The X-ray Sensitivity of an Amorphous Lead Oxide Photoconductor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
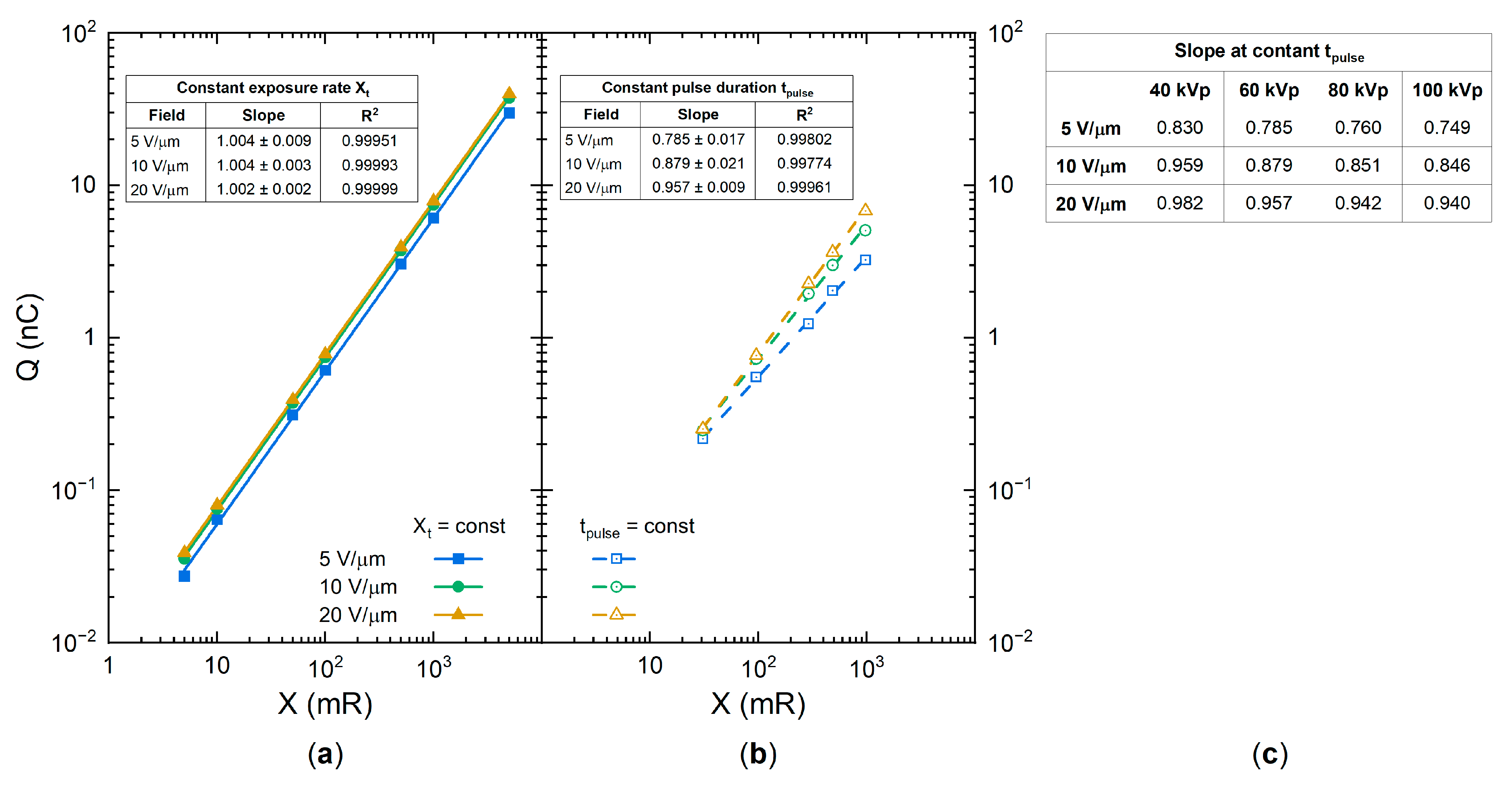
2.1. Exposure Dependency
2.2. Field Dependency
2.3. X-ray Energy Dependency
3. Materials and Methods
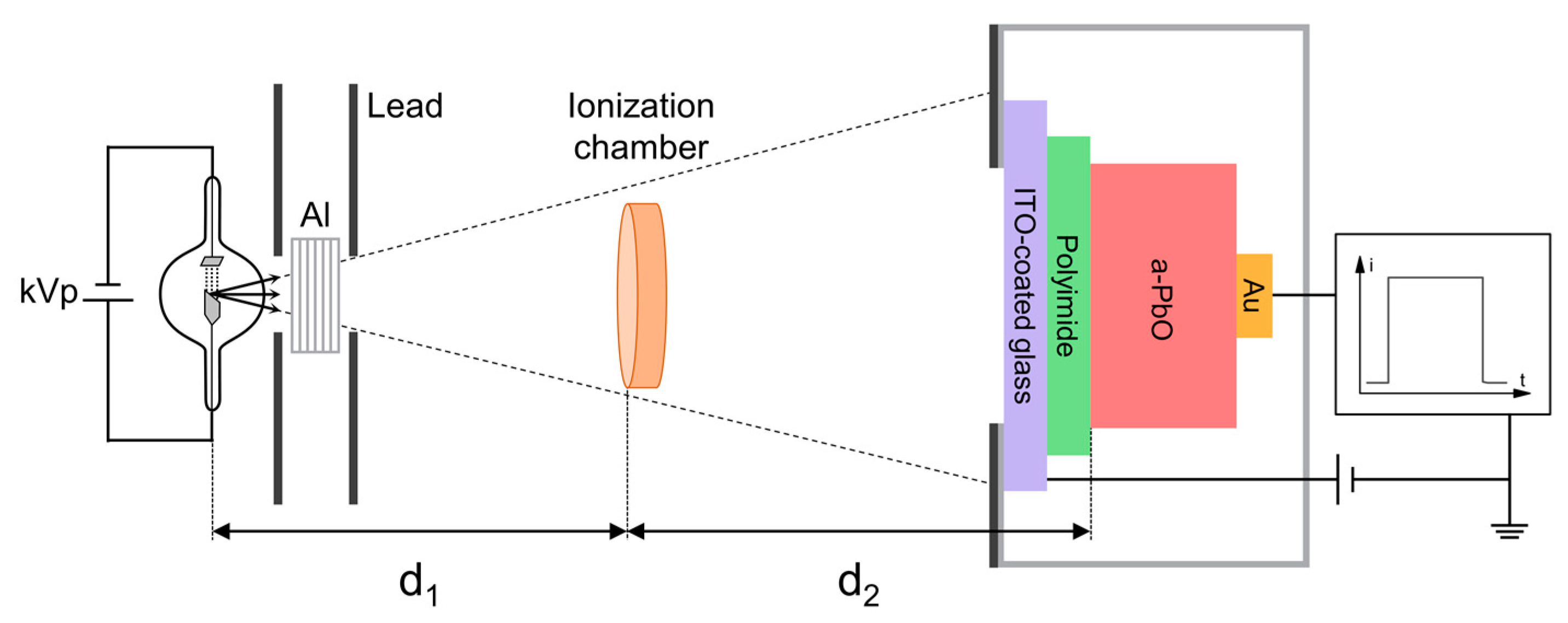
3.1. Detector Preparation
3.2. Experimental Apparatus
3.3. Monte Carlo Simulations
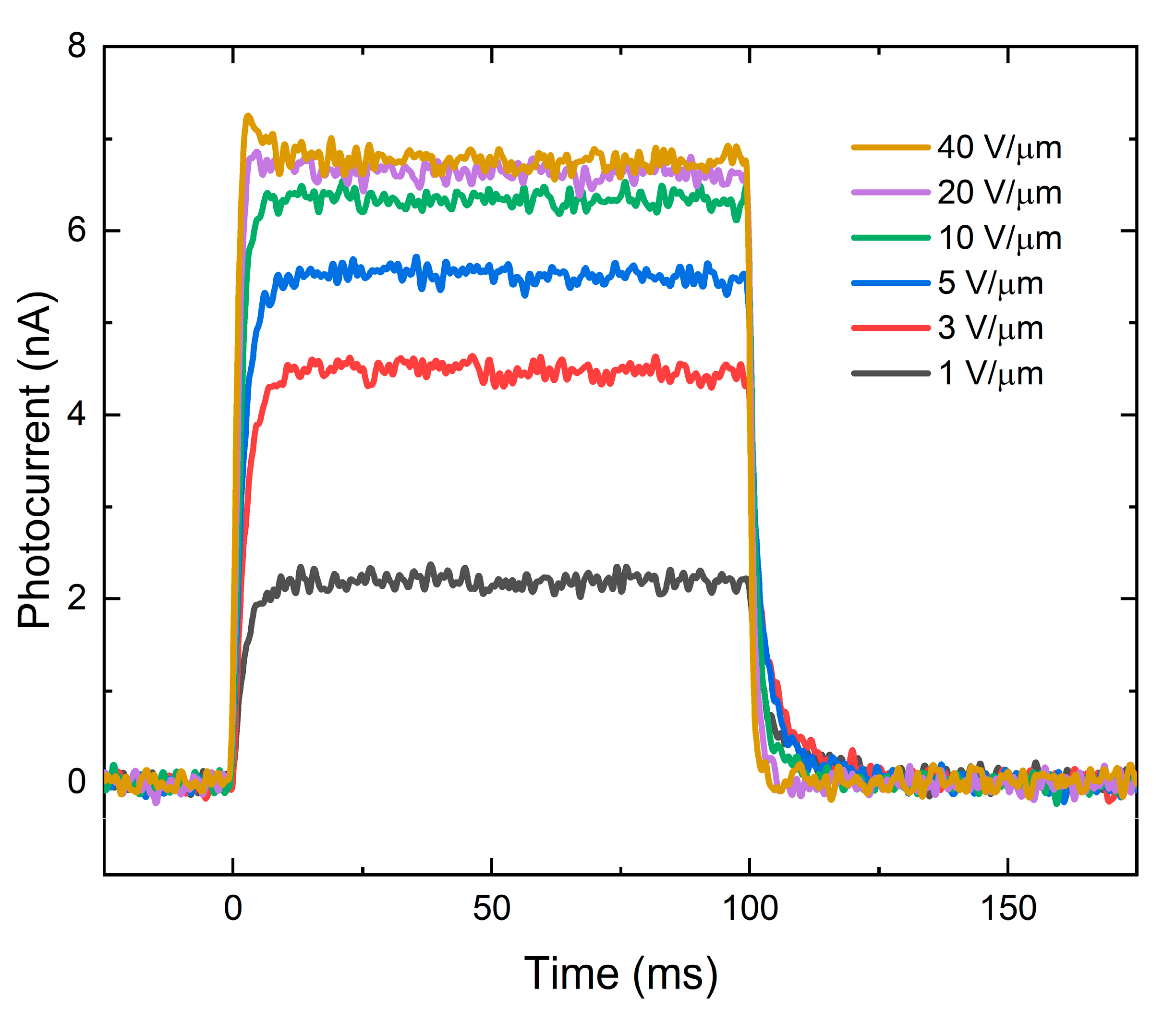
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. X-ray Sensitivity Calculations
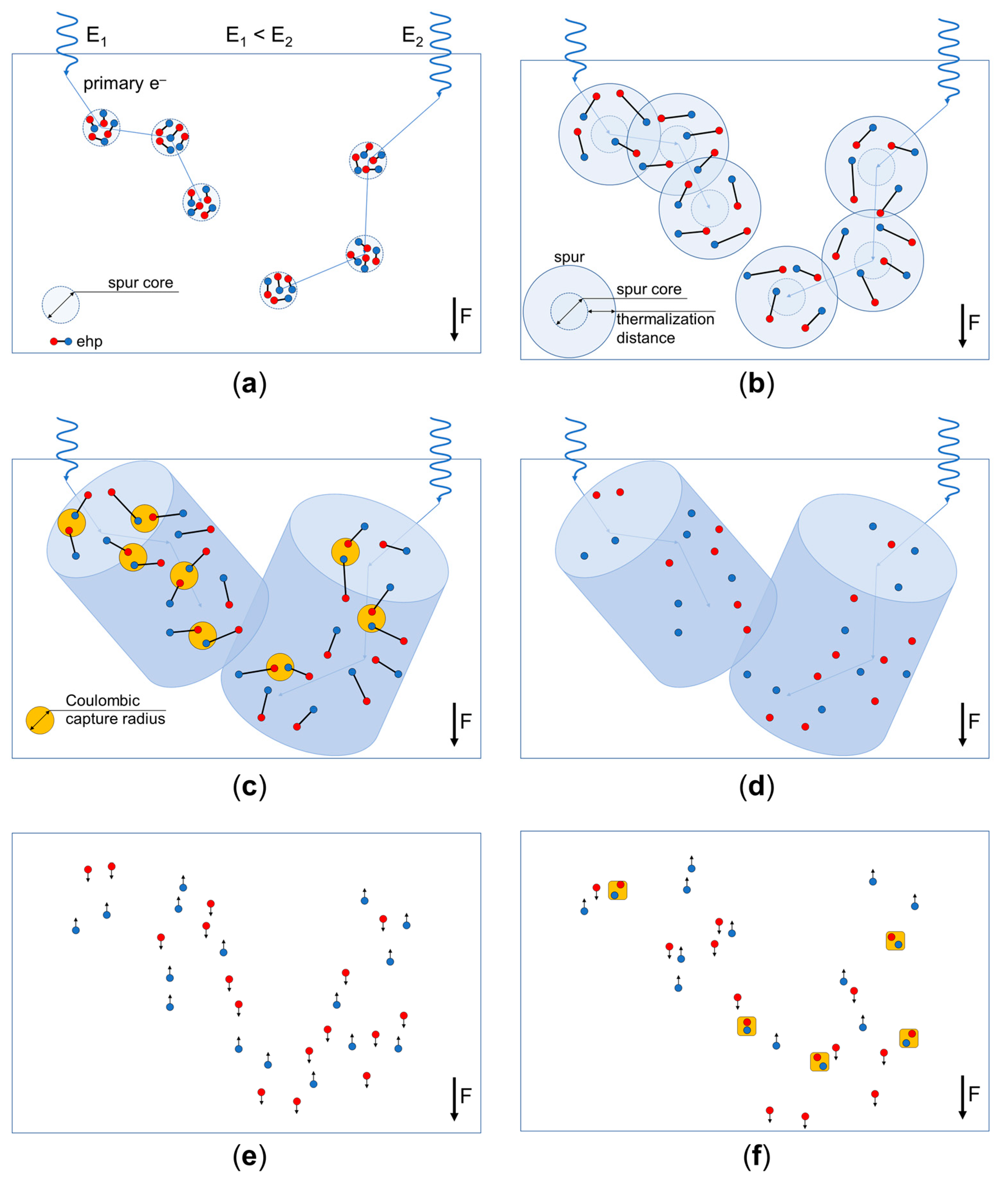
Appendix B. Model for the Charge Generation and Recombination Processes in a-PbO
References
- Kasap, S.O.; Frey, J.B.; Belev, G.; Tousignant, O.; Mani, H.; Greenspan, J.; Laperriere, L.; Bubon, O.; Reznik, A.; DeCrescenzo, G.; et al. Amorphous and Polycrystalline Photoconductors for Direct Conversion Flat Panel X-ray Image Sensors. Sensors 2011, 11, 5112–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, M.Z.; Kasap, S.O. Photoconductors for X-Ray Image Detectors. In Springer Handbook of Electronic and Photonic Materials, 2nd ed.; Kasap, S., Capper, P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1125–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasap, S.O.; Frey, J.B.; Belev, G.; Tousignant, O.; Mani, H.; Laperriere, L.; Reznik, A.; Rowlands, J.A. Amorphous selenium and its alloys from early xeroradiography to high resolution X-ray image detectors and ultrasensitive imaging tubes. Phys. Status Sol. 2009, 246, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belev, G.; Kasap, S.O. Amorphous selenium as an X-ray photoconductor. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2004, 345–346, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadeh, S.; Scott, C.C.; Bubon, O.; Reznik, A.; Karim, K.S. Enhanced Detection Efficiency of Direct Conversion X-ray Detector Using Polyimide as Hole-Blocking Layer. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, J.B.; Sadasivam, K.; Belev, G.; Mani, H.; Laperriere, L.; Kasap, S.O. Dark current–voltage characteristics of vacuum deposited multilayer amorphous selenium-alloy detectors and the effect of x-ray irradiation. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2019, 37, 061501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polischuk, B.T.; Savard, S.; Loustaneau, V.; Hansroul, M.; Cadieux, S.; Vaque, A. Se-based flat-panel detector for screening mammography. Med. Imaging 2001 Phys. Med. Imaging 2001, 4320, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhao, B.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, S.; Yang, D.; Wangyang, P.; Gao, X. Laser-induced surface recrystallization of polycrystalline PbI2 thick films for X-ray detector application. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condeles, J.F.F.; Mulato, M. Polycrystalline lead iodide films produced by solution evaporation and tested in the mammography X-ray energy range. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2016, 89, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, R.A.; Ready, S.E.; Van Schuylenbergh, K.; Ho, J.; Boyce, J.B.; Nylen, P.; Shah, K.; Melekhov, L.; Hermon, H. Comparison of PbI2 and HgI2 for direct detection active matrix X-ray image sensors. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 3345–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lee, K.; Seo, J. High signal-to-noise ratio HgI2 X-ray detector assisted with ultraviolet radiation. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2019, 941, 162364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonuk, L.E.; El-Mohri, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, H. Exploration of strategies for implementation of screen-printed mercuric iodide converters in direct detection AMFPIs for digital breast tomosynthesis. Med. Imaging 2017 Phys. Med. Imaging 2017, 10132, 101320A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.S.; Ko, K.R.; Lee, G.H.; Lee, D.J.; Kim, N.W.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, N.W.; Im, S. Direct Thermal Growth of Large Scale Cl-doped CdTe Film for Low Voltage High Resolution X-ray Image Sensor. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Znamenshchykov, Y.V.; Kosyak, V.V.; Kononov, O.K.; Shpetnyi, I.O.; Grebinaha, V.I.; Fochuk, P.M.; Opanasyuk, A.S. Electrical, structural and optical properties of Cd1-xZnxTe thick polycrystalline films. Vacuum 2018, 149, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Yang, D.; Wangyang, P.; Gao, X.; Gou, Z.; Zhu, X. Electrical properties of x-ray detector based on bismuth tri-iodide single crystal with electrode configuration considering. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 055902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, X.; He, Y.; Chen, L.; Xu, M.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, S.; Ouyang, X. A High-Resistivity ZnO Film-Based Photoconductive X-Ray Detector. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2019, 31, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; Ford, R.A.; Franklin, A.R.; Grabowski, S.P.; Menser, B.; Much, G.; Nascetti, A.; Overdick, M.; Powell, M.J.; Wiechert, D.U. PbO as direct conversion x-ray detector material. Med. Imaging 2004 Phys. Med. Imaging 2004, 5368, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeniuk, O.; Grynko, O.; Decrescenzo, G.; Juska, G.; Wang, K.; Reznik, A. Characterization of polycrystalline lead oxide for application in direct conversion X-ray detectors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowlands, J.A. Material change for X-ray detectors. Nature 2017, 550, 47–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semeniuk, O.; Grynko, O.; Juska, G.; Reznik, A. Amorphous lead oxide (a-PbO): Suppression of signal lag via engineering of the layer structure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grynko, O.; Thibault, T.; Pineau, E.; Reznik, A. Engineering of a Blocking Layer Structure for Low-Lag Operation of the a-PbO-Based X-Ray Detector. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2021, 68, 2335–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; Ford, R.A.; Franklin, A.R.; Grabowski, S.P.; Menser, B.; Much, G.; Nascetti, A.; Overdick, M.; Powell, M.J.; Wiechert, D.U. Analysis of lead oxide (PbO) layers for direct conversion X-ray detection. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2005, 52, 2035–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousignant, O.; Demers, Y.; Laperriere, L.; Mani, H.; Gauthier, P.; Leboeuf, J. Spatial and temporal image characteristics of a real-time large area a-Se x-ray detector. Proc. SPIE 2005, 5745, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, A.; Yamada, S.; Tomisaki, T.; Tanaka, M.; Sakaguchi, T.; Asahina, H.; Suzuki, K.; Ikeda, M. Development and evaluation of a large-area selenium-based flat-panel detector for real-time radiography and fluoroscopy. Med. Imaging 1999 Phys. Med. Imaging 1999, 3659, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, A.; Yamada, S.; Tomisaki, T.; Tanaka, M.; Sakaguchi, T.; Asahina, H.; Nishiki, M. Development of a selenium-based flat-panel detector for real-time radiography and fluoroscopy. Med. Imaging 1998 Phys. Med. Imaging 1998, 3336, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, S.; Hori, N.; Sato, K.; Tokuda, S.; Sato, T.; Uehara, K.; Izumi, Y.; Nagata, H.; Yoshimura, Y.; Yamada, S. Experimental evaluation of a-Se and CdTe flat-panel x-ray detectors for digital radiography and fluoroscopy. Proc. SPIE 2000, 3977, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, D.C.; Tousignant, O.; Rowlands, J.A. Evaluation of the imaging properties of an amorphous selenium-based flat panel detector for digital fluoroscopy. Med. Phys. 2004, 31, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhao, W. Temporal performance of amorphous selenium mammography detectors. Med. Phys. 2004, 32, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semeniuk, O.; Reznik, A.; Sukhovatkin, V. Amorphous lead oxide based energy detection devices and methods of manufacture thereof. U.S. Patent 10,163,970 B2, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, C.A. Bandgap Dependence and Related Features of Radiation Ionization Energies in Semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. 1968, 39, 2029–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blevis, I.M.; Hunt, D.C.; Rowlands, J.A. Measurement of x-ray photogeneration in amorphous selenium. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 7958–7963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, W.; Rowlands, J.A. X-ray photogeneration in amorphous selenium: Geminate versus columnar recombination. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 51, 10500–10507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasap, S.O. X-Ray Photoconductivity of Stabilized Amorphous Selenium. In The World Scientific Reference of Amorphous Materials; Kolobov, A.V., Shimakawa, K., Eds.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2021; pp. 519–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.Z.; Arnab, S.M.; Hijazi, N. Electron–hole pair creation energy in amorphous selenium: Geminate versus columnar recombination. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 21059–21063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, N.; Panneerselvam, D.; Kabir, M.Z. Electron–hole pair creation energy in amorphous selenium for high energy photon excitation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubon, O.; Jandieri, K.; Baranovskii, S.D.; Kasap, S.O.; Reznik, A. Columnar recombination for X-ray generated electron-holes in amorphous selenium and its significance in a-Se x-ray detectors. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachaine, M.; Fallone, B.G. Monte Carlo simulations of X-ray induced recombination in amorphous selenium. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2000, 33, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasap, S.O.; Rowlands, J.A. X-ray photoconductors and stabilized a-Se for direct conversion digital flat-panel X-ray image-detectors. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2000, 11, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasap, S.O.; Haugen, C.; Nesdoly, M.; Rowlands, J.A. Properties of a-Se for use in flat panel X-ray image detectors. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2000, 266–269, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, C.; Kasap, S.O.; Rowlands, J.A. Charge transport and electron-hole-pair creation energy in stabilized a-Se x-ray photoconductors. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1999, 32, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, D.; Rowlands, J.A.; Rawlinson, J.A. Sensitivity of amorphous selenium to x rays from 40 kVp to 18 MV: Measurements and implications for portal imaging. Med. Phys. 1998, 25, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsager, L. Initial recombination of ions. Phys. Rev. 1938, 54, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffé, G. Zur Theorie der Ionisation in Kolonnen. Ann. Phys. 1913, 347, 303–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, J.; Jahankhani, H. The carrier yield in a-Se under electron bombardment. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1989, 1, 8789–8798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kasap, S.O.; Fogal, B.; Kabir, M.Z.; Johanson, R.E.; O’Leary, S.K. Recombination of drifting holes with trapped electrons in stabilized a-Se photoconductors: Langevin recombination. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 1991–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, C.; Kasap, S.O. Langevin recombination of drifting electrons and holes in stabilized a-Se (Cl-doped a-Se: 0.3% As). Philos. Mag. B 1995, 71, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznik, A.; Jandieri, K.; Gebhard, F.; Baranovskii, S.D. Non-Onsager mechanism of long-wave photogeneration in amorphous selenium at high electric fields. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Qian, W.; Xiao, S.; Wang, J.; Zheng, S.; Yang, S. Halide perovskites: A dark horse for direct X-ray imaging. EcoMat 2020, 2, e12064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, H.E.; Cunningham, J.R. The Physics of Radiology, 4th ed.; Charles C Thomas: Springfield, IL, USA, 1983; ISBN 0-398-04669-7. [Google Scholar]
- Stone, M.F.; Zhao, W.; Jacak, B.V.; O’Connor, P.; Yu, B.; Rehak, P. The x-ray sensitivity of amorphous selenium for mammography. Med. Phys. 2002, 29, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasap, S.O.; Aiyah, V.; Polischuk, B.; Baillie, A. X-ray sensitivity of a-Se for x-ray imaging with electrostatic readout. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 2879–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, H.; Laugwitz, F. Quantum efficiency of electroradiographic selenium layers. J. Fuer Signalaufzeichn. 1981, 9, 229–235. [Google Scholar]
- Fourkal, E.; Lachaine, M.; Fallone, B.G. Signal formation in amorphous-Se-based x-ray detectors. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 63, 195204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahyun, M.R.V. Monte Carlo modeling of electrophotographic x-ray detectors. J. Appl. Phys. 1982, 53, 6253–6261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Badal, A.; Allec, N.; Karim, K.S.; Badano, A. Monte Carlo simulation of amorphous selenium imaging detectors. In Medical Imaging 2010: Physics of Medical Imaging, Proceedings of the SPIE Medical Imaging, San Diego, CA, USA, 13–18 February 2010; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2010; Volume 7622, p. 762214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeniuk, O.; Csik, A.; Kökényesi, S.; Reznik, A. Ion-assisted deposition of amorphous PbO layers. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 7937–7946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demers, H.; Poirier-Demers, N.; Couture, A.R.; Joly, D.; Guilmain, M.; de Jonge, N.; Drouin, D. Three-dimensional electron microscopy simulation with the CASINO Monte Carlo software. Scanning 2011, 33, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbell, J.H.; Seltzer, S.M. Tables of X-Ray Mass Attenuation Coefficients and Mass Energy-Absorption Coefficients from 1 keV to 20 MeV for Elements Z = 1 to 92 and 48 Additional Substances of Dosimetric Interest. 2004. Available online: http://physics.nist.gov/xaamdi (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Drouin, D.; Couture, A.R.; Joly, D.; Tastet, X.; Aimez, V.; Gauvin, R. CASINO V2.42—A Fast and Easy-to-use Modeling Tool for Scanning Electron Microscopy and Microanalysis Users. Scanning 2007, 29, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, D.C. Monte Carlo Modeling for Electron Microscopy and Microanalysis; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; ISBN 978-0-1950-8874-8. [Google Scholar]
- Vilar-Palop, J.; Vilar, J.; Hernández-Aguado, I.; González-Álvarez, I.; Lumbreras, B. Updated effective doses in radiology. J. Radiol. Prot. 2016, 36, 975–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowlands, J.A.; Yorkston, J. Flat Panel Detectors for Digital Radiography. In Handbook of Medical Imaging, Volume 1. Physics and Psychophysics; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2000; pp. 223–328. ISBN 978-0-8194-7772-9. [Google Scholar]
- Boone, J. X-ray Production, Interaction, and Detection in Diagnostic Imaging. In Handbook of Medical Imaging, Volume 1. Physics and Psychophysics; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2000; pp. 1–78. ISBN 978-0-8194-7772-9. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, M.J.; Hubbell, J.H.; Seltzer, S.M.; Chang, J.; Coursey, J.S.; Sukumar, R.; Zucker, D.S.; Olsen, K. XCOM: Photon Cross Sections Database. 2010. Available online: http://physics.nist.gov/xcom (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Grynko, O.; Thibault, T.; Pineau, E.; Juska, G.; Reznik, A. Bilayer lead oxide X-ray photoconductor for lag-free operation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, D.M.; Barnes, G.T.; Chakraborty, D.P. Semiempirical model for generating tungsten target X-ray spectra. Med. Phys. 1991, 18, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knights, J.C.; Davis, E.A. Photogeneration of charge carriers in amorphous selenium. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1974, 35, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.J.; Coursey, J.S.; Zucker, M.A.; Chang, J. Stopping-Power & Range Tables for Electrons, Protons, and Helium Ions. 2017. Available online: http://physics.nist.gov/Star (accessed on 1 October 2021).
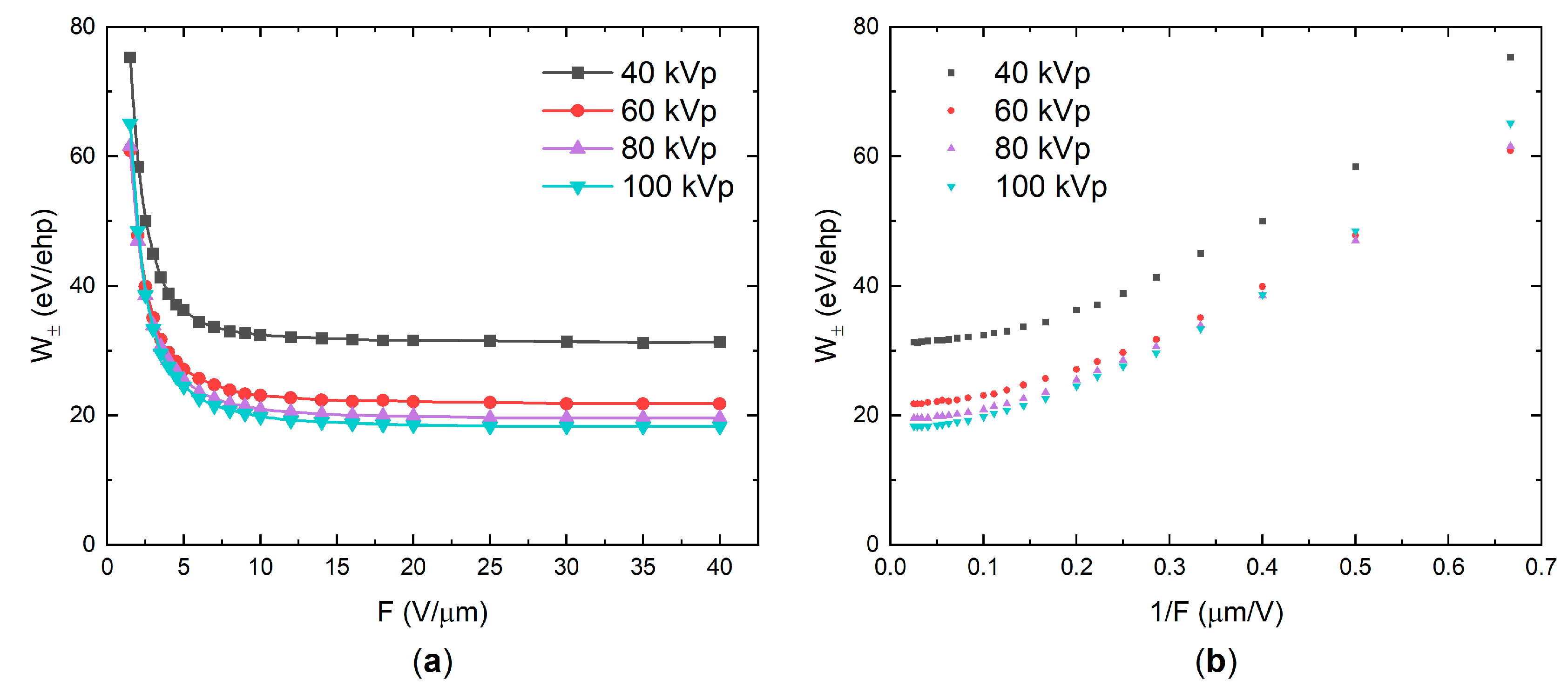

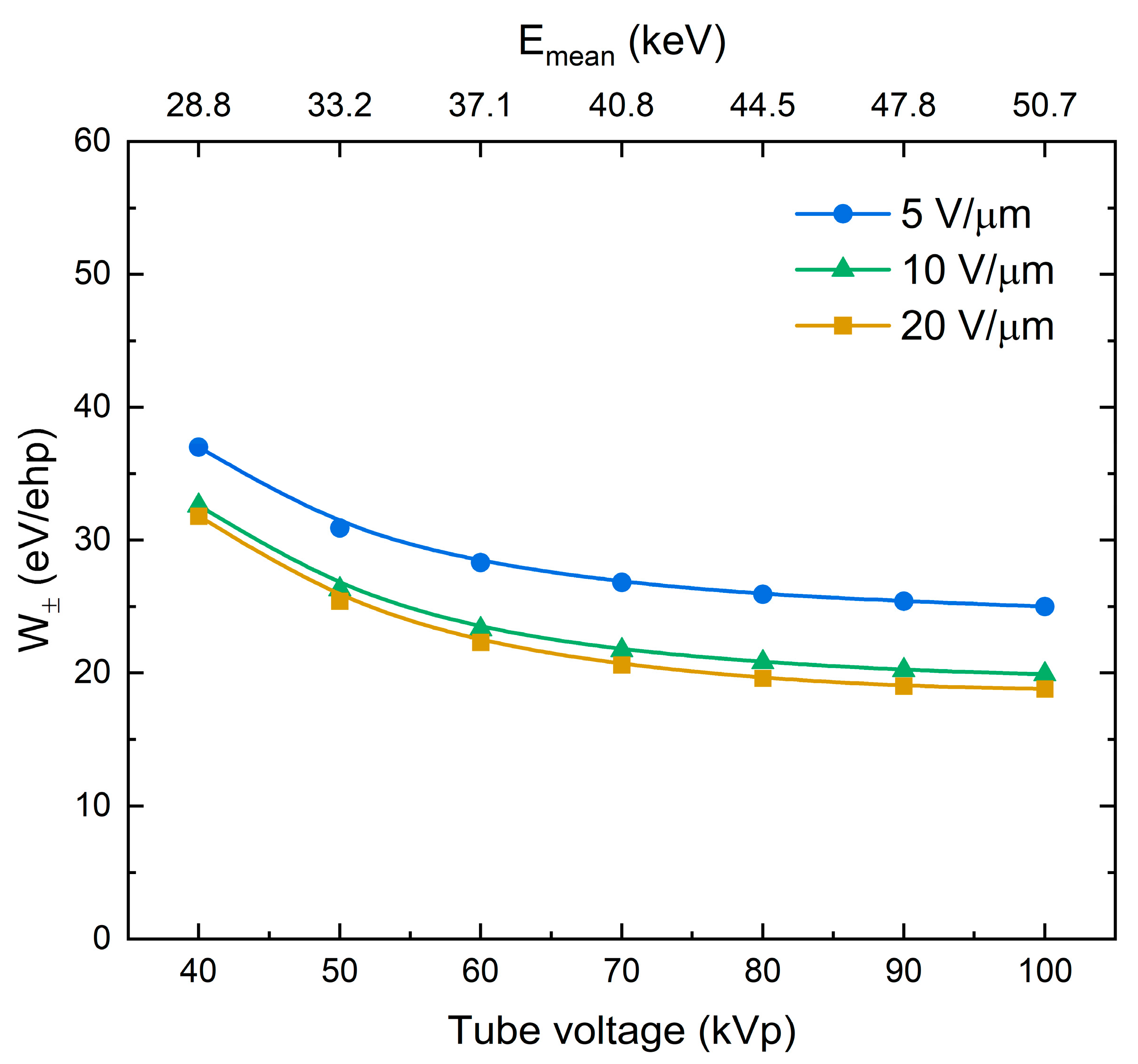


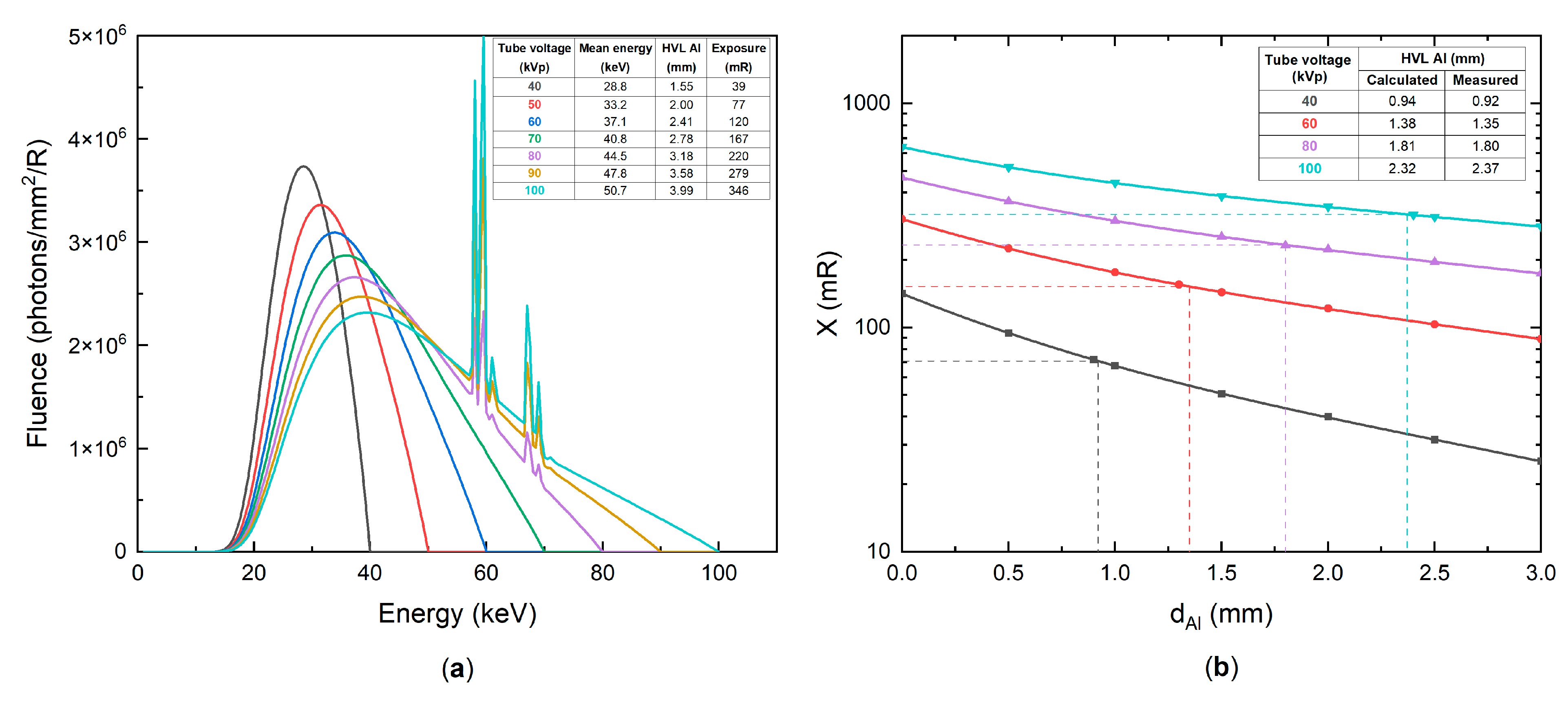
| Tube Voltage (kVp)/ Mean X-ray Energy (keV) | Electron Energy (keV) | Dissipated Energy Per Collision (eV) | Mean Free Path (nm) | Range (μm) | Energy Deposition Rate (eV/nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40/28.8 | 15.8 | 35.3 | 3.9 | 1.6 | 11.8 |
| 60/37.1 | 24.1 | 33.9 | 5.0 | 3.3 | 9.0 |
| 80/44.5 | 31.5 | 33.4 | 5.9 | 5.1 | 7.7 |
| 100/50.7 | 37.7 | 33.6 | 6.5 | 6.8 | 7.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grynko, O.; Thibault, T.; Pineau, E.; Reznik, A. The X-ray Sensitivity of an Amorphous Lead Oxide Photoconductor. Sensors 2021, 21, 7321. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217321
Grynko O, Thibault T, Pineau E, Reznik A. The X-ray Sensitivity of an Amorphous Lead Oxide Photoconductor. Sensors. 2021; 21(21):7321. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217321
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrynko, Oleksandr, Tristen Thibault, Emma Pineau, and Alla Reznik. 2021. "The X-ray Sensitivity of an Amorphous Lead Oxide Photoconductor" Sensors 21, no. 21: 7321. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217321
APA StyleGrynko, O., Thibault, T., Pineau, E., & Reznik, A. (2021). The X-ray Sensitivity of an Amorphous Lead Oxide Photoconductor. Sensors, 21(21), 7321. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217321






