Reliability of Vibroarthrography to Assess Knee Joint Sounds in Motion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethics
2.2. Participants
2.3. Measurement Protocol
2.4. Sound Signal Assessment, Extraction, and Processing
2.5. Statistics
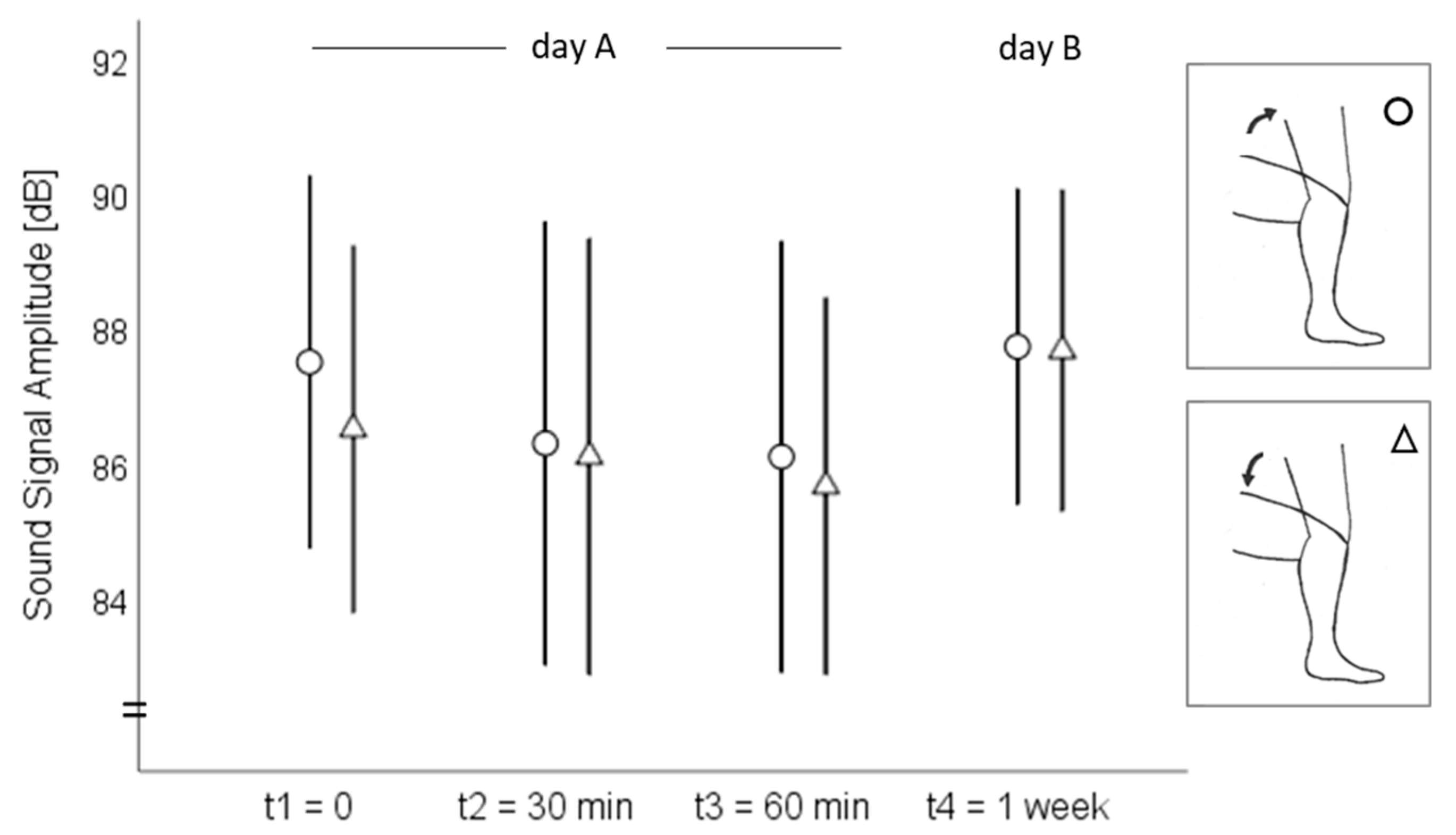
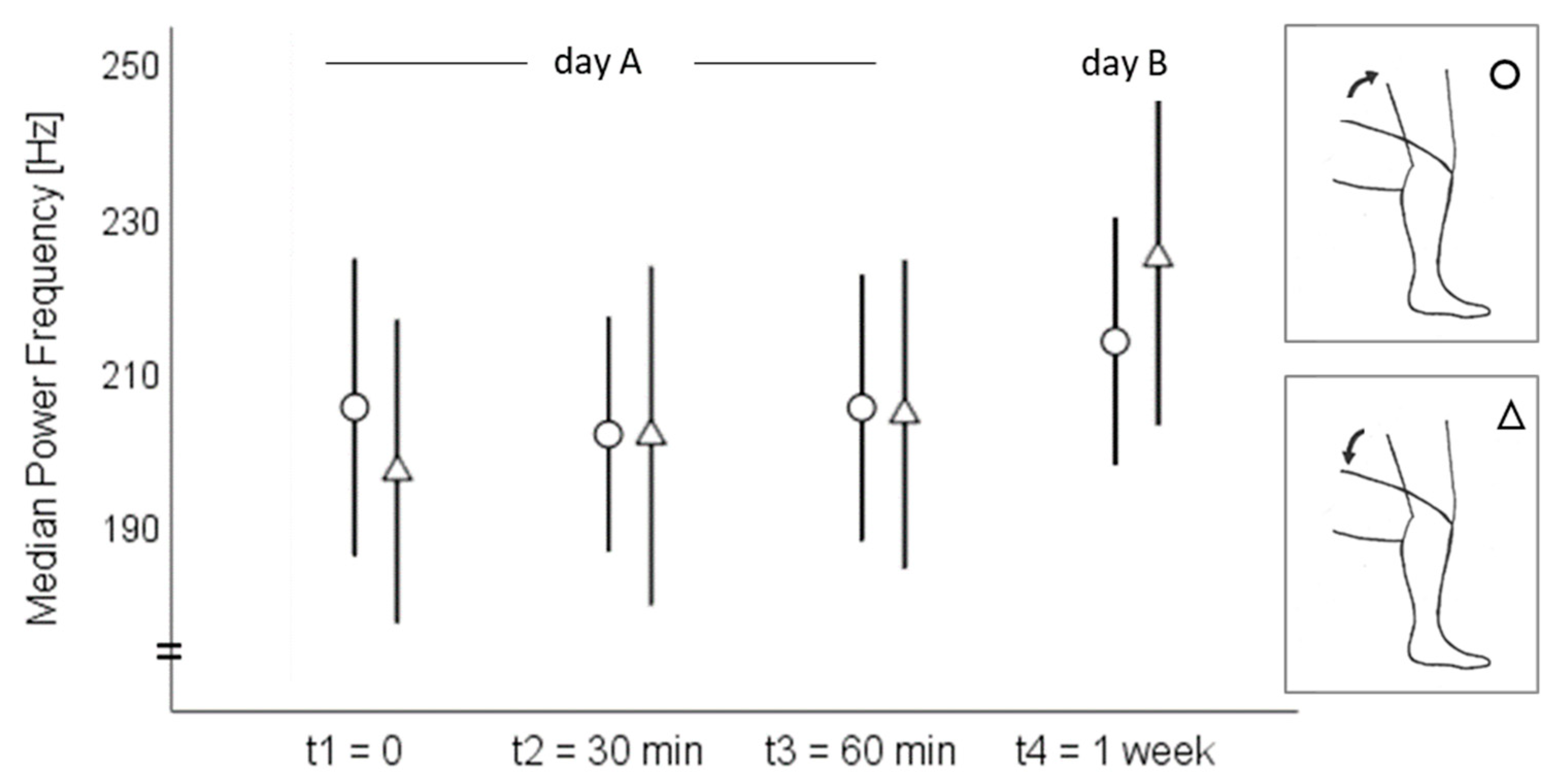
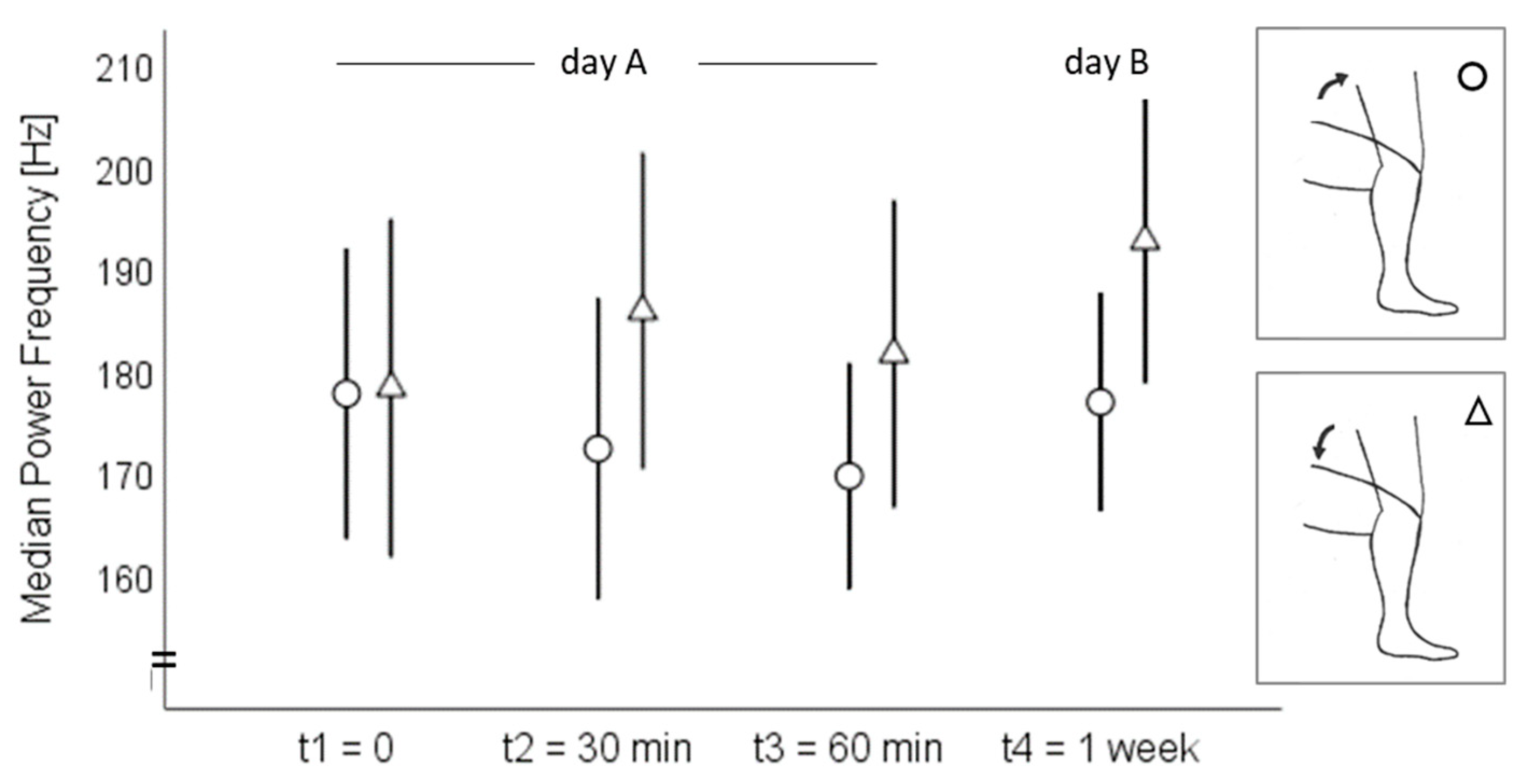
3. Results
3.1. Acoustic Emission Values
3.2. Intrasession Reliability
3.3. Interday Reliability
4. Discussion
4.1. Intrasession Reliability
4.2. Interday Reliability
4.3. Practical Relevance
4.4. Limitations and Future Study
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolus, N.B.; Jeong, H.K.; Whittingslow, D.C.; Inan, O.T. A Glove-Based Form Factor for Collecting Joint Acoustic Emissions: Design and Validation. Sensors 2019, 19, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiselev, J.; Ziegler, B.; Schwalbe, H.J.; Franke, R.P.; Wolf, U. Detection of osteoarthritis using acoustic emission analysis. Med. Eng. Phys. 2019, 65, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, G.F.; McCrea, J.D.; Beverland, D.E.; Kernohan, W.G.; Mollan, R.A. Vibration arthrography as a diagnostic aid in diseases of the knee. A preliminary report. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1987, 69, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, R.E.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Madeleine, P. Knee joint vibroarthrography of asymptomatic subjects during loaded flexion-extension movements. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Befrui, N.; Elsner, J.; Flesser, A.; Huvanandana, J.; Jarrousse, O.; Le, T.N.; Müller, M.; Schulze, W.H.W.; Taing, S.; Weidert, S. Vibroarthrography for early detection of knee osteoarthritis using normalized frequency features. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2018, 56, 1499–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bączkowicz, D.; Kręcisz, K.; Borysiuk, Z. Analysis of patellofemoral arthrokinematic motion quality in open and closed kinetic chains using vibroarthrography. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalo, K.; Niederer, D.; Sus, R.; Sohrabi, K.; Banzer, W.; Groß, V.; Vogt, L. The detection of knee joint sounds at defined loads by means of vibroarthrography. Clin. Biomech. 2020, 74, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeleine, P.; Andersen, R.E.; Larsen, J.B.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Samani, A. Wireless multichannel vibroarthrographic recordings for the assessment of knee osteoarthritis during three activities of daily living. Clin. Biomech. 2019, 72, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, K.; Skiba, G.; Czerner, M.; Szmajda, M.; Bączkowicz, D. Effects of Viscosupplementation on Knee Joint Arthrokinematics-Pilot Study. Ortop. Traumatol. Rehabil. 2018, 20, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toreyin, H.; Jeong, H.K.; Hersek, S.; Teague, C.N.; Inan, O.T. Quantifying the Consistency of Wearable Knee Acoustical Emission Measurements during Complex Motions. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 20, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teague, C.N.; Hersek, S.; Toreyin, H.; Millard-Stafford, M.L.; Jones, M.L.; Kogler, G.F.; Sawka, M.N.; Inan, O.T. Novel Methods for Sensing Acoustical Emissions from the Knee for Wearable Joint Health Assessment. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottner, J.; Audigé, L.; Brorson, S.; Donner, A.; Gajewski, B.J.; Hróbjartsson, A.; Roberts, C.; Shoukri, M.; Streiner, D.L. Guidelines for Reporting Reliability and Agreement Studies (GRRAS) were proposed. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascaro, B.; Prior, J.; Shark, L.-K.; Selfe, J.; Cole, P.; Goodacre, J. Exploratory study of a non-invasive method based on acoustic emission for assessing the dynamic integrity of knee joints. Med. Eng. Phys. 2009, 31, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleiss, J.L. The Design and Analysis of Clinical Experiments; Wiley Classics Library Ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999; ISBN 0471820474. [Google Scholar]
- Weir, J.P. Quantifying test-retest reliability using the intraclass correlation coefficient and the SEM. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2005, 19, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertus-Kajee, Y.; Tucker, R.; Derman, W.; Lamberts, R.P.; Lambert, M.I. Alternative methods of normalising EMG during running. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2011, 21, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobson, S.A.; Hopker, J.; Arkesteijn, M.; Passfield, L. Inter- and intra-session reliability of muscle activity patterns during cycling. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2013, 23, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi Oskouei, A.; Paulin, M.G.; Carman, A.B. Intra-session and inter-day reliability of forearm surface EMG during varying hand grip forces. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2013, 23, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankaerts, W.; O’Sullivan, P.B.; Burnett, A.F.; Straker, L.M.; Danneels, L.A. Reliability of EMG measurements for trunk muscles during maximal and sub-maximal voluntary isometric contractions in healthy controls and CLBP patients. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2004, 14, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorbie, G.G.; Williams, M.J.; Boyle, D.W.; Gray, A.; Brouner, J.; Gibson, N.; Baker, J.S.; Easton, C.; Ugbolue, U.C. Intra-session and Inter-day Reliability of the Myon 320 Electromyography System During Sub-maximal Contractions. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carius, D.; Kugler, P.; Kuhwald, H.-M.; Wollny, R. Absolute and relative intrasession reliability of surface EMG variables for voluntary precise forearm movements. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2015, 25, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, B.; Månsson, B.; Karlberg, C.; Syvertsson, P.; Elert, J.; Gerdle, B. Reproducibility of surface EMG variables and peak torque during three sets of ten dynamic contractions. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 1999, 9, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincivero, D.M.; Green, R.C.; Mark, J.D.; Campy, R.M. Gender and muscle differences in EMG amplitude and median frequency, and variability during maximal voluntary contractions of the quadriceps femoris. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2000, 10, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussavi, Z.M.; Rangayyan, R.M.; Bell, G.D.; Frank, C.B.; Ladly, K.O.; Zhang, Y.T. Screening of vibroarthrographic signals via adaptive segmentation and linear prediation modeling. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1996, 43, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shark, L.-K.; Chen, H.; Goodacre, J. Discovering differences in acoustic emission between healthy and osteoarthritic knees using a four-phase model of sit-stand-sit movements. Open Med. Inform. J. 2010, 4, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, S.; Eng, J.J.; MacIntyre, D.L. Reliability of surface EMG during sustained contractions of the quadriceps. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2005, 15, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamanidis, K.; Arampatzis, A.; Brüggemann, G.P. Reproduzierbarkeit elektromyographischer und dynamischer Parameter bei bewusster Änderung der Lauftechnik auf dem Laufband. Dtsch. Z. Sportmed. 2002, 53, 107–111. [Google Scholar]


| ICC | 95% Confidence Interval | SEM | CV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | SEM% | |||||
| Medial tibial plateau | |||||||
| Standing up | MPF | 0.85 * | 0.71 | 0.93 | 13.78 Hz | 7 | 0.06 |
| amplitude | 0.95 * | 0.89 | 0.98 | 1.44 dB | 0.02 | ||
| Sitting down | MPF | 0.93 * | 0.85 | 0.97 | 11.44 Hz | 6 | 0.05 |
| amplitude | 0.94 * | 0.88 | 0.98 | 1.44 dB | 0.02 | ||
| Patella | |||||||
| Standing up | MPF | 0.73 * | 0.51 | 0.87 | 14.47 Hz | 8 | 0.07 |
| amplitude | 0.86 * | 0.72 | 0.94 | 2.38 dB | 0.02 | ||
| Sitting down | MPF | 0.87 * | 0.74 | 0.94 | 11.73 Hz | 6 | 0.06 |
| amplitude | 0.85 * | 0.72 | 0.94 | 2.36 dB | 0.02 | ||
| ICC | 95% Confidence Interval | SEM | SEM% | CV | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||||||
| Medial tibial plateau | |||||||
| Standing up | MPF | 0.24 | −0.26 | 0.64 | 31.27 Hz | 15 | 0.11 |
| amplitude | 0.33 | −0.16 | 0.69 | 4.19 dB | 0.04 | ||
| Sitting down | MPF | 0.33 | −0.16 | 0.69 | 35.39 Hz | 17 | 0.14 |
| amplitude | 0.27 | −0.22 | 0.66 | 4.39 dB | 0.04 | ||
| Patella | |||||||
| Standing up | MPF | 0.62 * | 0.22 | 0.85 | 15.64 Hz | 9 | 0.07 |
| amplitude | 0.16 | −0.33 | 0.59 | 6.27 dB | 0.05 | ||
| Sitting down | MPF | 0.82 * | 0.56 | 0.93 | 13.56 Hz | 7 | 0.08 |
| amplitude | 0.00 | −0.51 | 0.42 | 6.85 dB | 0.06 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalo, K.; Niederer, D.; Sus, R.; Sohrabi, K.; Groß, V.; Vogt, L. Reliability of Vibroarthrography to Assess Knee Joint Sounds in Motion. Sensors 2020, 20, 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20071998
Kalo K, Niederer D, Sus R, Sohrabi K, Groß V, Vogt L. Reliability of Vibroarthrography to Assess Knee Joint Sounds in Motion. Sensors. 2020; 20(7):1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20071998
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalo, Kristin, Daniel Niederer, Rainer Sus, Keywan Sohrabi, Volker Groß, and Lutz Vogt. 2020. "Reliability of Vibroarthrography to Assess Knee Joint Sounds in Motion" Sensors 20, no. 7: 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20071998
APA StyleKalo, K., Niederer, D., Sus, R., Sohrabi, K., Groß, V., & Vogt, L. (2020). Reliability of Vibroarthrography to Assess Knee Joint Sounds in Motion. Sensors, 20(7), 1998. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20071998





