A Calibration/Disaggregation Coupling Scheme for Retrieving Soil Moisture at High Spatio-Temporal Resolution: Synergy between SMAP Passive Microwave, MODIS/Landsat Optical/Thermal and Sentinel-1 Radar Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and In Situ Data
2.2. Remote Sensing Data
2.2.1. SMAP
2.2.2. MODIS
2.2.3. Landsat
2.2.4. Sentinel-1
2.2.5. Vegetation Descriptors
2.3. Remote Sensing Method
2.3.1. DISPATCH
2.3.2. Active Microwave Radiative Transfer Models
2.3.3. Coupling DISPATCH Data with Sentinel-1-Based SM Retrieval Algorithms
2.3.4. Calibration Parameters
3. Results
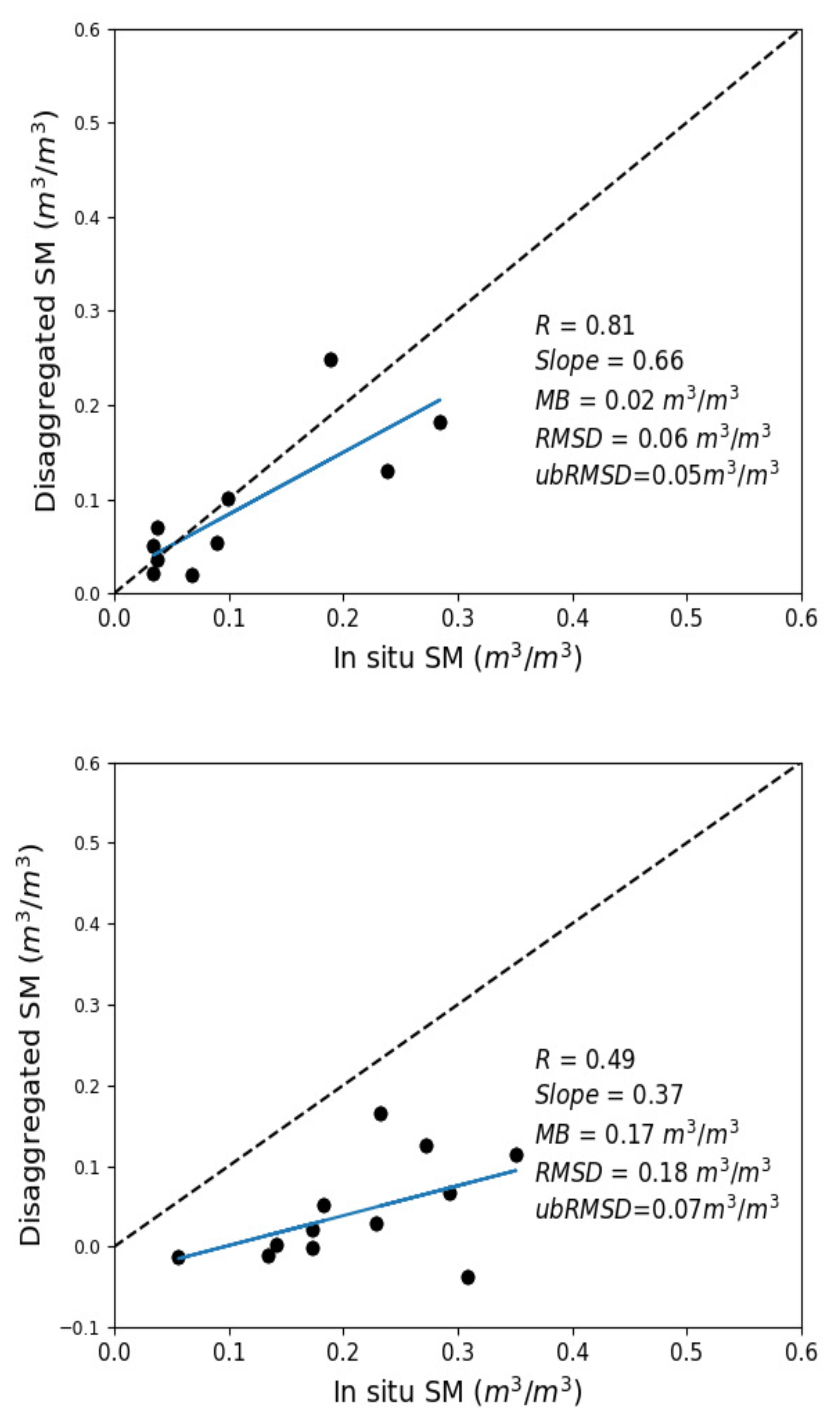
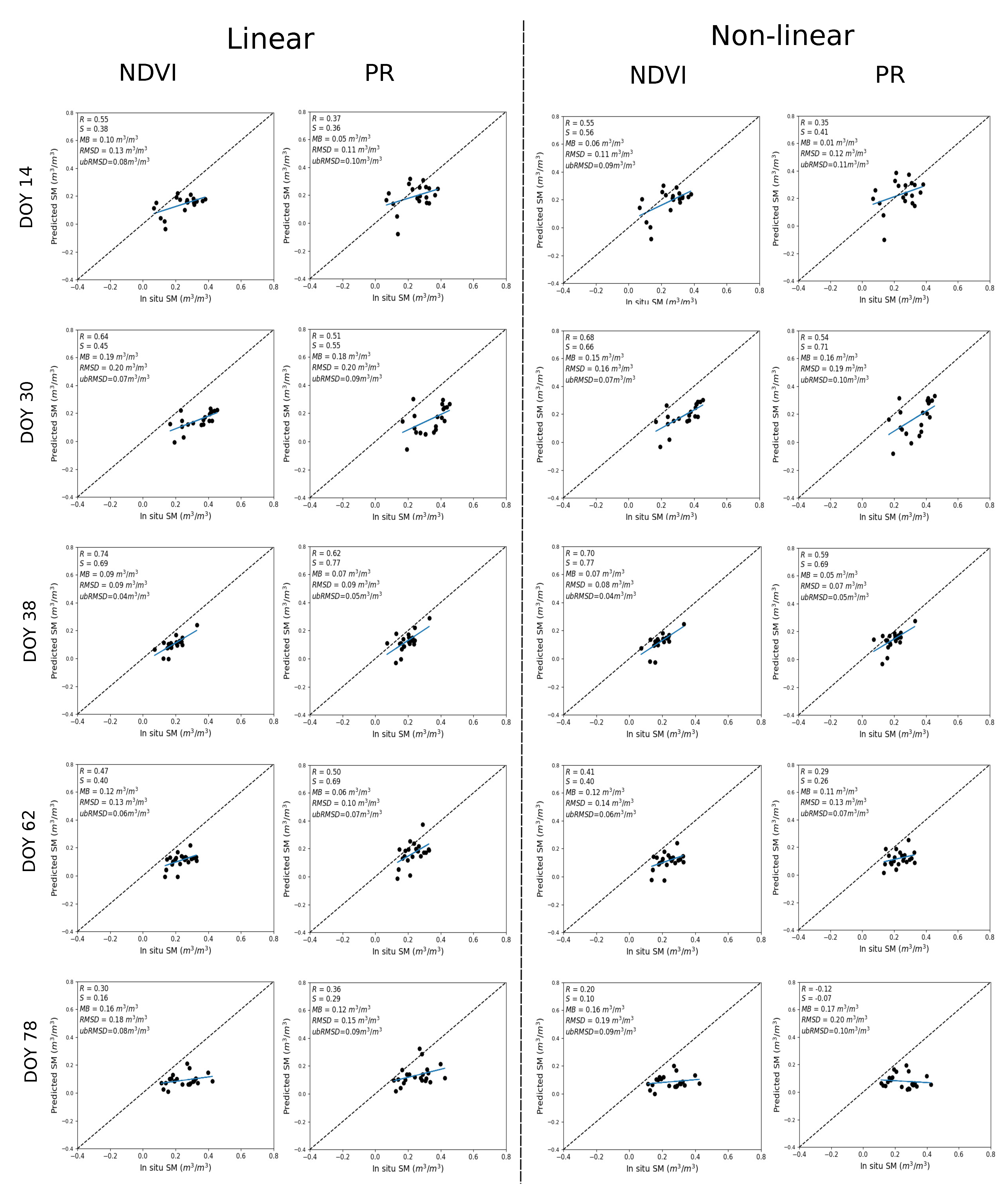
3.1. Accuracy of DISPATCH SM
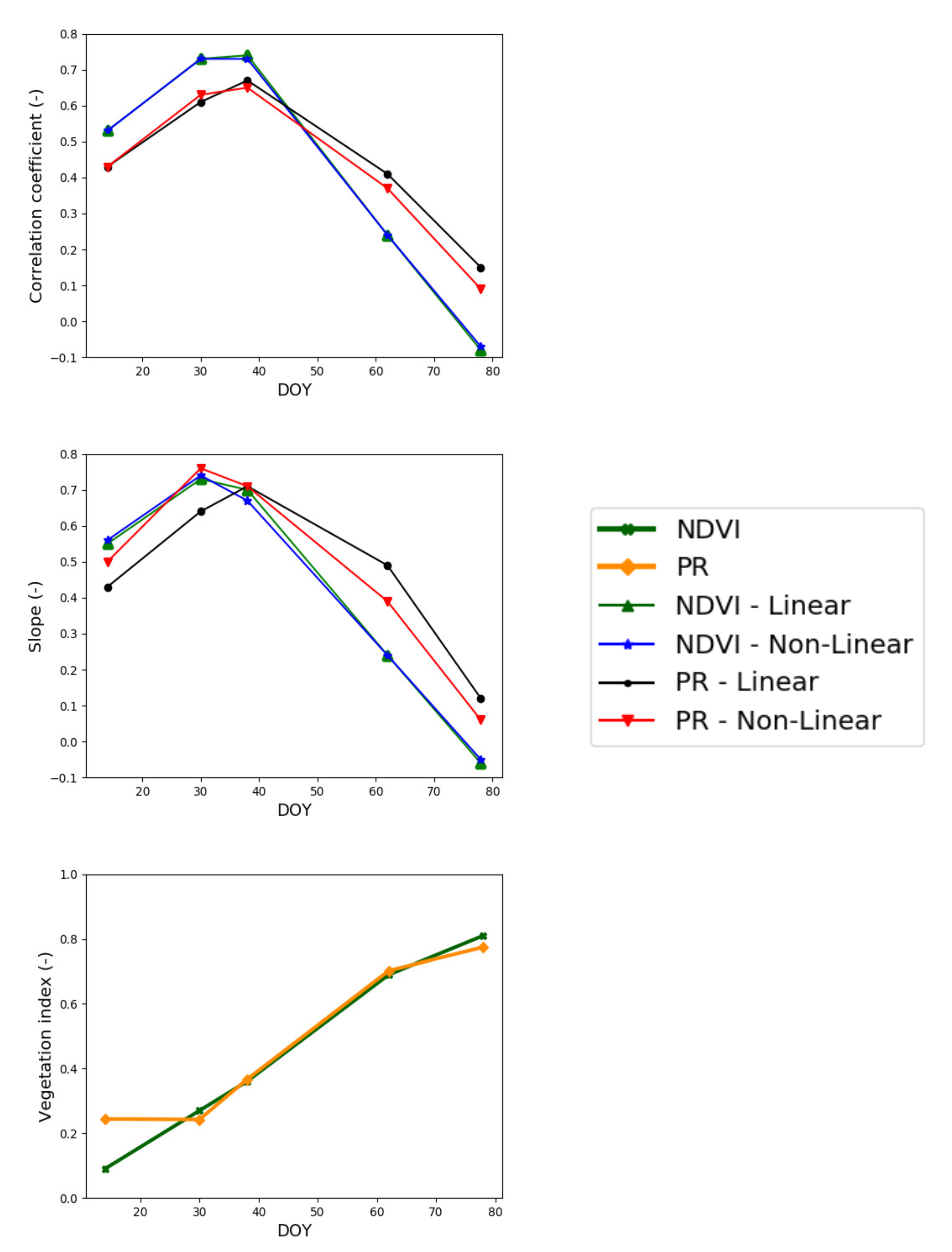
3.2. Evaluation of Calibration Parameters
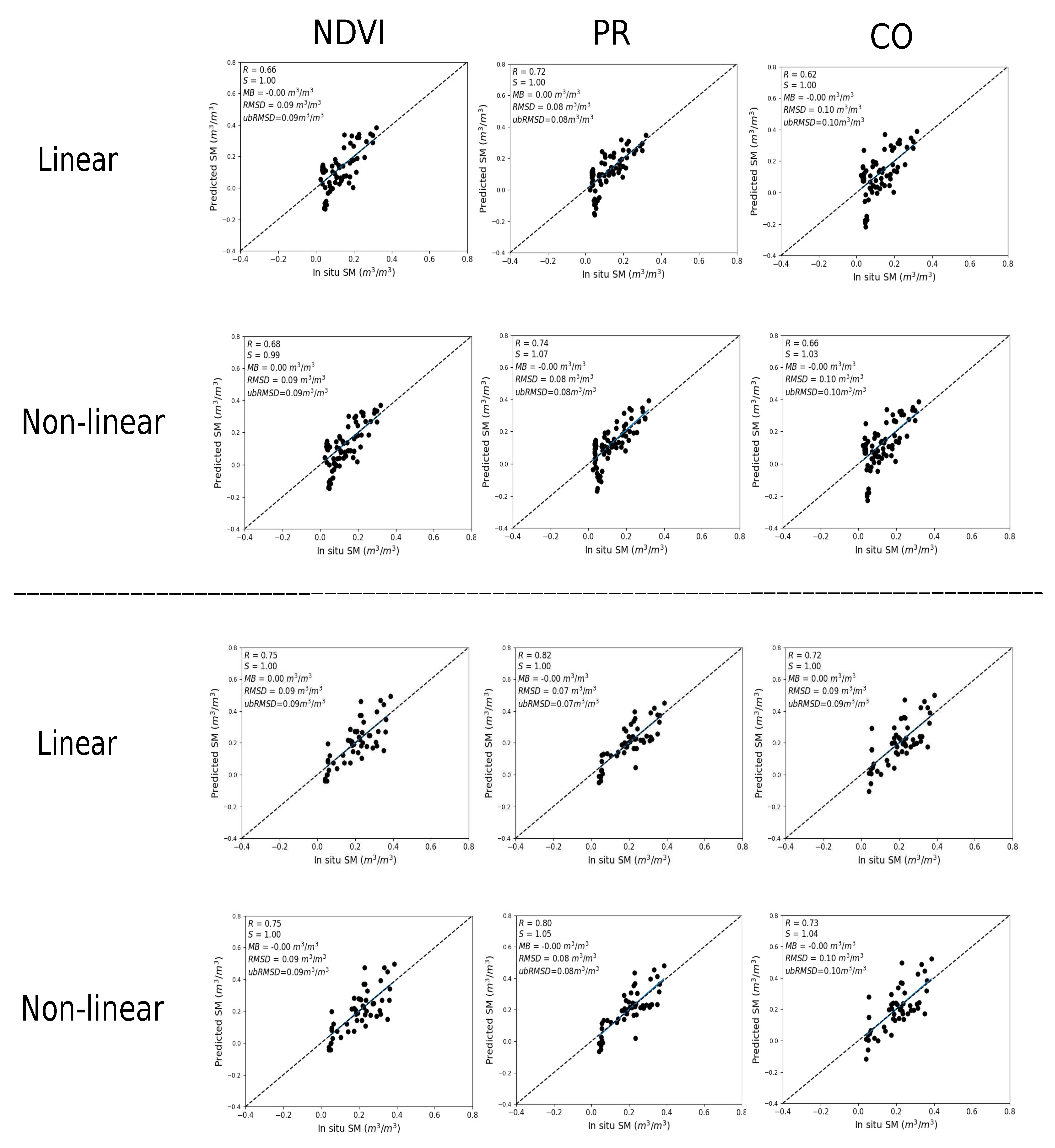
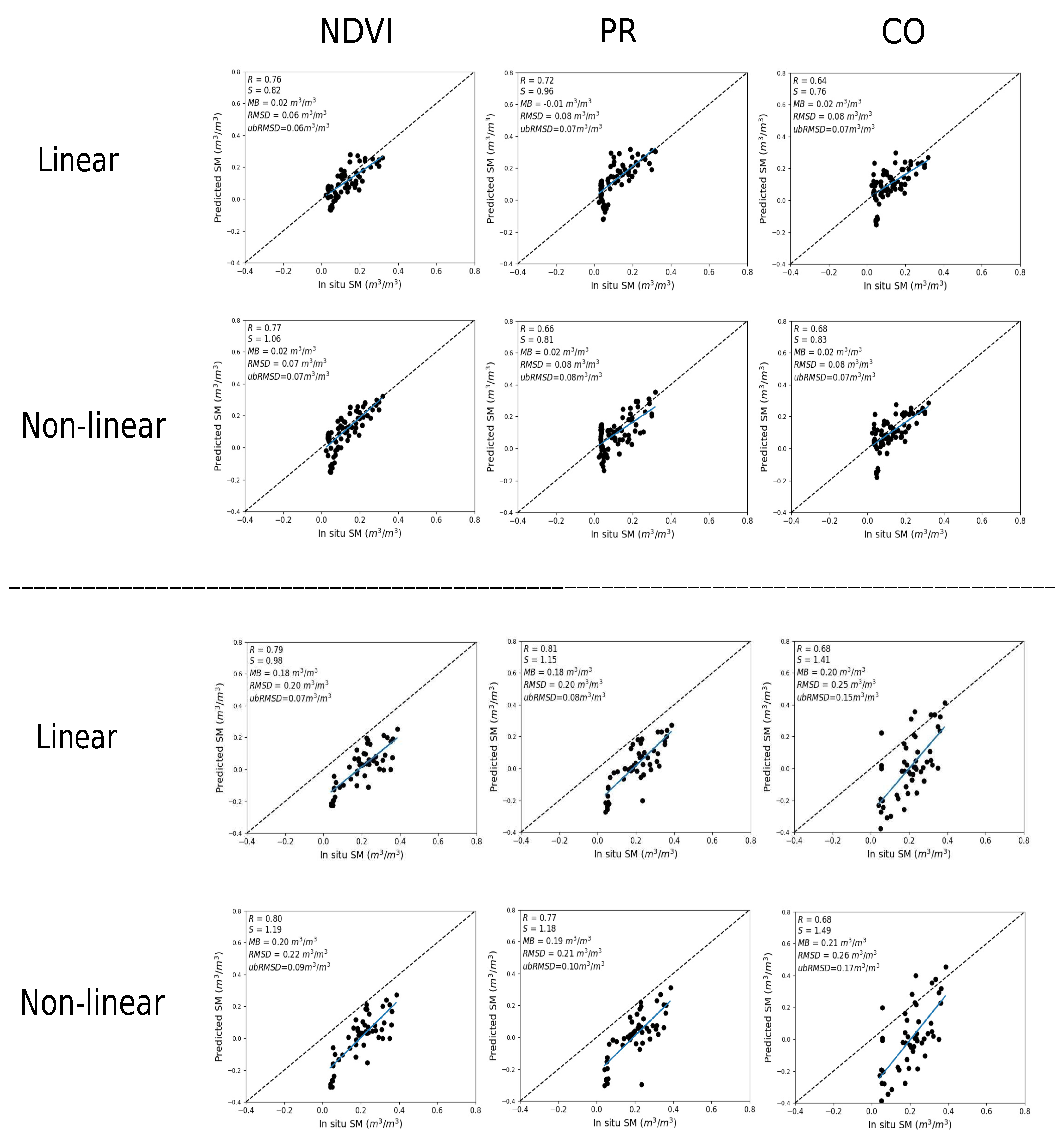
3.3. Evaluation of SM Estimates
3.3.1. Temporal Analysis
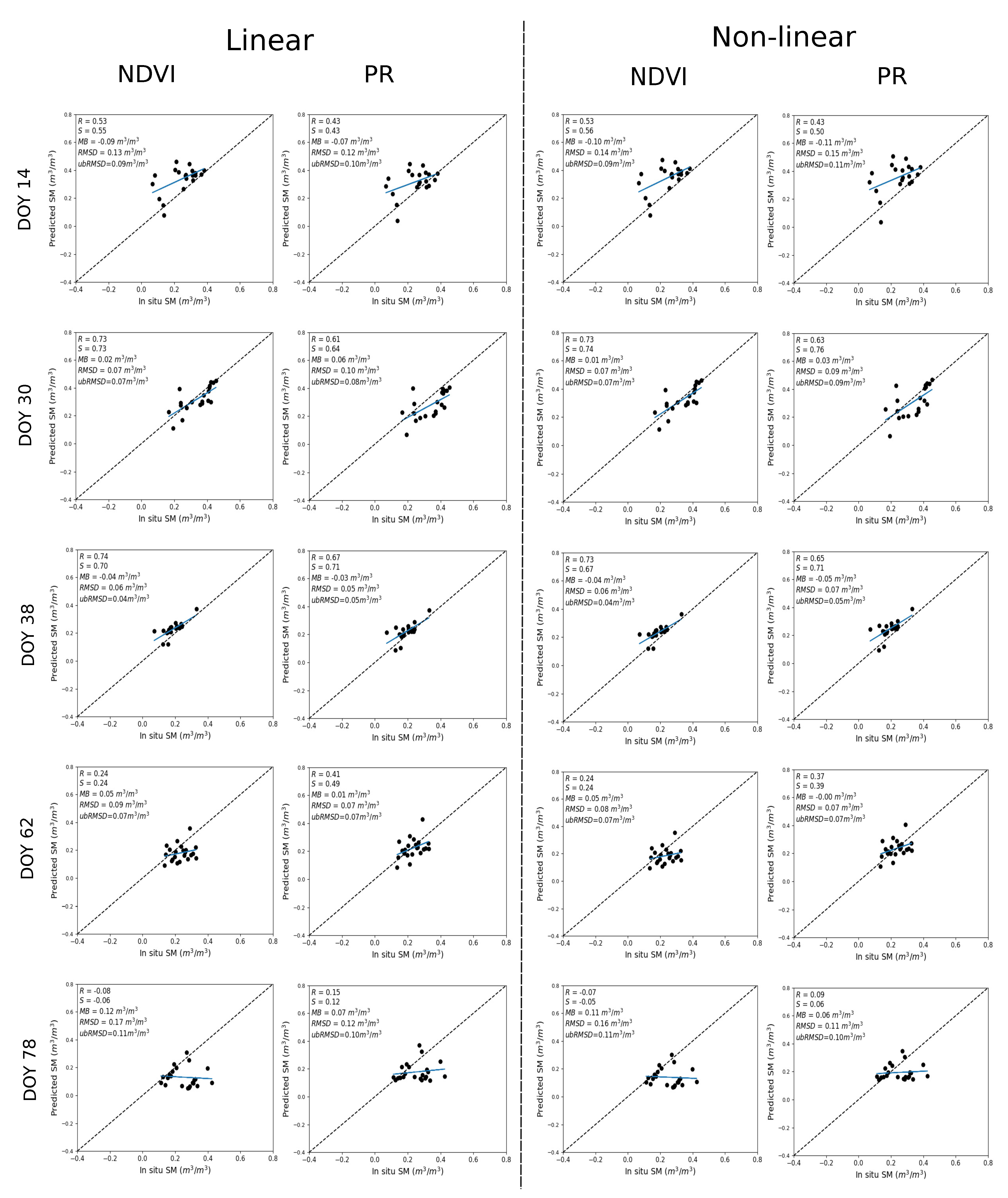
3.3.2. Spatio-Temporal Analysis
3.3.3. Gain in Accuracy at the Fine Scale Compared to SMAP
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robinson, D.; Campbell, C.; Hopmans, J.; Hornbuckle, B.K.; Jones, S.B.; Knight, R.; Ogden, F.; Selker, J.; Wendroth, O. Soil moisture measurement for ecological and hydrological watershed-scale observatories: A review. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 358–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanson, B.; Orloff, S.; Peters, D. Monitoring soil moisture helps refine irrigation management. Calif. Agric. 2000, 54, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brocca, L.; Ciabatta, L.; Massari, C.; Camici, S.; Tarpanelli, A. Soil moisture for hydrological applications: Open questions and new opportunities. Water 2017, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.R.; O’Neill, P.E.; Jackson, T.J.; Engman, E.T. Multifrequency measurements of the effects of soil moisture, soil texture, and surface roughness. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1983, GE-21, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.; Gallardo, M.; Valdez, L.; Fernández, M. Using plant water status to define threshold values for irrigation management of vegetable crops using soil moisture sensors. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 88, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardossi, A.; Incrocci, L.; Incrocci, G.; Malorgio, F.; Battista, P.; Bacci, L.; Rapi, B.; Marzialetti, P.; Hemming, J.; Balendonck, J. Root zone sensors for irrigation management in intensive agriculture. Sensors 2009, 9, 2809–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Richaume, P.; Wigneron, J.P.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Mahmoodi, A.; Al Bitar, A.; Cabot, F.; Gruhier, C.; Juglea, S.E.; et al. The SMOS soil moisture retrieval algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1384–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; O’Neill, P.E.; Kellogg, K.H.; Crow, W.T.; Edelstein, W.N.; Entin, J.K.; Goodman, S.D.; Jackson, T.J.; Johnson, J.; et al. The soil moisture active passive (SMAP) mission. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigneron, J.P.; Jackson, T.; O’neill, P.; De Lannoy, G.; De Rosnay, P.; Walker, J.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Mironov, V.; Bircher, S.; Grant, J.; et al. Modelling the passive microwave signature from land surfaces: A review of recent results and application to the L-band SMOS & SMAP soil moisture retrieval algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 238–262. [Google Scholar]
- Dari, J.; Quintana-Seguí, P.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Stefan, V.; Brocca, L.; Morbidelli, R. Detecting and mapping irrigated areas in a Mediterranean environment by using remote sensing soil moisture and a land surface model. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 126129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievens, H.; Tomer, S.K.; Al Bitar, A.; De Lannoy, G.J.; Drusch, M.; Dumedah, G.; Franssen, H.J.H.; Kerr, Y.H.; Martens, B.; Pan, M.; et al. SMOS soil moisture assimilation for improved hydrologic simulation in the Murray Darling Basin, Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 168, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, N.; Bierkens, M.F.; de Jong, S.M.; de Roo, A.; Karssenberg, D. The benefits of using remotely sensed soil moisture in parameter identification of large-scale hydrological models. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 6874–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, J.; Niesel, J.; Loew, A. Evaluation of soil moisture downscaling using a simple thermal-based proxy—The REMEDHUS network (Spain) example. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4765–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabaghy, S.; Walker, J.P.; Renzullo, L.J.; Akbar, R.; Chan, S.; Chaubell, J.; Das, N.; Dunbar, R.S.; Entekhabi, D.; Gevaert, A.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of alternative downscaled soil moisture products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 239, 111586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.N.; Entekhabi, D.; Njoku, E.G.; Shi, J.J.; Johnson, J.T.; Colliander, A. Tests of the SMAP combined radar and radiometer algorithm using airborne field campaign observations and simulated data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backus, G.; Gilbert, F. Uniqueness in the inversion of inaccurate gross earth data. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. Math. Phys. Sci. 1970, 266, 123–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, N.N.; Entekhabi, D.; Dunbar, R.S.; Colliander, A.; Chen, F.; Crow, W.; Jackson, T.J.; Berg, A.; Bosch, D.D.; Caldwell, T.; et al. The SMAP mission combined active-passive soil moisture product at 9 km and 3 km spatial resolutions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.; Miller, S.; Ardanuy, P. Spaceborne soil moisture estimation at high resolution: A microwave-optical/IR synergistic approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4599–4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, O.; Walker, J.P.; Chehbouni, A.; Kerr, Y. Towards deterministic downscaling of SMOS soil moisture using MODIS derived soil evaporative efficiency. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3935–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Hogue, T.S. Evaluation and sensitivity testing of a coupled Landsat-MODIS downscaling method for land surface temperature and vegetation indices in semi-arid regions. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 063569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amazirh, A.; Merlin, O.; Er-Raki, S.; Gao, Q.; Rivalland, V.; Malbeteau, Y.; Khabba, S.; Escorihuela, M.J. Retrieving surface soil moisture at high spatio-temporal resolution from a synergy between Sentinel-1 radar and Landsat thermal data: A study case over bare soil. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 211, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, V.G.; Merlin, O.; Er-Raki, S.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Khabba, S. Consistency between in situ, model-derived and high-resolution-image-based soil temperature endmembers: Towards a robust data-based model for multi-resolution monitoring of crop evapotranspiration. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 10444–10479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verhoest, N.E.; Lievens, H.; Wagner, W.; Álvarez-Mozos, J.; Moran, M.S.; Mattia, F. On the soil roughness parameterization problem in soil moisture retrieval of bare surfaces from synthetic aperture radar. Sensors 2008, 8, 4213–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, Y. Quantitative retrieval of soil moisture content and surface roughness from multipolarized radar observations of bare soil surfaces. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellndorfer, J.; Walker, W.; Pierce, L.; Dobson, C.; Fites, J.A.; Hunsaker, C.; Vona, J.; Clutter, M. Vegetation height estimation from shuttle radar topography mission and national elevation datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattia, F.; Le Toan, T.; Souyris, J.C.; De Carolis, C.; Floury, N.; Posa, F.; Pasquariello, N. The effect of surface roughness on multifrequency polarimetric SAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 954–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W.; Lemoine, G.; Borgeaud, M.; Rott, H. A study of vegetation cover effects on ERS scatterometer data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zyl, J.J.; Chapman, B.D.; Dubois, P.; Shi, J. The effect of topography on SAR calibration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1993, 31, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornelsen, K.C.; Coulibaly, P. Advances in soil moisture retrieval from synthetic aperture radar and hydrological applications. J. Hydrol. 2013, 476, 460–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Razani, M.; Dobson, M.C. Effects of vegetation cover on the microwave radiometric sensitivity to soil moisture. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1983, GE-21, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouaadi, N.; Jarlan, L.; Ezzahar, J.; Zribi, M.; Khabba, S.; Bouras, E.; Bousbih, S.; Frison, P.L. Monitoring of wheat crops using the backscattering coefficient and the interferometric coherence derived from Sentinel-1 in semi-arid areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 112050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.; Cresson, R.; El Hajj, M.; Ludwig, R.; La Jeunesse, I. Soil parameters estimation over bare agriculture areas from C-band polarimetric SAR data using neural networks. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2012, 9, 2897–2933. [Google Scholar]
- Zribi, M.; Dechambre, M. A new empirical model to retrieve soil moisture and roughness from C-band radar data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, A.K.; Li, Z.; Chen, K.S. Backscattering from a randomly rough dielectric surface. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.; Choker, M.; Zribi, M.; Hajj, M.E.; Paloscia, S.; Verhoest, N.E.; Lievens, H.; Baup, F.; Mattia, F. A new empirical model for radar scattering from bare soil surfaces. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubois, P.C.; Engman, T. Corrections to “Measuring Soil Moisture with Imaging Radars”. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attema, E.; Ulaby, F.T. Vegetation modeled as a water cloud. Radio Sci. 1978, 13, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.; Han, X.; Jin, R. Estimation of surface soil moisture and roughness from multi-angular ASAR imagery in the Watershed Allied Telemetry Experimental Research (WATER). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bindlish, R.; Kustas, W.P.; French, A.N.; Diak, G.R.; Mecikalski, J.R. Influence of near-surface soil moisture on regional scale heat fluxes: Model results using microwave remote sensing data from SGP97. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lievens, H.; Verhoest, N.E. On the retrieval of soil moisture in wheat fields from L-band SAR based on water cloud modeling, the IEM, and effective roughness parameters. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zribi, M.; Saux-Picart, S.; André, C.; Descroix, L.; Ottlé, C.; Kallel, A. Soil moisture mapping based on ASAR/ENVISAT radar data over a Sahelian region. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 3547–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.; Allen, C.; Eger Iii, G.; Kanemasu, E. Relating the microwave backscattering coefficient to leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1984, 14, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevot, L.; Dechambre, M.; Taconet, O.; Vidal-Madjar, D.; Normand, M.; Gallej, S. Estimating the characteristics of vegetation canopies with airborne radar measurements. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 2803–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowska-Zielinska, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kowalik, W.; Gruszczynska, M. Inferring the effect of plant and soil variables on C-and L-band SAR backscatter over agricultural fields, based on model analysis. Adv. Space Res. 2007, 39, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, N.; Merlin, O.; Molero, B.; Suere, C.; Olivera-Guerra, L.; Ait Hssaine, B.; Amazirh, A.; Al Bitar, A.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Er-Raki, S. Stepwise disaggregation of SMAP soil moisture at 100 m resolution using Landsat-7/8 data and a varying intermediate resolution. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merlin, O.; Rudiger, C.; Al Bitar, A.; Richaume, P.; Walker, J.P.; Kerr, Y.H. Disaggregation of SMOS soil moisture in Southeastern Australia. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1556–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merlin, O.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Mayoral, M.A.; Hagolle, O.; Al Bitar, A.; Kerr, Y. Self-calibrated evaporation-based disaggregation of SMOS soil moisture: An evaluation study at 3 km and 100 m resolution in Catalunya, Spain. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Hajj, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Zribi, M.; Rodríguez-Fernández, N.; Wigneron, J.P.; Al-Yaari, A.; Al Bitar, A.; Albergel, C.; Calvet, J.C. Evaluation of SMOS, SMAP, ASCAT and Sentinel-1 soil moisture products at sites in Southwestern France. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, J.; Loew, A.; Merlin, O.; Verhoest, N.E. A review of spatial downscaling of satellite remotely sensed soil moisture. Rev. Geophys. 2017, 55, 341–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abowarda, A.S.; Bai, L.; Zhang, C.; Long, D.; Li, X.; Huang, Q.; Sun, Z. Generating surface soil moisture at 30 m spatial resolution using both data fusion and machine learning toward better water resources management at the field scale. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 255, 112301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, I.; Yeo, I.Y.; Willgoose, G.; Hancock, G. Disaggregating satellite soil moisture products based on soil thermal inertia: A comparison of a downscaling model built at two spatial scales. J. Hydrol. 2021, 594, 125894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wen, F.; Wang, Q.; Sanchez, N.; Piles, M. Seamless downscaling of the ESA CCI soil moisture data at the daily scale with MODIS land products. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanet, M.; Fernàndez-Garcia, D.; Ferrer, F. The value of satellite remote sensing soil moisture data and the DISPATCH algorithm in irrigation fields. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 5889–5900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ojha, N.; Merlin, O.; Suere, C.; Escorihuela, M.J. Extending the Spatio-Temporal Applicability of DISPATCH Soil Moisture Downscaling Algorithm: A Study Case Using SMAP, MODIS and Sentinel-3 Data. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlin, O.; Malbéteau, Y.; Notfi, Y.; Bacon, S.; Khabba, S.E.R.S.; Jarlan, L. Performance metrics for soil moisture downscaling methods: Application to DISPATCH data in central Morocco. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 3783–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali Eweys, O.; Escorihuela, M.J.; Villar Mir, J.M.; Er-Raki, S.; Amazirh, A.; Olivera, L.; Jarlan, L.; Khabb, S.; Merlin, O. Disaggregation of SMOS soil moisture to 100m resolution using MODIS optical/thermal and sentinel-1 radar data: Evaluation over a bare soil site in morocco. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hssaine, B.A.; Merlin, O.; Rafi, Z.; Ezzahar, J.; Jarlan, L.; Khabba, S.; Er-Raki, S. Calibrating an evapotranspiration model using radiometric surface temperature, vegetation cover fraction and near-surface soil moisture data. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 256, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rafi, Z.; Merlin, O.; Le Dantec, V.; Khabba, S.; Mordelet, P.; Er-Raki, S.; Amazirh, A.; Olivera-Guerra, L.; Hssaine, B.A.; Simonneaux, V.; et al. Partitioning evapotranspiration of a drip-irrigated wheat crop: Inter-comparing eddy covariance-, sap flow-, lysimeter-and FAO-based methods. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 265, 310–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarlan, L.; Khabba, S.; Er-Raki, S.; Le Page, M.; Hanich, L.; Fakir, Y.; Merlin, O.; Mangiarotti, S.; Gascoin, S.; Ezzahar, J.; et al. Remote sensing of water resources in semi-arid Mediterranean areas: The joint international laboratory TREMA. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 4879–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, G.W.; Bauder, J.; Klute, A. Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1, Physical and Mineralogical Methods; Soil Science Society of America Book Series; American Society of Agronomy, Inc.; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 404–410. [Google Scholar]
- Ouaadi, N.; Ezzahar, J.; Khabba, S.; Er-Raki, S.; Chakir, A.; Ait Hssaine, B.; Le Dantec, V.; Rafi, Z.; Beaumont, A.; Kasbani, M.; et al. C-band radar data and in situ measurements for the monitoring of wheat crops in a semi-arid area (center of Morocco). Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2021, 13, 3707–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Hssaine, B.; Chehbouni, A.; Er-Raki, S.; Khabba, S.; Ezzahar, J.; Ouaadi, N.; Ojha, N.; Rivalland, V.; Merlin, O. On the Utility of High-Resolution Soil Moisture Data for Better Constraining Thermal-Based Energy Balance over Three Semi-Arid Agricultural Areas. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molero, B.; Merlin, O.; Malbéteau, Y.; Al Bitar, A.; Cabot, F.; Stefan, V.; Kerr, Y.; Bacon, S.; Cosh, M.; Bindlish, R.; et al. SMOS disaggregated soil moisture product at 1 km resolution: Processor overview and first validation results. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardy, B.; Rivalland, V.; Huc, M.; Hagolle, O.; Marcq, S.; Boulet, G. A software tool for atmospheric correction and surface temperature estimation of Landsat infrared thermal data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagolle, O.; Huc, M.; Villa Pascual, D.; Dedieu, G. A multi-temporal and multi-spectral method to estimate aerosol optical thickness over land, for the atmospheric correction of FormoSat-2, LandSat, VENμS and Sentinel-2 images. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2668–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bamler, R.; Hartl, P. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Inverse Probl. 1998, 14, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzi, R.; Lopes, A.; Bruniquel, J.; Vachon, P. Coherence estimation for SAR imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 135 –149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merlin, O.; Stefan, V.G.; Amazirh, A.; Chanzy, A.; Ceschia, E.; Er-Raki, S.; Gentine, P.; Tallec, T.; Ezzahar, J.; Bircher, S.; et al. Modeling soil evaporation efficiency in a range of soil and atmospheric conditions using a meta-analysis approach. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 3663–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marquardt, D.W. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 1963, 11, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdadi, N.; El Hajj, M.; Zribi, M.; Bousbih, S. Calibration of the water cloud model at C-band for winter crop fields and grasslands. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Ripley, D.A. On the relation between NDVI, fractional vegetation cover, and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagouarde, J.P.; Bhattacharya, B.K.; Crebassol, P.; Gamet, P.; Babu, S.S.; Boulet, G.; Briottet, X.; Buddhiraju, K.M.; Cherchali, S.; Dadou, I.; et al. The Indian-French Trishna mission: Earth observation in the thermal infrared with high spatio-temporal resolution. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 4078–4081. [Google Scholar]



| Vegetation Descriptors | Chichaoua | Sidi Rahal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | Calibration parameter (dB*)/(dB) | NDVI | 19/−3/−14 | 20/−0.7/−18 |
| PR | 16/−6/−12 | 20/−4/−16 | ||
| CO | 15/3/−16 | 17/3/−19 | ||
| Standard error percentage std(%)/std(%)/std(%) | NDVI | 17/28/2 | 15/124/3 | |
| PR | 12/11/3 | 10/21/3 | ||
| CO | 16/18/3 | 14/30/3 | ||
| Non-linear | Calibration parameter (dB*)/(dB)/(dB)/(dB) | NDVI | 18/−3/−14/−0.28 | 19/−0.7/−18/−0.04 |
| PR | 11/−6/−11/−0.9 | 17/−4/−16/−0.4 | ||
| CO | 18/3/−17/0.2 | 18/3/−19/0.15 | ||
| Standard error percentage std(%)/std(%)/std(%)/std(%) | NDVI | 13/28/2/21 | 14/124/3/175 | |
| PR | 11/11/4/12 | 11/21/4/26 | ||
| CO | 14/18/3/14 | 14/30/4/33 |
| Vegetation Descriptors | Chichaoua | Sidi Rahal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | Calibration parameter (dB*(dB)/(dB) | NDVI | 34/−7/−14 | 26/−4/−12 |
| PR | 19/−9/−11 | 19/−6/−12 | ||
| CO | 23/5/−18 | 11/4/−16 | ||
| Standard error percentage std(%)/std(%)/std(%) | NDVI | 27/46/6 | 38/47/10 | |
| PR | 29/24/8 | 41/27/8 | ||
| CO | 28/29/7 | 121/67/9 | ||
| Non-linear | Calibration parameter (dB*)/(dB)/(dB)/(dB) | NDVI | 20/−7/−13/−0.76 | 19/−4/−12/−4 |
| PR | 10/−9/−10/−2 | 14/−6/−11/−0.78 | ||
| CO | 25/5/−18/0.27 | 12/4/−16/0.24 | ||
| Standard error percentage std(%)/std(%)/std(%)/std(%) | NDVI | 25/46/6/41 | 41/47/11/54 | |
| PR | 32/24/12/31 | 44/27/9/31 | ||
| CO | 29/29/8/30 | 122/67/9/67 |
| Calibration | In Situ SM Datasets | DSIAPTCH SM Datasets | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | R (-) | Slope (-) | MB (m/m) | RMSD (m/m) | ubRMSD (m/m) | R (-) | Slope (-) | Absolute MB (m/m) | RMSD (m/m) | ubRMSD (m/m) | |
| Linear | NDVI | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.54 | 0.42 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.07 |
| PR | 0.45 | 0.48 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.47 | 0.53 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.08 | |
| Non-linear | NDVI | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.51 | 0.50 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.07 |
| PR | 0.43 | 0.48 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.33 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.09 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ojha, N.; Merlin, O.; Amazirh, A.; Ouaadi, N.; Rivalland, V.; Jarlan, L.; Er-Raki, S.; Escorihuela, M.J. A Calibration/Disaggregation Coupling Scheme for Retrieving Soil Moisture at High Spatio-Temporal Resolution: Synergy between SMAP Passive Microwave, MODIS/Landsat Optical/Thermal and Sentinel-1 Radar Data. Sensors 2021, 21, 7406. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217406
Ojha N, Merlin O, Amazirh A, Ouaadi N, Rivalland V, Jarlan L, Er-Raki S, Escorihuela MJ. A Calibration/Disaggregation Coupling Scheme for Retrieving Soil Moisture at High Spatio-Temporal Resolution: Synergy between SMAP Passive Microwave, MODIS/Landsat Optical/Thermal and Sentinel-1 Radar Data. Sensors. 2021; 21(21):7406. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217406
Chicago/Turabian StyleOjha, Nitu, Olivier Merlin, Abdelhakim Amazirh, Nadia Ouaadi, Vincent Rivalland, Lionel Jarlan, Salah Er-Raki, and Maria Jose Escorihuela. 2021. "A Calibration/Disaggregation Coupling Scheme for Retrieving Soil Moisture at High Spatio-Temporal Resolution: Synergy between SMAP Passive Microwave, MODIS/Landsat Optical/Thermal and Sentinel-1 Radar Data" Sensors 21, no. 21: 7406. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217406
APA StyleOjha, N., Merlin, O., Amazirh, A., Ouaadi, N., Rivalland, V., Jarlan, L., Er-Raki, S., & Escorihuela, M. J. (2021). A Calibration/Disaggregation Coupling Scheme for Retrieving Soil Moisture at High Spatio-Temporal Resolution: Synergy between SMAP Passive Microwave, MODIS/Landsat Optical/Thermal and Sentinel-1 Radar Data. Sensors, 21(21), 7406. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217406










