Highly Sensitive Voltammetric Determination of Acrylamide Based on Ibuprofen Capped Mercury Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Synthesis of Ibu-HgNPs
2.4. STEM Characterization of HgNPs
2.5. Cleaning and Modification of Glassy Carbon Electrode
2.6. Voltammetric Studies
2.7. Application of Ibu-HgNPs-GCE to Tap Water Samples and River Indus Water Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Modified Electrode (Ibu-HgNPs-GCE)
3.1.1. UV-Vis Spectrophotometry
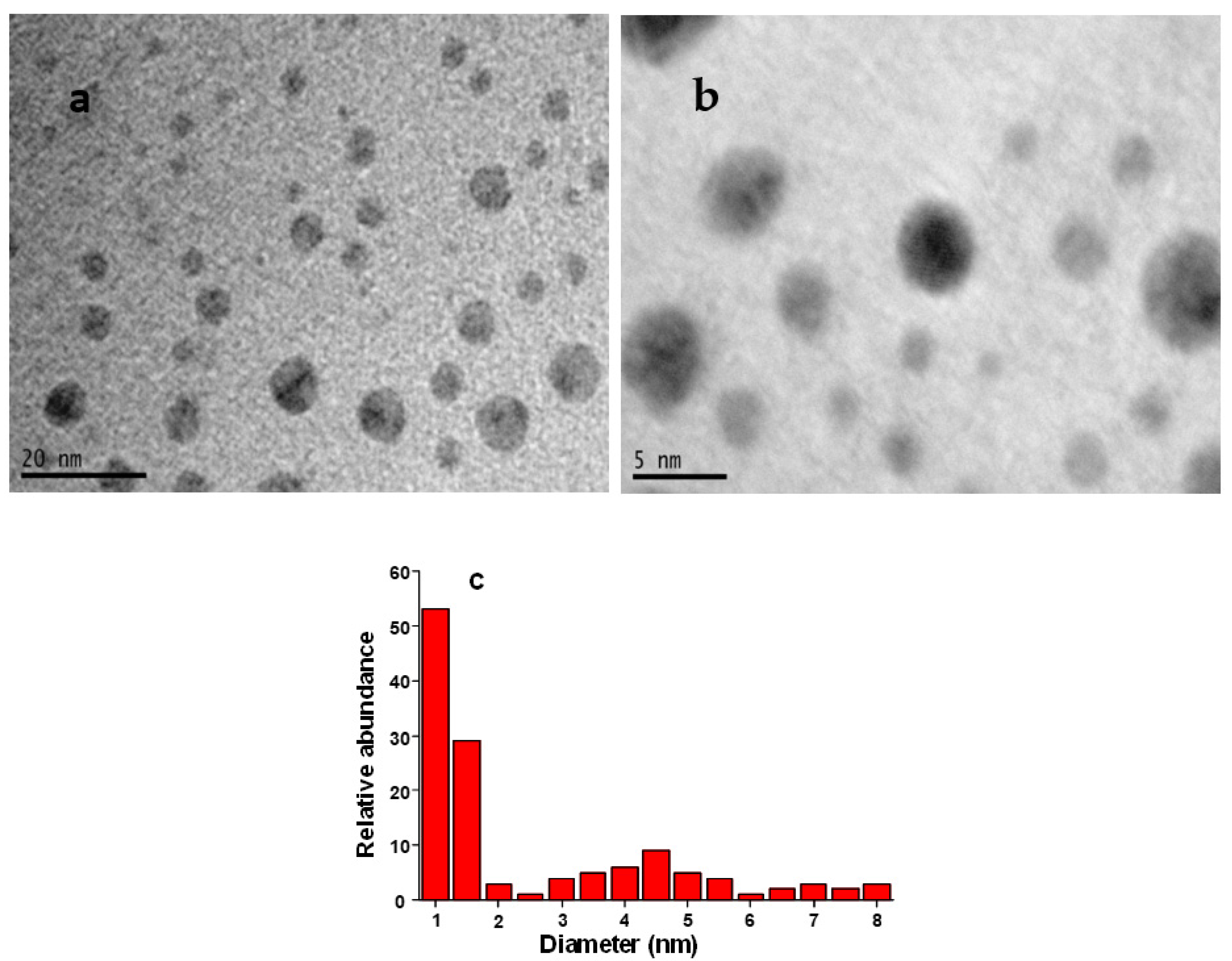
3.1.2. TEM Characterization of HgNPs
 or
or  -OOC-I show the interaction of ibuprofen with HgNPs, resulting in their stabilization against agglomeration. Firstly, hydrazine (N2H2) is converted into gaseous N2 and H2 where N2 plays the role of remover of oxygen from water, thus hindering oxygen attack on HgNPs and hence avoiding the formation of HgO, while H2 works as a strong reducer for the conversion of Hg2+ ions into HgNPs. Ibuprofen (represented as I-COOH in Figure 4) is present at the used pH in dissociated-form I-COO-. As soon as the HgNPs are formed via reduction by hydrazine, the ibuprofen interacts with HgNPs to keep them small and stabilized against agglomeration. The TEM images in Figure 3 prove the presence of small and ibuprofen-stabilized HgNPs.
-OOC-I show the interaction of ibuprofen with HgNPs, resulting in their stabilization against agglomeration. Firstly, hydrazine (N2H2) is converted into gaseous N2 and H2 where N2 plays the role of remover of oxygen from water, thus hindering oxygen attack on HgNPs and hence avoiding the formation of HgO, while H2 works as a strong reducer for the conversion of Hg2+ ions into HgNPs. Ibuprofen (represented as I-COOH in Figure 4) is present at the used pH in dissociated-form I-COO-. As soon as the HgNPs are formed via reduction by hydrazine, the ibuprofen interacts with HgNPs to keep them small and stabilized against agglomeration. The TEM images in Figure 3 prove the presence of small and ibuprofen-stabilized HgNPs.3.2. Voltammetric Study
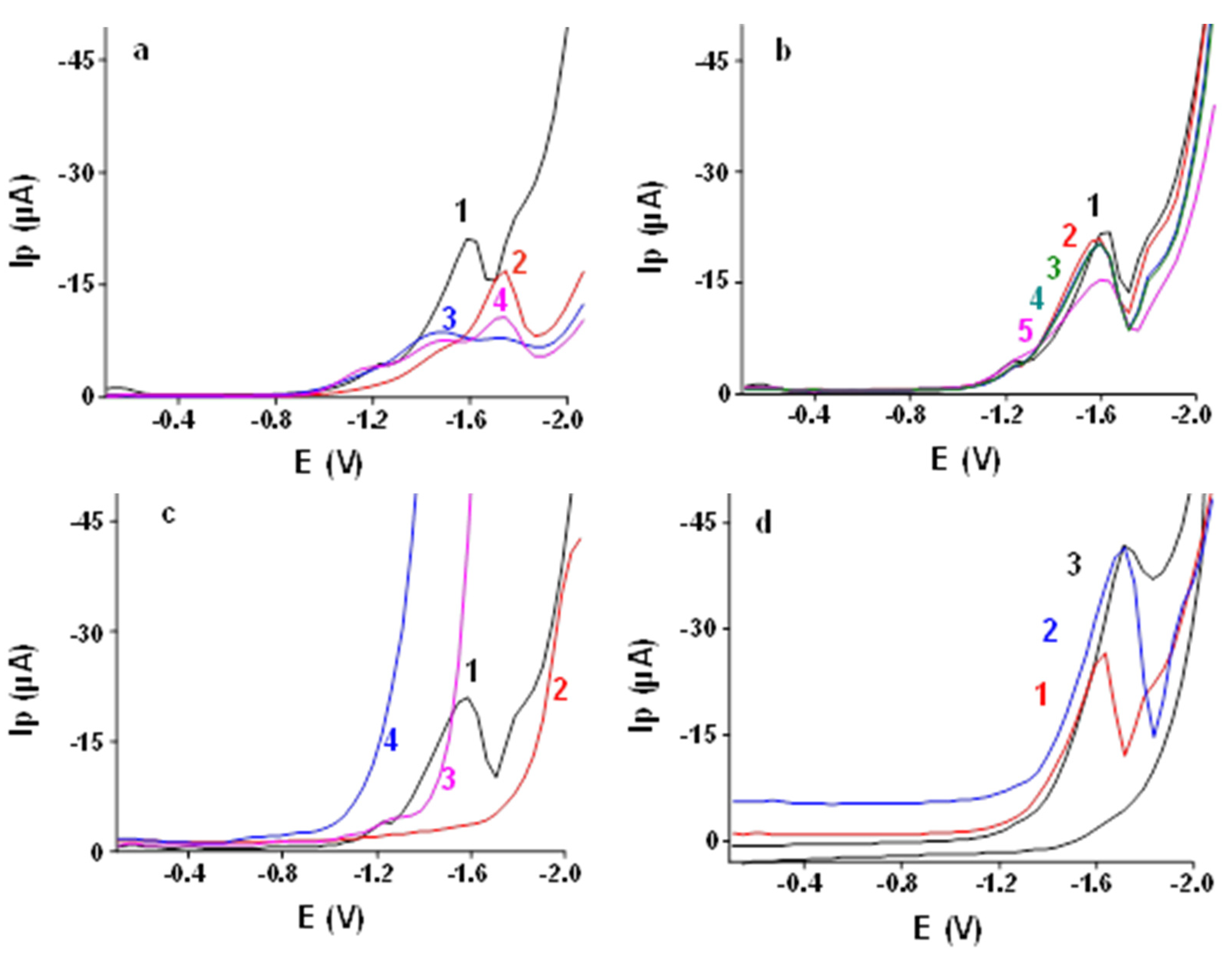
3.2.1. Effect of Different Supporting Electrolytes
3.2.2. Effect of Ratio of LiCl to TMAB in Supporting Electrolytes
3.2.3. Comparison of Different Working Electrodes
3.2.4. Comparison of Different Voltammetric Techniques
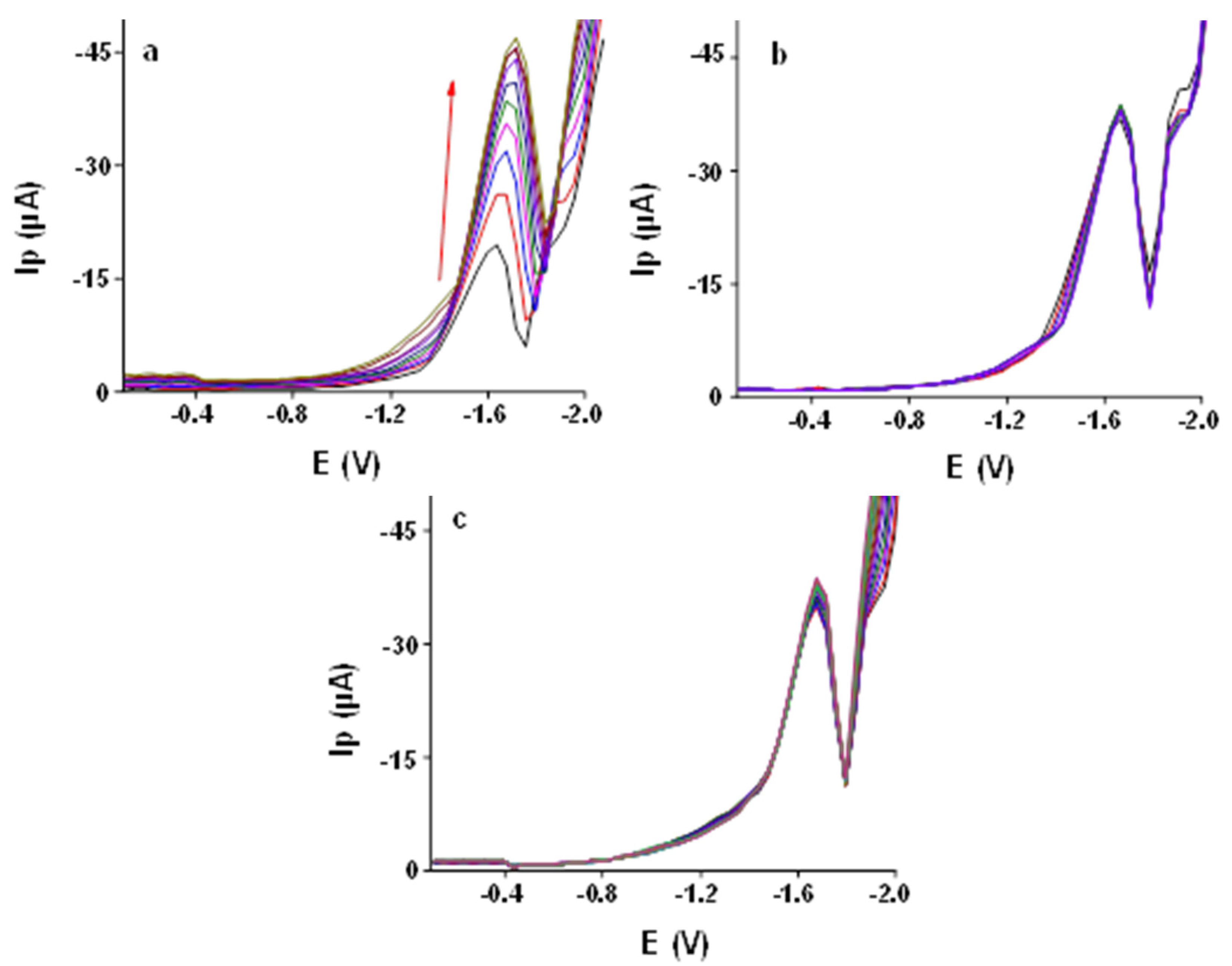
3.2.5. Effect of SWV Frequency
3.2.6. Effect of Accumulation Time and Stirring Rate
3.2.7. Effect of Initial Potential
3.2.8. Repeatability Test
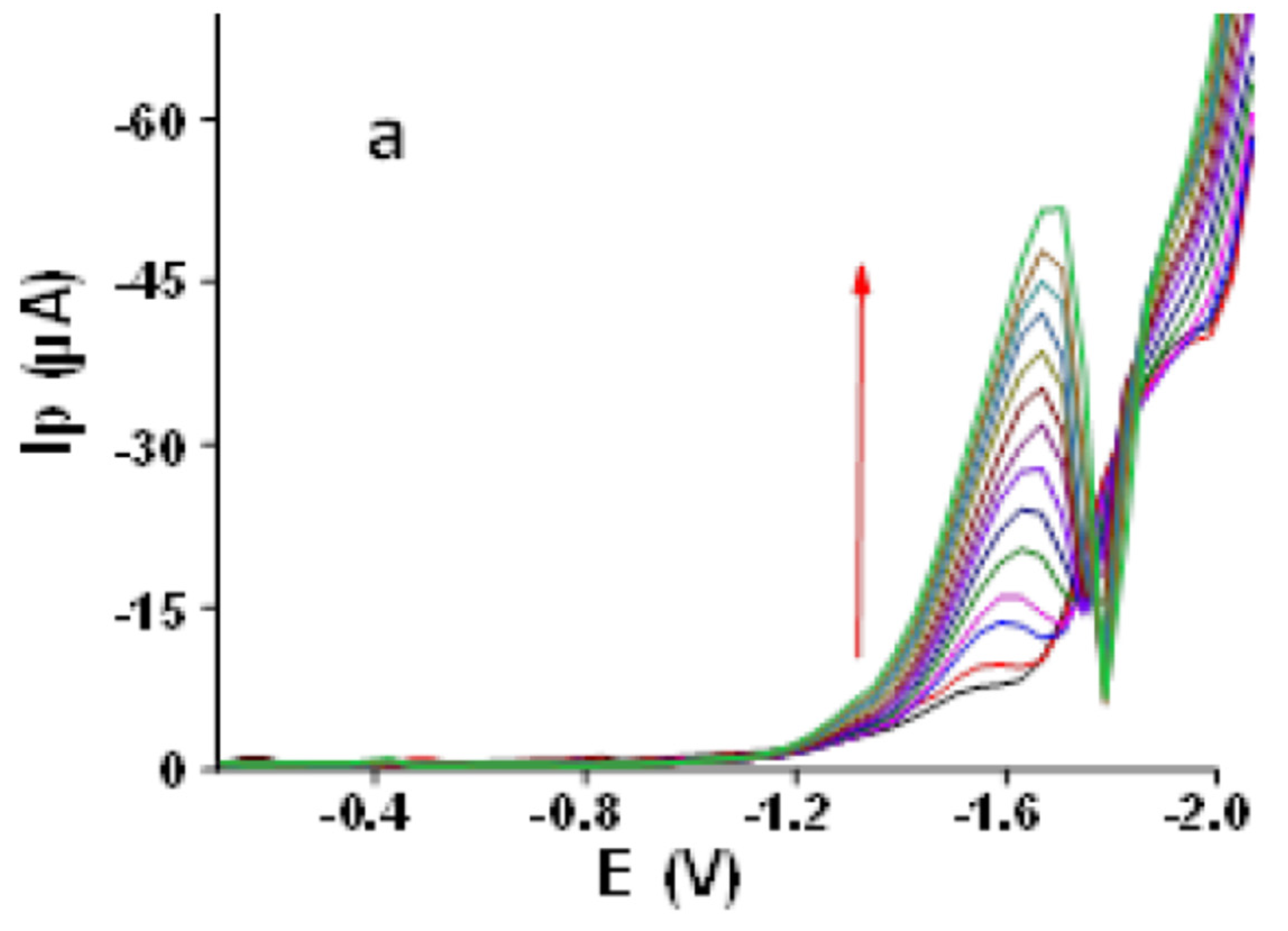
3.2.9. Calibration Plot
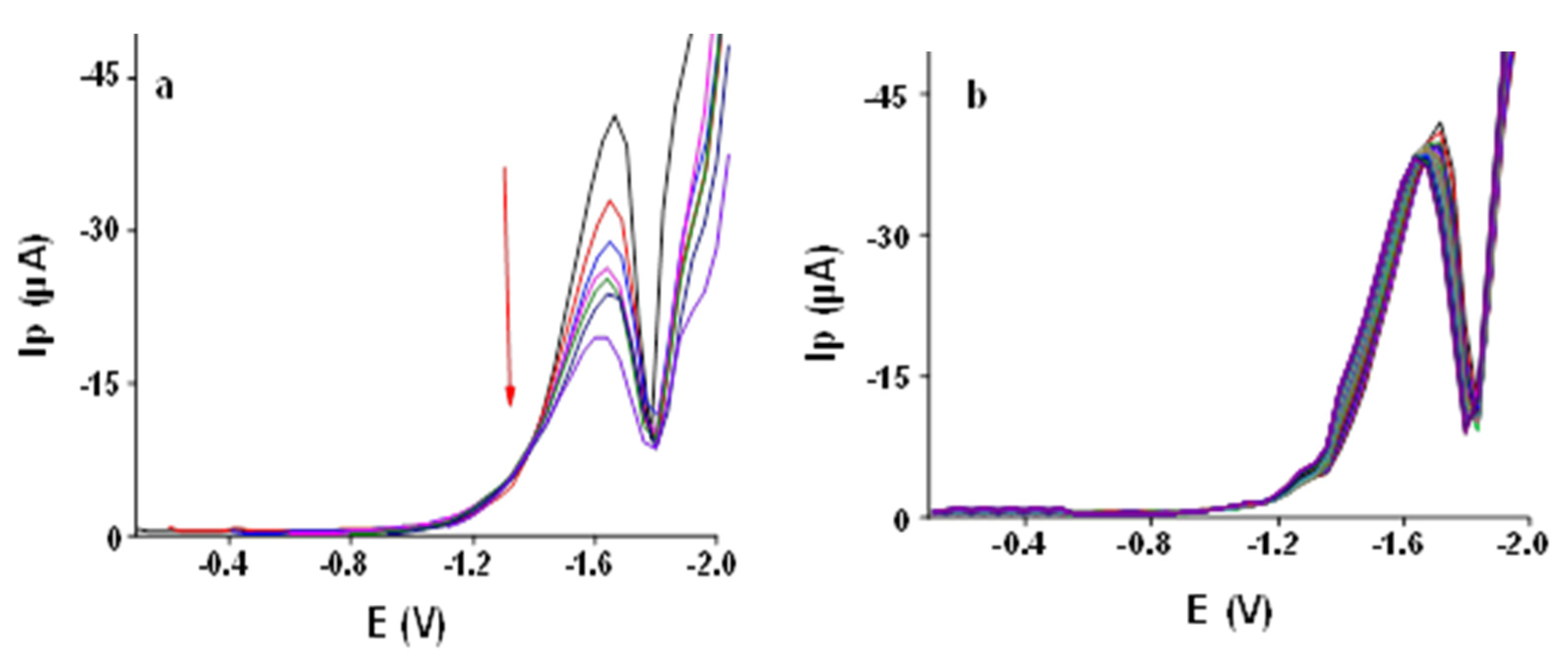
3.2.10. Interferences
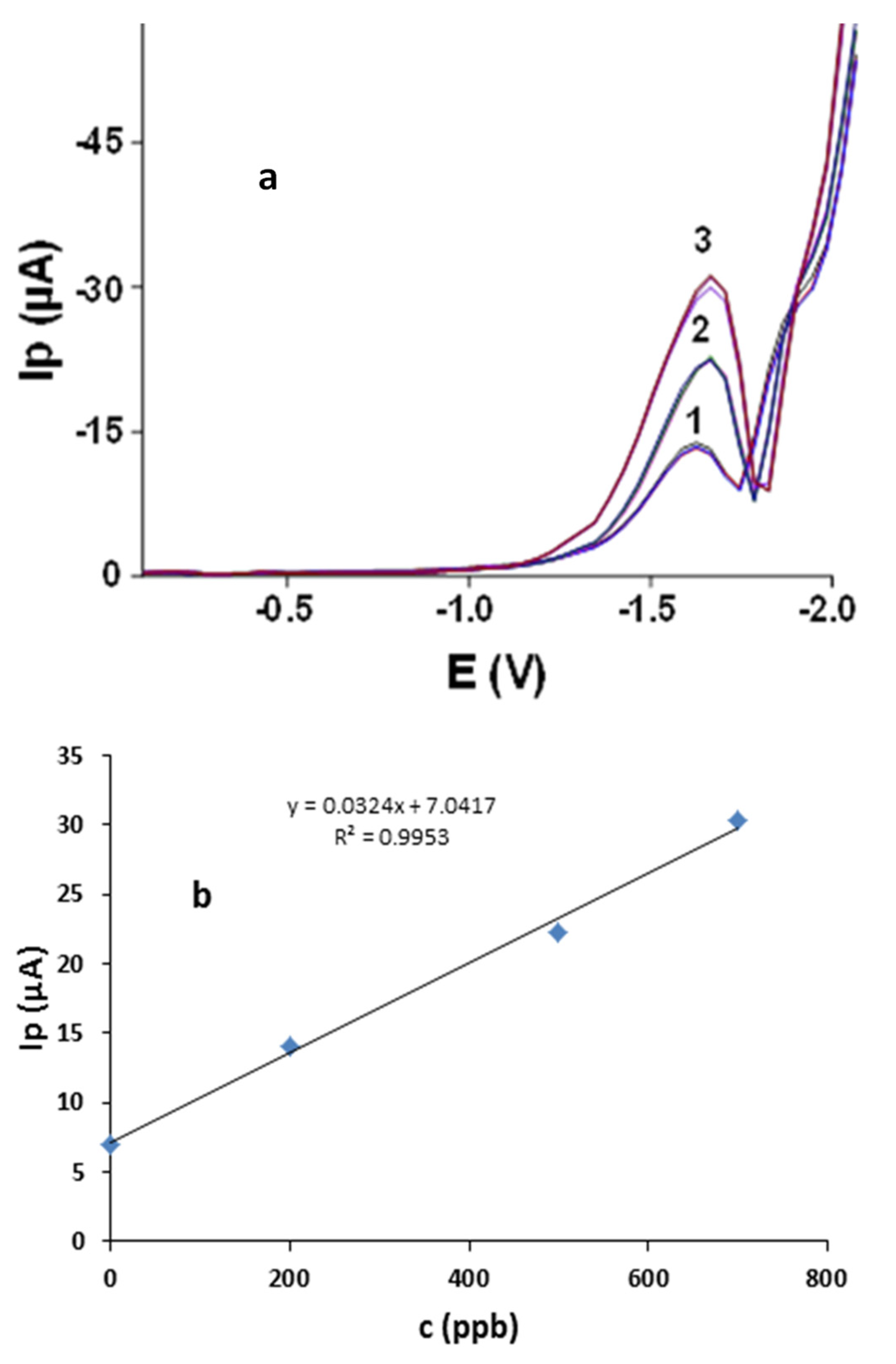
3.2.11. Application of Ibu-HgNPs-GCE to Real Water Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedman, M. Chemistry, biochemistry and safety of acrylamide: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 4504–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpmann, A.; Morlock, G. Rapid and sensitive determination of acrylamide in drinking water by planar chromatography and fluorescence detection after derivatization with dansulfinic acid. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurenkov, V.F.; Hartan, H.-G.; Lobanov, F.I. Application of polyacrylamide flocculants for water treatment. Chem. Comput. Simul. Butl. Commun. 2002, 3, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Dearfield, K.L.; Douglas, G.R.; Ehling, U.H.; Moore, M.M.; Sega, G.A.; Brusick, D.J. Acrylamide: A review of its genotoxicity and an assessment of heritable genetic risk. Mutat. Res. 1995, 330, 71–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, I.G.; Pierri, M.; Contursi, M. Determination of acrylamide and acrylic acid by isocratic liquid chromatography with pulsed electrochemical detection. J. Chromatogr. A. 2006, 1107, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Z.; Jiang, R.; Chen, M. Determination of acrylamide in starch-based foods by ion-exclusion liquid chromatography. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2008, 21, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, G.; Duan, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y. Application of the standard addition method for the determination of acrylamide in heat-processed starchy foods by gas chromatography with electron capture detector. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermudo, E.; Moyano, E.; Puignou, L.; Galceran, M.T. Determination of acrylamide in foodstuffs by liquid chromatography ion-trap tandem mass-spectrometry using an improved clean-up procedure. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 559, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarrke, E.; Rudberg, P.; Karlsen, P.; Eriksson, S.; Tornqvist, M. Analysis of acrylamide, a carcinogen formed in heated foodstuffs. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4998–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, S.; Polesello, S.; Saccani, G. Determination of acrylamide in drinking water by large-volume direct injection and ion-exclusion chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1039, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, D.S.; Hunt, J.; Pachin, R.M.L.; Ehrich, M. Determination of acrylamide and glycidamide in rat plasma by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2001, 758, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Singh, P.; Raja, R.B. Determination of acrylamide concentration in processed food products using normal phase high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 8085–8091. [Google Scholar]
- Karasek, L.; Wenzl, T.; Anklam, E. Determination of acryl amide in roasted chest nuts and chestnut-based foods by isotopes dilution HPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1555–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Fu, Y.; Xu, X.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, R.Y.; Zhang, Y. Li, A colorimetric detection of acrylamide in potato chips based on nucleophile-initiated thiol-ene Michael addition. Analyst 2016, 141, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharinikoo, L.; Chaichi, M.J.; Ganjali, M. Detecting the quantity of acrylamide in potato chips utilizing CdTe surface functionalized quantum dots with fluorescence spectroscopy. Int. J. Pept. Res. Therap. 2020, 26, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargar, B.; Sahraie, N.R.; Khoshnam, F. Catalytic square-wave voltammetric determination of acrylamide in Potato Chips. Anal. Lett. 2009, 42, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaz, A.; Sirajuddin; Shah, A.; Bhanger, M.I.; Saeed, M.; Jamali, M.K.; Arain, M.B. A new simple sensitive differential pulse polarographic method for the determination of acrylamide in aqueous solution. Talanta 2008, 74, 1608–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, A.; Radecki, J.; Radecka, H.A. Voltammetric biosensor based on glassy carbon electrodes modified with single-walled carbon nanotubes/hemoglobin for detection of acrylamide in water extracts from potato crisps. Sensors 2008, 8, 5832–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Mao, L.-G.; Wang, Y.-L.; Shi, X.-B.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; He, Z. Electrochemical sensor based on imprinted sol-gel polymer on AuNPs-MWCNTs-CS modified electrode for the determination of acrylamide. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnaashari, M.; Kenari, R.E.; Farahmandfar, R.; Abnous, K.; Taghdis, S.M. An electrochemical biosensor based on hemoglobin-oligonucleotides modified electrode for detection of acrylamide in potato fries. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagar, Z.A.; Sirajuddin; Memon, N.; Kalhoro, M.S.; O’Brien, P.; Malik, M.I.; Abro, M.A.; Hassan, N.H.; Kalwar, S.S.; Junejo, Y. Highly sensitive, selective and stable multi-metal ions sensor based on ibuprofen capped mercury nanoparticles. Sens Actuators B 2012, 173, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harika, V.H.; Penki, T.R.; Loukya, B.; Samanta, A.; Xu, G.-L.; Sun, C.-J.; Grinberg, I.; Deepak, F.L.; Amine, K.; Aurbach, D.; et al. Sustainable existence of solid mercury (Hg) nanoparticles at room temperature and their applications. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 3226–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugo, P.; Cavalieri, F.; Rudello, D.; Moreto, L.M. Nafion Coated Electrodes as Voltammetric Sensors for Iron Analysis in Sediments and Pore Waters: An Example from the Lagoon of Venice. Sensors 2001, 1, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macwilliams, D.C.; Kaufman, D.C.; Waling, B.F. Polarographic and spectrophotometric determination of acrylamide in acrylamide polymers and copolymers. Anal. Chem. 1965, 37, 1546–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Lu, S.; Huang, C.; Sheng, J.; Zhang, L.; Su, W.; Xiao, Q. An electrochemical biosensor based on single-stranded DNA modified gold electrode for acrylamide determination. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 224, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucur, M.P.; Bucur, B.; Radu, G.L. Simple, selective and fast detection of acrylamide based on glutathione S-transferase. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 23931–23936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Interferent | Interference, % |
|---|---|
| K+ | +1.2 |
| Na+ | +1.5 |
| Ca2+ | +2 |
| NH4+ | +2.6 |
| Acetone | −1.1 |
| Formaldehyde | −1.5 |
| Acrolein | +0.7 |
| Acrylic acid | +0.5 |
| Maleic acid | −3.5 |
| Glucose | −2.1 |
| Citric acid | −3.4 |
| Starch | +0 |
| Local Water Sample | AA Added (ppb) | AA Found ± SD (ppb) * | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | - a | |
| 2 | 200 | 198 ± 0.6 | 99 |
| 3 | 500 | 501 ± 0.4 | 100.2 |
| 4 | 700 | 699 ± 1 | 99.8 |
| Mean 99.6 |
| Indus River Water | AA Added a (ppb) | AA Found ± SD (ppb) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kotri site | 150 | 148 ± 3.8 | 98.7 |
| Al-Manzar site | 300 | 295 ± 2.8 | 98.3 |
| Jamshoro site | 500 | 505 ± 4.1 | 101 |
| Technique | Electrode | Linear Range | LOD | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DP polarography | DME | 0.2–20 ppm | 27 ppb | [17] |
| DPV | AuNPs-MWCNTs-CS-GCE | 0.05–5 ppm | 28 ppb | [21] |
| SWV | DNA/HG/SPGE | 0.142–355.4 ppm | 11.23 ppb | [22] |
| Polarography | DME | 100–5000 ppm | 70 ppm | [24] |
| DPV | SH-ssDNA-Au electrode | 0.028–14216 ppm | 0.58 ppb | [25] |
| Amperometry | Co-phthalocyanine modified SPE | 0.5–3500 ppm | 355 ppb | [26] |
| SWV | HgNPs-GCE | 0.1–1.3 ppm | 8.5 ppb | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sirajuddin; Tagar, Z.A.; Ul Haq, M.A.; Shah, M.R.; Mujeeb-ur-Rehman; Sherazi, S.T.H.; Barek, J.; Kalhoro, M.S. Highly Sensitive Voltammetric Determination of Acrylamide Based on Ibuprofen Capped Mercury Nanoparticles. Sensors 2021, 21, 7302. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217302
Sirajuddin, Tagar ZA, Ul Haq MA, Shah MR, Mujeeb-ur-Rehman, Sherazi STH, Barek J, Kalhoro MS. Highly Sensitive Voltammetric Determination of Acrylamide Based on Ibuprofen Capped Mercury Nanoparticles. Sensors. 2021; 21(21):7302. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217302
Chicago/Turabian StyleSirajuddin, Zulfiqar Ali Tagar, Muhammad Anwar Ul Haq, Muhammad Raza Shah, Mujeeb-ur-Rehman, Syed Tufail Hussain Sherazi, Jiri Barek, and Muhammad Siddique Kalhoro. 2021. "Highly Sensitive Voltammetric Determination of Acrylamide Based on Ibuprofen Capped Mercury Nanoparticles" Sensors 21, no. 21: 7302. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217302
APA StyleSirajuddin, Tagar, Z. A., Ul Haq, M. A., Shah, M. R., Mujeeb-ur-Rehman, Sherazi, S. T. H., Barek, J., & Kalhoro, M. S. (2021). Highly Sensitive Voltammetric Determination of Acrylamide Based on Ibuprofen Capped Mercury Nanoparticles. Sensors, 21(21), 7302. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217302








