Analysis of Postural Control in Sitting by Pressure Mapping in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis, Spinal Cord Injury and Friedreich’s Ataxia: A Case Series Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Sample
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edwards, D.H.; Prilutsky, B.I. Sensory feedback in the control of posture and locomotion. In Neurobiology of Motor Control: Fundamental Concepts and New Directions; Hooper, S.L., Büschges, A., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 263–304. [Google Scholar]
- Takakusaki, K.; Takahashi, M.; Obara, K.; Chiba, R. Neural substrates involved in the control of posture. Adv. Robot. 2017, 31, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, K.; Müller, F.; Krewer, C.; Bergmann, J. Multisensory control of posture: Clinical assessment and disorders. Neurol. Rehabil. 2019, 25, S23–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnath, H.O.; Ferber, S.; Dichgans, J. The neural representation of postural control in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13931–13936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidler, R.D.; Bernard, J.A.; Burutolu, T.B.; Fling, B.W.; Gordon, M.T.; Gwin, J.T.; Kwak, Y.; Lipps, D.B. Motor control and aging: Links to age-related brain structural, functional, and biochemical effects. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabanas-Valdés, R.; Cuchi, G.U.; Bagur-Calafat, C. Trunk training exercises approaches for improving trunk performance and functional sitting balance in patients with stroke: A systematic review. NeuroRehabilitation 2013, 33, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruyama, K.; Kawakami, M.; Otsuka, T. Effect of core stability training on trunk function, standing balance, and mobility in stroke patients: A randomized controlled trial. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair. 2017, 31, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidler, R.D.; Alberts, J.L.; Stelmach, G.E. Changes in multi-joint performance with age. Motor Control 2002, 6, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debû, B.; Godeiro, C.D.O.; Lino, J.C.; Moro, E. Managing gait, balance, and posture in Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2018, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonnekes, J.; Goselink, R.J.; Růžička, E.; Fasano, A.; Nutt, J.G.; Bloem, B.R. Neurological disorders of gait, balance and posture: A sign-based approach. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leirós-Rodríguez, R.; García-Soidán, J.L.; Romo-Pérez, V. Analyzing the use of accelerometers as a method of early diagnosis of alterations in balance in elderly people: A systematic review. Sensors 2019, 19, 3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukita, A.; Abe, M.; Kishigami, H.; Hatta, T. Influence of back support shape in wheelchairs offering pelvic support on asymmetrical sitting posture and pressure points during reaching tasks in stroke patients. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardone, A.; Schieppati, M. The role of instrumental assessment of balance in clinical decision making. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 46, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reguera-García, M.M.; de Souza-Teixeira, F.; Fernández, J.A.P. Test-retest reliability of static postural control in people with multiple sclerosis. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2017, 29, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, J.; Andersson, H.; Sidén, J. Sitting posture recognition using screen printed large area pressure sensors. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Sensors, Glasgow, UK, 29 October–1 November 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland-Walsh, H.; Teleten, O.; Wilson, M.; Raingruber, B. Pressure mapping comparison of four OR surfaces. AORN J. 2015, 102, e1–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Abreu, C.L.; Naves, E.L.; de Sá, A.A.; de Freitas, D.G. Analysis of the influence of the seat foam density in the posture of hemiplegic wheelchair users using computerized photogrammetry. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguiña, P.; Kirkland-Walsh, H. Hospital-acquired pressure ulcer prevention. J. Burn Care Res. 2014, 35, e287–e293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-mental state”: A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Cork, R. X-SENSOR technology: A pressure imaging overview. Sens. Rev. 2007, 27, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson-Pell, M.W.; Cardi, M.D. Prototype development and comparative evaluation of wheelchair pressure mapping system. Assist. Technol. 1993, 5, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarin, M.; Andreoni, G.; Pedotti, A. Comparative biomechanical evaluation of different wheelchair seat cushions. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2000, 37, 315–324. [Google Scholar]
- Hobson, D.A. Comparative effects of posture on pressure and shear at the body-seat interface. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 1992, 29, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motamedi, S.M.; de Grood, J.; Harman, S.; Sargious, P.; Baylis, B.; Flemons, W.; Ghali, W.A. The effect of continuous pressure monitoring on strategic shifting of medical inpatients at risk for PUs. J. Wound Care 2012, 21, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wininger, M.; Crane, B.A. Prevalence of sensor saturation in wheelchair seat interface pressure mapping. Assist. Technol. 2015, 27, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauer, S.; Burns, Y.; Galley, P. Lateral reach: A clinical measure of medio-lateral postural stability. Physiother. Res. Int. 1999, 4, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, J.A.; Gear, M.; Pauli, A.; Cowan, P.; Finnigan, C.; Hunter, H.; Mobberley, C.; Nock, A.; Sims, R.; Thain, J. The effect of core stability training on balance and mobility in ambulant individuals with multiple sclerosis: A multi-centre series of single case studies. Mult. Scler. 2010, 16, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, P.W.; Weiner, D.K.; Chandler, J.; Studenski, S. Functional reach: A new clinical measure of balance. J. Gerontol. 1990, 45, M192–M197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, H.S.; Min, D.; Ahn, J. Effects of anterior weight-shifting methods on sitting balance in wheelchair-dependent patients with spinal cord injury. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2018, 30, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Berg, K.O.; Wood-Dauphinee, S.L.; Williams, J.I.; Maki, B. Measuring balance in the elderly: Validation of an instrument. Can. J. Public Health 1992, 83, S7–S11. [Google Scholar]
- Downs, S.; Márquez, J.; Chiarelli, P. The Berg Balance Scale has high intra- and inter-rater reliability but absolute reliability varies across the scale: A systematic review. J. Physiother. 2013, 59, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodby-Bousquet, E.; Agústsson, A.; Jónsdóttir, G.; Czuba, T.; Johansson, A.C.; Hägglund, G. Interrater reliability and construct validity of the Posture and Postural Ability Scale in adults with cerebral palsy in supine, prone, sitting and standing positions. Clin. Rehabil. 2014, 28, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodby-Bousquet, E.; Persson-Bunke, M.; Czuba, T. Psychometric evaluation of the Posture and Postural Ability Scale for children with cerebral palsy. Clin. Rehabil. 2016, 30, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, S.L.; Radtka, S.; Melnick, M.E.; Abrams, G.M.; Byl, N.N. Development and validation of the function in sitting test in adults with acute stroke. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2010, 34, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, S.L.; Rivera, M.; McCarthy, L. Reliability of the Function in Sitting Test (FIST). Rehabil. Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Abou, L.; Sung, J.H.; Sosnoff, J.J.; Rice, L.A. Reliability and validity of the function in sitting test among non-ambulatory individuals with spinal cord injury. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, E.; Marco, E.; Muniesa, J.M.; Belmonte, R.; Díaz, P.; Tejero, M.; Escalada, F. Trunk control test as a functional predictor in stroke patients. J. Rehabil. Med. 2002, 34, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlak-Demir, Y.; Yıldırım, S.A. Reliability and validity of Trunk Control Test in patients with neuromuscular diseases. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2015, 31, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, S.A.; Stinson, M.D.; Walsh, D.M.; Porter-Armstrong, A.P. Impact of sitting time on seat-interface pressure and on pressure mapping with multiple sclerosis patients. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 1221–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinson, M.D.; Crawford, S.A.; Porter-Armstrong, A.P. Interface pressure measurements: Visual interpretation of pressure maps with MS clients. Disabil. Rehabil. 2008, 30, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frzovic, D.; Morris, M.E.; Vowels, L. Clinical tests of standing balance: Performance of persons with multiple sclerosis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2000, 81, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizony, R.; Raz, L.; Katz, N.; Weingarden, H.; Weiss, P.L.T. Video-capture virtual reality system for patients with paraplegic spinal cord injury. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2005, 42, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.H.; Ousley, C.M.; Shen, S.; Isaacs, Z.J.K.; Sosnoff, J.J.; Rice, L.A. Reliability and validity of the function in sitting test in nonambulatory individuals with multiple sclerosis. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2016, 39, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, C.; Wade, D. Assessing motor impairment after stroke: A pilot reliability study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1990, 53, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetisli-Korkmaz, N.; Can-Akman, T.; Kilavuz-Oren, G.; Bir, L.S. Trunk control: The essence for upper limb functionality in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2018, 24, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinzaños, J.; Villa, A.R.; Flores, A.A.; Pérez, R. Proposal and validation of a clinical trunk control test in individuals with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2014, 52, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eftekharsadat, B.; Babaei-Ghazani, A.; Mohammadzadeh, M.; Talebi, M.; Eslamian, F.; Azari, E. Effect of virtual reality-based balance training in multiple sclerosis. Neurol. Res. 2015, 37, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.A.; Polonini, C.; Horsczaruk, C.H.R.; Lima, D.C.; Pereira, J.V.; Rocha, L.F.; Carvalho, E. Decreasing fall risk in spinocerebellar ataxia. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 1223–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

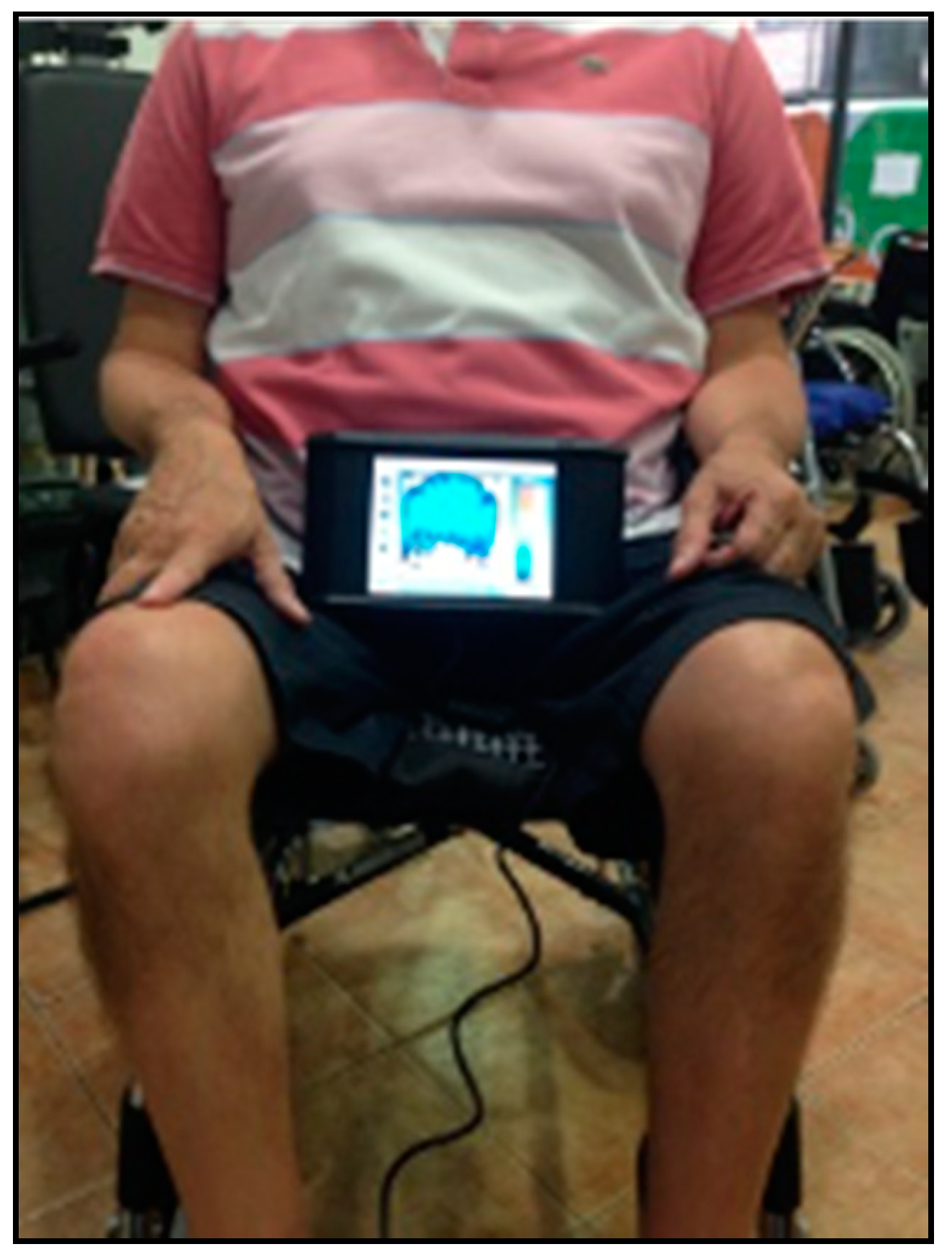
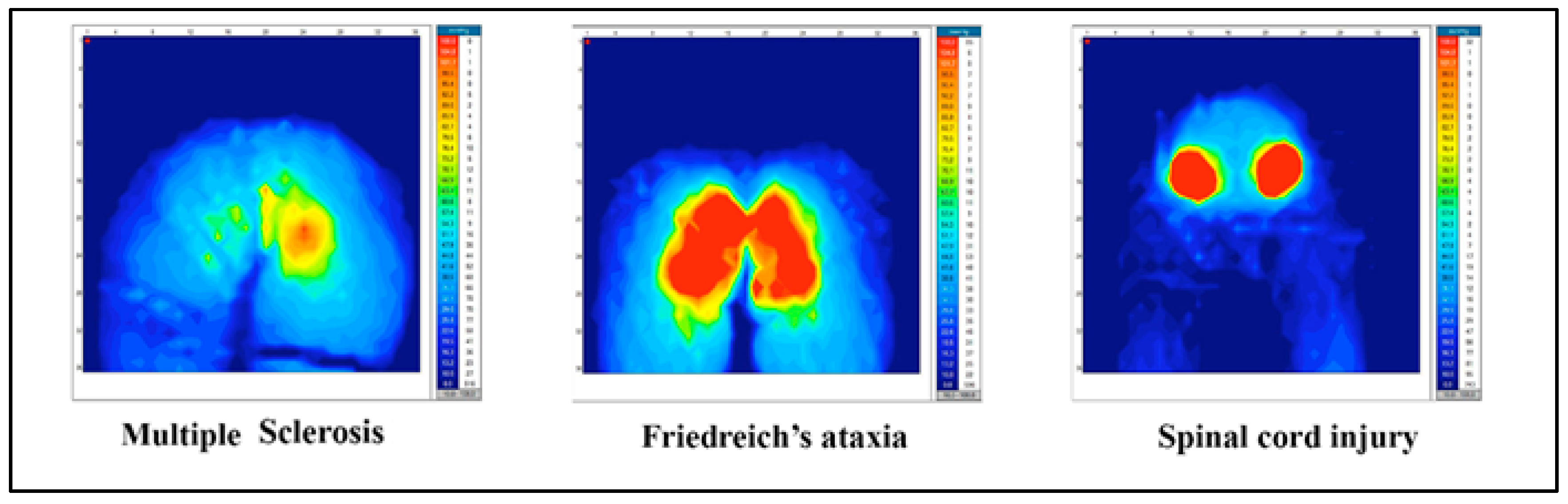
| All (n = 10) | Multiple Sclerosis (n = 2) | Friedreich’s Ataxia (n = 4) | Spinal Cord Injury (n = 4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 49 ± 9.2 | 57 ± 4.2 | 49.3 ± 8.9 | 44.8 ± 10.1 |
| Height (cm) | 168.7 ± 10.7 | 160 ± 11.3 *, &&& | 165.6 ± 7.9 *, ## | 176.3 ± 9.9 &&&, ## |
| Sitting height (cm) | 80 ± 7.3 | 71 ± 0 &&& | 77 ± 3.5 ## | 87.5 ± 2.4 &&&, ## |
| Weight (kg) | 67.8± 11.6 | 61.1 ± 1.3 | 68.1 ± 10.8 | 70.9 ± 15.7 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.4 ± 3.16 | 24 ± 2.8 | 24.7 ± 1.8 | 24.2 ± 4.9 |
| Duration of disease (years) | 20.3 ± 1.2 | 19.5 ± 3.5 *** | 35.2 ± 10 ***, ## | 8.2 ± 4.8 ## |
| Previous ulcers (n) | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 1 ± 0 * | 2 ± 0 * | 1.5 ± 0.6 |
| Current ulcers (n) | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 2 ± 0 | 1.8 ± 0.5 | 1.8 ± 0.5 |
| MMSE (points) | 29.4 ± 4.2 | 29 ± 4.6 | 29.8 ± 0.5 | 28.4 ± 2.6 |
| LRT (cm) | 14.7 ± 11.5 | 6.8 ± 1.8 ** | 24.9 ± 11.9 **, ## | 8.5 ± 4.8 ## |
| FRT (cm) | 24.9 ± 16.9 | 16.5 ± 4.9 ** | 38.7 ± 13.6 **, ## | 15.3 ± 15.4 ## |
| BBS (points) | 10.9 ± 7.7 | 5.5 ± 0.7 & | 9.3 ± 2.9 # | 15.3 ± 11.1 #, & |
| PPAS1 (points) | 9.8 ± 4 | 6 ± 8.5 & | 10.5 ± 3 | 11 ± 2 & |
| PPAS2 (scale) | 5.4 ± 1.2 | 4.5 ± 0.7 | 6 ± 0 | 5.2 ± 1.7 |
| FIST (points) | 35.5 ± 11.8 | 37.5 ± 3.5 | 42.8 ± 1.9 ## | 27.3 ± 15.7 ## |
| TCT (points) | 66.2 ± 24.1 | 55 ± 8.5 **, & | 74.3 ± 20.8 ** | 71.3 ± 33.2 & |
| All (n = 10) | Multiple Sclerosis (n = 2) | Friedreich’s Ataxia (n = 4) | Spinal Cord Injury (n = 4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMEAN (mmHg) | 45.8 ± 6.6 | 41.7 ± 5.7 * | 52.3 ± 3.9 *, ## | 41.3 ± 3.2 ## |
| PMAX (mmHg) | 239.4 ± 33.6 | 204.7 ± 72.6 | 244.5 ± 22.9 | 251.5 ± 8.9 |
| PMIN (mmHg) | 10.2 ± 0.2 | 10.1 ± 0.1 | 10.3 ± 0.2 | 10.1 ± 0.9 |
| A (cm2) | 1095.3 ± 208.5 | 1036.7 ± 310.8 | 1073 ± 106.7 | 1146.9 ± 283.4 |
| Variables Included | Seated Lateral Reach Test | Seated Functional Reach Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | SE | R2 | B | SE | R2 | |
| PMEAN | 1.13 * | 0.471 | 0.25 *** | 1.82 * | 0.637 | 0.29 ** |
| PMAX | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.025 * | 0.08 | 0.175 | 0.26* |
| PMIN | 53.1 ** | 14.788 | 0.32 *** | 82.24 *** | 19.588 | 0.33 *** |
| A | −0.02 | 0.019 | 0.26 ** | −0.02 | 0.028 | 0.26 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reguera-García, M.M.; Leirós-Rodríguez, R.; Álvarez-Barrio, L.; Alonso-Cortés Fradejas, B. Analysis of Postural Control in Sitting by Pressure Mapping in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis, Spinal Cord Injury and Friedreich’s Ataxia: A Case Series Study. Sensors 2020, 20, 6488. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226488
Reguera-García MM, Leirós-Rodríguez R, Álvarez-Barrio L, Alonso-Cortés Fradejas B. Analysis of Postural Control in Sitting by Pressure Mapping in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis, Spinal Cord Injury and Friedreich’s Ataxia: A Case Series Study. Sensors. 2020; 20(22):6488. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226488
Chicago/Turabian StyleReguera-García, María Mercedes, Raquel Leirós-Rodríguez, Lorena Álvarez-Barrio, and Beatriz Alonso-Cortés Fradejas. 2020. "Analysis of Postural Control in Sitting by Pressure Mapping in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis, Spinal Cord Injury and Friedreich’s Ataxia: A Case Series Study" Sensors 20, no. 22: 6488. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226488
APA StyleReguera-García, M. M., Leirós-Rodríguez, R., Álvarez-Barrio, L., & Alonso-Cortés Fradejas, B. (2020). Analysis of Postural Control in Sitting by Pressure Mapping in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis, Spinal Cord Injury and Friedreich’s Ataxia: A Case Series Study. Sensors, 20(22), 6488. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20226488








