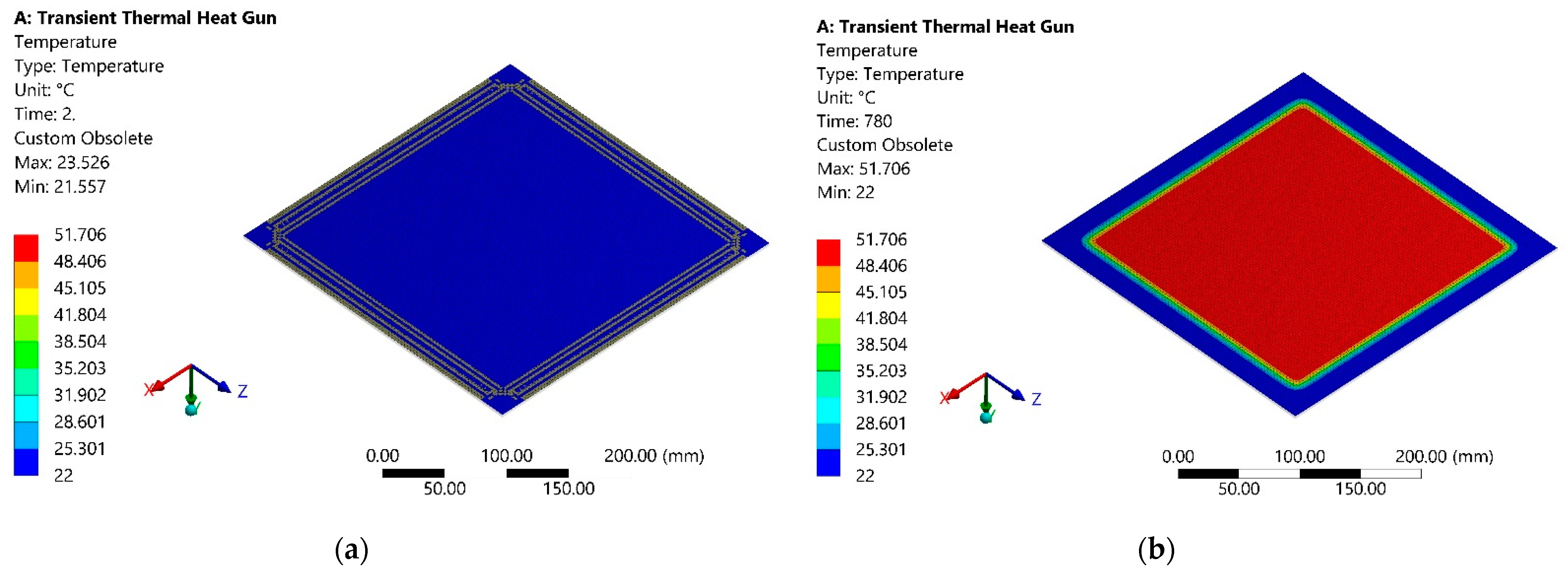
- The numerical study of the polymer sheet heating parameters was conducted by blowing it with a stream of hot air, performed using the ANSYS transient thermal and transient structural analysis, which revealed the temperature dependency from heating time and thus deformation time.
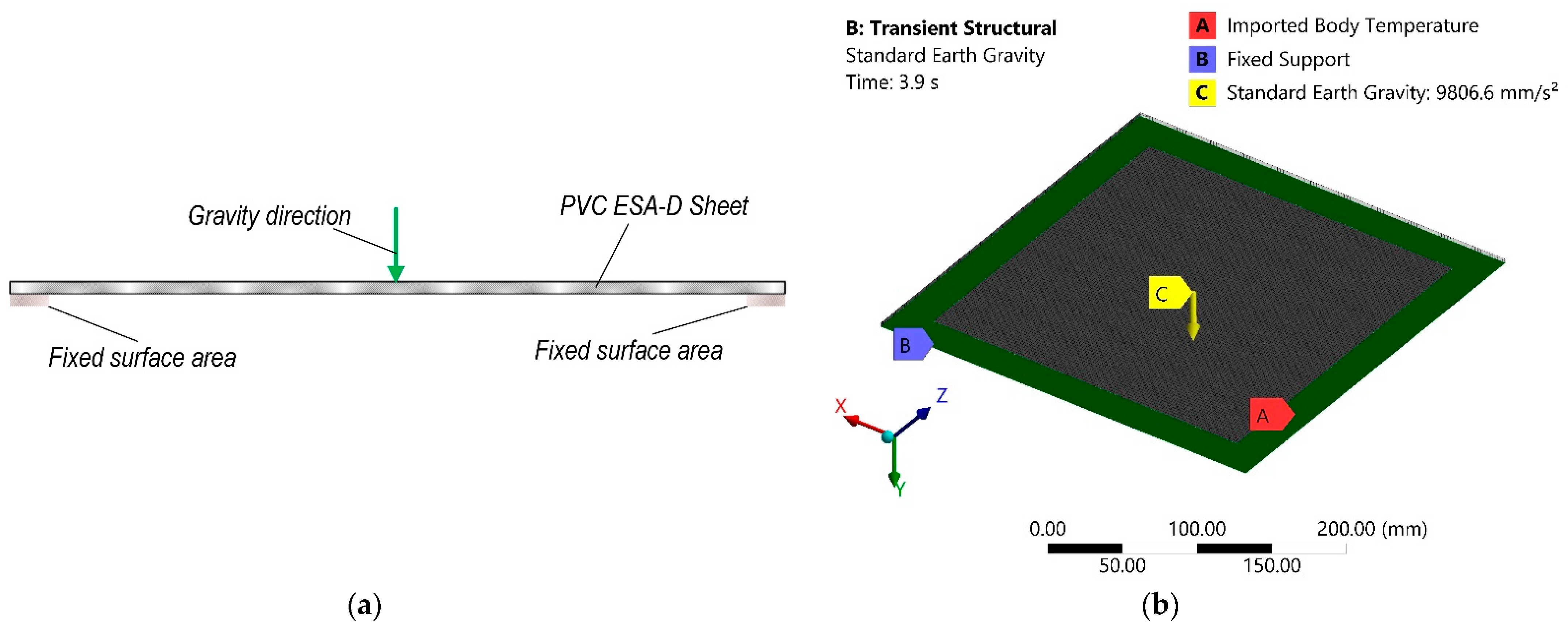
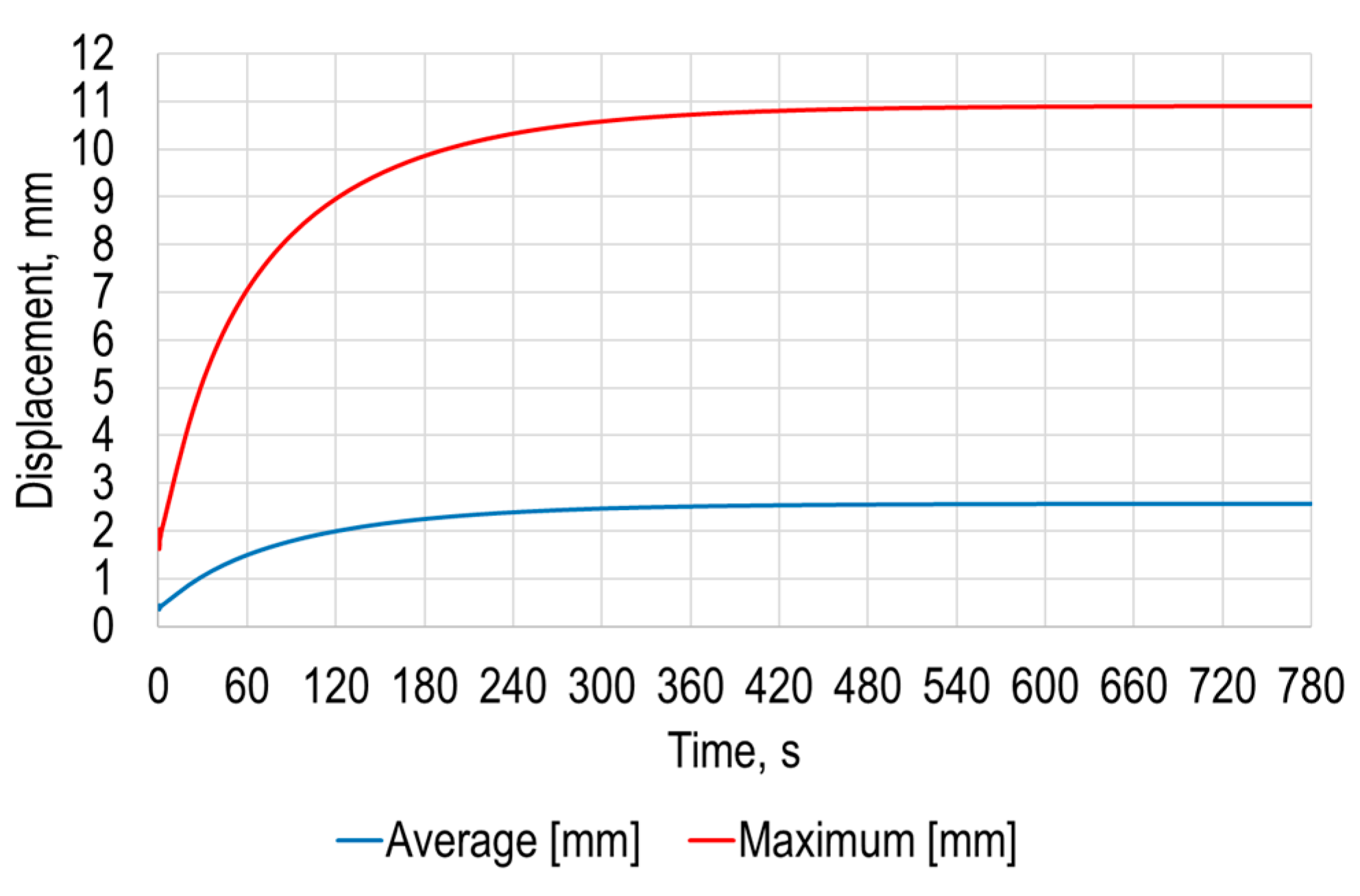
- The results showed that average temperature of the opposite to the heating surface is equal to 42.4 °C after 780 s from the start of heating and that the maximum is equal to 51.7 °C at the same instance. The maximum deformation of the polymer sheet from standard earth gravity exceeds 10.9 mm, while the average deformation of the sheet was 2.6 mm.
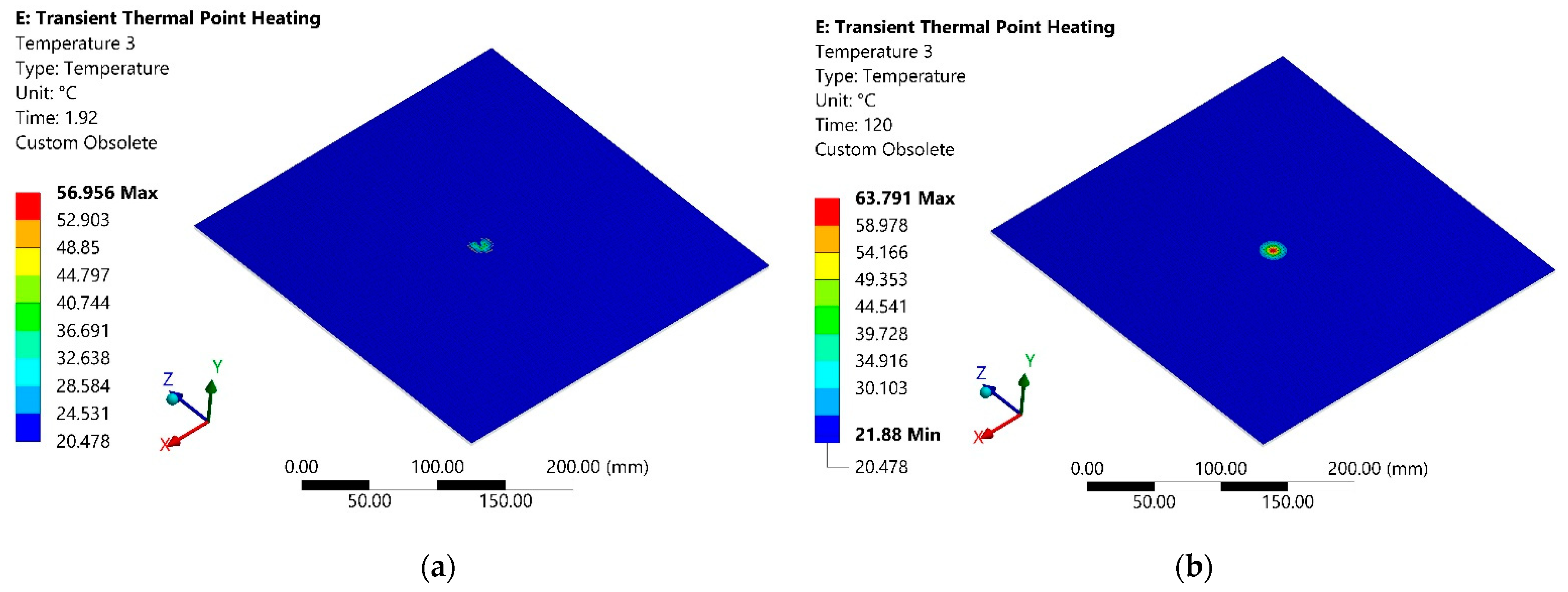
- An innovative solution was proposed to heat the polymer sheet at the point of contact with the forming tool using laser beam energy.
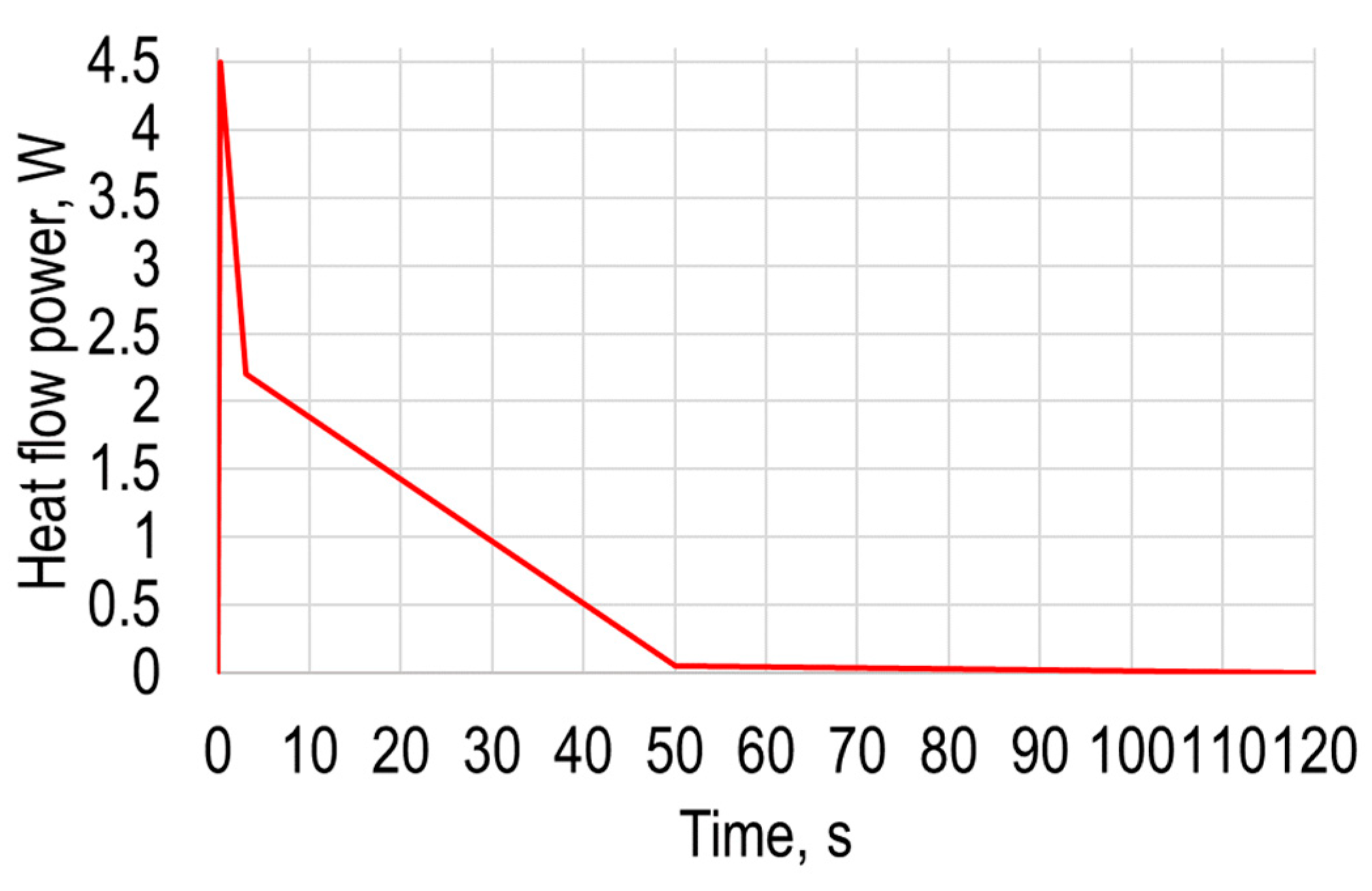
- The numerical simulation results of the point-heated device showed that the heating time to maximum temperature of 57.9 °C was 1.86 s. The maximum deformation from gravity and temperature did not exceed 1.9 mm, with an average of 0.42 mm during the 120 s time interval.
- The experimental studies of the robotized polymer sheet SPIF have shown that in the case of the proposed point heating method the forming force decreases, the heating time of the sheet decreases, and the forming process takes place without supporting the polymer sheet by backing plate.
8. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, H.; Ou, H.; Popov, A. Incremental sheet forming of thermoplastics: A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 111, 565–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzen, V.; Kwiatkowski, L.; Martins, P.A.F.; Tekkaya, A.E. Single point incremental forming of PVC. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.A.F.; Kwiatkowski, L.; Franzen, V.; Tekkaya, A.E.; Kleiner, M. Single point incremental forming of polymers. CIRP Ann. 2009, 58, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.Q. Study on process parameters on single point incremental forming of PVC. Mater. Sci. Forum 2017, 878, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, F.; Bambach, M. Revealing the Dominant Forming Mechanism of Single Point Incremental Forming (SPIF) by Splitting Plastic Energy Dissipation. Procedia Eng. 2017, 183, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Sanchez, G.; Garcia-Collado, A.; Carou, D.; Dorado-Vicente, R. Force prediction for incremental forming of polymer sheets. Materials 2018, 11, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le, V.S.; Ghiotti, A.; Lucchetta, G. Preliminary studies on single point incremental forming for thermoplastic materials. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2008, 1, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarpanah, M.A.; Malhotra, R. Effect of incremental depth and part shape on failure modes in single point incremental forming of polymers. In ASME 2015 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference; American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection: Charlotte, NC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Davarpanah, M.A.; Mirkouei, A.; Yu, X.; Malhotra, R.; Pilla, S. Effects of incremental depth and tool rotation on failure modes and microstructural properties in Single Point Incremental Forming of polymers. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 222, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Sánchez, L.M.; Bagudanch, I.; Sustaita, A.O.; Iturbe-Ek, J.; Elizalde, L.E.; Garcia-Romeu, M.L.; Elías-Zúñiga, A. Single-Point Incremental Forming of Two Biocompatible Polymers: An insight into their thermal and structural properties. Polymers 2018, 10, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bagudanch, I.; Lozano-Sanchez, L.M.; Puigpinos, L.; Sabater, M.; Elizalde, L.E.; Elias-Zuniga, A.; Garcia-Romeu, M.L. Manufacturing of biocompatible cranial geometry by single point incremental forming. Procedia Eng. 2015, 132, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabater, M.; Garcia-Romeu, M.L.; Vives-Mestres, M.; Ferrer, I.; Bagudanch, I. Process parameter effects on biocompatible thermoplastic sheets produced by incremental forming. Materials 2018, 11, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conte, R.; Ambrogio, G.; Pulice, D.; Gagliardi, F.; Filice, L. Incremental sheet forming of a composite made of thermoplastic matrix and glass-fiber reinforcement. Procedia Eng. 2017, 207, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, A.O.; Kunke, A.; Kräusel, V. Hot single-point incremental forming of glass-fiber-reinforced polymer (PA6GF47) supported by hot air. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 43, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano-Sánchez, L.M.; Sustaita, A.O.; Soto, M.; Biradar, S.; Ge, L.; Segura-Cardenas, E.; Diabb, J.; Elizade, L.E.; Barrera, E.V.; Elías-Zúñiga, A. Mechanical and structural studies on single point incremental forming of polypropylene-MWCNTs composite sheets. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 242, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarpanah, M.A.; Malhotra, R. Formability and failure modes in Single Point Incremental Forming of Metal-Polymer Laminates. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 26, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Sreedhara, V.S.M.; Mocko, G. Heat Assisted Single Point Forming of Polymer Sheets. In Proceedings of the ASME 2016 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Charlotte, NC, USA, 21–24 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rochling Industrial Materials. Available online: https://www.roechling.com/industrial/materials/thermoplastics/detail/trovidur-esa-d-261 (accessed on 7 October 2021).
- Ostasevicius, V.; Jurenas, V.; Bubulis, A.; Eidukynas, D.; Paulauskaite-Taraseviciene, A.; Paleviciute, I. Sheet Parts Incremental Forming Device. Patent Application No. LT2021 549, 8 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Littmann, W.; Storck, H.; Wallaschek, J. Reduction of friction using piezoelectrically excited ultrasonic vibrations. In Smart Structures and Materials 2001: Damping and Isolation; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2001; Volume 4331, pp. 302–311. [Google Scholar]
- Ostasevicius, V.; Jurenas, V.; Eidukynas, D.; Bubulis, A.; Paleviciute, I. Incremental Forming Machine for Sheet Plastic Parts. Patent Application No. LT2020 528, 16 June 2020. [Google Scholar]











| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length × width of the sheet | 300 × 300 | mm |
| Thickness of the sheet | 3 | mm |
| Density | 1.41 | g/cm3 |
| Tensile stress at yield | 47.75 | N/mm2 |
| Elongation at break | 30.3 | % |
| Modulus of elasticity in tension | 2643 | N/mm2 |
| Notched Impact strength | 9.09 | mJ/mm2 |
| Compressive strength | 65.4 | MPa |
| Vicat-softening temperature | 75.0 | °C |
| Coefficient of linear thermal expansion | 70 | 10−6/K |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mesh elements method | Hex Dominant | - |
| Number of finite elements | 3600 | - |
| Number of nodal points | 25,803 | - |
| Convection film coefficient of the heat gun surface area | 47 | W/m2 |
| Convection temperature of the heat gun surface area | 80 | °C |
| Convection film coefficient of the rest ambient surface area | 25 | W/m2 |
| Convection temperature of the rest ambient surface area | 22 | °C |
| Total time of calculation | 780 | s |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mesh elements method | Hex Dominant | - |
| Number of finite elements | 3600 | - |
| Number of nodal points | 25,803 | - |
| Input load | Temperature | °C |
| Acceleration of gravity | 9806.6 | mm/s2 |
| Total time of calculation | 780 | s |
| Time, s | Heat Flow Power, W |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 0.18 | 4.5 |
| 3 | 2.2 |
| 50 | 0.05 |
| 120 | 0 |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Mesh elements method | Hex Dominant | - |
| Number of finite elements | 15,124 | - |
| Number of nodal points | 103,231 | - |
| Heat flow application geometry | Ø10 mm circle | - |
| Heat flow magnitude | Tabular (see Table 4) | W |
| Convection film coefficient of the rest ambient surface area | 25 | W/m2 |
| Convection temperature of the rest ambient surface area | 22 | °C |
| Total time of calculation | 120 | s |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Radius of the forming tool sphere | 8.5 | mm |
| Step down | 0.5 | mm |
| Radial step | 0.5 | mm |
| Total forming depth | 30 | mm |
| Feed rate | 100 | mm/s |
| Major diameter of the geometric figure | 150 | mm |
| Minor diameter of the geometric figure | 90 | mm |
| Minimum temperature of the surface | 40 | °C |
| Maximum temperature of the surface | 60 | °C |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ostasevicius, V.; Eidukynas, D.; Jurenas, V.; Paleviciute, I.; Gudauskis, M.; Grigaliunas, V. Investigation of Advanced Robotized Polymer Sheet Incremental Forming Process. Sensors 2021, 21, 7459. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227459
Ostasevicius V, Eidukynas D, Jurenas V, Paleviciute I, Gudauskis M, Grigaliunas V. Investigation of Advanced Robotized Polymer Sheet Incremental Forming Process. Sensors. 2021; 21(22):7459. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227459
Chicago/Turabian StyleOstasevicius, Vytautas, Darius Eidukynas, Vytautas Jurenas, Ieva Paleviciute, Marius Gudauskis, and Valdas Grigaliunas. 2021. "Investigation of Advanced Robotized Polymer Sheet Incremental Forming Process" Sensors 21, no. 22: 7459. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227459
APA StyleOstasevicius, V., Eidukynas, D., Jurenas, V., Paleviciute, I., Gudauskis, M., & Grigaliunas, V. (2021). Investigation of Advanced Robotized Polymer Sheet Incremental Forming Process. Sensors, 21(22), 7459. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227459







