A Low-Cost Paper Glucose Sensor with Molecularly Imprinted Polyaniline Electrode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
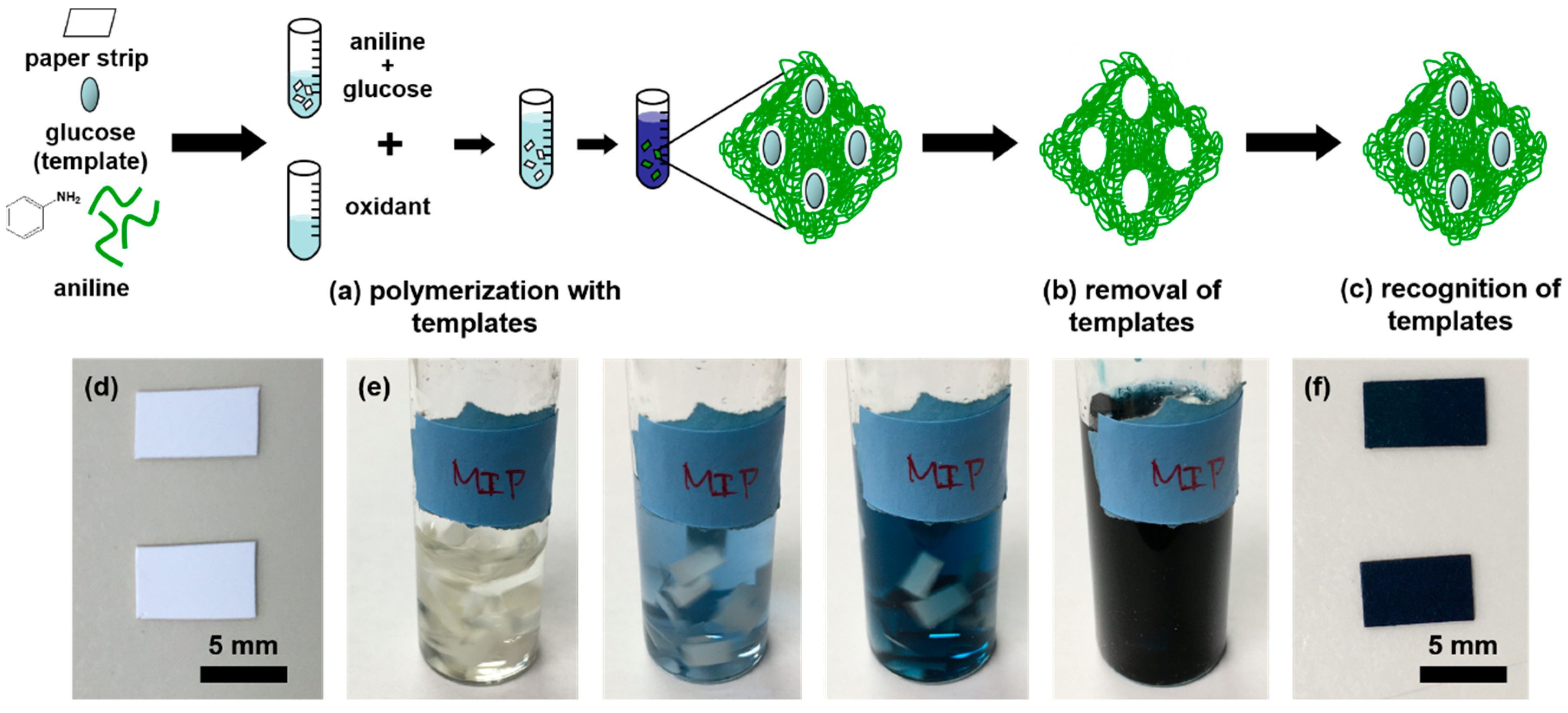
2.1. Molecularly Imprinted Polyaniline Paper Sensor Preparation
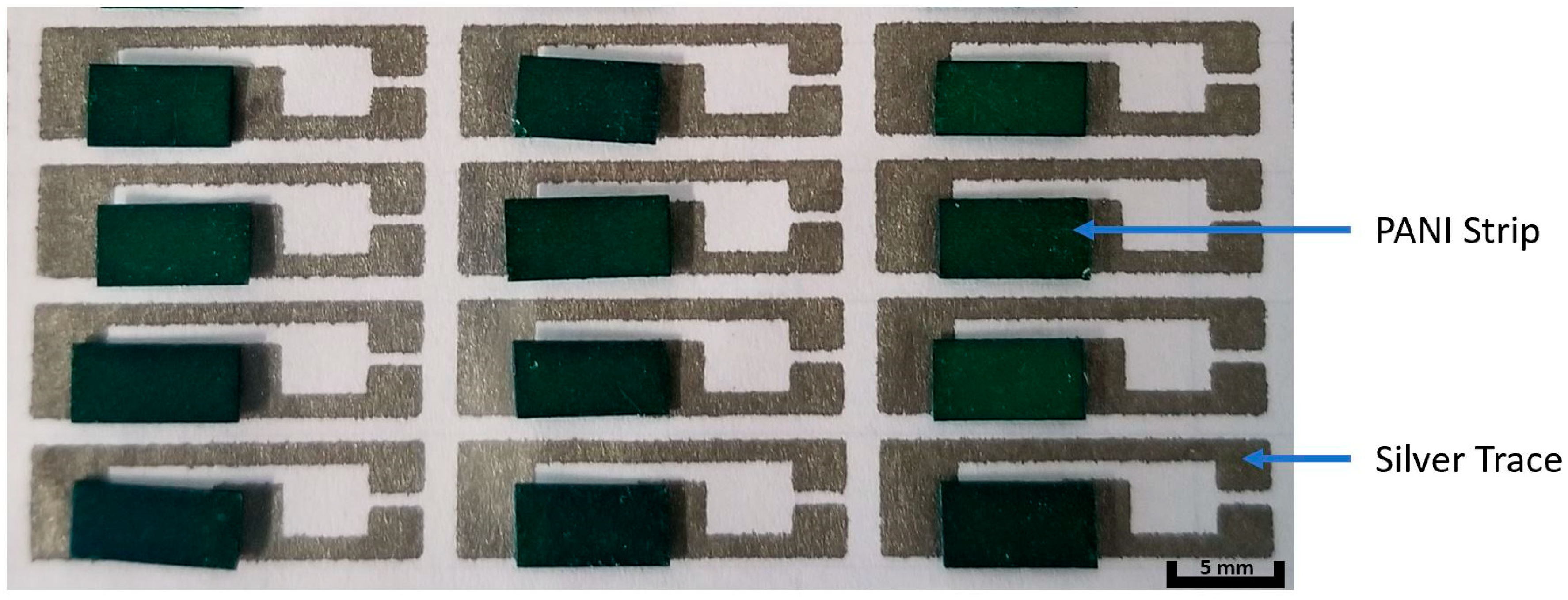
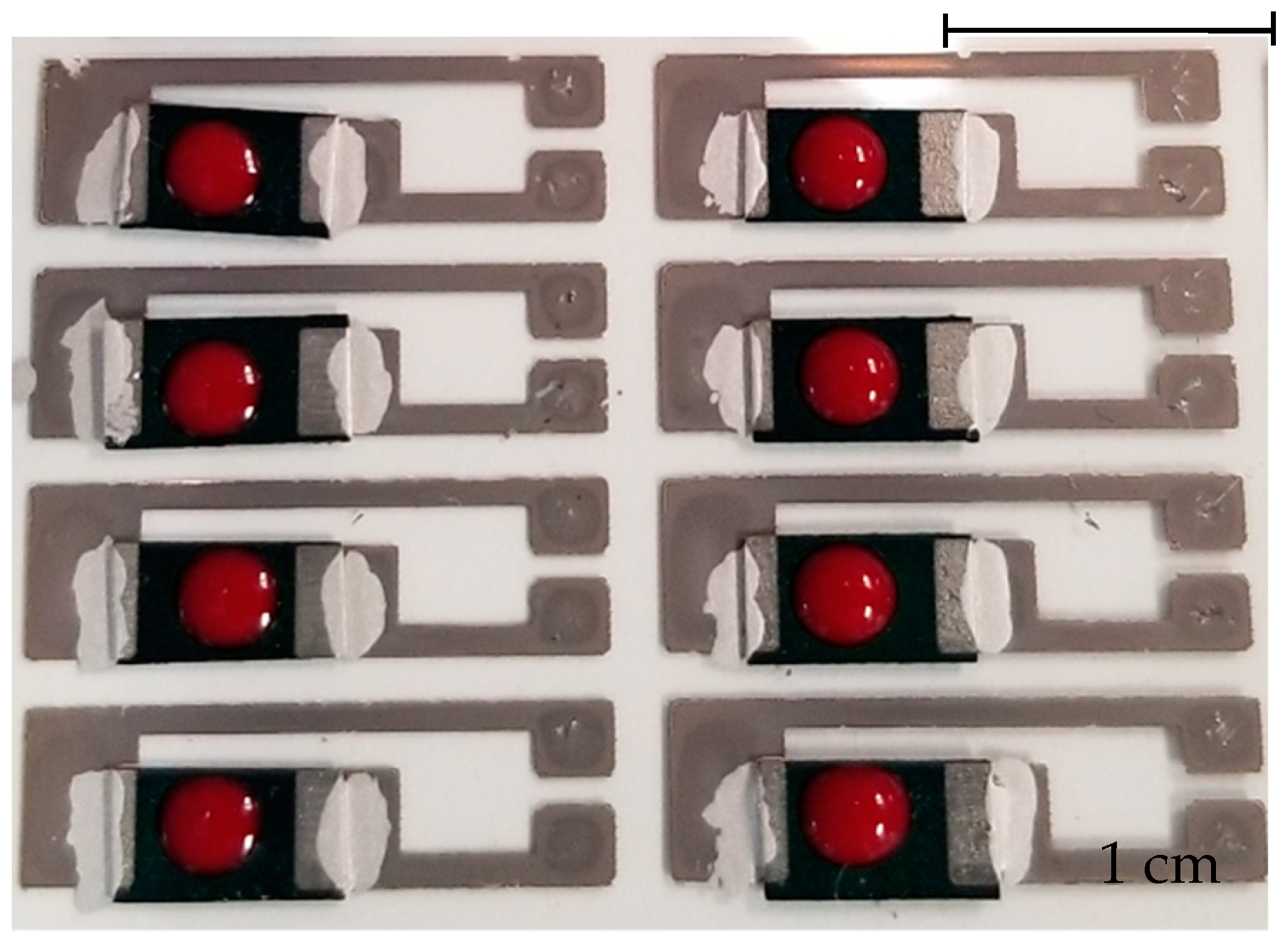
2.2. Glucose Paper Sensor Fabrication
2.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
2.4. I-V Curve Measurement
2.5. Glucose Concentration Measurement
3. Results
3.1. FTIR Spectra
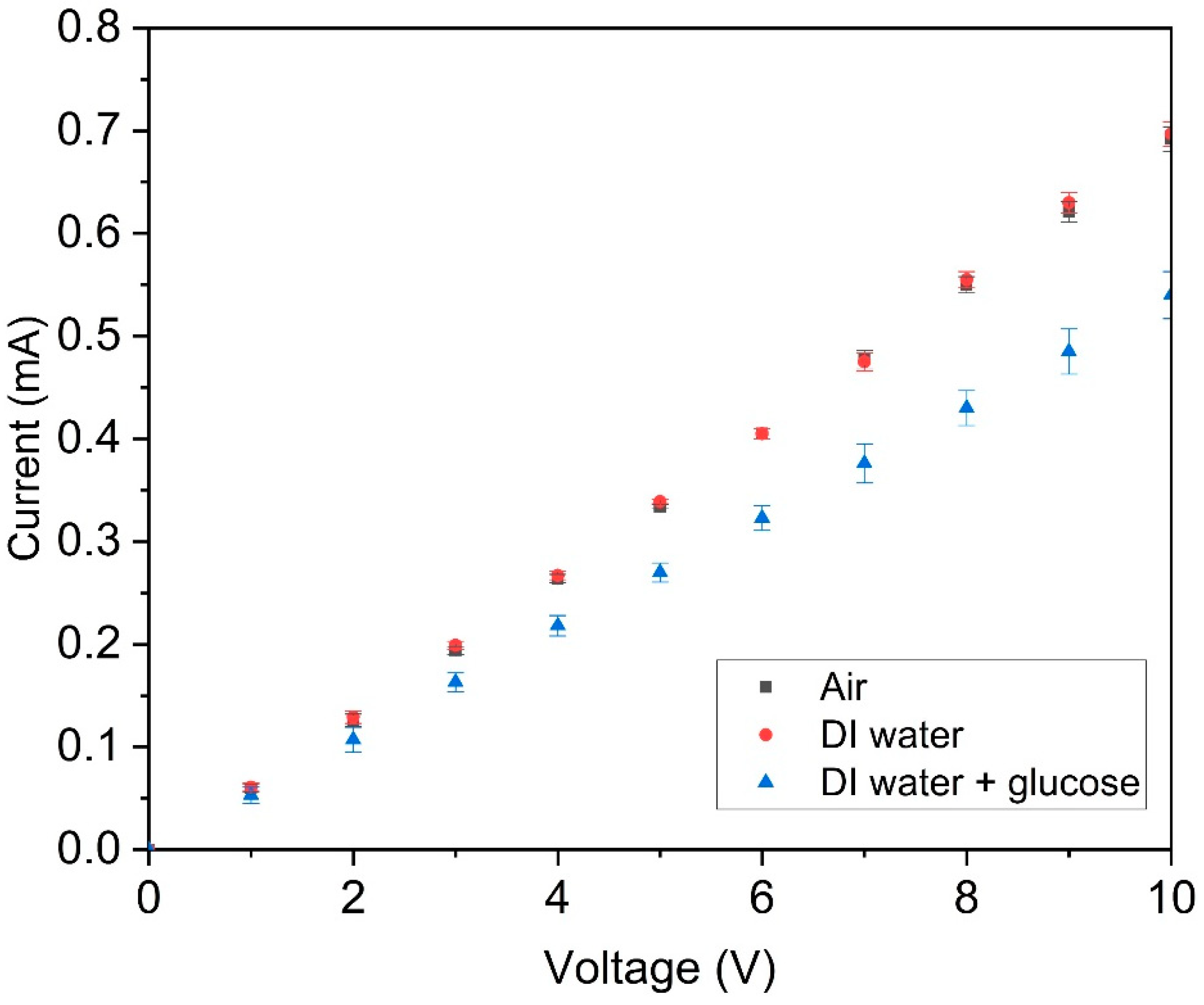
3.2. I-V Curve of the MIP-PANI Paper Sensors
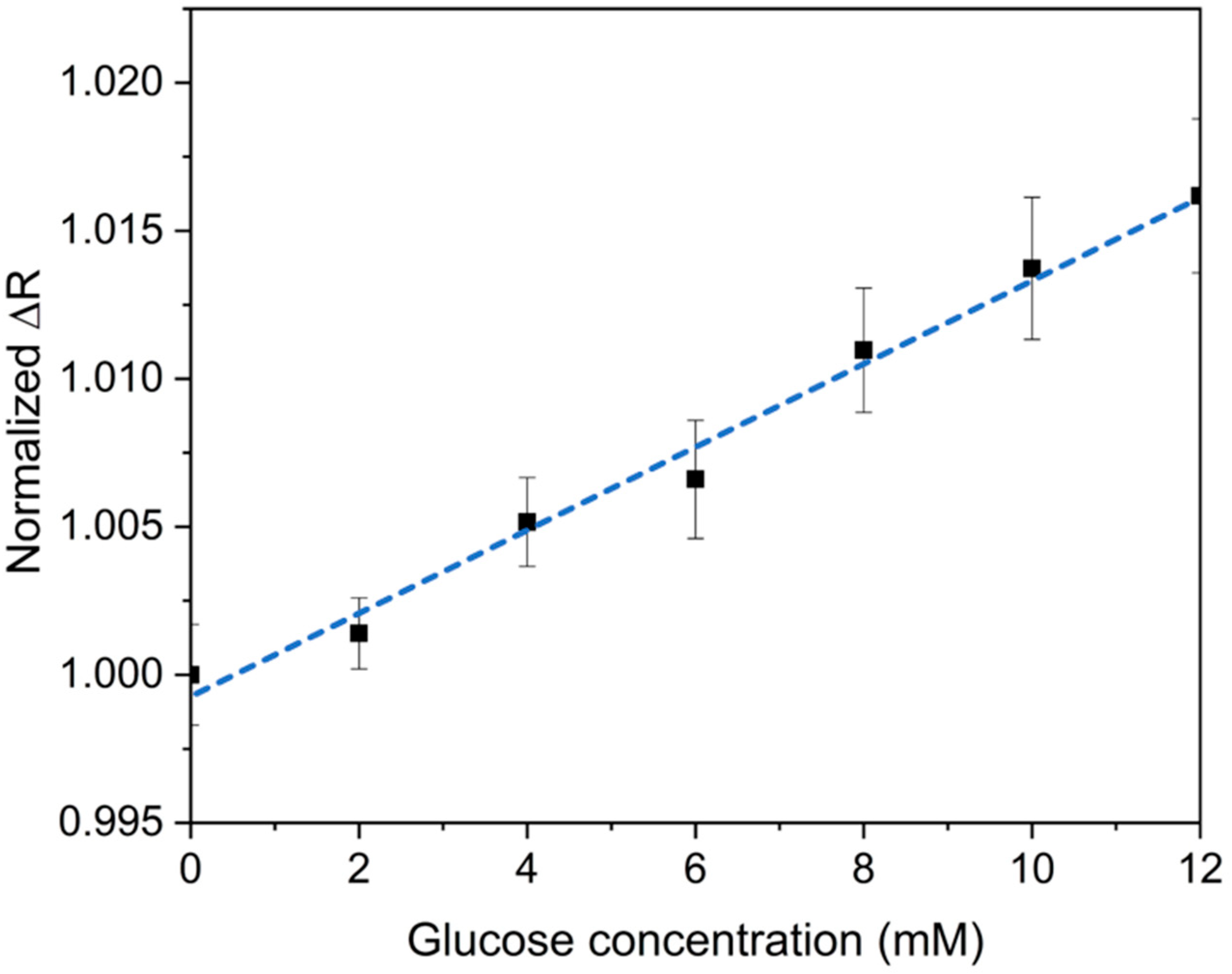
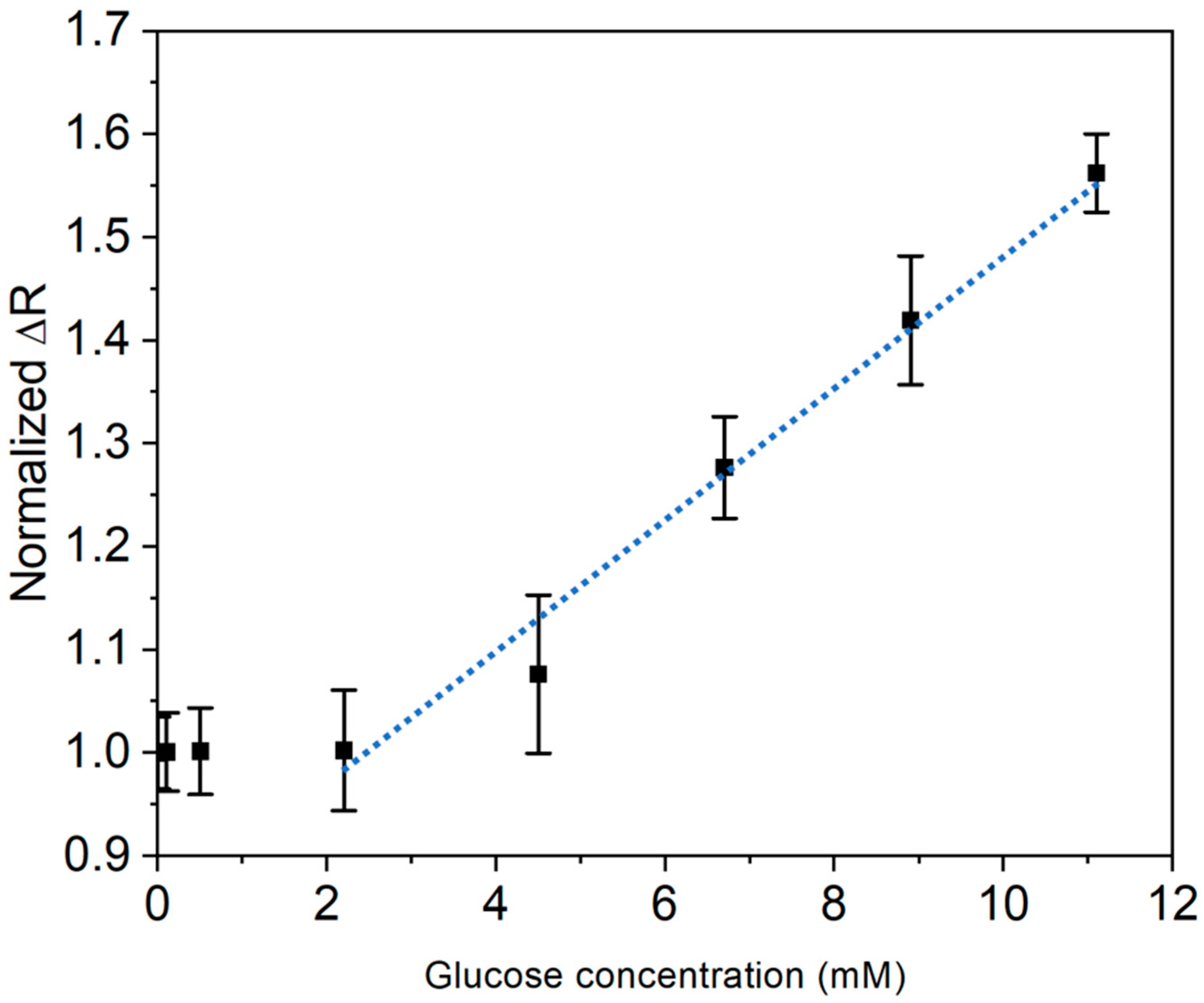
3.3. Glucose Detection in Aqueous Solution
3.4. Glucose Detection in Bovine Blood
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Parameter | Nozzle Spacing | Nozzles Activated | Nozzle Diameter | Frequency | Cartridge Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 254 µm | 16 | 21 µm | 30 kHz | 10 pL |
| Parameter | Substrate Temperature | Jetting Frequency | Applied Voltage | Drop Spacing | Drop Angle |
| Value | 30 °C | 5 Hz | 30 V | 20 µm | 4.4° |
References
- GlucoWatch approved for children with diabetes. FDA Consum. 2002, 36, 6.
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2004, 27 Suppl. 1, S5–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coster, S.; Gulliford, M.C.; Seed, P.T.; Powrie, J.K.; Swaminathan, R. Monitoring blood glucose control in diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Health Technol. Assess. 2000, 4, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruen, D.; Delaney, C.; Florea, L.; Diamond, D. Glucose Sensing for Diabetes Monitoring: Recent Developments. Sensors 2017, 17, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, E.H.; Lee, S.Y. Glucose Biosensors: An Overview of Use in Clinical Practice. Sensors 2010, 10, 4558–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toghill, K.E.; Compton, R.G. Electrochemical Non-enzymatic Glucose Sensors: A Perspective and an Evaluation. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2010, 5, 1246–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister, J.J.; Arnold, M.A.; Small, G.W. Noninvasive blood glucose measurements by near-infrared transmission spectroscopy across human tongues. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2000, 2, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiga, N.; Hamada, C.; Ikeda, J. Near infrared spectroscopy assessment of the glucose solution processed by ultrasonic cavitation. Ultrasonics 2006, 44 Suppl. 1, e101–e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.C., Jr.; Lyons, C. Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1962, 102, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, A.; Feldman, B. Electrochemistry in Diabetes Management. Accounts Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.J.; Li, C.M.; Zang, J.F.; Cui, X.Q.; Qiao, Y.; Guo, J. New nanostructured TiO2 for direct electrochemistry and glucose sensor applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Yang, Q. Mediator-free amperometric determination of glucose based on direct electron transfer between glucose oxidase and an oxidized boron-doped diamond electrode. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, N.S.; Toumazou, C.; Cass, A.E.G.; Johnston, D.G. Glucose sensors: A review of current and emerging technology. Diabetic Med. 2009, 26, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.W.; Lee, S.; Seo, M.; Chung, T.D. Recent advances in electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1033, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.C.; Kim, K.B.; Gurudatt, N.G.; Hussain, K.K.; Choi, C.S.; Park, D.S.; Shim, Y.B. Comparison of enzymatic and non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on hierarchical Au-Ni alloy with conductive polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 130, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, B.G.; Masud, J.; Nath, M. A non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on a CoNi2Se4/rGO nanocomposite with ultrahigh sensitivity at low working potential. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 2338–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erturk, G.; Mattiasson, B. Molecular Imprinting Techniques Used for the Preparation of Biosensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asliyuce, S.; Uzun, L.; Rad, A.Y.; Unal, S.; Say, R.; Denizli, A. Molecular imprinting based composite cryogel membranes for purification of anti-hepatitis B surface antibody by fast protein liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 889-890, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.M.; Sun, Z.; Chen, C.B.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhu, S.H. Simultaneous separation and determination of fructose, sorbitol, glucose and sucrose in fruits by HPLC-ELSD. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempe, M.; Mosbach, K. Molecular Imprinting Used for Chiral Separations. J. Chromatogr. A 1995, 694, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, S.; Buffon, R.; Rossi, A.V. Molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction of fluconazole from pharmaceutical formulations. Talanta 2015, 134, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, H.; Pacheco, J.G.; Magalhaes, J.M.C.S.; Viswanathan, S.; Delerue-Matos, C. MIP-graphene-modified glassy carbon electrode for the determination of trimethoprim. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Lin, L.; Ji, M.Z.; Zhang, S.M.; Yang, M.B.; Fu, Q. Progress on the morphological control of conductive network in conductive polymer composites and the use as electroactive multifunctional materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 627–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, M.M.; Goudini, L.; Piri, F.; Zamani, A.; Saadati, F. Molecular imprinting method for fabricating novel glucose sensor: Polyvinyl acetate electrode reinforced by MnO2/CuO loaded on graphene oxide nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimi, Y.; Narimatsu, A.; Nakayama, K.; Sekine, S.; Hattori, K.; Sakai, K. Development of an enzyme-free glucose sensor using the gate effect of a molecularly imprinted polymer. J. Artif. Organs 2009, 12, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.S.; Pietrzyk-Le, A.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Electrochemically synthesized polymers in molecular imprinting for chemical sensing. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 3177–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Huang, J.; Wu, Y.N.; Sun, J.; Wei, W.; Liu, X.Y. Synthesis of hydrophilic and conductive molecularly imprinted polyaniline particles for the sensitive and selective protein detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessaire, B.; Mathieu, M.; Salles, V.; Yeghoyan, T.; Celle, C.; Simonato, J.P.; Brioude, A. Synthesis of Continuous Conductive PEDOT:PSS Nanofibers by Electrospinning: A Conformal Coating for Optoelectronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehler, C.; Oberueber, F.; Schlabach, S.; Stieglitz, T.; Asplund, M. Long-Term Stable Adhesion for Conducting Polymers in Biomedical Applications: IrOx and Nanostructured Platinum Solve the Chronic Challenge. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, N.; Murray, R.E.; Shah, S.I.; Kiick, K.L.; Martin, D.C. Biofunctionalization of PEDOT films with laminin-derived peptides. Acta Biomater. 2016, 41, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borysiak, M.D.; Thompson, M.J.; Posner, J.D. Translating diagnostic assays from the laboratory to the clinic: Analytical and clinical metrics for device development and evaluation. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1293–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Wright, C.; Dincel, O.; Chi, T.-Y.; Kameoka, J. A Low-Cost Paper Glucose Sensor with Molecularly Imprinted Polyaniline Electrode. Sensors 2020, 20, 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041098
Chen Z, Wright C, Dincel O, Chi T-Y, Kameoka J. A Low-Cost Paper Glucose Sensor with Molecularly Imprinted Polyaniline Electrode. Sensors. 2020; 20(4):1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041098
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zheyuan, Christopher Wright, Onder Dincel, Ting-Yen Chi, and Jun Kameoka. 2020. "A Low-Cost Paper Glucose Sensor with Molecularly Imprinted Polyaniline Electrode" Sensors 20, no. 4: 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041098
APA StyleChen, Z., Wright, C., Dincel, O., Chi, T.-Y., & Kameoka, J. (2020). A Low-Cost Paper Glucose Sensor with Molecularly Imprinted Polyaniline Electrode. Sensors, 20(4), 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041098






