Horizontally Elongated Time Domain Reflectometry System for Evaluation of Soil Moisture Distribution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
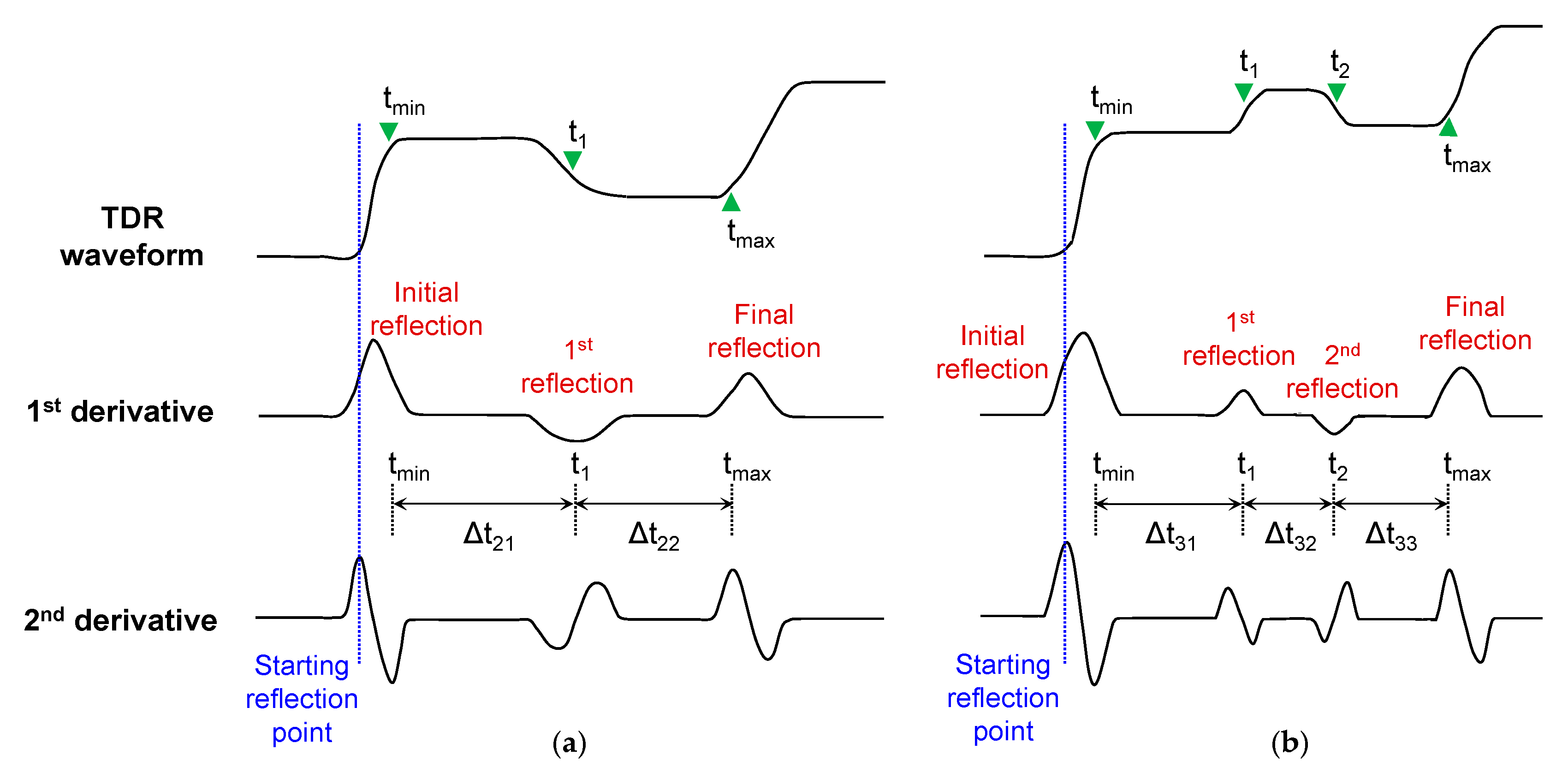
2.1. Theoretical Background
2.2. HETDR
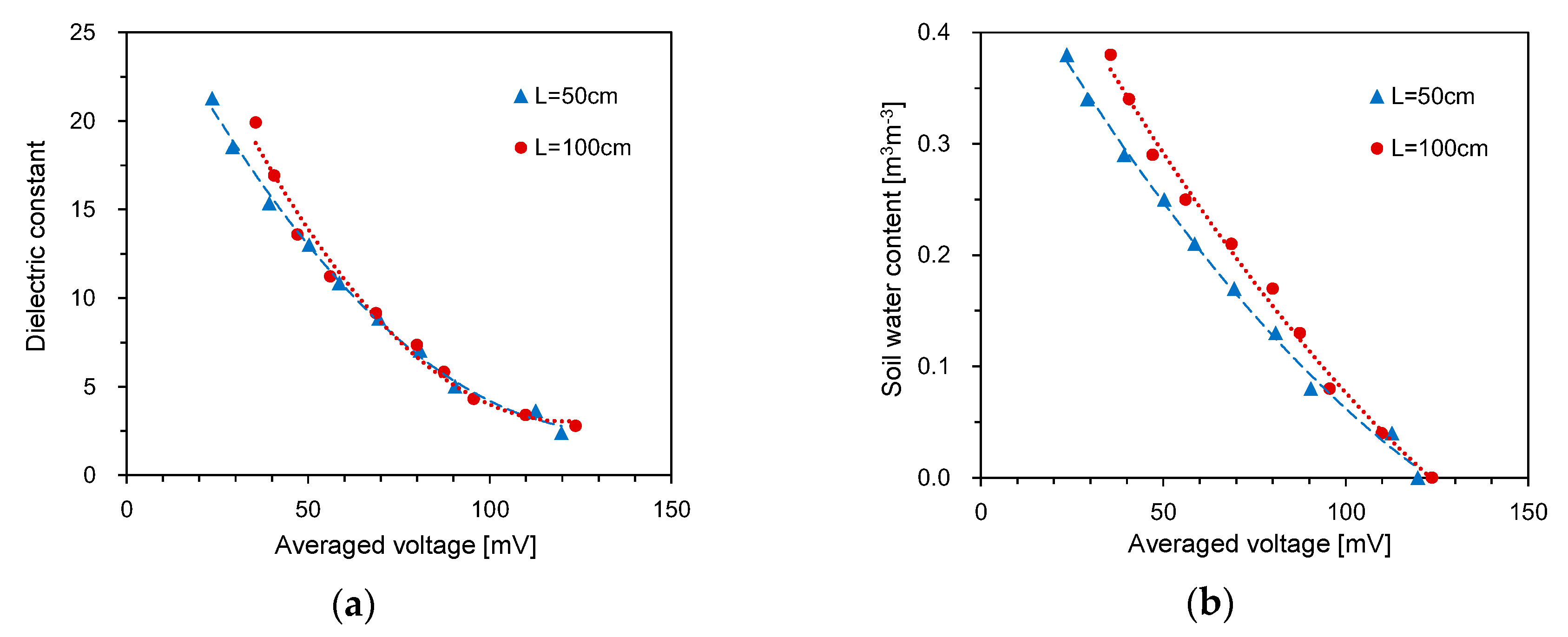
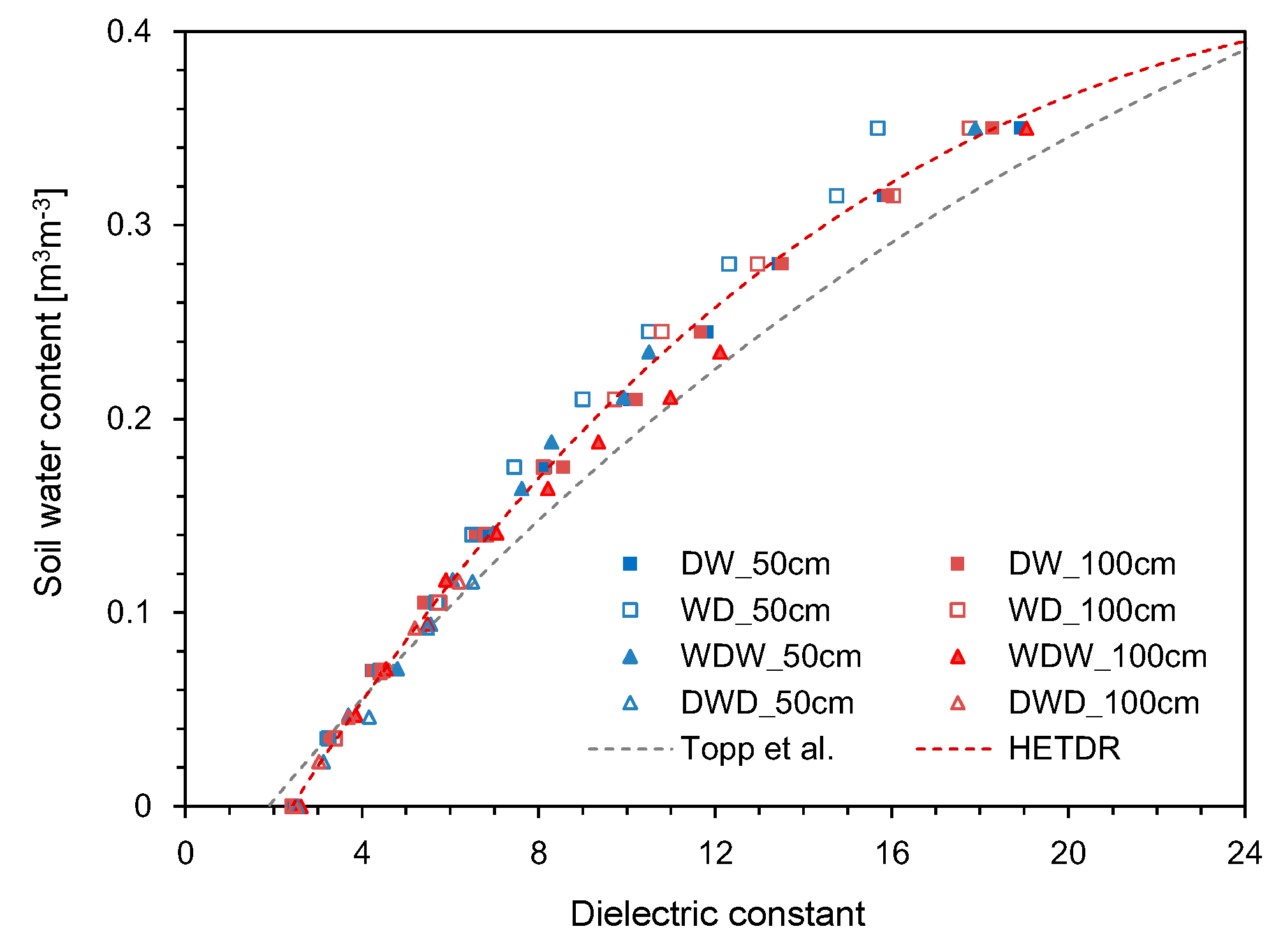
2.3. Calibration
2.4. Model Test
3. Results
3.1. Probe Length and Spacing
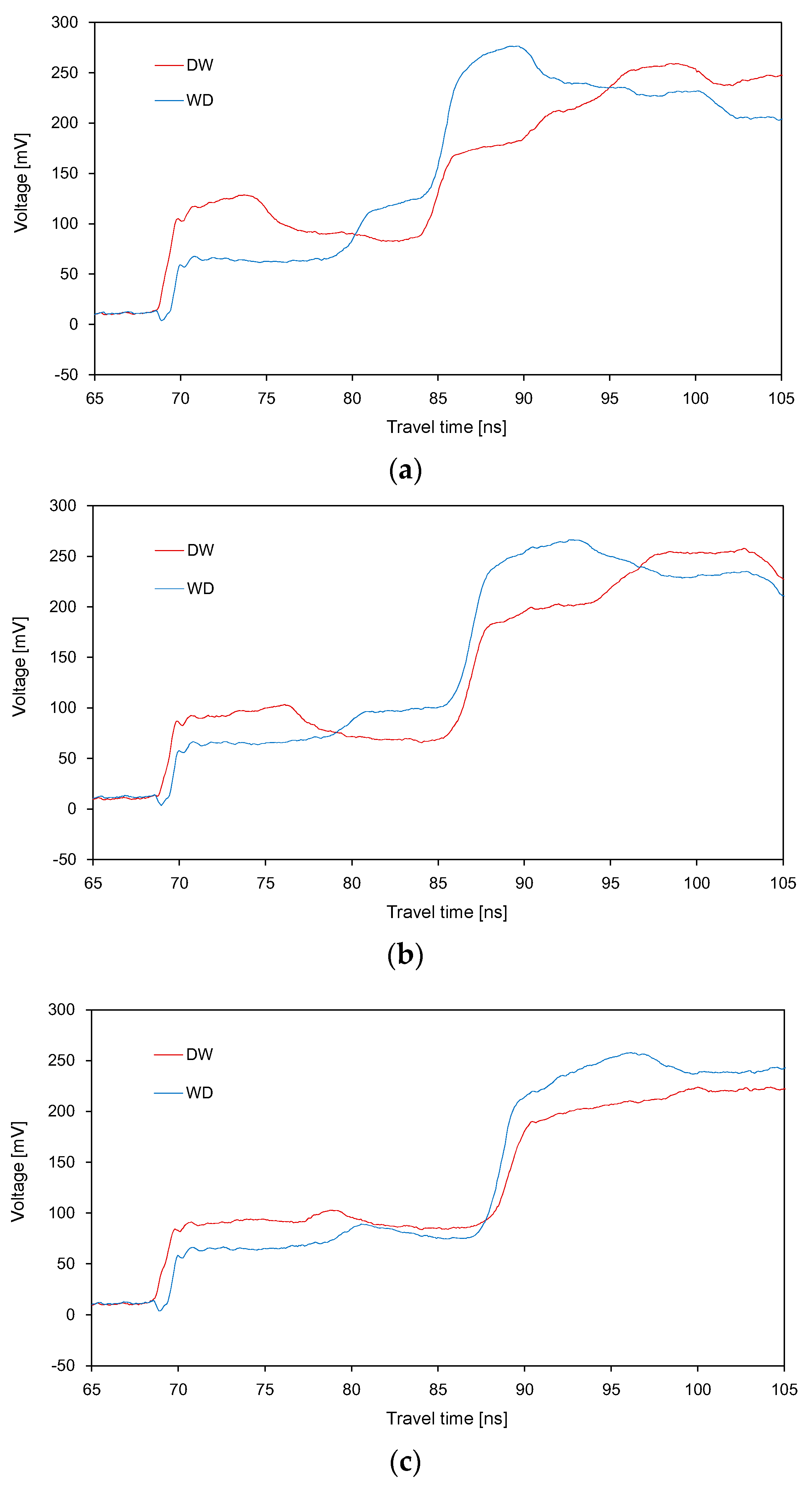
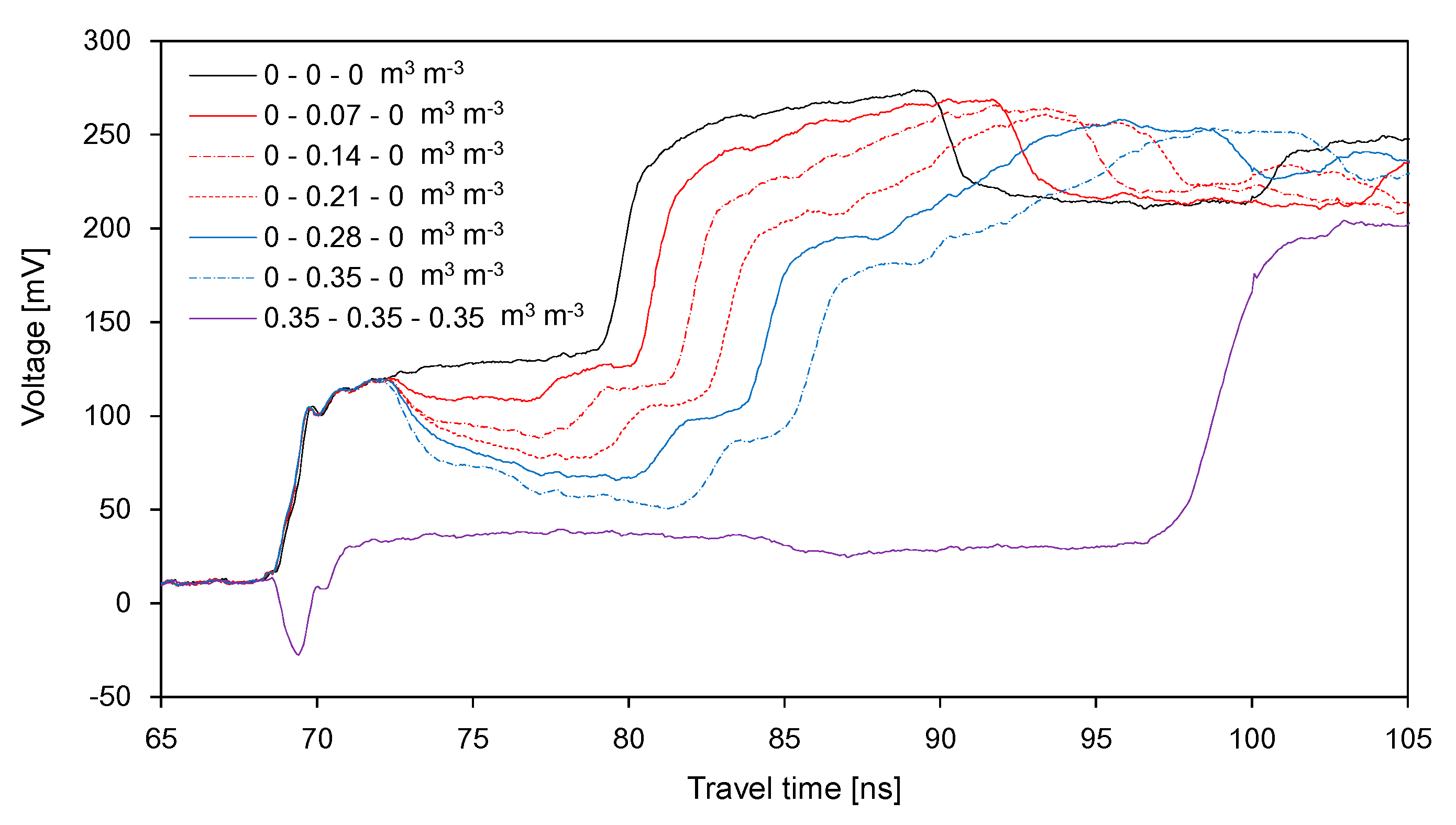
3.2. TDR Waveforms
4. Analyses
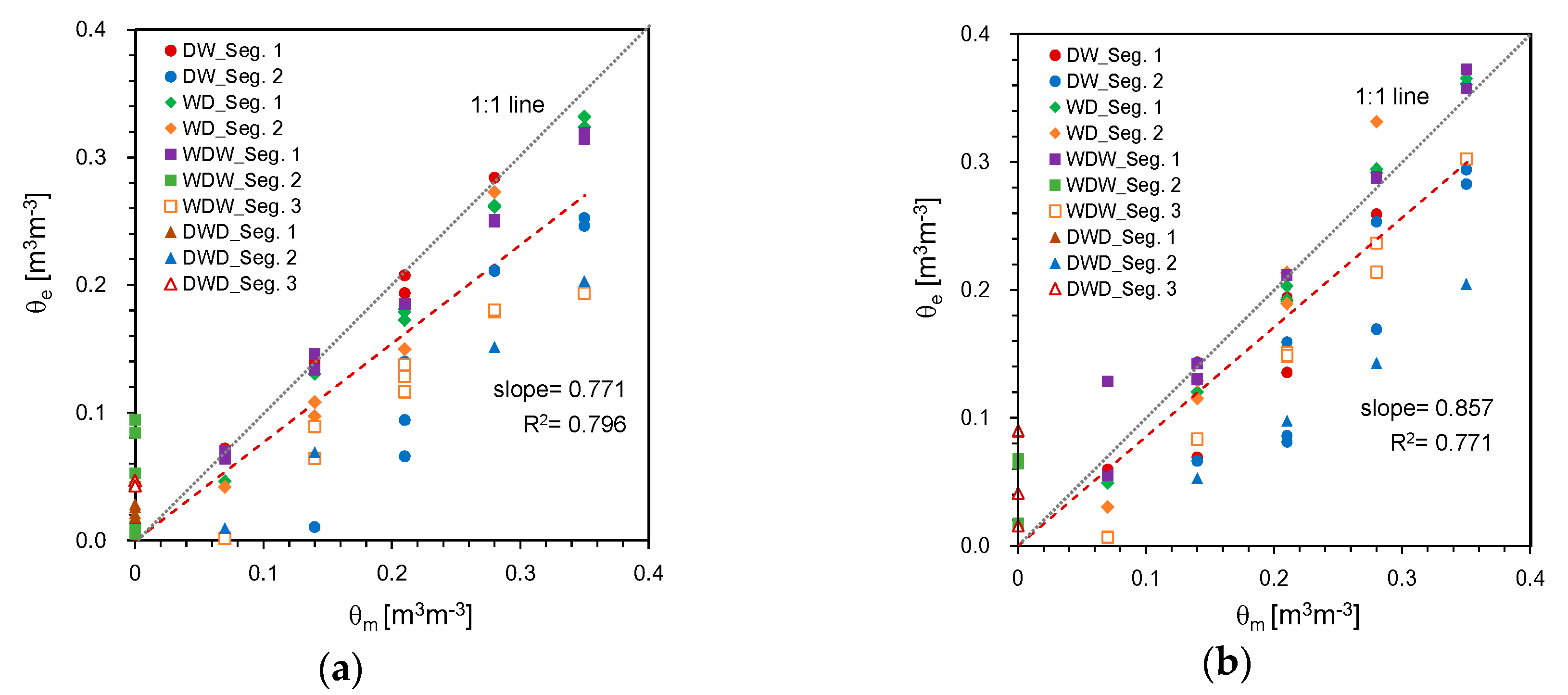
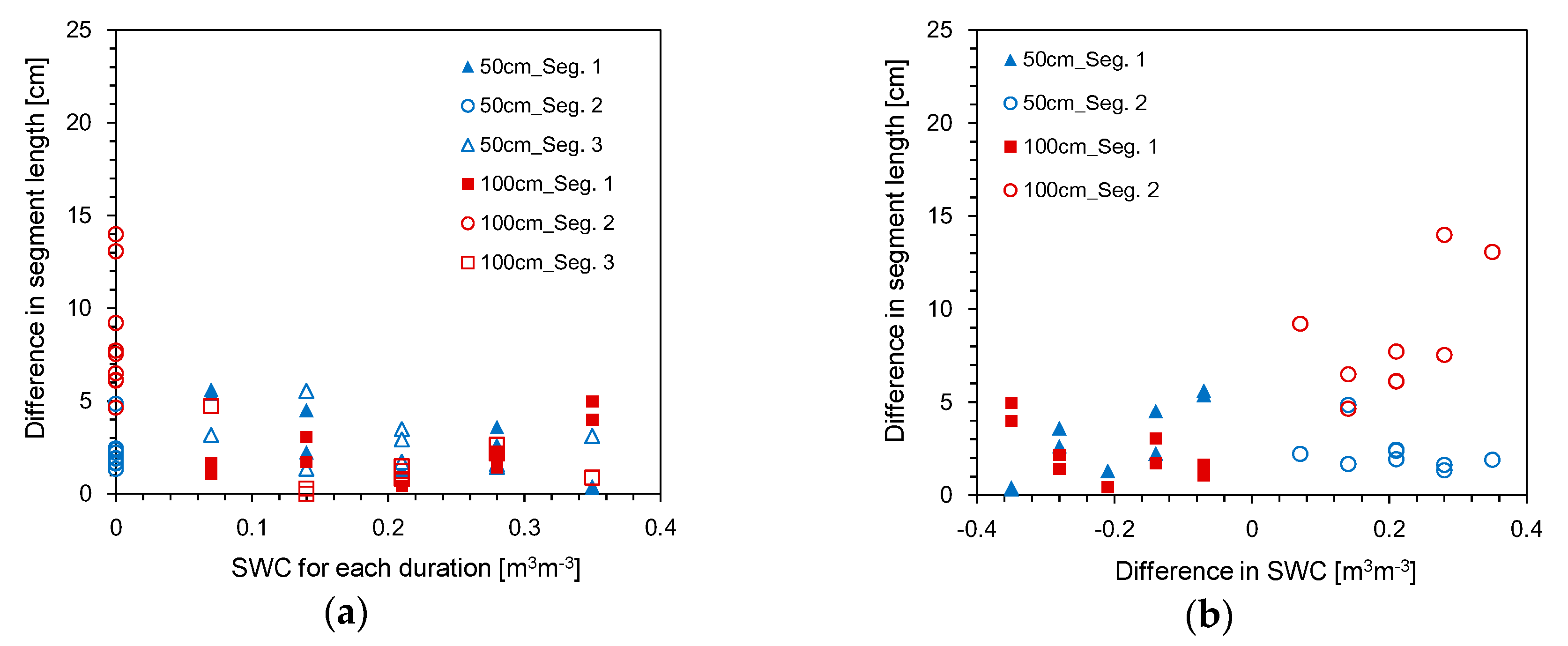
4.1. Estimation of Segment Length and Water Content
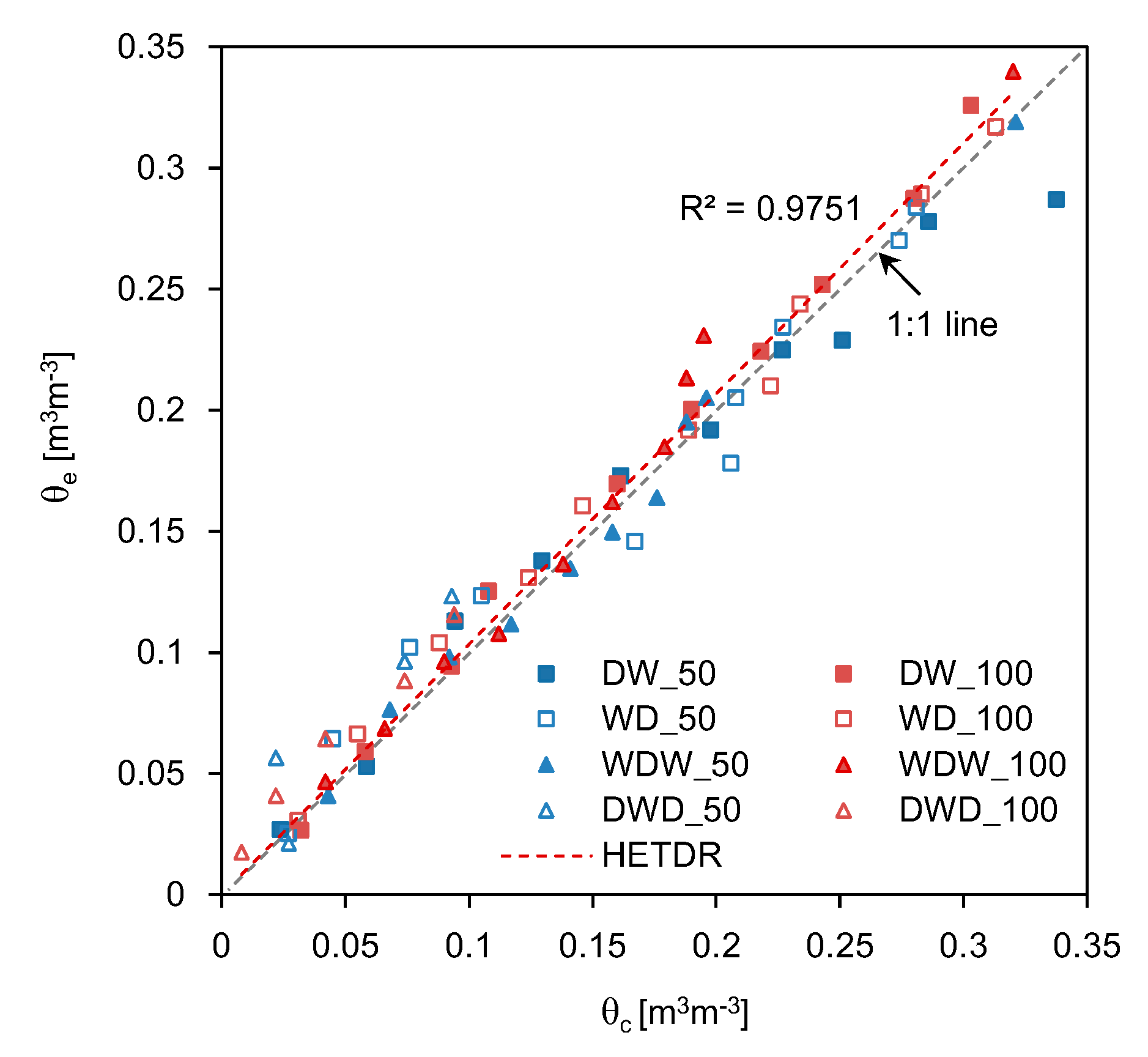
4.2. Estimation of Average SWC
4.3. HETDR versus Conventional TDR
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, S.; Zhang, S. Controlled alternate partial root-zone irrigation: Its physiological consequences and impact on water use efficiency. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 2437–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morison, J.I.L.; Baker, N.R.; Mullineaux, P.M.; Davies, W.J. Improving water use in crop production. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 639–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonari, E.; Mazzoncini, M.; Peruzzi, A. Effects of conventional and minimum tillage on winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) in sandy soil. Soil Tillage Res. 1995, 33, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, A.P.; Tennant, D. The influence of tillage on soil water behavior. Soil Sci. 1981, 132, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddell, J.T.; Weil, R.R. Water distribution in soil under ridge-till and no-till corn. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Topp, G.C.; Davis, J.L. Time-domain reflectometry (TDR) and its application to irrigation scheduling. Adv. Irrig. 1985, 3, 107–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zauzuetta, F.S.; Xin, J. Soil moisture sensors. Soil Sci. 1994, 73, 391–401. [Google Scholar]
- Sudduth, K.A.; Kitchen, N.R.; Wiebold, W.J.; Batchelor, W.D.; Bollero, G.A.; Bullock, D.G.; Clay, D.E.; Palm, H.L.; Pierce, F.J.; Schuler, R.T.; et al. Relating apparent electrical conductivity to soil properties across the north-central USA. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 46, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, A.D.L.Á.C.; de Almeida, C.D.G.C.; Júnior, J.A.S.; de Morais, J.E.F.; de Almeida, B.G.; de Andrade, F.H.N. Accuracy of capacitive sensors for estimating soil moisture in northeastern Brazil. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouazen, A.M.; Al-Asadi, R.A. Influence of soil moisture content on assessment of bulk density with combined frequency domain reflectometry and visible and near infrared spectroscopy under semi field conditions. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 176, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.L. Relative permittivity measurements of a sand and clay soil in situ. Geol. Surv. Can. 1975, 75-1C, 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- Topp, G.C.; Davis, J.L.; Annan, A.P. Electromagnetic determination of soil water content: Measurements in coaxial transmission line. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, G.C.; Davis, J.L. Measurement of soil water content using time-domain reflectometry (TDR): A field evaluation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Benedetto, E.; Cannazza, G.; Masciullo, A.; Demitri, C.; Cataldo, A. Reflectometric system for continuous and automated monitoring of irrigation in agriculture. Adv. Agric. 2018, 2018, 284925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.L. Electrical property measurements of sea ice in situ using a wide-band borehole radar and a time-domain reflectometer. Proc. Int. Workshop Remote Estim. Sea Ice Thick. St. John’s Nfld. 1980, 80, 155–187. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, S.F.; Selker, J.S.; Green, J.L. Using short soil moisture probes with high-bandwidth time domain reflectometry measurements. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1995, 59, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malicki, M.A.; Plagge, R.; Renger, M.; Walczak, R.T. Application of time-domain reflectometry (TDR) soil moisture miniprobe for the determination of unsaturated soil water characteristics from undisturbed soil cores. Irrig. Sci. 1992, 13, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, J.; Kane, D.L. Monitoring the unfrozen water content of soil and snow using time domain reflectometry. Water Resour. Res. 1983, 19, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegline, S.J.; White, I.; Jenkins, D.R. Improved field probes for soil water content and electrical conductivity measurement using time domain reflectometry. Water Resour. Res. 1989, 25, 2367–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selker, J.S.; Graff, L.; Steenhuis, T. Noninvasive time domain reflectometry moisture measurement probe. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 934–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.T.; Jung, Y.S.; Lee, J.S.; Byun, Y.H. Development and application of TDR penetrometer for evaluation of soil water content of subsoil. J. Korean Geotech. Soc. 2015, 31, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.T.; Yu, J.D.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.S. Dynamic cone penetrometer in corporated with time domain reflectometry (TDR) sensors for the evaluation of water contents in sandy soils. Sensors 2019, 19, 3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Hong, W.T.; Park, K.; Hong, S.S.; Lee, S.H.; Byun, Y.H. Evaluation of water content in an active layer using penetration-type time domain reflectometry. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, G.C.; Davis, J.L.; Annan, A.P.; Electromagnetic determination of soil water content using TDR: I. Applications to wetting fronts and steep gradients. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, T.; Kobayashi, R.; Annaka, T.; Chikushi, J. Applicability of multiple length TDR probes to measure water distributions in an andisol under different tillage systems in Japan. Soil Tillage Res. 2001, 60, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.D.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, J.S. Nondestructive health monitoring of soil nails using electromagnetic wave. Can. Geotech. J. 2018, 55, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Song, J.U.; Hong, W.T.; Yu, J.D. Application of time domain reflectometer for detecting necking defects in bored piles. NDT E Int. 2018, 100, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.D.; Lee, J.S. Smart sensing using electromagnetic waves for inspection of defects in rock bolts. Sensors 2020, 20, 2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.D.; Lee, J.S.; Yoon, H.K. Circular time-domain reflectometry system for monitoring bridge scour depth. Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 2020, 38, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noborio, K. Measurement of soil water content and electrical conductivity by time domain reflectometry: A review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2001, 31, 213–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J.H. Sensitivity of time domain reflectometry measurements to lateral variations in soil water content. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 2345–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, L.W.; Thomsen, A.; Moldrup, P.; Jacobsen, O.H.; Rolston, D.E. High-resolution time domain reflectometry: Sensitivity dependency on probe-design. Soil Sci. 1995, 159, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadler, A.; Dasberg, S.; Lapid, I. Time domain reflectometry measurements of water content and electrical conductivity of layered soil columns. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1991, 55, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, F.N.; Herkelrath, W.N.; Rawlins, D.S.; Rhoades, J.D. Time-domain reflectometry: Simultaneous measurement of soil water content and electrical conductivity with a single probe. Science 1984, 224, 898–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topp, G.C.; Yanuka, M.; Zebchuk, W.D.; Zegelin, S. Determination of electrical conductivity using time domain reflectometry: Soil and water experiments in coaxial lines. Water Resour. Res. 1988, 24, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loon, W.K.P.; Perfect, E.; Groenevelt, P.H.; Kay, B.D. A new method to measure bulk electrical conductivity in soils with time domain reflectometry. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1990, 70, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, Y.H.; Hong, W.T.; Yoon, H.K. Characterization of cementation factor of unconsolidated granular materials through time domain reflectometry with variable saturated conditions. Materials 2019, 12, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadler, A.; Frenkel, H.; Mantell, A. Applicability of the four-probe technique under extremely variable water contents and salinity distribution. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1984, 48, 1258–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasberg, S.; Dalton, F.N. Time domain reflectometry field measurements of soil water content and electrical conductivity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1985, 49, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachanoski, R.G.; Pringle, E.; Ward, A. Field measurement of solute travel times using time domain reflectometry. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.L.; Kachanoski, R.G.; Elrick, D.E. Laboratory measurements of solute transport using time domain reflectometry. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogeler, I.; Clothier, B.E.; Green, S.R. TDR estimation of the resident concentration of electrolyte in the soil solution. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1997, 35, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| No. | Length, L (cm) | Spacing, s (cm) | Width, D (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.5 | 5 | |
| 2 | 50 | 5.0 | 10 |
| 3 | 7.5 | 15 | |
| 4 | 2.5 | 5 | |
| 5 | 75 | 5.0 | 10 |
| 6 | 7.5 | 15 | |
| 7 | 2.5 | 5 | |
| 8 | 100 | 5.0 | 10 |
| 9 | 7.5 | 15 |
| Treatment | Average | Two Segments | Treatment | Average | Three Segments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWC | First | Second | SWC | First | Second | Third | ||
| Dry-Wet (DW) | 0 | 0 | 0 | Wet-Dry-Wet (WDW) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.035 | 0 | 0.07 | 0.047 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.07 | ||
| 0.070 | 0 | 0.14 | 0.070 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.14 | ||
| 0.105 | 0 | 0.21 | 0.093 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.14 | ||
| 0.140 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 0.117 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.21 | ||
| 0.175 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.140 | 0.21 | 0 | 0.21 | ||
| 0.210 | 0.14 | 0.28 | 0.163 | 0.28 | 0 | 0.21 | ||
| 0.245 | 0.21 | 0.28 | 0.187 | 0.28 | 0 | 0.28 | ||
| 0.280 | 0.21 | 0.35 | 0.210 | 0.35 | 0 | 0.28 | ||
| 0.315 | 0.28 | 0.35 | 0.233 | 0.35 | 0 | 0.35 | ||
| 0.350 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.350 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.35 | ||
| Wet-Dry (WD) | 0 | 0 | 0 | Dry-Wet-Dry (DWD) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.035 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.023 | 0 | 0.07 | 0 | ||
| 0.070 | 0.14 | 0 | 0.047 | 0 | 0.14 | 0 | ||
| 0.105 | 0.21 | 0 | 0.070 | 0 | 0.21 | 0 | ||
| 0.140 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.093 | 0 | 0.28 | 0 | ||
| 0.175 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.117 | 0 | 0.35 | 0 | ||
| 0.210 | 0.28 | 0.14 | 0.350 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.35 | ||
| 0.245 | 0.28 | 0.21 | ||||||
| 0.280 | 0.35 | 0.21 | ||||||
| 0.315 | 0.35 | 0.28 | ||||||
| 0.350 | 0.35 | 0.35 | ||||||
| Probe Length | A | B | C | R2 | D | E | F | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 cm | 0.0015 | 0.4021 | 29.348 | 0.996 | 1 × 10−5 | 0.0058 | 0.5038 | 0.996 |
| 100 cm | 0.0022 | 0.5211 | 34.566 | 0.986 | 1 × 10−5 | 0.0064 | 0.5766 | 0.993 |
| Probe Length | DW | WD | WDW | DWD | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seg. 1 | Seg. 2 | Seg. 1 | Seg. 2 | Seg. 1 | Seg. 2 | Seg. 3 | Seg. 1 | Seg. 2 | Seg. 3 | ||
| 50 cm | Slope | 0.989 | 0.646 | 0.912 | 0.812 | 0.908 | - | 0.594 | - | 0.550 | - |
| R2 | 0.993 | 0.720 | 0.983 | 0.887 | 0.993 | - | 0.910 | - | 0.955 | - | |
| 100 cm | Slope | 0.834 | 0.719 | 1.006 | 1.014 | 1.035 | - | 0.776 | - | 0.527 | - |
| R2 | 0.805 | 0.723 | 0.976 | 0.898 | 0.962 | - | 0.918 | - | 0.918 | - | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.-J.; Yu, J.-D.; Byun, Y.-H. Horizontally Elongated Time Domain Reflectometry System for Evaluation of Soil Moisture Distribution. Sensors 2020, 20, 6834. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236834
Kim D-J, Yu J-D, Byun Y-H. Horizontally Elongated Time Domain Reflectometry System for Evaluation of Soil Moisture Distribution. Sensors. 2020; 20(23):6834. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236834
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Dong-Ju, Jung-Doung Yu, and Yong-Hoon Byun. 2020. "Horizontally Elongated Time Domain Reflectometry System for Evaluation of Soil Moisture Distribution" Sensors 20, no. 23: 6834. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236834
APA StyleKim, D.-J., Yu, J.-D., & Byun, Y.-H. (2020). Horizontally Elongated Time Domain Reflectometry System for Evaluation of Soil Moisture Distribution. Sensors, 20(23), 6834. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20236834





