An Overview of Machine Learning within Embedded and Mobile Devices–Optimizations and Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We present a survey of machine learning models commonly used in embedded systems applications.
- We describe an overview of compute-intensive machine learning models such as HMMs, k-NNs, SVMs, GMMs, and DNNs.
- We provide an overview of different optimization schemes adopted for these algorithms.
- We present an overview of the implementation of these algorithms within resource-limited environments such as MCUs, mobile devices, hardware accelerators, and TinyML.
- We survey the challenges faced in embedded machine learning and review different optimization techniques to enhance the execution of deep learning models within resource-constrained environments.
- We present diverse application areas of embedded machine learning, identify open issues and highlight key lessons learned for future research exploration.
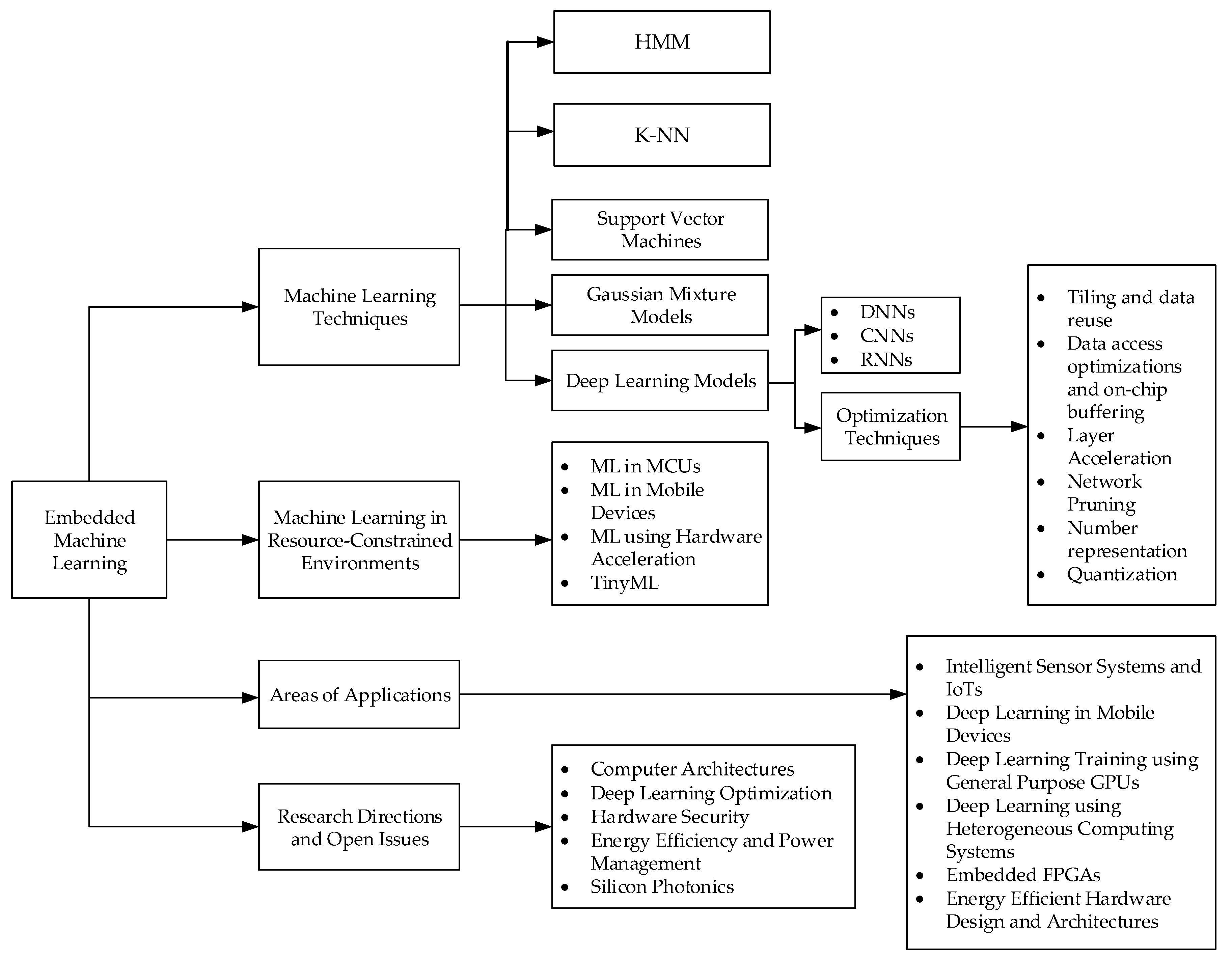
2. Embedded Machine Learning Techniques
2.1. Scope of ML Techniques Overview
2.2. Hidden Markov Models
2.2.1. The HMM Algorithm
2.2.2. Some HMM Optimization Schemes
2.3. k-Nearest Neighbours
2.3.1. The k-NN Algorithm
2.3.2. Some k-NN Optimization Schemes
2.4. Support Vector Machines
2.4.1. The SVM Algorithm
| Algorithm 1. Pseudocode for training a support vector machine |
| Require:X and y loaded with training labeled data, or α partially trained SVM 1: C some value (10 for example) 2: repeat 3: for all do 4: Optimize 5: end for 6: until no changes in or other resource constraint criteria met Ensure: Retain only the support vectors () |
2.4.2. Some SVM Optimizations Schemes
2.5. Gaussian Mixture Model
2.5.1. The GMM Algorithm
2.5.2. Some GMM Optimization Schemes
2.6. Deep Learning Models
2.6.1. Convolution Layers
2.6.2. Pooling Layers
2.6.3. Normalization Layers
2.6.4. Fully-Connected Layers
2.6.5. Fully-Connected Deep Neural Networks
2.6.6. Convolutional Neural Networks
2.6.7. Recurrent Neural Networks
3. Machine Learning in Resource-Constrained Environments
3.1. Machine Learning Using Microcontrollers
3.2. Machine Learning Using Hardware Accelerators
3.3. Machine Learning in Mobile Devices
3.4. TinyML
4. Challenges and Optimization Opportunities in Embedded Machine Learning
4.1. Power Consumption
4.2. Memory Footprint
4.3. Latency and Throughput Concerns
4.4. Prediction Accuracy
4.5. Some Hardware-Oriented and Algorithm-Based Optimization Techniques
4.5.1. Tiling and Data Reuse
| Algorithm 2 Pseudocode of the Tiling Process |
| Require: Ni: the number of the input neurons No: the number of the output neurons Tile_Size: the tile size of the input data batchsize: the batch size of the input data forn = 0; n < batchsize; n ++ do for k = 0; k < Ni; k+ = Tile_Size do for j = 0; j < No; j ++ do y[n][j] = 0; for i = k; i < k + Tile_Size&&i < Ni; i ++ do y[n][j] + = w[i][j] * x[n][i] if i == Ni − 1 then y[n][j] = f(y[n][j]); end if end for end for end for end for |
4.5.2. Direct Memory Access and On-Chip Buffers
4.5.3. Layer Acceleration
4.5.4. Network Pruning
4.5.5. Reduced Precision
4.5.6. Quantization
5. Areas of Applications of Intelligent Embedded Systems
5.1. Intelligent Sensor Systems and IoTs
5.2. Deep Learning In Mobile Devices
5.3. Deep Learning Training Using Graphic Processors (GPUs)
5.4. Deep Learning Using Heterogeneous Computing Systems
5.5. Embedded Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs)
5.6. Energy Efficient Hardware Design and Architectures
6. Research Directions and Open Issues
6.1. Lessons Learned
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Meaning |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| ASIC | Application Specific Integrated Circuit |
| ASIP | Application-Specific Instruction-set Processor |
| CPU | Central Processing Unit |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| DCNN | Deep Convolutional Neural Network |
| DMA | Direct Memory Access |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network |
| DSA | Domain-Specific Architectures |
| DSP | Digital Signal Processor |
| EML | Embedded Machine Learning |
| FPAA | Field Programmable Analog Array |
| FPGA | Field Programmable Gate Array |
| FC | Fully Connected |
| GPGPU | General Purpose Graphic Processing Unit |
| GMM | Gaussian Mixture Model |
| HMM | Hidden Markov Model |
| IC | Integrated Circuit |
| I/O | Input/output |
| ISA | Instruction Set Architecture |
| ISF | Intelligent Sensor Framework |
| k-NN | k-Nearest Neighbors |
| LRN | Local Response Normalization |
| LSTM | Long Short Term Memory |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| MANET | Mobile Adhoc Network |
| MCU | Microcontroller Unit |
| PE | Processing Element |
| RAM | Random Access Memory |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| SoC | System on Chip |
| SVM | Support Vector Machines |
| SDG | Stochastic Descent Gradient |
| SVD | Singular Value Decomposition |
| TPU | Tensor Processing Unit |
| WSN | Wireless Sensor Network |
References
- Wayne, W. Praise of High-Performance Embedded Computing: Architectures, Applications, and Methodologies; Morgan Kaupmann Publishers: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Haigh, K.Z.; Mackay, A.M.; Cook, M.R.; Lin, L.G. Machine Learning for Embedded Systems: A Case Study; BBN Technologies: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; Volume 8571, pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks Alex. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, P.Y.; Reed, S.S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference Computer Vision Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real, E.; Moore, S.; Selle, A.; Saxena, S.; Suematsu, Y.L.; Tan, J.; Le, Q.V.; Kurakin, A. Large-scale evolution of image classifiers. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference Machine Learning ICML, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 4429–4446. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference Machine Learning ICML 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; pp. 10691–10700. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.; Deng, L.; Yu, D.; Dahl, G.E.; Mohamed, A.R.; Jaitly, N.; Senior, A.; Vanhoucke, V.; Nguyen, P.; Sainath, T.N.; et al. Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition. IEEE Signal. Process. Mag. 2012, 29, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.; Jaitly, N.; Le, Q.V.; Vinyals, O. Listen, attend and spell. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Schuster, M.; Chen, Z.; Le, Q.V.; Norouzi, M.; Macherey, W.; Krikun, M.; Cao, Y.; Gao, Q.; Macherey, K.; et al. Google’s neural machine translation system: Bridging the Gap between human and machine translation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.08144. [Google Scholar]
- Collobert, R.; Weston, J.; Bottou, L.; Karlen, M.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Kuksa, P. Natural language processing (almost) from scratch. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2493–2537. [Google Scholar]
- Haj, R.B.; Orfanidis, C. A discreet wearable long-range emergency system based on embedded machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops), Kassel, Germany, 22–26 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, J. The deep learning revolution and its implications for computer architecture and chip design. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 16–20 February 2020; pp. 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Liu, H.; Fan, M.; Ai, B.; Ma, D.; Yang, F. Seafloor habitat mapping using multibeam bathymetric and backscatter intensity multi-features SVM classification framework. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 174, 107728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Kim, J. Toward developing efficient Conv-AE-based intrusion detection system using heterogeneous dataset. Electronics 2020, 9, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, N.; Cao, Y. HeteroSpark: A heterogeneous CPU/GPU spark platform for machine learning algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference Networking, Architecture Storage, NAS, Boston, MA, USA, 6–7 August 2015; pp. 347–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raparti, V.Y.; Pasricha, S. RAPID: Memory-aware NoC for latency optimized GPGPU architectures. IEEE Trans. Multi-Scale Comput. Syst. 2018, 4, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Robaei, M.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, H.; Fang, J. A low-cost and energy-efficient noc architecture for GPGPUs. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2019, 4, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, H.; Mohanty, S.P.; Fang, J. Exploration of system configuration in effective training of CNNs on GPGPUs. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conferece Consumer Electronics ICCE, Las Vegas, NJ, USA, 11 January 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Wang, C.; Ma, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, X. A deep learning prediction process accelerator based FPGA. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/ACM 15th International Symposium Cluster Cloud, Grid Computer CCGrid 2015, Shenzhen, China, 4–7 May 2015; pp. 1159–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noronha, D.H.; Zhao, R.; Goeders, J.; Luk, W.; Wilton, S.J.E. On-chip FPGA debug instrumentation for machine learning applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM/SIGDA International Symposium on Field-Programmable Gate Arrays, Seaside, CA, USA, 24–26 February 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gong, L.; Yu, Q.; Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, X. DLAU: A scalable deep learning accelerator unit on FPGA. IEEE Trans. Comput. Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2016, 36, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.X.M.; Martini, B.; Culurciello, E. Recurrent Neural Networks Hardware Implementationon FPGA. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1511.05552 (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Branco, S.; Ferreira, A.G.; Cabral, J. Machine learning in resource-scarce embedded systems, FPGAs, and end-devices: A survey. Electronics 2019, 8, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, P.; Sun, G.; Guan, Y.; Xiao, B.; Cong, J. Optimizing FPGA-based accelerator design for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM/SIGDA International Symposium on Field-Programmable Gate Arrays, Monterey, CA, USA, 22–24 February 2015; pp. 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neshatpour, K.; Mokrani, H.M.; Sasan, A.; Ghasemzadeh, H.; Rafatirad, S.; Homayoun, H. Architectural considerations for FPGA acceleration of machine learning applications in MapReduce. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Embedded Computer Systems: Architectures, Modeling, and Simulation, Pythagorion, Greece, 15–19 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level Accuracy With 50× Fewer Parameters and <0.5 mb Model Size. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1602.07360 (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Deng, Y. Deep learning on mobile devices: A review. In Proceedings of the SPIE 10993, Mobile Multimedia/Image Processing, Security, and Applications 2019, 109930A, Baltimore, ML, USA, 14–18 April 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Ahn, J.; Yoo, S. A novel zero weight/activation-aware hardware architecture of convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2017 Design, Automation and Test in Europe DATE 2017, Lausanne, Switzerland, 27–31 March 2017; pp. 1462–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidhuber, J. Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. Neural Netw. 2015, 61, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawandhiya, P. Hardware design for machine learning. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Appl. 2018, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ran, X. Deep learning with edge computing: A review. Proc. IEEE 2019, 107, 1655–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.; Drikakis, D.; Charissis, V. Machine-learning methods for computational science and engineering. Computation 2020, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Niyato, D.; Deng, R.; Wang, P.; Wang, L.C. Deep reinforcement learning for mobile 5G and beyond: Fundamentals, applications, and challenges. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2019, 14, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonell, J.G. Machine learning research. ACM SIGART Bull. 1981, 18, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.D.; Channe, H.P. Comparative STUDY of K-NN, naive bayes and decision tree classification techniques. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2016, 5, 1842–1845. [Google Scholar]
- Chapter 4 Logistic Regression as a Classifier. Available online: https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~kdeng/thesis/logistic.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Salvadori, C.; Petracca, M.; del Rincon, J.M.; Velastin, S.A.; Makris, D. An optimisation of Gaussian mixture models for integer processing units. J. Real Time Image Process. 2017, 13, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Borisov, N.; Caesar, M. Do you hear what i hear? Fingerprinting smart devices through embedded acoustic components. In Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Computer, Communication and Security, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 3–7 November 2014; pp. 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojinov, H.; Michalevsky, Y.; Nakibly, G.; Boneh, D. Mobile Device Identification via Sensor Fingerprinting. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1408.1416 (accessed on 12 January 2021).
- Huynh, M.; Nguyen, P.; Gruteser, M.; Vu, T. Mobile device identification by leveraging built-in capacitive signature. In Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Compututer, Communication and Security, Denver, CO, USA, 12–16 October 2015; pp. 1635–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, S.; Sreeraj, K.P. FPGA implementation of feature extraction based on histopathalogical image and subsequent classification by support vector machine. IJISET Int. J. Innov. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2015, 2, 744–749. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Ukidave, Y.; Kaeli, D. GPU-accelerated HMM for speech recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference Parallel Processing Work, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 9–12 September 2014; pp. 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Yoon, C.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J. Smart wearable band for stress detection. In Proceedings of the 2015 5th International Conference IT Converg. Secur. ICITCS, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 24–27 August 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, A.; Valkama, M.; Lohan, E.S. K-means fingerprint clustering for low-complexity floor estimation in indoor mobile localization. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Globecom Work. GC Wkshps 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 6–10 December 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhide, V.H.; Wagh, S. I-learning IoT: An intelligent self learning system for home automation using IoT. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference Communication Signalling Process. ICCSP 2015, Melmaruvathur, India, 2–4 April 2015; pp. 1763–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munisami, T.; Ramsurn, M.; Kishnah, S.; Pudaruth, S. Plant Leaf recognition using shape features and colour histogram with K-nearest neighbour classifiers. Proc. Comput. Sci. 2015, 58, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowjanya, K.; Singhal, A.; Choudhary, C. MobDBTest: A machine learning based system for predicting diabetes risk using mobile devices. In Proceedings of the Souvenir 2015 IEEE Int. Adv. Comput. Conference IACC 2015, Banglore, India, 12–13 June 2015; pp. 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Stanley, M.; Spanias, A.; Tepedelenlioglu, C. Integrating machine learning in embedded sensor systems for Internet-of-Things applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology (ISSPIT), Limassol, Cyprus, 12–14 December 2016; pp. 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Wang, J.; Yao, S.; Guo, K.; Li, B.; Zhou, E.; Yu, J.; Tang, T.; Xu, N.; Song, S.; et al. Going deeper with embedded FPGA platform for convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the FPGA 2016ACM/SIGDA International Symposium Field-Programmable Gate Arrays, Monterey, CA, USA, 21–23 February 2016; pp. 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, L.N.; Balan, R.K.; Lee, Y. DeepSense: A GPU-based deep convolutional neural network framework on commodity mobile devices. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Wearable Systems and Application Co-Located with MobiSys 2016, Singapore, 30 June 2016; pp. 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuama, A.; Comby, F.; Chaumont, M. Camera model identification based machine learning approach with high order statistics features. In Proceedings of the 24th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Budapest, Hungary, 29 August–2 September 2016; pp. 1183–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, A.; Gascon, H.; Becker, T.; Rieck, K.; Freiling, F. Fingerprinting Mobile Devices Using Personalized Configurations. Proc. Priv. Enhanc. Technol. 2016, 1, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, M.A.; Perera, D.G. An FPGA-based hardware accelerator for k-nearest neighbor classification for machine learning on mobile devices. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, HEART 2018, Toronto, ON, Canada, 20–22 June 2018; pp. 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.S.; Thorat, S.A. Early detection of grapes diseases using machine learning and IoT. In Proceedings of the 2016 Second International Conference on Cognitive Computing and Information Processing (CCIP), Mysuru, India, 12–13 August 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollander, S.; Godin, C.; Campagne, A.; Charbonnier, S. A comparison of wearable and stationary sensors for stress detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference System Man, and Cybernetic SMC 2016, Budapest, Hungary, 9–12 October 2016; pp. 4362–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.W.L.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C.; Oliveira, A.M.B.; Saleem, K. Smart mobile system for pregnancy care using body sensors. In Proceedings of the International Conference Sel. Top. Mob. Wirel. Networking, MoWNeT 2016, Cairo Egypt, 11–13 April 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapsough, S.; Hesham, A.; Elkhorazaty, Y.; Zualkernan, I.A.; Aloul, F. Emotion recognition using mobile phones. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 18th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom), Munich, Germany, 14–16 September 2016; pp. 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, A.; Huq, M.S.; Shanta, S.; Ibrahim, B.S.K.K. Smartphone based data mining for fall detection: Analysis and design. Proc. Comput. Sci. 2016, 105, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronao, C.A.; Cho, S.B. Recognizing human activities from smartphone sensors using hierarchical continuous hidden Markov models. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2017, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodali, S.; Hansen, P.; Mulholland, N.; Whatmough, P.; Brooks, D.; Wei, G.Y. Applications of deep neural networks for ultra low power IoT. In Proceedings of the 35th IEEE International Conference on Computer Design ICCD 2017, Boston, MA, USA, 5–8 November 2017; pp. 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolution neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, G.; Dimc, F.; Kamnik, R.; Steri, G.; Giuliani, R.; Gentile, C. Identification of mobile phones using the built-in magnetometers stimulated by motion patterns. Sensors 2017, 17, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimi, I.; Anzanpour, A.; Rahmani, A.M.; Pahikkala, T.; Levorato, M.; Liljeberg, P.; Dutt, N. HiCH: Hierarchical fog-assisted computing architecture for healthcare IoT. ACM Trans. Embed. Comput. Syst. 2017, 16, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.S. Machine Learning and IoT for prediction and detection of stress. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications ICCSA 2017, Trieste, Italy, 3–6 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneha, H.R.; Rafi, M.; Kumar, M.V.M.; Thomas, L.; Annappa, B. Smartphone based emotion recognition and classification. In Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Technology ICECCT 2017, Coimbatore, India, 22–24 February 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mamun, M.A.; Puspo, J.A.; Das, A.K. An intelligent smartphone based approach using IoT for ensuring safe driving. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (ICECOS), Palembang, Indonesia, 22–23 August 2017; pp. 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyja, M.; Mumtaz, S.; Huq, K.M.S.; Busari, S.A.; Rodriguez, J.; Zhou, Z. An IoT-based e-health monitoring system using ECG signal. In Proceedings of the IEEE Global Communications Conference GLOBECOM 2017, Singapore, 4–8 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, C.; Suggala, A.S.; Goyal, A.; Simhadri, H.V.; Paranjape, B.; Kumar, A.; Goyal, S.; Udupa, R.; Varma, M.; Jain, P. ProtoNN: Compressed and accurate kNN for resource-scarce devices. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 1331–1340. [Google Scholar]
- Fafoutis, X.; Marchegiani, L.; Elsts, A.; Pope, J.; Piechocki, R.; Craddock, I. Extending the battery lifetime of wearable sensors with embedded machine learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE World Forum on Internet Things, WF-IoT 2018, Singapore, 5–8 February 2018; pp. 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damljanovic, A.; Lanza-Gutierrez, J.M. An embedded cascade SVM approach for face detection in the IoT edge layer. In Proceedings of the IECON 2018—44th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Washington, DC, USA, 21–23 October 2018; pp. 2809–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochstetler, J.; Padidela, R.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Q.; Fu, S. Embedded deep learning for vehicular edge computing. In Proceedings of the 3rd ACM/IEEE Symposium on Edge Computing SEC 2018, Seattle, WA, USA, 25–27 October 2018; pp. 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.; Marco, V.S.; Wolff, W.; Elkhatib, Y.; Wang, Z. Adaptive deep learning model selection on embedded systems. ACM SIGPLAN Not. 2018, 53, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strielkina, A.; Kharchenko, V.; Uzun, D. A markov model of healthcare internet of things system considering failures of components. CEUR Workshop Proc. 2018, 2104, 530–543. [Google Scholar]
- Vhaduri, S.; van Kessel, T.; Ko, B.; Wood, D.; Wang, S.; Brunschwiler, T. Nocturnal cough and snore detection in noisy environments using smartphone-microphones. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Healthcare Informatics, ICHI 2019, Xi’an, China, 10–13 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, H.; Bajwa, I.S.; Amin, R.U.; Sarwar, N.; Jamil, N.; Malik, M.A.; Mahmood, A.; Shafi, U. An IoT-based intelligent wound monitoring system. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 144500–144515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistu, D.; Frisk, F. Edge machine learning for energy efficiency of resource constrained IoT devices. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Smart Portable, Wearable, Implantable and Disabilityoriented Devices and Systems, SPWID 2019, Nice, France, 28 July–1 August 2019; pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Tuor, T.; Salonidis, T.; Leung, K.K.; Makaya, C.; He, T.; Chan, K. Adaptive Federated Learning in Resource Constrained Edge Computing Systems. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2019, 37, 1205–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, P.; Fernandez, S.G.; Vidyasagar, S.; Kalyanasundaram, V.; Vijayakumar, K.; Archana, V.; Chatterjee, S. Reduction of transients in switches using embedded machine learning. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2020, 11, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Giri, D.; Chiu, K.L.; di Guglielmo, G.; Mantovani, P.; Carloni, L.P. ESP4ML: Platform-based design of systems-on-chip for embedded machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 Design, Automation and Test in European Conference Exhibition DATE 2020, Grenoble, France, 9–13 March 2020; pp. 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiku, S.; Pasricha, S.; Notaros, B.; Han, Q. A hidden markov model based smartphone heterogeneity resilient portable indoor localization framework. J. Syst. Archit. 2020, 108, 101806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazlan, N.; Ramli, N.A.; Awalin, L.; Ismail, M.; Kassim, A.; Menon, A. A smart building energy management using internet of things (IoT) and machine learning. Test. Eng. Manag. 2020, 83, 8083–8090. [Google Scholar]
- Cornetta, G.; Touhafi, A. Design and evaluation of a new machine learning framework for iot and embedded devices. Electronics 2021, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiner, L.; Juang, B. An introduction to hidden Markov models. IEEE ASSP Mag. 1986, 3, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degirmenci, A. Introduction to hidden markov models. Harv. Univ. 2014, 3, 1–5. Available online: http://scholar.harvard.edu/files/adegirmenci/files/hmm_adegirmenci_2014.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2016).
- Tóth, B.; Németh, G. Optimizing HMM speech synthesis for low-resource devices. J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform. 2012, 16, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Zhao, Z.; Tu, Q. Reducing computational and memory cost for HMM-based embedded TTS system. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2011, 224, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baoli, L.; Shiwen, Y.; Qin, L. An improved K-nearest neighbor algorithm for text categorization. Dianzi Yu Xinxi Xuebao J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2005, 27, 487–491. [Google Scholar]
- Norouzi, M.; Fleet, D.J.; Salakhutdinov, R. Hamming distance metric learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 2, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Saikia, J.; Yin, S.; Jiang, Z.; Seok, M.; Seo, J.S. K-nearest neighbor hardware accelerator using in-memory computing SRAM. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design (ISLPED), Lausanne, Switzerland, 29–31 July 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, R.; Schoeberl, M. An embedded support vector machine. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Workshop on Intelligent Solutions in Embedded Systems, Vienna, Austria, 30 June 2006; pp. 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Fu, H.; Song, S.L.; Randles, A.; Kerbyson, D.; Marquez, A.; Yang, G.; Hoisie, A. Scaling support vector machines on modern HPC platforms. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2015, 76, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, A.; Pianegiani, F.; Petri, D. Low-power and low-cost implementation of SVMs for smart sensors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2007, 56, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afifi, S.M.; Gholamhosseini, H.; Sinha, R. Hardware implementations of SVM on FPGA: A state-of-the-art review of current practice. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2015, 2, 733–752. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Z.Q.; Yu, H.B.; Xu, H.R.; Xie, Y.Q.; Gao, J. Fast training support vector machines using parallel sequential minimal optimization. In Proceedings of the 2008 3rd International Conference on Intelligent System and Knowledge Engineering, Xiamen, China, 17–19 November 2008; pp. 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguita, D.; Ghio, A.; Oneto, L.; Parra, X.; Reyes-Ortiz, J.L. Human activity recognition on smartphones using a multiclass hardware-friendly support vector machine. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2012, 7657, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, T.; Matsumoto, Y. Chunking with support vector machines. In Proceedings of the Second Meeting of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics 2001, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2–7 June 2001; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuna, E.; Freund, R.; Girosi, F. Improved training algorithm for support vector machines. Neural Networks for Signal Processing VII. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE Signal Processing Society Workshop, Amelia Island, FL, USA, 24–26 September 1997; pp. 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Mangasarian, O. RSVM: Reduced Support vector machines. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2001 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, Chicago, IL, USA, 5–7 April 2001; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguita, D.; Ghio, A.; Pischiutta, S.; Ridella, S. A hardware-friendly support vector machine for embedded automotive applications. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–17 August 2007; pp. 1360–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguita, D.; Bozza, G. The effect of quantization on support vector machines with Gaussian kernel. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Montreal, QC, Canada, 31 July–4 August 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.M.; Arnold, M.G.; Pottenger, W.M. Hardware-based support vector machine classification in logarithmic number systems. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Kobe, Japan, 23–26 May 2005; pp. 5154–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguita, D.; Pischiutta, S.; Ridella, S.; Sterpi, D. Feed-forward support vector machine without multipliers. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2006, 17, 1328–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, D. Gaussian mixture models. Encycl. Biometr. 2009, 741, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorur, P.; Amrutur, B. Speeded up Gaussian mixture model algorithm for background subtraction. In Proceedings of the 2011 8th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), Klagenfurt, Austria, 30 August –2 September 2011; pp. 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Hu, W.; Liu, J.; Yang, M.; Wei, B.; Chou, C.T. Efficient background subtraction for real-time tracking in embedded camera networks. In Proceedings of the 10th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor System, Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–9 November 2012; pp. 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottou, L. Stochastic Gradient Descent Tricks. In Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Montavon, G., Orr, G.B., Müller, K.R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.; Zhang, T. Accelerating stochastic gradient descent using predictive variance reduction. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2013, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Bottou, L. Stochastic gradient learning in neural networks, Proc. Neuro-Nımes 1991, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J. An efficient hardware architecture for activation function in deep learning processor. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Image, Vision and Computing (ICIVC), Chongqing, China, 27–29 June 2018; pp. 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, N.; Chandra, V.; Dasika, G.; Mohanty, A.; Ma, Y.; Vrudhula, S.; Seo, J.S.; Cao, Y. Throughput-optimized OpenCL-based FPGA Accelerator for large-scale convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the ACM/SIGDA International Symposium on Field-Programmable Gate Arrays, Monterey, CA, USA, 21–23 February 2016; pp. 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Learning, S.D. Smartphones devices. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2017, 16, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Albawi, S.; Mohammed, T.A.; Al-Zawi, S. Understanding of a convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICET), Antalya, Turkey, 21–23 August 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, K.; Nash, R. An Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1511.08458 (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Lawrence, S.; Giles, L.; Tsoi, C.; Back, A. Face recognition: A convolutional neural-network approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1997, 8, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Haghi, B.; Kellis, S.; Bashford, L.; Kramer, D.; Lee, B.; Liu, C.; Andersen, R.; Emami, A. Decoding kinematics from human parietal cortex using neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 9th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–23 March 2019; pp. 1138–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lim, M.; Park, H.; Kang, Y.; Park, J.S.; Jang, G.J.; Kim, J.H. Long short-term memory recurrent neural network-based acoustic model using connectionist temporal classification on a large-scale training corpus. Chin. Commun. 2017, 14, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Si, X.; Zhang, J. A review of recurrent neural networks: LSTM cells and network architectures. Neural Comput. 2019, 31, 1235–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Karim, M.R.; Kim, Y. A two-stage big data analytics framework with real world applications using spark machine learning and long short-term memory network. Symmetry 2018, 10, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouppi, N.P.; Young, C.; Patil, N.; Patterson, D. A domain-specific architecture for deep neural networks. Commun. ACM 2018, 61, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2014, 8689, 818–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Pool, J.; Tran, J.; Dally, W.J. Learning both weights and connections for efficient neural networks. In Proceedings of the NIPS’15: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 1135–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Khoram, S.; Li, J. Adaptive quantization of neural networks. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2018), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kofahi, M.M.; Al-Shorman, M.Y.; Al-Kofahi, O.M. Toward energy efficient microcontrollers and Internet-of-Things systems. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2019, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keras, A. Keras API Reference/Keras Applications. Available online: https://keras.io/api/applications/ (accessed on 14 March 2021).
- Atmel. ATMEL—ATmega48P/88P/168P/328P. Available online: https://www.sparkfun.com/datasheets/Components/SMD/ATMega328.pdf (accessed on 14 March 2021).
- Atmel Corporation. ATMEL—ATmega640/V-1280/V-1281/V-2560/V-2561/V. Available online: https://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/devicedoc/atmel-2549-8-bit-avr-microcontroller-atmega640-1280-1281-2560-2561_datasheet.pdf (accessed on 14 March 2021).
- STMicroelectronics. STM32L073x8 STM32L073xB. Available online: https://www.st.com/resource/en/datasheet/stm32l073v8.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Atmel Corporation. 32-Bit ARM-Based Microcontrollers SAM D21E/SAM D21G/SAM D21J Summary. Available online: www.microchip.com (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Atmel. SAM3X / SAM3A Series datasheet. Available online: http://www.atmel.com/Images/Atmel-11057-32-bit-Cortex-M3-Microcontroller-SAM3X-SAM3A_Datasheet.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- STMicroelectronics. STM32F215xx STM32F217xx. Available online: https://www.st.com/resource/en/datasheet/stm32f215re.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- STMicroelectronics. STM32F469xx. Available online: https://www.st.com/resource/en/datasheet/stm32f469ae.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Raspberry Pi Dramble. Power Consumption Benchmarks. Available online: https://www.pidramble.com/wiki/benchmarks/power-consumption (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- The First Affordable RISC-V Computer Designed to Run Linux. Available online: https://www.seeedstudio.com/blog/2021/01/13/meet-beaglev-the-first-affordable-risc-v-single-board-computer-designed-to-run-linux/ (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Lane, N.D.; Bhattacharya, S.; Georgiev, P.; Forlivesi, C.; Jiao, L.; Qendro, L.; Kawsar, F. DeepX: A Software accelerator for low-power deep learning inference on mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 2016 15th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (IPSN), Vienna, Austria, 11–14 April 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, X.; Kong, D. DeepRebirth: Accelerating deep neural network execution on mobile devices. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2017; pp. 2322–2330. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, T.I.; Cavalcanti, G.D.C.; Gabriel, D.; Pinheiro, H.N.B. A Hybrid GMM Speaker Verification System for Mobile Devices in Variable Environments. In Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning—IDEAL 2012; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Yin, H., Costa, J.A.F., Barreto, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Senior, A.; Gruenstein, A.; Sorensen, J. Accurate and compact large vocabulary speech recognition on mobile devices. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association INTERSPEECH, Lyon, France, 25–29 August 2013; pp. 662–665. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Iborra, R.; Skarmeta, A.F. TinyML-enabled frugal smart objects: Challenges and opportunities. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2020, 20, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Naumov, M.; Basu, P.; Deng, S.; Kalaiah, A.; Khudia, D.; Law, J.; Malani, P.; Malevich, A.; Nadathur, S.; et al. Deep learning inference in facebook data centers: Characterization, performance optimizations and hardware implications. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.09886. [Google Scholar]
- Banbury, C.; Zhou, C.; Fedorov, I.; Matas, R.; Thakker, U.; Gope, D.; Janapa Reddi, V.; Mattina, M.; Whatmough, P. MicroNets: Neural network architectures for deploying TinyML Applications on commodity microcontrollers. In Proceedings of the 4th MLSys Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 4–7 April 2021; Available online: https://proceedings.mlsys.org/paper/2021/file/a3c65c2974270fd093ee8a9bf8ae7d0b-Paper.pdf (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- NVIDIA. NVIDIA V100 Tensor Core GPU. Available online: https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/data-center/v100/ (accessed on 20 February 2021).
- NVIDIA. The Ultimate PC GPU Nvidia Titan RTX. Available online: https://www.nvidia.com/content/dam/en-zz/Solutions/titan/documents/titan-rtx-for-creators-us-nvidia-1011126-r6-web.pdf (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- ST Microelectronics. STM32F745xx STM32F746xx Datasheet. Available online: http://www.st.com/content/ccc/resource/technical/document/datasheet/96/ed/61/9b/e0/6c/45/0b/DM00166116.pdf/files/DM00166116.pdf/jcr:content/translations/en.DM00166116.pdf (accessed on 22 January 2021).
- ST Microelectronics Inc. STM32F765xx, STM32F767xx Datasheet. Available online: https://pdf1.alldatasheet.com/datasheet-pdf/view/933989/STMICROELECTRONICS/STM32F767ZI.html (accessed on 17 January 2021).
- Capra, M.; Bussolino, B.; Marchisio, A.; Shafique, M.; Masera, G.; Martina, M. An Updated survey of efficient hardware architectures for accelerating deep convolutional neural networks. Future Internet 2020, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Cao, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, J. A survey of optimization methods from a machine learning perspective. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 50, 3668–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Mao, H.; Dally, W.J. Deep compression: Compressing deep neural networks with pruning, trained quantization and Huffman coding. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2–4 May 2016; pp. 1–14. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1510.00149 (accessed on 17 January 2021).
- Hubara, I.; Courbariaux, M.; Soudry, D.; El-Yaniv, R.; Bengio, Y. Quantized neural networks: Training neural networks with low precision weights and activations. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2018, 18, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, K.; Arikawa, Y.; Ito, T.; Morita, K.; Nemoto, N.; Miura, F.; Terada, K.; Teramoto, J.; Sakamoto, T. Communication-efficient distributed deep learning with GPU-FPGA heterogeneous computing. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Symposium on High-Performance Interconnects (HOTI), Piscataway, NJ, USA, 19–21 August 2020; pp. 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, N.; Bhattacharya, S.; Georgiev, P.; Forlivesi, C. Squeezing deep learning into mobile and embedded devices. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2017, 16, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gysel, P. Ristretto: Hardware-Oriented Approximation of Convolutional Neural Networks. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1605.06402 (accessed on 20 February 2021).
- Moons, B.; Goetschalckx, K.; van Berckelaer, N.; Verhelst, M. Minimum energy quantized neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 51st Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers ACSSC 2017, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 29 October–1 November 2017; pp. 1921–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Kirk, S.R.; Jenkins, S. Tiling for performance tuning on different models of GPUs. In Proceedings of the 2009 Second International Symposium on Information Science and Engineering ISISE 2009, Shanghai, China, 26–28 December 2009; pp. 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Tang, C. FPGA-based embedded system design. In Proceedings of the IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference Circuits Systems APCCAS, Macao, China, 30 November–3 December 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, W.; Schindler, G.; Zöhrer, M.; Pfeifenberger, L.; Peharz, R.; Tschiatschek, S.; Fröning, H.; Pernkopf, F.; Ghahramani, Z. Resource-Efficient Neural Networks for Embedded Systems. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2001.03048 (accessed on 27 March 2021).
- Courbariaux, M.; Bengio, Y.; David, J.P. Low Precision Storage for Deep Learning. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1511.00363%5Cnhttp://arxiv.org/abs/1412.7024 (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Courbariaux, M.; David, J.P.; Bengio, Y. Training deep neural networks with low precision multiplications. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 1–10. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.7024 (accessed on 20 February 2021).
- Tong, J.Y.F.; Nagle, D.; Rutenbar, R.A. Reducing power by optimizing the necessary precision/range of floating-point arithmetic. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2000, 8, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliavini, G.; Mach, S.; Rossi, D.; Marongiu, A.; Benin, L. A transprecision floating-point platform for ultra-low power computing. In Proceedings of the 2018 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Dresden, Germany, 19–23 March 2018; pp. 151–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langroudi, S.H.F.; Pandit, T.; Kudithipudi, D. Deep Learning inference on embedded devices: Fixed-point vs posit. In Proceedings of the 2018 1st Workshop on Energy Efficient Machine Learning and Cognitive Computing for Embedded Applications (EMC2), Williamsburg, VA, USA, 25–25 March 2018; pp. 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberstar, E. Fixed-Point Representation & Fractional Math. Available online: http://www.superkits.net/whitepapers/Fixed%20Point%20Representation%20&%20Fractional%20Math.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2021).
- Yates, R. Fixed-point arithmetic: An introduction. Technical Reference. Available online: https://courses.cs.washington.edu/courses/cse467/08au/labs/l5/fp.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Hwang, K.; Sung, W. Fixed-point feedforward deep neural network design using weights +1, 0, and −1. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Workshop on Signal Processing Systems (SiPS), Belfast, UK, 20–22 October 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Agrawal, A.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Narayanan, P. Deep learning with limited numerical precision. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning ICML 2015, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 1737–1746. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson, J.L.; Yonemoto, I. Beating floating point at its own game: Posit arithmetic. Supercomput. Front. Innov. 2017, 4, 71–86. [Google Scholar]
- Hammerstrom, D. A VLSI architecture for high-performance, low-cost, on-chip learning. In Proceedings of the IJCNN. International JT Conference Neural Network, San Diego, CA, USA, 17–21 June 1990; pp. 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courbariaux, M.; Hubara, I.; Soudry, D.; El-Yaniv, R.; Bengio, Y. Binarized Neural Networks: Training Deep Neural Networks with Weights and Activations Constrained to +1 or −1. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1602.02830 (accessed on 22 January 2021).
- Meng, W.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Z. Two-Bit Networks for Deep Learning on Resource-Constrained Embedded Devices. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1701.00485 (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- Park, E.; Ahn, J.; Yoo, S. Weighted-entropy-based quantization for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5456–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrascano, P. Learning vector quantization for the probabilistic neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1991, 2, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Tiku, S.; Pasricha, S. Adapting convolutional neural networks for indoor localization with smart mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 2018 on Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI, 2018; GLSVLSI’18, Chicago, IL, USA, 23–25 May 2018; pp. 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Tian, B.; Yin, S.; Wei, S. Efficient hardware architecture of softmax layer in deep neural network. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP), Shanghai, China, 19–21 November 2018; pp. 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessy, J.L.; Patterson, D.A. A new golden age for computer architecture. Commun. ACM 2019, 62, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.G.; Doppa, J.R.; Pande, P.P.; Marculescu, D.; Marculescu, R. Machine learning and manycore systems design: A Serendipitous symbiosis. Computer 2018, 51, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.G.; Doppa, J.R.; Pande, P.P. Machine learning for design space exploration and optimization of manycore systems. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), San Diego, CA, USA, 5–8 November 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, R.; Gordon-Ross, A.; Stitt, G. Machine learning-based prediction for dynamic architectural optimizations. In Proceedings of the 10th International Green and Sustainability Computing Conference IGSC 2019, Alexandria, VA, USA, 21–24 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, D.; Ma, Z.; Buttyan, L. Embedded systems security: Threats, vulnerabilities, and attack taxonomy. In Proceedings of the 2015 13th Annual Conference on Privacy, Security and Trust (PST), Izmir, Turkey, 21–23 July 2015; pp. 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbebor, J.O.; Imoize, A.L.; Atayero, A.A.-A. Energy Efficient Design Techniques in Next-Generation Wireless Communication Networks: Emerging Trends and Future Directions. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2020, 2020, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imoize, A.L.; Ibhaze, A.E.; Atayero, A.A.; Kavitha, K.V.N. Standard Propagation Channel Models for MIMO Communication Systems. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2021, 2021, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, S.I.; Jefia, A.; Atayero, A.A.; Kingsley, O.; Faruk, N.; Oseni, O.F.; Abolade, R.O. Determination of neural network parameters for path loss prediction in very high frequency wireless channel. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 150462–150483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, N.; Popoola, S.I.; Surajudeen-Bakinde, N.T.; Oloyede, A.A.; Abdulkarim, A.; Olawoyin, L.A.; Ali, M.; Calafate, C.T.; Atayero, A.A. Path loss predictions in the VHF and UHF bands within urban environments: Experimental investigation of empirical, heuristics and geospatial models. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 77293–77307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasricha, S.; Nikdast, M. A Survey of Silicon Photonics for Energy-Efficient Manycore Computing. IEEE Des. Test 2020, 37, 60–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soref, R. The past, present, and future of silicon photonics. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2006, 12, 1678–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittamuru, S.V.R.; Dang, D.; Pasricha, S.; Mahapatra, R. BiGNoC: Accelerating big data computing with application-specific photonic network-on-chip architectures. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2018, 29, 2402–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Machine Learning Techniques | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Supervised Learning | Unsupervised Learning | Reinforcement Learning | |
| Classification | Regression | Clustering | Genetic Algorithms |
| SVM | SVR | HMM | Estimated Value Functions |
| Naïve Bayes | Linear Regression | GMM | Simulated Annealing |
| k-NN | Decision Trees | k-means | |
| Logistic Regression | ANN | DNN | |
| Discriminant Analysis | Ensemble Methods | ||
| DNN | DNN | ||
| Reference | ML Method | Embedded/Mobile Platform | Application | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [2] | SVM | ARMv7, IBM PPC440 | Network Configuration | 2015 |
| [20] | DNN | FPGA Zedboard with 2 ARM Cortex Cores | Character Recognition | 2015 |
| [22] | DNN | Xilinx FPGA board | Image classification | 2016 |
| [23] | LSTM RNN | Zynq 7020 FPGA | Character Prediction | 2016 |
| [25] | CNN | VC707 Board with Xilinx FPGA chip | Image Classification | 2015 |
| [39] | GMM | Raspberry Pi | Integer processing | 2014 |
| [40] | k-NN, SVM | Mobile Device | Fingerprinting | 2014 |
| [41] | k-NN | Mobile Device | Fingerprinting | 2014 |
| [42] | k-NN, GMM | Mobile Device | Mobile Device Identification | 2015 |
| [43] | SVM | Xilinx Virtex 7 XC7VX980 FPGA | Histopathological image classification | 2015 |
| [44] | HMM | Nvidia Kepler | Speech Recognition | 2015 |
| [45] | Logistic Regression | Smart band | Stress Detection | 2015 |
| [46] | k-means | Smartphone | Indoor Localization | 2015 |
| [47] | Naïve Bayes | AVR ATmega-32 | Home Automation | 2015 |
| [48] | k-NN | Smartphone | Image Recognition | 2015 |
| [49] | Decision Tree | Mobile Device | Health Monitoring | 2015 |
| [50] | GMM | FRDM-K64F equipped with ARM Cortex-M4F core | IoT sensor data analysis | 2016 |
| [51] | CNN | FPGA Xilinx Zynq ZC706 Board | Image Classification | 2016 |
| [52] | CNN | Mobile Device | Mobile Sensing | 2016 |
| [53] | SVM | Mobile Device | Fingerprinting | 2016 |
| [54] | k-NN, SVM | Mobile Device | Fingerprinting | 2016 |
| [55] | k-NN | Xilinx Virtex-6 FPGA | Image Classification | 2016 |
| [56] | HMM | Arduino UNO | Disease detection | 2016 |
| [57] | Logistic Regression | Wearable Sensor | Stress Detection | 2016 |
| [58] | Naïve Bayes | Smartphone | Health Monitoring | 2016 |
| [59] | Naïve Bayes | Mobile Devices | Emotion Recognition | 2016 |
| [60] | k-NN | Smartphone | Data Mining | 2016 |
| [61] | HMM | Smartphone Sensors | Activity Recognition | 2017 |
| [62] | DNN | Smartphone | Face detection, activity recognition | 2017 |
| [63] | CNN | Mobile Device | Image classification | 2017 |
| [64] | SVM | Mobile Device | Mobile Device Identification | 2017 |
| [65] | SVM | Jetson-TK1 | Healthcare | 2017 |
| [66] | SVM, Logistic Regression | Arduino UNO | Stress Detection | 2017 |
| [67] | Naïve Bayes | Smartphone | Emotion Recognition | 2017 |
| [68] | k-means | Smartphones | Safe Driving | 2017 |
| [69] | HMM | Mobile Device | Health Monitoring | 2017 |
| [70] | k-NN | Arduino UNO | Image Classification | 2017 |
| [71] | SVM | Wearable Device (nRF51822 SoC+BLE) | Battery Life Management | 2018 |
| [72] | SVM | Zybo Board with Z-7010 FPSoC | Face Detection | 2018 |
| [73] | CNN | Raspberry Pi + Movidus Neural Compute Stick | Vehicular Edge Computing | 2018 |
| [74] | CNN | Jetson TX2 | Image Classification | 2018 |
| [75] | HMM | Smartphone | Healthcare | 2018 |
| [76] | k-NN | Smartphone | Health Monitoring | 2019 |
| [77] | Decision Trees | Arduino UNO | Wound Monitoring | 2019 |
| [78] | RNN | ATmega640 | Smart Sensors | 2019 |
| [79] | SVM, Logistic Regression, k-means, CNN | Raspberry Pi | Federated Learning | 2019 |
| [80] | DNN | Raspberry Pi | Transient Reduction | 2020 |
| [81] | MLP | Embedded SoC (ESP4ML) | Classification | 2020 |
| [82] | HMM | Smartphone | Indoor Localization | 2020 |
| [83] | k-NN | Smartphone | Energy Management | 2020 |
| [84] | ANN, Decision Trees | Raspberry Pi | Classification and Regression | 2021 |
| Problem | Algorithm | Definitions | Equation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Likelihood | Forward Algorithm | is the likelihood, is hidden state sequence and is observation sequence | (1) |
| Decoding | Viterbi Algorithm | is the Viterbi probability, is the previous Viterbi path probability, is transition probability and is the state observation likelihood | (2) |
| Learning | Baum-Welch Algorithm or Forward-Backward Algorithm. | X is a sequence of observations, Z is a hidden state sequence, and is the HMM model | (3) |
| Reference | Optimization Scheme | Application | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| [87] | Optimal HMM parameter selection reduced precision. | Speech Synthesis | This technique reduces general computation time and memory footprint however, fixed-point representation introduces accuracy errors to synthesizing. |
| [88] | HMM parameter reduction, model compression, feature vector size reduction, reduced precision | Speech Synthesis | This research successfully compressed the HMM from 293 MB to 3.61 MB. However, the accuracy of the speech synthesis is just fair owing to huge parameter reduction. |
| Function | Definitions | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| k-NN Prediction Function | is the predicted output, x is input and is Top1 and is the identity function. | (4) |
| Euclidean distance | is the Euclidean distance, p and q are subjects to be compared with n characteristics. | (5) |
| Reference | Optimization Scheme | Application | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| [90] | Binary code learning | Image classification | Although the k-NN model is highly compressed, accuracy is traded off for memory efficiency |
| [55,91] | FPGA Acceleration | Classification | Although computation time is reduced, FPGAs are difficult to program. |
| [70] | Model compression using Stochastic Gradient Descent | Binary and Multi-class classification | The k-NN model is highly compressed with good accuracy |
| TRAINING PHASE OPTIMIZATIONS | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| REFERENCE | Optimization Method | Overview | Comments |
| [98] | Chunking | This method solves the quadratic programming problem (QP) through the removal of rows and columns of zero Lagrange multipliers, thus reducing the entire memory footprint of the SVM model. | Although chunking reduces the size of the model, for large data sets, even the reduced non-zero multipliers are larger than the available memory of the system. |
| [99] | Decomposition | This method targets replacing the original QP problem with a sequence of smaller problems and, for every sub-problem, invokes an iterative numerical routine, which is expected to converge optimally, thus reducing memory footprint and computation requirement. | At every step, a numerical QP solver which may require numerical precision issues to be addressed is adopted. This process requires invoking an entire iterative QP library routine, thus introducing more computation time. |
| [96] | Sequential Minimal Optimization | This is the most widely used optimization technique. It involves breaking down the QP problem into sub-problems and subsequently solve the smallest possible optimization problem at every step. | By solving the smallest possible optimization problem at every step, SMO avoids extra matrix memory storage and invoking an entire library at every step. This technique thus saves computation time and memory footprint. |
| [93] | Accelerated SMO | In this research work, the SMO algorithm is accelerated by introducing an efficient adaptive method for processing data input, incorporating a two-level parallelization scheme, avoiding caching, reducing shrinking, and integrating data reuse. | This technique is not suitable for real-time applications and requires high computational resources to implement successfully. |
| [100] | Reduced SVM | In this work, a Smoothing Algorithm is proposed to solve the QP problem. The QP problem is first broken down by reducing the variables and constraints of the model. These samples can adequately represent the original variables and constraints of the entire dataset, and subsequently, the proposed algorithm is used to solve the problem. | This technique reduces the computational requirement of SVM but targets only non-linear kernel types. |
| INFERENCE PHASE OPTIMIZATIONS | |||
| [101] | Fixed Point Optimization | In this research, the SVM algorithm is implemented using fixed-point arithmetic. Fixed-point number representation, when compared with contemporary floating-point, is less compute-intensive. Thus, this reduced precision technique is adopted to execute the SVM model within a smartphone for a multiclass human activity recognition application. | When reducing precision, accuracy becomes a concern because the lower the bit precision adopted, the more likely it is to introduce classification errors. |
| [102] | Quantization | In this work, a probabilistic technique is used to observe the effect of introducing quantization to the SVM model. The parameters of the model are quantized and using two datasets (Iris and Sonar) which are embedded system-oriented models, the effect of quantization is measured | Although quantization reduces computation time and memory usage, the process introduces noise which could introduce errors except when fine-tuned. |
| [103] | Logarithmic SVM | In this research, instead of the contemporary floating-point or fixed-point arithmetic, the SVM classification is carried out using the Logarithmic Number System (LNS). The LNS is suitable for low-power applications as it avoids multiplication computations. This saves computation time. The LNS is suitable for machine learning kernel operations which are the computationally intensive sections of the ML algorithm. | Although LNS saves computation time, it requires more hardware resources to implement because it replaces multiplication computations with addition and subtraction. |
| [104] | Multiplication free SVM | In this research, To address the limitation of hardware resources in resource-constrained environments, The SVM parameters are converted to fixed-point representation, and a hardware-friendly kernel and CORDIC-like iterative algorithm are proposed to avoid multiplication computations using only adders and shifters. | This technique reduces the computational requirements of the system; however, reduced bit precision (fixed-point representation) introduces accuracy errors. |
| [94] | Order Model Selection | In this research, a model selection algorithm is proposed to select the hyper-parameters with the best Pareto-optimal state using the classification error and the number of support vectors. | This research adopted quantization techniques that introduce classification errors due to the influence of noise. |
| Reference | Optimization Method | Application | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| [106] | Minimization of Floating-Point Computations | Background Subtraction | The results of this research were impressive, showing no degradation in accuracy except for lower recall rates. |
| [107] | Comprehensive Sensing | Background Subtraction for real-time tracking in Embedded Vision | The results of this research reveal good performance for computational speed and reduce the memory footprint by 50% |
| [39] | Integer-based technique | Background/foreground Segmentation | This work shows good performance for processors without FPU, thus reducing computation cost and reducing the memory footprint to 1/12 of the original GMM; however, it cannot be adopted for models with more than two Gaussians |
| Name | FC | Conv | Vector | Pool | Total | Nonlinear Function | Weights |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLP0 | 5 | 5 | ReLU | 20 M | |||
| MLP1 | 4 | 4 | ReLU | 5 M | |||
| LSTM0 | 24 | 34 | 58 | Sigmoid, tanh | 52 M | ||
| LSTM1 | 37 | 19 | 56 | Sigmoid, tanh | 34 M | ||
| CNN0 | 16 | 16 | ReLU | 8 M | |||
| CNN1 | 72 | 13 | 89 | ReLU | 100 M |
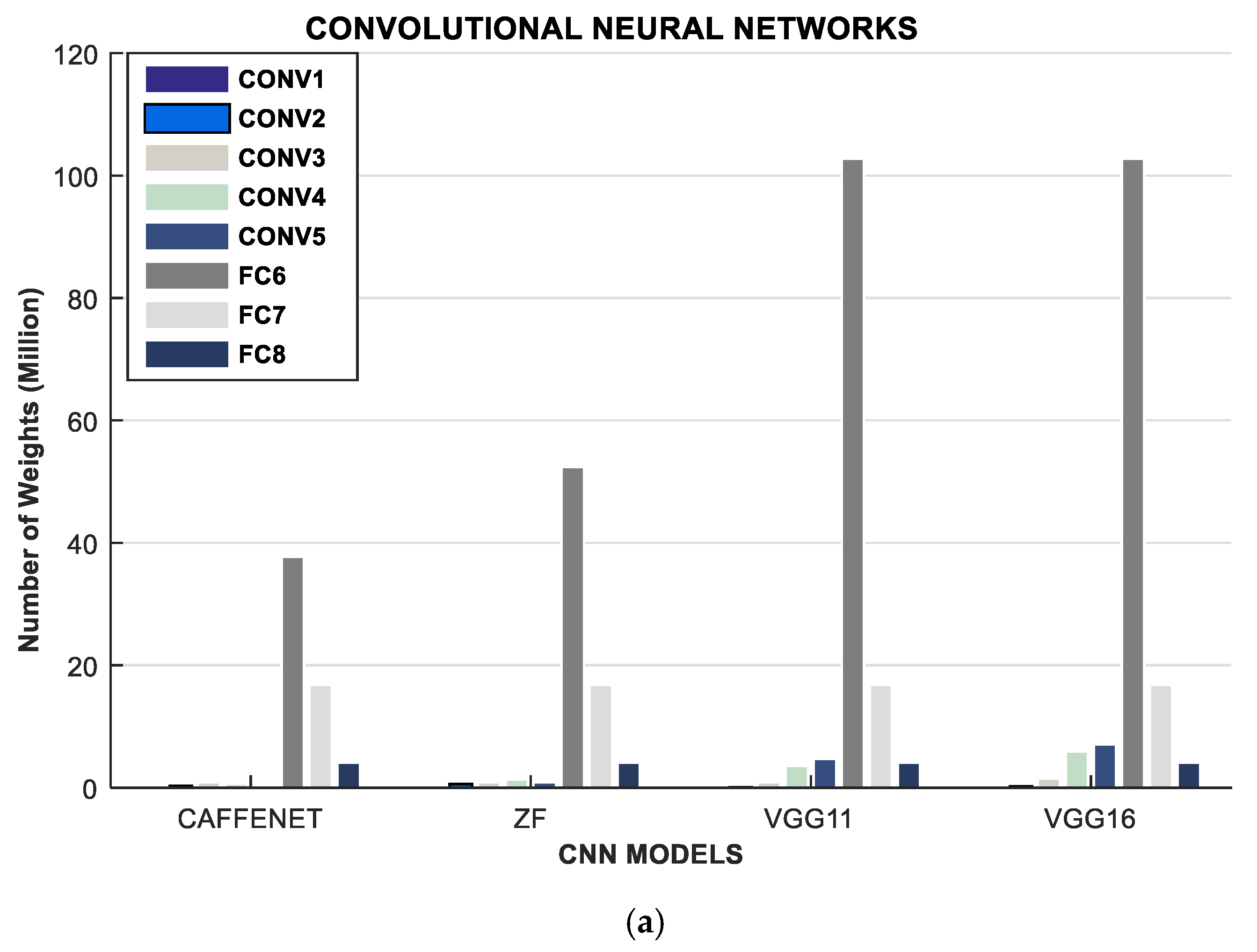
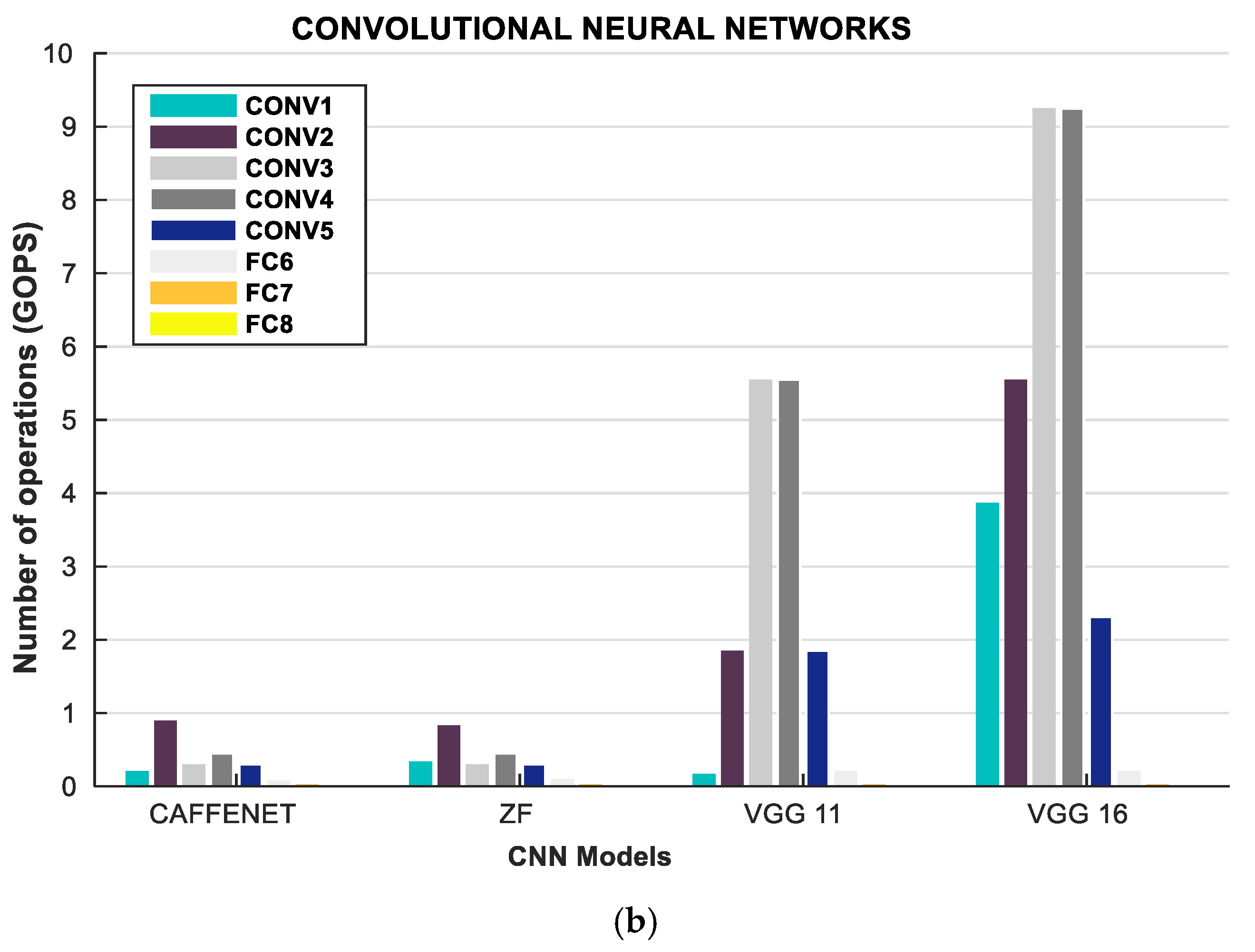
| CAFFENET [51] | ZF | VGG11 [51] | ||||
| LAYER | Weights | FLOP | Weights | FLOP | Weights | FLOP |
| CONV1 | 30 K | 210 M | 10 K | 340 M | 0.00 | 170 M |
| CONV2 | 31 K | 900 M | 610 K | 830 M | 70 K | 1850 M |
| CONV3 | 88 K | 300 M | 880 K | 300 M | 880 K | 5550 M |
| CONV4 | 66 K | 450 M | 1330 K | 450 M | 3540 K | 5550 M |
| CONV5 | 44 K | 300 M | 880 K | 300 M | 4720 K | 1850 M |
| FC1 | 37.75 M | 80 M | 52.43 M | 100 M | 102.76 M | 210 M |
| FC2 | 16.78 M | 30 M | 16.78 M | 30 M | 16.78 M | 30 M |
| FC3 | 4.1 M | 10 M | 4.10 M | 10 M | 4.1 M | 10 M |
| VGG16 [51] | VGG19 [51] | ALEXNET | ||||
| LAYER | Weights | FLOP | Weights | FLOP | Weights | FLOP |
| CONV1 | 40 K | 3870 M | 40 K | 3870 M | 35 K | 211 M |
| CONV2 | 220 K | 5550 M | 220 K | 5550 M | 307 K | 448 M |
| CONV3 | 1470 K | 9250 M | 2060 K | 12950 M | 885 K | 299 M |
| CONV4 | 5900 K | 9250 M | 8260 K | 12950 M | 663 K | 224 M |
| CONV5 | 7080 K | 2310 M | 9440 K | 3700 M | 442 K | 150 M |
| FC1 | 102.76 M | 210 M | 102.76 M | 210 M | 38 M | 75 M |
| FC2 | 16.78 M | 30 M | 16.78 M | 30 M | 17 M | 34 M |
| FC3 | 4.1 M | 10 M | 4.10 M | 10 M | 4 M | 8 M |
| Ref. | Embedded Architecture | Model | Optimization Techniques | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [20] | FPGA(Zedboard development board) | DNN(Mnist) | Data Access Optimization, Time-sharing computation | Image Recognition |
| [22] | Xilinx XC7Z2020 FPGA | DNN(Mnist) | Tiling and reuse techniques, FIFO Buffering, Pipelining | Image Recognition |
| [51] | Xilinx Zynq ZC706 FPGA | CNN(VGG16) | Simple Vector Decomposition, Quantization, Tiling, and reuse, Buffer Design | Image Classification |
| [112] | Altera Stratix-V FPGA (DE5-Net, P395-D8) | CNN(AlexNet, VGG) | Number Precision, Throughput optimization through design space exploration. | Image classification |
| [25] | Virtex7 VX485T FPGA | CNN | Loop unrolling, Pipelining, Tiling, and data reuse | Image classification |
| [111] | Xilinx XC6VLX240T FPGA | CNN(LeNet-5), DNN(AlexNet) | Acceleration of Activation function, Pipelining | Image recognition and Classification. |
| [27] | Xilinx Vertex-7 FPGA | CNN(AlexNet-5) | Network Pruning, Quantization, hardware acceleration | Computer Vision |
| [125] | Intel Core i7 CPU | CNN(LeNet-5) | Adaptive Quantization | Image classification |
| [23] | Xilinx Zynq ZC7020 FPGA | RNN(LSTM) | Data Access Optimization, reduced precision, Buffer design | Speech Recognition |
| Ref. | Name | Processor | Clock Frequency | Flash | SRAM | Current Consumption (mA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [128] | Arduino Uno | ATmega328P | 16 MHz | 32 KB | 2 KB | 12 mA |
| [129] | Arduino Mega | ATmega2560 | 16 MHz | 256 KB | 8 KB | 6 mA |
| [129] | Arduino Nano | ATmega2560 | 16 MHz | 26-32 KB | 1-2 KB | 6 mA |
| [130] | STM32L0 | ARM Cortex-M0 | 32 MHz | 192 KB | 20 KB | 7 mA |
| [131] | Arduino MKR1000 | ARM Cortex-M0 | 48 MHz | 256 KB | 32 KB | 4 mA |
| [132] | Arduino Due | ARM Cortex-M3 | 84 MHz | 512 KB | 96 KB | 50 mA |
| [133] | STM32F2 | ARM Cortex-M3 | 120 MHz | 1 MB | 128 KB | 21 mA |
| [134] | STM32F4 | ARM Cortex-M4 | 180 MHz | 2 MB | 384 KB | 50 mA |
| [135] | RPi A+ | ARM Cortex-A7 | 700 MHz | SD Card | 256 MB | 80 mA |
| [135] | RPi Zero | ARMV6 | 1 GHz | SD Card | 512 MB | 80 mA |
| [135] | RPi 3B | ARM Cortex-A53 | 1.2 GHz | SD Card | 1 GB | 260 mA |
| [136] | BeagleVTM | RISC-V U74 | 1.0 GHz | SD Card | 8 GB | 3000 mA |
| Accelerator | Processor Type | RAM | Flash Memory | Power | Application | Maker |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARM Ethos NPU | ARM ML processor | 1 GB | - | 4 TOPs/W | Image processing, voice recognition | ARM |
| BeagleBone AI | Cortex-A15, Sitara AM5729 | 1 GB | 16 GB | 500 mW | Computer vision | Texas Instruments |
| Google Coral Dev Board | GPU, TPU, CPU | 1 GB | 8 GB | (6–10) W | Image Processing | |
| Intel Movidus NCS | VPU | 1 GB | 4 GB | 500 mW | Classification, computer vision | Intel |
| Mustang-F100-A10 | Intel Arria 10 GX1150 FPGA | 8 GB | - | 40 W | Computer vision | Intel |
| NVIDIA Jetson NANO | GPU, CPU | 4 GB 64 it LPDDR4 25.6 GB/s | 16 GB eMMC, 5.1 Flash | (5–10) W | Computer vision, audio processing | NVIDIA |
| Ref. | Ml Algorithm | Optimization Method | Mobile Device | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [138] | GoogLeNet | Layer slimming and fine-tuning with model compression, | Samsung Galaxy S5 | Computer vision |
| [139] | GMM | Combination of k-Nearest Neighbor (kNN) and neural networks to improve GMM algorithm. | MIT Mobile device | Speaker Verification |
| [140] | DNN | Model Compression, reduced precision, and Rescoring Techniques | Nexus 4 Android Phone | Speech recognition |
| [52] | CNN(Vgg-F, Vgg-M, Vgg-16) | GPU-based acceleration, branch divergence, memory vectorization, and half floating-point computation. | Samsung S5, Samsung Note 4, Samsung S7 | Computer Vision |
| [63] | CNN | Pointwise group convolution and channel shuffling | ARM-based Mobile Device | Image classification, object detection |
| Computing Technology | Platform | Architecture | Memory | Storage | Power | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CloudML | Nvidia V100 | GPU Nvidia VoltaTM | 16 GB | 1 TBs-PBs | 250 W | [144] |
| Nvidia Titan RTX | GPU Nvidia TuringTM | 24 GB | 1 TBs-PBs | 280 W | [145] | |
| Nvidia V100S | GPU Nvidia VoltaTM | 32 GB | 1 TBs-PBs | 250 W | [144] | |
| TinyML | ST F446RE | Arm M4 | 128 KB | 0.5 MB | 0.1 W | [146] |
| ST F746ZG | Arm M7 | 320 KB | 1 MB | 0.3 W | [147] | |
| ST F767ZI | Arm M7 | 512 KB | 2 MB | 0.3 W | [147] |
| Framework | Supported mL Algorithm | Compatible Platforms | Languages | Main Developer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TensorFlow Lite | Neural networks | ARM Cortex-M | C++11 | |
| ELL | Neural networks | ARM Cortex-A Raspberry Pi Arduino micro:bit | C C++ | Microsoft |
| ARM-NN | Neural networks | ARM Cortex-A ARM Mali Graphics Processors ARM Ethos Processor ARM Cortex-M | C | ARM |
| CMSIS-NN | Neural networks | ARM Cortex-M | C99 | ARM |
| STM 32Cube. Al | Neural networks | STM32 | C | STMicroelectronics |
| AlfES | Neural networks | Window [DLL] Raspberry Pi Arduino ATMega32U4 STM32 F4 Series ARM Cortex-M4 | C | Fraunhofer IMS |
| NanoEdge Al Studio | Unsupervised learning | ARM Cortex-M | C | Cartesian |
| MicroMLGen | SVM RVM | Arduino ESP32 ESP8266 | C | Particular developer |
| Sklearnporter | SVM Decision tree Random Forest Ada BoostClassifier K-NN Neural networks | Multiple constrained & non-constrained platforms | C, GO Java, JavaScript, PHP, Ruby | Particular developer |
| m2cgen | Linear regression Logistic regression Neural networks SVM Decision tree Random Forest LGBM classifier | Multiple constrained & non-constrained platforms | C, C#, Dart Go, Java JavaScript PHP, PowerShell, Python, R Visual Basic | Particular developer |
| Weka-porter | Decision trees | Multiple constrained & non-constrained platforms | C, Java JavaScript | Particular developer |
| EmbML | Decision trees Neural networks SVM | Arduino Teensy | C++ | Research group |
| emlearn | Decision trees Neural networks Naïve Gaussian Bayes Random forest | AVR ATmega ESP8266 Linux | C | Particular developer |
| uTensor | Neural networks | mBed boards | C++11 | Particular developer |
| TinyMLgen | Neural networks | ARM Cortex-M ESP32 | C | Particular developer |
| Operation | Energy (pJ) |
|---|---|
| 8 bit int ADD | 0.03 |
| 16 bit int ADD | 0.05 |
| 32 bit int ADD | 0.1 |
| 16 bit float ADD | 0.4 |
| 32 bit float ADD | 0.9 |
| 8 bit MULT | 0.2 |
| 32 bit MULT | 3.1 |
| 16 bit float MULT | 1.1 |
| 32 bit float MULT | 3.7 |
| 32 bit SRAM READ | 5.0 |
| 32 bit DRAM READ | 640 |
| Year | Ref. | Application Area | Highlights | Key Findings | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | [2] | Mobile Adhoc Networks (MANETs) | This research investigates the automatic configuration of the radio and IP stack of a MANET at runtime using machine learning techniques. To achieve this, the SVM algorithm was implemented within two communication controllers with general-purpose processors (the ARMv7 and IBM PPC440GX). | To deploy the SVM efficiently, certain optimizations were carried out on the algorithm, and the corresponding effect of each optimization technique was observed whilst comparing each ablation with a baseline. The result of the proposed system showed improved performance reducing the runtime of the system in most cases. | In this research, accuracy was traded off for execution speed. The accuracy of SVM algorithms depends on their floating-point computations. However, floating-point operations were avoided by the optimization scheme, thereby reducing the overall accuracy. Also, computationally intensive machine learning methods are often executed using hardware acceleration units. This increases the accuracy and execution speed of the scheme. |
| 2016 | [50] | Intelligent Sensor Networks and the Internet of things | This research work investigates the use of a machine learning model deployed in an embedded environment to analyze sensor data at run time. The research explored the use of a Gaussian mixture model (GMM) on an FRDM-K64F embedded board to achieve this. For retrieving raw data intelligently, the research employed the NXP intelligent sensor framework (ISF), which collects the raw sensor data and stores them for sequel purposes. The GMM is then used to analyze the huge amount of sensor data for classification and clustering to detect the required processes. The intelligent sensor system is used to monitor the conditions of an intelligent stove and a water circulation system. | The GMM algorithm is optimized using the expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm and implemented using the minimum description length (MDL) criterion due to the intensive computational vector and matrix operations required and the limited computational power available. Furthermore, the fixed point number representation was used in the computation of the sensor data, while the hardware implementation was done using the imperfect floating-point unit. | The number representation adopted improves the speed of the implementation at the expense of accuracy. Although the analysis of raw sensor data reduces the network data traffic and enhances data security, employing the use of model parameters to depict sensor data reduces the effectiveness of the GMM since the accuracy of machine learning models largely depends on the volume of data for appropriate training. |
| 2017 | [62] | Intelligent Ultra-Low-Power IoT Systems | This research considers the efficient implementation of deep neural networks across diverse low-power IoT computing platforms. The different IoT applications considered in this research cut across voice, image, and activity recognition. The work proposes a fully-connected deep neural network for training the different datasets and consequently inferencing the trained model using an SoC-based hardware accelerator. A unique FC-NN topology is modeled for each application for high performance and trained using preprocessed datasets as required by the application. | The NN model is manually mapped to the hardware accelerator by extracting the weights and biases and converting them from 32-bit floating-point to 16-bit fixed-point values owing to the accelerator constraints indicated in the paper. The quantization method introduced to reduce the precision of the model reduces the prediction accuracy of the system which parameter retraining would address. The performance of this model was measured using accuracy, harmonic mean score, weighted harmonic mean score, and power consumption. The results of the research show that deep learning models can be executed efficiently using specialized hardware processors | Model scalability and battery life performance which are major concerns in IoT developments are not considered in the research. |
| 2018 | [71] | Intelligent Wearable Systems | This research investigates the integration of a machine learning algorithm executed on a wearable device to extract, analyze and classify sensor data on the embedded device, thereby saving the energy required to send for centralized processing. To achieve this, the research work entailed (1) sampling the data generated to avoid the generation of redundant input data, (2) carrying out appropriate feature extraction using the Integral of the modulus of acceleration (IMA) embedded machine learning method, which avoids sending the raw sensor data to a centralized processor for knowledge extraction and (3) executing the classification process using support vector machines (SVM). This machine learning sensing system was employed for the energy-efficient long-term monitoring of the physical activities of house occupants. | The results obtained were fascinating, revealing that employing adequate machine learning methods extends the battery life of a wearable sensor by 987 days when compared to transferring raw sensor data through the network. The research makes use of an SoC-based wearable sensor for data collection. | Data sampling reduces system accuracy because machine learning models depend on large sensor data for effective training. Also, SoCs are highly energy-efficient and demonstrate good performance, and they require a very high time-to-market compared to other embedded architectures. |
| Year | Reference | Application Area | Highlights | Key Findings | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | [74] | Image Processing | This research investigates an adaptive machine learning approach to selecting the most optimal DNN for a given input, thereby saving inference time. To achieve this, the research work trained an offline predictor (premodel) using the K-nearest neighbor classification models on 12 DNN models measuring the predictions under two metrics—response to the input data and precision required. The inference time for a DNN model is a function of these two parameters. | The premodel is then executed on embedded hardware to select from an option of 14 pre-trained CNN models, the most optimal model to employ for a particular input data and precision requirement, thereby reducing the inference time. The ML system was implemented on the NVIDIA Jetson TX2 deep learning platform, which had an embedded GPU | GPUs provide the necessary speed and efficiency for deep learning implementations but are power-hungry, making them unsuitable for embedded applications. |
| 2018 | [138] | Mobile Computing | This work investigates a novel optimization method for accelerating deep neural network models for resource-constrained environments like mobile devices. The research exploits the observation that deep learning execution time is majorly slowed by the non-tensor layers in the model (pooling, LRN, and normalization layers). An optimization framework, “DeepRebirth,” is proposed, which targets the regeneration of the non-tensor layers in the model using either streamline or branch slimming methods. The optimization method involves merging non-tensor layers with bottom tensor units and further fine-tuning the regenerated layer in streamline streaming. Branch slimming involves merging non-tensor layers with tensor units at the same level. | The performance of the optimized model was measured over the state of the art networks like GoogLeNet, AlexNet, and ResNet on different high-end and low-end mobile computing processors. The results of DeepRebirth reveal that the optimization method yields faster execution time, minimal accuracy loss, and reduced power consumption making the technique appropriate for heterogeneous mobile devices. | It is, however, observed that the optimization technique has little influence on mainstream ARM CPUs, which are the most ubiquitous processors in mobile devices. This limits the impact of optimization in the mobile computing world. More so, the inference was carried out during airplane mode, and thus, the metric for power consumption on mobile devices is not accurately measured. This metric is very important because battery life is a great concern in mobile computing and can constitute a major challenge to deep learning inferencing on mobile computing platforms. |
| 2018 | [174] | Indoor Navigation | A framework is presented in this work to improve WiFi-based fingerprinting indoor localization using commodity smart mobile devices. The research proposes the utilization of a CNN model in predicting the location of a user in an indoor environment. The WiFi access points are used in creating the image database, which models the different locations on the navigation path, which are then used to train the CNN model. The real-time AP data are subsequently used by CNN to predict the location of the user at run time. | The CNN model used in the research “CNN-LOC” eliminates the pooling layer owing to the size of the grids, thereby eliminating the need for subsampling. This consequently reduces the training and inference times and power consumption during execution, making it suitable for resource-constrained mobile computing. The research also introduces scalability by proposing a hierarchal classifier for large area localization. The performance of this research is measured by comparing the prediction accuracy across other indoor localization frameworks using SVR, KNN, and DNN approaches. The results show that the CNN-LOC framework outperforms the others. | However, the research overlooks the limitation of battery life in smartphones during the execution of computationally intensive deep learning models like CNN using WiFi APs. WiFi has been observed to be one of the applications responsible for draining the power in mobile devices, thereby shortening the battery life. |
| 2018 | [163] | Energy Efficiency of Embedded Devices | This work investigates a novel low precision arithmetic approach to optimize the power consumption and memory utilization of DCNN inferencing in the embedded system domain. To achieve this, the work explored the use of the posit number system over the contemporary fixed and floating-point number representation. The process involves converting the posit number to a decimal floating-point number and subsequently a binary floating-point number for reading and writing to memory and vice versa during the processing period. | The system is executed using three datasets and compared to a reference point which is the single floating-point representation. The results are fascinating in terms of memory utilization during inferencing, and the accuracy obtained despite using low precision estimation | The hardware specifications are not given in the research. |
| Year | Reference | Application Area | Highlights | Key Findings | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | [19] | GPGPU based CNN Training | GPUs are one of the major hardware acceleration tools for Deep learning algorithms owing to their suitability for high thread-level parallelism. This research Investigates an optimal system configuration for GPGPUs in training CNN models effectively. Two image classification CNN models (LeNet and MiniNet) are executed using different GPU configurations to determine the most optimal configuration. The research employs GPGPU-sim, a GPU simulator, in executing the CNN model whilst observing the effect of modifying the configuration of the GPU in terms of the NoC architecture used, the size of the L1D and the L2D caches, and network traffic intensity on the different layers of the CNNs (convolutional, pooling and fully connected layers). | The result of the research reveals that the Mesh Network outperforms the Perfect Network at the fully connected layers. Also, modification in the size of the L1 affects the performance of the CNN, while changes in the L2 cache do not influence the CNN performance. Also, the network traffic intensity differs across the layers. | GPGPUs are very cost-intensive and energy-intensive. Thus, they are unsuitable for embedded applications. |
| Year | Reference | Application Area | Highlights | Key Findings | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | [16] | Heterogeneous multicore Architecture | A Heterogeneous multi-core architecture to facilitate the high-performance execution of Machine learning algorithms is explored in this research work. The middleware platform called HeteroSpark involves the integration of a GPU accelerator into an already existing CPU-based architecture (Spark) to accelerate computationally intensive machine learning methods. Employing Java virtual machines, data is moved between the CPU and the GPU when required for intensive computations. The GPU is positioned in Spark’s worker nodes. The GPU relieves the CPU of workload, thus accelerating the entire computation process due to GPUs’ thread-level parallelism. The process is abstracted from the user through user-friendly APIs. | The performance of the proposed heterogeneous framework is compared to a baseline (Spark), and the results were fascinating, with GPU acceleration yielding 18.6x when HeteroSpark is scaled up to “32CPU cores: 8 GPUs” and Spark uses “32 Cores: no GPUs”. | The research focuses on a software approach to the problem and not a hardware perspective. |
| Year | Reference | Application Area | Highlights | Key Findings | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | [25] | CNN Optimization using FPGAs | This work proposes a development scheme to accelerate the execution of convolutional neural networks in resource-constrained FPGAs by exploring the design space of the system. The roofline model, which uses a computation and communication approach to measure the performance of the system, was adopted to explore the design space to affect the optimization of the computation and memory access process. | The computation process is accelerated by loop unrolling, pipelining, and tile sizing using a polyhedral-based optimization technique. Memory access is optimized by adopting loop promotion and transformations for efficient data reuse. Optimal parameters are first determined for single convolutional layers and then unified unroll factors are used for CNNs with multiple convolutional layers. The performance of the proposed architecture is estimated by observing the computational performance, resource utilization, and power consumption. The proposed scheme reveals brilliant results in outperforming prior works. | The research, however, focused on accelerating the feedforward inference process and optimized only the convolutional layers neglecting the pooling, normalization, and fully connected layers which are required in real-world scenarios. Besides, tiling introduces some accuracy loss to the model execution. |
| 2015 | [20] | Deep Learning FPGA Architecture | The acceleration of deep learning inference, particularly to large-scale networks using an FPGA, is considered in this work. The research exploits the high performance, reduced power consumption, and low-cost advantages of employing the FPGA to accelerate the prediction process of a DNN model. The research was limited to the prediction process. The Accelerator Architecture proposed by the research contained a direct memory access module, a deep learning module with an ARM Cortex CPU. To tackle the challenge of mapping in large neural networks owing to constrained computational resources, a time-sharing computational technique is adopted in the execution of data fragments that have been previously partitioned using the tiling technique. | The performance of the architecture is improved by cache reuse effected by introducing a Block RAM module. Furthermore, the throughput was increased by incorporating a pipelining methodology in the DL module. To address the flexibility challenge of the FPGAs, a software library is proposed to make the system user-accessible. The performance of the proposed model is measured by comparing the results with a MATLAB-based Core2 CPU baseline. The results show improved performance in power consumption and data throughput | The tiling technique introduces some accuracy errors in computation. The research adopted a high floating-point computation. However, a low fixed-point precision approximation of the DNN model if introduced, could further save memory usage and improve performance. |
| 2016 | [22] | Energy Efficient Hardware Acceleration | This work targets an FPGA-based accelerator design to improve the training and inference of computationally intensive deep learning models. The research proposes an architecture, “DLAU”, pivoted on introducing scalability to accommodate diverse network sizes of deep learning models and employing the tiling technique, which entails splitting the large volume of data introduced into smaller grids and distributing them to effect the parallel computing technique, which is suitable for deep learning models. The DLAU Acceleration model exploits the computational methods required by deep learning models (matrix multiplication and activation functions). | The architecture introduces three fully pipelined processing units (Tiled Matrix Multiplication Unit, Part Sum Accumulation Unit, and Activation Function Acceleration Unit) to execute these kinds of computations efficiently, thereby offloading the main processor of intensive computations increasing overall execution speed and throughput at low cost. The performance and cost of the proposed model are measured using the execution speed, resource utilization and power consumed. The results reveal that the DLAU accelerator outperforms other acceleration techniques. | The research focuses on hardware design alone. However, FPGAs, although flexible owing to their reconfigurable characteristic, are difficult to program employing a hardware/software approach that is more suitable for developers. More so, power consumption can be further reduced by employing low precision approximation techniques for deep learning models which are not employed in the paper. |
| 2016 | [51] | Embedded FPGA | A hardware/software co-design approach to accelerate large-scale convolutional neural networks in the embedded system domain is considered in this work. The framework proposed entails the decomposition and quantization of large-scale CNN models at the software level and the design of an FPGA-based CNN accelerator at the hardware level. The optimization at the software level targets the high memory space required by fully-connected layers and high computational demand required by the convolutional layers in the CNN model, while the hardware level optimization entailed the design of an application-specific FPGA architecture to meet the computational and high memory bandwidth required for the efficient execution of the model. To achieve this, the Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) technique was adopted to accelerate the fully connected layers, and dynamic-precision quantization using 16-bit fixed-point representation was used for the quantization process. | The hardware implementation entailed the design of a heterogeneous architecture of general-purpose processors and an FPGA consisting of appropriate buffers, processors, and memories to effect efficient parallel processing, matrix multiplication, tiling, and data reuse. The performance metrics of the proposed model are evaluated by implanting a very deep VGG CNN and the results are compared to CPU and GPU-based architectures and other FPGA-based CNN accelerators demonstrating brilliant performance. | The research, however, considers the optimization of convolutional and fully connected layers neglecting pooling and normalization layers. Besides, tiling and quantization techniques introduce accuracy errors which fine-tuning techniques ought to address but Parameter fine-tuning is not considered in this literature. Moreover, the reconfigurable advantage of FPGAs is not exploited in the research. Also, embedded platforms face battery life constraints which is also not considered in this research. |
| 2016 | [112] | OpenCL-based FPGA Hardware Acceleration | This work considers the acceleration of large-scale convolutional neural networks using an OpenCL-based FPGA Architecture focusing on optimizing the rate at which data is processed to improve throughput. To achieve high throughput, a precision study is carried out using the Caffe tool of two CNN models (AlexNet and VGG) for the convolution and fully connected layers to determine the optimal precision at which inference can be carried to avoid accuracy loss. At the hardware level, scalable modules are designed using OpenCL software design skit for accelerating each of the different layers in the CNN (convolution, pooling, normalization, and fully connected layers). In the OpenCL implementation phase, the convolution layer is accelerated by developing a scalable convolution block that performs the multiply and accumulates operations required by the convolution layer. The Normalization layer is accelerated by developing a module that performs exponent operations using a piece-wise linear approximation function. The pooling and fully connected layers are accelerated by implementing single work-item kernels. | For appropriate hardware resource utilization on the FPGA, a design space exploration is carried out using a genetic algorithm in Matlab to affect throughput. The proposed architecture is used to accelerate the AlexNet and VGG CNN models on two FPGA boards. The results are compared with prior FPGA-based architectures outperforming them. | The research, however, focused on optimizing throughput and not memory utilization which is a key concern for embedded platforms. Besides, power consumption is a key concern owing to the limited battery of embedded computing devices. |
| 2016 | [23] | FPGA based Hardware Acceleration | Hardware architecture for the efficient execution of recurrent neural networks (RNN) based on a long short term memory design approach is proposed in this work. The proposed solution targets the constraint involving vanishing or exploding gradients while executing RNNs by recommending a variation to the LSTM design approach. The recommended LSTM design method entails the definition of three gates (input, forget, and output) that learn to either remember, forget or output a result. This LSTM architecture is implemented using the FPGA which uses fixed-point approximations for computations. The matrix-vector multiplications are implemented using Multiply Accumulate units while the non-linear functions are computed using a MAC unit and a comparator. Direct memory access units are incorporated with a stream synchronization module to foster efficient communication of data between the processing logic units and the external memory. The module integrates a driver software to incorporate data reuse to avoid constant external memory accesses which consumes power. | The proposed architecture is implemented using Zedboard’s FPGA with dual ARM Cortex-A9 processor and compared to platforms using CPU and GPU computing units for performance evaluation outperforming them. | However, fixed-point representations introduce accuracy errors to the results, which parameter retraining or model fine-tuning ought to address. Besides, external memory accesses consume a lot of power owing to the high bandwidth requirement. Furthermore, the research focuses on the learning phase alone, neglecting inferencing. |
| Year | Ref. | Application Area | Highlights | Key Findings | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | [175] | Layer based Hardware Acceleration | This work explores the design of specialized hardware architecture to accelerate the execution of Softmax layers in deep learning applications. The research targets mitigating the challenge of employing existing direct-mapping techniques used for accelerating the hardware implementation of other layers (convolution, pooling, and normalization) of the CNN for the Softmax layer. This challenge pivots on the division and overflow problem which introduces high latency and high accuracy errors owing to the hardware complexity and resource constraints, respectively. | To overcome the division problem, a domain transformation which involves the replacement of the complex division operation with a logarithmic subtraction operation. This reduces the complexity of hardware implementation. Also, the overflow problem is overcome, downscaling is employed to reduce the bit width of the parameters. The downscaling method also reduces the complexity of the logarithmic operations addressing the issue of path delay, which informs reduced latency. | The research considers the hardware orientation of the acceleration process, neglecting the software which is sometimes required for data reuse. Besides, the research only considers the optimization of the Softmax layer; however, the generic optimization involving other layers is not considered. |
| 2017 | [29] | Weight/Activation based Hardware Acceleration | This research Investigates a hardware architecture aimed at accelerating the execution of convolution layers in a CNN by exploiting the zero weights and activations. By omitting the multiplication and accumulation of computations containing zero weights and activations often caused by pruning techniques and much more the effect of using the ReLU activation function, the research targets power reduction and faster speed in the execution of CNNs. Unlike other zero-aware accelerator architectures, to exploit both zero weights and activations, each of the Processing Elements (PE) of the proposed architecture performs single convolutions to avoid synchronicity. The proposed architecture contains two on-chip SRAMs (activation and weight), a PE Array, and a ReLU module. | The research implemented two architectures employing two data widths (16 bit fixed point and 5-bit logarithmic quantization). The proposed architecture introduces a challenge involving latency termed load imbalance which a zero-aware kernel allocation approach was used to resolve. The results of the research outperformed other non-zero acceleration architectures and partially zero-aware acceleration architectures. | However, the research only considered the acceleration of convolution layers. On-chip SRAM may be ineffective for large-scale CNNs. Besides, reduced precision and quantization techniques introduce accuracy errors for large-scale networks. |
| 2018 | [111] | Activation Function based Hardware Acceleration | A hardware architecture is designed and implemented to accelerate the execution of the activation function in deep neural networks in this research work. The proposed architecture introduces the flexibility of selecting between four activation functions (Sigmoid, Tanh, ReLU, and Softmax function) using a time multiplexing approach. The architecture employs 16-bit fixed-point precision arithmetic for computation and bus width. Furthermore, the piecewise linear interpolation method is employed in the approximate calculation of the activation function. The approximation is carried out using an on-chip lookup table designed using ROM. An address generator module is used to map the neuron data to the Lookup Table using an address mapping algorithm. | The hardware implementation is carried out using a CPU and GPU for training and an FPGA for inference the proposed architecture is used in implementing two CNNs (LeNets-5 and AlexNet) with the results compared using Matlab. The results of this architecture reveal high computation efficiency and flexibility. | However, the architecture is modeled for small neural networks. The on-chip lookup table implemented increases the on-chip memory storage required thus unsuitable for embedded applications with hardware resource constrain. |
| 2020 | [13] | Computer Architecture and Chip Design | This research surveys the influence and consequence of deep learning advances in computer architecture and chip design. The research survey points out the requirements of a specialized hardware architecture for deep learning implementation owing to the peculiar mathematical methods used in deep learning computations. The current optimization trends in general-purpose CPUs are not appropriate for these mathematical models more so as Moore’s law has slowed down in recent times. | The research survey suggests low precision approximations for machine learning models to enhance their execution and reduce their power consumption. Furthermore, the research survey reveals how machine learning techniques could also be used in the exploration of the design space for ASIC development. | The research survey focused on the hardware perspective alone. However, there are current software and hardware/software co-design approaches to enhance deep learning. More so, Photonics is a current promising research thrust owing to the promising characteristics of photonics-based architecture over electronic-based architecture. |
| S/N | Key Areas for Future Research | Possible Research Focus |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Computer Architecture | With the end of Dennard’s scaling and Moore’s law significantly slowing down, combined with the performance wall of Silicon, there remains an urgent need for innovation in the design and development of hardware architecture to meet the target for high-performance computing that face us today. In this respect, [176] suggests domain-specific architectures in the form of GPUs, FPGAs, TPUs, etc. as a research direction for future high-performance architectures. DSAs are different from ASICs in that DSAs introduce flexibility to the design due to their programmability. This is an open research area in computer architecture. Also, to generate highly efficient application-specific ASIC architecture designs, the design space is required to be explored efficiently, which is currently a stringent task carried out by human experts. However, [177,178] presents a frontier of employing machine learning techniques in exploring the design space at design time and runtime. Ruben et al. [179] proposed a machine learning-based prediction for the dynamic, runtime, and architectural optimizations of Embedded Systems. This is another open area of research—adopting machine learning in efficient computer architecture design and development |
| 2 | Deep Learning Optimizations | Deep learning models are computationally and memory intensive, and thus, implementing them within resource-constrained environments is tasking. There is, therefore, an opportunity for highly efficient optimization techniques to compress deep learning models efficiently with minimal or no accuracy loss. Although many research works have explored optimization techniques, optimization methods are infinite, and thus there remains an opportunity to optimize deep learning models still. Some optimization techniques are but are not limited to pruning, clustering, layer acceleration, quantization, and numeric precision. Some optimizations combine one or more of these techniques to compress a model successfully. |
| 3 | Hardware Security | Software security has been greatly explored, but little work has been done in hardware security which is a major concern in embedded systems development [180]. State-of-the-art embedded hardware architectures are prone to Trojan attacks, and thus, this creates the need for research in the design and development of secure embedded architectures for embedded applications. |
| 4 | Energy Efficiency and Power Management | Energy Efficiency is a critical issue in embedded computing systems because most embedded devices run on a battery [181]. Thus, to effect the continuous functionality of embedded devices, there remains the need to adequately design energy-efficient architectures and also adopt innovative power management techniques. This is a crucial research thrust in embedded computing technology, particularly to meet the requirements of high-performance machine learning applications [182,183,184]. |
| 5 | Silicon Photonics | Current Silicon technology is reaching its limit for performance and thus [185] surveys the exploration of photonics-based architectures as a substitute for silicon technology owing to the high bandwidth and data transfer speed of photonics-based architectures [186,187]. This is a key research direction for high-performance architectures |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ajani, T.S.; Imoize, A.L.; Atayero, A.A. An Overview of Machine Learning within Embedded and Mobile Devices–Optimizations and Applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 4412. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134412
Ajani TS, Imoize AL, Atayero AA. An Overview of Machine Learning within Embedded and Mobile Devices–Optimizations and Applications. Sensors. 2021; 21(13):4412. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134412
Chicago/Turabian StyleAjani, Taiwo Samuel, Agbotiname Lucky Imoize, and Aderemi A. Atayero. 2021. "An Overview of Machine Learning within Embedded and Mobile Devices–Optimizations and Applications" Sensors 21, no. 13: 4412. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134412
APA StyleAjani, T. S., Imoize, A. L., & Atayero, A. A. (2021). An Overview of Machine Learning within Embedded and Mobile Devices–Optimizations and Applications. Sensors, 21(13), 4412. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134412








