Recent Progress in Self-Powered Sensors Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Principle of TENG
2.1. Triboelectrification Effect (Contact Electrification)
2.2. Triboelectric Sequence
2.3. Maxwell’s Displacement Current
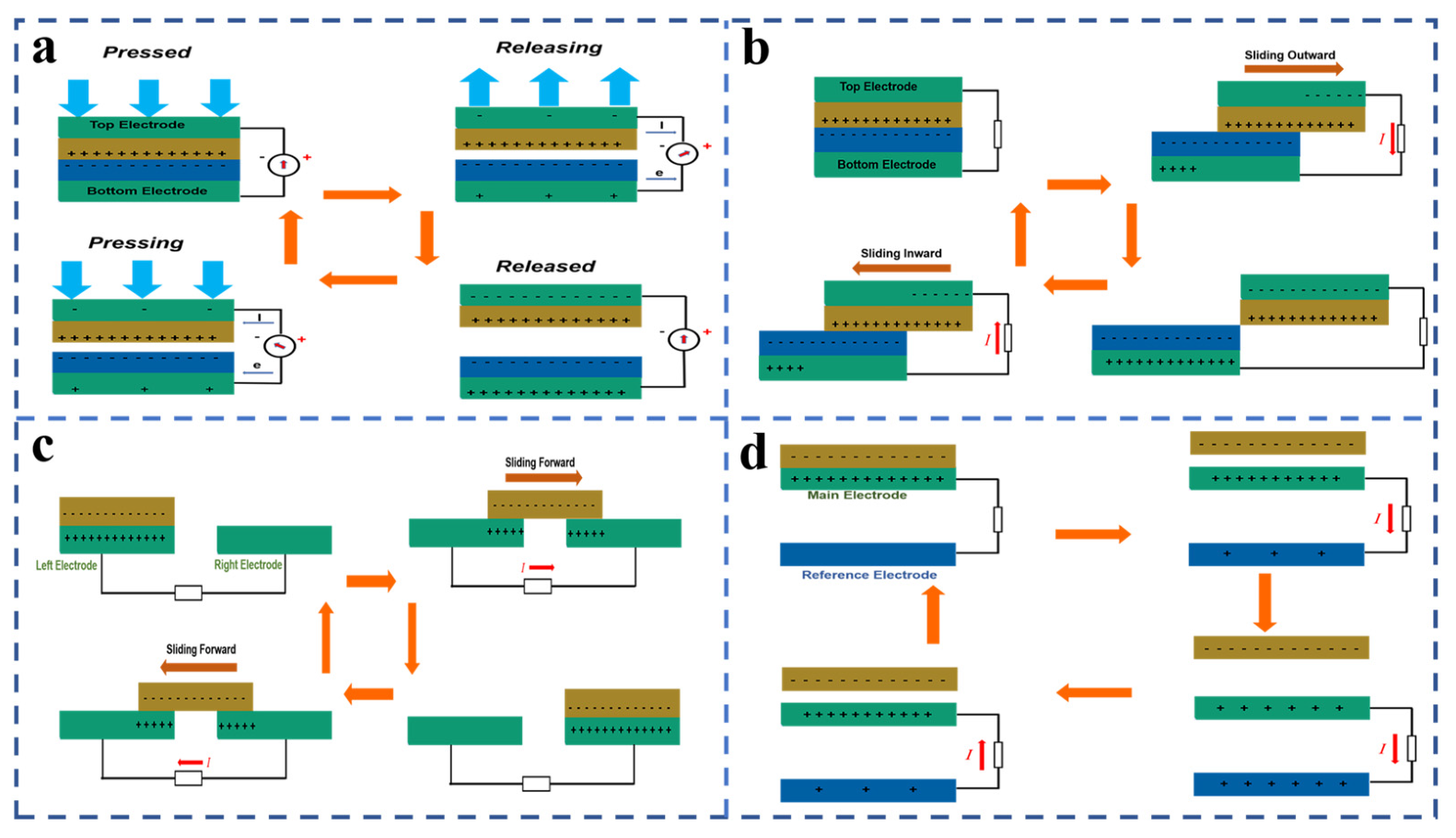
3. Main Working Mode and Quantitative Analysis Method of TENG
3.1. Main Working Modes of TENG
3.2. TENG Quantitative Analysis Method
4. Enhancing Output Performances
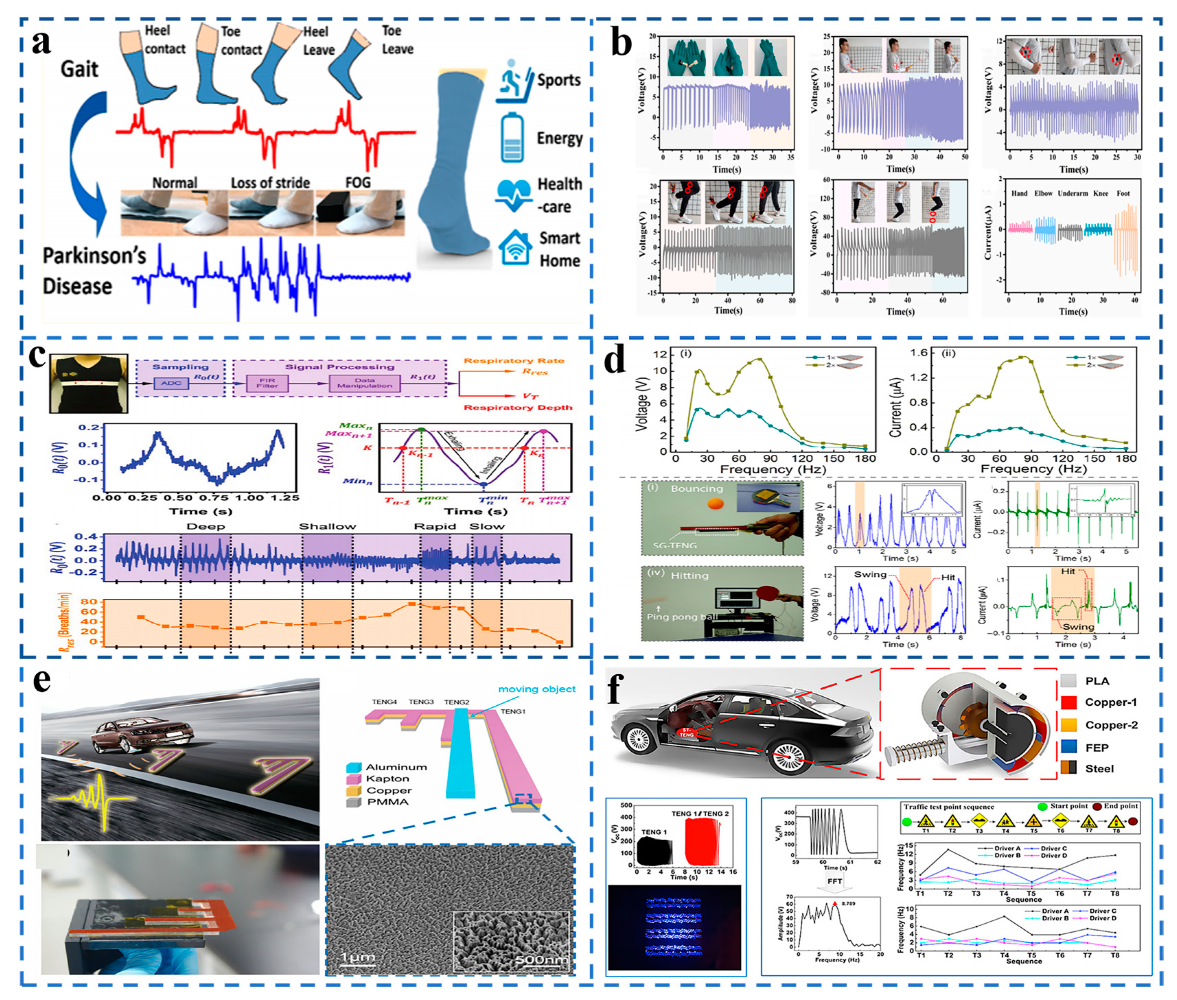
5. Application of TENG in the Field of Motion Detection
6. Application of TENG-Based Sensors in Marine Fields
7. Application of TENG in Environmental Monitoring
8. Medical Applications of TENG Sensors
9. Application of TENG in the Smart Skin Field
10. The Matching of Capacitance and Load in TENG Detection Systems and the Cost of TENG Detectors
11. Summary and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, F.-R.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as new energy technology for self-powered systems and as active mechanical and chemical sensors. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9533–9557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jsa, B.; Yu, C.A.; Lin, D.A.; Kz, A.; Qhb, C.; Jz, A.; Qc, B.; Ys, A.; Cpb, C.; Cs, A. MXene enhanced self-powered alternating current electroluminescence devices for patterned flexible displays. Nano Energy 2021, 86, 106077. [Google Scholar]
- Li, E.; Pan, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; Pan, C.; Liu, X. Multifunctional and superhydrophobic cellulose composite paper for electromagnetic shielding, hydraulic triboelectric nanogenerator and Joule heating applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, S.; Yue, X.; Pan, C.; Li, X. Energy efficiency characterization in heterogeneous Iot system with uav swarms based on wireless power transfer. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Lu, J.; Peng, D.; Ma, W.; Li, F.; Chen, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Liu, H.; Pan, C. Dynamically modulated GaN whispering gallery lasing mode for strain sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1905051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, K.H.; Chung, C.K. High-Performance Al/PDMS TENG with Novel Complex Morphology of Two-Height Microneedles Array for High-Sensitivity Force-Sensor and Self-Powered Application. Small 2020, 16, 2001209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Ma, C.; Sun, J.; Tian, L.; Li, X.; Li, F.; Han, X.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; et al. Detection of non-joint areas tiny strain and anti-interference voice recognition by micro-cracked metal thin film. Nano Energy 2017, 34, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. From contact electrification to triboelectric nanogenerators. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2021, 84, 096502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Zi, Y. Achieving ultrahigh instantaneous power density of 10 MW/m2 by leveraging the opposite-charge-enhanced transistor-like triboelectric nanogenerator (OCT-TENG). Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, G.; Xia, X.; Fu, J.; Huang, L.; Zi, Y. Standardization of triboelectric nanogenerators: Progress and perspectives. Nano Energy 2018, 56, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, J. Triboelectric nanogenerator: From alternating current to direct current. iScience 2020, 24, 102018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabish, T.J.; Duke, C.B. Molecular charge states and contact charge exchange in polymers. J. Appl. Phys. 1977, 48, 4256–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Wang, A.; Wu, C.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.L. Human-machine interfacing enabled by triboelectric nanogenerators and tribotronics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG)—Sparking an energy and sensor revolution. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, W.A.; Jia, C.A.; Zw, A.; Lj, A.; Zhong, L. Triboelectric nanogenerators for human-health care. Sci. Bull. 2020, 66, 490–511. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.L. Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science 2006, 312, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhong, L.W. Reviving vibration energy harvesting and self-powered sensing by a triboelectric nanogenerator. Joule 2017, 1, 480–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Jiang, T.; Xu, L. Toward the blue energy dream by triboelectric nanogenerator networks. Nano Energy 2017, 39, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Willatzen, M.; Jiang, T.; Tang, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Quantifying the power output and structural figure-of-merits of triboelectric nanogenerators in a charging system starting from the maxwell’s displacement current. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lau, T.H.; Guan, D.; Zi, Y. A universal method for quantitative analysis of triboelectric nanogenerators. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 19485–19494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.M.S.; Rahman, M.T.; Salauddin, M.; Sharma, S.; Maharjan, P.; Bhatta, T.; Cho, H.; Park, C.; Park, J.Y. Electrospun PVDF-TrFE/MXene nanofiber mat-based triboelectric nanogenerator for smart home appliances. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 4955–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Cho, H.; Han, M.; Jung, Y.; Kwak, S.S.; Yoon, H.; Park, B.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Park, J.; et al. Ultrahigh power output from triboelectric nanogenerator based on serrated electrode via spark discharge. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Wu, D.; Fu, J.; Hoque, N.A.; Ye, Y.; Xu, Z. A high-output triboelectric nanogenerator based on nickel–copper bimetallic hydroxide nanowrinkles for self-powered wearable electronics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 25995–26003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, H.E.; Wang, H.S.; Kang, S.; Lee, D.; Kim, Y.H.; Shin, J.H.; Lim, Y.; Lee, K.J.; Bae, B. Hierarchically surface-textured ultrastable hybrid film for large-scale triboelectric nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhang, L.; Xue, F.; Tang, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Multilayered electret films based triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Xu, G.; Li, C.; Xia, X.; Guan, D.; Li, J.; Huang, Z.; Zi, Y. Achieving ultrahigh output energy density of triboelectric nanogenerators in high-pressure gas environment. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2001757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Pan, C.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Lightweight, superelastic, and hydrophobic polyimide Nanofiber/MXene composite aerogel for wearable piezoresistive sensor and Oil/Water separation applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2008006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Bu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, C.; Pan, C.; Mi, L.; Guo, Z.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Stretchable conductive nonwoven fabrics with self-cleaning capability for tunable wearable strain sensor. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Shi, Q.; He, T.; Yi, Z.; Ma, Y.; Yang, B.; Chen, T.; Lee, C. Self-powered and self-functional cotton sock using piezoelectric and triboelectric hybrid mechanism for healthcare and sports monitoring. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1940–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Hao, Y.; Zhao, M.; Qiao, H.; Huang, F.; Li, D.; Wei, Q. Biomass-based wearable and Self-powered pressure sensor for human motion detection. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 146, 106412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yan, C.; Liu, Z.; Fu, X.; Peng, L.-M.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, Z. Machine-washable textile triboelectric nanogenerators for effective human respiratory monitoring through loom weaving of metallic yarns. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 10267–10274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zhu, W.; Gu, G.Q.; Jiang, T.; Xu, L.; Chen, B.D.; Han, C.B.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.L. Integrative square-grid triboelectric nanogenerator as a vibrational energy harvester and impulsive force sensor. Nano Res. 2017, 11, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Zhang, S.L.; Xu, S.; Guo, H.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Free-fixed rotational triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered real-time wheel monitoring. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2000918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, X.; Lin, L.; Du, W.; Han, X.; Zhu, J.; Pan, C.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as a self-powered motion tracking system. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5059–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Xu, Y.; Lu, X.; Cheng, T.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.L. Novel sweep-type triboelectric nanogenerator utilizing single freewheel for random triggering motion energy harvesting and driver habits mmonitoring. Nano Energy 2020, 68, 104360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Pan, C.; Wang, Z.L. Networks of high performance triboelectric nanogenerators based on liquid-solid interface contact electrification for harvesting low-frequency blue energy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhao, T.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.L.; Li, Z.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.L. High power density tower-like triboelectric Nanogenerator for harvesting arbitrary directional water wave energy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1932–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Han, J.; Li, L.; An, J.; Chen, P.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Spherical triboelectric nanogenerator based on spring-assisted swing structure for effective water wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2021, 83, 105836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Feng, Y.; An, J.; Chen, P.; Han, J.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Segmented swing-structured fur-based triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting blue energy toward marine environmental applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 2106398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, W.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. All-weather droplet-based triboelectric nanogenerator for wave energy harvesting. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 13200–13208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Fan, Z.; Zhao, T.; Dong, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Liu, C.; Pan, X.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Sandwich-like triboelectric nanogenerators integrated self-powered buoy for navigation safety. Nano Energy 2021, 84, 105920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Xu, L.; Zhang, P.; Chen, B.; Wang, G.; Ji, J.; Pu, X.; Wang, Z.L. Seawater degradable triboelectric nanogenerators for blue energy. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Qiao, L.; He, J.; Wang, S.; Yu, L.; Murto, P.; Li, X.; Xu, X. Solar-driven interfacial evaporation and self-powered water wave detection based on an all-cellulose monolithic design. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 31, 2008681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Li, N.; He, J.; Qiao, L.; Li, F.; Wang, S.; Yu, L.; Murto, P.; Li, X.; Xu, X. Design of self-righting steam generators for solar-driven interfacial evaporation and self-powered water wave detection. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 24664–24674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Yin, M.; Wang, J.; Gao, Q.; Yu, Y.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Z.L. Gravity triboelectric nanogenerator for the steady harvesting of natural wind energy. Nano Energy 2020, 82, 105740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Meng, H.; Li, C.; Gao, J.; Chen, S.; Hu, Q.; Li, H.; Feng, L. A Wearable toxic gas-monitoring device based on triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered aniline early warning. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1901087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Z.; Meng, K.; Lin, Z.; He, Q.; Sun, C.; Yang, J.; et al. Wireless self-powered sensor networks driven by triboelectric nanogenerator for in-situ real time survey of environmental monitoring. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Xu, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, G.; Zhou, H.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Breeze-wind-energy-powered autono-mous wireless anemometer based on rolling contact-electrification. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 2343–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.P.; Liang, W.; Song, W.Z.; Zhou, L.N.; Wang, X.X.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y.Z. An acid and alkali-resistant triboelectric nanogenerator. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 23225–23233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Zheng, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, F.; Wang, D. Biofilm material based triboelectric nanogenerator with high output performance in 95% humidity environment. Nano Energy 2020, 77, 105088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zeng, X.; Fu, X.; Hu, Y. Expandable microsphere-based triboelectric nanogenerators as ultrasensitive pressure sensors for respiratory and pulse monitoring. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.-J.; Song, W.-Z.; Wang, X.-X.; Zhang, J.; Fan, Z.; Yu, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y.-Z. A calibration-free self-powered sensor for vital sign monitoring and finger tap communication based on wearable triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, D.; Jo, S.H.; Ryu, Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D.H.; Park, H.-S. Wearable triboelectric nanogenerator based exercise system for upper limb rehabilitation post neurological injuries. Nano Energy 2020, 80, 105508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Shi, Z.; Zheng, R.; Ye, W.; Gao, X.; Zhao, W.; Yang, G. Superhydrophobic liquid-solid contact triboelectric nano-generator as a droplet sensor for biomedical applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 40021–40030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Zhou, N.; Xie, G.; Chen, Y.; Suo, H.; Xu, J.; Tao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J. Surface-engineered triboelectric nanogenerator patches with drug loading and electrical stimulation capabilities: Toward promoting infected wounds healing. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 106004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Park, H.-M.; Kim, M.-K.; Kim, B.; Myoung, H.S.; Kim, T.Y.; Yoon, H.-J.; Kwak, S.S.; Kim, J.; Hwang, T.H.; et al. Self-rechargeable cardiac pacemaker system with triboelectric nanogenerators. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Xu, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhai, W.; Yuan, Z.; Dai, K.; Zheng, G.; Mi, L.; Pan, C.; Liu, C.; et al. Tunable and nacremimetic multifunctional electronic skins for highly stretchable contact-noncontact sensing. Small 2021, 17, 2100542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, X.; Yuan, Z.; Zheng, G.; Dai, K.; Mi, L.; Pan, C.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Ultra-stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator as high-sensitive and self-powered electronic skins for energy harvesting and tactile sensing. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhu, J.; Ma, P.; Jie, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Cao, X. Fish bladder film-based triboelectric nanogenerator for noncontact position monitoring. ACS Energy Lett. 2020, 5, 3005–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.C.; Wu, H.M.; Lin, H.C.; Chang, C.L.; Chou, H.H.; Hsiao, Y.C.; Wu, Y.C. Entirely, intrinsically, and autonomously self-healable, highly transparent, and superstretchable triboelectric nanogenerator for personal power sources and self-powered electronic skins. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1904626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Pu, X.; Jiang, T.; Yu, A.; Xu, L.; Wang, Z.L. Tunable optical modulator by coupling a triboelectric nanogenerator and a dielectric elastomer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 27, 1603788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, P.; Bhatta, T.; Salauddin, M.; Rasel, M.; Rahman, M.T.; Rana, S.; Park, J.Y. A human skin-inspired self-powered flex sensor with thermally embossed microstructured triboelectric layers for sign language interpretation. Nano Energy 2020, 76, 105071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Zhang, Z.; He, T.; Lee, C. AI enabled sign language recognition and VR space bidirectional communication using triboelectric smart glove. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, K.; Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, K.; Sun, C.; He, Q.; Fan, W.; et al. Sign-to-speech translation using machine-learning-assisted stretchable sensor arrays. Nat. Electron. 2020, 3, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Pang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Tan, X.; Cao, C. Smart soft actuators and grippers enabled by self-powered tribo-skins. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1901075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yin, Y.; Yi, F.; Dai, K.; Niu, S.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; You, Z. Bioinspired stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator as energy-harvesting skin for self-powered electronics. Nano Energy 2017, 39, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, Z.; Wang, X.; Han, X.; Wu, W.; Wan, B.; Wang, H.; Zhai, J.; Tao, J.; Pan, C.; et al. High precision epidermal radio frequency antenna via nanofiber network for wireless stretchable multifunction electronics. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huo, Z.; Li, X.; Que, M.; Peng, Z.; Wang, H.; Pan, C. A highly stretchable transparent self-powered triboelectric tactile sensor with metallized nanofibers for wearable electronics. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X. Recent Progress in Self-Powered Sensors Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Sensors 2021, 21, 7129. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217129
Wu J, Zheng Y, Li X. Recent Progress in Self-Powered Sensors Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Sensors. 2021; 21(21):7129. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217129
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Junpeng, Yang Zheng, and Xiaoyi Li. 2021. "Recent Progress in Self-Powered Sensors Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators" Sensors 21, no. 21: 7129. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217129
APA StyleWu, J., Zheng, Y., & Li, X. (2021). Recent Progress in Self-Powered Sensors Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Sensors, 21(21), 7129. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217129





