A Novel Method for Effective Cell Segmentation and Tracking in Phase Contrast Microscopic Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
- An active contour model showing strong performance in shape detection was used for acquiring the shape of the cell in a phase contrast microscope.
- Since the halo effect that occurs in the phase contrast microscope interferes with the precise segmentation of the cell shape, we propose a solution to remove it.
- The conventional methods have performed the segmentation for the cell boundary through various complex image processing techniques that distinguish between the halo effect and the cell boundary. In this work, we propose a novel method that uses the ML technique K-means clustering method to separate and correct halo effects from the background signals and cell boundaries, eliminating the basic problem cause itself after denoising.
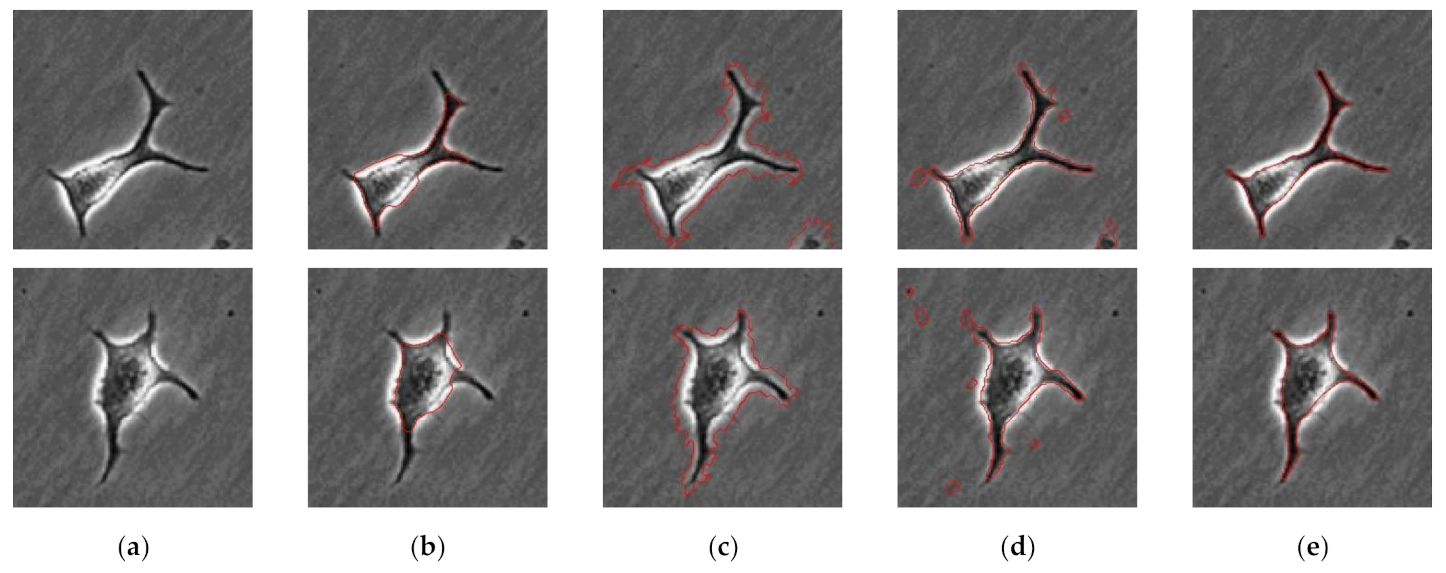
- The method of this study, which performed segmentation by removing the halo effect, was verified by comparing two methods, the method performed by the manual method, which is a basic method and is used a ground truth for the proposed method, and the method performed by segmentation without removing the halo effect.
- The results ensure the novelty and reliability of the method proposed in this study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and Experiment
2.2. Image Acquisition and Processing
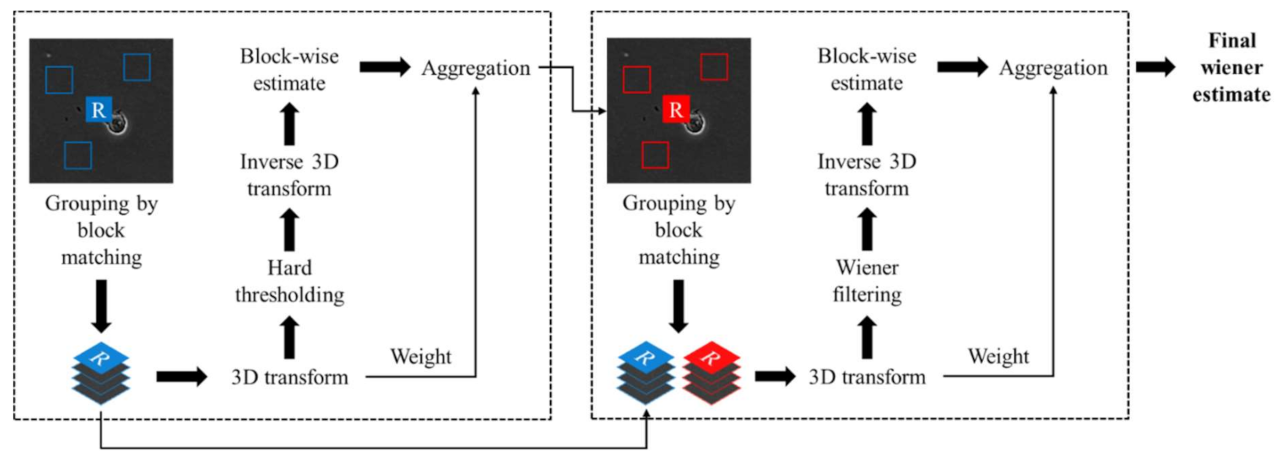
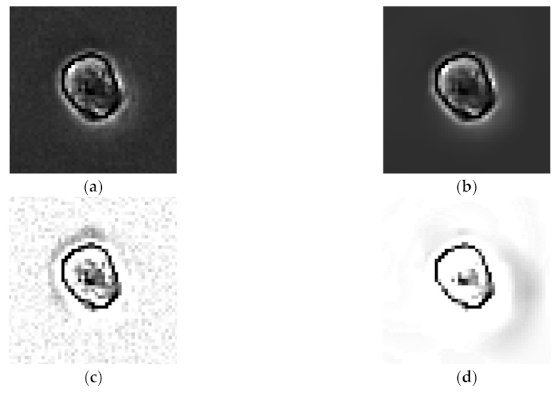
2.2.1. Denoising
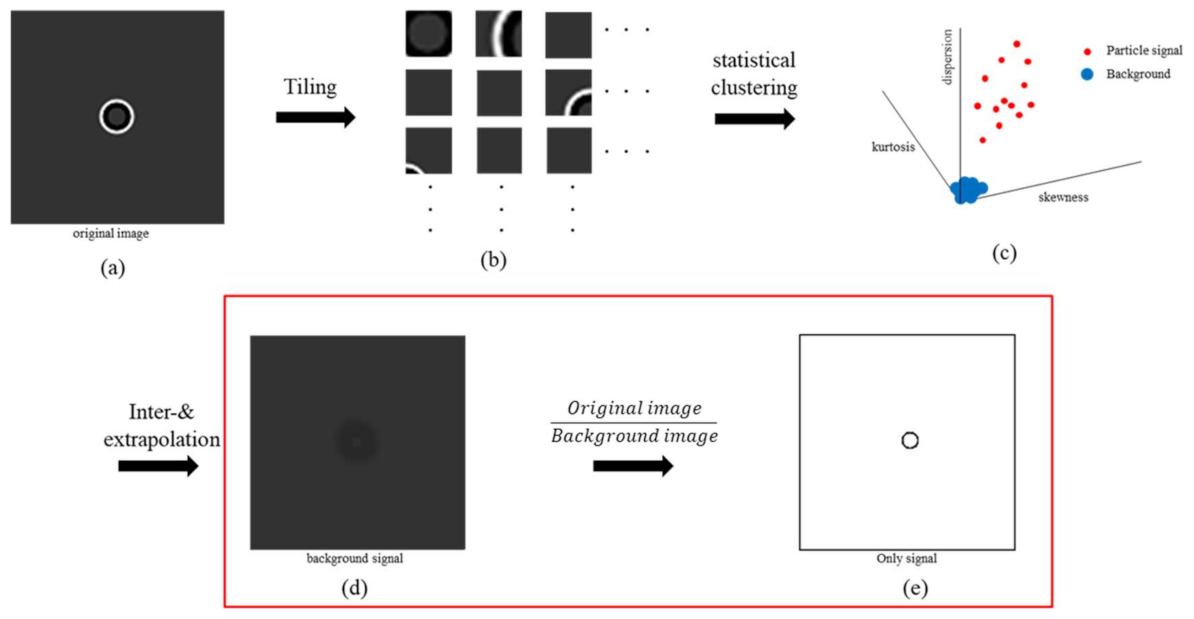
2.2.2. Halo Effect Elimination
2.2.3. Edge Detection of Cells
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lauffenburger, D.A.; Horwitz, A.F. Cell migration: A physically integrated molecular process. Cell 1996, 84, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, C.M.; Jones, G.E.; Ridley, A.J. Cell migration in development and disease. Dev. Cell 2002, 2, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuzzo, P.; Van Troys, M.; Ampe, C.; Martens, L. Taking aim at moving targets in computational cell migration. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 88–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theveneau, E.; Mayor, R. Neural crest delamination and migration: From epithelium-to-mesenchyme transition to collective cell migration. Dev. Biol. 2012, 366, 34–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, S.; Weigelin, B.; Wolf, K.; Tretiakov, K.V.; Polev, K.; Wilk, G.; Iwasa, M.; Emami, F.S.; Narojczyk, J.W.; Banaszak, M. Lévy-like movement patterns of metastatic cancer cells revealed in microfabricated systems and implicated in vivo. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debeir, O.; Adanja, I.; Kiss, R.; Decaestecker, C. Models of cancer cell migration and cellular imaging and analysis. Motile Actin Syst. Health Dis. 2008, 123–156. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Nørrelykke, S.F.; Cox, E.C. Persistent cell motion in the absence of external signals: A search strategy for eukaryotic cells. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krummel, M.F.; Bartumeus, F.; Gérard, A. T cell migration, search strategies and mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogilner, A.; Keren, K. The shape of motile cells. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, R762–R771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qi, S.; Jin, H.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, L.; Luo, Q. Zigzag generalized levy walk: The in vivo search strategy of immunocytes. Theranostics 2015, 5, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bise, R.; Kanade, T.; Yin, Z.; Huh, S.-i. Automatic cell tracking applied to analysis of cell migration in wound healing assay. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 6174–6179. [Google Scholar]
- Acton, S.T.; Wethmar, K.; Ley, K. Automatic tracking of rolling leukocytes in vivo. Microvasc. Res. 2002, 63, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.M.; Crookes, D.; Luo, N.; Davidson, M.W. Live-cell tracking using SIFT features in DIC microscopic videos. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 2219–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebata, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Tsuji, Y.; Sasaki, S.; Moriyama, K.; Kuboki, T.; Kidoaki, S. Persistent random deformation model of cells crawling on a gel surface. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ruprecht, V.; Wieser, S.; Callan-Jones, A.; Smutny, M.; Morita, H.; Sako, K.; Barone, V.; Ritsch-Marte, M.; Sixt, M.; Voituriez, R. Cortical contractility triggers a stochastic switch to fast amoeboid cell motility. Cell 2015, 160, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumier, A.; Olivo-Marin, J.C.; Arpin, M.; Michel, F.; Martin, M.; Mangeat, P.; Acuto, O.; Dautry-Varsat, A.; Alcover, A. The membrane-microfilament linker ezrin is involved in the formation of the immunological synapse and in T cell activation. Immunity 2001, 15, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, D.; Dias, O.; Amaral, A.; Ferreira, E. A comparison between bright field and phase-contrast image analysis techniques in activated sludge morphological characterization. Microsc. Microanal. 2010, 16, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zernike, F. Phase contrast, a new method for the microscopic observation of transparent objects part II. Physica 1942, 9, 974–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.-C.; Park, A.Y.; Guan, J.-L. In vitro scratch assay: A convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of cell migration in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ersoy, I.; Bunyak, F.; Mackey, M.A.; Palaniappan, K. Cell segmentation using Hessian-based detection and contour evolution with directional derivatives. In Proceedings of the 2008 15th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–15 October 2008; pp. 1804–1807. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, X.-H.; Meng, S.; Shen, H.-B. High density cell tracking with accurate centroid detections and active area-based tracklet clustering. Neurocomputing 2018, 295, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, E.; Xie, X. Phase contrast cell detection using multilevel classification. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2018, 34, e2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Taft, D.A.; Chen, Y.-J.; Zhang, J.; Wallace, C.T.; Xu, M.; Watkins, S.C.; Xing, J. Learn to segment single cells with deep distance estimator and deep cell detector. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 108, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambriz-Colin, F.; Torres-Cisneros, M.; Avina-Cervantes, J.; Saavedra-Martinez, J.; Debeir, O.; Sanchez-Mondragon, J. Detection of Biological Cells in Phase-Contrast Microscopy Images. In Proceedings of the 2006 Fifth Mexican International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Apizaco, Mexico, 13–17 October 2006; pp. 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Huh, S.; Bise, R.; Chen, M.; Kanade, T. Automated mitosis detection of stem cell populations in phase-contrast microscopy images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 30, 586–596. [Google Scholar]
- Thirusittampalam, K.; Hossain, M.J.; Ghita, O.; Whelan, P.F. A novel framework for cellular tracking and mitosis detection in dense phase contrast microscopy images. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2013, 17, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Bi, S. Segmentation of the clustered cells with optimized boundary detection in negative phase contrast images. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debeir, O.; Van Ham, P.; Kiss, R.; Decaestecker, C. Tracking of migrating cells under phase-contrast video microscopy with combined mean-shift processes. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2005, 24, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalfoun, J.; Majurski, M.; Peskin, A.; Breen, C.; Bajcsy, P.; Brady, M. Empirical gradient threshold technique for automated segmentation across image modalities and cell lines. J. Microsc. 2015, 260, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binici, R.C.; Şahin, U.; Ayanzadeh, A.; Töreyin, B.U.; Önal, S.; Okvur, D.P.; Özuysal, Ö.Y.; Ünay, D. Automated segmentation of cells in phase contrast optical microscopy time series images. In Proceedings of the 2019 Medical Technologies Congress (TIPTEKNO), Izmir, Turkey, 3–5 October 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, H.-F.; Gajda, J.; Sloan, T.F.; Rares, A.; Shen, A.Q. Usiigaci: Instance-aware cell tracking in stain-free phase contrast microscopy enabled by machine learning. SoftwareX 2019, 9, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaccard, N.; Szita, N.; Griffin, L.D. Segmentation of phase contrast microscopy images based on multi-scale local basic image features histograms. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. Imaging Vis. 2017, 5, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaccard, N.; Griffin, L.D.; Keser, A.; Macown, R.J.; Super, A.; Veraitch, F.S.; Szita, N. Automated method for the rapid and precise estimation of adherent cell culture characteristics from phase contrast microscopy images. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 504–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramapraba, P.; Chitra, M.; Prem Kumar, M. Effective lesion detection of colposcopic images using active contour method. Biomed. Res. 2017, 28, S255–S264. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Williams, B.M.; Vallabhaneni, S.R.; Czanner, G.; Williams, R.; Zheng, Y. Learning active contour models for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 11632–11640. [Google Scholar]
- Bensch, R.; Ronneberger, O. Cell segmentation and tracking in phase contrast images using graph cut with asymmetric boundary costs. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 12th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), New York, NY, USA, 16–19 April 2015; pp. 1220–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.; Yang, H. Research on K-value selection method of K-means clustering algorithm. J. Multidiscip. Res. 2019, 2, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghane, N.; Vard, A.; Talebi, A.; Nematollahy, P. Segmentation of white blood cells from microscopic images using a novel combination of K-means clustering and modified watershed algorithm. J. Med. Signals Sens. 2017, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foi, A.; Trimeche, M.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Practical Poissonian-Gaussian noise modeling and fitting for single-image raw-data. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2008, 17, 1737–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anscombe, F.J. The transformation of Poisson, binomial and negative-binomial data. Biometrika 1948, 35, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabov, K.; Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Image denoising with block-matching and 3D filtering. In Proceedings of the Image Processing: Algorithms and Systems, Neural Networks, and Machine Learning, San Jose, CA, USA, 17 February 2006; p. 606414. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; Wunsch, D. Survey of clustering algorithms. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2005, 16, 645–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankton, S.; Tannenbaum, A. Localizing region-based active contours. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2008, 17, 2029–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.F.; Vese, L.A. Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumford, D.B.; Shah, J. Optimal approximations by piecewise smooth functions and associated variational problems. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 1989, 42, 577–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | A = |Manual − Proposed Method| | B = |Manual − Active Contour Only| | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Number | |||||||
| Average (Pixel) | Max Diff. (Pixel) | Variance (Pixel) | Average (Pixel) | Max Diff. (Pixel) | Variance (Pixel) | ||
| 1 | 0.435 | 2.185 | 0.164 | 0.831 | 2.974 | 0.331 | |
| 2 | 0.332 | 1.607 | 0.088 | 0.560 | 1.847 | 0.150 | |
| 3 | 0.372 | 1.893 | 0.128 | 0.634 | 2.090 | 0.120 | |
| 4 | 0.257 | 1.139 | 0.043 | 0.322 | 1.159 | 0.067 | |
| 5 | 0.428 | 2.682 | 0.169 | 0.771 | 4.495 | 0.398 | |
| Average | 0.364 | 1.901 | 0.118 | 0.623 | 2.513 | 0.213 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jo, H.; Han, J.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, Y.; Yang, S. A Novel Method for Effective Cell Segmentation and Tracking in Phase Contrast Microscopic Images. Sensors 2021, 21, 3516. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103516
Jo H, Han J, Kim YS, Lee Y, Yang S. A Novel Method for Effective Cell Segmentation and Tracking in Phase Contrast Microscopic Images. Sensors. 2021; 21(10):3516. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103516
Chicago/Turabian StyleJo, Hongju, Junghun Han, Yoon Suk Kim, Yongheum Lee, and Sejung Yang. 2021. "A Novel Method for Effective Cell Segmentation and Tracking in Phase Contrast Microscopic Images" Sensors 21, no. 10: 3516. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103516
APA StyleJo, H., Han, J., Kim, Y. S., Lee, Y., & Yang, S. (2021). A Novel Method for Effective Cell Segmentation and Tracking in Phase Contrast Microscopic Images. Sensors, 21(10), 3516. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21103516







