A Robust Facial Expression Recognition Algorithm Based on Multi-Rate Feature Fusion Scheme
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We defines a multi-depth network based on multi-frame rate input.
- A structure that minimizes the overlapping between input frames to each model was designed.
- The proposed scheme reinforced the features that are the result of the networks by self-attention, and it showed a better result than each network’s result.
- We verified the robustness of the multi-depth network on the variation of dataset and different facial expression acquisition conditions.
2. Related Works
2.1. The Facial Expression Recognition Methods
2.1.1. Classical Feature-Based Approaches
Geometric Feature-Based Method
Appearance Feature-Based Method
2.1.2. Deep-Learning-Based Approaches
2.2. Multirate Filter Bank
2.3. Self-Attention
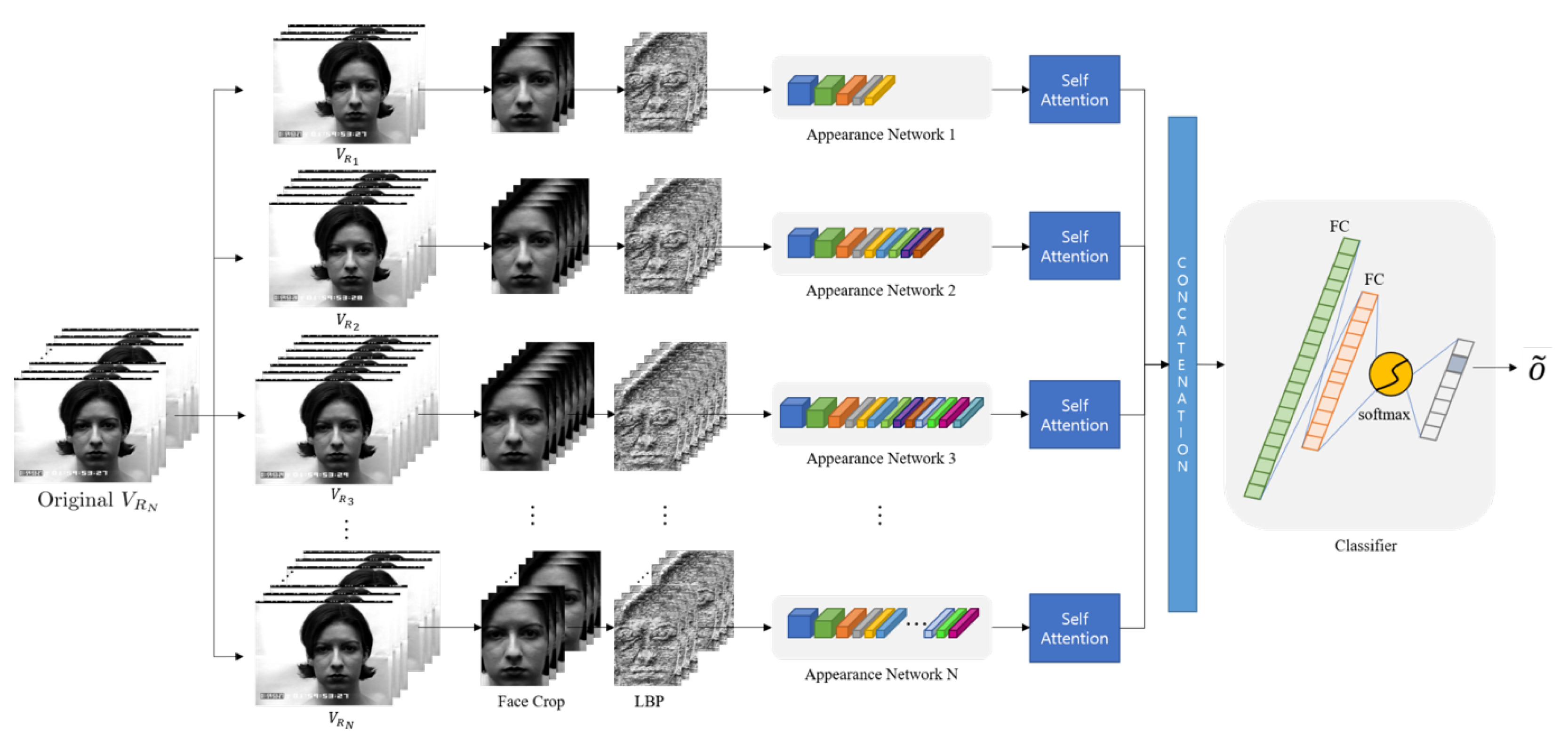
3. Proposed Scheme
3.1. Data Pre-Processing
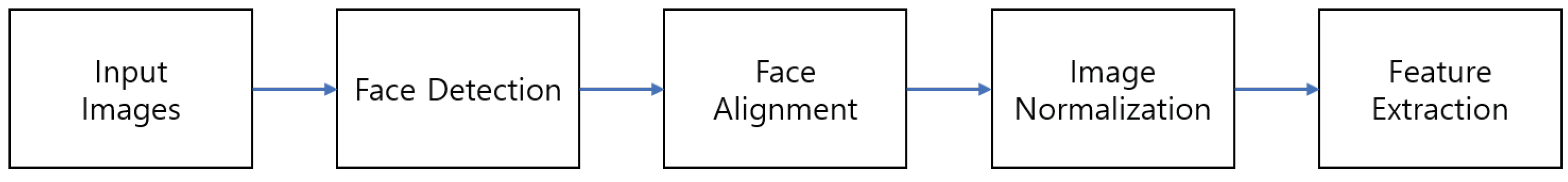
3.1.1. Image Pre-Processing
3.1.1.1. Face Detection
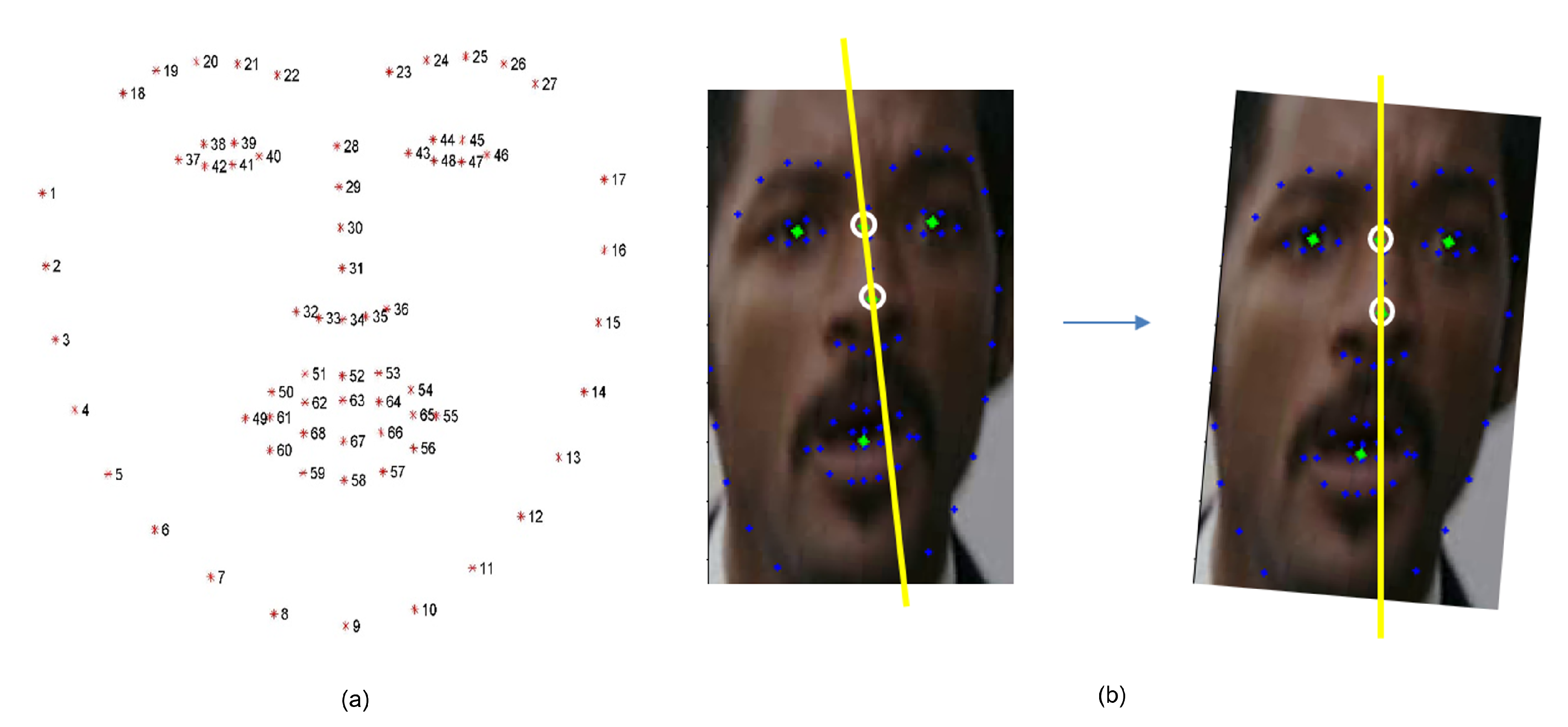
3.1.1.2. Face Alignment
3.1.1.3. Image Normalization
3.1.1.4. Feature Extraction Using LBP
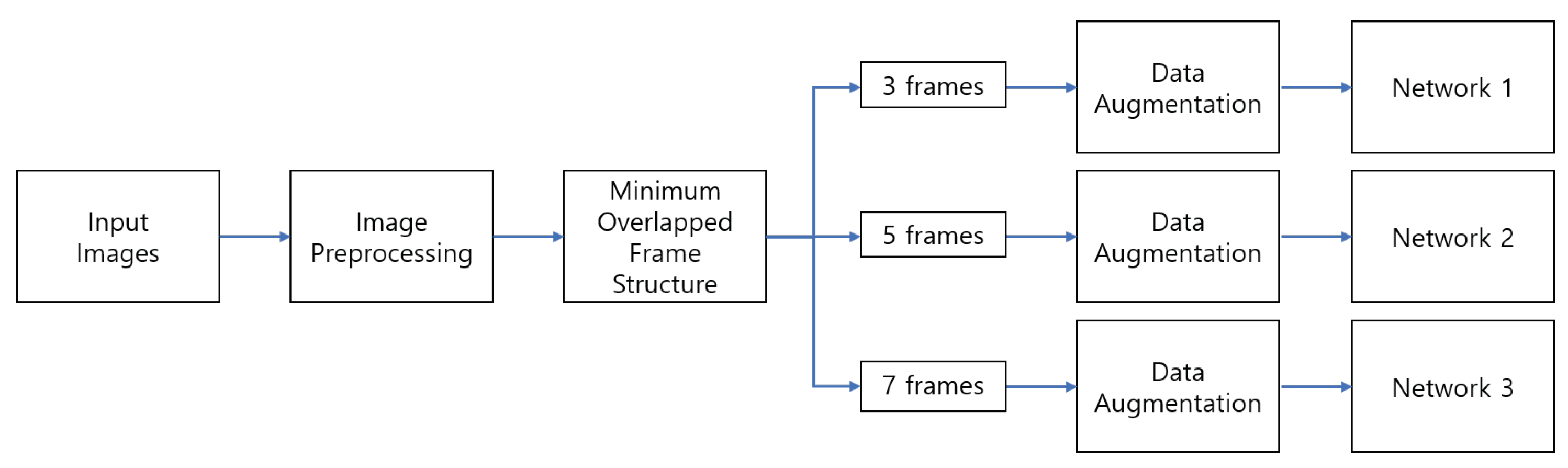
3.1.2. Minimum Overlapped Frame Structure
3.2. Data Preparation
3.2.1. Data Augmentation
3.2.2. Making Neutral Label of Dataset
3.3. 3D Convolutional Neural Network (3D CNN)
3.4. Joint Fusion Classifier Using Self-Attention
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Ablation Study
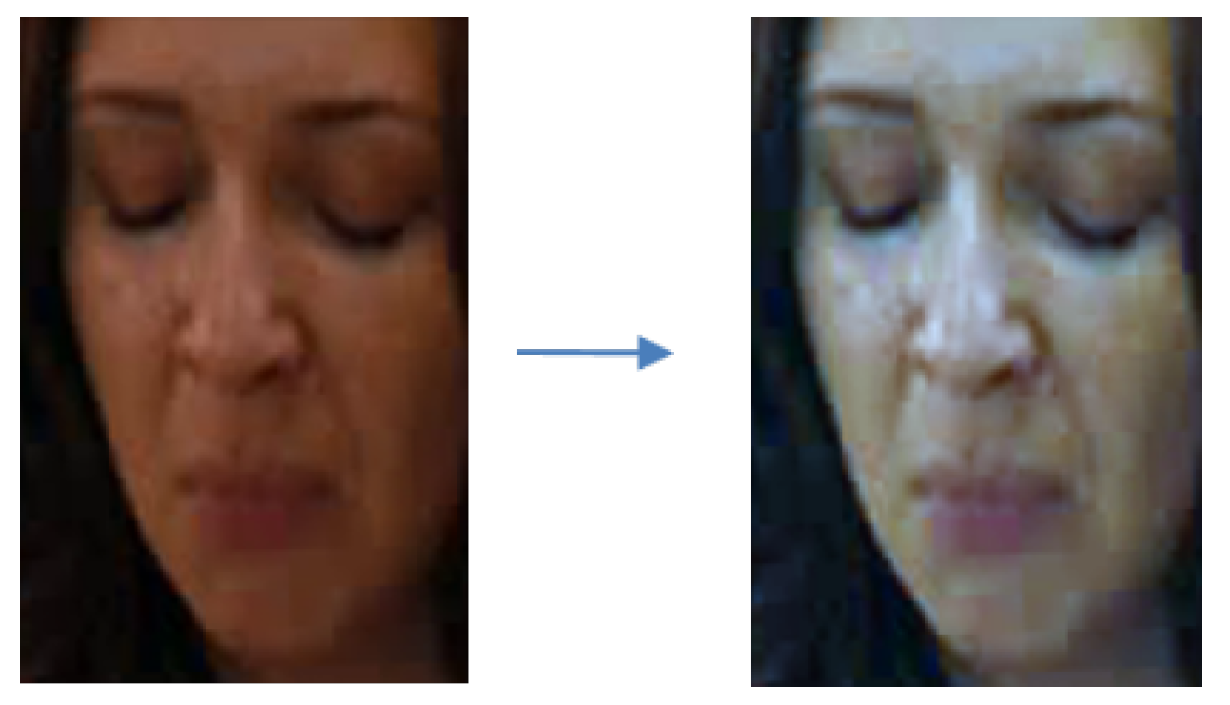
4.1.1. Performance of Image Normalization
4.1.2. Correlation between Depth of the Network and Frame Rate of Input
4.1.3. Performance of the Minimum Overlapped Frame Structure
4.1.4. Performance of Self-Attention Module
4.1.5. Effectiveness of Multi-Depth Network Structure
4.2. Overall Accuracy Performance of the Proposed Scheme
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenblum, L.D. See What I’m Saying: The Extraordinary Powers of Our Five Senses, 1st ed.; W. W. Norton Company: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, L.T.; Cooper, E.W.; Kamei, K. Development of facial expression recognition for training video customer service representatives. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems (FUZZ-IEEE), Beijing, China, 6–11 July 2014; pp. 1297–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Tischler, M.A.; Peter, C.; Wimmer, M.; Voskamp, J. Application of emotion recognition methods in automotive research. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Emotion and Computing—Current Research and Future Impact, Osnabrück, Germany, 9–13 October 2007; Volume 1, pp. 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, K.; Mitsukura, Y. An entertainment robot based on head pose estimation and facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the SICE Annual Conference (SICE), Akita, Japan, 20–23 August 2012; pp. 2057–2061. [Google Scholar]
- Khowaja, S.A.; Dahri, K.; Kumbhar, M.A.; Soomro, A.M. Facial expression recognition using two-tier classification and its application to smart home automation system. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Emerging Technologies (ICET), Peshawar, Pakistan, 19–20 December 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Blom, P.M.; Bakkes, S.; Tan, C.; Whiteson, S.; Roijers, D.; Valenti, R.; Gevers, T. Towards personalised gaming via facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Interactive Digital Entertainment, Raleigh, NC, USA, 3–7 October 2014; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Assari, M.A.; Rahmati, M. Driver drowsiness detection using face expression recognition. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Signal and Image Processing Applications (ICSIPA), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 16–18 November 2011; pp. 337–341. [Google Scholar]
- Kavitha, K.R.; Lakshmi, S.V.; Reddy, P.B.K.; Reddy, N.S.; Chandrasekhar, P.; Sisindri, Y. Driver Drowsiness Detection Using Face Expression Recognition. Ann. Rom. Soc. Cell Biol. 2021, 25, 2785–2789. [Google Scholar]
- Sajjad, M.; Zahir, S.; Ullah, A.; Akhtar, Z.; Muhammad, K. Human behavior understanding in big multimedia data using CNN based facial expression recognition. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2020, 25, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bediou, B.; Krolak-Salmon, P.; Saoud, M.; Henaff, M.-A.; Burt, M.; Dalery, J.; D’Amato, T. Facial expression and sex recognition in schizophrenia and depression. Can. J. Psychiatry 2005, 50, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Csukly, G.; Czobor, P.; Szily, E.; Takács, B.; Simon, L. Facial expression recognition in depressed subjects: The impact of intensity level and arousal dimension. J. Nerv. Mental Dis. 2009, 197, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehill, J.; Bartlett, M.; Movellan, J. Automatic facial expression recognition for intelligent tutoring systems. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.T.; Cheng, Y.J.; Shih, Y.C. Facial expression recognition for learning status analysis. In Human-Computer Interaction. Users and Applications, Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Orlando, FL, USA, 9–14 July 2011; Jacko, J.A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Khalfallah, J.; Slama, J.B.H. Facial expression recognition for intelligent tutoring systems in remote laboratories platform. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 73, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, W.V. Constants across cultures in the face and emotion. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1971, 17, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, W.V. A new pan-cultural facial expression of emotion. Motiv. Emot. 1986, 10, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.E. A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 1997, 55, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viola, P.; Jones, M. Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2001), Kauai, HI, USA, 8–14 December 2001; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Viola, P.; Jones, M. Robust real-time object detection. Int. J. Comput. Vision 2001, 4, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Haffner, P.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y. Object recognition with gradient-based learning. In Shape, Contour and Grouping in Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; pp. 319–345. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning Internal Representations by Error Propagation; Technical Report; California Univ San Diego La Jolla Inst for Cognitive Science: San Diego, CA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Xu, W.; Yang, M.; Yu, K. 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 35, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, B.G.; Roy, P.P.; Jeong, D.M. Efficient facial expression recognition algorithm based on hierarchical deep neural network structure. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 41273–41285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Kim, B.G.; Dong, S.Y. Deep Joint Spatiotemporal Network (DJSTN) for Efficient Facial Expression Recognition. Sensors 2020, 20, 1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.I.; Kanade, T.; Cohn, J.F. Recognizing action units for facial expression analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cootes, T.F.; Edwards, G.J.; Taylor, C.J. Active appearance models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ekman, P.; Rosenberg, E.L. What the Face Reveals: Basic and Applied Studies of Spontaneous Expression Using the Facial Action Coding System (FACS); Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Jepson, A.; Heeger, D. Linear subspace methods for recovering translational direction. In Spatial Vision in Humans and Robots; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, K. LIII. On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1901, 2, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mika, S.; Ratsch, G.; Weston, J.; Scholkopf, B.; Mullers, K.R. Fisher discriminant analysis with kernels. In Proceedings of the Neural Networks for Signal Processing IX: Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE Signal Processing Society Workshop (Cat. No. 98th8468), Madison, WI, USA, 25 August 1999; pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Comon, P. Independent component analysis, a new concept? Signal Process. 1994, 36, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabor, D. Theory of communication. Part 1: The analysis of information. J. Inst. Electr. Eng. Part III Radio Commun. Eng. 1946, 93, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ojala, T.; Pietikainen, M.; Maenpaa, T. Multiresolution gray-scale and rotation invariant texture classification with local binary patterns. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 971–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouellet, S. Real-time emotion recognition for gaming using deep convolutional network features. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1408.3750. [Google Scholar]
- Mollahosseini, A.; Chan, D.; Mahoor, M.H. Going deeper in facial expression recognition using deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Placid, NY, USA, 7–10 March 2016; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.H.; Baddar, W.J.; Jang, J.; Ro, Y.M. Multi-objective based spatio-temporal feature representation learning robust to expression intensity variations for facial expression recognition. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2017, 10, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddar, W.J.; Lee, S.; Ro, Y.M. On-the-Fly Facial Expression Prediction using LSTM Encoded Appearance-Suppressed Dynamics. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Lee, S.; Yim, J.; Park, S.; Kim, J. Joint fine-tuning in deep neural networks for facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2983–2991. [Google Scholar]
- Vetterli, M. A theory of multirate filter banks. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1987, 35, 356–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O.; Le, Q.V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 3104–3112. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Ba, J.; Kiros, R.; Cho, K.; Courville, A.; Salakhudinov, R.; Zemel, R.; Bengio, Y. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 2048–2057. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran, P.; Parmar, N.; Vaswani, A.; Bello, I.; Levskaya, A.; Shlens, J. Stand-alone self-attention in vision models. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.05909. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, X.; Lei, Z.; Shi, H.; Wang, X.; Li, S.Z. Faceboxes: A CPU real-time face detector with high accuracy. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), Denver, CO, USA, 1–4 October 2017; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Yan, Y.; Ouyang, W.; Yang, Y. Style aggregated network for facial landmark detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 379–388. [Google Scholar]
- Canedo, D.; Neves, A.J. Facial expression recognition using computer vision: A systematic review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, L.; Liu, Q.; Yang, P.; Liu, B.; Huang, J.; Metaxas, D.N. Learning active facial patches for expression analysis. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 2562–2569. [Google Scholar]
- Ahonen, T.; Hadid, A.; Pietikäinen, M. Face recognition with local binary patterns. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Prague, Czech Republic, 11–14 May 2004; pp. 469–481. [Google Scholar]
- Ballard, D.H. Modular learning in neural networks. AAAI 1987, 647, 279–284. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Deng, J. Spatio-temporal convolutional features with nested LSTM for facial expression recognition. Neurocomputing 2018, 317, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, P.; Cohn, J.F.; Kanade, T.; Saragih, J.; Ambadar, Z.; Matthews, I. The extended cohn-kanade dataset (ck+): A complete dataset for action unit and emotion-specified expression. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition-Workshops, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Kanade, T.; Cohn, J.F.; Tian, Y. Comprehensive database for facial expression analysis. In Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, Grenoble, France, 28–30 March 2000; pp. 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Pantic, M.; Valstar, M.; Rademaker, R.; Maat, L. Web-based database for facial expression analysis. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 6–8 July 2005; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Bänziger, T.; Scherer, K.R. Introducing the geneva multimodal emotion portrayal (gemep) corpus. Bluepr. Affect. Comput. Sourceb. 2010, 2010, 271–294. [Google Scholar]
- Dhall, A.; Goecke, R.; Lucey, S.; Gedeon, T. Collecting large, richly annotated facial-expression databases from movies. IEEE Ann. Hist. Comput. 2012, 19, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Lille, France, 7–9 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Diederik, P.; Kingma, J.B. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference for Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hasani, B.; Mahoor, M.H. Facial expression recognition using enhanced deep 3D convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Hasani, B.; Mahoor, M.H. Spatio-temporal facial expression recognition using convolutional neural networks and conditional random fields. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2017), Washington, DC, USA, 30 May–3 June 2017; pp. 790–795. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, R. Video facial emotion recognition based on local enhanced motion history image and CNN-CTSLSTM networks. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2019, 59, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, D.; Yan, Y.; Chen, S.; Xue, J.H.; Wang, H. Deep disturbance-disentangled learning for facial expression recognition. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 2833–2841. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, D.; Yan, Y.; Lai, S.; Chai, Z.; Shen, C.; Wang, H. Feature Decomposition and Reconstruction Learning for Effective Facial Expression Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 7660–7669. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, M.; Ding, X. Facial Expression Recognition Based on Multi-Features Cooperative Deep Convolutional Network. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Neu. | Ang. | Dis. | Fea. | Hap. | Sad. | Sur. | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK+ | 0 | 45 | 56 | 24 | 69 | 28 | 78 | 300 |
| MMI | 0 | 33 | 32 | 28 | 42 | 32 | 41 | 208 |
| FERA | 31 | 32 | − | 30 | 31 | 31 | − | 155 |
| AFEW (Train + Val.) | 143 | 146 | 77 | 80 | 156 | 119 | 74 | 795 |
| AFEW (Test) | 63 | 61 | 39 | 41 | 60 | 54 | 43 | 361 |
| Neu. | Ang. | Dis. | Fea. | Hap. | Sad. | Sur. | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK+ | 600 | 630 | 784 | 336 | 966 | 392 | 1092 | 4800 |
| MMI | 416 | 462 | 448 | 392 | 588 | 448 | 574 | 3328 |
| FERA | 434 | 448 | − | 420 | 434 | 434 | − | 2170 |
| AFEW (Train + Val.) | 572 | 584 | 308 | 320 | 624 | 476 | 296 | 3180 |
| AFEW (Test) | 126 | 122 | 78 | 82 | 120 | 108 | 86 | 722 |
| Datasets | Input Frames | Depth of Network | Image Normalization | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not Used | Used | |||
| CK+ | 3 | 5 | 98.65 | 98.02 |
| 10 | 98.02 | 98.33 | ||
| 15 | 97.92 | 97.81 | ||
| MMI | 3 | 5 | 95.58 | 96.19 |
| 10 | 94.97 | 97.1 | ||
| 15 | 94.40 | 93.75 | ||
| FERA | 3 | 5 | 98.85 | 100 |
| 10 | 99.77 | 99.77 | ||
| 15 | 99.31 | 100 | ||
| AFEW | 3 | 5 | 28.32 | 28.95 |
| 10 | 26.59 | 27.49 | ||
| 15 | 23.41 | 23.89 | ||
| Datasets | Depth of Network | Input Frames | Image Normalization |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK+ | 5 | 3 | 98.45 |
| 5 | 98.34 | ||
| 7 | 98.23 | ||
| 10 | 3 | 98.89 | |
| 5 | 97.90 | ||
| 7 | 98.31 | ||
| 15 | 3 | 97.90 | |
| 5 | 97.23 | ||
| 7 | 98.45 | ||
| MMI | 10 | 3 | 96.65 |
| 5 | 95.88 | ||
| 7 | 93.75 | ||
| 15 | 3 | 89.84 | |
| 5 | 92.99 | ||
| 7 | 94.67 | ||
| 20 | 3 | 90.85 | |
| 5 | 89.94 | ||
| 7 | 92.84 | ||
| FERA | 5 | 3 | 100 |
| 5 | 99.54 | ||
| 7 | 99.54 | ||
| 15 | 3 | 100 | |
| 5 | 100 | ||
| 7 | 99.77 | ||
| 25 | 3 | 98.85 | |
| 5 | 99.77 | ||
| 7 | 99.77 |
| Datasets | Minimum Overlapped Frame Structure | |
|---|---|---|
| Not Used | Used | |
| CK+ | 96.88 | 98.85 |
| MMI | 89.48 | 91.01 |
| FERA | 99.31 | 99.77 |
| AFEW | 27.70 | 28.67 |
| Datasets | Self-Attention | |
|---|---|---|
| Not Used | Used | |
| CK+ | 98.85 | 99.06 |
| MMI | 91.01 | 91.92 |
| FERA | 99.77 | 100.00 |
| AFEW | 28.67 | 29.09 |
| Depth Network 1 | Depth Network 2 | Depth Network 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | Layers | Params | Layers | Params | Layers | Params |
| 14,720 | ||||||
| 307,520 | ||||||
| 14,720 | 307,520 | |||||
| 307,520 | 615,040 | |||||
| 615,040 | 1,229,440 | |||||
| 14,720 | 1,229,440 | 1,229,440 | ||||
| Conv3d | 615,040 | 2,458,880 | 2,458,880 | |||
| +MaxPool | 5 | 2,458,880 | 10 | 4,916,480 | 15 | 4,916,480 |
| +BatchNorm | 9,832,960 | 9,832,960 | 4,916,480 | |||
| 19,663,360 | 19,663,360 | 9,832,960 | ||||
| 19,663,360 | 19,663,360 | |||||
| 19,663,360 | 19,663,360 | |||||
| 19,663,360 | ||||||
| 19,663,360 | ||||||
| 19,663,360 | ||||||
| Self-attention | 1 | 32,065 | 1 | 32,065 | 1 | 32,065 |
| 1,537,024 | ||||||
| Fully connected | 512,500 | |||||
| 3,507 | ||||||
| Total params | 237,244,586 | |||||
| Datasets | CK+ | MMI | GEMEP-FERA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Network | 96.11 | 92.52 | 93.38 |
| Proposed (Multi-depth network) | 96.23 | 96.69 | 99.79 |
| Method | Datasets | Input Construction | Models |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3DIR [65] | CK+, MMI, GEMEP-FERA | Multiple frames, facial landmarks | 3D CNN, LSTM, Inception-ResNet |
| STCNN-CRF [66] | CK+, MMI, GEMEP-FERA | Multiple frames | 2D CNN, CRF, Inception-ResNet |
| CNN-CTSLSTM [67] | CK+, MMI, AFEW | Multiple frames, facial landmarks | VGG-CTSLSTM, LEMHI-VGG |
| DDL [68] | CK+, MMI | Multiple frames | DFEM, DDM |
| DJSTN [26] | CK+, MMI, GEMEP-FERA | Multiple frames, facial landmarks | Hybrid network (App., Geo.) |
| FDRL [69] | CK+, MMI | Multiple frames | ResNet-18, FDN, FRN |
| MC-DCN [70] | CK+, MMI, GEMEP-FERA | Multiple frames | Hybrid network (C3Ds) |
| without Preprocessing | with Preprocessing | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 96.88 | 95.31 |
| 2 | 97.08 | 95.52 |
| 3 | 97.60 | 95.94 |
| 4 | 97.71 | 96.15 |
| 5 | 97.60 | 96.25 |
| 6 | 97.81 | 96.77 |
| 7 | 97.71 | 97.40 |
| 8 | 97.08 | 95.63 |
| 9 | 96.88 | 96.67 |
| 10 | 97.08 | 96.67 |
| Average | 97.33 | 96.23 |
| Methods | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| 3DIR [65] | 93.21 |
| STCNN-CRF [66] | 93.04 |
| CNN-CTSLSTM [67] | 93.90 |
| DDL [68] | 99.16 |
| DJSTN [26] | 99.21 |
| FDRL [69] | 99.54 |
| MC-DCN [70] | 95.50 |
| Proposed Scheme | 96.23 |
| without Preprocessing | with Preprocessing | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 89.48 | 97.87 |
| 2 | 92.07 | 98.02 |
| 3 | 92.23 | 95.27 |
| 4 | 92.53 | 96.95 |
| 5 | 93.29 | 97.26 |
| 6 | 91.31 | 95.12 |
| 7 | 92.53 | 95.43 |
| 8 | 89.18 | 95.88 |
| 9 | 92.99 | 97.25 |
| 10 | 93.45 | 94.35 |
| Average | 91.91 | 96.69 |
| Methods | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| 3DIR [65] | 77.50 |
| STCNN-CRF [66] | 68.51 |
| CNN-CTSLSTM [67] | 78.4 |
| DDL [68] | 83.67 |
| DJSTN [26] | 87.88 |
| FDRL [69] | 85.23 |
| MC-DCN [70] | 78.6 |
| Proposed Scheme | 96.69 |
| without Preprocessing | with Preprocessing | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 99.31 | 100.00 |
| 2 | 99.77 | 100.00 |
| 3 | 98.62 | 99.54 |
| 4 | 99.54 | 99.77 |
| 5 | 99.54 | 100.00 |
| 6 | 98.16 | 99.77 |
| 7 | 97.24 | 99.54 |
| 8 | 99.54 | 100.00 |
| 9 | 99.77 | 99.54 |
| 10 | 100.00 | 99.77 |
| Average | 99.15 | 99.79 |
| Methods | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| 3DIR [65] | 77.42 |
| STCNN-CRF [66] | 66.66 |
| DJSTN [26] | 91.83 |
| MC-DCN [70] | 78.3 |
| Proposed Scheme | 99.79 |
| without Preprocessing | with Preprocessing | |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 27.70 | 31.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.-J.; Kim, B.-G.; Chilamkurti, N. A Robust Facial Expression Recognition Algorithm Based on Multi-Rate Feature Fusion Scheme. Sensors 2021, 21, 6954. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21216954
Park S-J, Kim B-G, Chilamkurti N. A Robust Facial Expression Recognition Algorithm Based on Multi-Rate Feature Fusion Scheme. Sensors. 2021; 21(21):6954. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21216954
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Seo-Jeon, Byung-Gyu Kim, and Naveen Chilamkurti. 2021. "A Robust Facial Expression Recognition Algorithm Based on Multi-Rate Feature Fusion Scheme" Sensors 21, no. 21: 6954. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21216954
APA StylePark, S.-J., Kim, B.-G., & Chilamkurti, N. (2021). A Robust Facial Expression Recognition Algorithm Based on Multi-Rate Feature Fusion Scheme. Sensors, 21(21), 6954. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21216954








