Differential Inductive Sensing System for Truly Contactless Measuring of Liquids′ Electromagnetic Properties in Tubing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
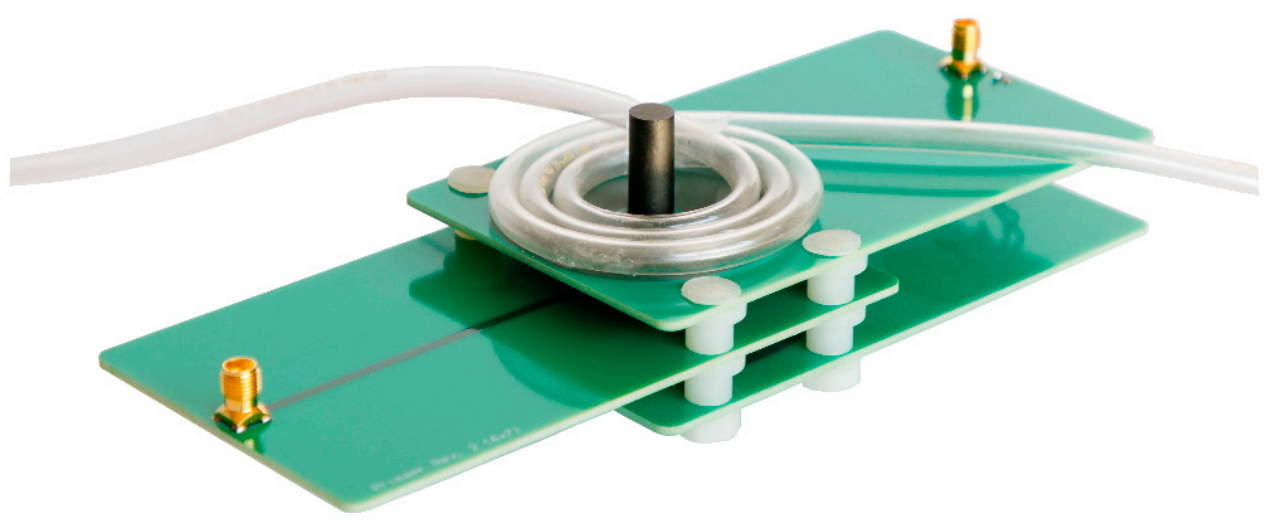
2.1. Printed Circuit Board (PCB)-Differential Transformer and the Experimental Setup
2.2. Numerical Simulation Model
3. Results and Discussion
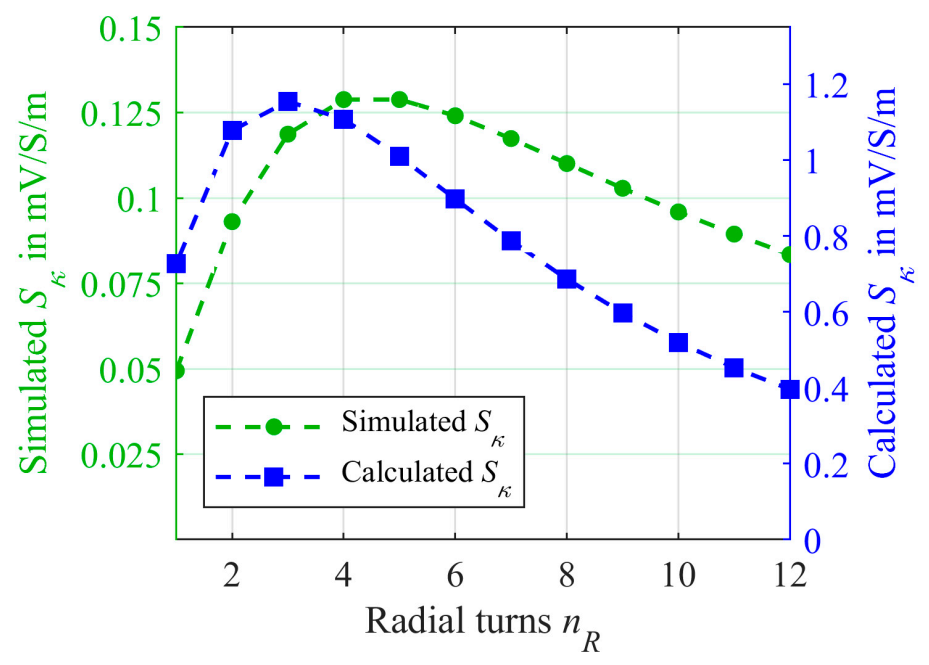
3.1. Radial Winding
3.1.1. Numerical Simulations for Radial Winding
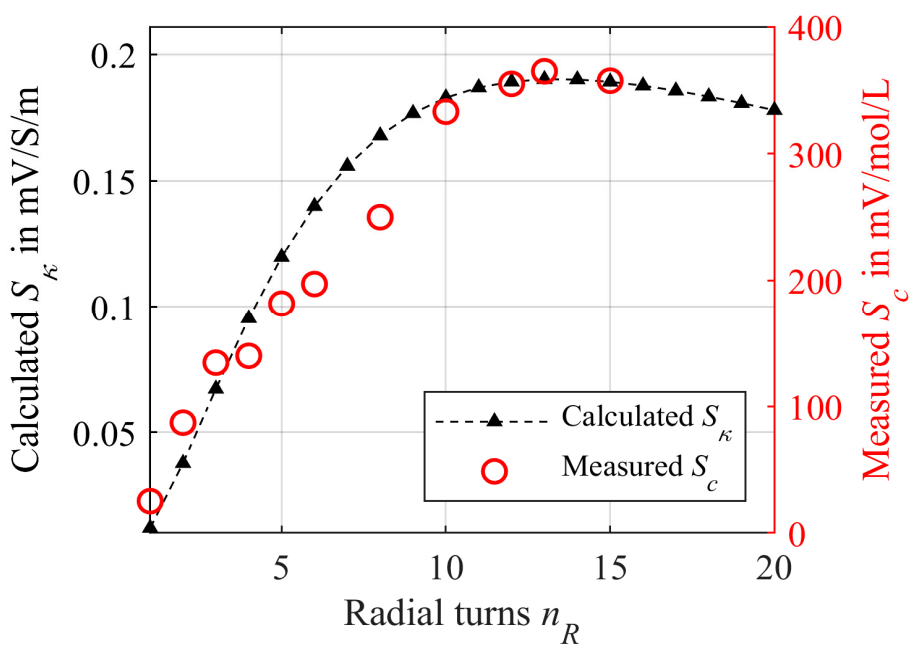
3.1.2. Mathematical Model for Radial Winding
3.1.3. Experimental Investigations for Radial Winding
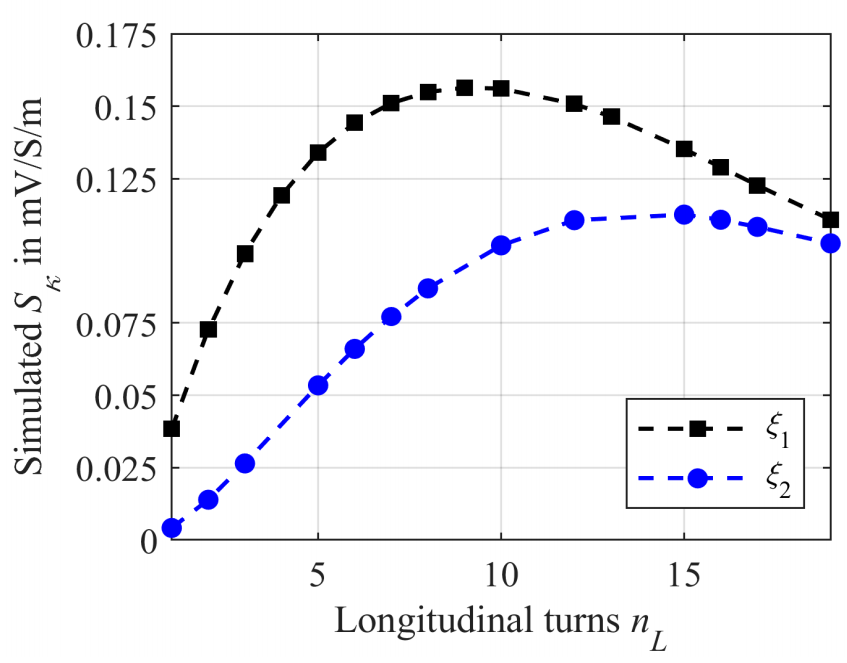
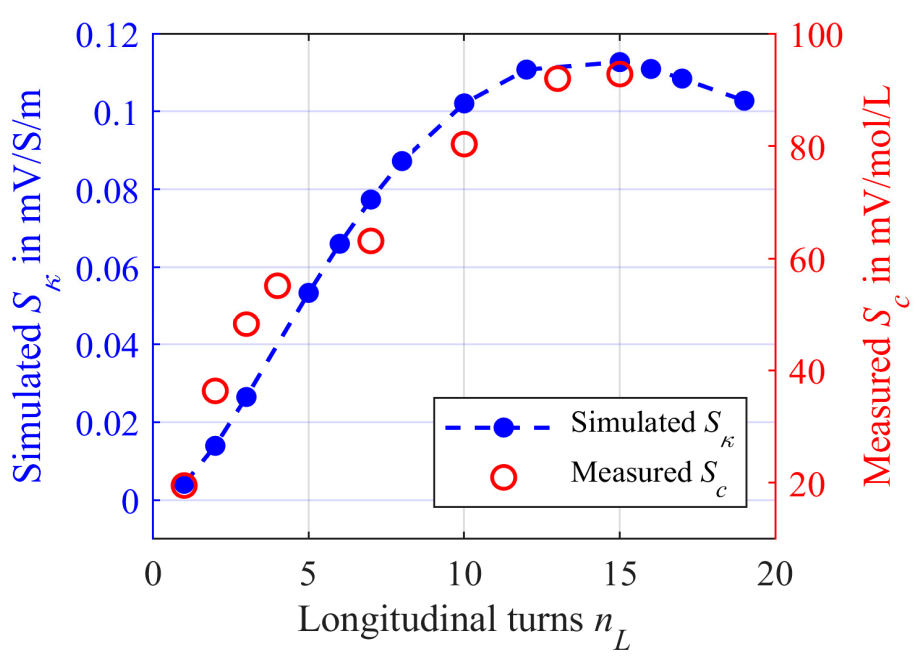
3.2. Longitudinal Winding
3.2.1. Numerical Simulations for Longitudinal Winding
3.2.2. Experimental Investigations for Longitudinal Winding
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tura, A.; Sbrignadello, S.; Mambelli, E.; Ravazzani, P.; Santoro, A.; Pacini, G. Sodium concentration measurement during hemodialysis through ion-exchange resin and conductivity measure approach: In vitro experiments. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitclerc, T.; Goux, N.; Reynier, A.L.; Béné, B. A Model for Non-invasive estimation of in vivo dialyzer performances and patient′s conductivity during hemodialysis. Int. J. Artif. Organs 1993, 16, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stragier, A.; Lopot, F.; Švára, F.; Polakovič, V. Fallacies and pitfalls of dialysis sodium prescription and control. Blood Purif. 2018, 46, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.; Sellering, F.; Rohrich, H.; Mansour, H.; Perl, T.; Zimmermann, S. A Differential Transformer for Noninvasive Continuous Sodium Monitoring During Dialysis Treatment. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (SAS), Sophia Antipolis, France, 11–13 March 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Locatelli, F.; La Milia, V.; Violo, L.; Del Vecchio, L.; Di Filippo, S. Optimizing haemodialysate composition. Clin. Kidney J. 2015, 8, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, F.; Di Filippo, S.; Manzoni, C. Relevance of the conductivity kinetic model in the control of sodium pool. Kidney Int. 2000, 58, S89–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.K.; Wieringa, F.; Frijns, A.J.; Kooman, J.P. On-line monitoring of electrolytes in hemodialysis: On the road towards individualizing treatment. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2016, 13, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, F.; Buoncristiani, U.; Canaud, B.; Köhler, H.; Petitclerc, T.; Zucchelli, P. Haemodialysis with on-line monitoring equipment: Tools or toys? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2005, 20, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.; Zygmanowski, A.; Sellering, F.; Röhrich, H.; Perl, T.; Mansour, H.; Zimmermann, S. Contactless and continuous sodium concentration monitoring during continuous renal replacement therapy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 320, 128372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Nandwani, V.; McCarthy, P.J.; Conrad, S.A.; Scott, L.K. Continuous renal replacement therapies: A brief primer for the neurointensivist. Neurocritical Care 2010, 13, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmon, M.; Pichon, M.; Schwebel, C.; Ruckly, S.; Adrie, C.; Haouache, H.; Azoulay, E.; Bouadma, L.; Clec′H, C.; Garrouste-Orgeas, M.; et al. Influence of early dysnatremia correction on survival of critically ill patients. Shock 2014, 41, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, M.; Dickie, H.; Tovey, L.; Treacher, D. Management of sodium disorders during continuous haemofiltration. Crit. Care 2010, 14, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paquette, F.; Goupil, R.; Madore, F.; Troyanov, S.; Bouchard, J. Continuous venovenous hemofiltration using customized replacement fluid for acute kidney injury with severe hypernatremia. Clin. Kidney J. 2016, 9, 540–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paula, F.M.; Peixoto, A.J.; Pinto, L.V.; Dorigo, D.; Patricio, P.J.; Santos, S.F. Clinical consequences of an individualized dialysate sodium prescription in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2004, 66, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, B.F. Individualizing the Dialysate in the Hemodialysis Patient. Semin. Dial. 2001, 14, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernsen, H.J.; Prick, M.J. Improvement of central pontine myelinolysis as demonstrated by repeated magnetic resonance imaging in a patient without evidence of hyponatremia. Acta Neurol. Belg. 1999, 99, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Mallick, N.P.; Gokal, R. Haemodialysis. Lancet 1999, 353, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwan, H.P. Electrical properties of blood and its constitutents: Alternating current spectroscopy. Ann. Hematol. 1983, 46, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, K.S.; Cole, R.H. Dispersion and Absorption in Dielectrics I. Alternating Current Characteristics. J. Chem. Phys. 1941, 9, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biechele, P.; Busse, C.; Solle, D.; Scheper, T.; Reardon, K. Sensor systems for bioprocess monitoring. Eng. Life Sci. 2015, 15, 469–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glindkamp, A.; Riechers, D.; Rehbock, C.; Hitzmann, B.; Scheper, T.; Reardon, K.F. Sensors in Disposable Bioreactors Status and Trends. Blue Biotechnol. 2009, 115, 145–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannizzaro, C.; Gugerli, R.; Marison, I.; Von Stockar, U. On-line biomass monitoring of CHO perfusion culture with scanning dielectric spectroscopy. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2003, 84, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.A.; Pereira, D.; Vieira, L.M.; Menezes, J.C. Real time monitoring biomass concentration in Streptomyces clavuligerus cultivations with industrial media using a capacitance probe. J. Biotechnol. 2000, 84, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allers, M.; Reinecke, T.; Nagraik, T.; Solle, D.; Bakes, K.; Berger, M.; Scheper, T.; Zimmermann, S. Differential inductive sensor for continuous non-invasive cell growth monitoring in disposable bioreactors. Procedings 2017, 1, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinecke, T.; Biechele, P.; Sobocinski, M.; Suhr, H.; Bakes, K.; Solle, D.; Jantunen, H.; Scheper, T.; Zimmermann, S. Continuous noninvasive monitoring of cell growth in disposable bioreactors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 251, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reinecke, T.; Biechele, P.; Frickhöffer, M.; Scheper, T.; Zimmermann, S. Non-Invasive Online Monitoring of Cell Growth in Disposable Bioreactors with a Planar Coil. Procedia Eng. 2016, 168, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubartallah, E.A.; Makahleh, A.; Quirino, J.P.; Saad, B. Determination of biogenic amines in seawater using capillary electrophoresis with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection. Molecules 2018, 23, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito-Neto, J.G.A.; Silva, J.; Blanes, L.; Lago, C.D. Understanding Capacitively Coupled Contactless Conductivity Detection in Capillary and Microchip Electrophoresis. Part 2. Peak Shape, Stray Capacitance, Noise, and Actual Electronics. Electroanalysis 2005, 17, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Ji, H.; Yang, S.; Huang, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, H. New C4D Sensor with a Simulated Inductor. Sensors 2016, 16, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivalingam, M.; Farrington, K. Haemodialysis. Medicine 2007, 35, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chater, K.; Kellum, J.A. Continuous vs. intermittent hemodialysis: With which spin will my patient win? Crit. Care 2007, 11, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wolf, M.; Gulich, R.; Lunkenheimer, P.; Loidl, A. Broadband dielectric spectroscopy on human blood. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1810, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Li, Z.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zang, X.-Q.; Ueno, K.; Misawa, H.; Sun, K. Bacterial Concentration Detection using a PCB-based Contactless Conductivity Sensor. Micromachines 2019, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenich, N. The extracorporeal circuit: Materials, problems, and solutions. Hemodial. Int. 2007, 11, S26–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivers-Tiffèe, E.; von Münch, W. Werkstoffe der Elektrotechnik; B.G. Teubner Verlag/GWV Fachverlage GmbH: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2007; ISBN 978-3-8351-0052-7. [Google Scholar]
- Parra, L.; Sendra, S.; Lloret, J.; Bosch, I. Development of a conductivity sensor for monitoring groundwater resources to optimize water management in smart city environments. Sensors 2015, 15, 20990–21015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danisi, A.; Masi, A.; Losito, R. Performance analysis of the ironless inductive position sensor in the large hadron collider collimators environment. Sensors 2015, 15, 28592–28602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loughlin, C. Sensors for Industrial Inspection; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Usher, M.J. Sensors and Transducers; Macmillan Education: London, UK, 1985; ISBN 978-0-333-38710-8. [Google Scholar]
- Petchmaneelumka, W.; Koodtalang, W.; Riewruja, V. Simple Technique for Linear-Range Extension of Linear Variable Differential Transformer. IEEE Sensors J. 2019, 19, 5045–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripka, P.; Blažek, J.; Mirzaei, M.; Lipovský, P.; Šmelko, M.; Draganová, K. Inductive position and speed sensors. Sensors 2019, 20, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwan, H.P. Electrical Properties of Tissue and Cell Suspensions. Adv. Biol. Med Phys. 1957, 5, 147–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, A.M.; Hwang, N.H. Human red blood cell hemolysis in a turbulent shear flow: Contribution of Reynolds shear stresses. Biorheology 1984, 21, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameneva, M.V.; Burgreen, G.W.; Kono, K.; Repko, B.; Antaki, J.F.; Umezu, M. Effects of Turbulent Stresses upon Mechanical Hemolysis: Experimental and Computational Analysis. ASAIO J. 2004, 50, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.; Zygmanowski, A.; Zimmermann, S. How Geometry affects sensitivity of a differential transformer for contactless characterization of liquids. Sensors 2021, 21, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TYGON®-ND 100-65 Tubing. Available online: https://www.medical.saint-gobain.com/sites/imdf.medical.com/files/tygon-nd-100-65-datasheet-f19_1_0.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2021).
- Ismatec Ecoline VC-380 Pump. Available online: http://www.ismatec.de/ch_d/pumpen/s_ecoline/eco_vc380.htm (accessed on 7 August 2021).
- Wu, Y.C.; Berezansky, P.A. Low Electrolytic Conductivity Standards. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 1995, 100, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronstein, I.N.; Semendjajew, K.A.; Musiol, G.; Mühlig, H. Taschenbuch der Mathematik, 8th ed.; Vollst. überarb. Aufl.: Frankfurt, Germany, 2012; ISBN 978-3-8171-2008-6. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Billah, S.M.R. Dielectric Polymers. In Cellulose-Based Superabsorbent Hydrogels; Mondal, M.I.H., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–49. ISBN 978-3-319-76573-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bénéteau-Burnat, B.; Pernet, P.; Pilon, A.; Latour, D.; Goujon, S.; Feuillu, A.; Vaubourdolle, M. Evaluation of the GEM® Premier™ 4000: A compact blood gas CO-Oximeter and electrolyte analyzer for point-of-care and laboratory testing. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2008, 46, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








Publisher′s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berger, M.; Zygmanowski, A.; Zimmermann, S. Differential Inductive Sensing System for Truly Contactless Measuring of Liquids′ Electromagnetic Properties in Tubing. Sensors 2021, 21, 5535. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165535
Berger M, Zygmanowski A, Zimmermann S. Differential Inductive Sensing System for Truly Contactless Measuring of Liquids′ Electromagnetic Properties in Tubing. Sensors. 2021; 21(16):5535. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165535
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerger, Marc, Anne Zygmanowski, and Stefan Zimmermann. 2021. "Differential Inductive Sensing System for Truly Contactless Measuring of Liquids′ Electromagnetic Properties in Tubing" Sensors 21, no. 16: 5535. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165535
APA StyleBerger, M., Zygmanowski, A., & Zimmermann, S. (2021). Differential Inductive Sensing System for Truly Contactless Measuring of Liquids′ Electromagnetic Properties in Tubing. Sensors, 21(16), 5535. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21165535






