Frequency Invariant Beamforming for a Small-Sized Bi-Cone Acoustic Vector–Sensor Array
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
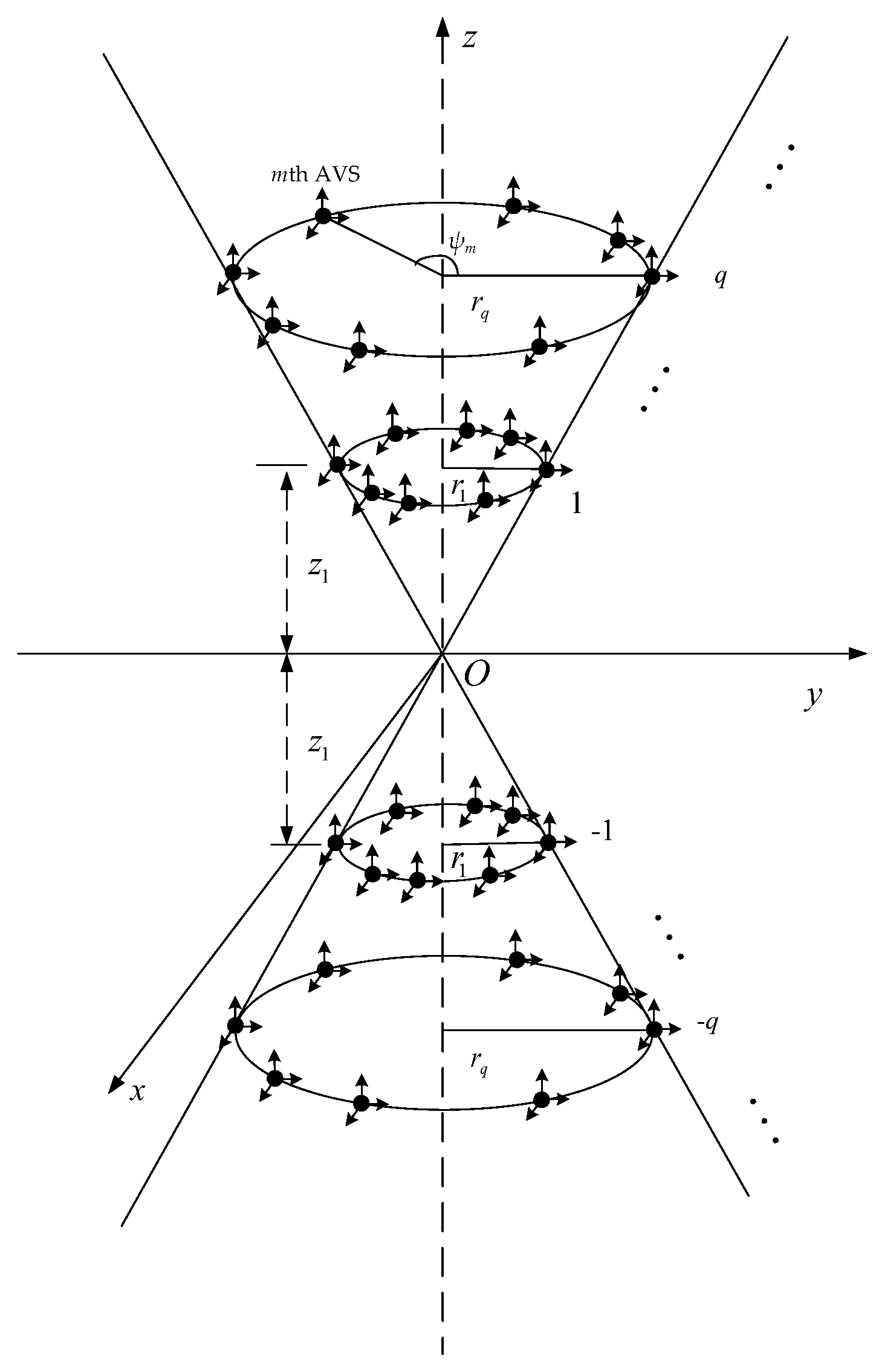
2.1. Measurement Model of BCAVSA
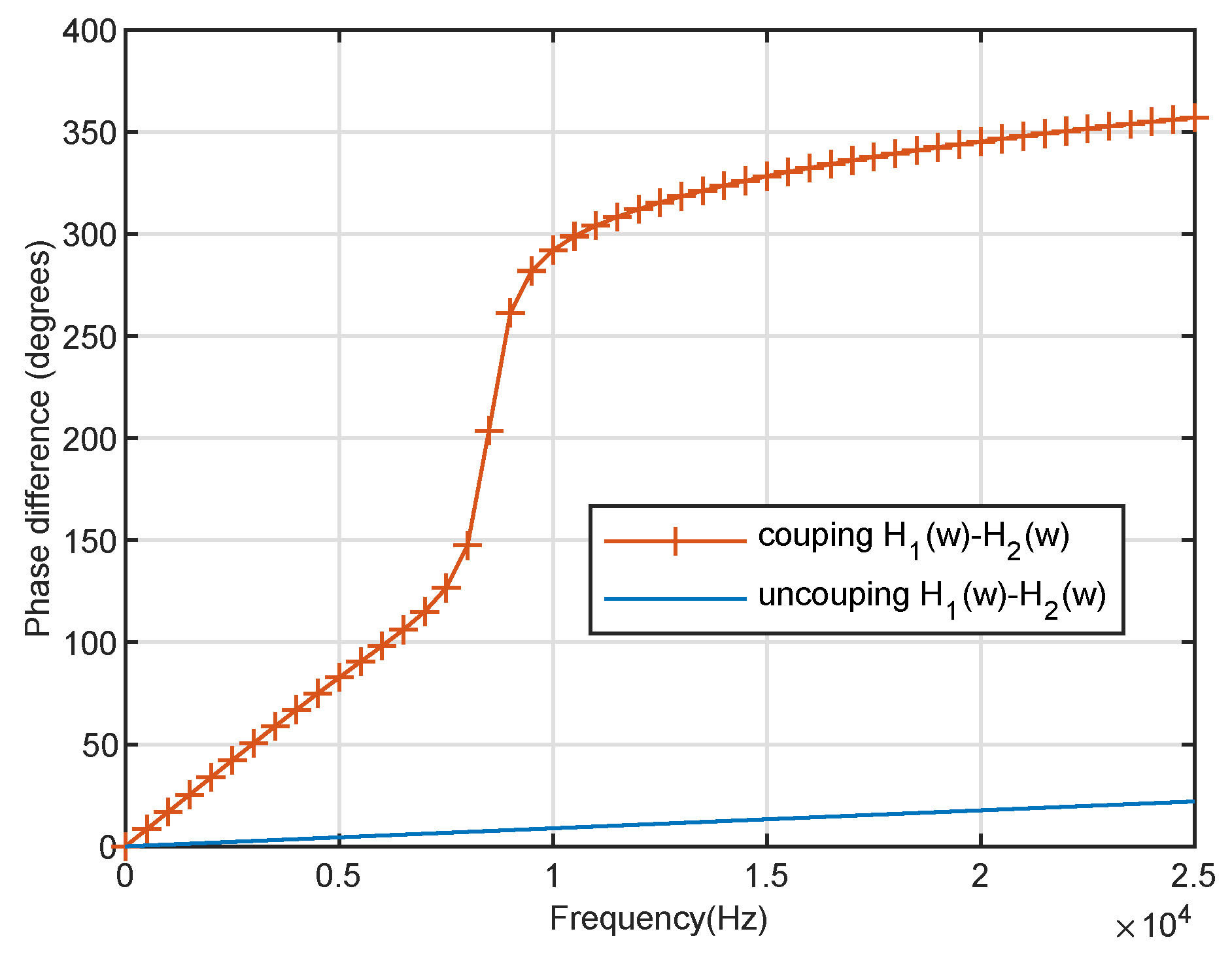
2.2. Mechanical Coupling System of Ormia ochracea’s Ears
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Coupling Magnified BCAVSA
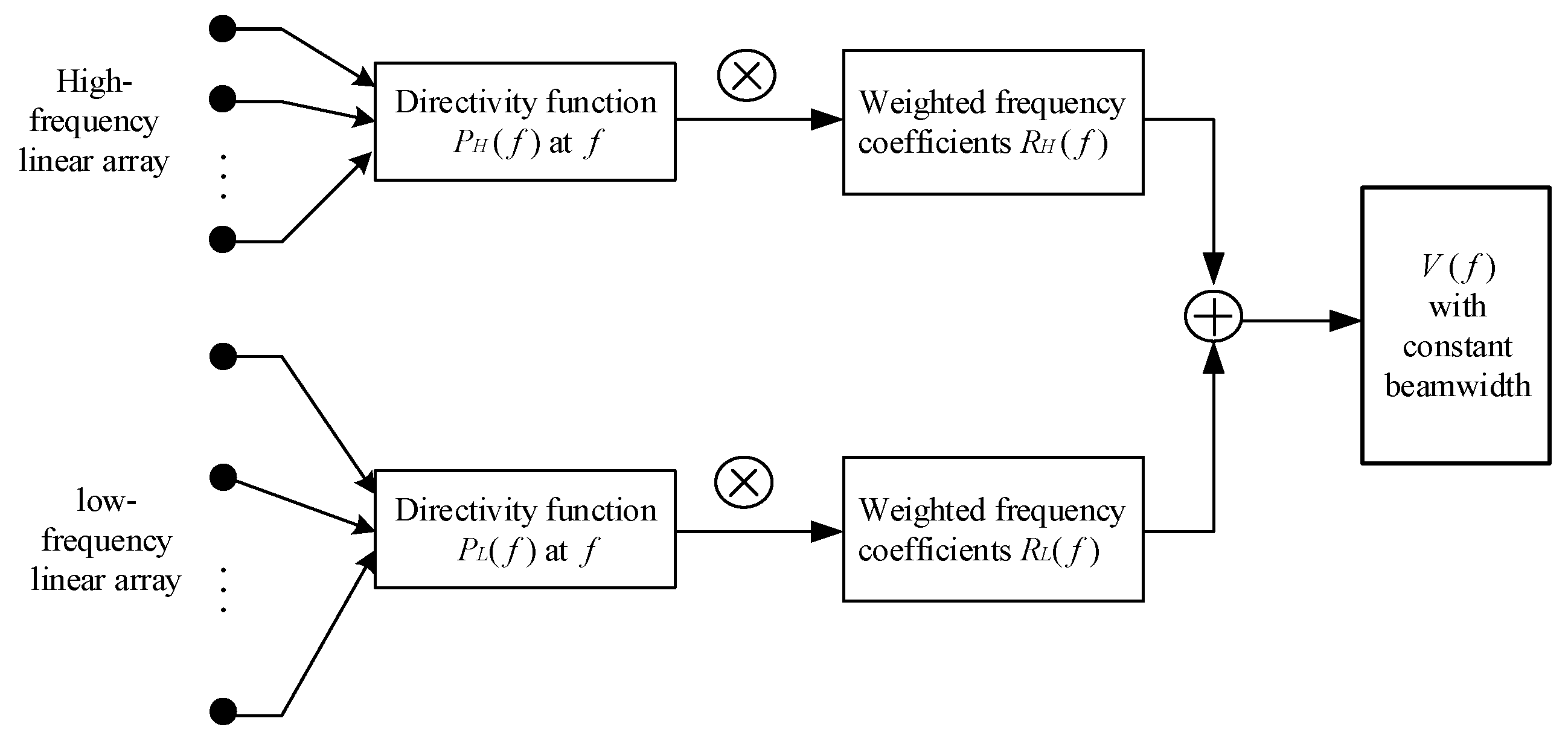
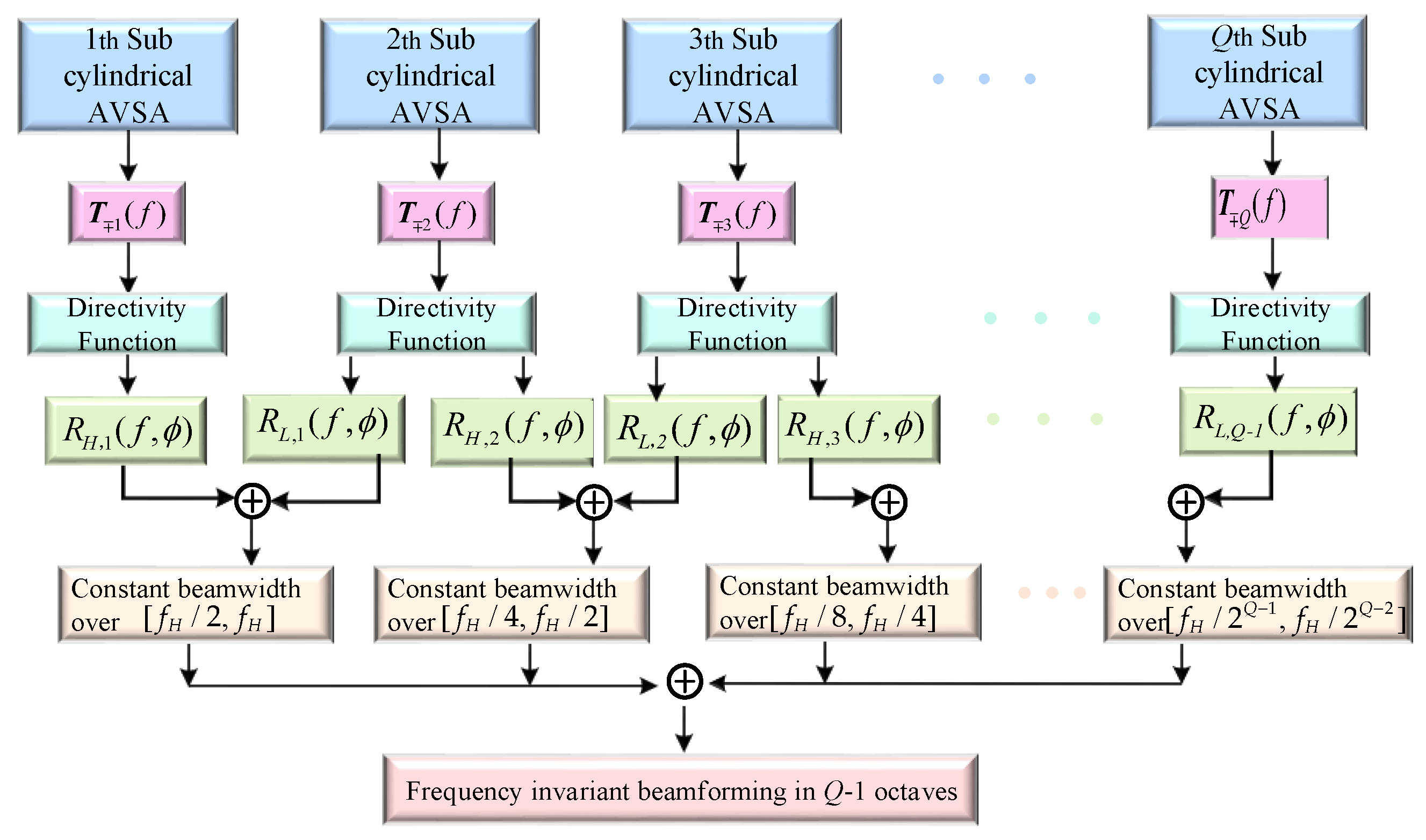
3.2. Frequency Invariant Beamforming Method
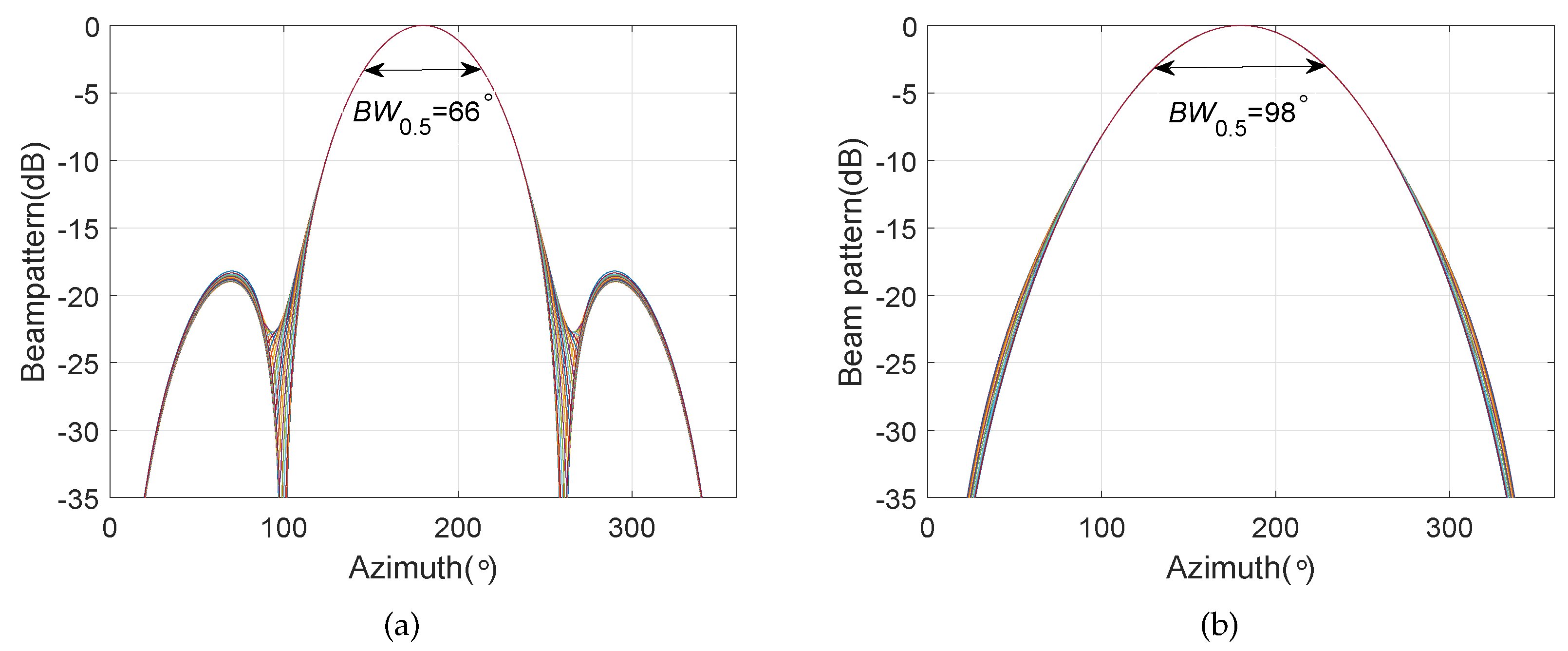
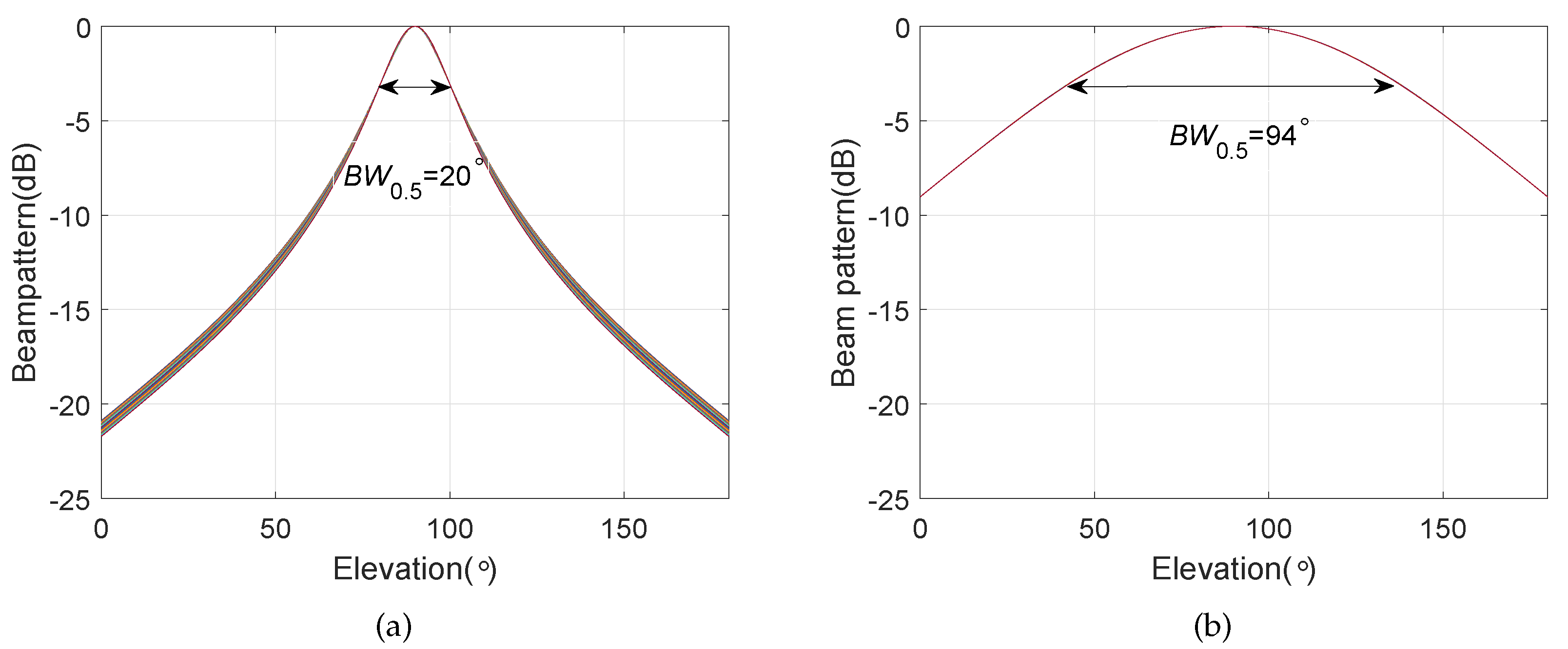
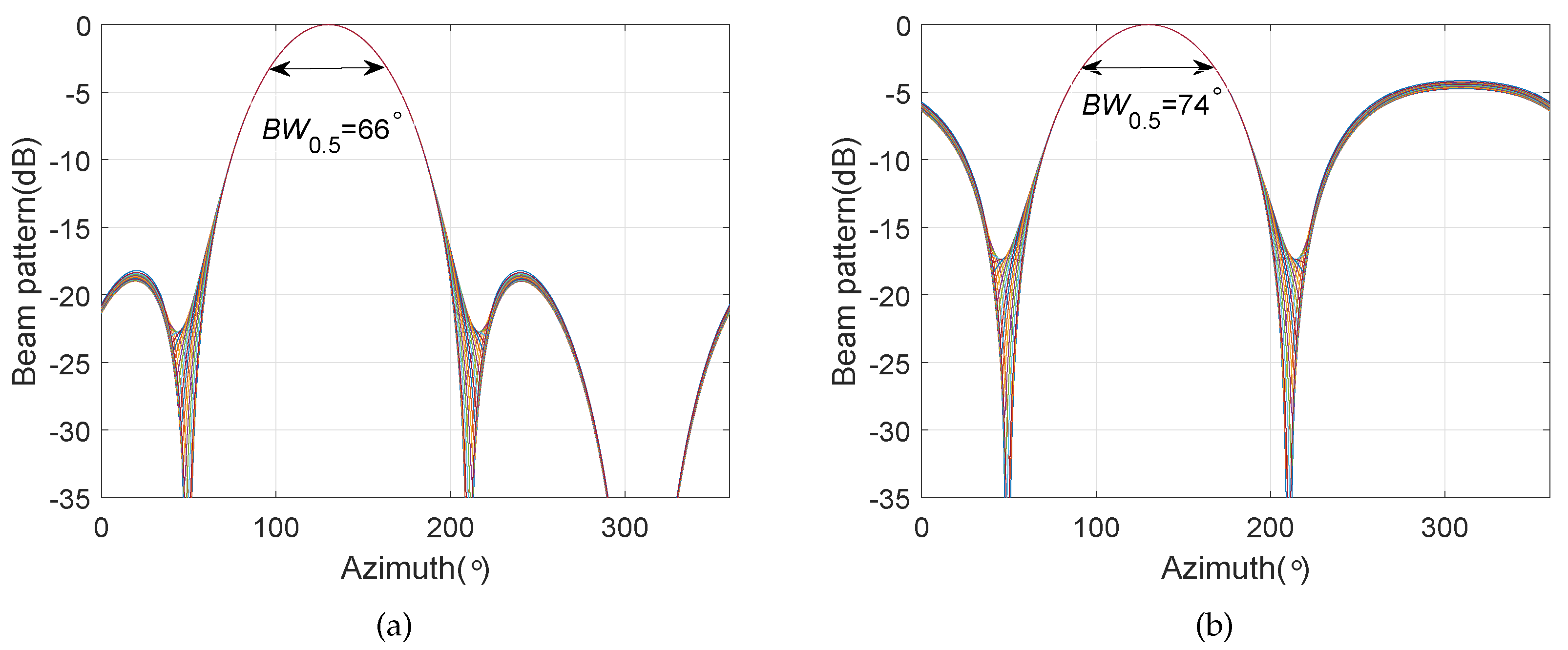
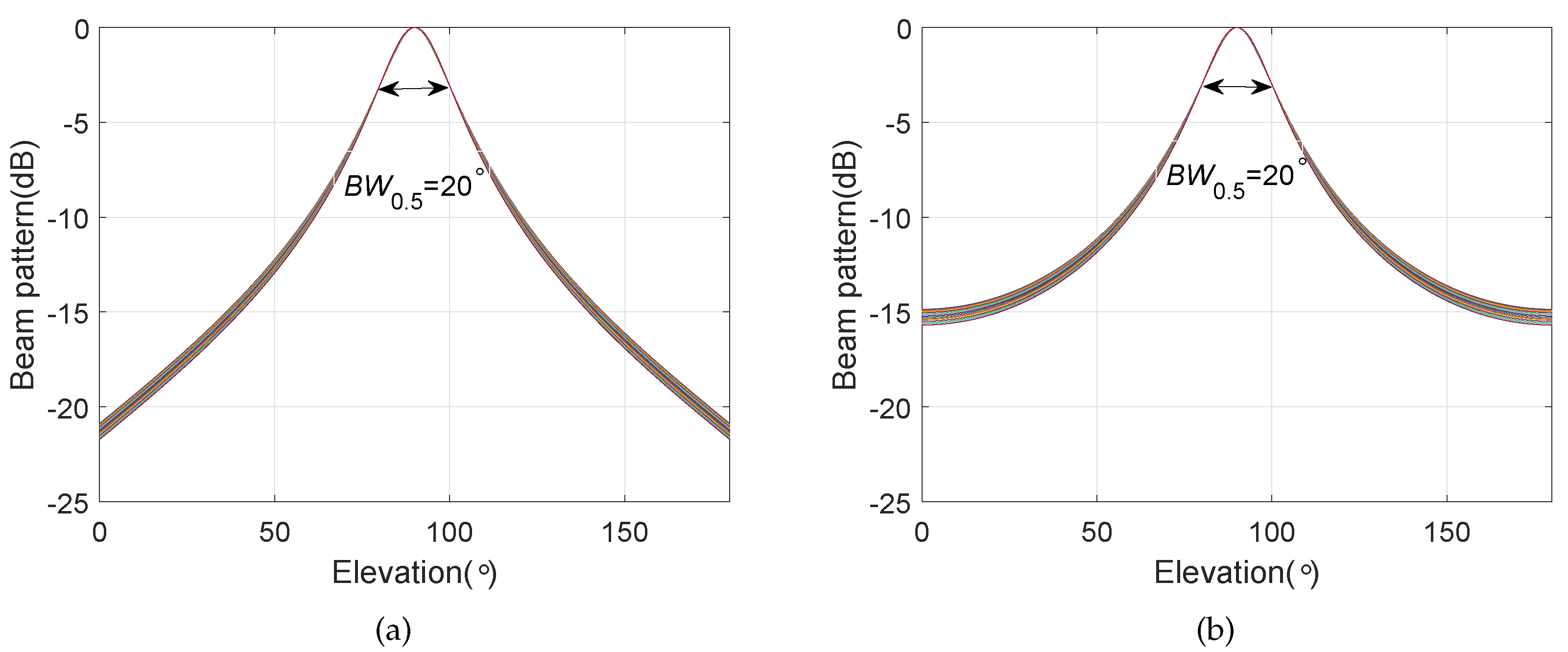
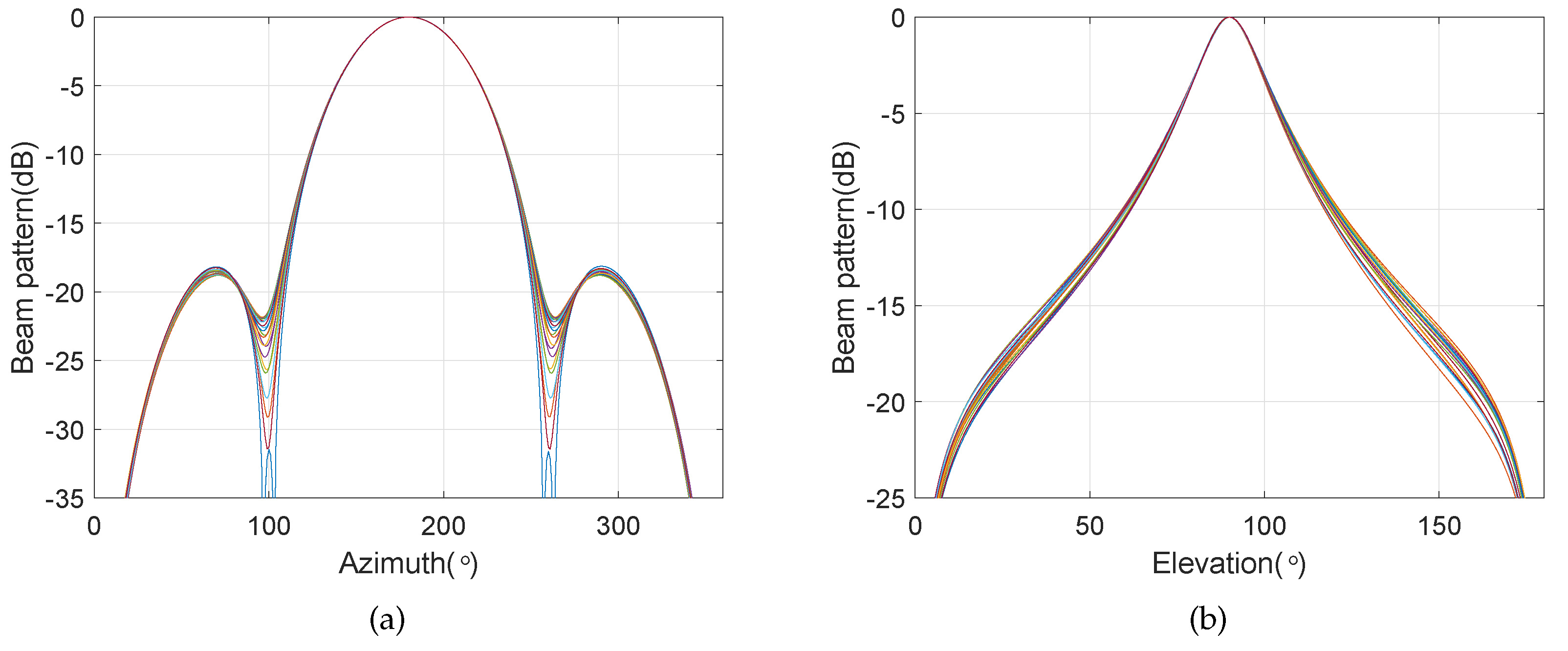
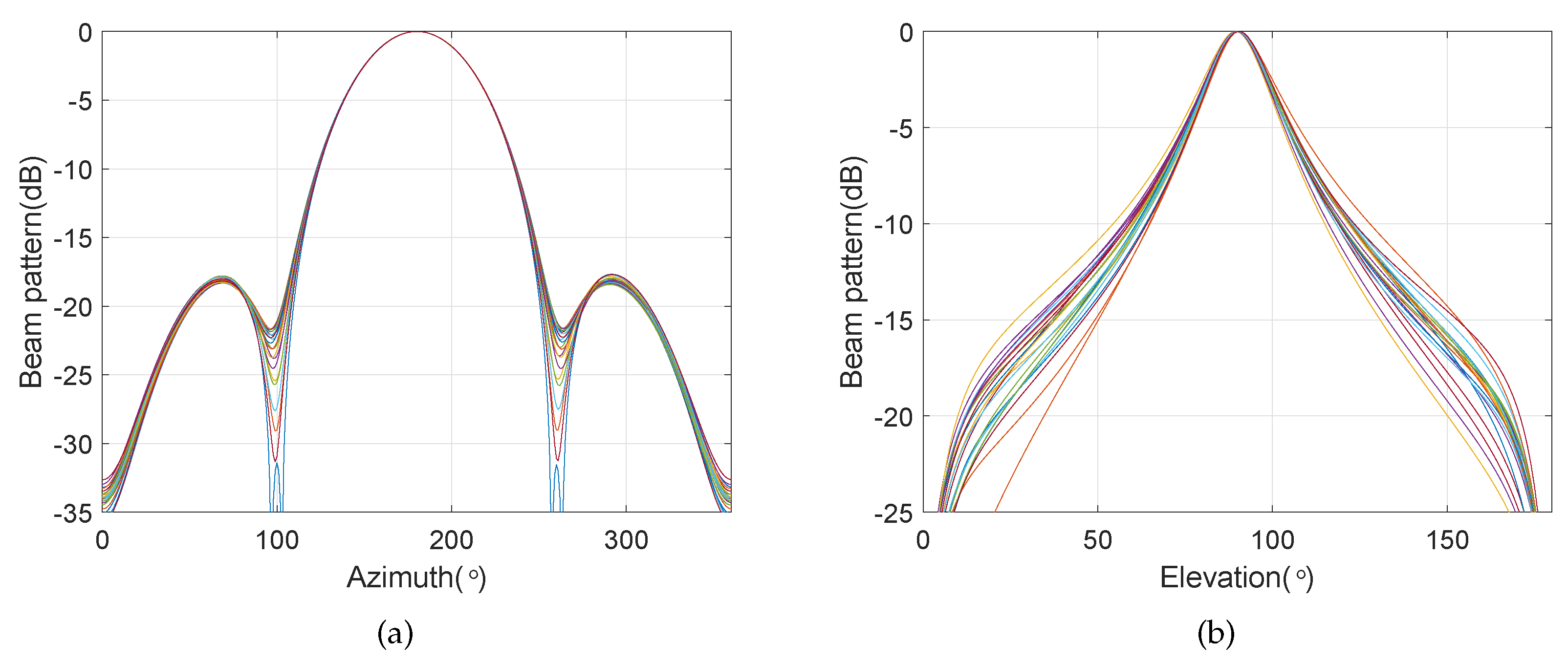
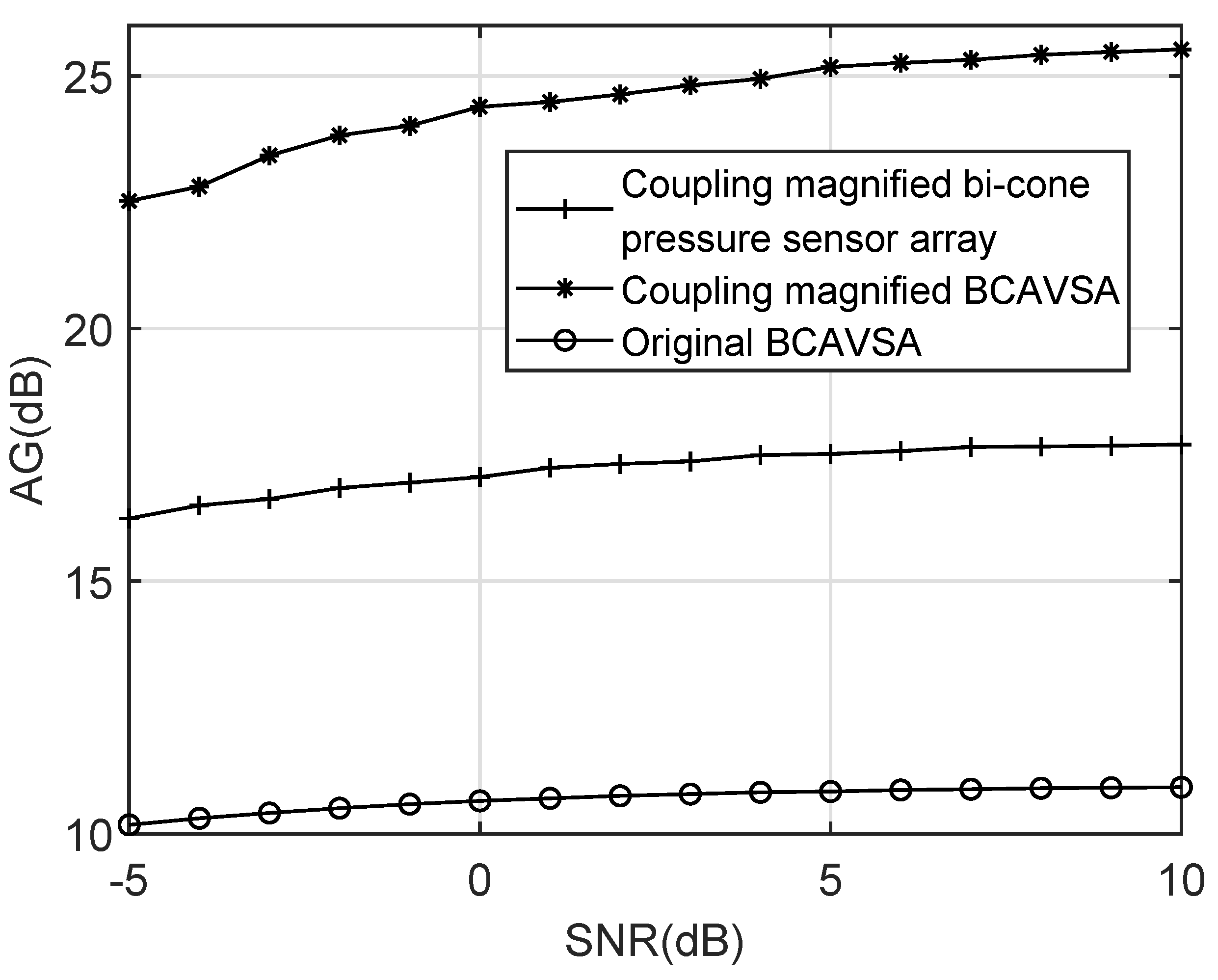
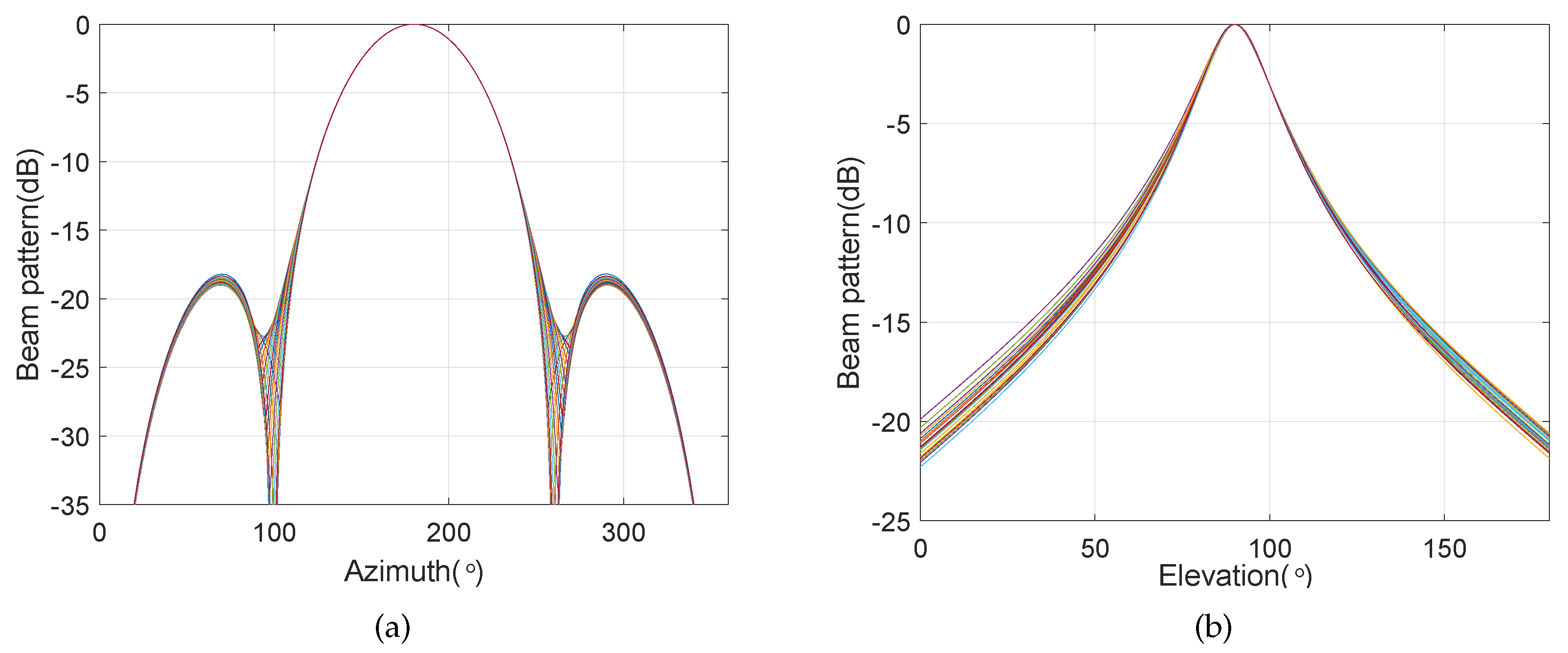
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Original BCAVSA and Coupling Magnified BCAVSA
4.2. Coupling Magnified BCAVSA and a Bi-Cone Pressure Sensor Array
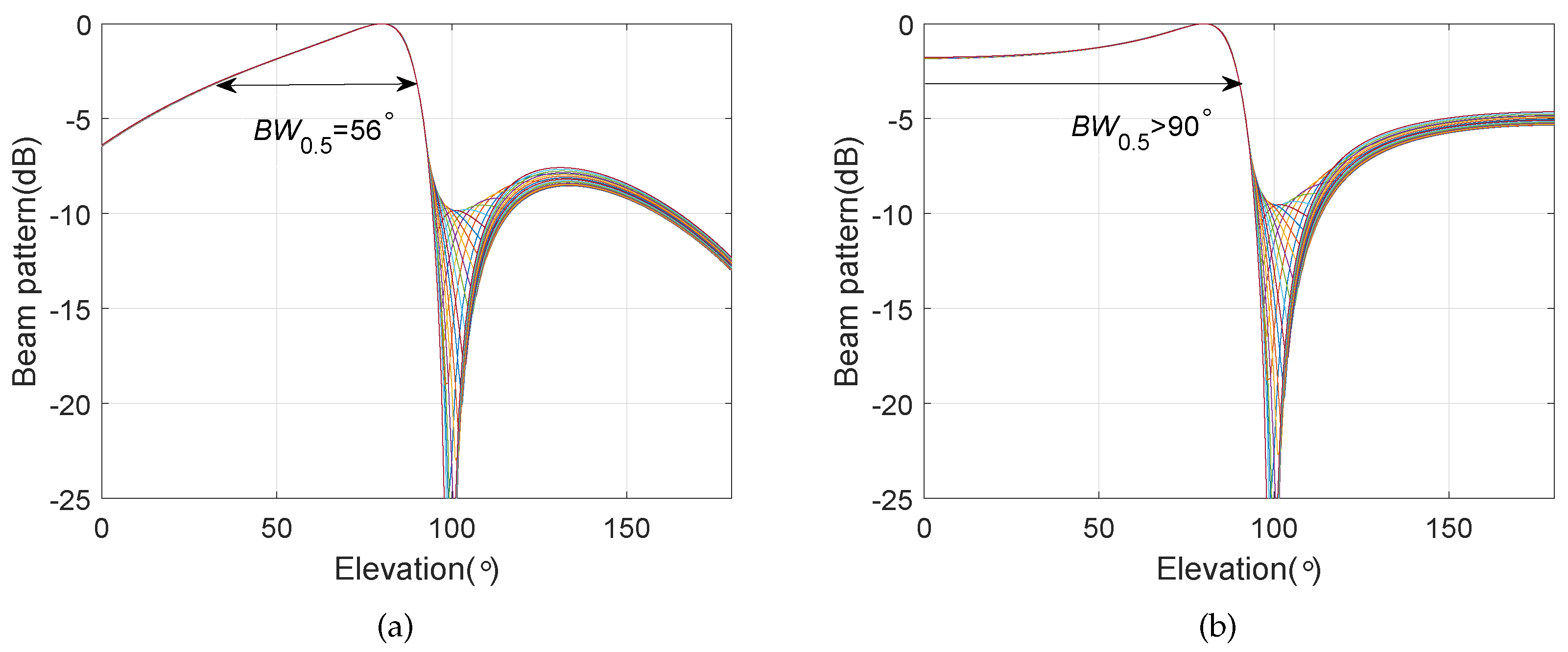
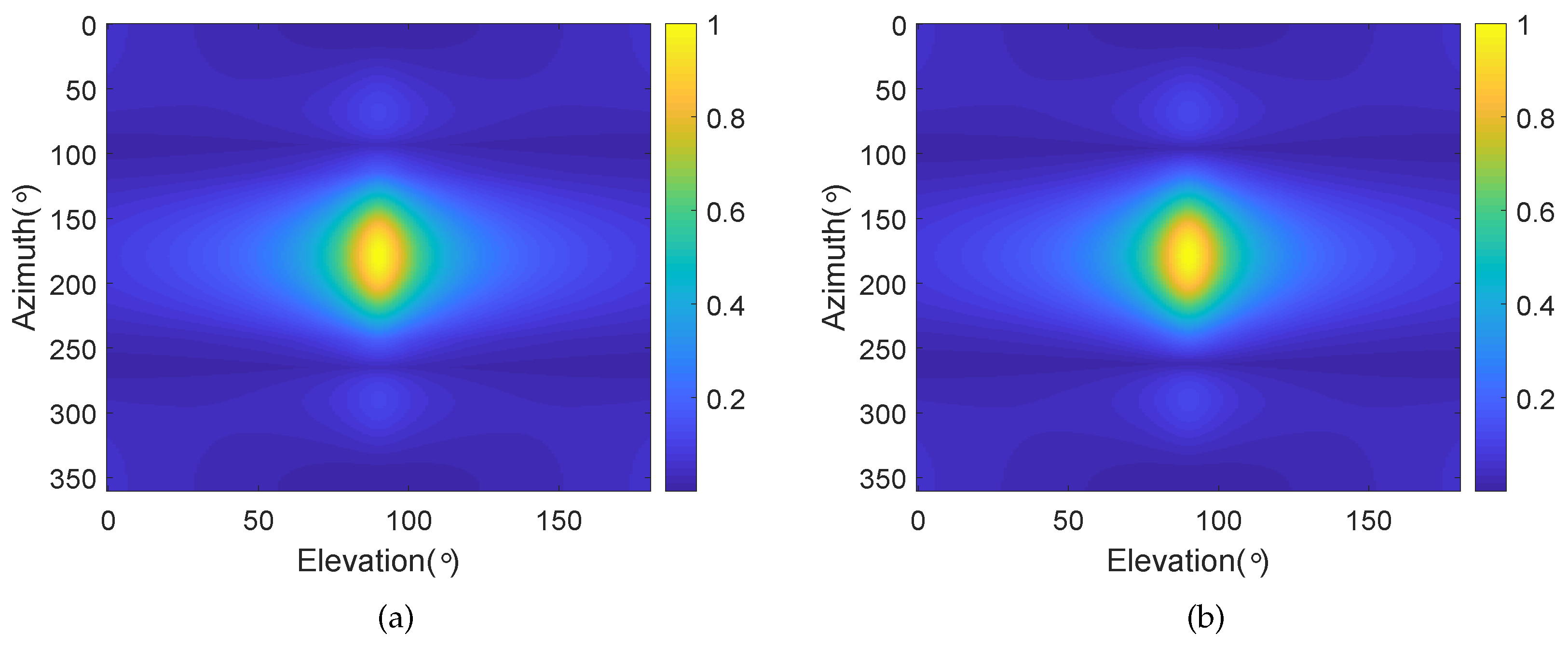
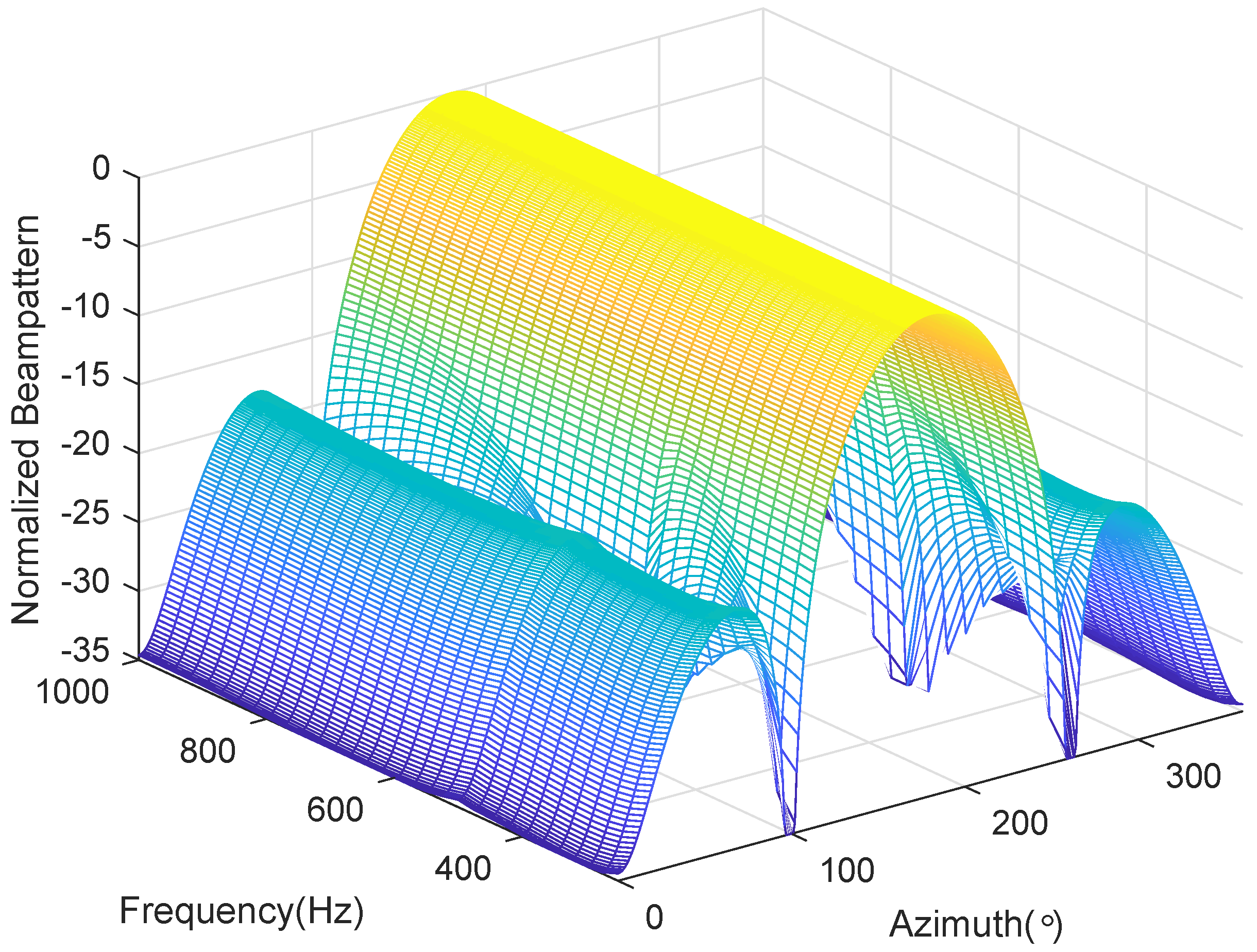
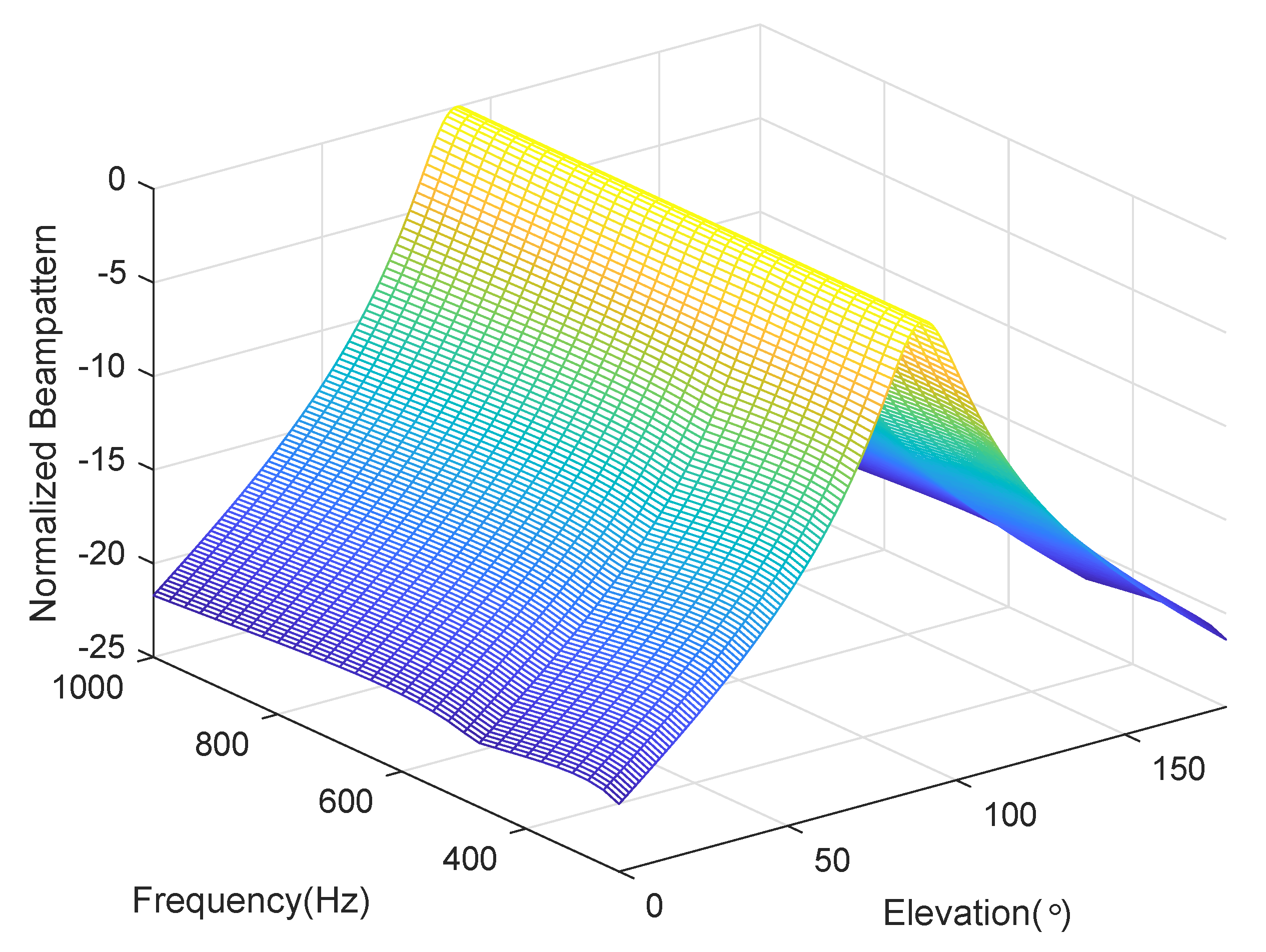
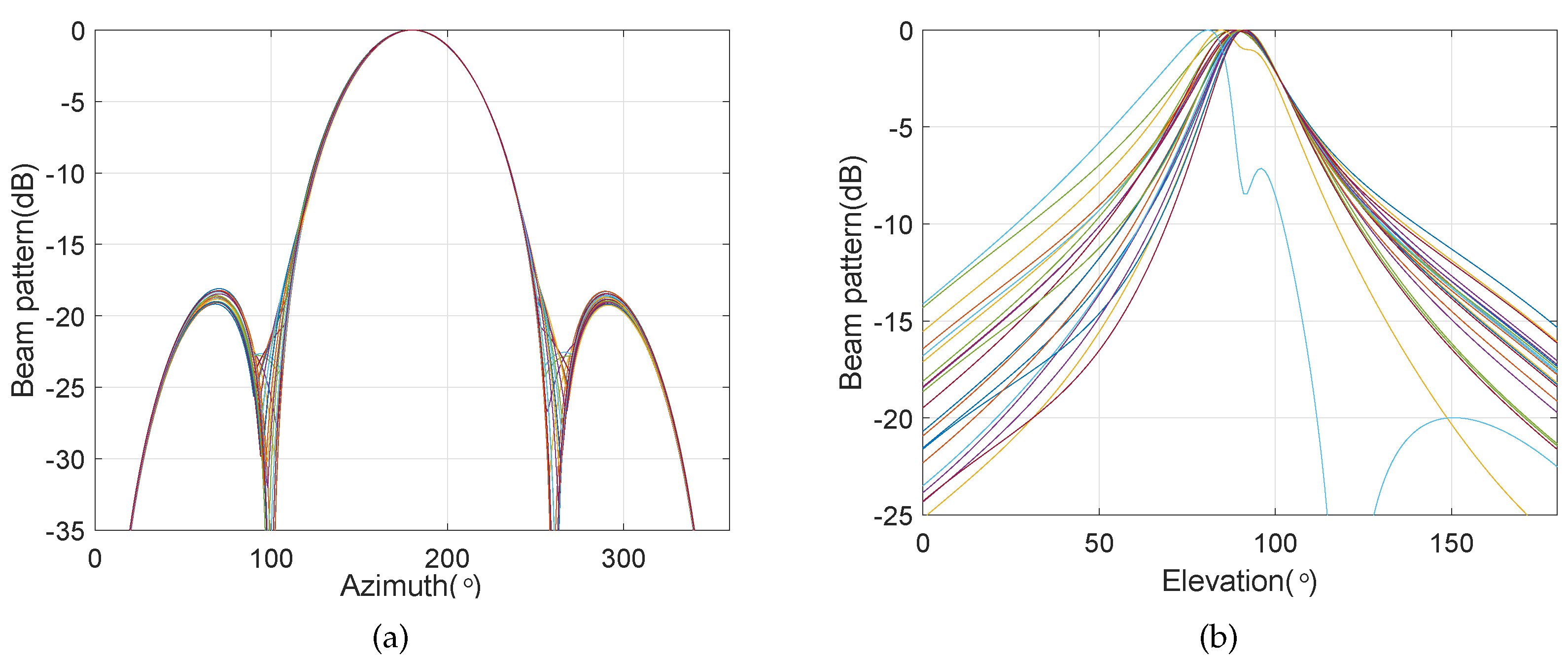
4.3. Frequency Invariant Beampattern of BCAVSA over Multiple Octaves
4.4. Frequency Invariant Beamforming in the Presence of the Noise
4.5. Frequency Invariant Beamforming in the Presence of the Steering Vector Error
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knight, W.C.; Pridham, R.G.; Kay, S.M. Digital signal processing for sonar. Proc. IEEE 1981, 69, 1451–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehorai, A.; Paldi, E. Acoustic vector-sensor array processing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1994, 42, 2481–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, J. Coherent signal-subspace processing of acoustic vector sensor array for DOA estimation of wideband sources. Signal Process. 2005, 85, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, M.; Nehorai, A. Acoustic vector-sensor correlations in ambient noise. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2001, 26, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichavský, P.; Wong, K.T.; Zoltowski, M.D. Near-field/far-field azimuth and elevation angle estimation using a single vector hydrophone. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2001, 49, 2498–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, M.; Nehorai, A. Wideband source localization using a distributed acoustic vector-sensor array. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2003, 51, 1479–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, M.; Nehorai, A. Acoustic vector-sensor beamforming and Capon direction estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1998, 46, 2291–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X. Partial Angular Sparse Representation Based DOA Estimation Using Sparse Separate Nested Acoustic Vector Sensor Array. Sensors 2018, 18, 4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Bi, X.; Hui, J.; Zeng, C.; Ma, L. A Three-Dimensional Target Depth-Resolution Method with a Single-Vector Sensor. Sensors 2018, 18, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cray, B.; Nuttall, A. Directivity factors for linear arrays of velocity sensors. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2001, 110, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSen, Y.; ZhongRui, Z. Direction-of-arrival estimation for a uniform circular acoustic vector-sensor array mounted around a cylindrical baffle. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2012, 55, 2338–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagananda, K.G.; Anand, G.V. Subspace intersection method of high-resolution bearing estimation in shallow ocean using acoustic vector sensors. Signal Process. 2010, 90, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S. Optimal design of FIR beamformer with frequency invariant patterns. Appl. Acoust. 2006, 67, 511–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.B.; Kennedy, R.A.; Williamson, R.C. Theory and design of broadband sensor arrays with frequency invariant far-field beam patterns. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1995, 97, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Weiss, S.; McWhirter, J.G.; Proudler, I.K. Frequency invariant beamforming for two-dimensional and three-dimensional arrays. Signal Process. 2007, 87, 2535–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Su, T. Reference Beam Pattern Design for Frequency Invariant Beamforming Based on Fast Fourier Transform. Sensors 2016, 16, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Benesty, J.; Chen, J. On the Design of Frequency-Invariant Beampatterns With Uniform Circular Microphone Arrays. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2017, 25, 1140–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H.; Chan, S.C.; Ho, K.L. Adaptive Beamforming Using Frequency Invariant Uniform Concentric Circular Arrays. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2007, 54, 1938–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.C.; Chen, H.H. Uniform Concentric Circular Arrays With Frequency-Invariant Characteristics mdash; Theory, Design, Adaptive Beamforming and DOA Estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2007, 55, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Tsui, K.; Chan, S. Frequency Invariant Uniform Concentric Circular Arrays with Directional Elements. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2013, 49, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Huang, L. Wideband beamforming with broad nulls of nested array. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Third International Conference on Information Science and Technology (ICIST), Yangzhou, China, 23–25 March 2013; pp. 1645–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, M. Multirate Method for Constant Beamwidth Beamforming of Nested Array. In Proceedings of the 2009 5th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, Beijing, China, 24–26 September 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lardies, J.; Guihot, J. Acoustic ring array with constant beamwidth over a very wide frequency range. Acoust. Lett. 1989, 13, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, E.Z.; Li, D.F. Performance simulation of line array in nonprime axis wideband radiated noise measurement. J. Vib. Shock 2012, 31, 176–180. [Google Scholar]
- Han, R.; Fang, E. Research on wideband beamforming with constant beamwidth using vector sensor array. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation, Harbin, China, 20–23 June 2010; pp. 1289–1293. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, A.; Oshinsky, M.; Hoy, R. Hyperacute directional hearing in a microscale auditory system. Nature 2001, 410, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, D.; Miles, R.N.; Hoy, R.R. Directional hearing by mechanical coupling in the parasitoid fly Ormia ochracea. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1996, 179, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, R.N.; Robert, D.; Hoy, R.R. Mechanically coupled ears for directional hearing in the parasitoid fly Ormia ochracea. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1995, 98, 3059–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, A.; Ishfaque, A.; Jung, H.; Kim, B. Bio-Inspired Rectangular Shaped Piezoelectric MEMS Directional Microphone. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, A.; Ishfaque, A.; Kim, B. Effect of Torsional Beam Length on Acoustic Functionalities of Bio-Inspired Piezoelectric MEMS Directional Microphone. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 6046–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, V.S.; Rudresha, K.J.; Pinjare, S.L. Design, Fabrication and Characterization of a Biologically Inspired MEMS Directional Microphone. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE SENSORS, New Delhi, India, 28–31 October 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Masoumi, A.R.; Behdad, N. An Improved Architecture for Two-Element Biomimetic Antenna Arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 6224–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, A.R.; Yusuf, Y.; Behdad, N. Biomimetic Antenna Arrays Based on the Directional Hearing Mechanism of the Parasitoid Fly Ormia Ochracea. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 2500–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Ta, N.; Rao, Z. A Miniature Four-Microphone Array for Two-Dimensional Direction-of-Arrival Estimation Based on Biomimetic Time-Delay Magnification. J. Vib. Acoust. Trans. ASME 2019, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcakaya, M.; Muravchik, C.H.; Nehorai, A. Biologically Inspired Coupled Antenna Array for Direction-of-Arrival Estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 4795–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, K.; Matsuzuka, I. Radiation field consideration of biconical horn antenna with different flare angles. IEEE Trans. on Antennas Propag. 1988, 36, 1306–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.D.; Pang, Q.Y.; Lv, Z.P. Far field radiation characteristics of linear biconical antenna array. In Proceedings of the 2011 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Management Science and Electronic Commerce (AIMSEC), Dengleng, China, 8–10 August 2011; pp. 3976–3979. [Google Scholar]
- Samaddar, S.N.; Mokole, E.L. Biconical antennas with unequal cone angles. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1998, 46, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwaszczewski, R.S.; Slater, M.A.; Snyder, J.K.; Tietje, E.D.; Green, R.C. Reinventing submarine signature measurements: Installation of the High Gain Measurement System at SEAFAC. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2009, Biloxi, MS, USA, 26–29 October 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Urick, R.J. Principles of Underwater Sound. 1983. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/50330063_Principles_of_Underwater_Sound (accessed on 1 July 2019).



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, E.; Gui, C.; Yang, D.; Zhu, Z. Frequency Invariant Beamforming for a Small-Sized Bi-Cone Acoustic Vector–Sensor Array. Sensors 2020, 20, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030661
Fang E, Gui C, Yang D, Zhu Z. Frequency Invariant Beamforming for a Small-Sized Bi-Cone Acoustic Vector–Sensor Array. Sensors. 2020; 20(3):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030661
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Erzheng, Chenyang Gui, Desen Yang, and Zhongrui Zhu. 2020. "Frequency Invariant Beamforming for a Small-Sized Bi-Cone Acoustic Vector–Sensor Array" Sensors 20, no. 3: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030661
APA StyleFang, E., Gui, C., Yang, D., & Zhu, Z. (2020). Frequency Invariant Beamforming for a Small-Sized Bi-Cone Acoustic Vector–Sensor Array. Sensors, 20(3), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20030661




