Distributed Target Tracking in Challenging Environments Using Multiple Asynchronous Bearing-Only Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Statement
2.1. Target Model
2.2. Sensor Model
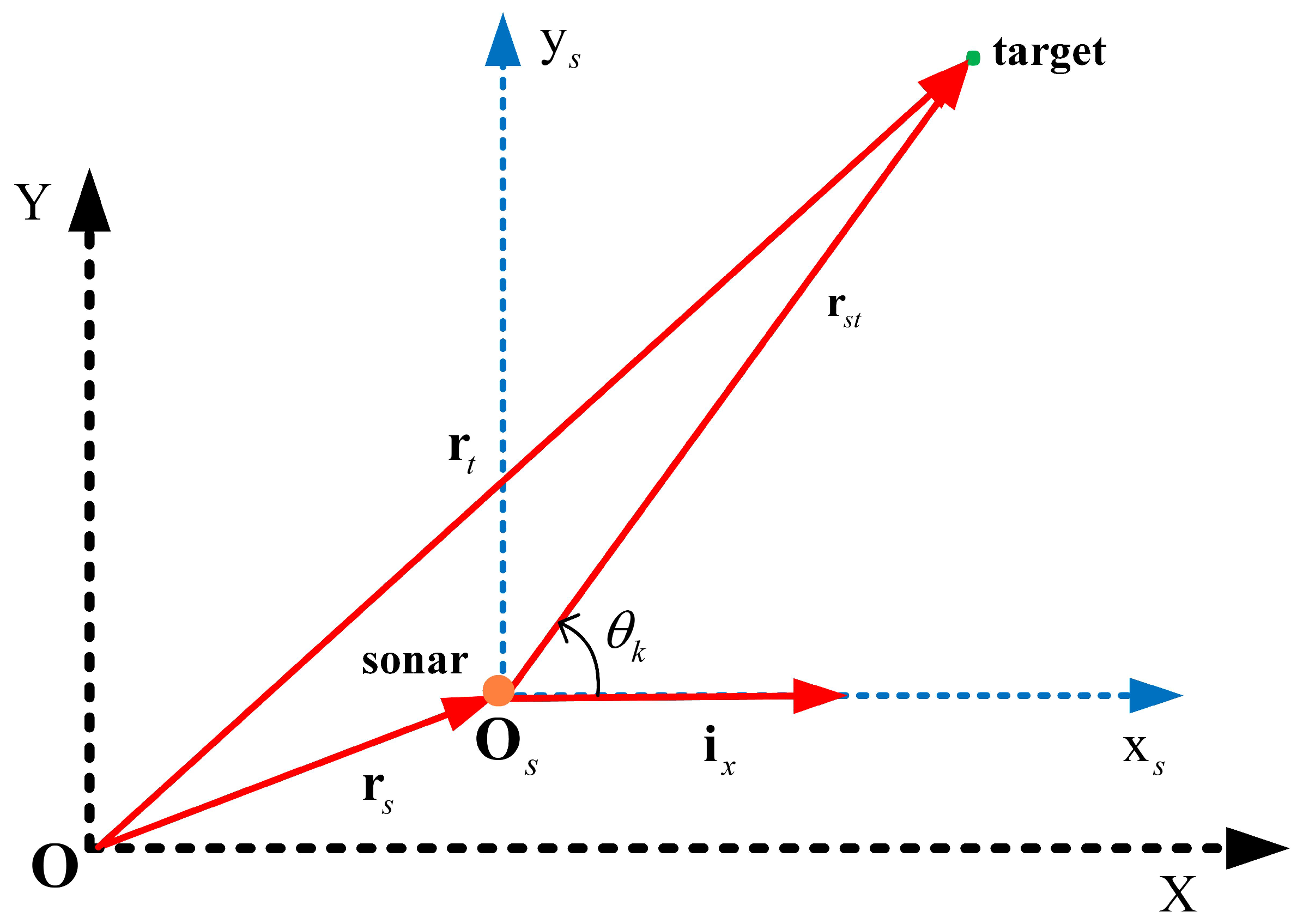
2.2.1. Target Measurement
2.2.2. Clutter Measurement
3. Overview of Automatic Target Tracking in Challenging Environments
3.1. Track Hybrid State Prediction
3.2. Gating and Likelihood
3.3. Data Association
3.4. Track Hybrid State Estimation
4. Distributed Target Tracking in Challenging Environments Using Multiple Asynchronous BO Sensors
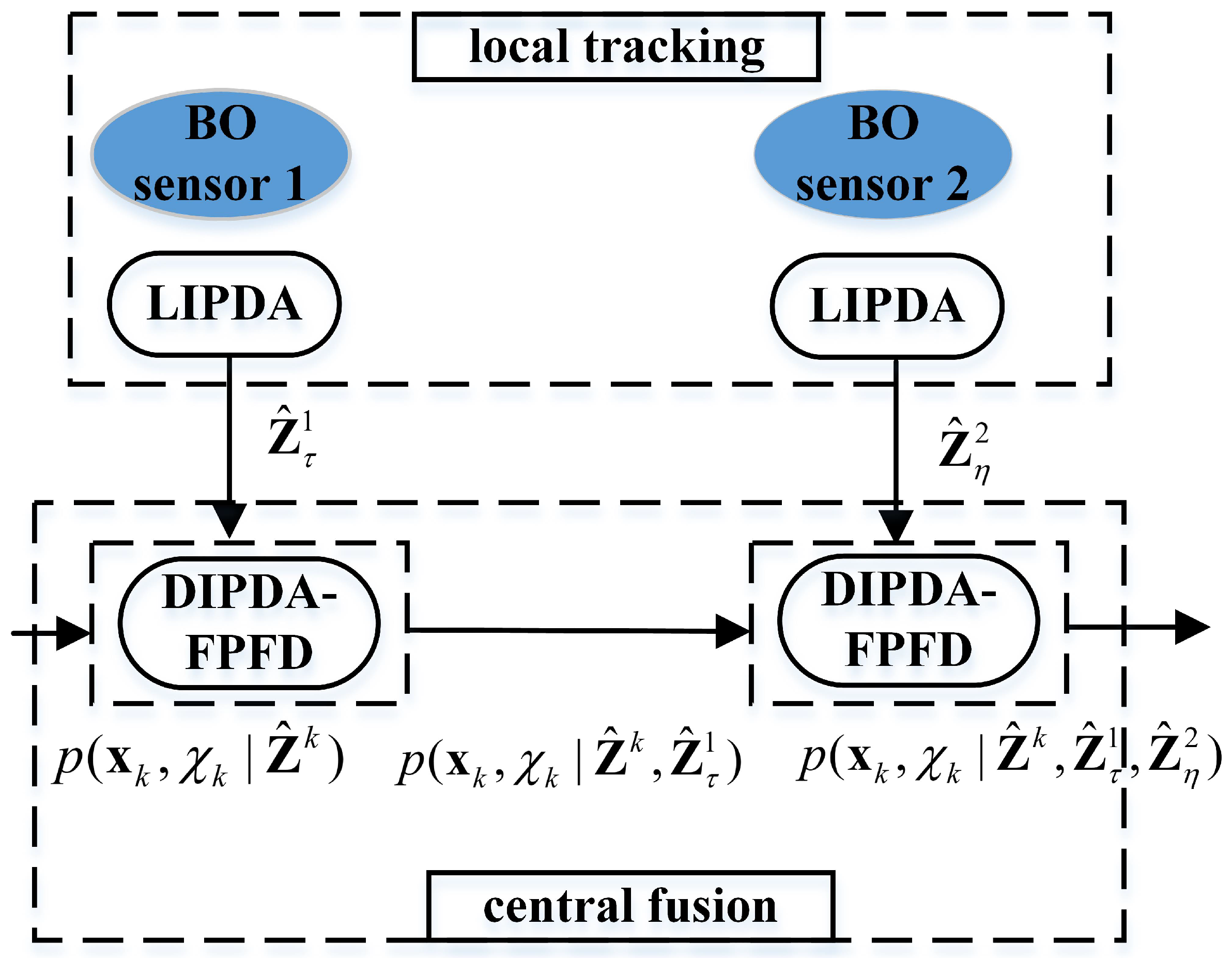
4.1. Framework of Proposed Methodology
4.2. Local IPDA (LIPDA)
4.3. Distributed IPDA-Forward Prediction Fusion and Decorrelation (DIPDA-FPFD) Technique
4.3.1. Forward Predict Hybrid State without OOS Information from Time to
4.3.2. Forward Predict Hybrid State with OOS Information from Time to
4.3.3. Decorrelate OOS Information Updated Hybrid State
4.3.4. Fuse the Current-Time Filtered Hybrid State Using OOS Information
5. Implementation
5.1. Pseudo Track/Track Management
5.2. Storage Consideration
- where , which requires scalars indicating the time stamp for which the central track is updated, with OOS information arrives at the fusion center between and .
- , requires scalars that indicates the mean of the filtered kinematic state of central track c from time to , with m denotes the dimension of the kinematic state.
- , requires scalars that indicates the error covariance of the filtered kinematic state estimation of central track c from time to .
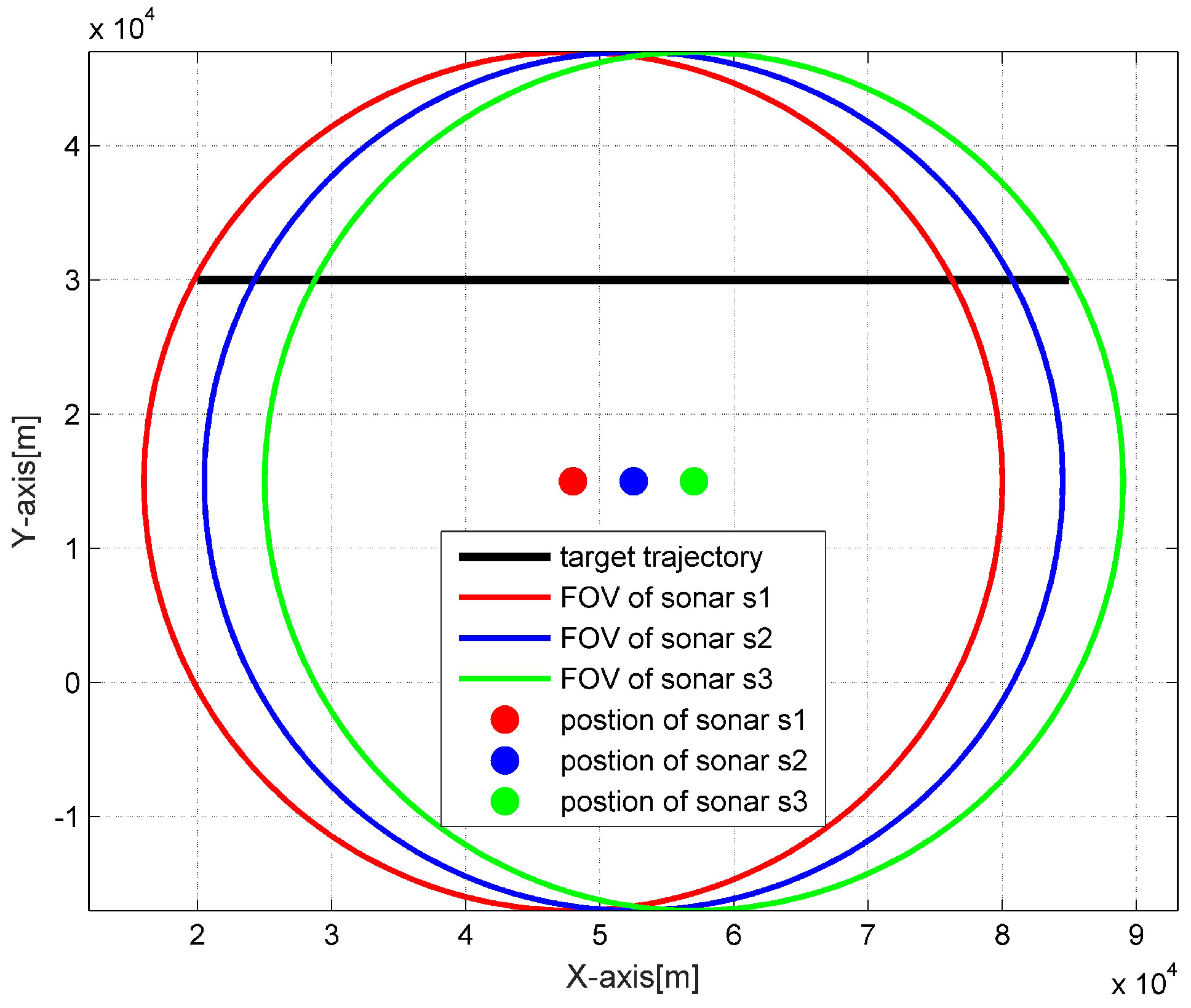
6. Simulation Validation
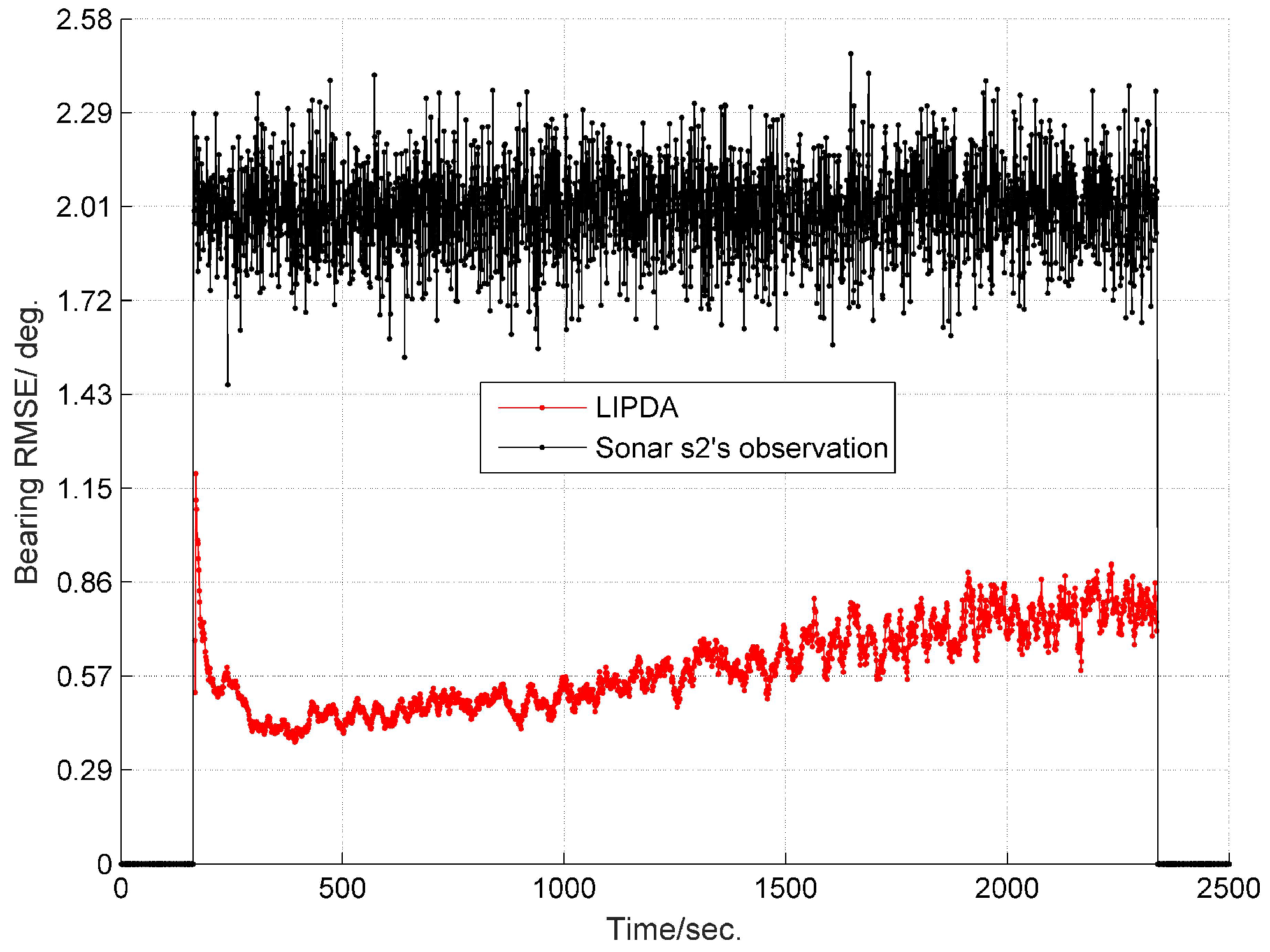
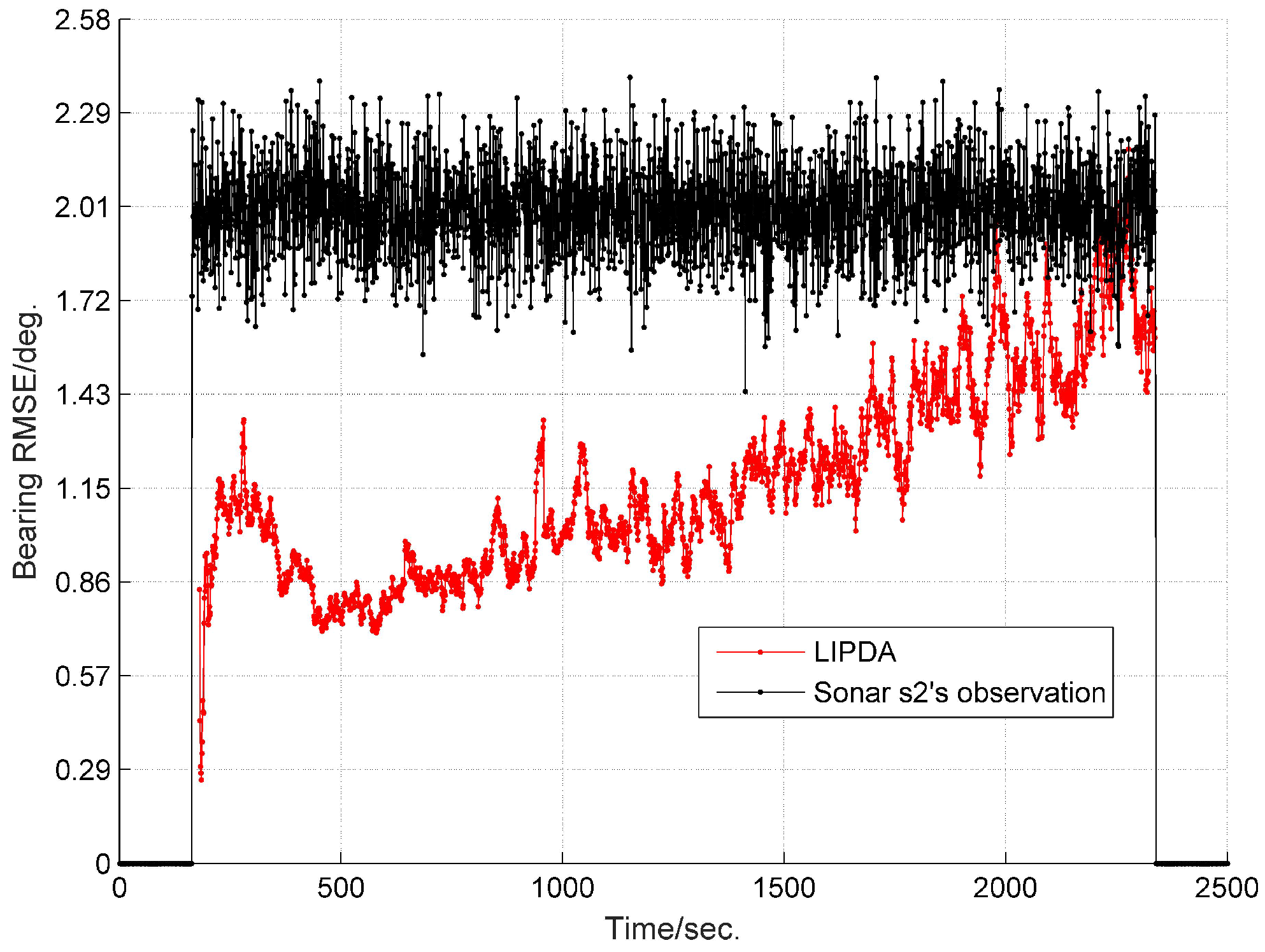
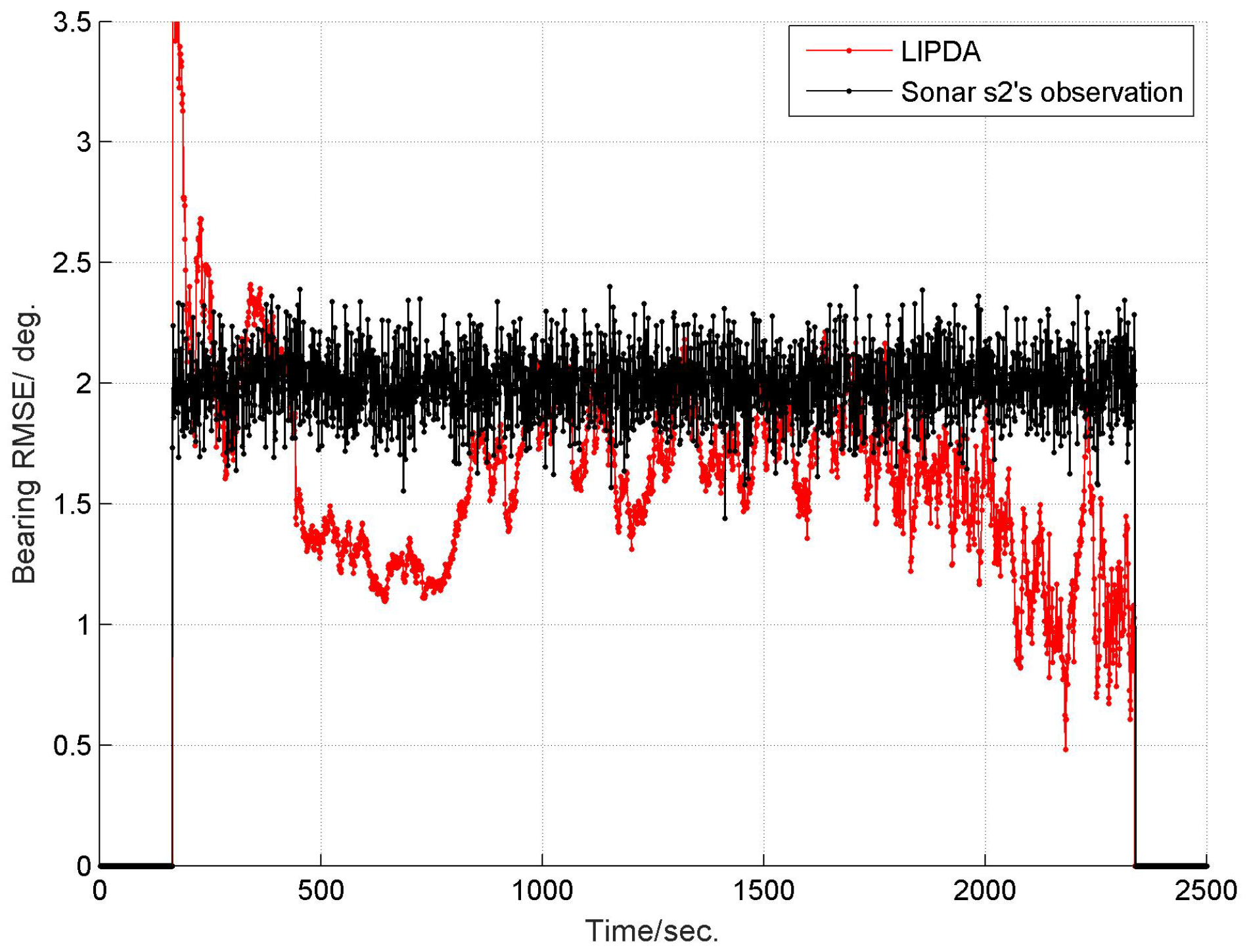
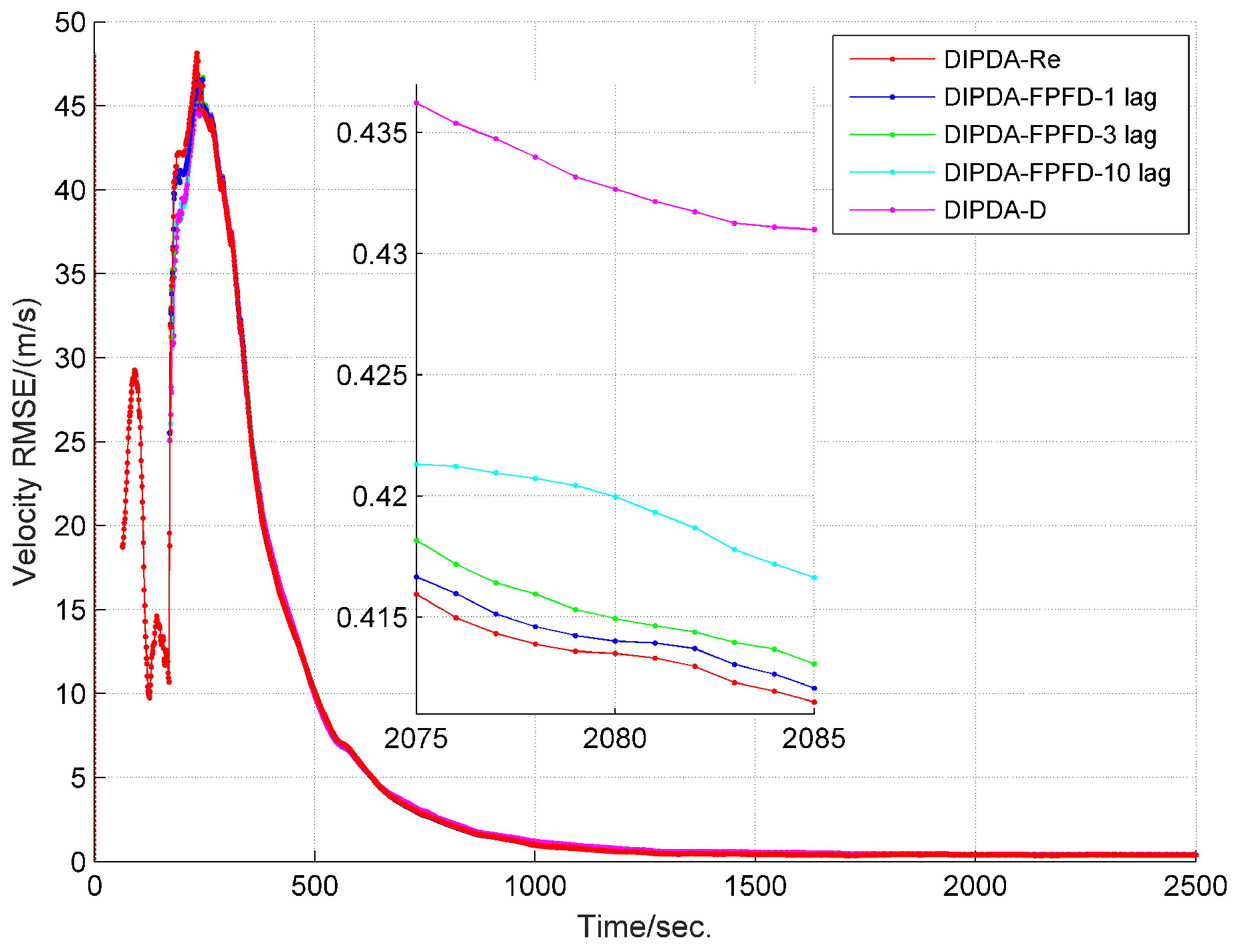
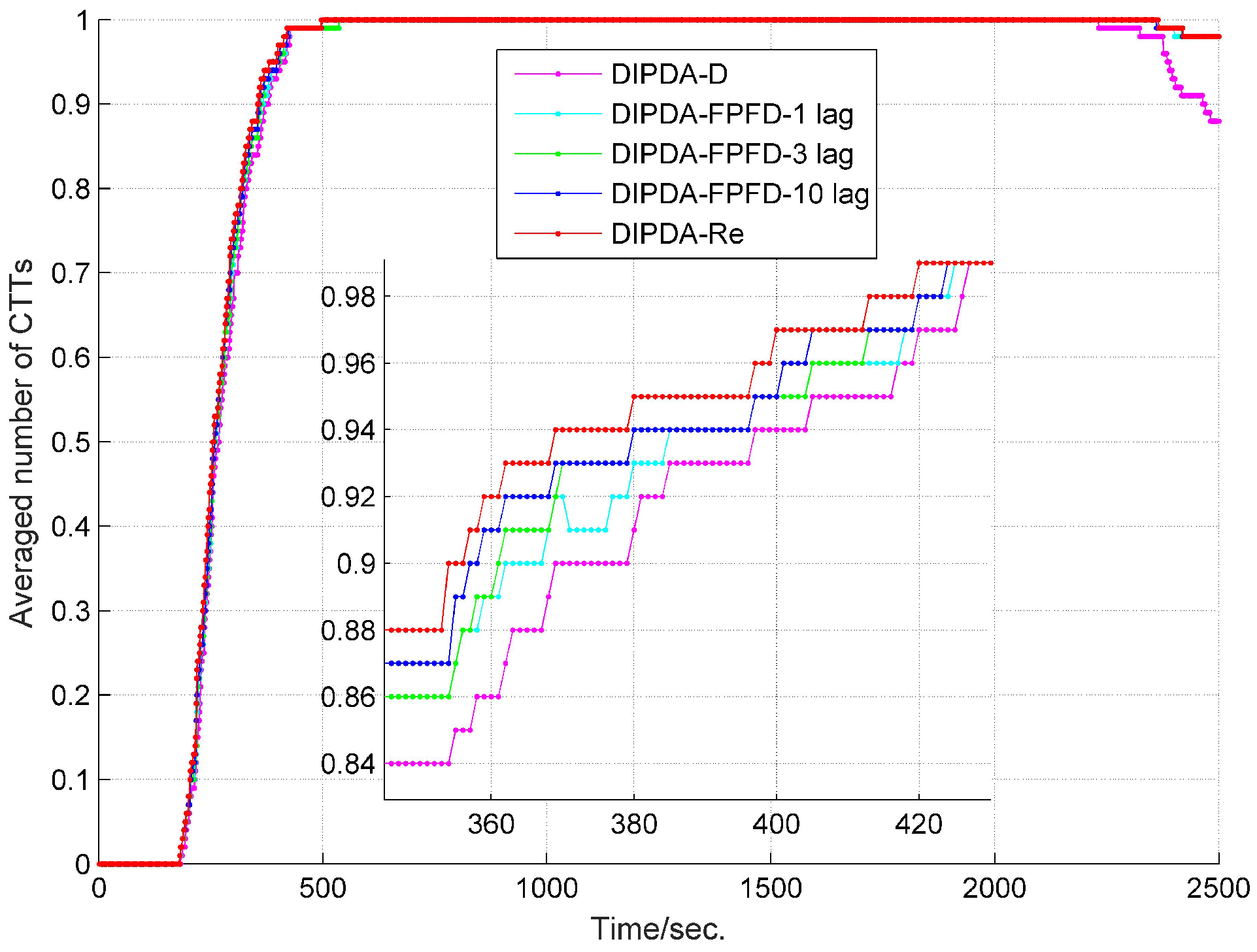
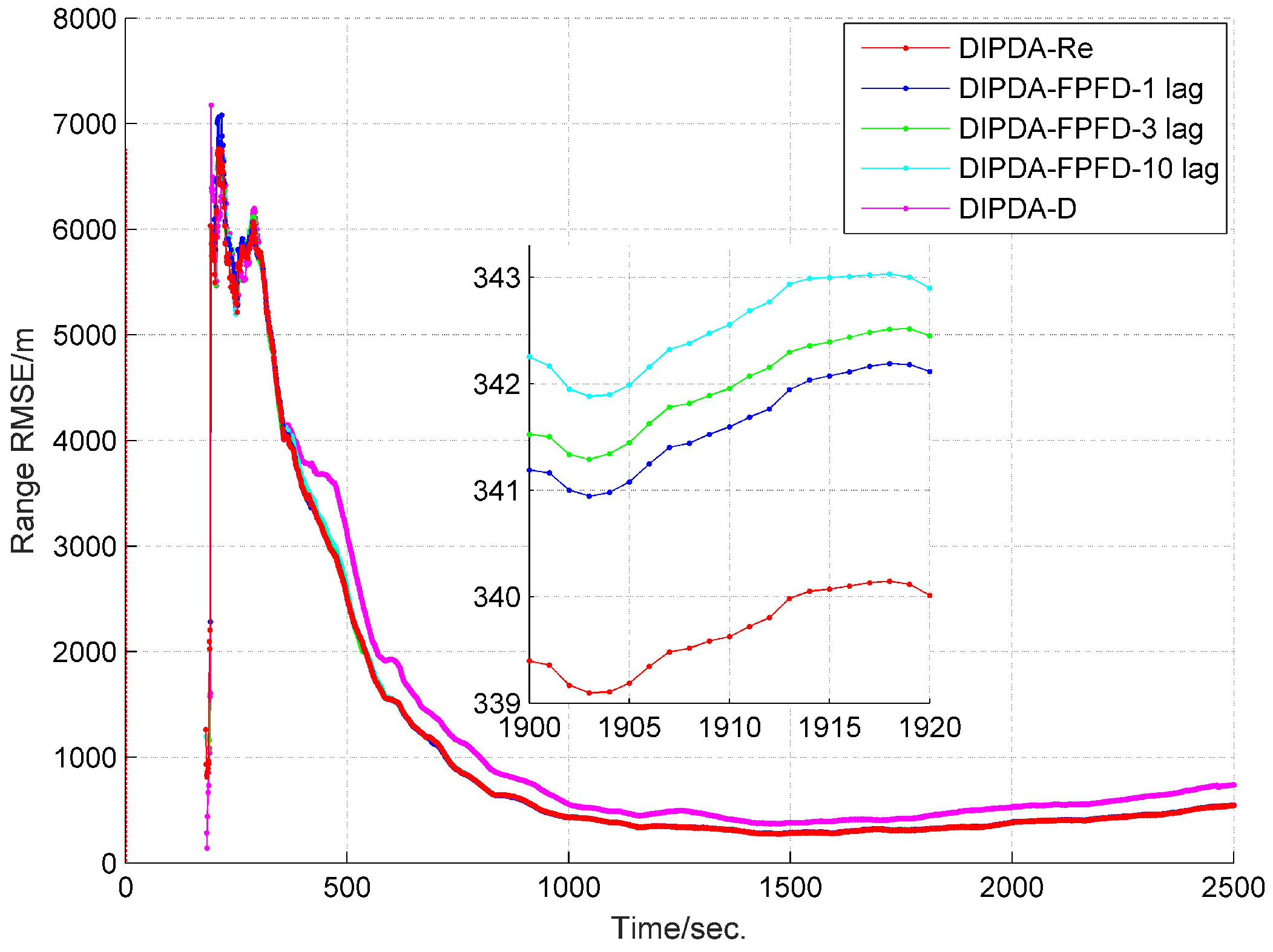
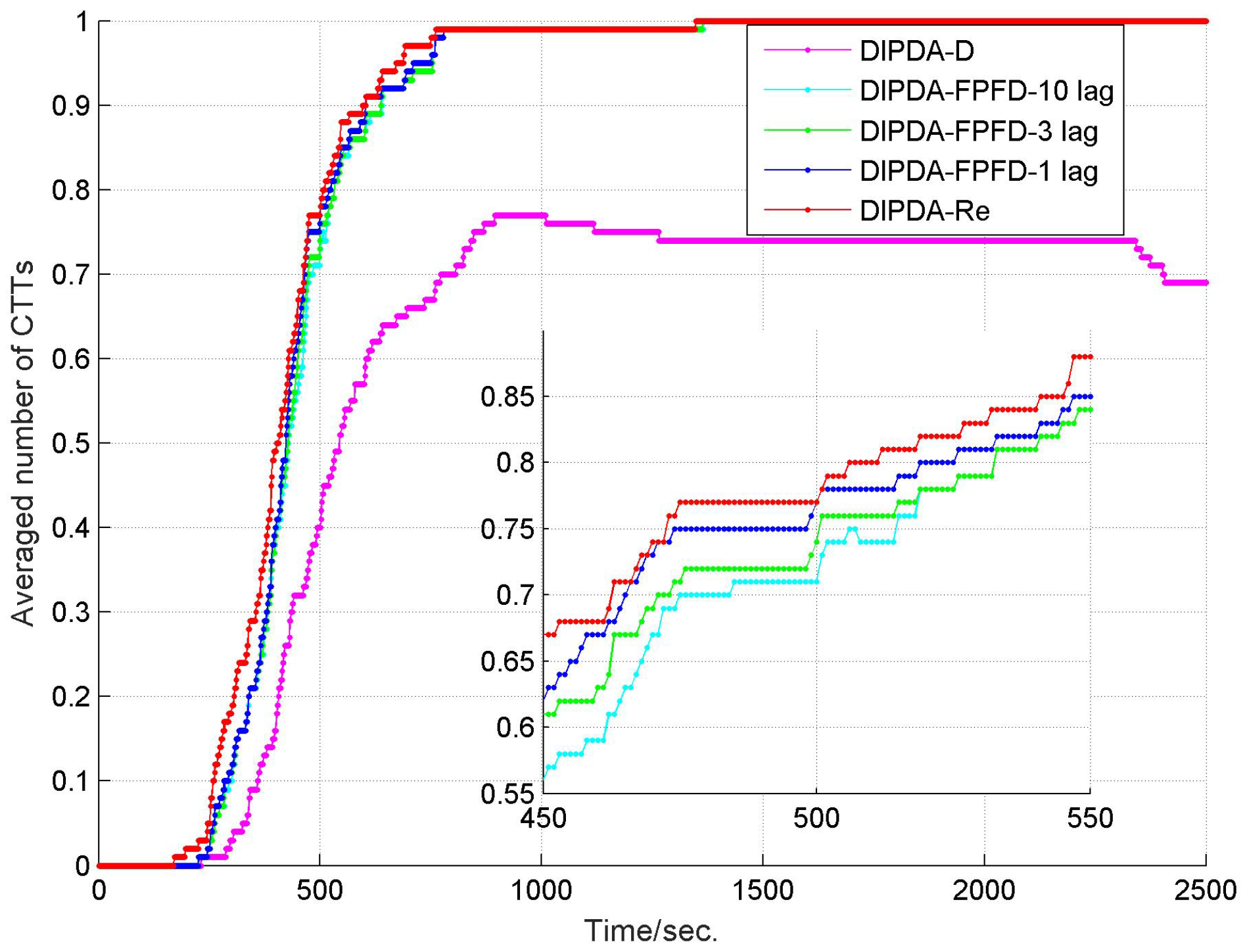
6.1. Local Tracking Results
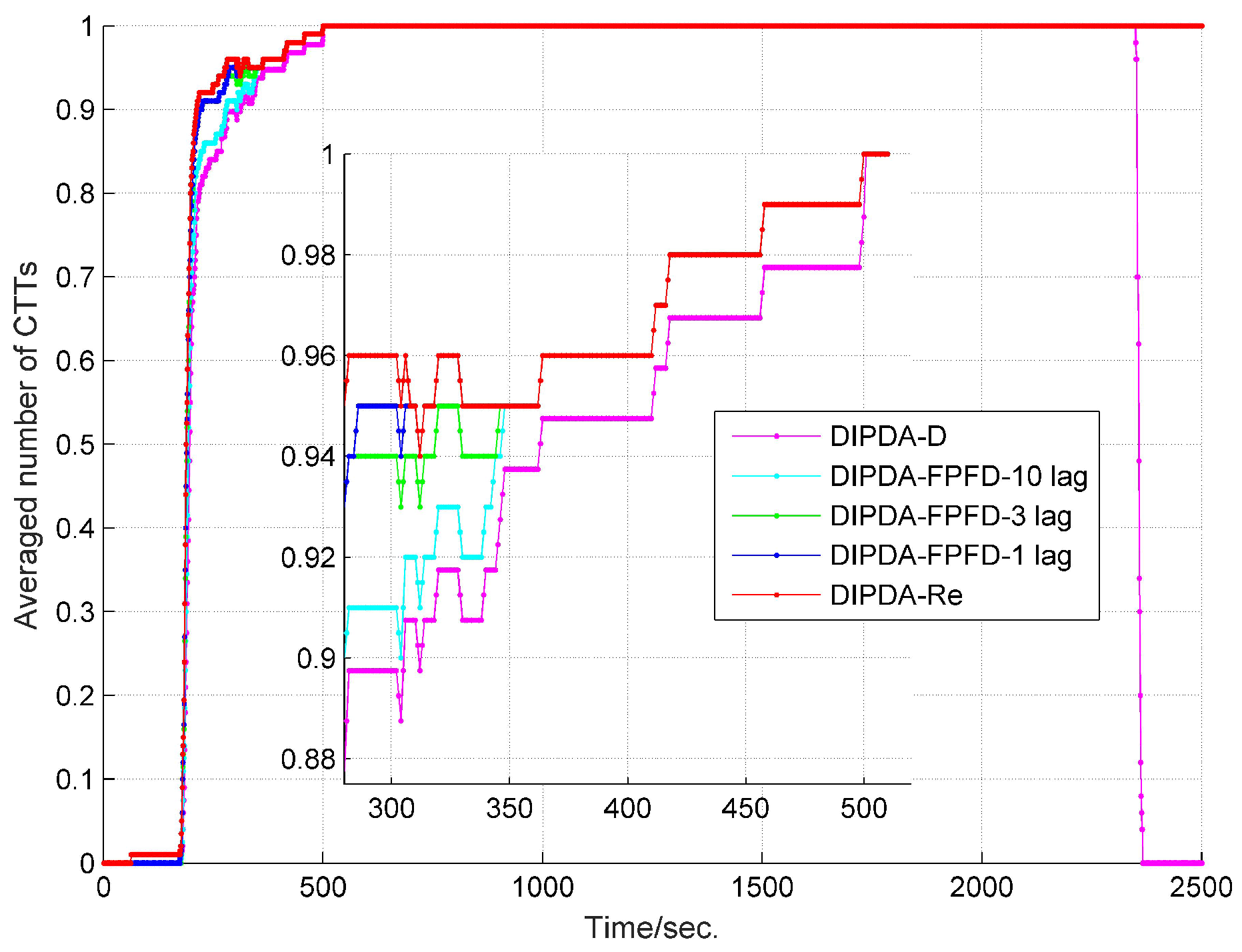
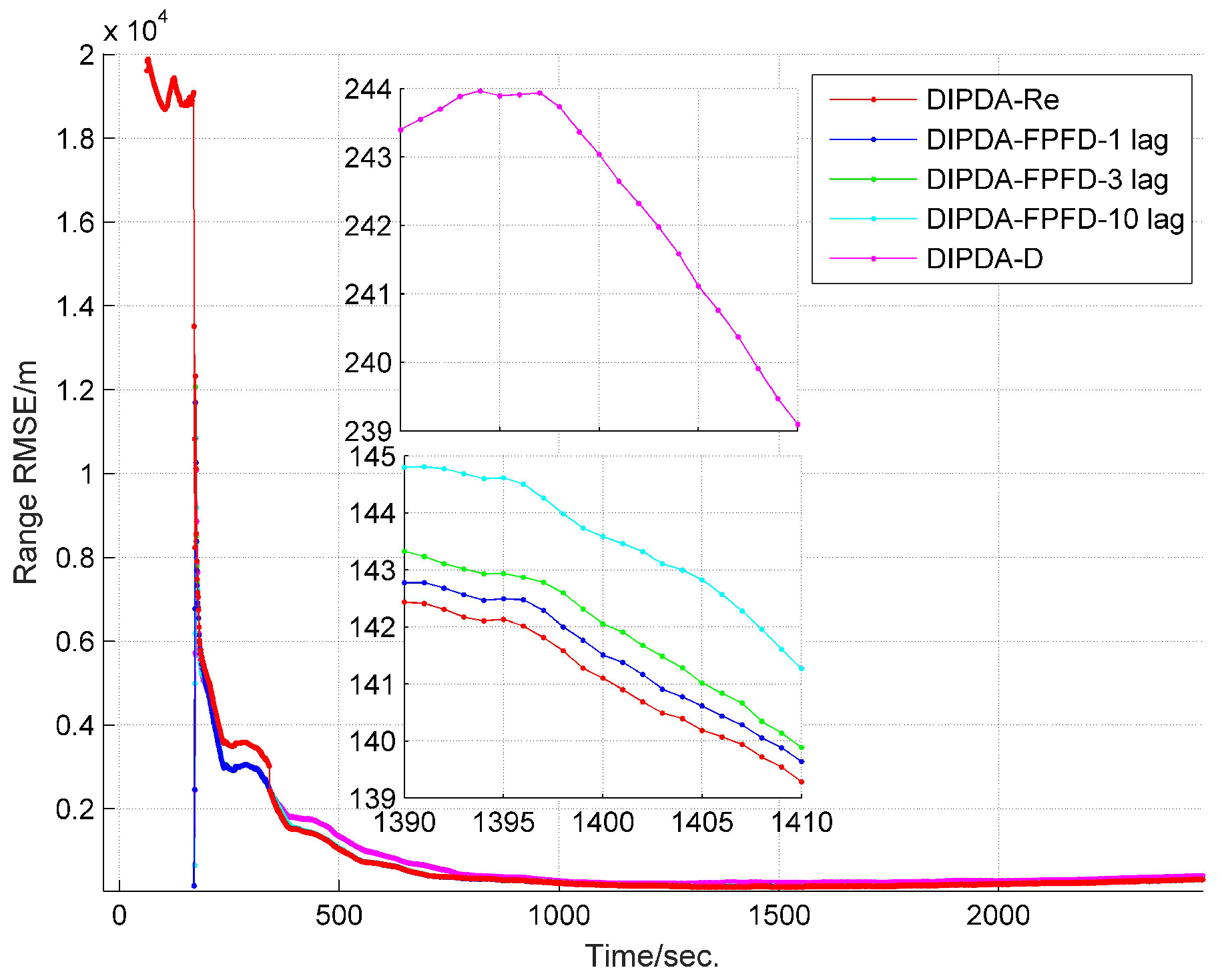
6.2. Central Tracking Results
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| A. Acronyms | |
| BO | Bearing-only |
| OOSM | Out-of-sequence measurement |
| IPDA | Integrated probabilistic data association |
| IPDA-EKF | Integrated probabilistic data association-extended Kalman filter |
| LIPDA | Local integrated probabilistic data association |
| DIPDA-FPFD | Distributed integrated probabilistic data association-forward prediction fusion and decorrelation |
| SPRT | Sequential probability ratio test |
| PTE | Probability of target existence |
| LOS | Line-of-sight |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| DIPDA-Re | Distributed integrated probabilistic data association-reprocessing |
| DIPDA-D | Distributed integrated probabilistic data association-discarding |
| CFT | Confirmed false track |
| CTT | Confirmed true track |
| Gmix | Gaussian mixture |
| Probability density function | |
| B. Notations | |
| The probability that target exists at time k given that it existed at time | |
| The time interval of two consecutive scans | |
| The averaged target existence duration | |
| The event of target existence at time | |
| The target kinematic state at time , with position component and velocity component | |
| The pseudo track state at time | |
| The kinematic state transition matrix from time to | |
| The measurement state transition matrix from time to | |
| The process noise of target dynamic model, with zero mean and covariance | |
| The process noise of measurement state model, with zero mean and covariance | |
| The set of measurements received by sensor s at time with cardinality | |
| The ith measurement of | |
| The set of sensor s received measurements up to and including time | |
| The set of measurements collected by all sensors up to and including time | |
| The set of selected measurements at time , with cardinality | |
| The ith measurement of | |
| The set of refined bearing measurements of sensor s at time | |
| The set of refined bearing measurements collected by all sensors up to and including time | |
| Target detection probability | |
| The sensor kinematic state at time , with position component and velocity component | |
| The sensor noise with zero mean and covariance | |
| The Gaussian distribution of variable with mean and its error covariance | |
| Mean and covariance of posterior kinematic state estimate at time | |
| Mean and covariance of predicted kinematic state estimate at time | |
| The likelihood of measurement | |
| The probability that target measure falls into the validation gate | |
| The clutter measurement density of | |
| The association probability that each measurement originates from the target | |
| Mean and covariance of kinematic state updated using at time | |
| Mean and covariance of posterior local measurement state estimate at time | |
| The unit vector of the X-axis of the sonar s local Cartesian coordinate | |
| The unit vector of the sonar s position vector in the global Cartesian coordinate | |
| The maximum velocity of target and sonar s, respectively | |
| Mean and covariance of predicted kinematic state of central track c from to | |
| Mean and covariance of track c kinematic state updated by at time | |
| Mean and covariance of track c predicted kinematic state from time to | |
| Mean and covariance of track c kinematic state purely updated by at time | |
| Mean and covariance of fused track c kinematic state at time |
Appendix A
References
- Hall, D.; Chong, C.Y.; Linas, J.; Liggins, M. Distributed Data Fusion for Network-Centric Operations; CRC Press, Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.; Yang, Y.; Gao, T. Variational Bayesian Based Adaptive Shifted Rayleigh Filter for Bearings-Only Tracking in Clutters. Sensors 2019, 19, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, S.S.; Bruno, M.S. Cooperative target tracking using decentralized particle filtering and RSS sensors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challa, S.; Morelande, M.R.; Mušicki, D.; Evans, R.J. Fundamentals of Object Tracking; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, W. Tracking and Sensor Data Fusion: Methodological Framework and Selected Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Huai, T.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, S. Multisensor Multi-Target Tracking Based on GM-PHD Using Out-Of-Sequence Measurements. Sensors 2019, 19, 4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Shalom, Y.; Li, X.R. Multitarget-Multisensor Tracking: Principles, Techniques and Software; YBS Publishing: Storrs, CT, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, D.B. An algorithm for tracking multiple targets. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1979, 24, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, S.S. Multiple hypothesis tracking for multiple target tracking. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2004, 19, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colegrove, B.S.; Pardini, S. PDAF with multiple clutter regions and target models. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2003, 39, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mušicki, D.; Evans, R.; Stankovic, S. Integrated probabilistic data association. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1994, 39, 1237–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mušicki, D.; Evans, R. Joint integrated probabilistic data association: JIPDA. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2004, 40, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.; Liang, Y.; Xu, L.F.; Zhang, W.Y. Concave Optimization-Based Approach for Joint Multi-Target Track Initialization. IEEE Access 2019, 2019, 108551–108560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mušicki, D.; Evans, R.; La Scala, B.F. Integrated track splitting filter-efficient multi-scan single target tracking in clutter. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2007, 43, 1409–1425. [Google Scholar]
- Zaitouny, A.; Stemler, T.; Algar, S. Optimal Shadowing Filter for a Positioning and Tracking Methodology with Limited Information. Sensors 2019, 19, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaitouny, A.; Stemler, T.; Judd, K. Tracking Rigid Bodies Using Only Position Data: A Shadowing Filter Approach Based on Newtonian Dynamics. Digit. Signal Process. 2017, 67, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitouny, A.; Stemler, T.; Small, M. Tracking a single pigeon using a shadowing filter algorithm. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 4419–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaitouny, A.; Stemler, T.; Small, M. Modelling and tracking the flight dynamics of flocking pigeons based on real GPS data (small flock). Ecol. Model. 2017, 344, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, B.; Ander, R.; Karl-Eric, A. Rao-blackwellized particle filter with out-of-sequence measurement processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 6454–6467. [Google Scholar]
- Blackman, S.S.; Popoli, R. Design and Analysis of Modern Tracking Systems; Artech House: Fitchburg, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hilton, R.D.; Martin, D.A.; Blair, W.D. Tracking with Time-Delayed Data in Multisensor Systems; NSWCDD/TR-93/351; Naval Surface Warfare Center: Dahlgren, VA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Li, X.R.; Zhu, Y. Optimal update with out-of-sequence measurements for distributed filtering. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Information Fusion, Annapolis, MD, USA, 8–11 July 2002; pp. 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shalom, Y. Update with out-of-sequence measurements in tracking: Exact solution. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2002, 38, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettleton, E.W.; Durrant-Whyte, H. Delayed and asequent data in decentralized sensing networks. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Systems and Advanced Manufacturing, Boston, MA, USA, 28–31 October 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Challa, S.; Evans, R.J.; Wang, X. A Bayesian solution and its approximations to out-of-sequence measurement problem. J. Inf. Fusion 2003, 4, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Shalom, Y.; Mallick, M.; Chen, H. One-step solution for the general out-of-sequence measurement problem in tracking. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2004, 40, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Qureshi, M.; Khan, U.; Memon, S.; Shi, Y.F.; Peng, D.L. Multisensor-based target-tracking algorithm with out-of-sequence-measurements in cluttered environment. Sensors 2018, 18, 4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Françoi, R.; Benaskeur, A.R. Forward prediction-based approach to target-tracking with Out-of-Sequence Measurements. In Proceedings of the 47th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Cancun, Mexico, 9–11 December 2008; pp. 1326–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Duraisamy, B.; Schwarz, T. Track to Track Fusion Incorporating Out of Sequence Track Based on Information Matrix Fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Las Palmas, Spain, 15–18 September 2015; pp. 2651–2658. [Google Scholar]
- Song, T.L.; Kim, T.H.; Mušicki, D. Distributed (nonlinear) target tracking in clutter. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2015, 51, 654–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Bar-Shalom, Y.; Willett, P. Track-to-track fusion with cross-covariances from Radar and IR/EO Sensor. In Proceedings of the 22th International Conference on Information Fusion, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2–5 July 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]




| Scan Index | 500 | 1000 | 1500 | 2000 | 2500 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # of initialized pseudo tracks | 207,144 | 409,344 | 611,521 | 814,362 | 1,020,037 |
| # of transmitted pseudo tracks | 25,297 | 81,277 | 138,342 | 188,992 | 214,774 |
| Reduced rate (%) | 87.79 | 80.14 | 77.38 | 76.79 | 78.94 |
| Scan Index | 500 | 1000 | 1500 | 2000 | 2500 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # of initialized pseudo tracks | 70,258 | 130,507 | 187,483 | 238,134 | 293,029 |
| # of transmitted pseudo tracks | 14,935 | 63,964 | 112,198 | 160,006 | 187,107 |
| midrule Reduced rate (%) | 78.75 | 50.99 | 40.16 | 32.81 | 36.15 |
| Scan Index | 500 | 1000 | 1500 | 2000 | 2500 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # of initialized pseudo tracks | 18,621 | 48,633 | 78,536 | 103,614 | 119,274 |
| # of transmitted pseudo tracks | 16,229 | 33,495 | 47,700 | 61,795 | 75,722 |
| Reduced rate (%) | 12.84 | 31.13 | 39.26 | 40.36 | 36.51 |
| DIPDA-FPFD | DIPDA-D | DIPDA-Re | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Lag | 3 Lag | 10 Lag | / | 1 Lag | 3 Lag | 10 Lag | |
| Sonar’s sampling interval (ms) | 1000 | ||||||
| Averaged elapsed time per scan (ms) | 37.03 | 37.04 | 37.07 | 36.81 | 1037.42 | 1038.22 | 1041.02 |
| Real time or delayed implementation | real time | real time | delayed | ||||
| Scan Index | 400 | 1300 | 2100 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | ||||
| DIPDA-FPFD | 28,182 | 24,948 | 25,872 | |
| DIPDA-Re | 117,214 | 113,118 | 11,554 | |
| DIPDA-D | 3782 | 3472 | 3596 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Y.; Choi, J.W.; Xu, L.; Kim, H.J.; Ullah, I.; Khan, U. Distributed Target Tracking in Challenging Environments Using Multiple Asynchronous Bearing-Only Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20092671
Shi Y, Choi JW, Xu L, Kim HJ, Ullah I, Khan U. Distributed Target Tracking in Challenging Environments Using Multiple Asynchronous Bearing-Only Sensors. Sensors. 2020; 20(9):2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20092671
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Yifang, Jee Woong Choi, Lei Xu, Hyung June Kim, Ihsan Ullah, and Uzair Khan. 2020. "Distributed Target Tracking in Challenging Environments Using Multiple Asynchronous Bearing-Only Sensors" Sensors 20, no. 9: 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20092671
APA StyleShi, Y., Choi, J. W., Xu, L., Kim, H. J., Ullah, I., & Khan, U. (2020). Distributed Target Tracking in Challenging Environments Using Multiple Asynchronous Bearing-Only Sensors. Sensors, 20(9), 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20092671






