A Novel Adaptive Recursive Least Squares Filter to Remove the Motion Artifact in Seismocardiography
Abstract
1. Introduction
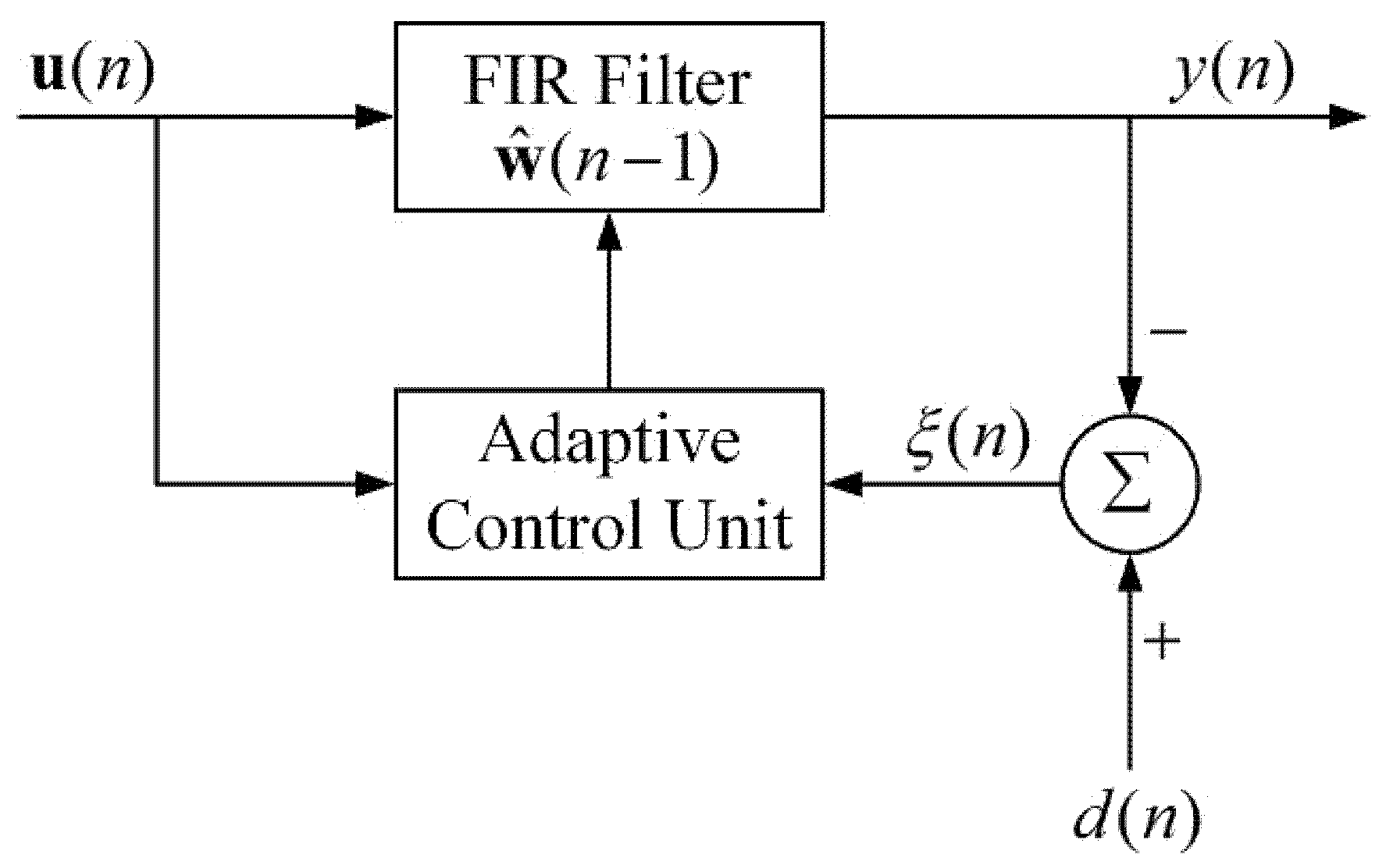
2. Theory of Adaptive Recursive Least Squares Filter (ARLSF)
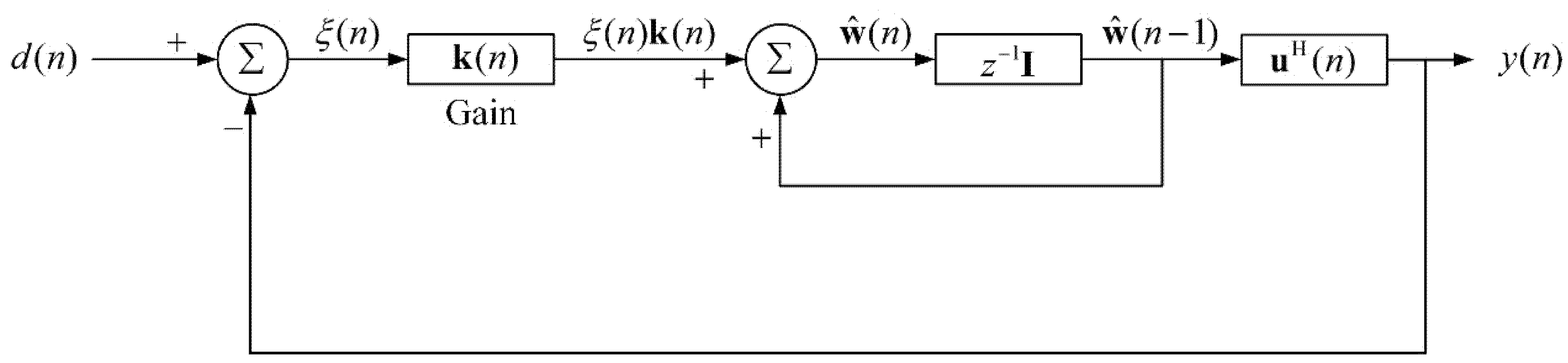
2.1. The Principle of Adaptive Recursive Least Squares Filter
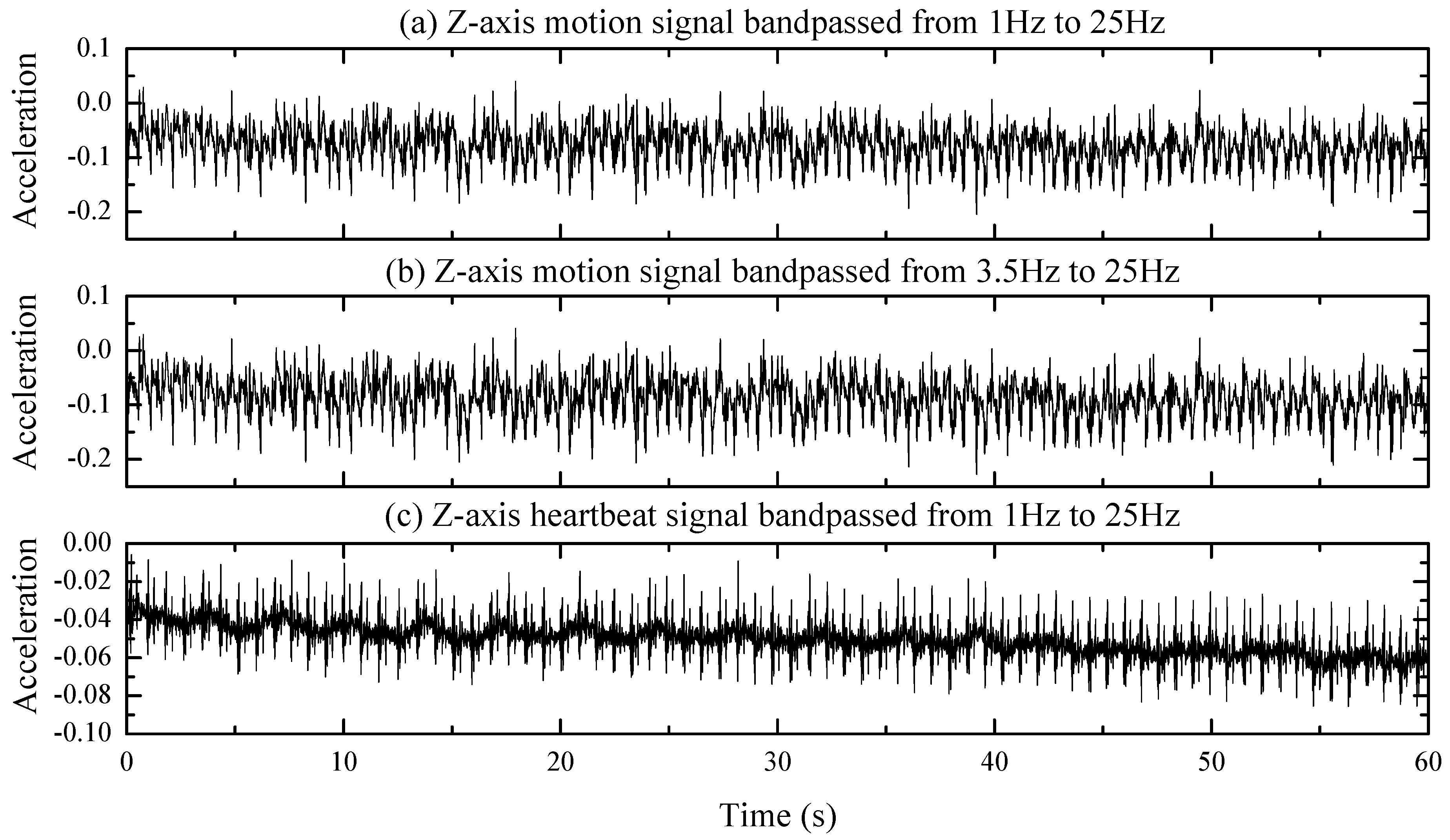
2.2. Discussion of the Desired Signal
2.3. Discussion of the Forgetting Factor
3. Measurement Technique
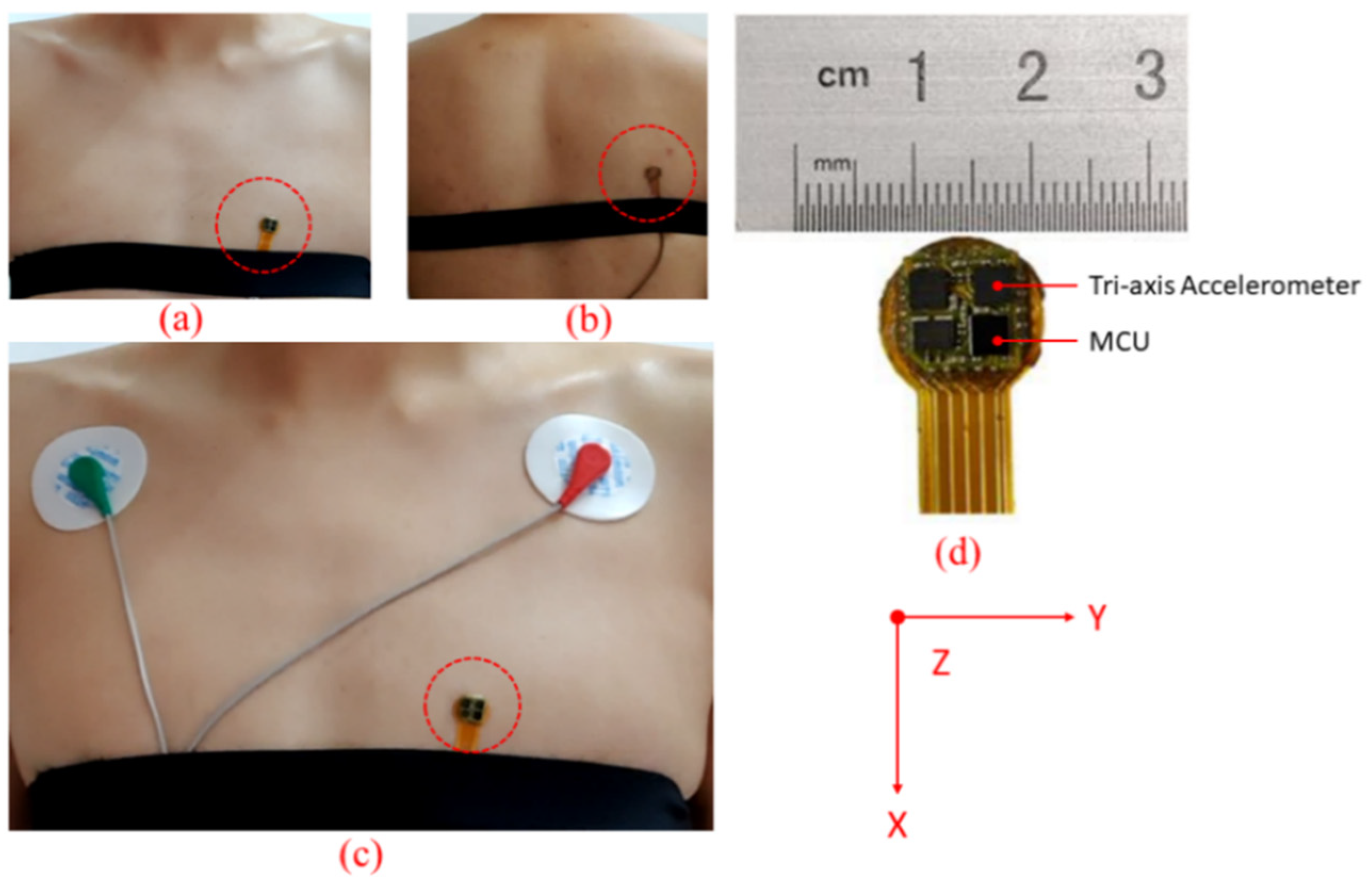
3.1. Hardware System
3.2. Experiment Setup
3.3. Software System
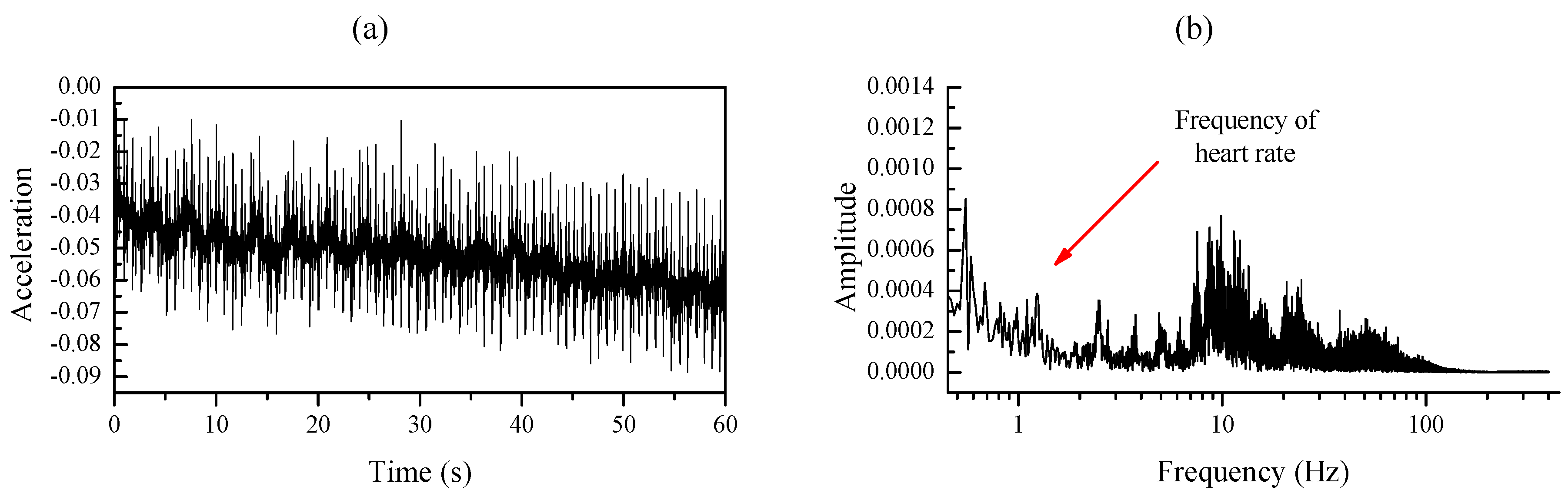
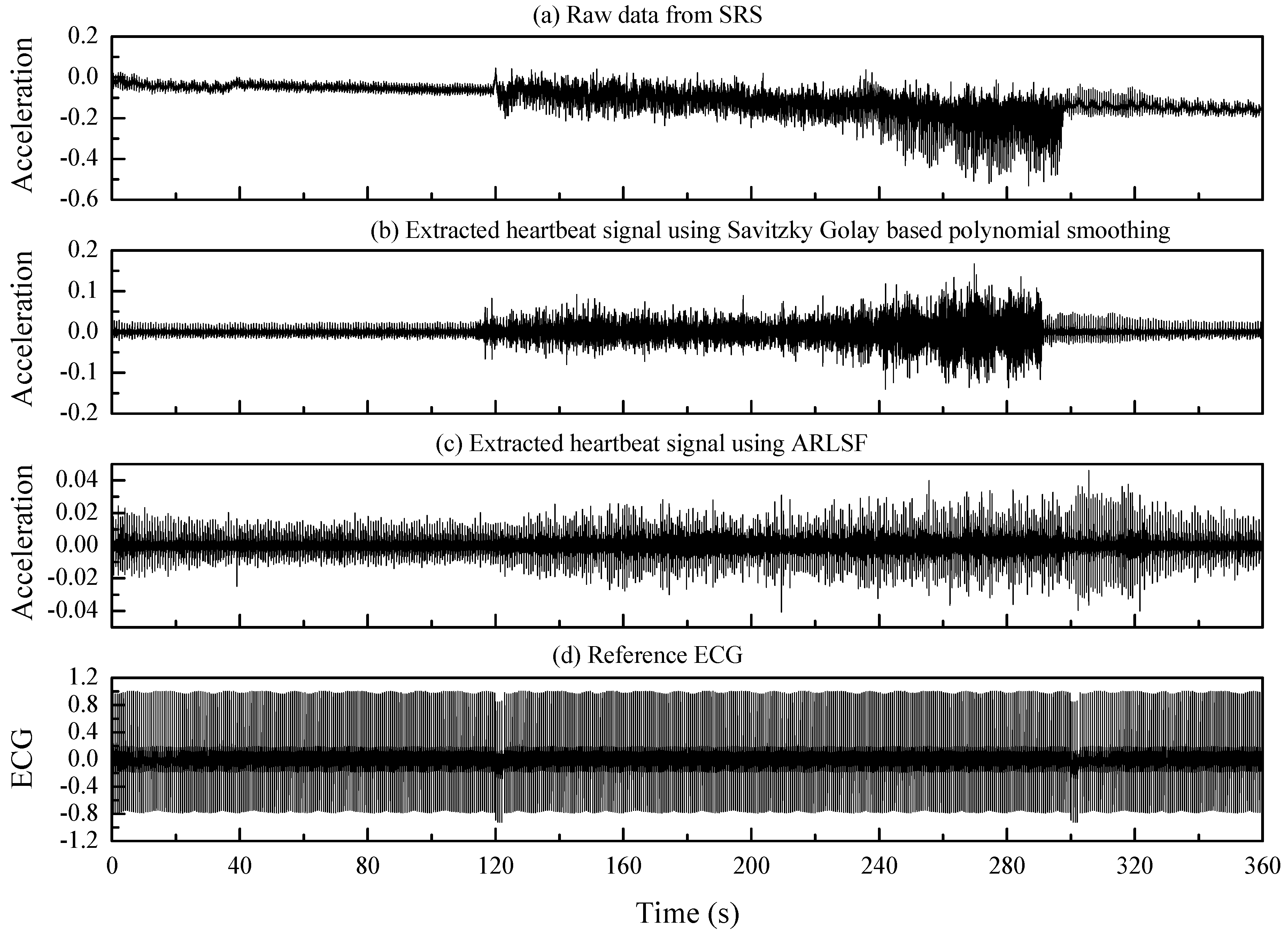
3.3.1. Signal Preprocessing
3.3.2. ARLSF
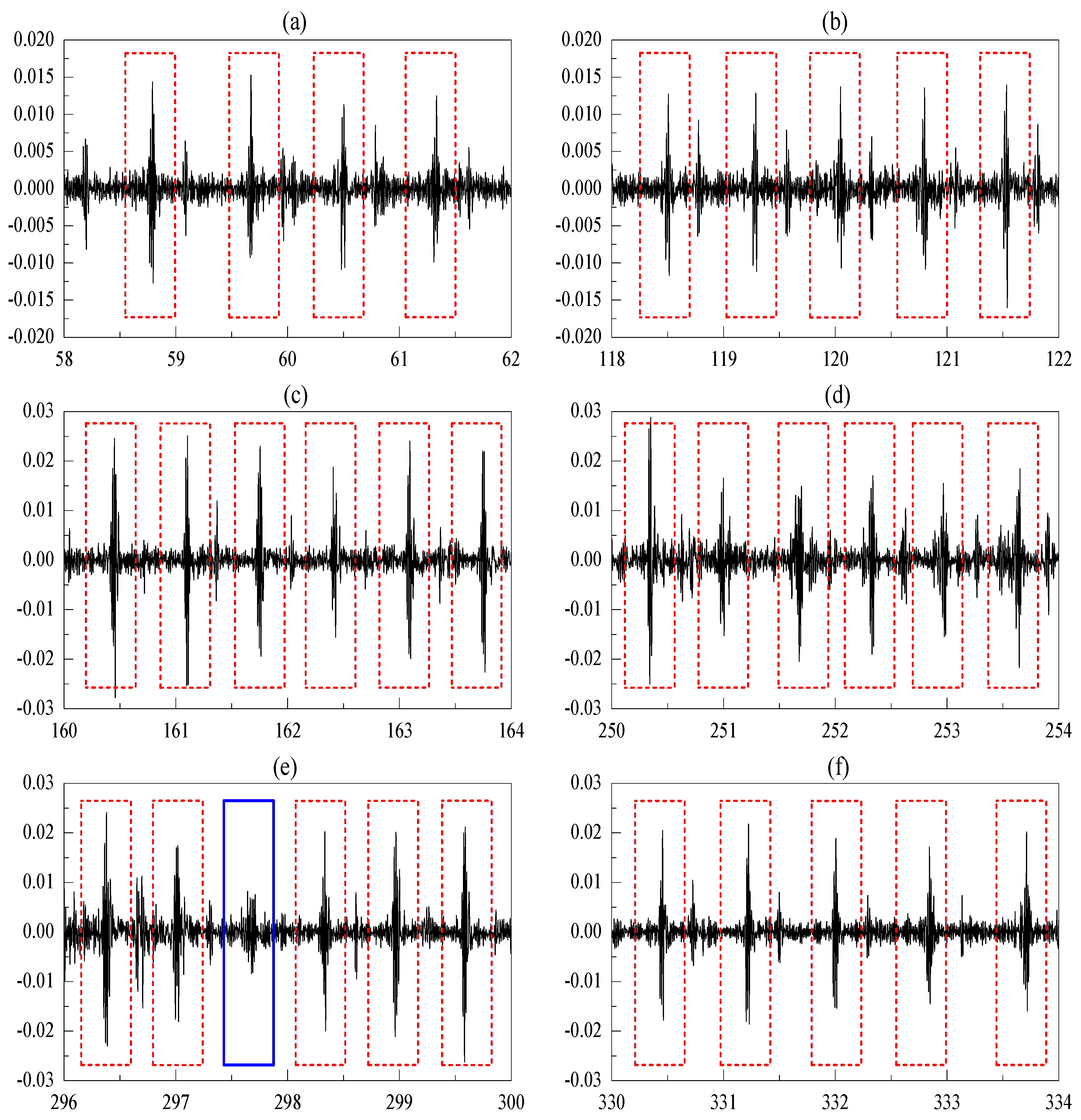
3.3.3. Feature Extraction
4. Results
4.1. Heartbeat Detection Accuracy
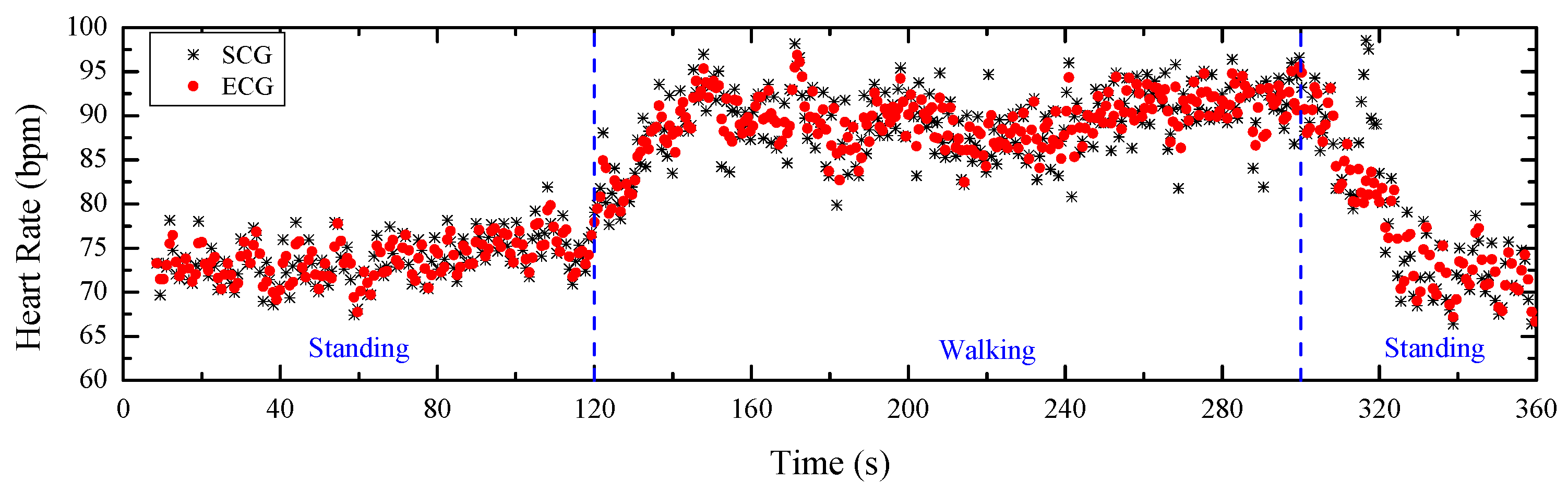
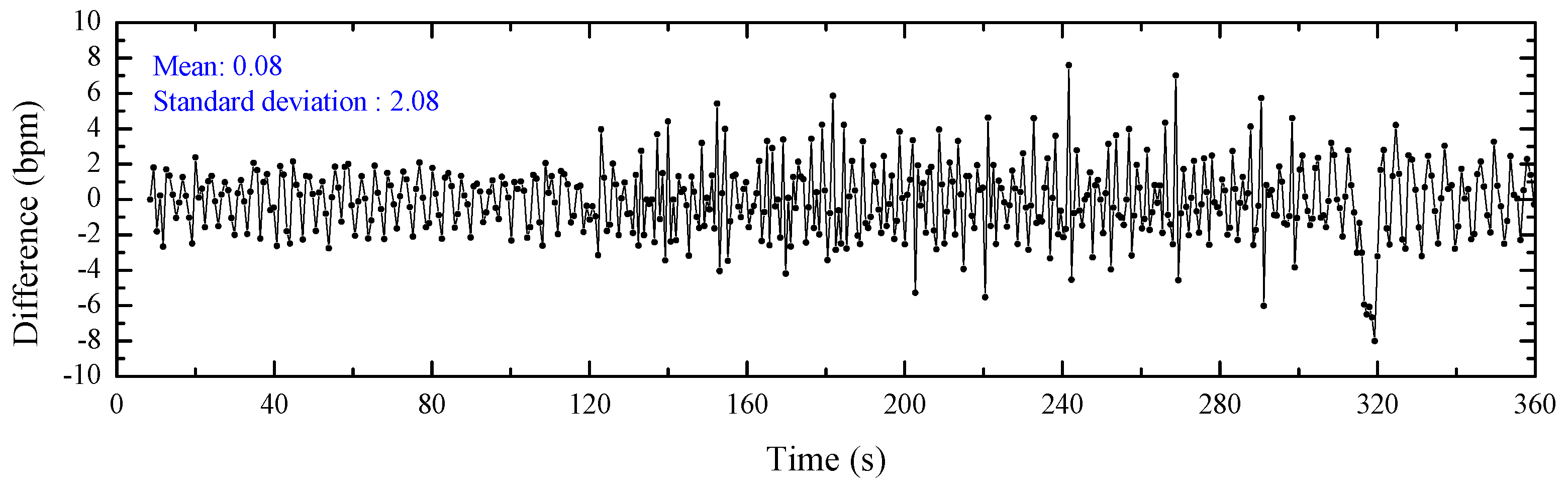
4.2. Heart Rate Estimations
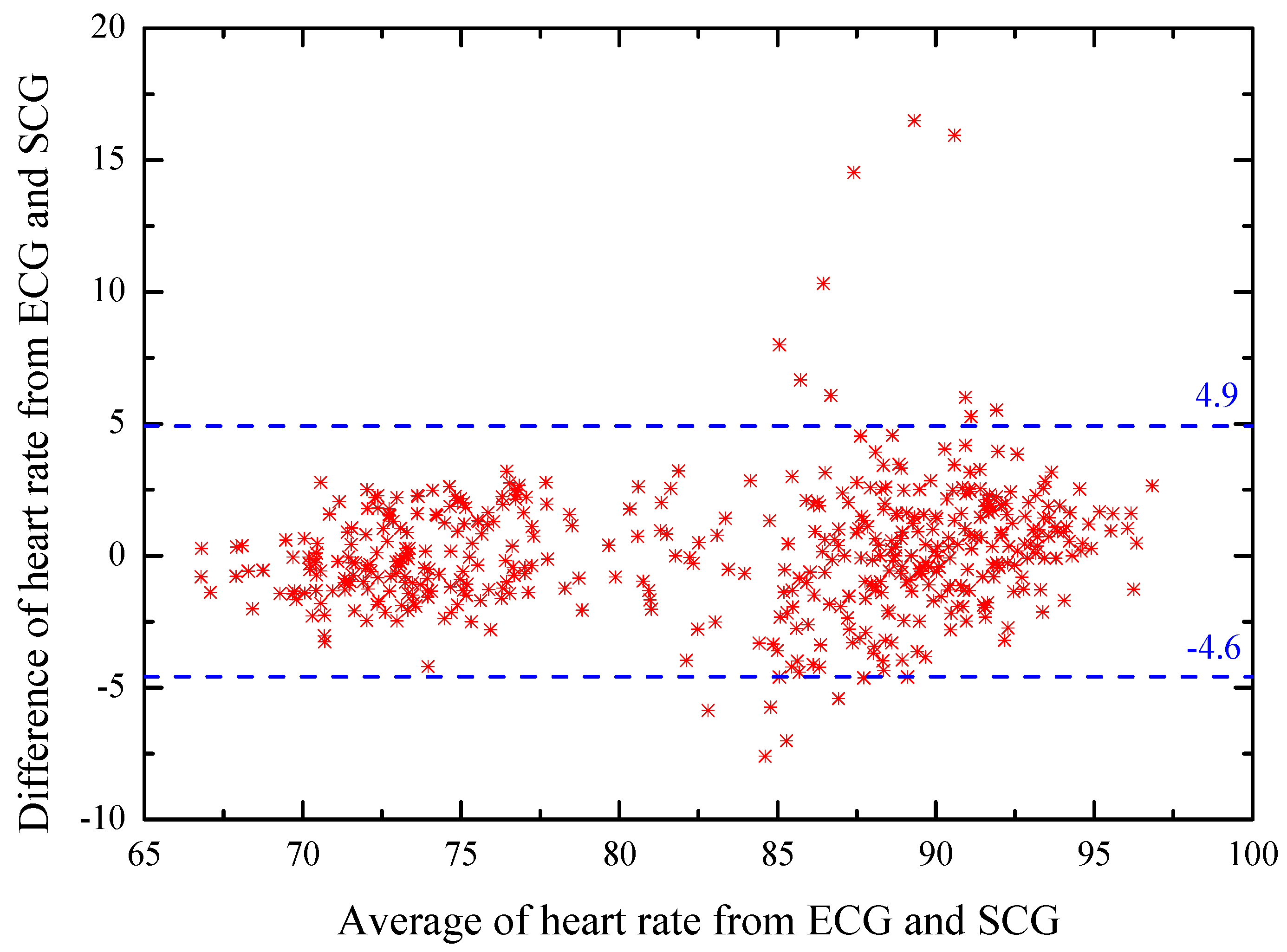
4.3. Bland–Altman Analyzation
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bozhenko, B.S. Seismocardiography—a new method in the study of functional conditions of the heart. Ter Arkh 1961, 33, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Salerno, D.M.; Zanetti, J. Seismocardiography for monitoring changes in left ventricular function during ischemia. Chest J. 1991, 100, 991–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, O.T.; Migeotte, P.F.; Park, K.S.; Etemadi, M.; Tavakolian, K.; Casanella, R.; Zanetti, J.; Tank, J.; Funtova, I.; Prisk, G.K.; et al. Ballistocardiography and seismocardiography: A review of recent advances. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2014, 19, 1414–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taebi, A.; Solar, B.E.; Bomar, A.J.; Sandler, R.H.; Mansy, H.A. Recent Advances in Seismocardiography. Vibration 2019, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, H.; Whang, M. An enhanced method to estimate heart rate from seismocardiography via ensemble averaging of body movements at six degrees of freedom. Sensors 2018, 18, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.; Sahakian, A.V.; Swiryn, S. Accelerometer-based body- position sensing for ambulatory electrocardiographic monitoring. Biomed Instrum. Technol. 2003, 37, 338–346. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.; Min, S.; Yun, Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, M. Adaptive motion artifacts reduction using 3-axis accelerometer in e-textile ecg measurement system. J. Med. Syst. 2008, 2, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H. Motion artifact reduction in electrocardiogram using adaptive filter. J. Med. Bio Log. Eng. 2011, 31, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Tavassolian, N. An Independent Component Analysis Approach to Motion Noise Cancelation of Cardio-Mechanical Signals. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Tavassolian, N. Motion noise cancellation in seismocardiogram of ambulant subjects with dual sensors. In Proceedings of the International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 5881–5884. [Google Scholar]
- Taebi, A.; Mansy, H.A. Noise cancellation from vibrocardiographic signals based on the ensemble empirical mode decomposition. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 2, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, A.Q.; Ashouri, H.; Dorier, A.; Etemadi, M.; Heller, J.A.; Roy, S.; Inan, O.T. Quantifying and Reducing Motion Artifacts in Wearable Seismocardiogram Measurements During Walking to Assess Left Ventricular Health. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rienzo, M.; Meriggi, P.; Vaini, E.; Castiglioni, P.; Rizzo, F. 24h seismocardiogram monitoring in ambulant subjects. In Proceedings of the International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 5050–5053. [Google Scholar]
- Pandia, K.; Ravindran, S.; Cole, R.; Kovacs, G.; Giovangrandi, L. Motion artifact cancellation to obtain heart sounds from a single chest-worn accelerometer. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Dallas, TX, USA, 14–19 March 2010; pp. 590–593. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar Jain, P.; Kumar Tiwari, A. A novel method for suppression of motion artifacts from the seismocardiogram signal. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 16–18 October 2016; pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, T.; Sharma, L.N.; Bhuyan, M.K. Heart Sound Extraction from Sternal Seismocardiographic Signal. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Tavassolian, N. Motion artifact cancellation of seismocardiographic recording from moving subjects. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 5702–5708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, P.S.R. Adaptive Filtering: Algorithms and Practical Implementation, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 209–248. [Google Scholar]
- Haykin, S.O. Adaptive Filter Theory, 5th ed.; Pearson: Upper Saddle River, TX, USA, 2013; pp. 449–472. [Google Scholar]
- Reinvuo, T.; Hannula, M.; Sorvoja, H.; Alasaarela, E.; Myllyla, R. Measurement of respiratory rate with high-resolution accelerometer and emfit pressure sensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium, Houston, TX, USA, 22–25 October 2006; pp. 192–195. [Google Scholar]
- Morillo, D.S.; Ojeda, J.L.R.; Foix, L.F.P.; Jimenez, A.L. An accelerometer-based device for sleep apnea screening. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, F.; Sorrell, V.; Zanetti, J.; Bosnos, M.; Baweja, G.; Perlick, D.; Ott, P.; Indik, J.; He, D.S.; Gear, K. Accelerometer-derived time intervals during various pacing modes in patients with biventricular pacemakers: Comparison with normals. PACE 2007, 30, 1476–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, J.M.; Tavakolian, K. Seismocardiography: Past, present and future. In Proceedings of the International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 7004–7007. [Google Scholar]
- Roskamm, H. Optimum patterns of exercise for healthy adults. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1967, 96, 895–900. [Google Scholar]
- Robergs, R.A.; Landwehr, R. The surprising history of the "HRmax=220-age" equation. J. Exerc. Physiol. Online 2002, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, H.; Monahan, K.D.; Seals, D.R. Age-predicted maximal heart rate revisited. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 37, 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Pachi, A.; Ji, T. Frequency and velocity of people walking. Struct. Eng. 2005, 83, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ratner, B. The correlation coefficients: Its values range between or do they? J. Target. Meas. Anal. Mark. 2009, 17, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, H.N. New Technique for Recursive Least Square Adaptive Algorithm for Acoustic Echo Cancellation of Speech signal in an auditorium. Int. Research J. Eng. Technol. 2015, 36, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- LabVIEW 2013 System Identification Toolkit Help. Available online: http://zone.ni.com/reference/en-XX/help/372458D-01/lvsysidconcepts/recursive_ls/ (accessed on 28 February 2020).
- Pan, J.; Tompkins, W.J. A Real-Time QRS Detection Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1985, 32, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosrow, K.F.; Tavakolian, K.; Menon, C. Moving toward automatic and standalone delineation of seismocardiogram signal. In Proceedings of the International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 7163–7166. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, K.; Schmidt, S.E.; Jensen, A.S. Definition of Fiducial Points in the Normal Seismocardiogram. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 1999, 8, 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Subject No. | ECG Peaks Detected | SCG Peaks Detected | SCG Peaks Missing | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 483 | 478 | 5(2) | 98.9% |
| 2 | 475 | 468 | 7(4) | 98.5% |
| 3 | 472 | 468 | 4(3) | 99.1% |
| 4 | 480 | 475 | 5(3) | 98.9% |
| 5 | 488 | 483 | 5(3) | 98.9% |
| 6 | 478 | 473 | 5(2) | 98.9% |
| 7 | 492 | 483 | 9(6) | 98.1% |
| 8 | 501 | 496 | 5(2) | 99.0% |
| 9 | 495 | 490 | 5(2) | 98.9% |
| 10 | 490 | 486 | 4(1) | 99.1% |
| 11 | 477 | 471 | 6(5) | 98.7% |
| 12 | 486 | 483 | 3(2) | 99.3% |
| 13 | 496 | 491 | 5(3) | 98.9% |
| 14 | 491 | 489 | 2(2) | 99.5% |
| 15 | 485 | 477 | 8(4) | 98.3% |
| 16 | 482 | 474 | 8(6) | 98.3% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.; Liu, S. A Novel Adaptive Recursive Least Squares Filter to Remove the Motion Artifact in Seismocardiography. Sensors 2020, 20, 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061596
Yu S, Liu S. A Novel Adaptive Recursive Least Squares Filter to Remove the Motion Artifact in Seismocardiography. Sensors. 2020; 20(6):1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061596
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Shuai, and Sheng Liu. 2020. "A Novel Adaptive Recursive Least Squares Filter to Remove the Motion Artifact in Seismocardiography" Sensors 20, no. 6: 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061596
APA StyleYu, S., & Liu, S. (2020). A Novel Adaptive Recursive Least Squares Filter to Remove the Motion Artifact in Seismocardiography. Sensors, 20(6), 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20061596




