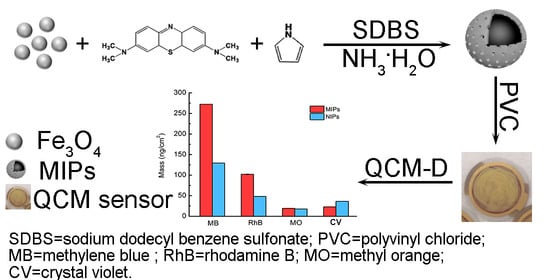
Magnetic Imprinted Polymer-Based Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor for Sensitive Label-Free Detection of Methylene Blue in Groundwater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Instrumentation
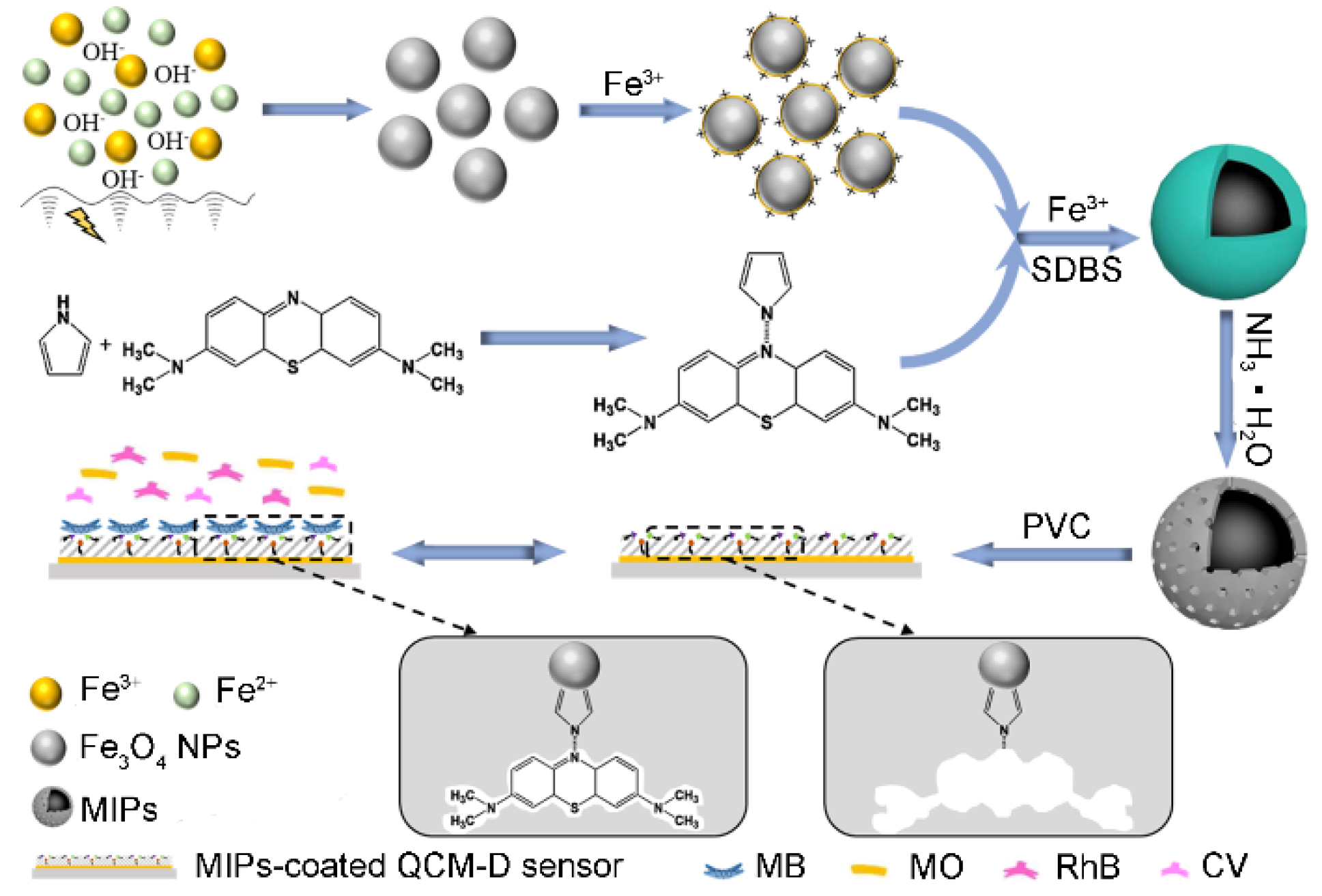
2.3. Preparation of MIPs
2.4. Binding Experiments
2.5. Immobilization of MIPs on QCM-D Sensors
2.6. Preparation of Water Samples
2.7. QCM-D Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
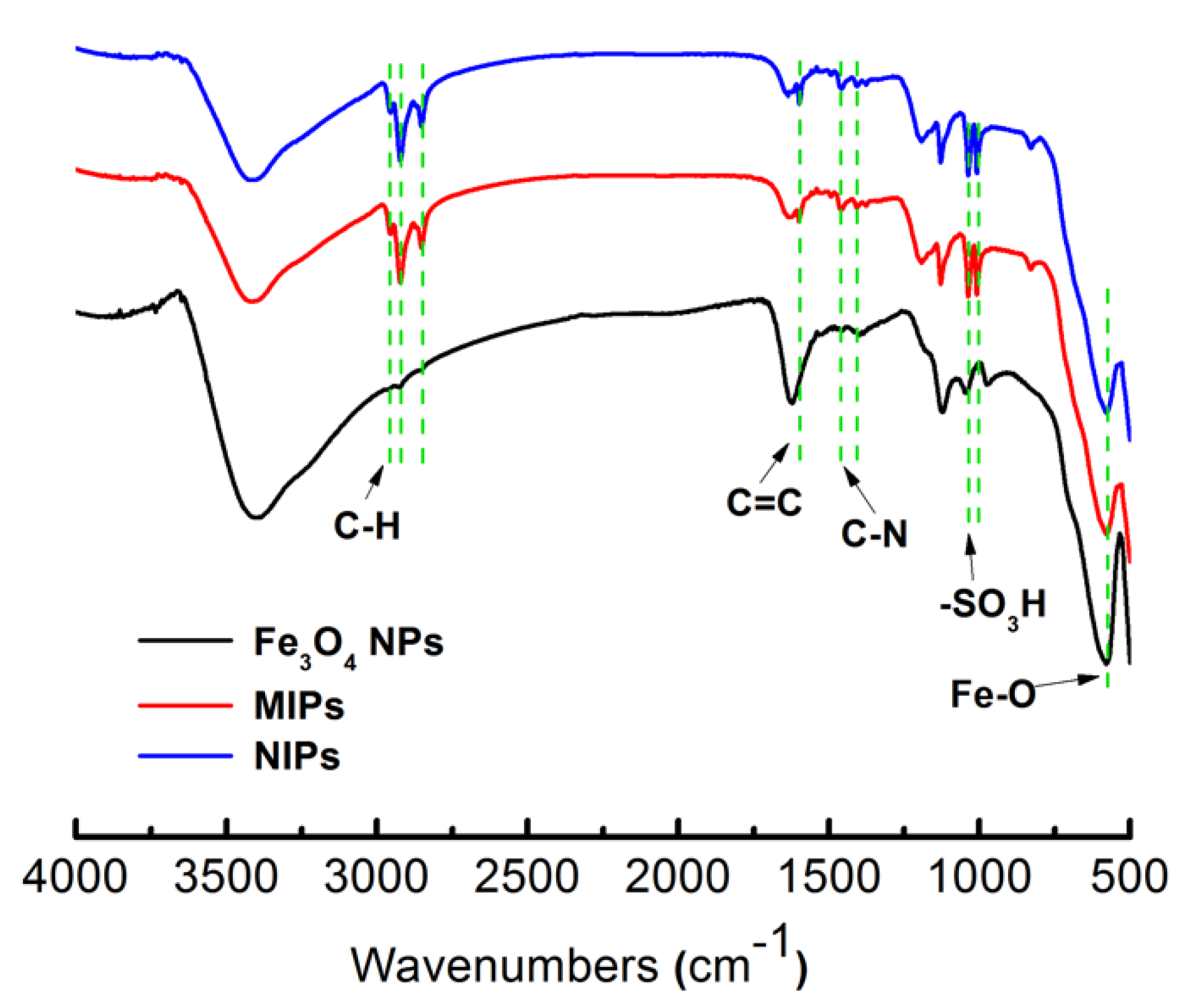
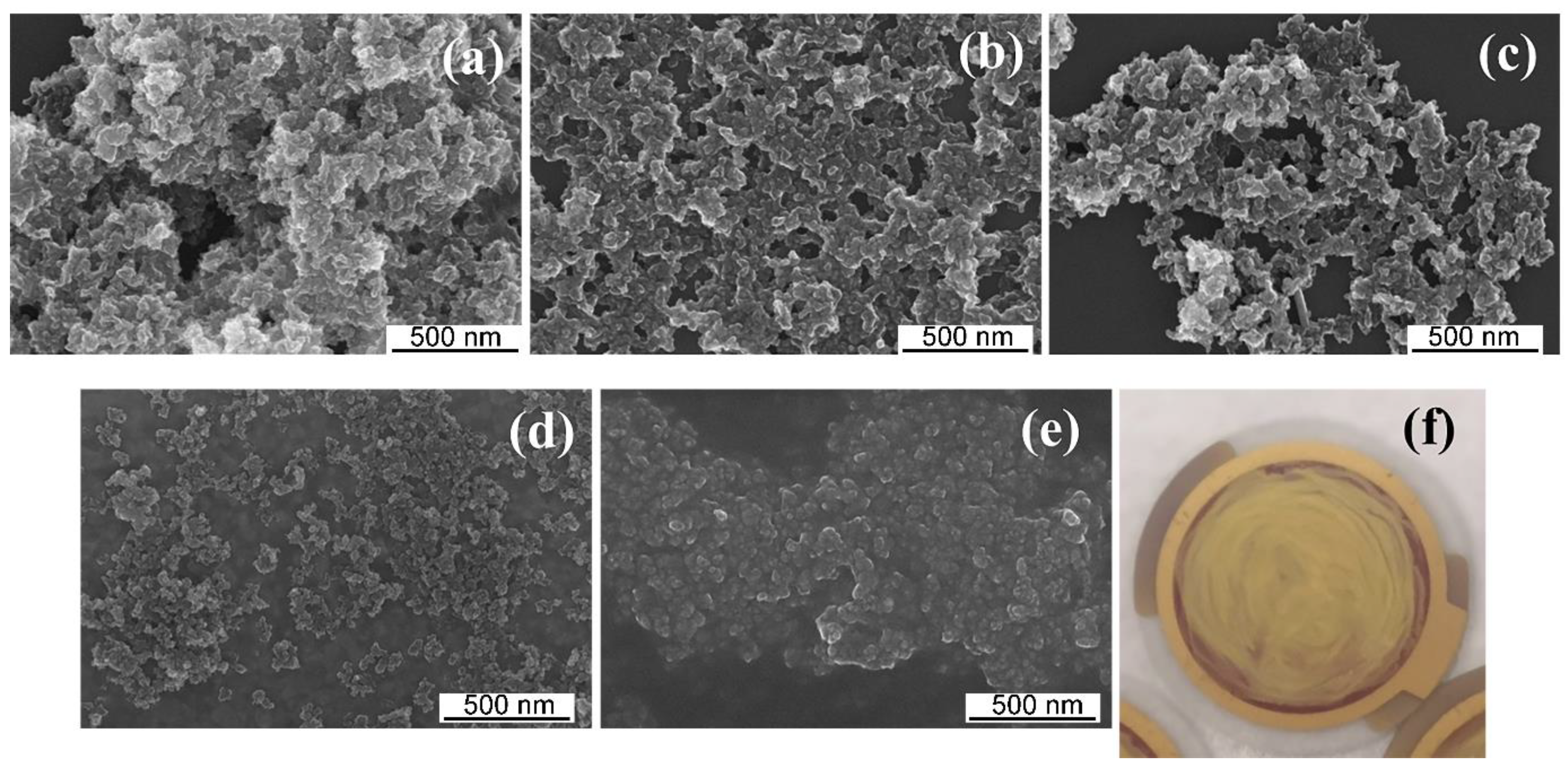
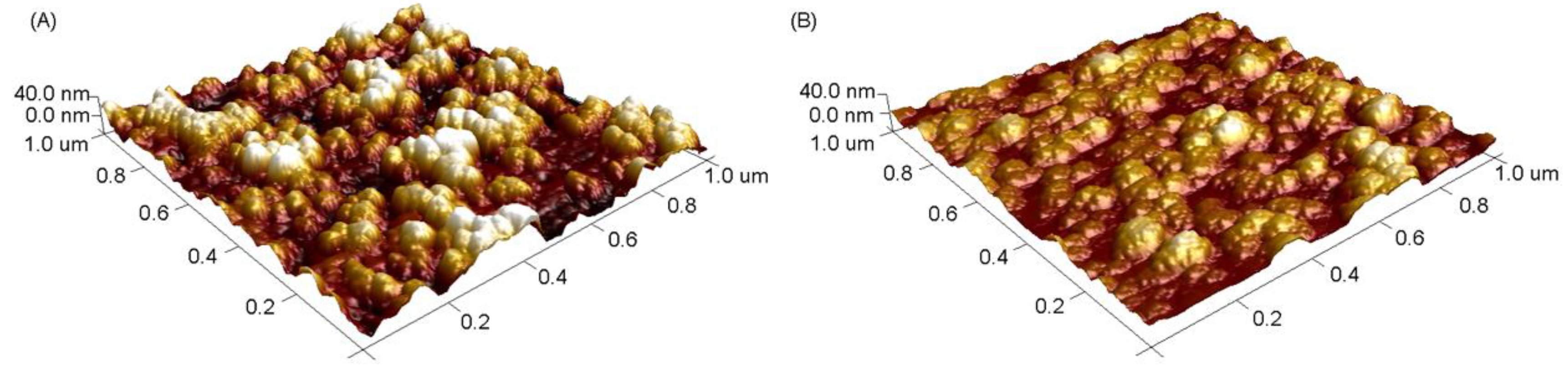
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of the MIPs-Coated QCM-D Sensors
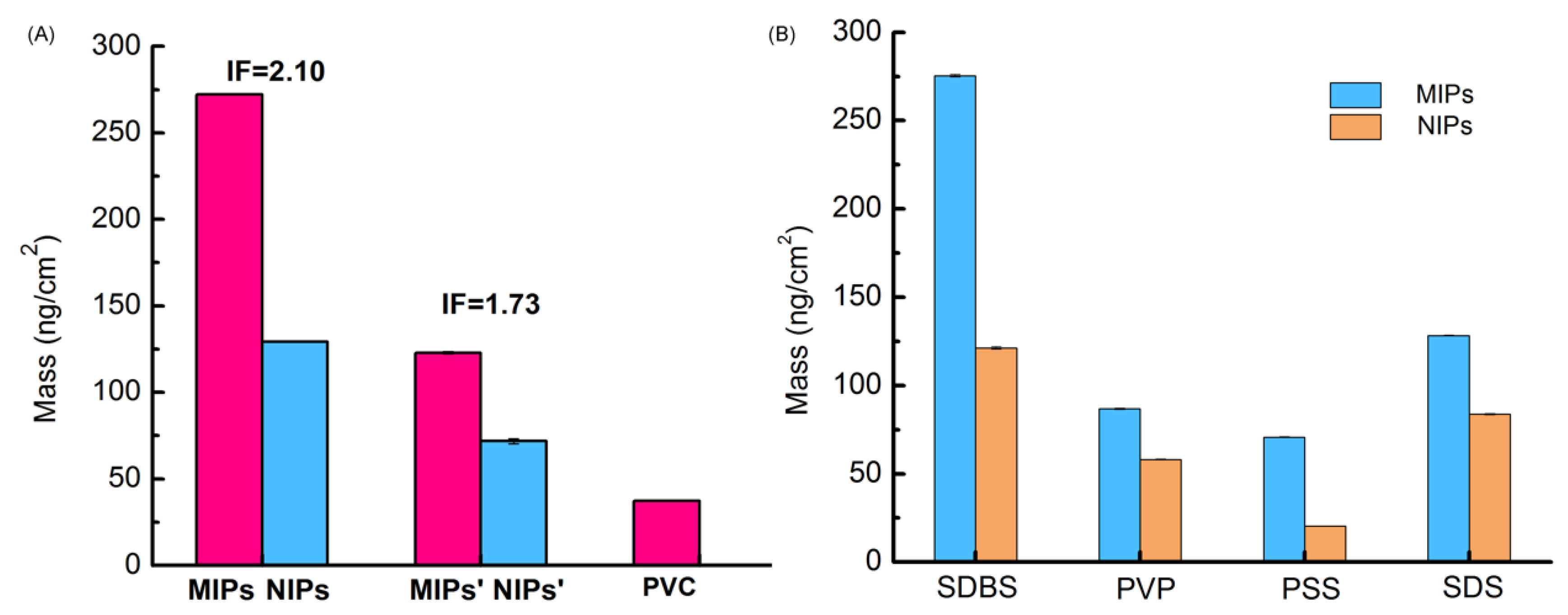
3.2. Selecting the Surfactant Used in the MIPs-Coated QCM-D Sensors
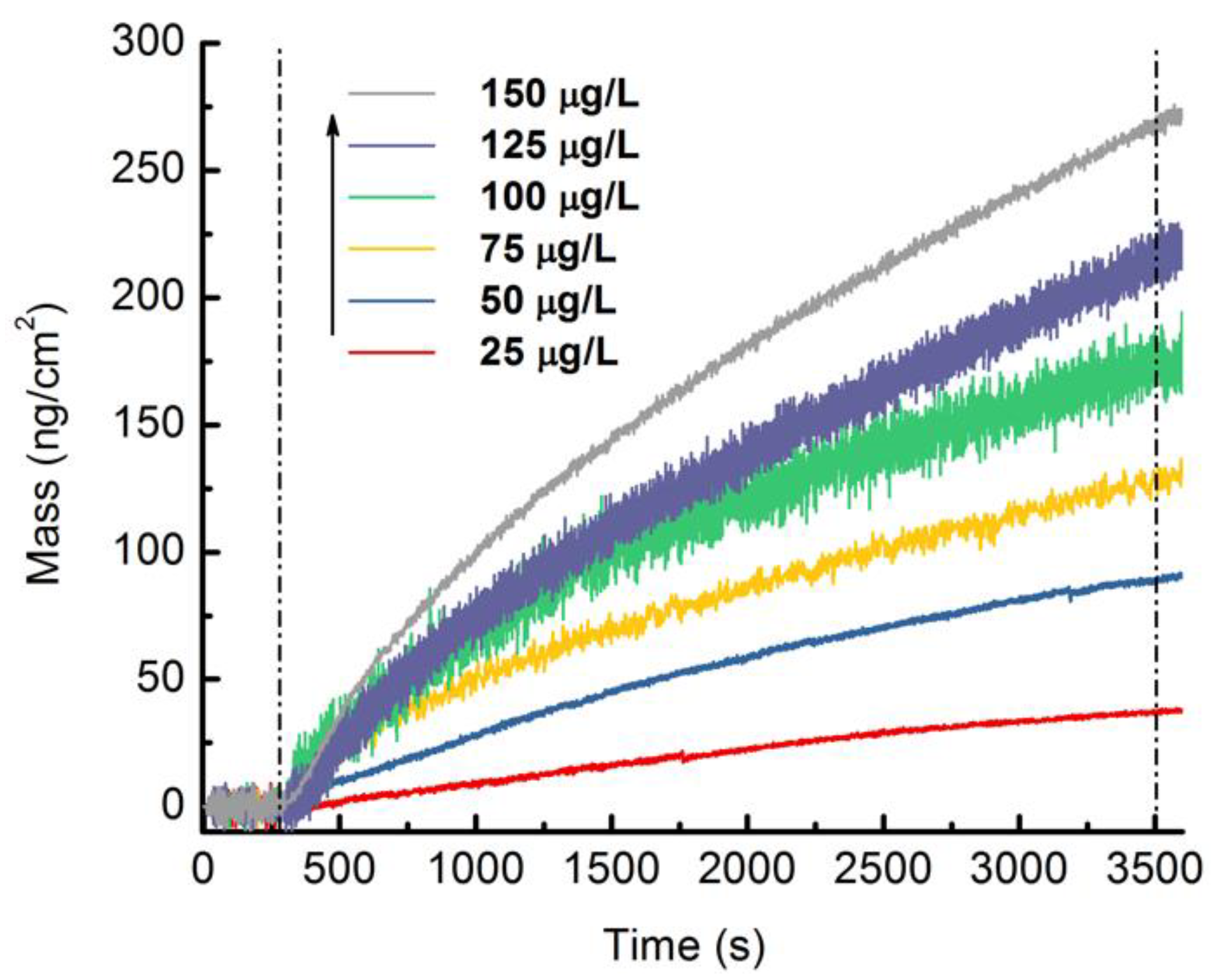
3.3. Analytical Performance of the MIPs-Coated QCM-D Sensor
3.4. Selectivity and Reproducibility of the MIPs-Coated QCM-D Sensor
3.5. Application of the MIPs-Coated QCM-D Sensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiao, X.X.; Zhang, X.J.; Tian, Y.; Meng, Y.G. Progresses on the theory and application of quartz crystal microbalance. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2016, 3, 031106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujahid, A.; Afzal, A.; Dickert, F.L. An overview of high frequency acoustic sensors—QCMs, SAWs and FBARs—chemical and biochemical applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.Y.; Penn, L.S.; Xi, J. Quartz crystal microbalance: Sensing cell-substrate adhesion and beyond. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 99, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchmenko, T.A.; Lvova, L.B. A perspective on recent advances in piezoelectric chemical sensors for environmental monitoring and foodstuffs analysis. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emir Diltemiz, S.; Keçili, R.; Ersöz, A.; Say, R. Molecular imprinting technology in quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) Sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BelBruno, J.J. Molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.R.; Feng, T.Y.; Xu, J.; Xue, C.H. Recent advances of molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensors in the detection of food safety hazard factors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujahid, A.; Mustafa, G.; Dickert, F.L. Label-free bioanalyte detection from nanometer to micrometer dimensions—molecular imprinting and QCMs. Biosensors 2018, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battal, D.; Akgonullu, S.; Yalcin, M.S.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A. Molecularly imprinted polymer based quartz crystal microbalance sensor system for sensitive and label-free detection of synthetic cannabinoids in urine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 111, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.F.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, J.P.; Yun, Y.G.; Wang, S. Reproducible molecularly imprinted QCM sensor for accurate, stable, and sensitive detection of enrofloxacin residue in animal-derived food. Food Anal. Method. 2018, 11, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.F.; Wang, C.; Li, X.D.; Liu, L.F. Preparation and application of epitope magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for enrichment of sulfonamide antibiotics in water. Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 2462–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.T.; Hu, X.L.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, Q.; He, C.Y. Rapid degradation of Congo red by molecularly imprinted polypyrrole-coated magnetic TiO2 nanoparticles in dark at ambient conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 294, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.F.; Liu, J.; Xing, H.W.; Zhou, H.; Wu, M.H. Fabrication and application of magnetically catalytic imprinting nanozymes. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 8248–8288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wei, C.; Xu, Q.; Xu, J. Polyppyrrole-coated cotton fabrics used for removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. J. Textile Inst. 2017, 108, 1847–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiee, H.; Zanjanchi, M.A.; Zamani, A.; Fashi, A. Hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction based on the use of a rotating extraction cell: A green approach for trace determination of rhodamine 6G and methylene blue dyes. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.T.; Wang, X.H.; Huang, Y.Q.; Lai, K.Q.; Fan, Y.X. Rapid detection of trace methylene blue and malachite green in four fish tissues by ultra-sensitive surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy coated with gold nanorods. Food Chem. 2019, 106, 106720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Gao, B.; He, F.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Ding, C.; Tang, J.; Crittenden, J.C. Experimental and modeling investigations of ball-milled biochar for the removal of aqueous methylene blue. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Zhou, M.; Oturan, M.A. An overview on the removal of synthetic dyes from water by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 210–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, M.M.; Amer, W.A.; Zaghlol, S.; Minisy, L.M.; Bober, P.; Stejskal, J. Polypyrrole-coated cotton textile as adsorbent of methylene blue dye. Chem. Pap. 2018, 72, 1605–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.S.; Zhang, X.D.; Liu, H.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Ding, J.; Liu, Y.S.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, J.M. Fabrication of SDBS intercalated-reduced graphene oxide/polypyrrole nanocomposites for supercapacitors. Synthetic. Met. 2014, 196, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Feng, J.; Yan, W. Influence of metal oxides on the adsorption characteristics of ppy/metal oxides for methylene blue. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2016, 475, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rico-Yuste, A.; Carrasco, S. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based hybrid materials for the development of optical sensors. Polymers 2019, 11, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reviakine, I.; Johannsmann, D.; Richter, R.P. Hearing what you cannot see and visualizing what you hear. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8838–8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borwitzky, H.; Haefeli, W.E.; Burhenne, J. Analysis of methylene blue in human urine by capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 826, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, X.M.; Wei, C.J.; Qu, Y.M.; Xiao, X.C.; Cheng, H. One-step synthesis of red-emitting carbon dots via a solvothermal method and its application in the detection of methylene blue. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 29533–29540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Gong, L.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, H. Adsorption of hydrophobically modified polyacrylamide p(am-naaa-c16dmaac) on model coal and clay surfaces and the effect on selective flocculation of fine coal. Miner. Eng. 2019, 142, 105887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Z.; Xu, Y.; Tan, X.J.; Tapas, S.; Zhang, J.L. Aim and shoot: Molecule-imprinting polymer coated MoO3 for selective SERS detection and photocatalytic destruction of low-level organic contaminants. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 36201–36207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patskovsky, S.; Dallaire, A.; Meunier, M. Electrochemical surface plasmon resonance sensing with absorptive redox mediator film. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 222, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Materials | Qe (mg·g−1) | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| k2 (g·mg−1·min−1) | Qeq (mg·g−1) | R2 | ||
| MIPs | 12.9 | 0.169 | 12.9 | 0.9998 |
| NIPs | 5.6 | 0.254 | 5.4 | 0.9904 |
| MIPs-SDS | 8.4 | 1.157 | 8.4 | 0.9999 |
| NIPs-SDS | 5.5 | 0.974 | 5.5 | 0.9999 |
| MIPs-PSS | 11.0 | 0.894 | 10.1 | 0.9994 |
| NIPs-PSS | 6.8 | 0.401 | 6.7 | 0.9975 |
| MIPs-PVP | 6.7 | 0.123 | 6.7 | 0.9995 |
| NIPs-PVP | 4.5 | 0.796 | 4.5 | 0.9991 |
| Samples | Matrix Calibration Curve | Matrix Effect |
|---|---|---|
| River water | y=1.6157x + 63.473 | 115% |
| Seawater | y=1.5590x + 48.788 | 128% |
| Samples | Cadded (µg/L) | Cfound (µg/L) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%, n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| River water | 50 | 48.4 | 96.8 | 4.2 |
| 100 | 95.6 | 96.4 | 4.1 | |
| 150 | 140.4 | 93.6 | 4.1 | |
| Seawater | 50 | 46.6 | 93.3 | 0.9 |
| 100 | 92.5 | 92.5 | 2.8 | |
| 150 | 129.5 | 86.3 | 1.3 |
| Methods | Linear Range (µg/L) | LOD (µg/L) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE | 1.0 × 103–1.2 × 106 | 1.0 × 103 | [24] |
| UV-Vis spectrophotometry | 2.0–6.0 × 102 | 0.6 | [15] |
| HPLC-UV/Vis | 1.6–6.0 × 102 | 0.5 | [15] |
| Fluorescence | 16–3.0 × 103 | 3.2 | [25] |
| SERS | 3.2–3.2 × 108 | 3.2 | [26] |
| MIPs-SERS | - | 3.7 × 102 | [27] |
| SPR | 1.6 × 103–1.6 × 105 | 1.6 × 103 | [28] |
| QCM-D | 25–1.5 × 102 | 1.4 | This study |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Xing, H.; Li, G.; Wu, M. Magnetic Imprinted Polymer-Based Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor for Sensitive Label-Free Detection of Methylene Blue in Groundwater. Sensors 2020, 20, 5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20195506
Hu Y, Xing H, Li G, Wu M. Magnetic Imprinted Polymer-Based Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor for Sensitive Label-Free Detection of Methylene Blue in Groundwater. Sensors. 2020; 20(19):5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20195506
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yufeng, Hanwen Xing, Gang Li, and Minghuo Wu. 2020. "Magnetic Imprinted Polymer-Based Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor for Sensitive Label-Free Detection of Methylene Blue in Groundwater" Sensors 20, no. 19: 5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20195506
APA StyleHu, Y., Xing, H., Li, G., & Wu, M. (2020). Magnetic Imprinted Polymer-Based Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor for Sensitive Label-Free Detection of Methylene Blue in Groundwater. Sensors, 20(19), 5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20195506