Optical Fibre Sensor for Simultaneous Measurement of Capillary Refill Time and Contact Pressure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
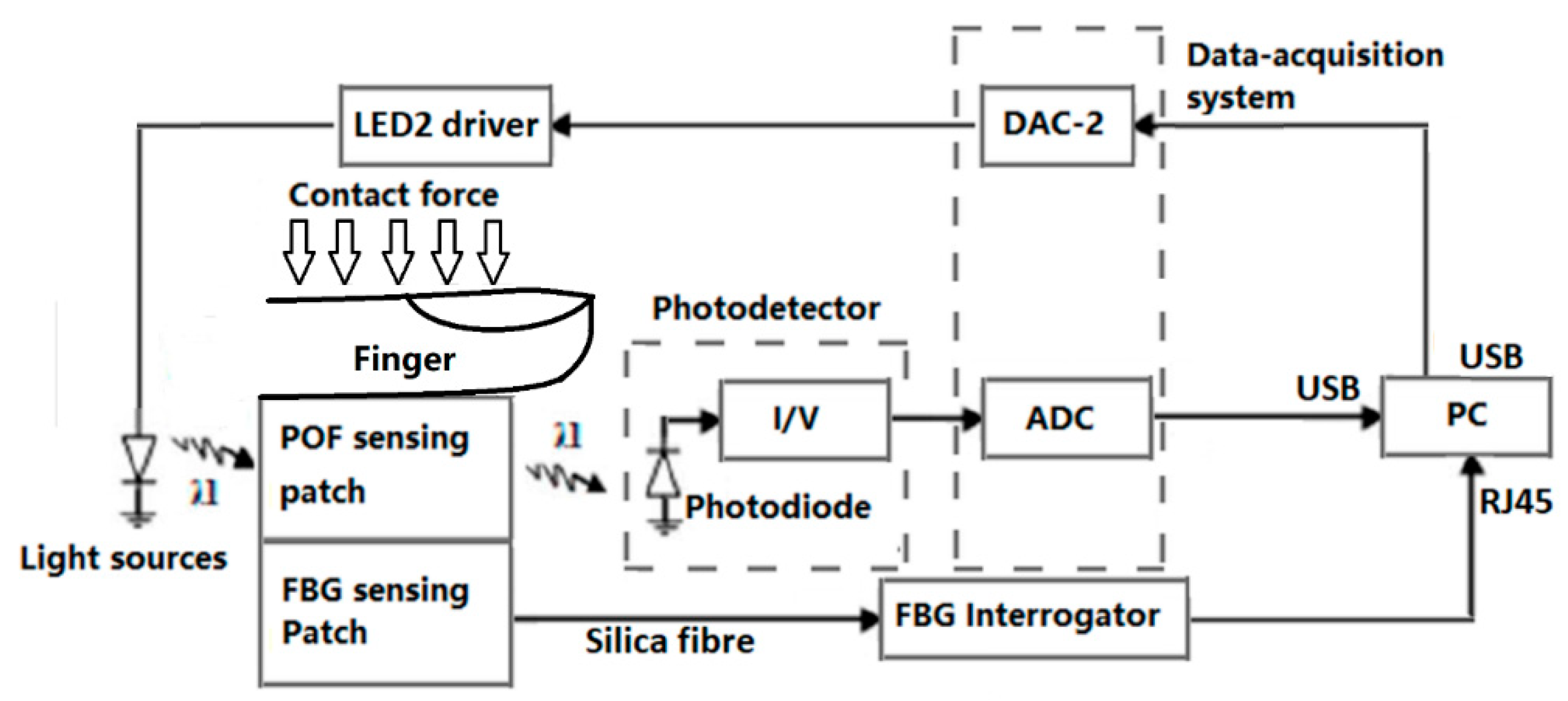
2.1. CRT Monitoring System
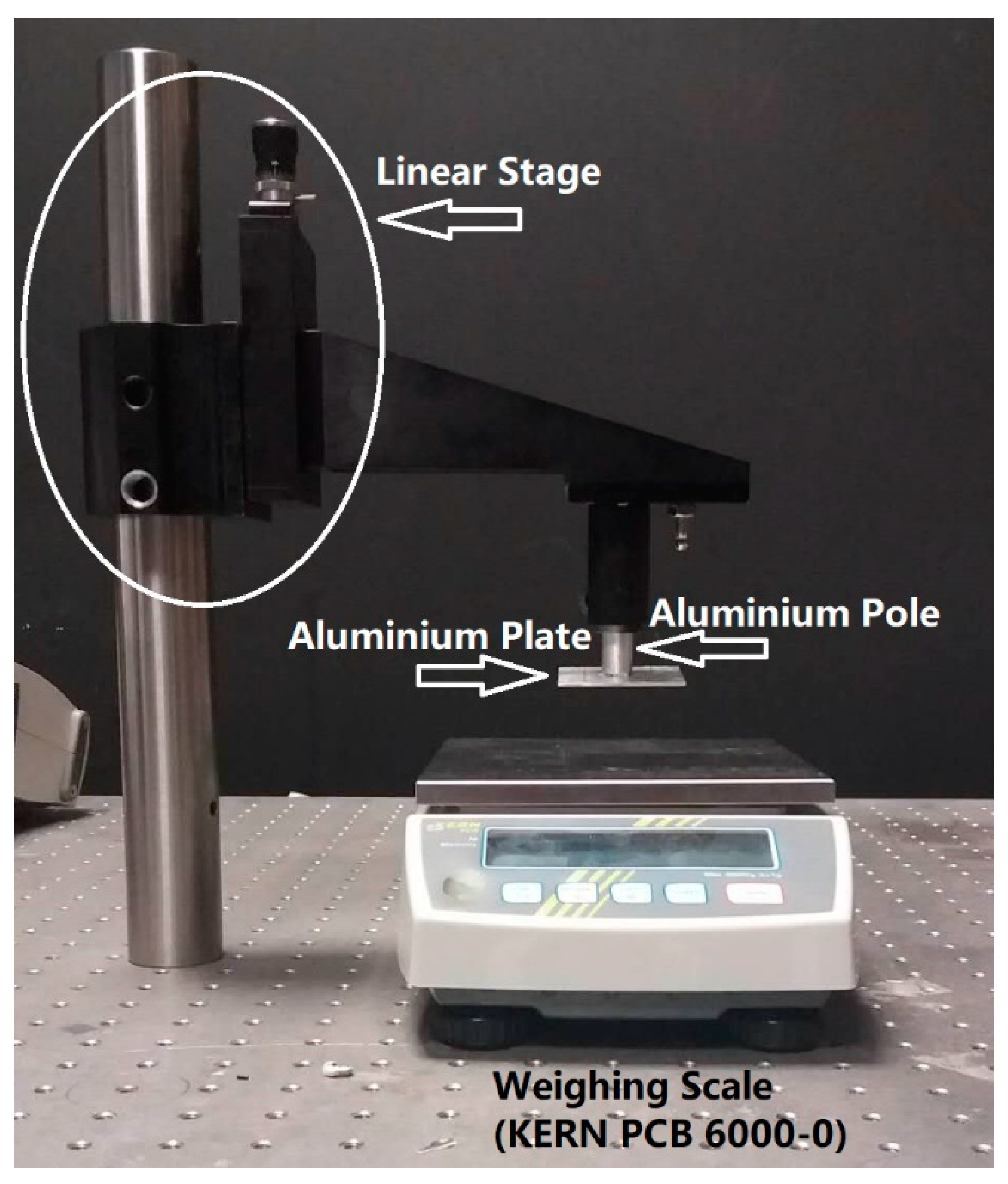
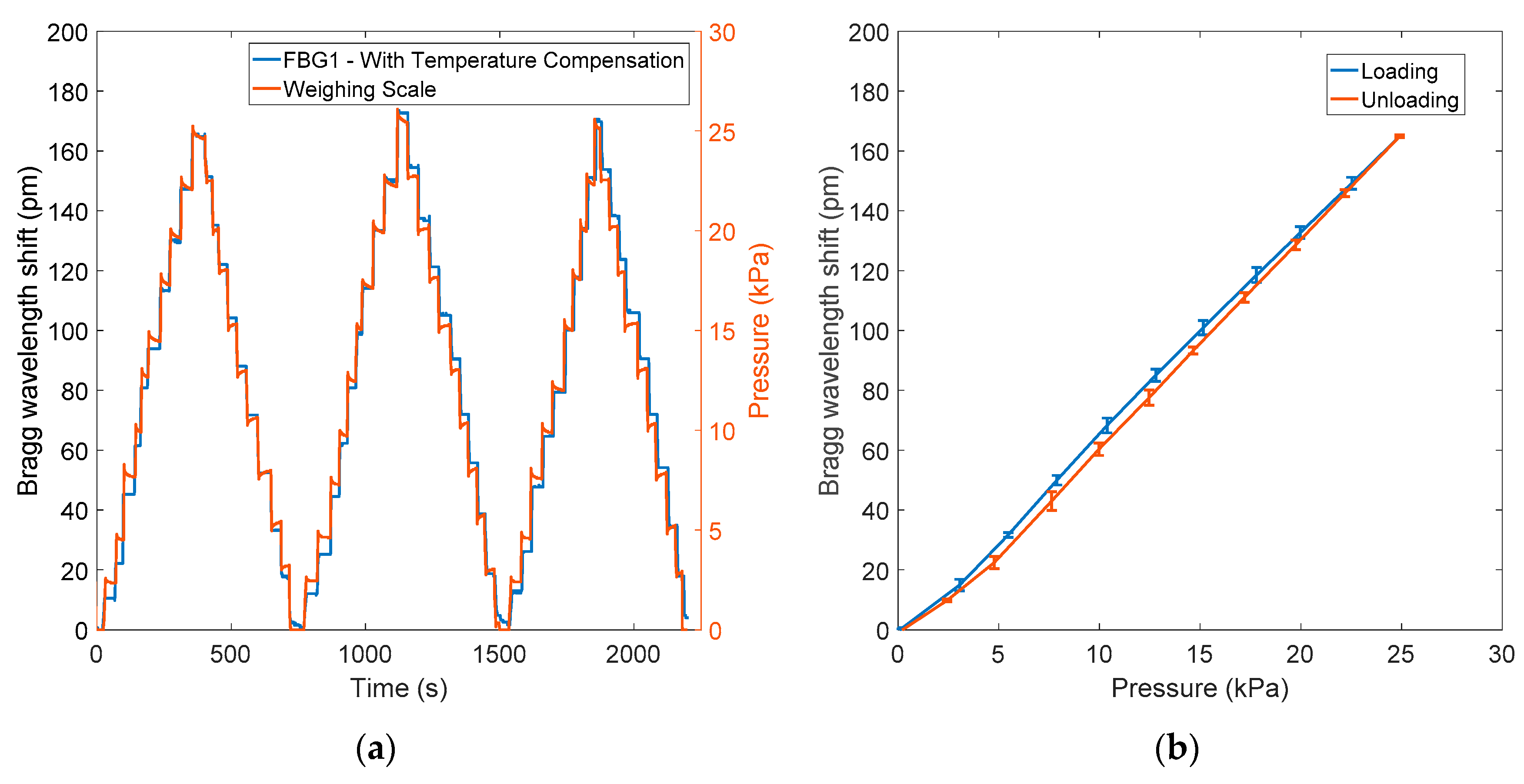
2.2. FBG Calibration and Validation
2.3. Signal Processing
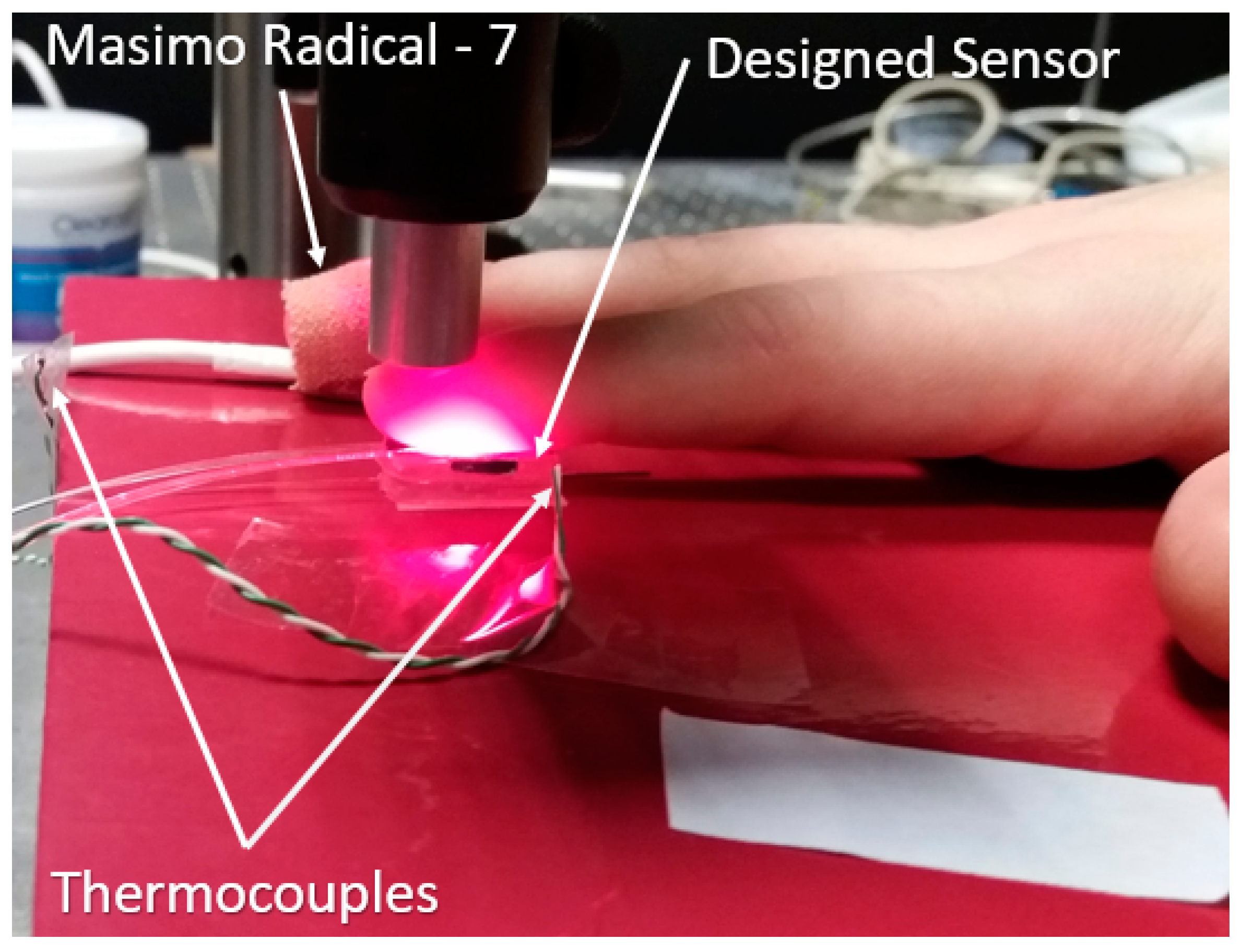
2.4. In Vivo Capillary Refill Time Test Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
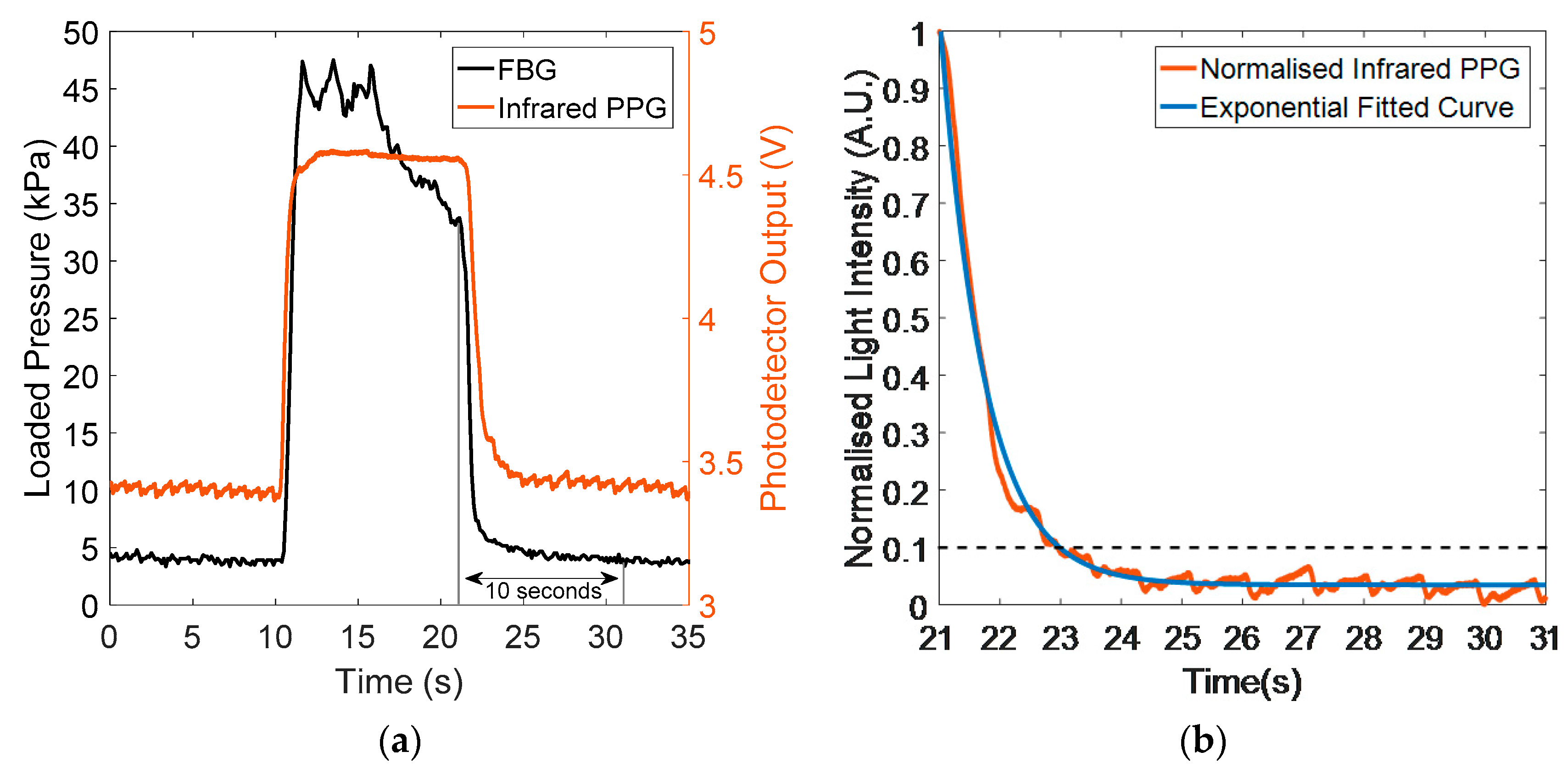
3.1. Integrated Sensor Pressure Testing
3.2. In Vivo Capillary Refill Time and Pressure Monitoring
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical Statements
References
- Klupp, N.L.; Keenan, A.-M. An evaluation of the reliability and validity of capillary refill time test. Foot 2007, 17, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayesu, J.K.; Lozner, A.W. Pediatrics, dehydration. Pediatrics 1910, 8, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Guedel, A.E. Cyclopropane anesthesia. Anesthesiol. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 1940, 1, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crismon, J.; Fuhrman, F. Studies on gangrene following cold injury: VI. Capillary blood flow after cold injury, the effects of rapid warming, and sympathetic block. J. Clin. Investig. 1947, 26, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, D.; Evans, N.; Kluckow, M. Clinical detection of low upper body blood flow in very premature infants using blood pressure, capillary refill time, and central-peripheral temperature difference. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2004, 89, F168–F173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, E.J.; Ahroni, J.H.; Davignon, D.; Stensel, V.; Prigeon, R.L.; Smith, D.G. Diagnostic utility of the history and physical examination for peripheral vascular disease among patients with diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1997, 50, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, I.; Edelman, S. Evaluation and treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Clin. Diabetes 2006, 24, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kviesis-Kipge, E.; Curkste, E.; Spigulis, J.; Eihvalde, L. Real-time analysis of skin capillary-refill processes using blue LED. In Biophotonics: Photonic Solutions for Better Health Care II; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Diego, CA, USA, 2010; Volume 7715, p. 771523. [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan, D.C.; Baker, S.D.; Kayser, S.A.; Jones, D.; Hansen, M.L. Variability of Capillary Refill Time among Physician Measurements. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 53, e51–e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaxter, L.L.; Morris, D.E.; Crowe, J.A.; Henry, C.; Hill, S.; Sharkey, D.; Vyas, H.; Hayes-Gill, B.R. An automated quasi-continuous capillary refill timing device. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 37, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, L.W. Handbook of Signs & Symptoms, 3rd ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi, R.; Nakada, T.; Oshima, T.; Shinozaki, M.; Nakaguchi, T.; Haneishi, H.; Oda, S. Optimal pressing strength and time for capillary refilling time. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.T.; Henricson, J.; Junker, J.; Jonson, C.; Nilsson, G.E.; Wilhelms, D.; Anderson, C.D. A cool response—The influence of ambient temperature on capillary refill time. J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201700371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, S.; Gill, P.; Jones, C.; Taylor, J.A.; Van den Bruel, A.; Heneghan, C. Validity and reliability of measurement of capillary refill time in children: A systematic review. Arch. Dis. Child. 2015, 100, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ait-Oufella, H.; Bige, N.; Boelle, P.Y.; Pichereau, C.; Alves, M.; Bertinchamp, R.; Baudel, J.L.; Galbois, A.; Maury, E.; Guidet, B. Capillary refill time exploration during septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 2014, 40, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, N.V.; Maisels, M.J.; Kring, L.; Schwarz-Warner, L. Capillary refill time in the hands and feet of normal newborn infants. Clin. Paediatr. 1999, 38, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, T.; Kyriacou, P.A.; Pal, S. Free flap pulse oximetry utilizing reflectance photoplethysmography. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 4046–4049. [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki, K.; Capilupi, M.J.; Saeki, K.; Hirahara, H.; Horie, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Weisner, S.; Kim, J.; Lampe, J.W.; Becker, L.B. Blood refill time: Clinical bedside monitoring of peripheral blood perfusion using pulse oximetry sensor and mechanical compression. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 36, 2310–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezzerides, V.; Neuman, M.I. Capillary Refill Time Diagnostic Apparatus and Methods. U.S. Patent 9603559B2, 28 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- John, R.T.; Henricson, J.; Anderson, C.D.; Wilhelms, D.B. Man versus machine: Comparison of naked-eye estimation and quantified capillary refill. Emerg. Med. J. 2019, 36, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.T.; Henricson, J.; Nilsson, G.E.; Wilhelms, D.; Anderson, C.D. Reflectance spectroscopy: To shed new light on the capillary refill test. J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201700043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kviesis-Kipge, E.; Curkste, E.; Spigulis, J.; Gardovska, D. Optical studies of the capillary refill kinetics in fingertips. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, Munich, Germany, 7–12 September 2009; pp. 377–379. [Google Scholar]
- Kyriacou, P.A.; Powell, S.; Langford, R.M.; Jones, D.P. Esophageal pulse oximetry utilizing reflectance photoplethysmography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 49, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickard, A.; Karlen, W.; Ansermino, J.M. Capillary refill time: Is it still a useful clinical sign? Anesth. Analg. 2011, 113, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Correia, R.; Ballaji, H.; Korposh, S.; Hayes-Gill, B.R.; Morgan, S.P. Optical Fibre-Based Pulse Oximetry Sensor with Contact Force Detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.S.; Asundi, A. Real-time cure monitoring of smart composite materials using extrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometer and fiber Bragg grating sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhou, X. Pressure sensor based on the fiber-optic extrinsice Fabry-Perot interferometer. Photonic Sensors 2011, 1, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Lan, X.; Yuan, L.; Xiao, H. Simultaneous measurement of temperature and pressure with cascaded extrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometer and intrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometer sensors. Opt. Eng. 2014, 53, 067101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffar, A.; Hou, Y.L.; Liu, W.Y.; Dharejo, F.A.; Zhang, H.X.; Jia, P.G.; Yanyun, H.; Liu, J.; Yunjun, Z.; Nasir, Z. Two-dimensional displacement optical fiber sensor based on macro-bending effect. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 120, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.H.; Chen, P.C.; Chen, Y.C. Plastic optical fiber displacement sensor based on dual cycling bending. Sensors 2010, 10, 10198–10210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, K.; Capilupi, M.J.; Saeki, K.; Hirahara, H.; Horie, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Weisner, S.; Kim, J.; Lampe, J.W.; Becker, L.B. Low temperature increases capillary blood refill time following mechanical fingertip compression of healthy volunteers: Prospective cohort study. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2019, 33, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, J.J.; Hickey, M.; Phillips, J.P.; Kyriacou, P. Method for producing angled optical fiber tips in the laboratory. Opt. Eng. 2016, 55, 026120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, R.; Chehura, E.; Li, J.; James, S.W.; Tatam, R.P. Enhanced sensitivity fibre Bragg grating (FBG) load sensor. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 094006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, R.; Blackman, O.; Hernandez, F.; Korposh, S.; Morgan, S.; Hayes-Gill, B.; James, S.W.; Evans, D.; Norris, A. Highly sensitive contact pressure measurements using FBG patch in endotracheal tube cuff. In Proceedings of the Sixth European Workshop on Optical Fibre Sensors, Washington, DC, USA, 30 May 2016; Volume 9916, p. 99161F. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Geiger, H.; Dakin, J. Fibre grating pressure sensor with enhanced sensitivity using a glass-bubble housing. Electron. Lett. 1996, 32, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.J.; Archambault, L.; Reekie, L.; Dakin, J. Discrimination between strain and temperature effects using dual-wavelength fibre grating sensors. Electron. Lett. 1994, 30, 1085–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, M.H.; Shaw, K.N.; Baker, M.D. Effect of ambient temperature on capillary refill in healthy children. Pediatrics 1993, 92, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schriger, D.L.; Baraff, L. Schriger D L, Baraff L. Defining normal capillary refill: Variation with age, sex, and temperature. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1988, 17, 932–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, J.; Kotilahti, K.M.; Ilmoniemi, R.; Noponen, T.E.; Virtanen, J. Accelerometer-based method for correcting signal baseline changes caused by motion artifacts in medical near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 087005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzahrani, A.; Hu, S.; Azorin-Peris, V.; Barrett, L.; Esliger, D.; Hayes, M.; Akbare, S.; Achart, J.; Kuoch, S. A multi-channel opto-electronic sensor to accurately monitor heart rate against motion artefact during exercise. Sensors 2015, 15, 25681–25702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Correia, R.; Ballaji, H.; Korposh, S.; Hayes-Gill, B.; Morgan, S. Optical Fibre Sensor for Simultaneous Measurement of Capillary Refill Time and Contact Pressure. Sensors 2020, 20, 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051388
Liu C, Correia R, Ballaji H, Korposh S, Hayes-Gill B, Morgan S. Optical Fibre Sensor for Simultaneous Measurement of Capillary Refill Time and Contact Pressure. Sensors. 2020; 20(5):1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051388
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chong, Ricardo Correia, Hattan Ballaji, Serhiy Korposh, Barrie Hayes-Gill, and Stephen Morgan. 2020. "Optical Fibre Sensor for Simultaneous Measurement of Capillary Refill Time and Contact Pressure" Sensors 20, no. 5: 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051388
APA StyleLiu, C., Correia, R., Ballaji, H., Korposh, S., Hayes-Gill, B., & Morgan, S. (2020). Optical Fibre Sensor for Simultaneous Measurement of Capillary Refill Time and Contact Pressure. Sensors, 20(5), 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20051388





