Design and Evaluation of LYSO/SiPM LIGHTENING PET Detector with DTI Sampling Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
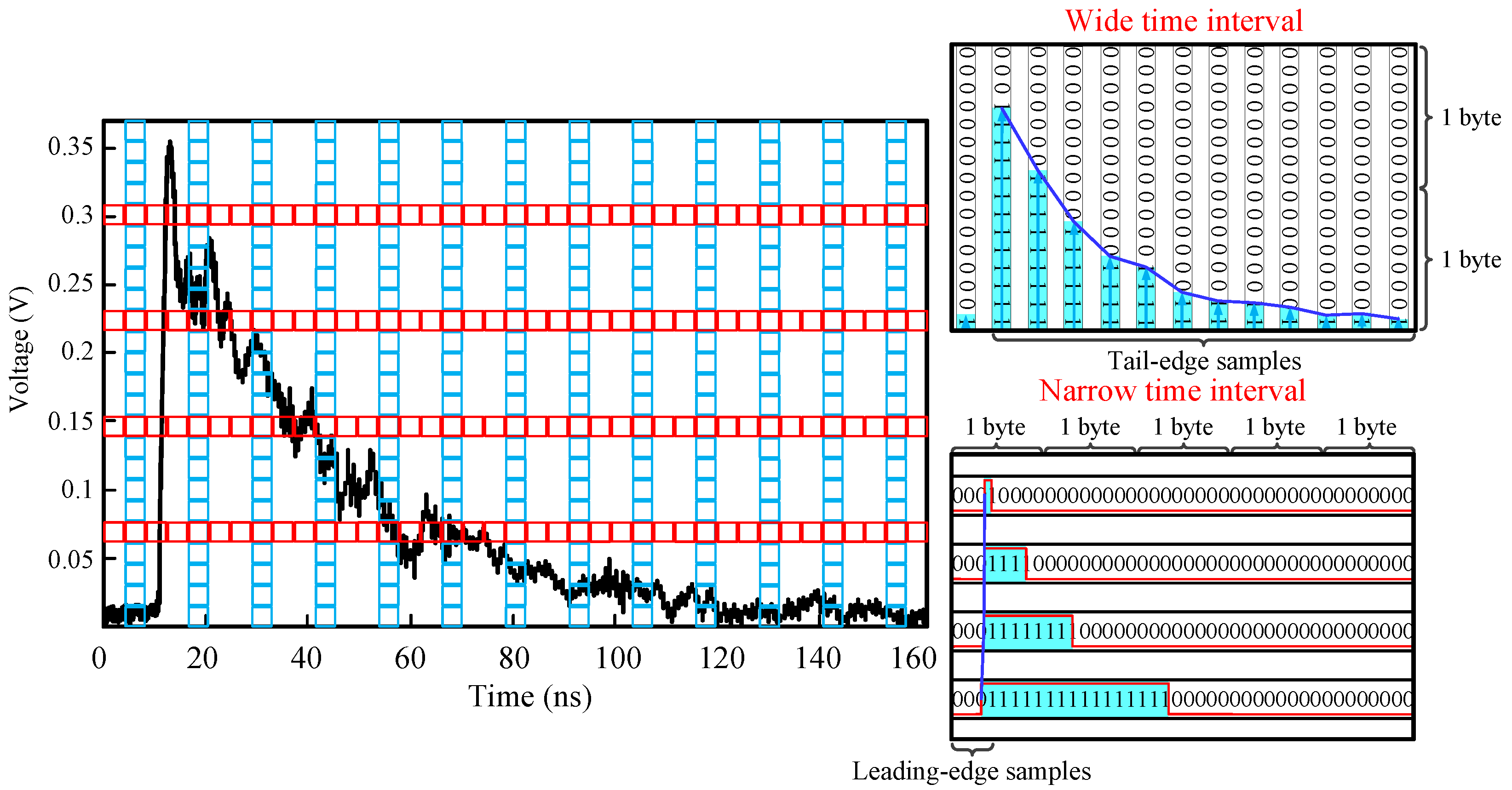
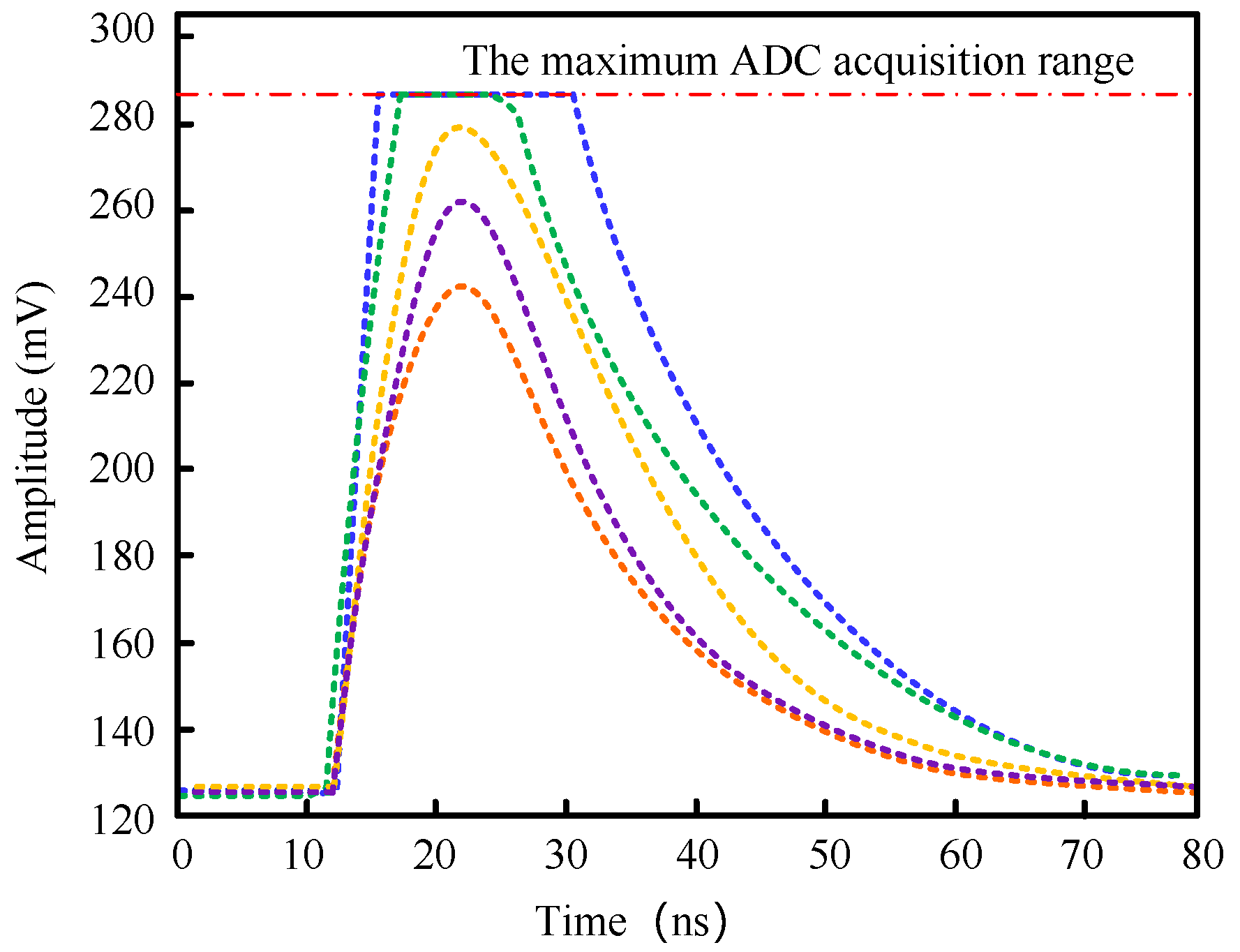
- A novel sampling method related to the dual time interval (DTI) method is presented. The method uses a narrow time interval to sample the fast leading edge by employing a few discriminators with programmable voltage thresholds to determine the time points when the scintillation pulse crosses the set thresholds. The wide time interval used to sample the tail edge of the scintillation pulse employs a conventional analog-to-digital (AD) chip. The method effectively realizes the sampling of fast scintillation pulses while significantly reducing the hardware cost.
- (2)
- A multiplexing method was designed to multiplex the fast output by symmetric charge division (SCD) circuit and multiplex standard output via a signal driven multiplexing (SDM) circuit. The number of readout channels and the complexity of subsequent acquisition circuits are greatly reduced with the multiplex circuit.
- (3)
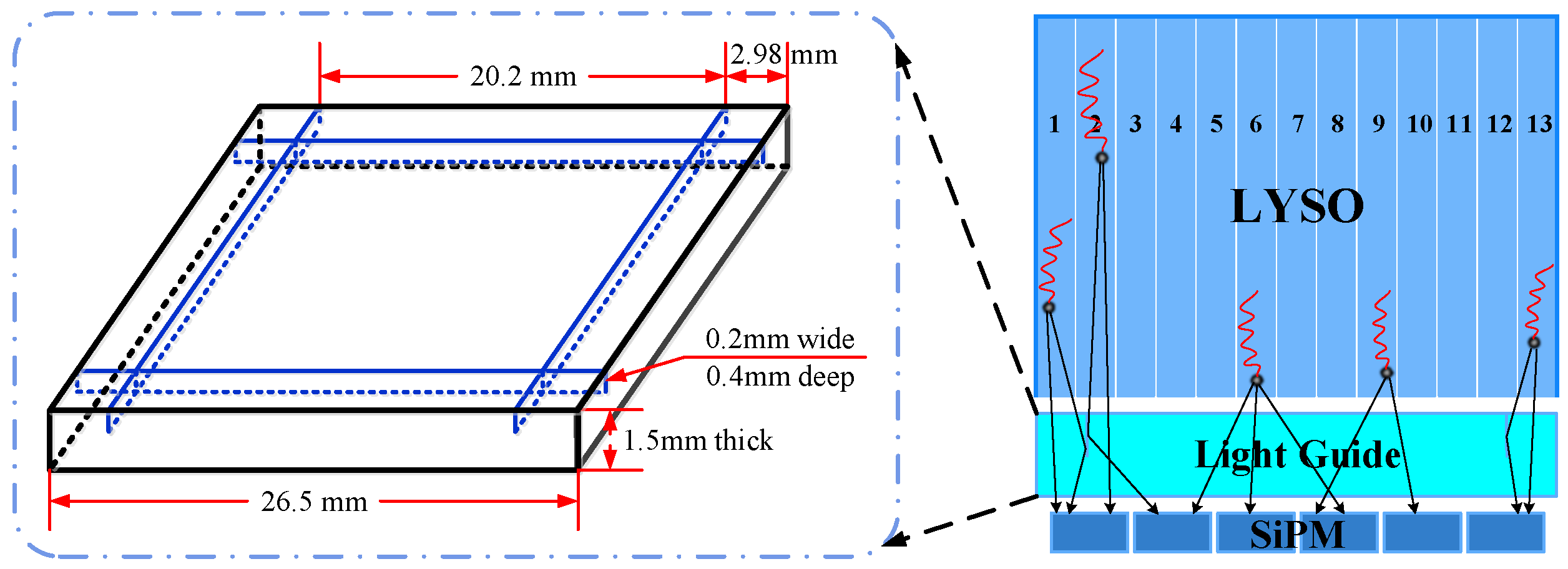
- A semi-cut light guide with a gap cut in the middle of the second crystal pixel at the edge was designed, and it enhanced the resolution ability of crystal pixels on the edge of the crystal array significantly.
- (4)
- A gain adaptive method based on adjustable resistance is proposed to minimize the gain difference of different SiPM channels and improve the uniformity of the flood histogram.
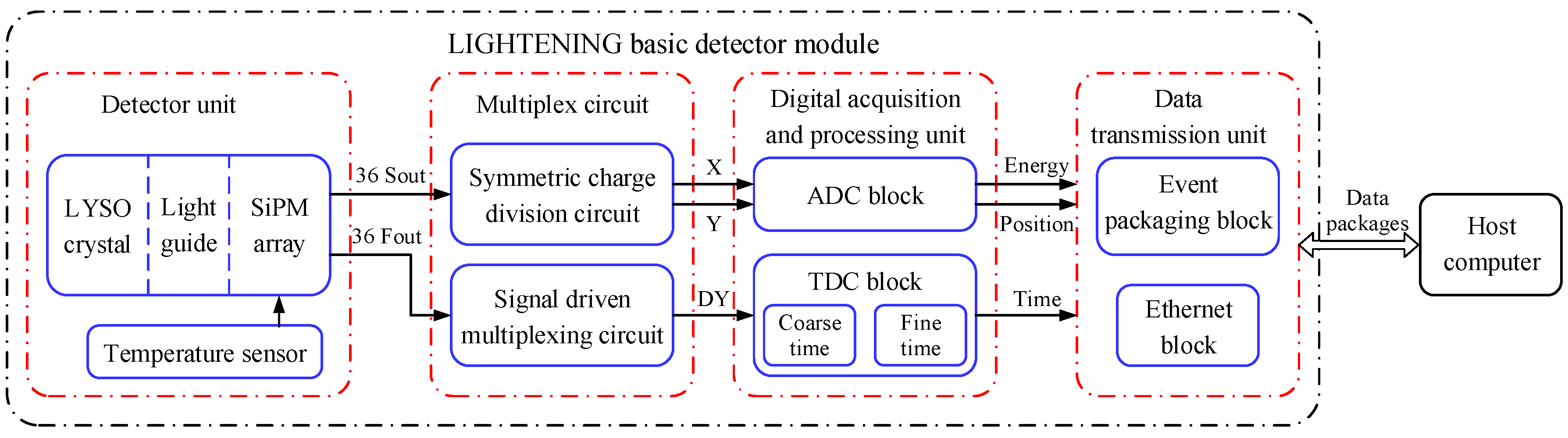
2. Detector Design and Data Processing Method
2.1. General Description
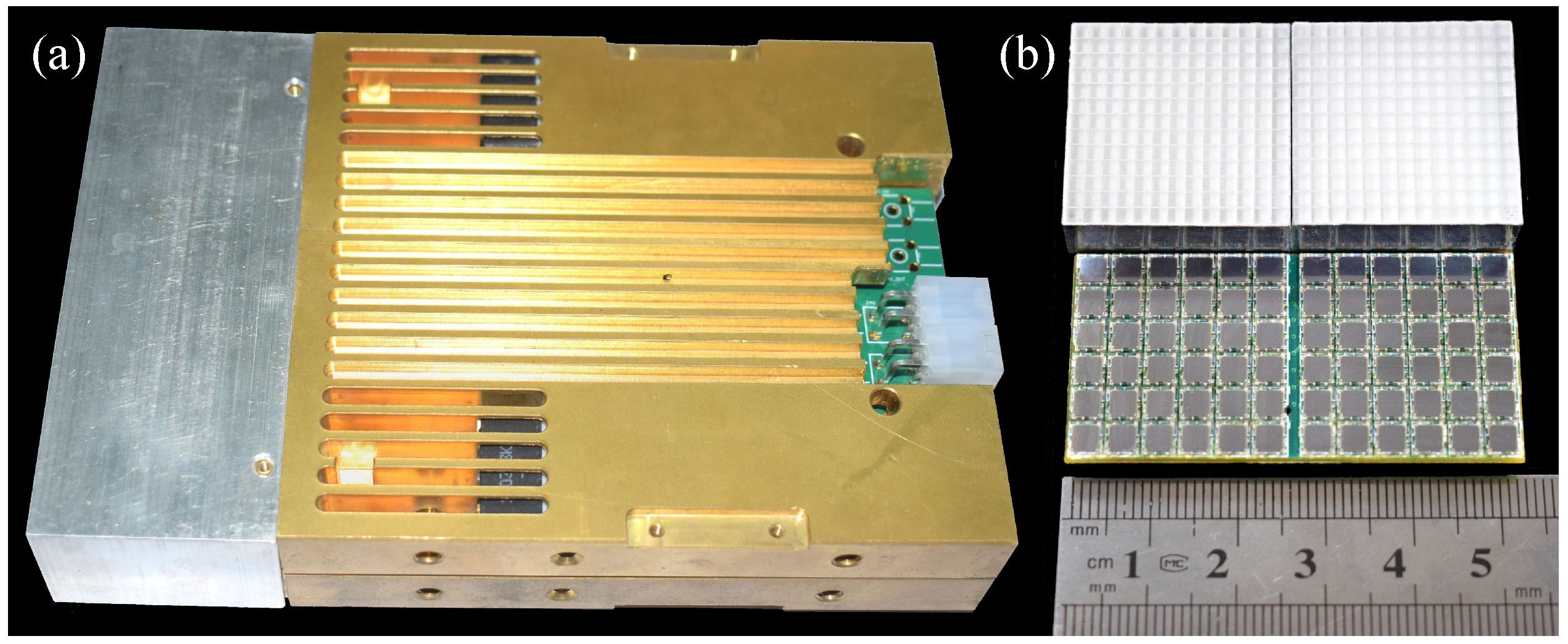
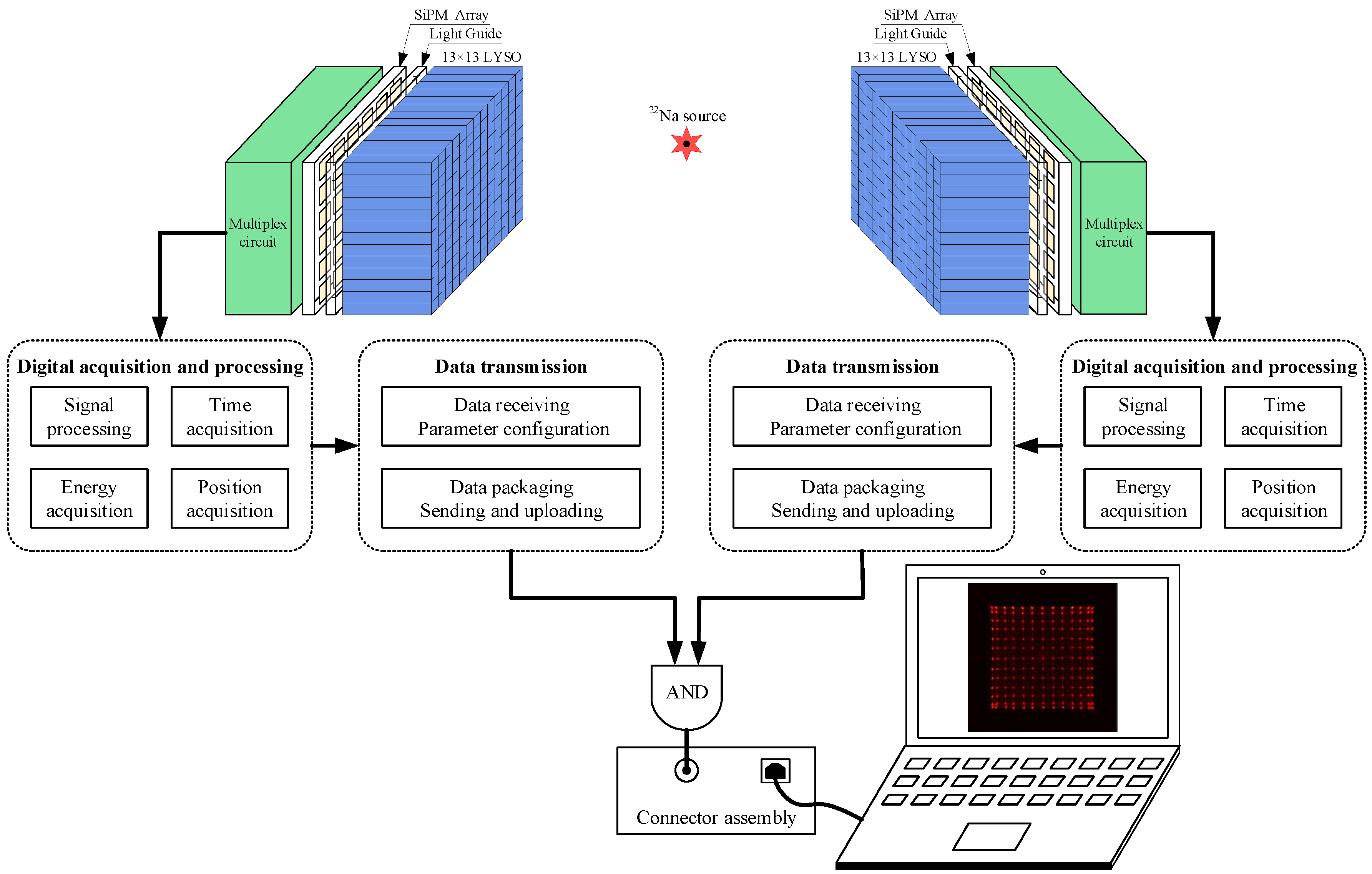
2.2. The Detector Unit
2.3. Multiplex Circuit
2.4. The Digital Acquisition and Processing Unit
2.5. The Data Transmission Unit
3. Experiment and Results
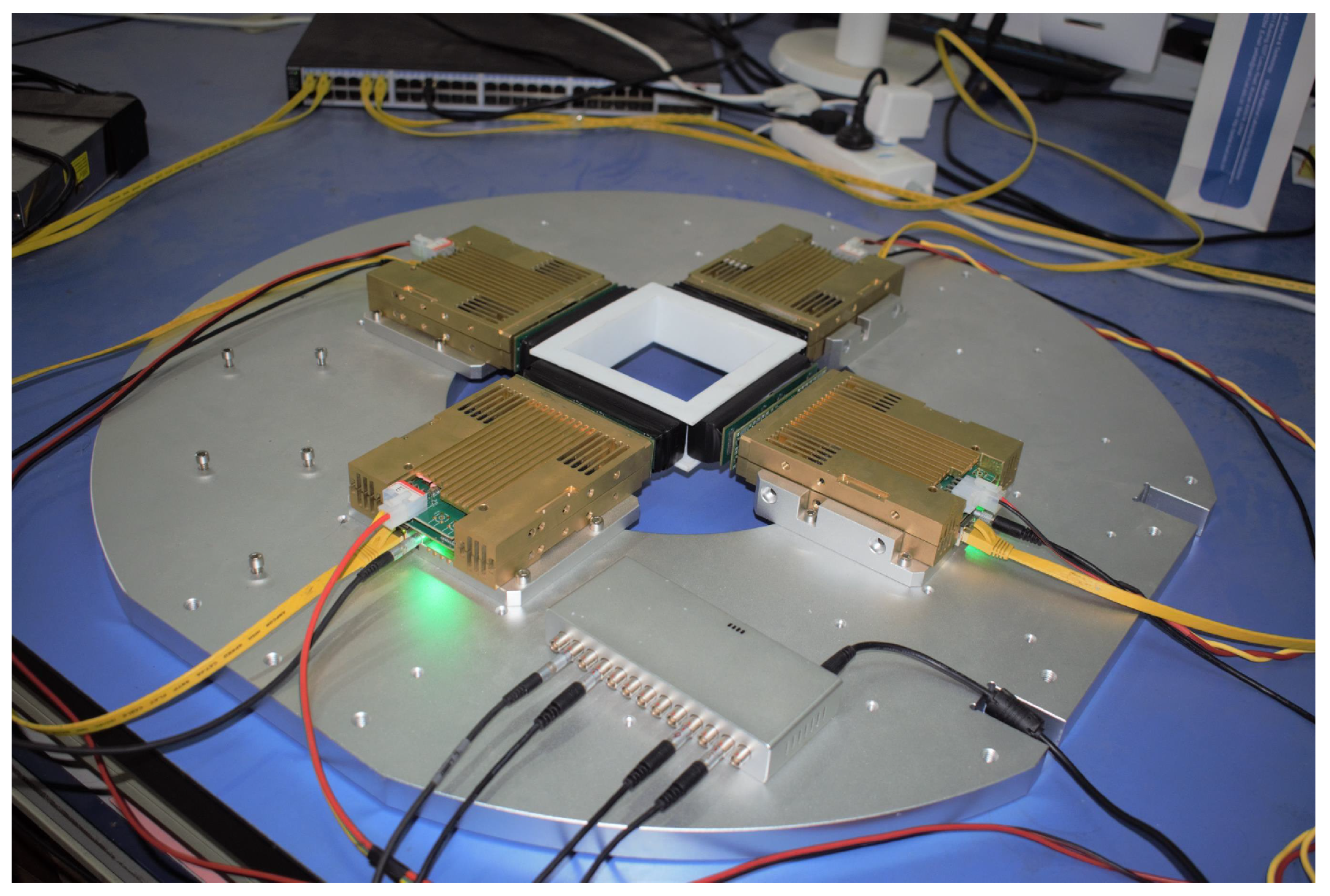
3.1. Experiment Setup
3.2. Flood Histogram and Spatial Resolution
3.3. Energy Resolution
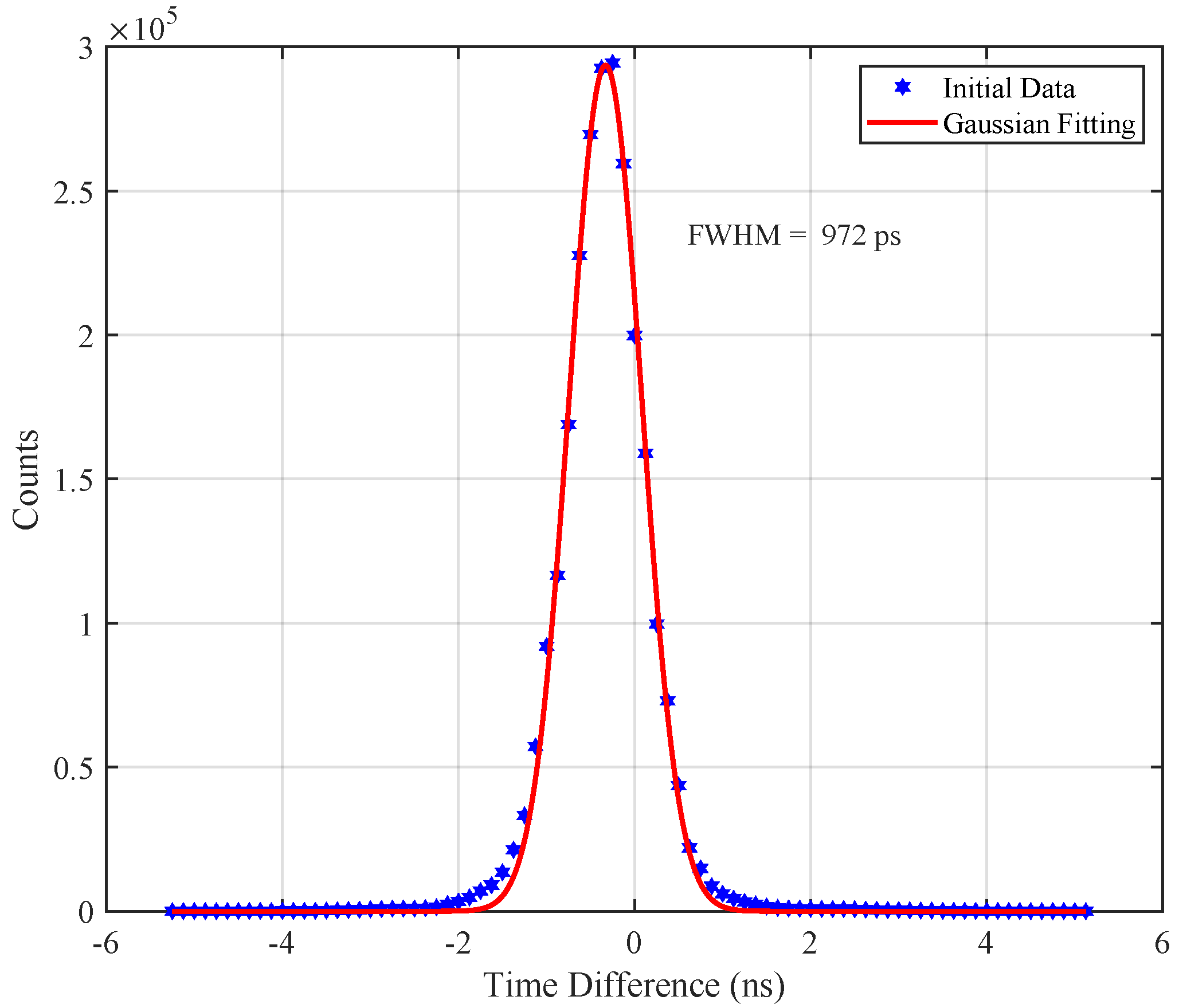
3.4. Timing Resolution
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Badawi, R.D.; Shi, H.; Hu, P.; Chen, S.; Xu, T.; Price, P.M.; Ding, Y.; Spencer, B.A.; Nardo, L.; Liu, W.; et al. First human imaging studies with the explorer total-body PET scanner. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- States, L.J.; Reid, J.R. Whole-body PET/MRI applications in pediatric oncology. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horst, F.; Adi, W.; Aricò, G.; Brinkmann, K.T.; Durante, M.; Reidel, C.A.; Rovituso, M.; Weber, U.; Zaunick, H.G.; Zink, K.; et al. Measurement of PET isotope production cross sections for protons and carbon ions on carbon and oxygen targets for applications in particle therapy range verification. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Hu, P.C.; Wu, R.Z.; Gu, Y.S.; Chen, S.G.; Yu, H.J.; Wang, X.Q.; Song, J.; Shi, H.C. The image quality, lesion detectability, and acquisition time of 18F-FDG total-body PET/CT in oncological patientss. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, C.J.; Goertzen, A.L.; Thiessen, J.D.; Bishop, D.; Stortz, G.; Kozlowski, P.; Retière, F.; Zhang, X.; Sossi, V. Development of a PET scanner for simultaneously imaging small animals with MRI and PET. Sensors 2014, 14, 14654–14671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.G.; Takyu, S.; Fumihiko, N.; Yamaya, T. A staggered three-layer DOI PET detector with a 1 mm crystal pitch for a high resolution small animal PET imaging. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 529. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, A.; Schramm, G.; Laere, K.V.; Nuyts, J. Estimation of crystal timing properties and efficiencies for the improvement of (Joint) maximum-likelihood reconstructions in TOF-PET. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2020, 39, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundacker, S.; Turtos, R.M.; Kratochwil, N.; Pots, R.H.; Paganoni, M.; Lecoq, P.; Auffray, E. Experimental time resolution limits of modern SiPMs and TOF-PET detectors exploring different scintillators and Cherenkov emission. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 025001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundacker, S.; Turtos, R.M.; Auffray, E.; Paganoni, M.; Lecoq, P. High-frequency SiPM readout advances measured coincidence time resolution limits in TOF-PET. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 055012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Watabe, H.; Kanai, Y.; Kato, K.; Hatazawa, J. Development of a high resolution YSO gamma camera system employing less than 1 mm pixels. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 2157. [Google Scholar]
- Godinez, F.; Chaudhari, A.J.; Yang, Y.; Farrell, R.; Badaw, R.D. Characterization of a high-resolution hybrid DOI detector for a dedicated breast PET/CT scanner. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 3435–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishnamoorthy, S.; LeGeyt, B.; Werner, M.E.; Kaul, M.; Newcomer, F.M.; Karp, J.S.; Surti, S. Design and performance of a high spatial resolution, time-of-flight PET detector. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2014, 61, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.; Chalich, Y.; Deen, M.J. Sensors for positron emission tomography applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pizzichemi, M.; Polesel, A.; Stringhini, G.; Gundacker, S.; Lecoq, P.; Tavernier, S.; Paganoni, M.; Auffray, E. On light sharing TOF-PET modules with depth of interaction and 157 ps FWHM coincidence time resolution. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 155008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zang, J.; Sui, H.; Wang, R.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Z. Evaluation of a novel brain PET scanner consisted of LYSO scintillation detectors and Silicon photomultipliers. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 143. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, D.F.C.; Ilan, E.; Peterson, W.T.; Uribe, J.; Lubberink, M.; Levin, C.S. Studies of a next-generation silicon-photomultiplier–based time-of-flight PET/CT system. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1511–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Q.; Wang, L.; Kuang, J.; Xiao, Y. Comparison of three pre-amplifier circuits for time readout of SiPM in TOF-PET detectors. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Sapporo, Japan, 26–29 May 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rosado, J. Modeling the nonlinear response of silicon photomultipliers. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 12031–12039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanzaro, M.; Signorelli, F.; Gattari, P.; Tosi, A.; Zappa, F. 0.16 μm-BCD silicon photomultipliers with sharp timing response and reduced correlated noise. Sensors 2018, 18, 3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orive-Miguel, D.; Sieno, L.D.; Behera, A.; Ferocino, E.; Contini, D.; Condat, L.; Hervé, L.; Mars, J.; Torricelli, A.; Pifferi, A.; et al. Real-time dual-wavelength time-resolved diffuse optical tomography system for functional brain imaging based on probe-hosted silicon photomultipliers. Sensors 2020, 20, 2815–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.I.; Roncali, E.; Gola, A.; Paternoster, G.; Piemonte, C.; Cherry, S.R. Dual-ended readout of bismuth germanate to improve timing resolution in time-of-flight PET. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Wu, H.; Luo, J.; Deng, Z.; Ge, C.; Chen, C.; Jiang, X.; Yin, W.-J.; Niu, G.; Zhu, L.; et al. Cs2AgBiBr6 single-crystal X-ray detectors with a low detection limit. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundacker, S.; Auffray, E.; Pauwels, K.; Lecoq, P. Measurement of intrinsic rise times for various L(Y)SO and LuAG scintillators with a general study of prompt photons to achieve 10 ps in TOF-PET. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, 2802–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malberti, M. Precision timing with LYSO: Ce crystals and SiPM sensors in the CMS MTD barrel timing layer. J. Inst. 2020, 15, C04014. [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, A.; Gola, A.; Serra, N.; Tarolli, A.; Zorzi, N.; Piemonte, C. Performance of FBK high-density SiPM technology coupled to Ce:LYSO and Ce:GAGG for TOF-PET. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 54, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackberg, L.; Sajedi, S.; Fakhri, G.E.; Sabet, H. Novel staggered scintillator configurations for brain TOF-DOI PET detector. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 386. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, F.R.; Shimazoe, K.; Somlai-Schweiger, I.; Ziegler, S.I. A PET detector prototype based on digital SiPMs and GAGG scintillators. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 045008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groll, A.; Levin, C.S. Analysis of data corrections for the first-generation radiofrequency-penetrable PET insert for simultaneous PET/MR. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC), Manchester, UK, 26 October 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Selfridge, A.; Cherry, S.; Badawi, R. Characterization of four readout circuits for an MR compatible, preclinical PET detector. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 125008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Kuang, Z.; Sang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Du, J. Performance comparison of two signal multiplexing readouts for SiPM-based pet detector. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 023NT02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parka, H.; Lee, J.S. Highly multiplexed SiPM signal readout for brain-dedicated TOF-DOI PET detectors. Phys. Medica 2019, 68, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Choi, Y.; Jung, J.H.; Jung, J.; Kim, K.B.; Choe, H.j.; Leem, H.T.; Lee, H.; Huh, Y.M. Performance evaluation of a small animal PET scanner a high level of multiplexing and charge-signal transmission. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 045015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Wang, S.; Wei, Q.; Liu, W.; Gong, G.; Deng, Z.; Ma, T.; Liu, Y. Development of multi-channel fast SiPM readout electronics for clinical TOF PET detector. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, 3517–3519. [Google Scholar]
- Melroy, S.; Bauer, C.; McHugh, M.; Carden, G.; Stolin, A.; Majewski, S.; Brefczynski-Lewis, J.; Wuest, T. Development and design of next-generation head-mounted ambulatory microdose positron-emission tomography (AM-PET) system. Sensors 2017, 17, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ascenzo, N.D.; Gao, M.; Antonecchia, E.; Gnudi, P.; Chen, H.H.; Chen, F.H.; Hong, J.H.; Hsiao, I.T.; Yen, T.C.; Wang, W.; et al. New digital plug and imaging sensor for a proton therapy monitoring system based on positron emission tomography. Sensors 2018, 18, 3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poladyan, H.; Buban, O.; Senchurov, S.; Teymurazyan, A.; Reznik, A. Improved coordinate reconstruction for SiPM based gamma detector with pixelated scintillating crystal and multiplexed readout. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference Proceedings (NSS/MIC), Sydney, Australia, 10–17 November 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Bai, X.; Liu, C.C.; Qi, J.; Cherry, S.R. Design and evaluation of gapless curved scintillator arrays for simultaneous high-resolution and high-sensitivity brain PET. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 235004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.B.; Kang, H.G.; Song, S.H.; Ko, G.B.; Lee, J.S.; Hong, S.J. SiPM-based dual-ended-readout DOI-TOF PET module based on mean-time method. J. Inst. 2019, 14, P02023. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.; Ma, T.; Jiang, N.; Xu, T.; Lyu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y. A side-by-side LYSO/GAGG phoswich detector aiming for SPECT imaging. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2020, 953, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Z.; Wang, X.; Fu, X.; Ren, N.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, C.; Wu, S.; Sang, Z.; Hu, Z.; et al. Dual-ended readout small animal PET detector by using 0.5 mm pixelated LYSO crystal arrays and SiPMs. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2020, 917, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiFilippo, F.P. Enhanced PET resolution by combining pinhole collimation and coincidence detection. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 7969–7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.W. Fundamental limits of spatial resolution in PET. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2011, 648, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LaBella, A.; Cao, X.; Petersen, E.; Lubinsky, R.; Biegon, A.; Zhao, W.; Goldan, A.H. High resolution depth-encoding PET detector module with prismatoid light guide array. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 2573–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.Y.; Wu, H.; Komarov, S.; Siegel, S.B.; Tai, Y.C. A sub-millimeter resolution PET detector module using a multi-pixel photon counter array. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 2573–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pichler, B.J.; Swann, B.K.; Rochelle, J.; Nutt, R.E.; Cherry, S.R.; Siegel, S.B. Lutetium oxyorthosilicate block detector readout by avalanche photodiode arrays for high resolution animal PET. Phys. Med. Biol. 2004, 49, 4305–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
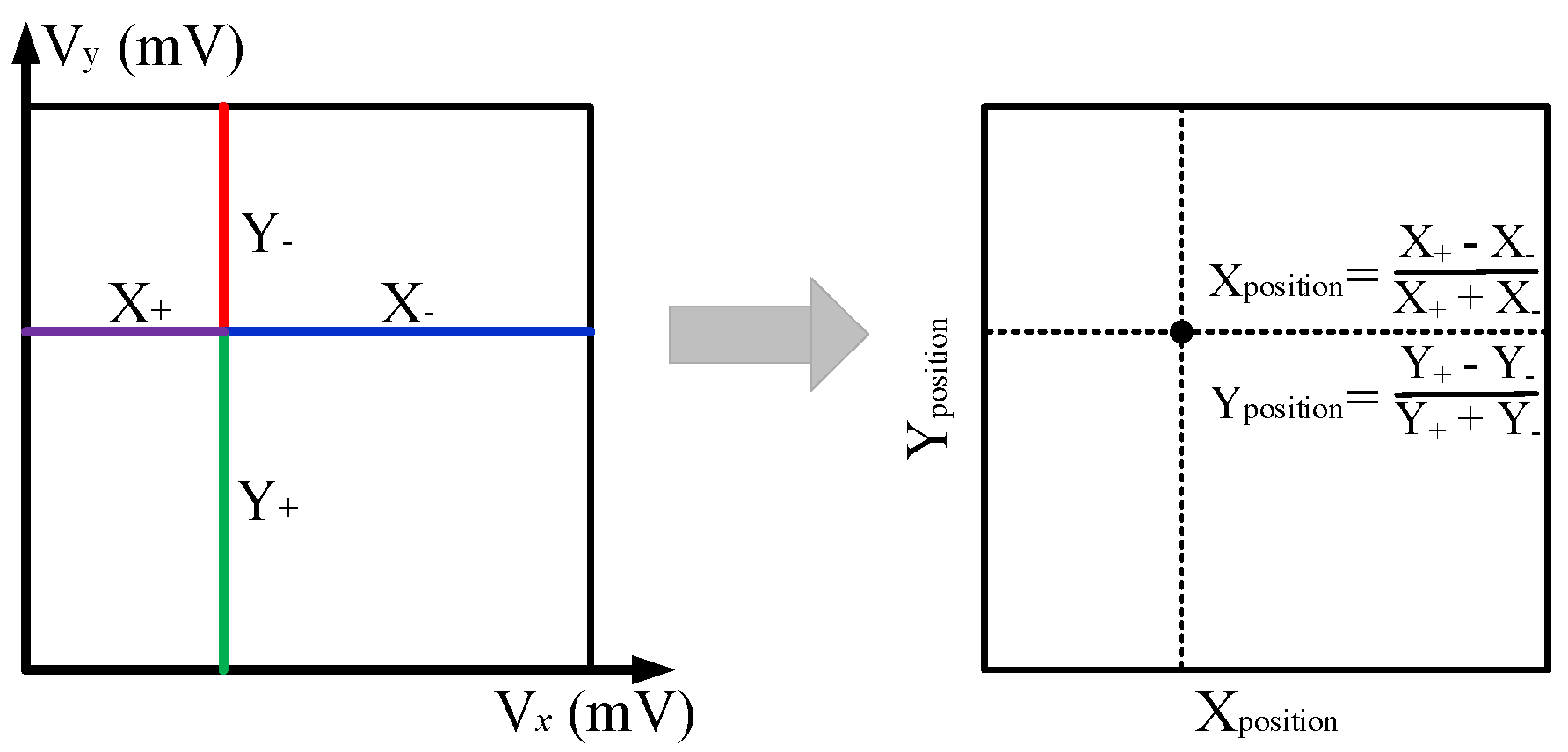
- Siegel, S.; Silverman, R.; Shao, Y.; Cherry, S.R. Simple charge division readouts for imaging scintillator arrays using a multi-channel PMT. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1996, 43, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poladyan, H.; Bubon, O.; Teymurazyan, A.; Senchurov, S.; Reznik, A. Gaussian position-weighted center of gravity algorithm for multiplexed readout. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 165003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poladyan, H.; Bubon, O.; Teymurazyan, A.; Senchurov, S.; Reznik, A. Gain invariant coordinate reconstruction for SiPM-based pixelated gamma detectors with multiplexed readout. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 69, 4281–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



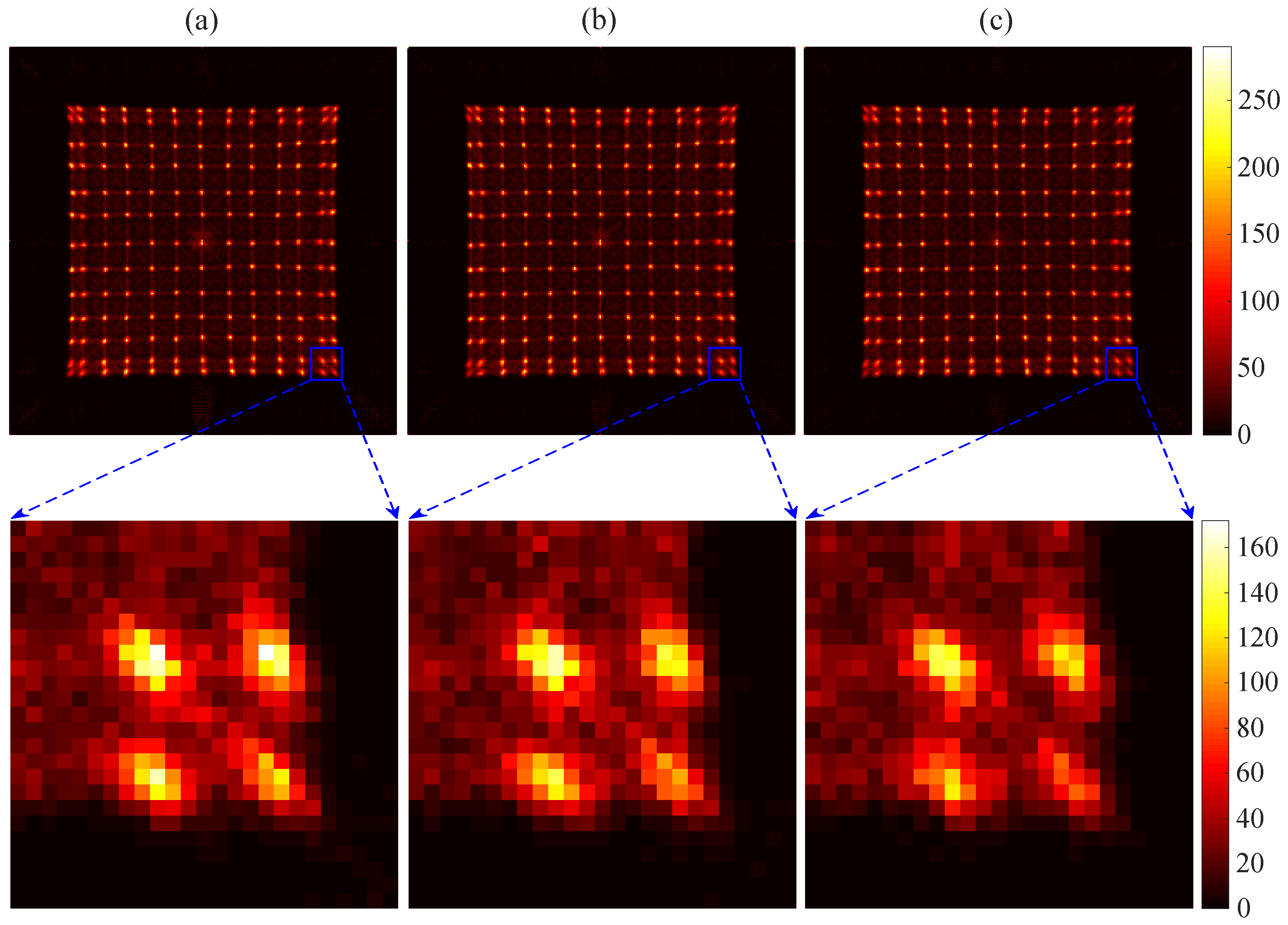

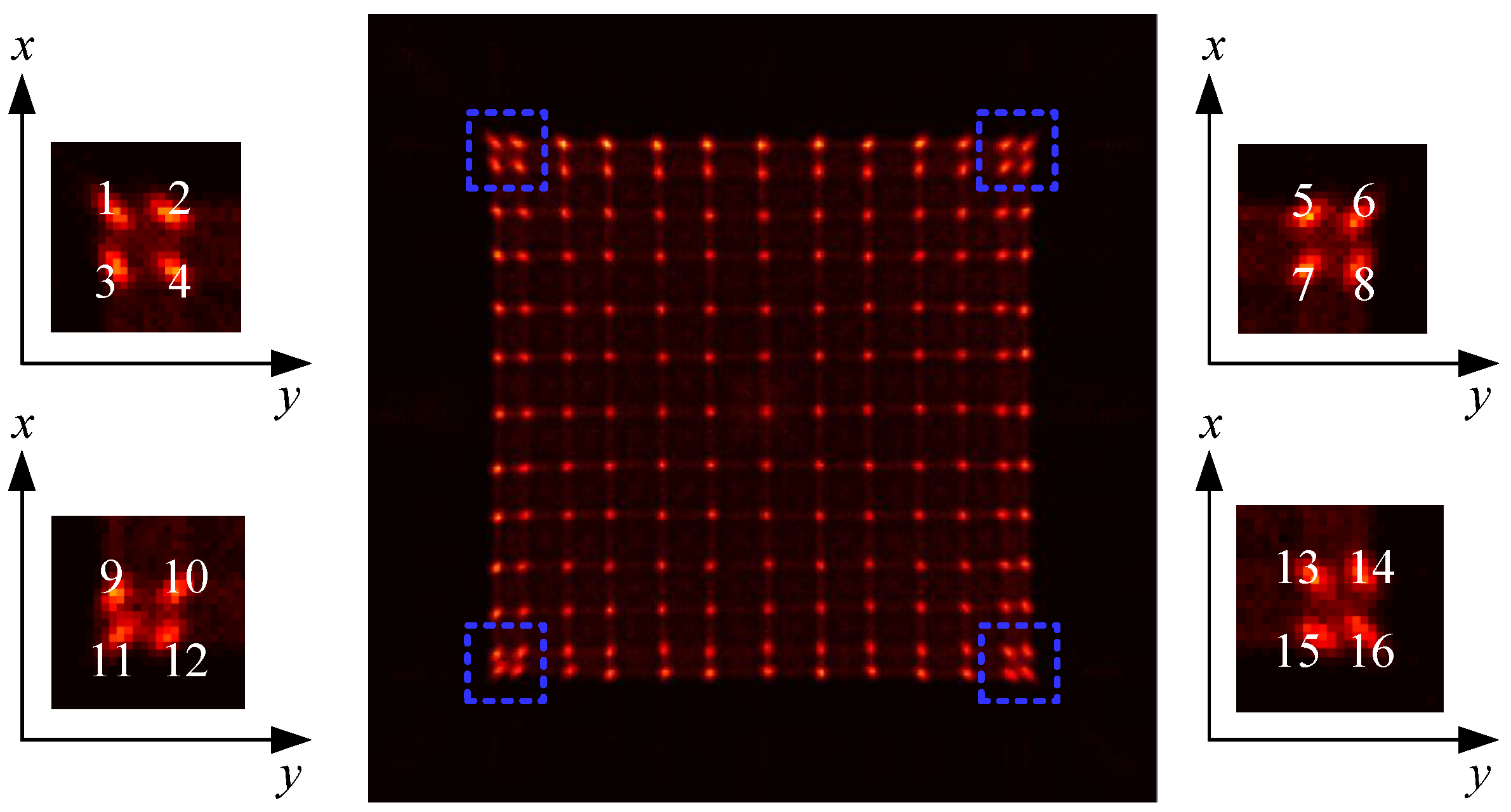
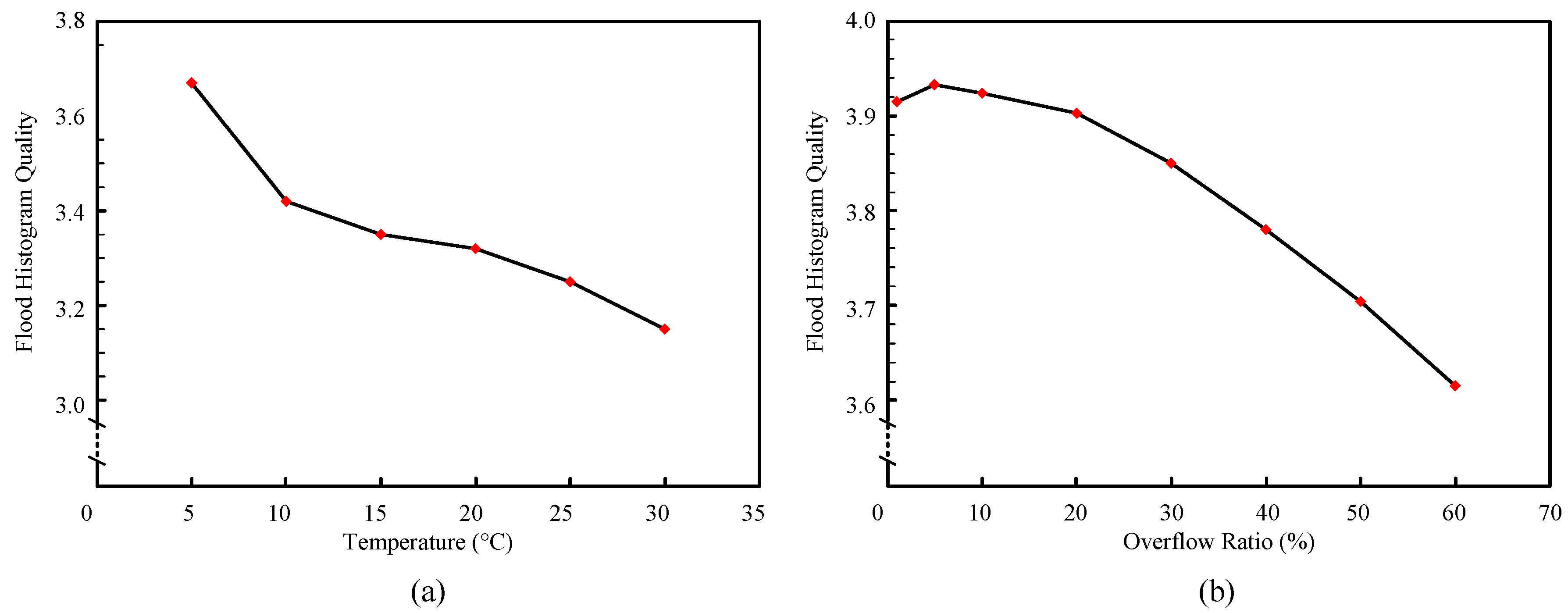

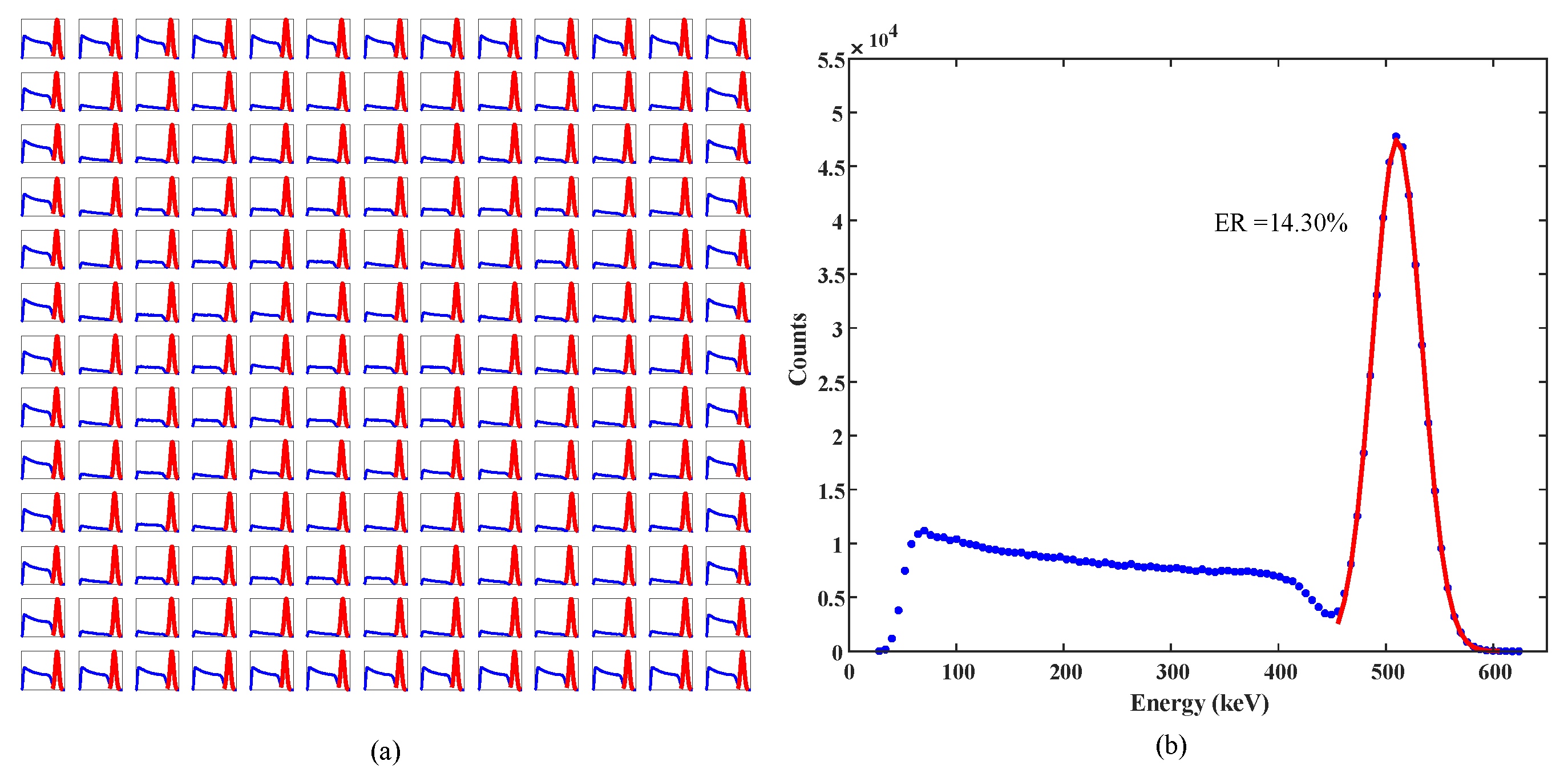
| Crystal Array | SiPM Array | ER | CTR | SR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOF-PET detector [33] | 12 × 12 | 8 × 8 | 15.6% | 514 ps | / |
| head-mounted micro-dose PET [34] | 32 × 32 | 10 × 10 | / | / | 2–3 mm |
| proton therapy monitoring system [35] | 6 × 6 | 6 × 6 | 24% | / | 3 mm |
| small-scale PET system [36] | 24 × 24 | 8 × 8 | 13.9% | / | / |
| proof-of-concept detector [37] | 8 × 4 | 8 × 4 | 14.6% | 495 ps | 2.77 mm |
| DOI-TOF PET module [38] | 6 × 6 | 4 × 4 | 11.7% | 349 ps | 3.5 mm |
| side-by-side phoswich detector [39] | 12 × 12 | 8 × 8 | 15.6% | / | 1.35 mm |
| Dual-ended readout PET detector [40] | 17 × 17 | 4 × 4 | 21.0% | 1230 ps | 0.5 mm |
| Category | Characteristics | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal | Crystal material | LYSO |
| Block | Crystal size (mm) | 1.92 × 1.92 × 13.00 |
| Crystal pitch (mm) | 2.02 × 2.02 | |
| Crystal array | 13 × 13 | |
| BDM | LYSO/SiPM block | 1 × 4 |
| LYSO Dimension (mm) | 26.5 × 106.0 × 13.0 | |
| Scanner | Number of BDMs | 4 |
| Number of crystal pixels | 2704 | |
| Bore diameter (cm) | 15.0 | |
| Transaxial field-of-view (TFOV) (cm) | 10.6 | |
| Axial field-of-view (AFOV) (cm) | 2.65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, Z.; Deng, Y.; Chen, G. Design and Evaluation of LYSO/SiPM LIGHTENING PET Detector with DTI Sampling Method. Sensors 2020, 20, 5820. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20205820
Deng Z, Deng Y, Chen G. Design and Evaluation of LYSO/SiPM LIGHTENING PET Detector with DTI Sampling Method. Sensors. 2020; 20(20):5820. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20205820
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Zhenzhou, Yushan Deng, and Guandong Chen. 2020. "Design and Evaluation of LYSO/SiPM LIGHTENING PET Detector with DTI Sampling Method" Sensors 20, no. 20: 5820. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20205820
APA StyleDeng, Z., Deng, Y., & Chen, G. (2020). Design and Evaluation of LYSO/SiPM LIGHTENING PET Detector with DTI Sampling Method. Sensors, 20(20), 5820. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20205820





